Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast: A report of nine cases and a review of the literature
|
|
|
- Francis Stewart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: , 2015 Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast: A report of nine cases and a review of the literature YIZI CONG *, GUANGDONG QIAO *, HAIDONG ZOU, JUN LIN, XINGMIAO WANG, XIAOHUI LI, YALUN LI and SHIGUANG ZHU Department of Breast Surgery, Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital Affiliated to the Medical College of Qingdao University, Yantai, Shandong , P.R. China Received May 2, 2014; Accepted February 5, 2015 DOI: /ol Abstract. Nine cases of infiltrating cribriform carcinoma (ICC) of the breast are reported and the clinicopathological features, particularly the imaging findings, are analyzed in the present study. Sonograms revealed that all masses exhibited a hypoechoic internal echo texture (9/9) and that a number of masses presented with an irregular shape (8/9), obscure boundary (5/9), partially microlobulated (5/9) or well circumscribed (4/9) margins, and an inhomogeneous echo (8/9). Mammographic imaging revealed increased radiological density masses (6/8), and sand like calcification was not observed in all patients. In two patients, the tumors were mammographically occult. Magnetic resonance imaging performed on one patient revealed a slightly high signal intensity on fat saturated T1 and T2 weighted images. Following contrast enhancement, a homogeneous early enhancement was revealed with a quick ascent and quick descent time density curve. Immunohistochemistry revealed that all ICCs expressed estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor, but that none were positive for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. The Ki 67 labeling index was 3.75% (range, 2 5%) in the tumor tissue. Four patients were treated with mastectomy and the others with breast conserving surgery. Six clinically node negative patients underwent sentinel lymph node biopsy; three then received axillary lymph node dissection. Following surgery, three patients received adjuvant chemotherapy, radiotherapy and hormonal therapy, respectively. With a median follow up time of 38 months (range, 4 70 months), one patient developed local Correspondence to: Professor Shiguang Zhu, Department of Breast Surgery, Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital Affiliated to Medical College of Qingdao University, 20 Yudong Road, Yantai, Shandong , P.R. China E mail: ytzhushiguang@medmail.com.cn * Contributed equally Key words: breast, invasive cribriform carcinoma, ultrasound, mammography, magnetic resonance imaging, prognosis recurrence following breast conserving surgery; axillary lymph nodes and distant metastases were not observed. This study confirms that this type of carcinoma has unique biological characteristics and a favorable prognosis, but that it remains possible to experience local recurrence. Introduction Infiltrating cribriform carcinoma (ICC) of the breast, which is characterized by a predominant cribriform growth pattern of its invasive component, is a distinct histological type of invasive carcinoma first described by Page et al in 1983 (1). The incidence of ICC is reported to range from 0.3 to 3.5% (1 4). The carcinoma has a low frequency of axillary nodal metastases and a favorable prognosis (2). Previous immunohistochemical studies (2,5-7)have revealed that the majority of patients with ICC exhibited estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) positive tumors, while human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) amplification was rarely observed (5). For this reason, some people recommended that this favorable histotype with luminal tumor may be suitable for no therapy or endocrine therapy alone (8). However, no standard treatment guidelines exist for ICC and thus, treatment is mostly based on that for invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC). Clinically, the tumor usually presents as a mass, but is frequently asymptomatic. The tumor is not usually detected by mammography, but may be identified as a non-malignant mass on sonography. However, few studies have described its radiological features. In the present study, nine cases of ICC of the breast are presented in order to provide additional clinicopathological data; in particular, imaging findings for its diagnosis and treatment. Patients and methods Patient selection. Nine patients diagnosed with ICC were treated at the Department of Breast Surgery, Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital Affiliated to the Medical College of Qingdao University (Yantai, Shandong, China) between 2007 and Based on the new definition by the World Health Organization (WHO) (9) and the description by Page et al in 1983, all cases were pure ICC. The study protocol was approved by the Human Ethics Committee of the Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital Affiliated to the Medical College of
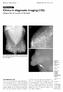
2 1754 CONG et al: INVASIVE CRIBRIFORM CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST A B C D Figure 1. Case 5 from Table I (A) Oblique and (B) axial mammography findings. A high uneven density mass measuring 2.5 cm, with fuzzy boundaries, was observed in the superior external quadrant of the right breast. Enlarged lymph nodes were not observed in the right axilla. (C) Echography imaging revealed a low uneven echo mass range of 2.4x2.0 cm that was lobulated with clear boundaries, crude edges and an irregular shape. Color Doppler flow imaging revealed a rich blood flow signal in and around the mass. (D) Pathological results revealed invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast (hematoxylin and eosin staining; magnification, x100). Qingdao University. Informed consent was obtained from all patients prior to the surgery and the examination of the specimens. Patient history. The medical records of the patients were retrieved from the hospital registry and the clinicopathological characteristics, including age, menopausal status, family history, laterality, tumor size, lymph node status, hormone receptor status, HER2 status and radiological examinations, were analyzed, as well as the treatment and outcome. Pathological examination. The histology of the primary tumor was reviewed by an expert pathologist. The pathological tumor stage (tumor node metastasis stage) was assessed according to the criteria established by the sixth edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging manual (10). Specimens were considered to be HER2-positive when they scored +3 by immunohistochemistry or were shown to be positive by fluorescent in situ hybridization (9). Results Patient characteristics. The patient characteristics are shown in Table I. All nine cases were of females. The median age was 55 years (range, years) at diagnosis. Four cases were premenopausal and the rest were menopausal. A mass or lump in the breast was the main symptom in all patients. The tumor involved the left breast in four patients and the right breast in five patients. The tumors were mainly located in the upper outer quadrant (5/9). The median size of the tumors was 1.7 cm (range, cm). Examination findings. Tumor marker detection revealed that the level of carcinoembryonic antigen in the blood serum was high in one patient (4.01 ng/ml; normal range, ng/ml) and that the ferritin level was high in two patients (193.0 and ng/ml; normal range, ng/ml). Pre operative sonographic findings were available for review for all patients. Sonograms revealed that all masses exhibited a hypoechoic
3 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: , Table I. Patient characteristics. Case Age, Family Location Tumor Metastatic TNM Endocrine Follow-up, no. years Menopause history Laterality (quadrant) size, cm Surgery LNs, n stage Immunohistochemistry Chemotherapy Radiotherapy therapy months 1 49 No Yes Right Superior external 1.5 BCS+ALND 5 ⅢA ER(++), CEF b Yes None 28 PR(+), HER2(+) 2 40 Yes Yes Right Superior external 1.7 BCS+SLNB 0 Ⅰ ER(++), PR(++), None Yes Tamoxifen 70 HER2(-) (6 months) 3 41 No No Right Superior external 1.1 BCS+SLNB+ALND 1 ⅡA ER(++), PR(++), None None None 69 HER2(-) 4 69 Yes No Right Superior internal 1.0 BCS+SLNB 0 Ⅰ ER(+++), PR(+++), None None None 48 HER2(-), p53(-), Ki 67 3%, CK5/6(-), CD10, p63 focal(+), 34βE12(+) 5 68 Yes No Right Superior external 3.2 BCS+ALND 0 ⅡA ER(+++), PR(+++), HER2(++) a, None Yes Letrozole 17 p53 2%, Ki 67 5%, CK5/6(-), (17 months) CD56(-), CgA(-), Syn(-) 6 46 No Yes Left Superior internal 2.5 M+SLNB+ALND 1 ⅡB ER(+), PR(+++), HER2(-) TE b None Unknown Yes No Left Superior external 3.0 M+ALND 1 ⅡB ER(+), PR(++), HER2(-) None None None Unknown 8 55 No Yes Left Inferior external 2.0 M+SLNB+ALND 2 ⅡA ER(+), PR(++), HER2(-), CEF c None None 53 p53(-), Ki 67 5% 9 71 Yes Yes Left Inferior internal 1.2 M+SLNB 0 Ⅰ ER(+), PR(+), HER2(-), None None Arimidex 25 p53 focal(+), Ki 67 2% (25 months) a Immunohistochemistry revealed HER2(++), fluorescence in situ hybridization confirmed HER2(-); b four cycles; c six cycles. LNs, lymph nodes; BCS, breast conserving surgery; M, mastectomy; SLNB, sentinel lymph node biopsy; ALND, axillary lymph node dissection; ER, estrogen receptor; PR, progesterone receptor; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; TNM, tumor node metastasis; CEF, cyclophosphamide, epirubicin and fluorouracil; TE, docetaxel and epirubicin.
4 1756 CONG et al: INVASIVE CRIBRIFORM CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST A B C D Figure 2. Case 4 from Table I. (A and B) Magnetic resonance imaging findings. The mass measuring 1.3x0.9 cm exhibited a slightly high signal intensity on fat saturated T1 and T2 weighted images. Following contrast enhancement, (A) a homogeneous early enhancement was revealed with (B) a quick ascent and descent time density curve. (C) Echography imaging revealed that the low echo mass range of 1.2x0.7 cm was less regular in morphology with a well-defined margin and uneven echo. Color Doppler flow imaging detected no blood flow signal in and around the mass. (D) Pathological results revealed invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast (hematoxylin and eosin staining; magnification, x100). internal echo texture (9/9) and that a number of masses presented with an irregular shape (8/9), obscure boundary (5/9), partially microlobulated (5/9) or well circumscribed (4/9) margins, and an inhomogeneous echo (8/9). Color Doppler flow imaging revealed markedly increased flow signals in two patients and a resistance index of 0.77 in one patient. Pre operative mammographic imaging was available for review for eight patients. The tumors in two patients were mammographically occult. The other six tumors that were visible exhibited increased radiological density masses, and sand like calcification was not observed in all patients (Fig. 1). Magnetic resonance imaging performed in one patient revealed that the mass exhibited a slightly high signal intensity on fat saturated T1 and T2 weighted images. Following contrast enhancement, a homogeneous early enhancement was revealed with a quick ascent and quick descent time density curve (Fig. 2). Pathological findings. Surgery was the primary treatment for all patients. The frozen section technique was used for intraoperative evaluation, but only 50% (4/8) of patients could be accurately diagnosed. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and immunohistochemistry confirmed all cases. Six clinically node negative patients underwent sentinel lymph node biopsy; three of whom exhibited lymph node metastasis and then received axillary lymph node dissection. Four patients were treated with mastectomy and the others with breast conserving surgery. The pathological findings revealed five cases with lymph node involvement, one of which exhibited metastasis in more than three lymph nodes. Immunohistochemistry revealed that all ICCs expressed ER and PR, but that none were positive for HER2. An average of 3.75% (range, 2 5%) tumor cells exhibited nuclear staining for Ki 67 (n=4). Treatment and follow up. Following surgery, three patients received adjuvant chemotherapy, three patients received radiotherapy and three patients received adjuvant hormonal therapy. Follow up was undertaken for eight cases. With a median follow up time of 38 months (range, 4 70 months), all cases survived without axillary lymph node or distant metastases. However, one patient (case 2; Table I) who received radiotherapy and tamoxifen for six months without chemotherapy developed local recurrence 49 months after breast conserving surgery. Breast conserving surgery was performed again
5 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: , for local recurrence at Qilu hospital of Shandong University (Jinan, China). Following surgery, the patient received six cycles of chemotherapy (the specific chemotherapy regimen is unknown) and adjuvant hormonal therapy (letrozole). Subsequent to being followed up for 22 months, the patient was alive with a disease free status. Discussion ICC of the breast is characterized by a predominant cribriform growth pattern of its invasive component according to the new definition by the WHO (9) and the description by Page et al from 1983 (1). Pure ICC is defined as being almost entirely (>90%) of an invasive cribriform pattern, while lesions that demonstrate a predominantly cribriform differentiation with the remaining component limited to a tubular carcinoma (TC) pattern are also included in the category of ICC. Cases with a component that is <50% of a carcinoma type other than TC should be regarded as a mixed type of ICC. In histopathological specimens, this type of carcinoma must be distinguished from other invasive breast carcinomas that exhibit a cribriform pattern, including adenoid cystic carcinoma. Immunocytochemical staining for basement membrane materials or an ultrastructural examination is recommended when accurate diagnosis is difficult (12). In the cases of the present study, it was observed that 50% (4/8) of patients could not be correctly diagnosed by intraoperative frozen section, while H&E staining and immunohistochemistry were able to confirm all cases. The radiological findings of ICC are not well known, since few studies have described the disease. Stutz et al (4) reported that the tumor was mammographically occult in four (50%) cases. The other four tumors all showed as large (20-35 mm) spiculated masses and two contained a few flecks of punctate calcification. Another case report described a circumscribed high density mass with microcalcifications on mammography, which was described as a borderline lesion on sonography (13). In the present series, all tumors demonstrated an increased radiological density mass with the exception of two (25%), which were mammographically occult, but sand like calcification was not observed. The ultrasound appearances were not all entirely typical of breast carcinoma. The study by Stutz et al revealed that the majority of tumors (3/4) presented as an ill defined, inhomogeneous solid mass, but without distal acoustic attenuation (4). Another study revealed masses with an oval (2/3) or irregular (1/3) shape, partially microlobulated (2/3) or well-circumscribed (1/3) margins, and a hypoechoic (2/3) or an isoechoic (1/3) internal echo texture. Sonographic assessments were classified as Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System category 4A in two cases and 4C in one case (n=3) (13). In the cases of the present study, all masses exhibited a hypoechoic internal echo texture (9/9) and a number of masses presented with an irregular shape (8/9), obscure boundary (5/9), partially microlobulated (5/9) or well circumscribed (4/9) margins, and an inhomogeneous echo (8/9). Although the sonographic findings are usually highly suggestive of malignancy, this type of carcinoma may also be shown as a non-malignant mass on sonography. Magnetic resonance imaging is also an essential examination technique for breast cancer. In the present study, the tumor revealed slightly high signal intensity on fat saturated T1- and T2 weighted images in one patient. Following contrast enhancement, a homogeneous early enhancement was revealed with a quick ascent and quick descent time density curve. However, homogeneous early enhancement with a delayed wash out kinetic pattern was also reported (6). ICC is a well differentiated neoplasm architecturally, cytologically, ultrastructurally and functionally. The nuclear grade is usually low or moderate, and the ultrastructural features suggest a high degree of differentiation (12). In a previous study, immunohistochemistry revealed that all patients with pure ICC were ER-positive, compared with 20/21 (95.2%) among the mixed ICC cases. PR expression was positive in 26/30 (86.7%) pure ICC cases and 19/21 (90.5%) mixed ICC cases. However, HER2 amplification was rarely observed (5). As in the present cases, all ICCs expressed ER and PR, but none were positive for HER2. Intraductal carcinoma, generally of the cribriform type, and mutifocality are often observed in cases of ICC (1,2,9). Clinically, the tumor usually presents as a mass, but is frequently occult. For this reason, the lesions are usually larger at presentation, although they grow slowly the majority of the time (3). However, in the present cases, the median size of the tumors (1.7 cm) was not large. The axillary lymph nodes are less frequently involved in ICC than in IDC (1). Venable et al (2) reported that the maximal number of metastatic lymph nodes in pure ICC was not more than three, and that there was no marked difference in the positive lymph node rate among the pure ICC, mixed ICC and IDC control groups. As in the present cases, 55.6% (5/9) of patients presented with lymph node metastasis, but only one case involved more than three lymph nodes. Internal mammary node metastasis has also been reported in pure ICC (15). ICC manifests a better prognosis than that of IDC. The 10 year overall survival rate for ICC is %, and the outcome of mixed ICC is reported to be less favorable than that of the pure form, but better than that of common ductal carcinoma (1,3,16). In the present study, ICC was identified to be associated with a series of favorable prognostic factors, including a smaller tumor size, less frequent axillary lymph node metastasis, a higher positive rate of ER and PR expression, no HER2 expression and a lower proliferation index. Sand like calcification, which may be the result of an active secretory process by the tumor cells, was not observed in any of the cases. We believe that these factors lead to its excellent prognosis. Zhang et al observed a significantly higher number of positive lymph nodes in mixed ICC than in the pure form. In addition, mixed ICC cases exhibited a higher proliferation index than pure ICC cases, regardless of the positivity rate or the average Ki 67 percentage (5). This result demonstrated that the prognosis of mixed ICC is less favorable than that of the pure form (1,3,15). However, pure ICC could also result in distant (bone) metastasis if untreated (7). In the present study, one patient who received radiotherapy and short term hormonal therapy without chemotherapy developed local recurrence following breast conserving surgery, which indicated that adjuvant chemotherapy may play an essential role following surgery. Surgery was the primary treatment for ICC. Sentinel lymph node biopsy was more suitable due to its lower rate of lymph
6 1758 CONG et al: INVASIVE CRIBRIFORM CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST node metastasis. A molecular classification of breast cancer has been proposed for a better understanding of its biology and treatment. Using immunohistochemistry, the present study found all cases to be of the luminal subtype. The study by Colleoni et al (8) recommended that favorable histotypes (e.g., the tubular, cribriform, mucinous and papillary types) with luminal tumors may be suitable for no therapy or endocrine therapy alone. However, such decisions must be made cautiously, as it is still possible to have local recurrence, as in the present case, or distant (bone) metastasis if not treated (7). We therefore hypothesize that chemotherapy and radiotherapy remain necessary for high risk patients. Endocrine therapy has a significant effect, since the majority of tumors are positive for ER or PR expression. In summary, the present study described the clinicopathological features, in particular the imaging findings, of nine cases of ICC of the breast. ICC was found to exhibit unique biological characteristics and manifested a good prognosis, as it revealed more favorable prognostic factors. Although local recurrence is possible, when considering the benign course of pure ICC, chemotherapy and radiotherapy may not be indicated in all cases. In the future, larger samples and an increased follow up time will be required when further examining these findings. References 1. Page DL, Dixon JM, Anderson TJ, Lee D and Stewart HJ: Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast. Histopathology 7: , Venable JG, Schwartz AM and Silverberg SG: Infiltrating cribriform carcinoma of the breast: a distinctive clinicopathologic entity. Hum Pathol 21: , Ellis IO, Galea M, Broughton N, Locker A, Blamey RW and Elston CW: Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. II. Histological type. Relationship with survival in a large study with long term follow up. Histopathology 20: , Stutz JA, Evans AJ, Pinder S, et al: The radiological appearances of invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast. Nottingham Breast Team. Clin Radiol 49: , Zhang W, Zhang T, Lin Z, et al: Invasive cribriform carcinoma in a Chinese population: comparison with low grade invasive ductal carcinoma not otherwise specified. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 6: , Lim HS, Jeong SJ, Lee JS, et al: Sonographic findings of invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast. J Ultrasound Med 30: , Zhang W, Lin Z, Zhang T, Liu F and Niu Y: A pure invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast with bone metastasis if untreated for thirteen years: a case report and literature review. World J Surg Oncol 10: 251, Colleoni M, Russo L and Dellapasqua S: Adjuvant therapies for special types of breast cancer. Breast 20 Suppl 3: , Rakha E, Pinder SE, Shin SJ and Tsuda H: Tubular carcinoma and cribriform carcinoma. In: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Breast. Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Tan PH and van de Vijver MJ (eds). 4th edition. IARC Press, Lyon, pp43 45, Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, et al (eds): Breast. In: American Joint Committee on Cancer Cancer Staging Manual. 6th edition. Springer, New York, NY, pp , Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, et al; American Society of Clinical Oncology; College of American Pathologists: Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/ College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol 31: , Wells CA and Ferguson DJ: Ultrastructural and immunocytochemical study of a case of invasive cribriform breast carcinoma. J Clin Pathol 41: 17 20, Nishimura R, Ohsumi S, Teramoto N, Yamakawa T, Saeki T and Takashima S: Invasive cribriform carcinoma with extensive microcalcifications in the male breast. Breast Cancer 12: , Gatti G, Pruneri G, Gilardi D, Brenelli F, Bassani G and Luini A: Report on a case of pure cribriform carcinoma of the breast with internal mammary node metastasis: description of the case and review of the literature. Tumori 92: , Colleoni M, Rotmensz N, Maisonneuve P, et al: Outcome of special types of luminal breast cancer. Ann Oncol 23: , 2012.
Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti. Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS
 Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS Histological diversity of breast adenocarcinomas Different histological types are defined according to specific
Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS Histological diversity of breast adenocarcinomas Different histological types are defined according to specific
Clinical and pathological portraits of axillary presentation breast cancer and effects of preoperative systemic therapy
 Case Series Clinical and pathological portraits of axillary presentation breast cancer and effects of preoperative systemic therapy Ling Xu 1*, Fang Li 1,2*, Yinhua Liu 1, Xuening Duan 1, Jingming Ye 1,
Case Series Clinical and pathological portraits of axillary presentation breast cancer and effects of preoperative systemic therapy Ling Xu 1*, Fang Li 1,2*, Yinhua Liu 1, Xuening Duan 1, Jingming Ye 1,
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging?
 Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Original Article Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast: a clinicopathological analysis of 12 cases with review of literature
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(9):9917-9924 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059886 Original Article Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast: a clinicopathological analysis of 12 cases with review
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(9):9917-9924 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059886 Original Article Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast: a clinicopathological analysis of 12 cases with review
A pure invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast with bone metastasis if untreated for thirteen years: a case report and literature review
 Zhang et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:251 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY CASE REPORT Open Access A pure invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast with bone metastasis if untreated
Zhang et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:251 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY CASE REPORT Open Access A pure invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast with bone metastasis if untreated
Rare types of breast carcinoma
 Open Med. 2015; 10: 92-96 Research Article Open Access Daiva Gudaviciene*, Laura Steponaviciene, Raimundas Meskauskas, Giedre Smailyte, Eduardas Aleknavicius Rare types of breast Abstract: Breast cancer
Open Med. 2015; 10: 92-96 Research Article Open Access Daiva Gudaviciene*, Laura Steponaviciene, Raimundas Meskauskas, Giedre Smailyte, Eduardas Aleknavicius Rare types of breast Abstract: Breast cancer
Basement membrane in lobule.
 Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 Imaging Pathology
 Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICO-IMAGING STUDY OF INVASIVE DUCTAL BREAST CARCINOMAS CORRELATED TO HORMONAL RECEPTORS AND HER2/NEU ONCOPROTEIN
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICO-IMAGING STUDY OF INVASIVE DUCTAL BREAST CARCINOMAS CORRELATED TO HORMONAL RECEPTORS AND HER2/NEU ONCOPROTEIN
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update Stuart J. Schnitt, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Papillary Lesions of the Breast
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update Stuart J. Schnitt, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Papillary Lesions of the Breast
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity.
 Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity.
 Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
Breast Cancer. Most common cancer among women in the US. 2nd leading cause of death in women. Mortality rates though have declined
 Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Neuroendocrine differentiation in pure type mammary mucinous carcinoma is associated with favorable histologic and immunohistochemical parameters
 & 2004 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/04 $25.00 www.modernpathology.org Neuroendocrine differentiation in pure type mammary mucinous carcinoma is associated with favorable histologic and immunohistochemical
& 2004 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/04 $25.00 www.modernpathology.org Neuroendocrine differentiation in pure type mammary mucinous carcinoma is associated with favorable histologic and immunohistochemical
It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue
 59 Breast cancer 1 It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue including both early stages which are potentially curable, and metastatic breast cancer (MBC) which is usually incurable. Most breast
59 Breast cancer 1 It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue including both early stages which are potentially curable, and metastatic breast cancer (MBC) which is usually incurable. Most breast
Original Report. Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Appearances. Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2
 Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
A712(18)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues
 A712(18)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
A712(18)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
Histological Type. Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer. Nottingham Tenovus Primary Breast Cancer Study. Survival (%) Ian Ellis
 Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer Ian Ellis Molecular Medical Sciences, University of Nottingham Department of Histopathology, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust Histological Type
Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer Ian Ellis Molecular Medical Sciences, University of Nottingham Department of Histopathology, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust Histological Type
Breast Cancer. Saima Saeed MD
 Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
neuroendocrine breast cancer NEBC non-palpable breast lesion NPBL NEBC
 2013 2 33 2 TUMOR Vol. 33, February 2013 www.tumorsci.org 171 Clinical Research DOI: 10.3781/j.issn.1000-7431.2013.02. 011 Copyright 2013 by TUMOR 10 1* 1* 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 3 2 1. 2. 3. 100730 neuroendocrine
2013 2 33 2 TUMOR Vol. 33, February 2013 www.tumorsci.org 171 Clinical Research DOI: 10.3781/j.issn.1000-7431.2013.02. 011 Copyright 2013 by TUMOR 10 1* 1* 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 3 2 1. 2. 3. 100730 neuroendocrine
Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance
 Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance Anne Moore, MD Medical Oncology Syed Hoda, MD Surgical Pathology The pathologist is central to the team approach needed to manage the patient with breast
Surgical Pathology Issues of Practical Importance Anne Moore, MD Medical Oncology Syed Hoda, MD Surgical Pathology The pathologist is central to the team approach needed to manage the patient with breast
Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients
 236 Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients Mingfian Yang Hao Long Jiehua He Xi Wang Zeming Xie Department of Thoracic Oncology, Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou
236 Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients Mingfian Yang Hao Long Jiehua He Xi Wang Zeming Xie Department of Thoracic Oncology, Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach. Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina
 Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Outcomes of patients with inflammatory breast cancer treated by breast-conserving surgery
 Breast Cancer Res Treat (2016) 160:387 391 DOI 10.1007/s10549-016-4017-3 EDITORIAL Outcomes of patients with inflammatory breast cancer treated by breast-conserving surgery Monika Brzezinska 1 Linda J.
Breast Cancer Res Treat (2016) 160:387 391 DOI 10.1007/s10549-016-4017-3 EDITORIAL Outcomes of patients with inflammatory breast cancer treated by breast-conserving surgery Monika Brzezinska 1 Linda J.
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Journal of Breast Cancer
 CSE REPORT Journal of reast Cancer J reast Cancer 2016 December; 19(4): 459-464 Increased Malignant Microcalcifications after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in dvanced reast Cancer Gi Won Shin, Young Mi Park,
CSE REPORT Journal of reast Cancer J reast Cancer 2016 December; 19(4): 459-464 Increased Malignant Microcalcifications after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in dvanced reast Cancer Gi Won Shin, Young Mi Park,
Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography
 Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography Eyad Fawzi AlSaeed 1 and Mutahir A. Tunio 2* 1 Consultant Radiation Oncology, Chairman
Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography Eyad Fawzi AlSaeed 1 and Mutahir A. Tunio 2* 1 Consultant Radiation Oncology, Chairman
Ductal Carcinoma-in-Situ: New Concepts and Controversies
 Ductal Carcinoma-in-Situ: New Concepts and Controversies James J. Stark, MD, FACP Medical Director, Cancer Program and Palliative Care Maryview Medical Center Professor of Medicine, EVMS Case Presentation
Ductal Carcinoma-in-Situ: New Concepts and Controversies James J. Stark, MD, FACP Medical Director, Cancer Program and Palliative Care Maryview Medical Center Professor of Medicine, EVMS Case Presentation
ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES. At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to:
 1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
Invasive Papillary Breast Carcinoma
 410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine
 Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide
 Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide Breast Cancer - Understanding Your Pathology Report Pathology Reports can be overwhelming. They contain scientific terms that are unfamiliar and might be a bit
Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide Breast Cancer - Understanding Your Pathology Report Pathology Reports can be overwhelming. They contain scientific terms that are unfamiliar and might be a bit
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Modified primary tumour/vessel tumour/nodal tumour classification for patients with invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast
 British Journal of Cancer (2011) 105, 698 708 All rights reserved 0007 0920/11 www.bjcancer.com Modified primary tumour/vessel tumour/nodal tumour classification for patients with invasive ductal carcinoma
British Journal of Cancer (2011) 105, 698 708 All rights reserved 0007 0920/11 www.bjcancer.com Modified primary tumour/vessel tumour/nodal tumour classification for patients with invasive ductal carcinoma
Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast:
 J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
NEUROENDOCRINE DIFFERENTIATED BREAST CARCINOMA
 + NEUROENDOCRINE DIFFERENTIATED BREAST CARCINOMA + INTRODUCTION + NEUROENDOCRINE FEATURES IN BREAST CARCINOMA Incidence of 2-5% Seen in various histopathological types of breast carcinoma Seen in both
+ NEUROENDOCRINE DIFFERENTIATED BREAST CARCINOMA + INTRODUCTION + NEUROENDOCRINE FEATURES IN BREAST CARCINOMA Incidence of 2-5% Seen in various histopathological types of breast carcinoma Seen in both
Case Scenario 1. 2/15/2011 The patient received IMRT 45 Gy at 1.8 Gy per fraction for 25 fractions.
 Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Comparison of clinical characteristics between occult and non-occult breast cancer
 JBUON 2014; 19(3): 662-666 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of clinical characteristics between occult and non-occult
JBUON 2014; 19(3): 662-666 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of clinical characteristics between occult and non-occult
A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer
 Elmer ress Original Article World J Oncol. 2017;8(3):71-75 A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer Hui Hu a, Wei Wei a, Xin Yi a, Ling Xin
Elmer ress Original Article World J Oncol. 2017;8(3):71-75 A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer Hui Hu a, Wei Wei a, Xin Yi a, Ling Xin
Q&A. Fabulous Prizes. Collecting Cancer Data: Breast 4/4/13. NAACCR Webinar Series Collecting Cancer Data Breast
 Collecting Cancer Data Breast NAACCR 2012 2013 Webinar Series Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this webinar
Collecting Cancer Data Breast NAACCR 2012 2013 Webinar Series Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this webinar
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience.
 MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology. Report. Key Questions. Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help:
 Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report Key Questions Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help: Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report 1. Is this
Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report Key Questions Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help: Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report 1. Is this
Leonard M. Glassman MD
 BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
ACRIN 6666 IM Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US
 Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Breast Cancer Earlier Disease. Stefan Aebi Luzerner Kantonsspital
 Breast Cancer Earlier Disease Stefan Aebi Luzerner Kantonsspital stefan.aebi@onkologie.ch Switzerland Breast Cancer Earlier Disease Diagnosis and Prognosis Local Therapy Surgery Radiation therapy Adjuvant
Breast Cancer Earlier Disease Stefan Aebi Luzerner Kantonsspital stefan.aebi@onkologie.ch Switzerland Breast Cancer Earlier Disease Diagnosis and Prognosis Local Therapy Surgery Radiation therapy Adjuvant
Case study 1. Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research
 NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features
 Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features Hee Jung Shin, MD 1 Hak Hee Kim, MD 1 Sun Mi Kim, MD 1 Dae Bong Kim, MD 1 Ye Ri Lee, MD 1 Mi-Jung Kim,
Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features Hee Jung Shin, MD 1 Hak Hee Kim, MD 1 Sun Mi Kim, MD 1 Dae Bong Kim, MD 1 Ye Ri Lee, MD 1 Mi-Jung Kim,
04/10/2018. Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast INTRADUCTAL PAPILLOMA
 Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Basal phenotype: a powerful prognostic factor in small screen-detected invasive breast cancer with long-term follow-up ...
 21 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Basal phenotype: a powerful prognostic factor in small screen-detected invasive breast cancer with long-term follow-up A J Evans, E A Rakha, S E Pinder, A R Green, C Paish and I O Ellis...
21 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Basal phenotype: a powerful prognostic factor in small screen-detected invasive breast cancer with long-term follow-up A J Evans, E A Rakha, S E Pinder, A R Green, C Paish and I O Ellis...
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma with Fibrotic Focus: Mammographic and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues
 A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
CASE REPORT GASTRIC ADENOCARCINOMA METASTASIS TO THE BREAST- A DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS WITH PRIMARY BREAST ADENOCARCINOMA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE.
 GASTRIC ADENOCARCINOMA METASTASIS TO THE BREAST- A DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS WITH PRIMARY BREAST ADENOCARCINOMA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE. Ashwin Hebbar.K 1, Shashidar. K 2, Kamal Kishor 3, Manjunath 4, Shivakumar.H.
GASTRIC ADENOCARCINOMA METASTASIS TO THE BREAST- A DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS WITH PRIMARY BREAST ADENOCARCINOMA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE. Ashwin Hebbar.K 1, Shashidar. K 2, Kamal Kishor 3, Manjunath 4, Shivakumar.H.
Breast pathology. 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University
 Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
THE MALE BREAST CARCINOMA: EARLY DETECTION HOPE. Author (s) Supreethi Kohli a, Pragya Garg b
 Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
and verbal and/or written consent was obtained from each of the patient at each visit during which their database was
 Imaging Characteristics of Triple Receptor Negative versus Triple Receptor Positive Breast Cancer Dr. Abdullateef Aliasghar M.B.CH.B., C.A.B.M.S-RAD, Lecturer, National Cancer Research Center, Baghdad
Imaging Characteristics of Triple Receptor Negative versus Triple Receptor Positive Breast Cancer Dr. Abdullateef Aliasghar M.B.CH.B., C.A.B.M.S-RAD, Lecturer, National Cancer Research Center, Baghdad
Primary Breast Liposarcoma
 Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience
 Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience Curzon M, Curzon C, Heidel RE, Desai P, McLoughlin J, Panella T, Bell
Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience Curzon M, Curzon C, Heidel RE, Desai P, McLoughlin J, Panella T, Bell
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
American Journal of Cancer Case Reports. Invasive Papillary Carcinoma of Male Breast: A Rare Case Report
 American Journal of Cancer Case Reports http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajccr SantraAetal. American Journal of Cancer Case Reports 2014, 3:56-61 Page 1 of 6 Vol 3 Article ID 20140617, 6 pages Case Report
American Journal of Cancer Case Reports http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajccr SantraAetal. American Journal of Cancer Case Reports 2014, 3:56-61 Page 1 of 6 Vol 3 Article ID 20140617, 6 pages Case Report
ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form
 S1 ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form 6666 Instructions: Complete a separate S1 form for each separate area of each breast excised with the intent to treat a cancer (e.g. each lumpectomy or mastectomy).
S1 ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form 6666 Instructions: Complete a separate S1 form for each separate area of each breast excised with the intent to treat a cancer (e.g. each lumpectomy or mastectomy).
Reporting of Breast Cancer Do s and Don ts
 Reporting of Breast Cancer Do s and Don ts 7 th SGH Annual Breast Pathology Course Professor Michael Bilous Conjoint Professor Western Sydney University Consultant Pathologist, Australian Clinical Labs,
Reporting of Breast Cancer Do s and Don ts 7 th SGH Annual Breast Pathology Course Professor Michael Bilous Conjoint Professor Western Sydney University Consultant Pathologist, Australian Clinical Labs,
DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated. FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia.
 DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated BENIGN BREAST DISORDERS (Essential Surg 2 nd Ed, pp 540) FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia. Fibroadenosis is the distortion
DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated BENIGN BREAST DISORDERS (Essential Surg 2 nd Ed, pp 540) FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia. Fibroadenosis is the distortion
Results of the ACOSOG Z0011 Trial
 DCIS and Early Breast Cancer Symposium JUNE 15-17 2012 CAPPADOCIA Results of the ACOSOG Z0011 Trial Kelly K. Hunt, M.D. Professor of Surgery Axillary Node Dissection Staging, Regional control, Survival
DCIS and Early Breast Cancer Symposium JUNE 15-17 2012 CAPPADOCIA Results of the ACOSOG Z0011 Trial Kelly K. Hunt, M.D. Professor of Surgery Axillary Node Dissection Staging, Regional control, Survival
Medical Education. CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M
 1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
Breast Cancer? Breast cancer is the most common. What s New in. Janet s Case
 Focus on CME at The University of Calgary What s New in Breast Cancer? Theresa Trotter, MD, FRCPC Breast cancer is the most common malignancy affecting women in Canada, accounting for almost a third of
Focus on CME at The University of Calgary What s New in Breast Cancer? Theresa Trotter, MD, FRCPC Breast cancer is the most common malignancy affecting women in Canada, accounting for almost a third of
Problems in staging breast carcinoma
 Problems in staging breast carcinoma Primary systemic therapy (PST) of breast carcinoma pathologists tasks Dr. Janina Kulka, 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Budapest Austro-Hungarian
Problems in staging breast carcinoma Primary systemic therapy (PST) of breast carcinoma pathologists tasks Dr. Janina Kulka, 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Budapest Austro-Hungarian
Primary squamous cell carcinoma of the breast: a rare entity, representation of two cases
 International Surgery Journal Siripurapu Y et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Aug;4(8):2848-2853 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173434
International Surgery Journal Siripurapu Y et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Aug;4(8):2848-2853 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173434
UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium. Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin
 UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin Professor of Surgery National University of Ireland, Galway and Galway University
UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin Professor of Surgery National University of Ireland, Galway and Galway University
University Journal of Pre and Para Clinical Sciences
 ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer. Cheol Min Kang 2018/04/05
 Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Surgical Therapy: Sentinel Node Biopsy and Breast Conservation
 Surgical Therapy: Sentinel Node Biopsy and Breast Conservation Stephen B. Edge, MD Professor of Surgery and Oncology Roswell Park Cancer Institute University at Buffalo Dr. Roswell Park: Tradition in Cancer
Surgical Therapy: Sentinel Node Biopsy and Breast Conservation Stephen B. Edge, MD Professor of Surgery and Oncology Roswell Park Cancer Institute University at Buffalo Dr. Roswell Park: Tradition in Cancer
Key Words: Cytology, Grading, Breast Carcinoma
 BREAST CARCINOMA ASPIRATES: A STUDY ON CYTOLOGICAL GRADING *Subhashish Das, Kalyani and Harendra Kumar Department of Pathology; Sri Devaraj Urs Medical College, Tamaka, Kolar *Author for Correspondence
BREAST CARCINOMA ASPIRATES: A STUDY ON CYTOLOGICAL GRADING *Subhashish Das, Kalyani and Harendra Kumar Department of Pathology; Sri Devaraj Urs Medical College, Tamaka, Kolar *Author for Correspondence
Invasive Cribriform Carcinoma Arising in Malignant Phyllodes Tumor of Breast: A Case Report
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2012; 46: 205-209 CASE REPORT Invasive Cribriform Carcinoma Arising in Malignant Phyllodes Tumor of Breast: A Case Report Yoomi Choi Kyoung Yul Lee Min Hye Jang Hyesil Seol
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2012; 46: 205-209 CASE REPORT Invasive Cribriform Carcinoma Arising in Malignant Phyllodes Tumor of Breast: A Case Report Yoomi Choi Kyoung Yul Lee Min Hye Jang Hyesil Seol
AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018
 AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018 60-year-old woman with a left breast mass noted on screening mammography. Catherine McNulty, MS4 Tulane University School of Medicine Dr. Robin Sobolewski Breast
AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018 60-year-old woman with a left breast mass noted on screening mammography. Catherine McNulty, MS4 Tulane University School of Medicine Dr. Robin Sobolewski Breast
Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ).
 SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
Table of contents. Page 2 of 40
 Page 1 of 40 Table of contents Introduction... 4 1. Background Information... 6 1a: Referral source for the New Zealand episodes... 6 1b. Invasive and DCIS episodes by referral source... 7 1d. Age of the
Page 1 of 40 Table of contents Introduction... 4 1. Background Information... 6 1a: Referral source for the New Zealand episodes... 6 1b. Invasive and DCIS episodes by referral source... 7 1d. Age of the
Debate Axillary dissection - con. Prof. Dr. Rodica Anghel Institute of Oncology Bucharest
 Debate Axillary dissection - con Prof. Dr. Rodica Anghel Institute of Oncology Bucharest Summer School of Oncology, third edition Updated Oncology 2015: State of the Art News & Challenging Topics Bucharest,
Debate Axillary dissection - con Prof. Dr. Rodica Anghel Institute of Oncology Bucharest Summer School of Oncology, third edition Updated Oncology 2015: State of the Art News & Challenging Topics Bucharest,
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING
 OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING A Novel Fusion of Functional and Morphologic Imaging Reni S. Butler, MD A. Thomas Stavros, MD F. Lee Tucker, MD Michael J. Ulissey, MD PURPOSE 1. Explain opto-acoustic (OA)
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING A Novel Fusion of Functional and Morphologic Imaging Reni S. Butler, MD A. Thomas Stavros, MD F. Lee Tucker, MD Michael J. Ulissey, MD PURPOSE 1. Explain opto-acoustic (OA)
Ines Buccimazza 16 TH UP CONTROVERSIES AND PROBLEMS IN SURGERY SYMPOSIUM
 BILATERAL MASTECTOMY IS NOT ROUTINELY JUSTIFIED IN PATIENTS WITH BILATERAL AXILLARY LYMPHADENOPATHY AND ONLY ONE DETECTABLE PRIMARY BREAST CANCER LESION SURGERY SYMPOSIUM Ines Buccimazza Breast Unit Department
BILATERAL MASTECTOMY IS NOT ROUTINELY JUSTIFIED IN PATIENTS WITH BILATERAL AXILLARY LYMPHADENOPATHY AND ONLY ONE DETECTABLE PRIMARY BREAST CANCER LESION SURGERY SYMPOSIUM Ines Buccimazza Breast Unit Department
Post Neoadjuvant therapy: issues in interpretation
 Post Neoadjuvant therapy: issues in interpretation Disclosure: Overview D Prognostic features in assessment of post treatment specimens: Tumor size Cellularity Grade Receptors LN Neoadjuvant chemotherapy:
Post Neoadjuvant therapy: issues in interpretation Disclosure: Overview D Prognostic features in assessment of post treatment specimens: Tumor size Cellularity Grade Receptors LN Neoadjuvant chemotherapy:
Understanding Your Pathology Report
 Understanding Your Pathology Report Because every person s breast cancer is unique, it s important to understand the underlying biology of your tumor to personalize your treatment plan. Your physicians
Understanding Your Pathology Report Because every person s breast cancer is unique, it s important to understand the underlying biology of your tumor to personalize your treatment plan. Your physicians
Breast Carcinoma in Pakistani Females: A. Morphological Study of 572 Breast Specimens
 Breast Carcinoma in Pakistani Females: A. Morphological Study of 572 Breast Specimens M. Shahid Siddiqui,Naila Kayani,Sara Sulaiman,Akbar S. Hussainy,Sajid H. Shah,Suhail Muzaffar ( Faculty of Health Sciences,
Breast Carcinoma in Pakistani Females: A. Morphological Study of 572 Breast Specimens M. Shahid Siddiqui,Naila Kayani,Sara Sulaiman,Akbar S. Hussainy,Sajid H. Shah,Suhail Muzaffar ( Faculty of Health Sciences,
Int. J. Curr. Res. Med. Sci. (2018). 4(7): 1-7. International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 4, Issue 7-2018 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2018.04.07.001
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 4, Issue 7-2018 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2018.04.07.001
Department of Endocrine & Breast Surgery Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India
 Department of Endocrine & Breast Surgery Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India Evidence-Based Pragmatic SGPGI Breast Cancer Management Protocols (Summary) Background:
Department of Endocrine & Breast Surgery Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India Evidence-Based Pragmatic SGPGI Breast Cancer Management Protocols (Summary) Background:
Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography
 Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(5) : 229-233 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography M Muttarak, S Pojchamarnwiputh,
Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(5) : 229-233 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography M Muttarak, S Pojchamarnwiputh,
Prediction of Lymph Node Involvement in Patients with Breast Tumors Measuring 3 5 cm in a Middle-Income Setting: the Role of CancerMath
 DOI 10.1007/s00268-014-2752-3 BRIEF ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC REPORT Prediction of Lymph Node Involvement in Patients with Breast Tumors Measuring 3 5 cm in a Middle-Income Setting: the Role of CancerMath E.
DOI 10.1007/s00268-014-2752-3 BRIEF ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC REPORT Prediction of Lymph Node Involvement in Patients with Breast Tumors Measuring 3 5 cm in a Middle-Income Setting: the Role of CancerMath E.
Papillary Lesions of the Breast
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast Laura C. Collins, M.D. Associate Professor of Pathology Associate Director, Division of Anatomic Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School
Papillary Lesions of the Breast Laura C. Collins, M.D. Associate Professor of Pathology Associate Director, Division of Anatomic Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School
Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer
 Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer Epidemiology & etiology The most common type of cancer & the 2 nd most common cause of cancer death in women 1 of 8 women in USA Affects 7% of women Peak at
Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer Epidemiology & etiology The most common type of cancer & the 2 nd most common cause of cancer death in women 1 of 8 women in USA Affects 7% of women Peak at
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Eight Year Survival Analysis of Patients with Triple Negative Breast Cancer in India
 APJCP.2016.17.6.2995 RESEARCH ARTICLE Eight Year Survival Analysis of Patients with Triple Negative Breast Cancer in India Dinesh Chandra Doval 1,2 *, P Suresh 1, Rupal Sinha 2, Saud Azam 2, Ullas Batra
APJCP.2016.17.6.2995 RESEARCH ARTICLE Eight Year Survival Analysis of Patients with Triple Negative Breast Cancer in India Dinesh Chandra Doval 1,2 *, P Suresh 1, Rupal Sinha 2, Saud Azam 2, Ullas Batra
Toru Nakamura 1, Takashi Fukutomi 1, Hitoshi Tsuda 2, Sadako Akashi-Tanaka 1, Kaneyuki Matsuo 1, Chikako Shimizu 1 and Kunihisa Miyakawa 3
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 2000;30(10)453 457 Changes in Findings of Mammography, Ultrasonography and Contrast-enhanced Computed Tomography of Three Histological Complete Responders with Primary Breast Cancer Before
Jpn J Clin Oncol 2000;30(10)453 457 Changes in Findings of Mammography, Ultrasonography and Contrast-enhanced Computed Tomography of Three Histological Complete Responders with Primary Breast Cancer Before
Overview of breast cancerpatients and their prognostic factors treated in Baghdad teaching hospital/ oncology department in the year 2010
 Original Article Overview of breast cancerpatients and their prognostic factors treated in Baghdad teaching hospital/ oncology department in the year 21 * DMRT clinical oncology, MSc. pathology. Summary:
Original Article Overview of breast cancerpatients and their prognostic factors treated in Baghdad teaching hospital/ oncology department in the year 21 * DMRT clinical oncology, MSc. pathology. Summary:
Balancing Evidence and Clinical Practice in the Treatment of Localized Breast Cancer May 5, 2006
 Balancing Evidence and Clinical Practice in the Treatment of Localized Breast Cancer May 5, 2006 Deborah Hamolsky MS, RN : DCIS Carol Franc Buck Breast Care Center UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center Jane
Balancing Evidence and Clinical Practice in the Treatment of Localized Breast Cancer May 5, 2006 Deborah Hamolsky MS, RN : DCIS Carol Franc Buck Breast Care Center UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center Jane
Position Statement on Management of the Axilla in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer
 - Official Statement - Position Statement on Management of the Axilla in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer Sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy has replaced axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) for the
- Official Statement - Position Statement on Management of the Axilla in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer Sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy has replaced axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) for the
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
A comparison of Ki 67 proliferative index in primary tumor and axillary metastatic lymph nodes with length of survival in patients with breast cancer
 DOI: 10.4149/BLL_2013_138 Bratisl Lek Listy 2013; 114 (11) CLINICAL STUDY A comparison of Ki 67 proliferative index in primary tumor and axillary metastatic lymph nodes with length of survival in patients
DOI: 10.4149/BLL_2013_138 Bratisl Lek Listy 2013; 114 (11) CLINICAL STUDY A comparison of Ki 67 proliferative index in primary tumor and axillary metastatic lymph nodes with length of survival in patients
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Pathology. AGO e. V. in der DGGG e.v. sowie in der DKG e.v.
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Pathology Pathology Versions 2004 2017: Blohmer / Costa / Fehm / Friedrichs / Huober / Kreipe / Lück / Schneeweis / Sinn /
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Pathology Pathology Versions 2004 2017: Blohmer / Costa / Fehm / Friedrichs / Huober / Kreipe / Lück / Schneeweis / Sinn /
Epithelial Columnar Breast Lesions: Histopathology and Molecular Markers
 29th Annual International Conference Advances in the Application of Monoclonal Antibodies in Clinical Oncology and Symposium on Cancer Stem Cells 25 th -27t h June, 2012, Mykonos, Greece Epithelial Columnar
29th Annual International Conference Advances in the Application of Monoclonal Antibodies in Clinical Oncology and Symposium on Cancer Stem Cells 25 th -27t h June, 2012, Mykonos, Greece Epithelial Columnar
