Overview on Gastric Cancer
|
|
|
- Rodney Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 5 Postoperative Radiotherapy : Delineation of Target Volumes and Organs at Risk H Ben Salah 1 *; J Daoud 1 1 Radiotherapy department, university Habib-Bourguiba hospital of Sfax Tunisia, Tunisia. *Correspondence to: H Ben Salah, Radiotherapy department, university Habib-Bourguiba hospital of Sfax Tunisia, Tunisia. Overview on Gastric Cancer bensalahh73@gmail.com Abstract 1. Introduction It is imperative to review surgical and pathology reports and discuss with the surgeon, Prior to radiotherapy planning,to identify the areas considered to be at the highest risk for recurrence. The type of operation needs to be noted. Radiotherapy planning CT scans should be done with a patient in the supine position with arms over head, from top of diaphragm (for stomach) or carina (for tumor of oesogastric junction or cardia) to the bottom of L4. Preoperative CT scans should be used to aid identification of preoperative tumor volume and nodal groups to be treated. Clinical target volume for adjuvant radiation therapy for gastric cancer depends on the location of the primary disease as well as the status of lymph node metastasis. Postoperative radiotherapy was integrated into the routine care of gastric cancer patients since the results of INT0116 study was published [1] This trial showed a survival and locoregional control benefit of adjuvant radiochemotherapy. Recommendations for postoperative radiation fields design have been published [2,3]. However they were largely based on two-dimensional radiotherapy planning using bony anatomic landmarks. Their implementation in three-dimensional (3D) conformal RT practice is challenging, which results in a large inter- and intraobserver variability in target volume delineation [4,5]. There are no consensus guidelines for target volume definition for postoperative radiotherapy in gastric cancer. This makes 3D computed tomography (CT)-based contouring of a clinical target volume (CTV) very difficult. Even with an anatomical delineation atlas, substantial variations in the CTV
2 delineation still occur between physiciens (Figure 1) [4,5]. Overview on Gastric Cancer Ben Salah H Figure 1: Anteroposterior and posterior views of a gastric cancer planning target volume. Red demonstrates large interobserver variability and blue small variability [4]. 2. Definition of Target Volumes 2.1. Cinical Target Volume (CTV) The definition of target volumes is based on the characteristics of the tumor extension and the patterns of locoregional recurrence. Tumor extension includes invasion by contiguity, lymphatic extension and metastatic extension. Lymph node extension is very frequent conditioning the prognosis. Predicting lymph node involvement is difficult because of the submucosal or sub-serous lymphatics and abundant lymphatic chanels following the artery from the stomach. All lymph nodes schould be considered as a potential affected site [2,3,6]. In most studies of adjuvant radiotherapy, the target volume range is extremely diverse. Postoperative radiotherapy volume based on patterns of failure after radical surgery has been defined as the primary tumor bed, anastomosis site, duodenal stump, and regional lymph nodes [2,3]. If necessary, the remnant stomach in patients who underwent a subtotal gastrectomy has been often included [2,3]. Tumors confined to one of the proximal, middle or distal thirds of the stomach were analyzed with subdivision according to the position of the tumor on the circumference by Maruyama [7]. The incidence of metastases to any perigastric node station was highest when the tumor was located close to it, even though there was little variation in the metastatic pattern along the lesser curvature between tumors in the different thirds [7]. Station numbers 2 (left cardial) and 5 (suprapyloric, right gastric artery) were low-incidence stations for all locations of tumors (Table 1). The position of the tumor on the stomach circumference had a similar impact, as shown for distal cancers (Table 1). Similarly tumors along the lesser curvature or on the anterior or posterior walls had splenic hilar node metastases in up to 6% [7]. 2
3 Table 1: Incidence of node metastases from cancer s in various part of the stomach [7]. A tumors on the Overview on Gastric Cancer Lymph Node station Number A N=339 M N=318 C N=150 Lesser Curvature Anterior Wall Greater Curvature Posterior Wal (0-1) (0-1) (0-1) (0-1) (0-1) (0-1) (0-1) (0-1) ,14,15,16 (0-5) (0-5) (0-5) (0-5) (0-5) (0-5) (0-5) A,M,C: distal,middle and proximal thirds of the stomach, respectively. The inclusion of node stations in the CTV is based on these findings. The 2002 Gastric Surgical Adjuvant Radiotherapy Consensus Report discussed gastric anatomy and pathways of tumor spread, described patterns of failure, and detailed treatment planning guidelines for adjuvant 2 D radiotherapy. This report mandated coverage of the gastric tumor bed, the anastomosis or stumps, and the regional lymphatics. Detailed recommendations was made in this report [2]. Administration of barium at the time of simulation was recommanded to identify the anastomosis and gastric stump. Review of preoperative computed tomography (CT) scans was mandatory to identify the preoperative location of the tumor and regional lymphatics, and placement of radiopaque clips at the time of surgical resection (figure 2,3 and 4) [2]. Figure 2: Simulation film for T4 (diaphragm invasion) cardial tumor with 4of 15 nodes involved with tumor. Preoperative CT identifies tumor bed. The anastomotic line is easily identified on barium swallow and by staple line. Regional lymph node location is reconstructed from CT scan. 3
4 Figure 3: Simulation film for a T3 antral primary two of six regional nodes. The Billroth I anastomosis staple line is identified that connect the gastric remnant with the duodenum. Beam's-eyes-view reconstruction identifies the original tumor bed, the anastomosis and regional nodes (perigastric, retropancreatic, porta hepatis, celiac and pancreaticoduodenal nodes that are in an aberrant location because of the Billroth I procedure) at risk.though splenic nodes are at relatively low risk, their proximity to residual perigastric nodes makes inclusion of these nodes not an issue of increased radiotherapy toxicity [2]. Tepper and Gunderson published a report entitled Radiation Treatment Parameters in the Adjuvant Postoperative Therapy of Gastric Cancer. This report provided detailed guidelines on appropriate radiation treatment volumes stratified by primary tumor site within the stomach (oesogastric jonction, proximal, middle and distal staomach) and by tumor (T) and node (N) stage[3]. Delineation of target volumes for tridimensional conformal radiotherapy requires intravenous contrast-enhanced planning CT with a 3-5mm slice thickness. This CT simulation is performed in the supine position with arms overhead, from top of diaphragm (for stomach) or carina (for tumor of oesogastric junction or cardia) to the bottom of L4. Patients should be fasted for 2 3 hours. Intravenous contrast is preferred to demonstrate blood vessels and guide clinical target volume (CTV) delineation, particularly for lymph nodes.the already defined lead marks are taped to the skin. 4
5 Figure 4: Simulation film for T3 antral tumor with two of five peritumoral lymph nodes metastatically involved. Simulation film shows areas at risk of locoregional relapse. Preoperative tumor bed is identified by preoperative CT scan: staple lines help locate duodenal stump and area of gastric transection. Regional lymphatics are identified from CT scan. Splenic nodes are included with tolerable kidney volumes [2]. The CTV is defined in the best conditions from the preoperative dosimetric scan and an image adjustment performed with the postoperative CT scan (figure 5,6) [8]. In the absence of a preoperative dosimetric scanner, a fusion of the diagnostic scanner and the scanner in the treatment position is performed [8]. Whatever the seat of gastric cancer - apart from cardiac tumors - all the stomach is included in CTV as well as anastomoses and lymph nodes. These structures are contoured on each CT slice for delineation of the clinical target volume (CTV) [8]. Two CTV are described. A first CTV which includes the oes-jejunal or gastro-jejunal anastomosis, the gastric stump, the gastric bed reconstructed from a preoperative scan and lymph node areas. Ideally, clips are set up by the surgeon to delimit the operating bed, the initial site of the tumor and sites at risk of relapse (R2 residue, fixed lymph node groups). The second CTV includes sites at risk of relapse [8,9]. For most gastric cancers, L3 represents the lower limit of CTV. This lower limit allows the inclusion of nodes 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 12 [8,9]. 2 Mineur and al detailed nodal sites included in the volume CTV 1 as follows in the table 5
6 Table 2 : nodal sites included in the volume CTV 1 according to Mineur [8]. Overview on Gastric Cancer Tumor site Nodal sites included in CTV1 Cardia 1,2,3,7,8,9 Fundus 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11 The lesser curvature or the greater curvature 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11 The gastric antrum 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16 Hennequin detailed nodal sites included in the volume CTV 1 as follows in the table 3 Table 3: nodal sites included in the volume CTV 1 according to Hennequin [9]. Tumor site 2.2. Planning target volume (PTV) Nodal sites included in CTV1 Gastric body or fundus 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 Oesogastric junction 1,2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11 The gastric antrum 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 The margin defining PTV is 2 cm [8,9,10]. This margin corresponds to the positioning errors and to the movements of organs. The median displacements of the critical organs are 6 mm in a cranio-caudal axis and 2 mm in the other directions. Wysocka et al. Recommended a caudal-caudal margin of 1 cm and a margin of 5 mm in the other axes with an individual approach for patients with high respiratory amplitude [11]. Caudry et al. Have proposed to reduce this margin to 10 mm under the condition of rigorous control of patient placement (restraint, laser, supine position, portal imaging) [12]. 3. Delineation of Target Volumes As radiation treatment fields become increasingly conformal in an attempt to limit dose to normal critical structures, it becomes increasingly important to accurately identify treatment volumes on CT-based planning images. Based on studies evaluating the patterns of relapse after surgical resection, general guidelines have been proposed to aid in definition of the clinical target volume for adjuvant radiation treatment fields based on location, T stage of the primary tumor, and N-stage. For node positive disease, wide coverage of the tumor bed, residual stomach, resection margins, and nodal drainage regions have been generally recommended. Mineur has published illustrative figures of the delineation of CTV (figure 5,6)[8]. 6
7 Figure 5: CT delimitation of the subdiaphragmatic lymph node territories involved in stomach cancers on preoperative and postoperative CT. 7: left gastric artery (Cs), 8: common hepatic artery (Hc); 9: celiac trunk; 11: splenic artery lymph nodes; 12: hepatic artery (Hp). AO: descending aorta; Rd: right kidney; Rg: left kidney; F: liver [8]. Figure 6: repositionning of the stomach on the postoperative CT after adjustment (brown dotted line) and identification of lymph node territories, view with representation of areas 3,4 (small and large curvature, 7 (left gastric artery) 10,11 (splenic artery and hilum) [8] By inclusion of the preoperative tumor bed and resection margin, more often than not the preoperative perigastric lymph node drainage basin is naturally included within the target volume [13]. A gastric lymph node (LN) contouring atlas is meant to supplement the previously established guidelines for definition of CTV in the adjuvant treatment of gastric cancer [13]. This report serves as a template for the delineation of gastric lymph node stations to aid in the definition of elective clinical target volumes to be used in conformal treatment planning [13]. Although generally the radiographic definitions of gastric LN stations described for intact gastris anatomy can be applied in the postoperative setting (figure 7), due to the potential for differences in postsurgical anatomy it is important to discuss radiographic identification of gastric LN stations in the setting of the most common oncologic surgeries employed for resection of gastric cancers (figure 8,9,10) 7
8 Figure 7: intact gastric anatomy. (A) left paracardial (orange); (B) greater curvature (blue), splenic hilum (brown), right paracardial (forest green); (C) greater curvature (blue), lesser curvature (dark blue), splenic hilum (brown); (D) greater curvature (blue), lesser curvature (dark blue), splenic (sky blue), splenic hilum (brown), left gastric (aquamarine, dashed); (E) greater curvature (blue), lesser curvature (dark blue), splenic (sky blue), left gastric (aquamarine, dashed), paraortic (red), hepatoduodenal (bright green); (F) greater curvature (blue), lesser curvature (dark blue), splenic (sky blue), paraortic (red), hepatoduodenal (bright green), common hepatic (dark purple), celiac (pink); (G) greater curvature (blue), ), lesser curvature (dark blue), paraortic (red), hepatoduodenal (bright green), suprapyloric (yellow); (H) greater curvature (blue), ), paraortic (red), pancreatic (lime green), superior mesenteric (violet), infrapyloric (green dashed). 8
9 Figure 8: Ivor-Lewis eosophagogastrectomy. (A) Greater curvature (blue), lesser curvature (dark blue), splenic hilum (brown), splenic (sky blue); (B) greater curvature (blue), lesser curvature (dark blue), splenic (sky blue), hepatoduodenal (bright green), suprapyloric (yellow), celiac (salmon pink), common hepatic (dark purple), left gastric (aquamarine, dashed), paraortic (red); (C) greater curvature (blue), pancreatic (lime green), celiac (salmon pink), splenic (sky blue), paraortic (red), infrapyloric (green dashed); (D) greater curvature (blue), superior mesenteric (violet), pancreatic (lime green), paraortic (red); (E), ), pancreatic (lime green), paraortic (red). Figure 9: Total gastrectomy with roux-en-y esophagojejunostomy. (A) splenic hilum (brown), splenic (sky blue); (B) splenic hilum (brown), splenic (sky blue), hepatoduodenal (spring green), common hepatic (dark purple), suprapyloric (yellow); (C) splenic hilum (brown), paraortic (red), celiac (salmon pink), pancreatic (lime green), infrapyloric (green dashed); (D) paraortic (red), pancreatic (lime green), superior mesenteric (violet). 9
10 Figure 10: Subtotal gastrectomy. (A) R paracardial (forest green), L paracardial (orange), splenic hilum (brown); (B) lesser curvature (dark blue), greater curvature (blue), splenic (sky blue), splenic hilum (brown), (C) greater curvature (blue), splenic (sky blue), paraortic (red), left gastric (aquamarine, dashed), celiac (salmon pink); (D) greater curvature (blue), splenic (sky blue), paraortic (red), left gastric (aquamarine, dashed), celiac (salmon pink), common hepatic (dark purple); (E) hepatoduodenal (spring green), paraortic (red); (F) pancreatic (lime green), paraortic (red), superior mesenteric (violet). 4. Organes at Risk easy. Organs at risk are kidneys, liver, heart, lung, and spinal cord. Their delineations is 5. References 1. Macdonald JS, Smalley SR, Benedetti J, Hundahl SA, Estes NC, Stemmermann GN, et al. Chemoradiotherapy after surgery compared with surgery alone for adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345: Smalley SR, Gunderson L, Tepper J, Martenson JA Jr, Minsky B, Willett C, et al. Gastric surgical adjuvant radiotherapy consensus report: rationale and treatment implementation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002; 52: Tepper JE, Gunderson LL. Radiation treatment parameters in the adjuvant postoperative therapy of gastric cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2002; 12: Jansen EPM, Nijkamp J, Gubanski M, Lind PA, Verheij M. Interobserver variation of clinical target volume delineation in gastric cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 77: Moretones C, Leo n D, Navarro A, Santacruz O, Boladeras AM, Macia ` M, et al. Interobserver variability in target volume delineation in postoperative radiochemotherapy for gastric cancer. A pilot prospective study. Clin Transl Oncol. 2012; 14: Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma-2nd English edition. Gastric Cancer. 1998; 1: Maruyama K, Gunven P, Okabayashi K. Lymph node metastases of gastric cancer : general pattern in 1931 patients. Ann Surg. 1989; 210: Mineur L, Jaegle E, Pointreau Y, Denis F. Cancer de l estomac. Cancer/Radiother. 2010; 14: Hennequin C, Quero L, Mineur L. Cancer de l estomac : doses et volumes-cibles. Cancer / Radiother 2008; 12: Matzinger O, Gerber E, Bernstein Z, Maingon P, Haustermans K, Bosset JF, et al. EORTC-RTOG expert opinion: radiotherapy volume and treatment guidelines for neoadjuvant radiation of adenocarcinomas of the gastroesophageal junction and the stomach. Radiother Oncol. 2009; 92: Wysocka B, Kassam Z, Lockwood G, Brierley J, Dawson LA, Buckley CA, et al. Interfraction and respiratory organ motion during conformal radiotherapy in gastric cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 77: Caudry M, Ratoanina JL, Escarmant P, Maire JP. Target volume in radiotherapy of gastric adenocarcinoma. Cancer Radiother. 2001; 5: Wo JY, Yoon SS, Guimaraes AR, Wolfgang J, Mamon HJ, Hong TS. Gastric lymph node contouring atlas: A tool to aid in clinical target volume definition in 3-dimensional treatment planning for gastric cancer. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2013; 3:
Classification of nodal stations in gastric cancer
 Review Article Classification of nodal stations in gastric cancer Fausto Rosa 1, Guido Costamagna 2, Giovanni Battista Doglietto 1, Sergio Alfieri 1 1 Department of Digestive Surgery, 2 Department of Digestive
Review Article Classification of nodal stations in gastric cancer Fausto Rosa 1, Guido Costamagna 2, Giovanni Battista Doglietto 1, Sergio Alfieri 1 1 Department of Digestive Surgery, 2 Department of Digestive
Surgical Problems in Proximal GI Cancer Management Cardia Tumours Question #1: What are cardia tumours?
 Surgical Problems in Proximal GI Cancer Management Cardia Tumours Question #1: What are cardia tumours? Question #2: How are cardia tumours managed? Michael F. Humer December 3, 2005 Vancouver, BC Case
Surgical Problems in Proximal GI Cancer Management Cardia Tumours Question #1: What are cardia tumours? Question #2: How are cardia tumours managed? Michael F. Humer December 3, 2005 Vancouver, BC Case
Limited en bloc Resection of the Gastroesophageal Junction with Isoperistaltic Jejunal Interposition
 22 Limited en bloc Resection of the Gastroesophageal Junction with Isoperistaltic Jejunal Interposition J.R. Izbicki, W.T. Knoefel, D. C. Broering ] Indications Severe dysplasia in the distal esophagus
22 Limited en bloc Resection of the Gastroesophageal Junction with Isoperistaltic Jejunal Interposition J.R. Izbicki, W.T. Knoefel, D. C. Broering ] Indications Severe dysplasia in the distal esophagus
Laparoscopy-assisted D2 radical distal subtotal gastrectomy
 Masters of Gastrointestinal Surgery Laparoscopy-assisted D2 radical distal subtotal gastrectomy Xiaogeng Chen, Weihua Li, Jinsi Wang, Changshun Yang Department of Tumor Surgery, Fujian Provincial Hospital,
Masters of Gastrointestinal Surgery Laparoscopy-assisted D2 radical distal subtotal gastrectomy Xiaogeng Chen, Weihua Li, Jinsi Wang, Changshun Yang Department of Tumor Surgery, Fujian Provincial Hospital,
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Overview on Gastric Cancer
 Chapter 5 Role of postoperative chemoradiotherapy in the therapeutic management of adenocarcinomas of the stomach and oesogastric junction Ben Salah H*; Bahri M; Dhouib F; Sallemi N; Bourmèche M; Daoud
Chapter 5 Role of postoperative chemoradiotherapy in the therapeutic management of adenocarcinomas of the stomach and oesogastric junction Ben Salah H*; Bahri M; Dhouib F; Sallemi N; Bourmèche M; Daoud
NEOADJUVANT THERAPY IN CARCINOMA STOMACH. Dr Jyotirup Goswami Consultant Radiation Oncologist Narayana Superspeciality Hospital, Howrah
 NEOADJUVANT THERAPY IN CARCINOMA STOMACH Dr Jyotirup Goswami Consultant Radiation Oncologist Narayana Superspeciality Hospital, Howrah NEOADJUVANT THERAPY?! Few believers Limited evidence Many surgeons
NEOADJUVANT THERAPY IN CARCINOMA STOMACH Dr Jyotirup Goswami Consultant Radiation Oncologist Narayana Superspeciality Hospital, Howrah NEOADJUVANT THERAPY?! Few believers Limited evidence Many surgeons
Gastric Cancer Staging AJCC eighth edition. Duncan McLeod Westmead Hospital, NSW
 Gastric Cancer Staging AJCC eighth edition Duncan McLeod Westmead Hospital, NSW Summary of changes New clinical stage prognostic groups, ctnm Postneoadjuvant therapy pathologic stage groupings, yptnm -
Gastric Cancer Staging AJCC eighth edition Duncan McLeod Westmead Hospital, NSW Summary of changes New clinical stage prognostic groups, ctnm Postneoadjuvant therapy pathologic stage groupings, yptnm -
Radiotherapy: from Planning to Delivery. D. Genovesi Istituto Radioterapia Oncologica CHIETI
 Radiotherapy: from Planning to Delivery D. Genovesi Istituto Radioterapia Oncologica CHIETI www.radioterapia.unich.it Radiotherapy: from Planning to Delivery TOPICS 1. Total Dose Prescription 2. Prescription
Radiotherapy: from Planning to Delivery D. Genovesi Istituto Radioterapia Oncologica CHIETI www.radioterapia.unich.it Radiotherapy: from Planning to Delivery TOPICS 1. Total Dose Prescription 2. Prescription
Guidelines for Extended Lymphadenectomy in Gastric Cancer: A Prospective Comparative Study
 Ann Surg Oncol DOI 10.1245/s10434-012-2544-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE GASTROINTESTINAL ONCOLOGY Guidelines for Extended Lymphadenectomy in Gastric Cancer: A Prospective Comparative Study Oktar Asoglu, MD 1, Tugba
Ann Surg Oncol DOI 10.1245/s10434-012-2544-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE GASTROINTESTINAL ONCOLOGY Guidelines for Extended Lymphadenectomy in Gastric Cancer: A Prospective Comparative Study Oktar Asoglu, MD 1, Tugba
SETTING Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center. RESPONSIBLE PARTY Haiquan Chen MD.
 OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
Three-dimensional computed tomography simulation for laparoscopic lymph node dissection in the treatment of proximal gastric cancer
 Review Article Three-dimensional computed tomography simulation for laparoscopic lymph node dissection in the treatment of proximal gastric cancer Hideki Sunagawa, Takahiro Kinoshita Gastric Surgery Division,
Review Article Three-dimensional computed tomography simulation for laparoscopic lymph node dissection in the treatment of proximal gastric cancer Hideki Sunagawa, Takahiro Kinoshita Gastric Surgery Division,
ARROCase: Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer
 ARROCase: Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer Resident: Jordan Kharofa, MD Staff: Beth Erickson, MD 8/2012 Medical College of Wisconsin Department of Radiation Oncology Case Presentation: 60 year old
ARROCase: Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer Resident: Jordan Kharofa, MD Staff: Beth Erickson, MD 8/2012 Medical College of Wisconsin Department of Radiation Oncology Case Presentation: 60 year old
Report. biology physics. Received Jul 21, 2011, and in revised form Jan 4, Accepted for publication Jan 5, 2012
 International Journal of Radiation Oncology biology physics www.redjournal.org Report Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Consensus Panel Guidelines for the Delineation of the Clinical Target Volume in the
International Journal of Radiation Oncology biology physics www.redjournal.org Report Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Consensus Panel Guidelines for the Delineation of the Clinical Target Volume in the
GASTRIC CANCER RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL ON D2 LINPHADENECTOMY VS STANDARD D1 LINPHADENECTOMY
 GASTRIC CANCER RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL ON D2 LINPHADENECTOMY VS STANDARD D1 LINPHADENECTOMY Maurizio Degiuli, MD Coordinator of the IGCSG (Italian Gastric Cancer Study Group) Antonio Ponti, MD MPH
GASTRIC CANCER RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL ON D2 LINPHADENECTOMY VS STANDARD D1 LINPHADENECTOMY Maurizio Degiuli, MD Coordinator of the IGCSG (Italian Gastric Cancer Study Group) Antonio Ponti, MD MPH
Michael A. Choti, MD, FACS Department of Surgery Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, MD
 Michael A. Choti, MD, FACS Department of Surgery Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, MD Surgical Therapy of Gastric Cancer CLINICAL QUESTIONS 1. How much of the stomach should be removed? 2. How many lymph
Michael A. Choti, MD, FACS Department of Surgery Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, MD Surgical Therapy of Gastric Cancer CLINICAL QUESTIONS 1. How much of the stomach should be removed? 2. How many lymph
The role of chemoradiotherapy in GE junction and gastric cancer. Karin Haustermans
 The role of chemoradiotherapy in GE junction and gastric cancer Karin Haustermans Overview Postoperative chemoradiotherapy Preoperative chemoradiotherapy Palliative radiation Technical aspects Overview
The role of chemoradiotherapy in GE junction and gastric cancer Karin Haustermans Overview Postoperative chemoradiotherapy Preoperative chemoradiotherapy Palliative radiation Technical aspects Overview
Distribution of FDG-avid nodes in esophageal cancer: implications for radiotherapy target delineation
 Garcia et al. Radiation Oncology (2016) 11:156 DOI 10.1186/s13014-016-0731-6 RESEARCH Distribution of FDG-avid nodes in esophageal cancer: implications for radiotherapy target delineation Brandon Garcia
Garcia et al. Radiation Oncology (2016) 11:156 DOI 10.1186/s13014-016-0731-6 RESEARCH Distribution of FDG-avid nodes in esophageal cancer: implications for radiotherapy target delineation Brandon Garcia
intent treatment be in the elderly?
 Gastric cancer: How strong can curative intent treatment be in the elderly? Caio Max S. Rocha Lima, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of Miami & Sylvester Cancer Center Gastric cancer: epidemiology
Gastric cancer: How strong can curative intent treatment be in the elderly? Caio Max S. Rocha Lima, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of Miami & Sylvester Cancer Center Gastric cancer: epidemiology
Surgical Treatment of Localized Gastric Cancer
 13 Surgical Treatment of Localized Gastric Cancer JOHN I. LEW, MD MITCHELL C. POSNER, MD Theodor Billroth performed the first successful gastric resection (a distal subtotal gastrectomy for stomach cancer)
13 Surgical Treatment of Localized Gastric Cancer JOHN I. LEW, MD MITCHELL C. POSNER, MD Theodor Billroth performed the first successful gastric resection (a distal subtotal gastrectomy for stomach cancer)
CHEMORADIOTHERAPY PLUS SURGERY FOR GASTRIC ADENOCARCINOMA
 CHEMORADIOTHERAPY PLUS SURGERY FOR GASTRIC ADENOCARCINOMA CHEMORADIOTHERAPY AFTER SURGERY COMPARED WITH SURGERY ALONE FOR ADENOCARCINOMA OF THE STOMACH OR GASTROESOPHAGEAL JUNCTION JOHN S. MACDONALD, M.D.,
CHEMORADIOTHERAPY PLUS SURGERY FOR GASTRIC ADENOCARCINOMA CHEMORADIOTHERAPY AFTER SURGERY COMPARED WITH SURGERY ALONE FOR ADENOCARCINOMA OF THE STOMACH OR GASTROESOPHAGEAL JUNCTION JOHN S. MACDONALD, M.D.,
Controversies in management of squamous esophageal cancer
 2015.06.12 12.47.48 Page 4(1) IS-1 Controversies in management of squamous esophageal cancer C S Pramesh Thoracic Surgery, Department of Surgical Oncology, Tata Memorial Centre, India In Asia, squamous
2015.06.12 12.47.48 Page 4(1) IS-1 Controversies in management of squamous esophageal cancer C S Pramesh Thoracic Surgery, Department of Surgical Oncology, Tata Memorial Centre, India In Asia, squamous
I patients with nonendocrine pancreas carcinoma
 LYMPH NODE INVOLVEMENT IN CARCINOMA OF THE HEAD OF THE PANCREAS AREA ANTONIO L. CUBILLA, MD,* JOSEPH FORTNER, MD,+~ AND PATRICK J. FITZGERALD, MD*~ A prospective study to determine the lymph node involvement
LYMPH NODE INVOLVEMENT IN CARCINOMA OF THE HEAD OF THE PANCREAS AREA ANTONIO L. CUBILLA, MD,* JOSEPH FORTNER, MD,+~ AND PATRICK J. FITZGERALD, MD*~ A prospective study to determine the lymph node involvement
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenocarcinoma, pancreatic ductal, laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy for, 61 Adrenal cortical carcinoma, laparoscopic adrenalectomy for, 114
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenocarcinoma, pancreatic ductal, laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy for, 61 Adrenal cortical carcinoma, laparoscopic adrenalectomy for, 114
Protocol of Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer
 106 年 12 月修訂 Protocol of Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer Indication of radiotherapy Indication of definitive radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy (1) Resectable, but medically unfit, or high
106 年 12 月修訂 Protocol of Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer Indication of radiotherapy Indication of definitive radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy (1) Resectable, but medically unfit, or high
د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
Significance of the lymph nodes in the 7th station in rational dissection for metastasis of distal gastric cancer with different T categories
 Original Article Significance of the lymph nodes in the 7th station in rational dissection for metastasis of distal gastric cancer with different T categories Wu Song, Yulong He, Shaochuan Wang, Weiling
Original Article Significance of the lymph nodes in the 7th station in rational dissection for metastasis of distal gastric cancer with different T categories Wu Song, Yulong He, Shaochuan Wang, Weiling
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 Final Pathology:
 Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Abstract. Introduction
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.1.37 RESEARCH ARTICLE Delineation of Margins for the Planning Target Volume (PTV) for Image-Guided Radiotherapy (IGRT) of Gastric Cancer Based on Intrafraction Motion Paulina
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.1.37 RESEARCH ARTICLE Delineation of Margins for the Planning Target Volume (PTV) for Image-Guided Radiotherapy (IGRT) of Gastric Cancer Based on Intrafraction Motion Paulina
Case Scenario 1. The patient has now completed his neoadjuvant chemoradiation and has been cleared for surgery.
 Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
The Whipple Operation Illustrations
 The Whipple Operation Illustrations Fig. 1. Illustration of the sixstep pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple operation) as described in a number of recent text books by Dr. Evans. The operation is divided
The Whipple Operation Illustrations Fig. 1. Illustration of the sixstep pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple operation) as described in a number of recent text books by Dr. Evans. The operation is divided
Impact of upfront randomization for postoperative treatment on quality of surgery in the CRITICS gastric cancer trial
 Gastric Cancer (219) 22:369 376 https://doi.org/1.7/s112-18-875-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impact of upfront randomization for postoperative treatment on quality of surgery in the CRITICS gastric cancer trial
Gastric Cancer (219) 22:369 376 https://doi.org/1.7/s112-18-875-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impact of upfront randomization for postoperative treatment on quality of surgery in the CRITICS gastric cancer trial
Gastroesophag Gastroesopha eal Junction Adenocarcinoma: What is the best adjuvant regimen? Michael G. G. H addock Haddock M.D.
 Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma: What is the best adjuvant regimen? Michael G. Haddock M.D. Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN Locally Advanced GE Junction ACA CT S CT or CT S CT/RT Proposition Chemoradiation
Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma: What is the best adjuvant regimen? Michael G. Haddock M.D. Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN Locally Advanced GE Junction ACA CT S CT or CT S CT/RT Proposition Chemoradiation
General Data. Gender : Male Birthday and age : 12/07/24,80 y/o Occupation : 無 Date of Admission :
 General Data Gender : Male Birthday and age : 12/07/24,80 y/o Occupation : 無 Date of Admission : 92-07-09 1 Chief complaint Upper abdominal fullness 30 minutes after having foods with sometimes epigastralgia
General Data Gender : Male Birthday and age : 12/07/24,80 y/o Occupation : 無 Date of Admission : 92-07-09 1 Chief complaint Upper abdominal fullness 30 minutes after having foods with sometimes epigastralgia
Quiz Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been increasing in the last 20 years. a. True b. False
 Quiz 1 1. Which of the following are risk factors for esophagus cancer. a. Obesity b. Gastroesophageal reflux c. Smoking and Alcohol d. All of the above 2. Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been
Quiz 1 1. Which of the following are risk factors for esophagus cancer. a. Obesity b. Gastroesophageal reflux c. Smoking and Alcohol d. All of the above 2. Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been
Gastric Cancer in a Young Postpartum Female. Kings County Hospital Center SUNY Downstate Case Conference May 24, 2012
 Gastric Cancer in a Young Postpartum Female Kings County Hospital Center SUNY Downstate Case Conference May 24, 2012 Case HPI: 31 yo F, G5P3, 3 weeks s/p C-section, with gastric outlet obstruction. Pt
Gastric Cancer in a Young Postpartum Female Kings County Hospital Center SUNY Downstate Case Conference May 24, 2012 Case HPI: 31 yo F, G5P3, 3 weeks s/p C-section, with gastric outlet obstruction. Pt
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF GASTRIC CANCER
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF GASTRIC CANCER Irina Kovatch, PGY 4 Kings County Medical Center Morbidity and Mortality January 13, 2011 Case Presentation 60 yo M admitted to medicine on 10/24/2010 with c/o persistent
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF GASTRIC CANCER Irina Kovatch, PGY 4 Kings County Medical Center Morbidity and Mortality January 13, 2011 Case Presentation 60 yo M admitted to medicine on 10/24/2010 with c/o persistent
Intraabdominal Roux-en-Y reconstruction with a novel stapling technique after laparoscopic distal gastrectomy
 Gastric Cancer (2009) 12: 164 169 DOI 10.1007/s10120-009-0520-0 Technical note 2009 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Intraabdominal Roux-en-Y reconstruction with a novel stapling
Gastric Cancer (2009) 12: 164 169 DOI 10.1007/s10120-009-0520-0 Technical note 2009 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Intraabdominal Roux-en-Y reconstruction with a novel stapling
Prognosis of Patients With Gastric Cancer Who Underwent Proximal Gastrectomy
 Int Surg 2012;97:275 279 Prognosis of Patients With Gastric Cancer Who Underwent Proximal Gastrectomy Masahide Ikeguchi, Abdul Kader, Seigo Takaya, Youji Fukumoto, Tomohiro Osaki, Hiroaki Saito, Shigeru
Int Surg 2012;97:275 279 Prognosis of Patients With Gastric Cancer Who Underwent Proximal Gastrectomy Masahide Ikeguchi, Abdul Kader, Seigo Takaya, Youji Fukumoto, Tomohiro Osaki, Hiroaki Saito, Shigeru
Completely laparoscopic extraperigastric lymph node dissection for gastric malignancies located in the middle or lower third of the stomach
 Gastric Cancer (1999) 2: 186 190 Technical note 1999 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Completely laparoscopic extraperigastric lymph node dissection for gastric malignancies located
Gastric Cancer (1999) 2: 186 190 Technical note 1999 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Completely laparoscopic extraperigastric lymph node dissection for gastric malignancies located
Pancreas Quizzes c. Both A and B a. Directly into the blood stream (not using ducts)
 Pancreas Quizzes Quiz 1 1. The pancreas produces hormones. Which type of hormone producing organ is the pancreas? a. Endocrine b. Exocrine c. Both A and B d. Neither A or B 2. Endocrine indicates hormones
Pancreas Quizzes Quiz 1 1. The pancreas produces hormones. Which type of hormone producing organ is the pancreas? a. Endocrine b. Exocrine c. Both A and B d. Neither A or B 2. Endocrine indicates hormones
Gastric Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma
 Gastric Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male Female Intersex/indeterminate
Gastric Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male Female Intersex/indeterminate
Radiotherapy Planning (Contouring Lung Cancer for Radiotherapy dose prescription) Dr Raj K Shrimali
 Radiotherapy Planning (Contouring Lung Cancer for Radiotherapy dose prescription) Dr Raj K Shrimali Let us keep this simple and stick to some basic rules Patient positioning Must be reproducible Must be
Radiotherapy Planning (Contouring Lung Cancer for Radiotherapy dose prescription) Dr Raj K Shrimali Let us keep this simple and stick to some basic rules Patient positioning Must be reproducible Must be
A Retrospective Study of Survival and Patterns of Failure in Gastric Cancer after Adjuvant Chemoradiation
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, December: 131-138, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Retrospective Study of Survival and Patterns of Failure in Gastric Cancer after Adjuvant Chemoradiation
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, December: 131-138, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Retrospective Study of Survival and Patterns of Failure in Gastric Cancer after Adjuvant Chemoradiation
ASTRO econtouring for Lymphoma. Stephanie Terezakis, MD
 ASTRO econtouring for Lymphoma Stephanie Terezakis, MD Disclosures No conflicts to disclose 1970 Total Lymphoid Irradiation (TLI) 1995 Involved-Field Radiotherapy (IFRT) 2008 Involved Node Radiotherapy
ASTRO econtouring for Lymphoma Stephanie Terezakis, MD Disclosures No conflicts to disclose 1970 Total Lymphoid Irradiation (TLI) 1995 Involved-Field Radiotherapy (IFRT) 2008 Involved Node Radiotherapy
Case Report pissn J Korean Soc Radiol 2012;67(4): INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 Focal Fat Deposition Developed in the Segment IV of the Liver Following Gastrectomy Mimicking a Hepatic Metastasis: Two Case Reports 1 위절제술후에간의제 4 분절에서발생한간전이를닮은국소지방침윤 : 두증례보고
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 Focal Fat Deposition Developed in the Segment IV of the Liver Following Gastrectomy Mimicking a Hepatic Metastasis: Two Case Reports 1 위절제술후에간의제 4 분절에서발생한간전이를닮은국소지방침윤 : 두증례보고
Rebecca K. S. Wong 1, Raymond Jang 2, Gail Darling 3. Review Article
 Review Article Postoperative chemoradiotherapy vs. preoperative chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced (operable) gastric cancer: clarifying the role and technique of radiotherapy Rebecca K. S. Wong 1,
Review Article Postoperative chemoradiotherapy vs. preoperative chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced (operable) gastric cancer: clarifying the role and technique of radiotherapy Rebecca K. S. Wong 1,
Subtotal gastrectomy for gastric cancer
 Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13667 World J Gastroenterol 2014 October 14; 20(38): 13667-13680 ISSN 1007-9327
Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13667 World J Gastroenterol 2014 October 14; 20(38): 13667-13680 ISSN 1007-9327
Research Article Survival Benefit of Adjuvant Radiation Therapy for Gastric Cancer following Gastrectomy and Extended Lymphadenectomy
 International Surgical Oncology Volume 2012, Article ID 307670, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2012/307670 Research Article Survival Benefit of Adjuvant Radiation Therapy for Gastric Cancer following Gastrectomy
International Surgical Oncology Volume 2012, Article ID 307670, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2012/307670 Research Article Survival Benefit of Adjuvant Radiation Therapy for Gastric Cancer following Gastrectomy
Satisfactory surgical outcome of T2 gastric cancer after modified D2 lymphadenectomy
 Original Article Satisfactory surgical outcome of T2 gastric cancer after modified D2 lymphadenectomy Shupeng Zhang 1, Liangliang Wu 2, Xiaona Wang 2, Xuewei Ding 2, Han Liang 2 1 Department of General
Original Article Satisfactory surgical outcome of T2 gastric cancer after modified D2 lymphadenectomy Shupeng Zhang 1, Liangliang Wu 2, Xiaona Wang 2, Xuewei Ding 2, Han Liang 2 1 Department of General
Lymph node metastasis in gastric cardiac adenocarcinoma in male patients
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i37.6245 World J Gastroenterol 2013 October 7; 19(37): 6245-6257 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online) 2013 Baishideng.
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i37.6245 World J Gastroenterol 2013 October 7; 19(37): 6245-6257 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online) 2013 Baishideng.
Original Article. Jin Suk Bae, MD 1, Dong Hyun Kim, MD 1,2, Won Taek Kim, MD 1,2, Yong Ho Kim, MS 1, Dahl Park, PhD 1,2, Yong Kan Ki, MD 1,2
 Original Article Radiat Oncol J 27;35():65-7 https://doi.org/.3857/roj.26.29 pissn 2234-9 eissn 2234-356 The role of surgical clips in the evaluation of interfractional uncertainty for treatment of hepatobiliary
Original Article Radiat Oncol J 27;35():65-7 https://doi.org/.3857/roj.26.29 pissn 2234-9 eissn 2234-356 The role of surgical clips in the evaluation of interfractional uncertainty for treatment of hepatobiliary
Case Scenario year-old white male presented to personal physician with dyspepsia with reflux.
 Case Scenario 1 57-year-old white male presented to personal physician with dyspepsia with reflux. 7/12 EGD: In the gastroesophageal junction we found an exophytic tumor. The tumor occupies approximately
Case Scenario 1 57-year-old white male presented to personal physician with dyspepsia with reflux. 7/12 EGD: In the gastroesophageal junction we found an exophytic tumor. The tumor occupies approximately
Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy
 Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2011;15:152-156 Original Article Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy Suzy Kim 1,#, Kyubo
Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2011;15:152-156 Original Article Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy Suzy Kim 1,#, Kyubo
Josh Howard CMD Upendra Parvathaneni MBBS, FRANZCR
 Anatomic and Dosimetric Correlation in the Treatment of Advanced Larynx Cancer- When is the Brachial Plexus at Risk? Josh Howard CMD Upendra Parvathaneni MBBS, FRANZCR AAMD 39th Annual Meeting - Seattle
Anatomic and Dosimetric Correlation in the Treatment of Advanced Larynx Cancer- When is the Brachial Plexus at Risk? Josh Howard CMD Upendra Parvathaneni MBBS, FRANZCR AAMD 39th Annual Meeting - Seattle
Clinical benefit of Totally Laparoscopic over Laparoscopically Assisted Distal Gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y Reconstruction for Early Gastric Cancer
 Med. Bull. Fukuoka Univ. 39 3/4 251 256 2012 Clinical benefit of Totally Laparoscopic over Laparoscopically Assisted Distal Gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y Reconstruction for Early Gastric Cancer Tatsuya HASHIMOTO,
Med. Bull. Fukuoka Univ. 39 3/4 251 256 2012 Clinical benefit of Totally Laparoscopic over Laparoscopically Assisted Distal Gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y Reconstruction for Early Gastric Cancer Tatsuya HASHIMOTO,
Potential systematic uncertainties in IGRT when FBCT reference images are used for pancreatic tumors
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 3, 2015 Potential systematic uncertainties in IGRT when FBCT reference images are used for pancreatic tumors Ahmad Amoush, May Abdel-Wahab,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 3, 2015 Potential systematic uncertainties in IGRT when FBCT reference images are used for pancreatic tumors Ahmad Amoush, May Abdel-Wahab,
COLLECTING CANCER DATA: STOMACH AND ESOPHAGUS
 COLLECTING CANCER DATA: STOMACH AND ESOPHAGUS 2017 2018 NAACCR WEBINAR SERIES Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching
COLLECTING CANCER DATA: STOMACH AND ESOPHAGUS 2017 2018 NAACCR WEBINAR SERIES Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching
Superior and Basal Segment Lung Cancers in the Lower Lobe Have Different Lymph Node Metastatic Pathways and Prognosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES: Superior and Basal Segment Lung Cancers in the Lower Lobe Have Different Lymph Node Metastatic Pathways and Prognosis Shun-ichi Watanabe, MD, Kenji Suzuki, MD, and Hisao Asamura, MD
ORIGINAL ARTICLES: Superior and Basal Segment Lung Cancers in the Lower Lobe Have Different Lymph Node Metastatic Pathways and Prognosis Shun-ichi Watanabe, MD, Kenji Suzuki, MD, and Hisao Asamura, MD
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR
 BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
RADIATION THERAPY WITH ONCE-WEEKLY GEMCITABINE IN PANCREATIC CANCER: CURRENT STATUS OF CLINICAL TRIALS
 doi:10.1016/s0360-3016(03)00449-8 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 56, No. 4, Supplement, pp. 10 15, 2003 Copyright 2003 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/03/$
doi:10.1016/s0360-3016(03)00449-8 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 56, No. 4, Supplement, pp. 10 15, 2003 Copyright 2003 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/03/$
To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis.
 GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
Totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy reconstructed by Rouxen-Y with D2 lymphadenectomy and needle catheter jejunostomy for gastric cancer
 Masters of Gastrointestinal Surgery Totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy reconstructed by Rouxen-Y with D2 lymphadenectomy and needle catheter jejunostomy for gastric cancer Xin Ye, Jian-Chun Yu, Wei-Ming
Masters of Gastrointestinal Surgery Totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy reconstructed by Rouxen-Y with D2 lymphadenectomy and needle catheter jejunostomy for gastric cancer Xin Ye, Jian-Chun Yu, Wei-Ming
Perigastric lymph node metastases in gastric cancer: comparison of different staging systems
 Gastric Cancer (1999) 2: 201 205 Original article 1999 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Perigastric lymph node metastases in gastric cancer: comparison of different staging systems
Gastric Cancer (1999) 2: 201 205 Original article 1999 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Perigastric lymph node metastases in gastric cancer: comparison of different staging systems
Laparoscopy-assisted radical total gastrectomy plus D2 lymph node dissection
 Masters of Gastrointestinal Surgery Laparoscopy-assisted radical total gastrectomy plus D2 lymph node dissection Chaohui Zheng, Changming Huang, Ping Li, Jianwei Xie, Jiabin Wang, Jianxian Lin, Jun Lu
Masters of Gastrointestinal Surgery Laparoscopy-assisted radical total gastrectomy plus D2 lymph node dissection Chaohui Zheng, Changming Huang, Ping Li, Jianwei Xie, Jiabin Wang, Jianxian Lin, Jun Lu
Evaluation of Whole-Field and Split-Field Intensity Modulation Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Techniques in Head and Neck Cancer
 1 Charles Poole April Case Study April 30, 2012 Evaluation of Whole-Field and Split-Field Intensity Modulation Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Techniques in Head and Neck Cancer Abstract: Introduction: This study
1 Charles Poole April Case Study April 30, 2012 Evaluation of Whole-Field and Split-Field Intensity Modulation Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Techniques in Head and Neck Cancer Abstract: Introduction: This study
Nordic Society for Gynecological Oncology Advisory Board of Radiotherapy
 Nordic Society for Gynecological Oncology Advisory Board of Radiotherapy Guidelines for postoperative irradiation of cervical cancer Contents: 1. Treatment planning for EBRT. 2 2. Target definition for
Nordic Society for Gynecological Oncology Advisory Board of Radiotherapy Guidelines for postoperative irradiation of cervical cancer Contents: 1. Treatment planning for EBRT. 2 2. Target definition for
Study of the Value of Combined Multiorgan Resection in Surgical Treatment of Carcinoma of the Gastric Cardia
 Chinese Journal of Clinical Oncology Apr. 2007, Vol. 4, No. 2 P 109~114 Xijiang Zhao et al [SpringerLink] DOI 10.1007/s11805-007-0109-5 109 Study of the Value of Combined Multiorgan Resection in Surgical
Chinese Journal of Clinical Oncology Apr. 2007, Vol. 4, No. 2 P 109~114 Xijiang Zhao et al [SpringerLink] DOI 10.1007/s11805-007-0109-5 109 Study of the Value of Combined Multiorgan Resection in Surgical
Index. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) 465 469 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adjuvant therapy, preoperative for gastric cancer, staging and, 339 B Breast cancer, metabolic
Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) 465 469 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adjuvant therapy, preoperative for gastric cancer, staging and, 339 B Breast cancer, metabolic
doi: /j.ijrobp
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.08.037 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 82, No. 1, pp. 475 482, 2012 Copyright Ó 2012 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/$ - see front
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.08.037 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 82, No. 1, pp. 475 482, 2012 Copyright Ó 2012 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/$ - see front
TUMORS OF THE STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL
 gastrointestinal tract and abdomen TUMORS OF THE STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL L. Mark Knab, MD, David J. Bentrem, MD, FACS, and Jeffrey D. Wayne, MD, FACS * Gastric Adenocarcinoma The incidence of gastric carcinoma
gastrointestinal tract and abdomen TUMORS OF THE STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL L. Mark Knab, MD, David J. Bentrem, MD, FACS, and Jeffrey D. Wayne, MD, FACS * Gastric Adenocarcinoma The incidence of gastric carcinoma
GASTRIC CANCER. Joyce Au SUNY Downstate Grand Rounds July 11, 2013
 GASTRIC CANCER Joyce Au SUNY Downstate Grand Rounds July 11, 2013 xxm with gastric adenocarcinoma on biopsy of antral lesion on EGD at outside hospital PMH: residual schizophrenia, HTN PSH: exploratory
GASTRIC CANCER Joyce Au SUNY Downstate Grand Rounds July 11, 2013 xxm with gastric adenocarcinoma on biopsy of antral lesion on EGD at outside hospital PMH: residual schizophrenia, HTN PSH: exploratory
Patterns of failure in gastric carcinoma after D2 gastrectomy and chemoradiotherapy: a radiation oncologist s view
 British Journal of Cancer (2004) 91, 11 17 All rights reserved 0007 0920/04 $30.00 www.bjcancer.com Patterns of failure in gastric carcinoma after D2 gastrectomy and chemoradiotherapy: a radiation oncologist
British Journal of Cancer (2004) 91, 11 17 All rights reserved 0007 0920/04 $30.00 www.bjcancer.com Patterns of failure in gastric carcinoma after D2 gastrectomy and chemoradiotherapy: a radiation oncologist
Protocol of Radiotherapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer
 107 年 12 月修訂 Protocol of Radiotherapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer Indication of radiotherapy Limited stage: AJCC (8th edition) stage I-III (T any, N any, M0) that can be safely treated with definitive RT
107 年 12 月修訂 Protocol of Radiotherapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer Indication of radiotherapy Limited stage: AJCC (8th edition) stage I-III (T any, N any, M0) that can be safely treated with definitive RT
Small Plicae Circularis. Short Closely packed together. Sparse, completely absent at distal part Lymphoid Nodule
 Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy- Valuable. Jayer Chung, MD University of Colorado Health Sciences Center December 11, 2006
 Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy- Valuable Jayer Chung, MD University of Colorado Health Sciences Center December 11, 2006 Overview Esophageal carcinoma What is minimally invasive esophagectomy (MIE)?
Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy- Valuable Jayer Chung, MD University of Colorado Health Sciences Center December 11, 2006 Overview Esophageal carcinoma What is minimally invasive esophagectomy (MIE)?
Esophageal cancer (EC) is the eighth most common cancer worldwide and the sixth most common cause of cancer-related mortality (Kamangar et al.
 Arch. Biol. Sci., Belgrade, 65 (3), 821-827, 2013 DOI:10.2298/ABS1303821L DETERMINING THE LYMPH NODE CLINICAL TARGET VOLUME OF UPPER ESOPHAGEAL CARCINOMA WITH COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY MINGHUAN LI 1, YUHUI LIU
Arch. Biol. Sci., Belgrade, 65 (3), 821-827, 2013 DOI:10.2298/ABS1303821L DETERMINING THE LYMPH NODE CLINICAL TARGET VOLUME OF UPPER ESOPHAGEAL CARCINOMA WITH COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY MINGHUAN LI 1, YUHUI LIU
Splenic hilar dissection in the treatment of proximal advanced gastric cancer: what is an adequate strategy?
 Editorial Splenic hilar dissection in the treatment of proximal advanced gastric cancer: what is an adequate strategy? Takahiro Kinoshita Gastric Surgery Division, National Cancer Center Hospital East,
Editorial Splenic hilar dissection in the treatment of proximal advanced gastric cancer: what is an adequate strategy? Takahiro Kinoshita Gastric Surgery Division, National Cancer Center Hospital East,
Tao Zhang, Zhi-Wen Liang, Jun Han, Jian-Ping Bi, Zhi-Yong Yang and Hong Ma *
 Zhang et al. Radiation Oncology (2015) 10:114 DOI 10.1186/s13014-015-0420-x RESEARCH Open Access Double-arc volumetric modulated therapy improves dose distribution compared to static gantry IMRT and 3D
Zhang et al. Radiation Oncology (2015) 10:114 DOI 10.1186/s13014-015-0420-x RESEARCH Open Access Double-arc volumetric modulated therapy improves dose distribution compared to static gantry IMRT and 3D
Dosimetric consequences of tumor volume changes after kilovoltage cone-beam computed tomography for non-operative lung cancer during adaptive
 Oncology and Translational Medicine October 2015, Vol. 1, No. 5, P195 200 DOI 10.1007/s10330-015-0054-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dosimetric consequences of tumor volume changes after kilovoltage cone-beam computed
Oncology and Translational Medicine October 2015, Vol. 1, No. 5, P195 200 DOI 10.1007/s10330-015-0054-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dosimetric consequences of tumor volume changes after kilovoltage cone-beam computed
Disclosure. Acknowledgement. What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Rectal cancer imaging. None
 What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal drainage, after hepatic resection, 159 160 Ablation, radiofrequency, for hepatocellular carcinoma, 160 161 Adenocarcinoma, pancreatic.
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal drainage, after hepatic resection, 159 160 Ablation, radiofrequency, for hepatocellular carcinoma, 160 161 Adenocarcinoma, pancreatic.
STOMACH and DUODENUM DISEASE
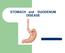 STOMACH and DUODENUM DISEASE STOMACH ANATOMY In the living and upright posture, the stomach is a j-shaped. It has two surfaces, two curvatures and two openings. Esophagus Fundus cardia Pylorus B o d y
STOMACH and DUODENUM DISEASE STOMACH ANATOMY In the living and upright posture, the stomach is a j-shaped. It has two surfaces, two curvatures and two openings. Esophagus Fundus cardia Pylorus B o d y
Dosimetric Analysis of 3DCRT or IMRT with Vaginal-cuff Brachytherapy (VCB) for Gynaecological Cancer
 Dosimetric Analysis of 3DCRT or IMRT with Vaginal-cuff Brachytherapy (VCB) for Gynaecological Cancer Tan Chek Wee 15 06 2016 National University Cancer Institute, Singapore Clinical Care Education Research
Dosimetric Analysis of 3DCRT or IMRT with Vaginal-cuff Brachytherapy (VCB) for Gynaecological Cancer Tan Chek Wee 15 06 2016 National University Cancer Institute, Singapore Clinical Care Education Research
Treatment Planning for Breast Cancer: Contouring Targets. Julia White MD Professor
 Treatment Planning for Breast Cancer: Contouring Targets Julia White MD Professor Outline 1. RTOG Breast Cancer Atlas 2. Target development on Clinical Trials Whole Breast Irradiation 2-D Radiotherapy
Treatment Planning for Breast Cancer: Contouring Targets Julia White MD Professor Outline 1. RTOG Breast Cancer Atlas 2. Target development on Clinical Trials Whole Breast Irradiation 2-D Radiotherapy
1. Epidemiology of Esophageal Cancer 2. Operative Strategies 3. Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy 4. Video
 Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy Guilherme M Campos, MD, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery Director G.I. Motility Center Director Bariatric Surgery Program University of California San Francisco ESOPHAGEAL
Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy Guilherme M Campos, MD, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery Director G.I. Motility Center Director Bariatric Surgery Program University of California San Francisco ESOPHAGEAL
Medicinae Doctoris. One university. Many futures.
 Medicinae Doctoris The Before and The After: Can chemotherapy revise the trajectory of gastric and esophageal cancers? Dr. David Dawe MD, FRCPC Medical Oncologist Assistant Professor Disclosures None All
Medicinae Doctoris The Before and The After: Can chemotherapy revise the trajectory of gastric and esophageal cancers? Dr. David Dawe MD, FRCPC Medical Oncologist Assistant Professor Disclosures None All
8. The polyp in the illustration can be described as (circle all that apply) a. Exophytic b. Pedunculated c. Sessile d. Frank
 Quiz 1 Overview 1. Beginning with the cecum, which is the correct sequence of colon subsites? a. Cecum, ascending, splenic flexure, transverse, hepatic flexure, descending, sigmoid. b. Cecum, ascending,
Quiz 1 Overview 1. Beginning with the cecum, which is the correct sequence of colon subsites? a. Cecum, ascending, splenic flexure, transverse, hepatic flexure, descending, sigmoid. b. Cecum, ascending,
Original article: new surgical approaches to the Klatskin tumour
 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Original article: new surgical approaches to the Klatskin tumour T. M. VAN GULIK*, S. DINANT*, O. R. C. BUSCH*, E. A. J. RAUWS, H. OBERTOP* & D. J. GOUMA Departments
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Original article: new surgical approaches to the Klatskin tumour T. M. VAN GULIK*, S. DINANT*, O. R. C. BUSCH*, E. A. J. RAUWS, H. OBERTOP* & D. J. GOUMA Departments
سرطان المعدة. Gastric Cancer حمود حامد
 سرطان المعدة Gastric Cancer ا أ لستاذ الدك تور حمود حامد عميد كلية الطب البشري بجامعة دمشق Epidemiology second leading cause of cancer death and fourth most common cancer worldwide Overall declining Histologic
سرطان المعدة Gastric Cancer ا أ لستاذ الدك تور حمود حامد عميد كلية الطب البشري بجامعة دمشق Epidemiology second leading cause of cancer death and fourth most common cancer worldwide Overall declining Histologic
REVISITING ICRU VOLUME DEFINITIONS. Eduardo Rosenblatt Vienna, Austria
 REVISITING ICRU VOLUME DEFINITIONS Eduardo Rosenblatt Vienna, Austria Objective: To introduce target volumes and organ at risk concepts as defined by ICRU. 3D-CRT is the standard There was a need for a
REVISITING ICRU VOLUME DEFINITIONS Eduardo Rosenblatt Vienna, Austria Objective: To introduce target volumes and organ at risk concepts as defined by ICRU. 3D-CRT is the standard There was a need for a
The Evolution of RT Techniques for Gynaecological Cancers in a developing country context
 The Evolution of RT Techniques for Gynaecological Cancers in a developing country context Hannah Simonds Stellenbosch University/ Tygerberg Academic Hospital ESMO Africa 2017 I have no disclosures External
The Evolution of RT Techniques for Gynaecological Cancers in a developing country context Hannah Simonds Stellenbosch University/ Tygerberg Academic Hospital ESMO Africa 2017 I have no disclosures External
Laparoscopic spleen-preserving complete splenic hilum lymphadenectomy for advanced proximal gastric cancer
 Review Article Page 1 of 5 Laparoscopic spleen-preserving complete splenic hilum lymphadenectomy for advanced proximal gastric cancer Wei Wang*, Wejun Xiong*, Qiqi Peng, Shanao Ye, Yansheng Zheng, Lijie
Review Article Page 1 of 5 Laparoscopic spleen-preserving complete splenic hilum lymphadenectomy for advanced proximal gastric cancer Wei Wang*, Wejun Xiong*, Qiqi Peng, Shanao Ye, Yansheng Zheng, Lijie
Anatomy of laparoscopy-assisted distal D2 radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer
 Masters of Gastrointestinal Surgery Anatomy of laparoscopy-assisted distal D2 radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer Da-Guang Wang, Liang He, Yang Zhang, Jing-Hai Yu, Yan Chen, Ming-Jie Xia, Jian Suo Department
Masters of Gastrointestinal Surgery Anatomy of laparoscopy-assisted distal D2 radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer Da-Guang Wang, Liang He, Yang Zhang, Jing-Hai Yu, Yan Chen, Ming-Jie Xia, Jian Suo Department
gastric cancer; lymph node dissection;
 Yonago Acta Medica 18;61:175 181 Original Article Therapeutic Value of Lymph Node Dissection Along the Superior Mesenteric Vein and the Posterior Surface of the Pancreatic Head in Gastric Cancer Located
Yonago Acta Medica 18;61:175 181 Original Article Therapeutic Value of Lymph Node Dissection Along the Superior Mesenteric Vein and the Posterior Surface of the Pancreatic Head in Gastric Cancer Located
Esophagus Stomach 4/2/15
 Collecting Cancer Data: Esophagus & Stomach 2014-2015 NAACCR Webinar Series April 2, 2015 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants
Collecting Cancer Data: Esophagus & Stomach 2014-2015 NAACCR Webinar Series April 2, 2015 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants
The Spleen. Dr Fahad Ullah
 The Spleen BY Dr Fahad Ullah Spleen The spleen is an largest lymphoid organ shaped like a shoe that lies relative to the 9th and 11th ribs and is located in the left hypochondrium. Thus, the spleen is
The Spleen BY Dr Fahad Ullah Spleen The spleen is an largest lymphoid organ shaped like a shoe that lies relative to the 9th and 11th ribs and is located in the left hypochondrium. Thus, the spleen is
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 6, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2005
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 6, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2005 Advantages of inflatable multichannel endorectal applicator in the neo-adjuvant treatment of patients with locally advanced
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 6, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2005 Advantages of inflatable multichannel endorectal applicator in the neo-adjuvant treatment of patients with locally advanced
Survival benefit of D2-plus gastrectomy in gastric cancer patients with duodenal invasion
 Gastric Cancer (2018) 21:296 302 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-017-0733-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Survival benefit of D2-plus gastrectomy in gastric cancer patients with duodenal invasion Koshi Kumagai 1 Takeshi
Gastric Cancer (2018) 21:296 302 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-017-0733-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Survival benefit of D2-plus gastrectomy in gastric cancer patients with duodenal invasion Koshi Kumagai 1 Takeshi
