Minami et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:22
|
|
|
- Arnold Walters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Minami et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:22 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Improvement of endocytoscopic findings after per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) in esophageal achalasia; does POEM reduce the risk of developing esophageal carcinoma? Per oral endoscopic myotomy, endocytoscopy and carcinogenesis Hitomi Minami 1, Naoyuki Yamaguchi 1, Kayoko Matsushima 1, Yuko Akazawa 1, Ken Ohnita 1, Fuminao Takeshima 1, Toshiyuki Nakayama 2, Tomayoshi Hayashi 2, Haruhiro Inoue 3, Kazuhiko Nakao 1 and Hajime Isomoto 1* Abstract Background: Per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) has been reported to be a new therapeutic option for esophageal achalasia. The possibility that POEM could reduce the risk of developing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma was evaluated. Methods: This was a single-centre, retrospective study. Fifteen consecutive patients with esophageal achalasia who underwent POEM in our institution between August 2010 and January 2012 were enrolled. Ultra-high magnification with endocytoscopy was performed, and both histopathological and immunohistochemical evaluations for Ki-67 and p53 were assessed before and 3 months after POEM. Results: POEM was successfully performed and effectively released the dysphagia symptom in all patients without severe complications. Subjective symptoms (mean Ekcardt score, before 7.4 vs. after 0.5, p<0.05) and manometric pressure studies (mean lower esophageal sphincter pressure), before 82.7 vs. after 22.9 mmhg, p<0.05) showed substantial improvement following POEM. The average numbers of esophageal epithelial nuclei before and after POEM on endocytoscopic images were and 78.0, respectively (p<0.05). The mean Ki-67-positive ratio was 26.0 (median 25.4, range, ) before and 20.7 (median 20.0, ; p=0.07) after POEM, and the mean p53-positive ratio was 2.35 (median 2.61, ) before and 0.97 (median 1.49, ; p<0.05) after POEM. A significant positive correlation was seen between the number of nuclei and the Ki-67-positive ratio (p<0.05). Conclusions: POEM appears to be an effective and less invasive treatment of choice against achalasia and may reduce the risk of esophageal carcinogenesis. Endocytoscopy can be useful for the assessment of esophageal cellular proliferation. Keywords: Esophageal achalasia, POEM, Per-oral endoscopic myotomy, Esophageal cancer, Squamous cell carcinoma * Correspondence: hajimei2002@yahoo.co.jp 1 Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Nagasaki University Hospital, 1-7-1, Sakamoto, Nagasaki , Japan Full list of author information is available at the end of the article 2013 Minami et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Minami et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:22 Page 2 of 9 Background Achalasia is a rare, chronic, esophageal motility disorder with an estimated annual prevalence of 1 per 100,000 subjects in Western populations [1]. The disease can occur at all ages, but the incidence seems to increase with age. The predominant symptoms are dysphagia and regurgitation, because of the impaired relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and the loss of normal peristalsis [2]. Persistent esophageal distension with retention of foods and fluids, bacterial overgrowth, and impaired clearance of regurgitated acid and gastric contents lead to chronic inflammation and passively cause dysplasia and carcinoma [3-5]. The aim of therapy is to reduce food stasis, which might interrupt the progression to carcinoma and thus reduce the risk of squamous cell carcinoma. In 1872, Fagge reported the first case of esophageal carcinoma developing in a patient with achalasia [6]. The reported incidence of concomitant carcinoma and achalasia ranges from 0.53% to 8.6% [7]. In a recent study, Meijssen et al. reported that the risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma in achalasia patients was increased 33-fold over that in the general population [8]. Leeuwenburgh et al. also reported that the relative hazard ratio of esophageal cancer was 28 (confidence interval 17 46) compared with an age- and sex-identical population in the same timeframe [1]. Although many investigators have warned clinicians about the high incidence of carcinogenesis in achalasia [9], the prognosis of patients who develop such carcinomas remains poor. Recently, per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) was introduced by Inoue et al. [10] as a less invasive and effective curative treatment option with minimal complications. In the present study, the clinical feasibility of POEM in achalasia patients in our hospital was evaluated. In addition, whether this innovative procedure could affect esophageal epithelial proliferation was examined by ultra-high magnification with endocytoscopy, along with immunohistochemical staining of targeted biopsies with antibody against Ki-67 nuclear antigen before and after POEM. Immunohistochemistry with anti-p53 antibody was also used to assess the alteration in squamous cell carcinoma risk with POEM. Methods Design This was a single-centre, retrospective study. This study was approved by ethics committee of Nagasaki University Hospital. Patients Fifteen consecutive cases of esophageal achalasia which underwent POEM in our institution between August 2010 and January 2012 were enrolled in this study. A clinical summary of the 15 patients (3 males, 12 females; mean age 51.7 years, age range years) with esophageal achalasia is shown in Table 1. The dilation grade of the disease was II in 6 patients and III in 1 patient. Prior endoscopic balloon dilation was performed in 5 patients. Two patients with sigmoid type achalasia were included. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects, a legal surrogate, the parents or legal guardians for minor subjects prior to their inclusion, in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration and under approval by the Nagasaki University Ethics Committee. All the subjects also consented for the publication of individual clinical details with a written informed consent. Dysphagia symptom scores To evaluate improvement of dysphagia objectively, a dysphagia symptom score and the Eckardt score (representative subjective symptom score) were used [11]. The dysphagia symptom score was defined as follows: the worst degree of dysphagia just before the treatment was scored as 10, and the best condition, before the patient developed achalasia, was scored as zero, in accordance with Inoue s report [10]. The post-procedural degree of dysphagia was scored between 0 and 10 in each patient. Scoring was done before POEM, after POEM on the day of discharge from hospital, and 3, 6, and 12 months later. Barium esophagogram The degree and shape of achalasia were assessed by barium passage. The maximum diameter of the thoracic esophagus was measured, and achalasia was classified into grade I (diameter <3.5 cm), grade II (3.5 cm < diameter < 6.0 cm), and grade III (diameter 6.0 cm), in accordance with the descriptive rules (Descriptive Rules for Achalasia of the Esophagus, Japan Society of Esophageal Diseases, June 2012, 4th Edition). On the day following POEM, a barium swallow was done to confirm passage of contrast media through the gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) without leakage. Achalasia shapes include straight, flask, and sigmoid types. Esophageal manometry Esophageal pull-through manometry was done in all cases before and after the procedure using the Polygraf ID (Medtronic Functional Diagnostics, Denmark). According to the manufacturer s data, the normal range for LES pressure with this device is from 14.3 to 34.5 mmhg. The manometry study could not be completed in case 15 before POEM because the measuring catheter did not pass through the narrow segment of the esophagus.
3 Minami et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:22 Page 3 of 9 Table 1 Patients characteristics No. Sex Age (years) BMI (kg/m2) Dilation Type Balloon dilation Systemic complication 1 female II straight - none 2 female II straight - none 3 male III sigmoid 3 sessions hypertension 4 female II sigmoid - breast cancer 5 female I straight - rheumatoid arthritis 6 female I straight - none 7 female I straight - none 8 female II straight 1 session none 9 female I straight - hypertension 10 female I straight 1 session pulmonary emphysema 11 male I straight - none 12 male I straight 5 sessions pulmonary emphysema 13 female I straight 2 sessions none 14 female II straight - none 15 female II straight - none maen POEM The POEM procedure received approval from the institutional review board (IRB) of Nagasaki University Hospital (approval number , issued on May, ). Written informed consent was obtained from all patients. A forward-viewing endoscope with an outer diameter of 9.8 mm (GIF-H260; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan), which is routinely used for upper gastrointestinal examination, was used with a transparent distal cap attachment (MH-588, Olympus). A triangle-tip knife (KD- 640 L; Olympus) was used to dissect the submucosal layer and to divide circular muscle bundles. A coagulating forceps (Coagrasper, FD-411QR; Olympus) was used to coagulate larger vessels prior to dissection and for hemostasis. The VIO 300D (ERBE, Tubingen, Germany) electrogenerator was used, and for final closure of the mucosal entry site, hemostatic clips (EZ-CLIP, HX- 110QR; Olympus) were applied. The procedures were performed under general anesthesia with positive pressure ventilation. The UCR CO 2 insufflator (Olympus) was used with a regular insufflating tube (MAJ-1742; Olympus), which maintained CO 2 insufflation at a constant rate of 1.2 L/min. The POEM procedures were done as previously described with slight modifications as follows. Submucosal injection was done first at the level of the middle thoracic esophagus, approximately 13 cm proximal to the GEJ. About 10 ml of saline supplemented with 0.3% indigocarmine were injected. A 2-cm, longitudinal mucosal incision was made on the mucosal surface to create a mucosal entry to the submucosal space (dry cut mode, 50 W, effect 3). Then, a technique similar to endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) was used to create a submucosal tunnel downwards, passing through the GEJ, and about 3 cm into the proximal stomach (Figure 1a). Spray coagulation mode (60 W, effect 2) was used to dissect the submucosal layer. Larger vessels in the submucosa were coagulated using the forceps in the soft coagulation mode (80 W, effect 5). Dissection of the circular muscle bundle was started at 2 cm distal from the mucosal entry. The sharp tip of the knife was used to capture only circular muscle bundles and then lift up toward the tunnel lumen (Figure 1b). The captured circular muscle bundle was cut by spray coagulation current (60 W, effect 2). Division of the sphincter muscle was continued from the proximal side towards the stomach until it passed 2 or 3 cm distal from the LES. After completion of the myotomy, smooth passage of the endoscope through the GEJ with minimal resistance was confirmed. The incised mucosal entry was closed with about five hemostatic clips after prophylactic antibiotic solution was sprayed inside the tunnel. Successful closure of the mucosal entry was confirmed by the endoscopic appearance. At the end of the procedure, the endoscope was again inserted into the original esophageal lumen down to the stomach, to confirm smooth passage through the GEJ. Endocytoscopy A prototype endocytoscope with an integrated dual charge-coupled device (CCD) (Figure 2) (GIF-Y0001, Olympus) was used. The dual-ccd integrated type endoscope has both conventional magnification (80-fold) and ultra-high magnification (450-fold) capabilities,
4 Minami et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:22 Page 4 of 9 Figure 1 POEM procedures. 1-a. A long submucosal tunnel is created. The blue color of the indigocarmine that was mixed with the glycerin solution helps discriminate the white muscle layer from submucosal tissue.1-b. Using a triangle-tip knife, the inner circular muscle is hooked and cut. Outer longitudinal muscles are seen behind the inner muscles. Outer muscles should be preserved to avoid severe complications such as compartment syndrome and mediastinitis. which can be easily interchanged at the push of a button on the endoscope. The clinical use of the prototype endoscope was approved by the hospital s ethics committee (IRB approval number , Oct ), and written informed consent was obtained from all patients. A mixture of 0.05% crystal violet and 0.1% methylene blue was used during endocytoscopy to obtain images similar to conventional pathological images using hematoxylin and eosin staining. Crystal violet effectively dyes the cytoplasm, whereas methylene blue allows detailed identification of the cell structure, including the nuclei and cytoplasm. Dilution of methylene blue with crystal violet seems to improve visualization of the lesion and may also decrease the potential risk of DNA damage due to a higher concentration of methylene blue [12]. Patients underwent both conventional endoscopy and endocytoscopy at the same time under conscious sedation with intravenous pethidine hydrochloride Figure 2 The dual-ccd endocytoscope carries lenses for both conventional magnification and ultra-high magnification. This scope enables us to obtain ultra-high magnifying images during usual endoscopic examination. (35 mg; Opystan, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Osaka, Japan), supplemented with diazepam (5 10 mg, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Osaka, Japan). After conventional endoscopic observation, ultra-high magnification was applied. The mucosa on the posterior wall 25 cm distal from the incisor was targeted. Still images were obtained from the targeted area, and 3 images of sufficient quality were selected for evaluation. Then, the average nuclei counts of the 3 images before and 3 months after POEM were compared. After endocytoscopic observation, biopsies were taken from the targeted area. All endocytoscopy examinations were recorded, and the location photographed during endocytoscopy coincided with the histopathological images. Nevertheless, complete correspondence between endocytoscopic images and microscopic images is still limited [13]. Immunohistochemistry using anti-ki-67 and anti-p53 antibodies Four-mm tissue sections of the formalin-fixed, paraffin wax-embedded samples were sliced and mounted on silane-coated glass slides, dried, deparaffinized with xylene and rehydrated through graded ethanol. Antigen retrieval was performed by boiling for 15 minutes in 10 mm monocitric acid buffer (ph 6.0) for anti-ki-67 staining and in 10 mm Tris/ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid buffer (ph 9.0) for anti-p53 staining. Prior to immune staining, endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked by incubating the slides in a 0.5% solution of H2O2 in phosphate-buffered citric acid for 15 minutes at room temperature. After washing 3 times with Trisbuffered saline (TBS) with a ph of 7.4, the sections were incubated in TBS buffer containing 10% rabbit nonimmune serum (DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark) and 10% normal human plasma (and 5% bovine serum albumin [BSA] for p53 staining) for 20 minutes. Then, the
5 Minami et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:22 Page 5 of 9 sections were incubated with the primary antibody against anti-human Ki-67 antigen (clone MIB-1, DAKO) in a 1:100 dilution or p53 antigen (clone DO-7, DAKO) in a 1:100 dilution for 14 hours at 4 C. Subsequently, biotin-labeled rabbit-anti-mouse antibody (DAKO) was used as the second antibody, followed by the addition of a streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase complex (DAKO). To detect Ki-67 and p53, 3-amino-9-ethylcarbazole was used as the substrate. One experienced pathologist who was blinded to the clinical data counted at least 300 nuclei in each sample. Cells were counted as positive when moderate to intense nuclear staining was found. Staining with the isotype immunoglobulin and diluted solution was performed in the same fashion for the negative controls. Statistics Statistical analyses were performed using Fisher s exact test, the χ 2 test, Student s t-test, the Mann Whitney U test, and the Kruskal-Wallis test, as appropriate. A P value <0.05 was accepted as significant. Data are expressed as means ± standard deviation (SD). Results POEM POEM was successfully performed in all 15 cases without severe complications such as perforation and mediastinitis. Details of the procedure outcomes are shown in Table 2. No massive pneumoperitoneum that required reduction of abdominal distention or capnomediastinum was observed. Two patients, who had a long disease history and severe submucosal fibrosis due to preceding repeat balloon dilation, experienced post-procedural bleeding, which resolved with conservative management. The mean LES pressure decreased from 82.7 to 22.9 mmhg, and the subjective symptom scores were also significantly lower after POEM (Ekcardt score p < 0.05, dysphagia symptom score p < 0.05). Even after a mean follow-up of 11.3 (range 8 25) months, no patient developed recurrent symptoms of dysphagia. Endoscopic reflux esophagitis was identified in 5 patients (33.3%) on follow-up endoscopy examination. Two (15.3%) patients received proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy, and the symptoms were easily controlled. Figure 3a-d shows the endoscopic images taken from the GEJ and mid-thoracic esophagus before and after POEM. Before POEM, the endoscope was passed through the GEJ with great resistance. The thickened esophageal mucosa showed turbidity and whitish color change, lacking permeability of the vascular structures. Following POEM, however, the resistance to endoscopic passage through the GEJ was completely resolved, and the mucosal abnormalities were substantially improved, without the whitish color change. The POEM procedure allowed detailed observation of the vascular structures of the mucosal surface. Endocytoscopic findings Thirteen achalasia patients underwent endocytoscopy and targeted biopsy before and after POEM. In Case 1, informed consent for the study was not obtained before the procedure, Table 2 Outcomes of the POEM procedure No Procedure Symptom LESP(mmHg) Eckardt score Myotomy Complications time (min) score Before After Before After length none none bleedind(day 10) none none none none none none none none bleedind(day 1) none none none mean
6 Minami et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:22 Page 6 of 9 Figure 3 Conventional endoscopic images of the EGJ and mid-thoracic esophagus before and after POEM. 3-a, b Before POEM, the EGJ is extremely tight. Whitish color change is seen on the surface mucosa without permeability of vascular structures. 3-c, d After POEM, the narrow segment of the EGJ has been totally released. The status of the surface mucosa is significantly improved, and permeability of the surface vascular patterns is restored. and Case 6 was excluded due to concerns about possible adverse effects of methylene blue on her pregnancy. The average counts of esophageal mucosal nuclei on endocytoscopy before and 3 months after POEM were (median 112.3, range ) and 78.7 (median 76.0, ) (Figure 4a), respectively. Thus, POEM significantly reduced the number of nuclei (p < 0.005). Compared to the endocytoscopic images obtained before POEM, cellular and nuclear structures and inter-cellular margins were observed more clearly in the images obtained after POEM (Figure 5). The nuclei numbers before POEM varied very widely, whereas they were distributed in a relatively narrow range after the procedure. There were no significant correlation between endoscopic nuclear counts and patients characteristics such as degree of dilation, type, and duration of dysphagia symptom. However, statistically significant correlation between endocytoscopic nuclear counts and Eckardt score before the procedure was observed (r = , ~ , p < 0.01). The number of nuclei in 3 non-achalasia patients (healthy controls) was also evaluated, and the average count was 88.5 (range, 76 97), which was the same level as the post-poem values in achalasia patients. Immunohistochemical analysis: Ki-67 and p53 immunostaining The mean Ki-67-positive ratios before and after the procedure were 26.0 (median 25.4, ) and 20.7 (median 20.0, ; p = 0.07), respectively (Figure 4b). There was a significant positive correlation between the esophageal epithelial nuclei numbers assessed by endocytoscopy and the Ki-67-positive ratios (correlation coefficient, 0.695, p < 0.05) (Figure 4d). The p53-positive ratios were decreased in the posttreatment group compared to the pre-treatment group with statistical significance. The mean positive ratios before and after the procedure were 2.35 (median 2.61, ) and 0.97 (median 1.49, ), respectively (Figure 4c). Histopathological evaluation with hematoxylin and eosin staining confirmed that all of the specimens were negative for dysplasia or squamous cell carcinoma.
7 Minami et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:22 Page 7 of 9 Figure 4 a-d. The endocytoscopic counts of nuclei are significantly improved after POEM (a). Also, the mean Ki-67-positive ratios before and after the procedure are 26.0 (median 25.4, ) and 20.7 (median 20.0, ), respectively (p = 0.07) (b, c). The mean p53-positive ratios before and after the procedure are 2.35 (median 2.61, ) and 0.97 (median 1.49, ). There was a significant positive correlation between the esophageal epithelial nuclei numbers assessed by endocytoscopy and the Ki-67-positive ratios (correlation coefficient, 0.695, p < 0.05) (Figure 4d). Discussion Recently, POEM has been developed in Japan [10] as a less invasive and effective curative treatment option with no cases of severe complications. Other therapeutic options include endoscopic balloon dilatation and surgical myotomy. Endoscopic balloon dilatation is still widely performed because of its relative noninvasiveness and simplicity, but it has a relatively lower success rate and often requires multiple treatment sessions [14]. Inoue et al. reported that there was no recurrence after the POEM procedure in their 17 case series of achalasia in their short-term results [10]. They also reported the lack of recurrence on 43 patients of maximum of 1 year 9 months observation [15] (Japanese manuscript). In the present 15 cases, no severe complications such as perforation and severe mediastinitis occurred, and the clinical course was uneventful in each case. Although the term has been relatively short, there has been no disease recurrence during the observation period. Surgical myotomy has been thought to be the curative therapeutic choice for symptomatic achalasia. However, it requires skin incisions and additional anti-reflux surgical intervention. Thus, POEM could be one of the most promising treatment options for symptomatic achalasia. On the basis of prior data, the overall prevalence of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in patients with achalasia has been estimated to be up to 8.6%, accounting for a 50-fold increase in cancer risk [7]. In achalasia patients, it has been suggested that chronic food stasis leads to chronic inflammation, epithelial hyperplasia,
8 Minami et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:22 Page 8 of 9 Figure 5 Comparison of endocytoscopic images between before and after POEM, including the shape and size of cells and the number of nuclei. The number of surface cells and cellular arrangement was significantly improved after POEM. multifocal dysplasia, and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) [1,16,17]. Previous studies showed that it would take a mean of 24 (range 10 43) years to establish carcinoma after symptom onset, and 3 to 4 years for carcinoma to develop from dysplasia [1,18,19]. Goldblum et al. noted that several epithelial abnormalities were seen in achalasia, including high-grade squamous dysplasia, superficial squamous cell carcinoma, and lymphocytic esophagitis [20], exclusively accompanied by diffuse squamous hyperplasia reflecting accelerated cellular turnover and proliferation. The changes in endocytoscopic images were examined together with the cellular proliferative ability of the mucosal surface in order to evaluate whether the POEM procedure improved cellular proliferation as well as mucosal inflammation. The ultra-high magnification enables us to observe cellular irregularity, similar to conventional pathological images [12,21]. Inoue et al. reported that there was a significant correlation between endocytoscopic images and histopathological images in various gastrointestinal disorders [12,21]. As shown in Figure 5, comparison of endocytoscopic images between before and after POEM revealed significant improvements in the nuclear counts and the irregularity of cellular arrangement. The endocytoscopic nuclear counts after POEM reached almost the same levels as healthy controls. The POEM procedure substantially reduced Ki-67 positivity. There was a significant correlation between Ki-67 expression and endocytoscopic nuclear counts (Figure 4d). Collectively, cellular proliferation ability could be assessed by endocytoscopic images. At the same time, endocytoscopy allows us to obtain information about cellular atypia [12,21]. Fujii et al. reported cases of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma concomitant with achalasia and found higher Ki-67 positivity in cancer lesions than in non-cancerous lesions [22]. Leeuwenburgh evaluated the expressions of both p53 and Ki-67 in achalasia patients and reported that overexpression of p53 could be an early marker of neoplastic progression in achalasia [23]. In esophageal adenocarcinoma, Reid and Kerkhof reported that both p53 and Ki-67 were effective for early discrimination [24,25]. The present data showed decreases of both Ki67 and p53 expressions after POEM, which implies that POEM could reduce the future risk of developing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Leeuwenburgh documented that Ki-67 expression was not a discriminative factor for carcinogenesis in achalasia patients. However, they targeted the GEJ, which could be easily affected by distention of food and fermentation. Expression of the Ki-67 protein is associated with the clinical course of cell proliferation that is closely linked to tissue inflammation [26]. Leeuwenburgh and his colleagues suggested taking a biopsy from the thoracic esophagus, not from the EGJ, to avoid the effects of severe inflammation. In the present series, biopsies were taken from the middle-thoracic esophagus to avoid sampling severely inflamed mucosa. Furthermore, advanced achalasia may conceal the dysphagia caused by cancer growth. Stasis of the esophageal contents and a severely inflamed mucosa make it almost impossible to detect early cancers. Improving visualization via the therapeutic intervention allows detailed observation and cancer inspection at an earlier stage. Therefore, we strongly insist that early release of the obstruction is essential for finding early cancers and preventing the development of advanced cancer. Brossard et al. showed that the incidence of squamous cell carcinoma was eight times higher in untreated patients with achalasia and 4.5 times higher in patients treated with pneumatic dilatation than in those treated with surgical myotomy [27]. Endoscopic myotomy may
9 Minami et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:22 Page 9 of 9 provide less risk of SCC development with a higher success rate than other options. Endoscopic balloon dilatation has a lower success rate [14] than the POEM procedure. Unlike surgical myotomy, POEM allows us to preserve the anatomical integrity of the LES and possibly minimize postoperative reflux [28,29]. Nevertheless, these LES pressure-lowering therapies could be ultimately complicated by the development of Barrett s esophagus and adenocarcinoma. Therefore, longer follow-up is obviously necessary to clarify the risk of Barrett s cancer due to reflux esophagitis, which was observed in some of our cases [19,30]. Conclusions POEM could be one of the most effective and less invasive treatment options against dysphagia and reduce the risk of developing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Endocytoscopy can be useful for the assessment of esophageal cellular proliferation. Competing interests The authors have nothing to declare. Authors' contributions Guarantor of the article: HM, Specific author contributions: HM, first author of the article treated and followed the patients. HI treated and followed the cohort and composed the database; KO has treated and followed the cohort. KM and NY conducted statistical analysis; YA and FT contributed statistical advice; TN and TH contributed to the pathological examination and analysis. KN and HI, supervisor, devised study protocol and co-wrote the article. All authors read and approve the final manuscript. Author details 1 Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Nagasaki University Hospital, 1-7-1, Sakamoto, Nagasaki , Japan. 2 Department of Pathology, Nagasaki University Hospital, 1-7-1, Sakamoto, Nagasaki , Japan. 3 Digestive Disease Center, Showa University Northern Yokohama Hospital, Yokohama, Japan. Received: 9 October 2012 Accepted: 23 January 2013 Published: 30 January 2013 References 1. Leeuwenburgh I, et al: Long-term esophageal cancer risk in patients with primary achalasia: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol 2010, 105 (10): Gockel I, Muller M, Schumacher J: Achalasia a disease of unknown cause that is often diagnosed too late. Dtsch Arztebl Int 2012, 109(12): Porschen R, et al: Achalasia-associated squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: flow-cytometric and histological evaluation. Gastroenterology 1995, 108(2): Streitz JM Jr, et al: Achalasia and squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: analysis of 241 patients. Ann Thorac Surg 1995, 59(6): West RL, et al: Long term results of pneumatic dilation in achalasia followed for more than 5 years. Am J Gastroenterol 2002, 97(6): Fagge CH: A case of simple stenosis of the esophagus followed by epithelioma. Guy's hosp Rep 1872, 17: Dunaway PM, Wong RK: Risk and surveillance intervals for squamous cell carcinoma in achalasia. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 2001, 11(2): Meijssen MA, et al: Achalasia complicated by oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a prospective study in 195 patients. Gut 1992, 33(2): Sandler RS, et al: The risk of esophageal cancer in patients with achalasia. A population-based study. JAMA 1995, 274(17): Inoue H, et al: Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Endoscopy 2010, 42(4): Eckardt VF, Aignherr C, Bernhard G: Predictors of outcome in patients with achalasia treated by pneumatic dilation. Gastroenterology 1992, 103 (6): Minami H, et al: Recent advancement of observing living cells in the esophagus using CM double staining: endocytoscopic atypia classification. Dis Esophagus 2012, 25(3): Inoue H: Endoscopic diagnosis of tissue atypism (EA) in the pharyngeal and esophageal squamous epithelium; IPCL pattern classification and ECA classification]. Kyobu Geka 2007, 60(8 Suppl): Campos GM, et al: Endoscopic and surgical treatments for achalasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg 2009, 249(1): Inoue H, Kudo SE: Per-oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for 43 consecutive cases of esophageal achalasia. Nihon Rinsho 2010, 68 (9): Lehman MB, et al: Squamous mucosal alterations in esophagectomy specimens from patients with end-stage achalasia. Am J Surg Pathol 2001, 25(11): Loviscek LF, et al: Early cancer in achalasia. Dis Esophagus 1998, 11(4): Eckardt AJ, Eckardt VF: Editorial: Cancer surveillance in achalasia: better late than never? Am J Gastroenterol 2010, 105(10): Leeuwenburgh I, et al: Oesophagitis is common in patients with achalasia after pneumatic dilatation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2006, 23(8): Goldblum JR, et al: Achalasia. A morphologic study of 42 resected specimens. Am J Surg Pathol 1994, 18(4): Inoue H, et al: In vivo observation of living cancer cells in the esophagus, stomach, and colon using catheter-type contact endoscope, "Endo- Cytoscopy system". Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 2004, 14(3): Fujii T, et al: Histopathological analysis of non-malignant and malignant epithelium in achalasia of the esophagus. Dis Esophagus 2000, 13(2): Leeuwenburgh I, et al: Expression of p53 as predictor for the development of esophageal cancer in achalasia patients. Dis Esophagus 2010, 23(6): Reid BJ: p53 and neoplastic progression in Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 2001, 96(5): Kerkhof M, et al: Aneuploidy and high expression of p53 and Ki67 is associated with neoplastic progression in Barrett esophagus. Cancer Biomark 2008, 4(1): Scholzen T, Gerdes J: The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol 2000, 182(3): Brossard E, et al: Achalasia and squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: is and endoscopic surveillance justified? Gastroenterology 1992, 102(Suppl)(A4(Abstract):. 28. Swanstrom LL, Rieder E, Dunst CM: A stepwise approach and early clinical experience in peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of achalasia and esophageal motility disorders. J Am Coll Surg 2011, 213 (6): von Renteln D, et al: Peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of achalasia: a prospective single center study. Am J Gastroenterol 2012, 107 (3): Zendehdel K, et al: Risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma in achalasia patients, a retrospective cohort study in Sweden. Am J Gastroenterol 2011, 106(1): doi: / x Cite this article as: Minami et al.: Improvement of endocytoscopic findings after per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) in esophageal achalasia; does POEM reduce the risk of developing esophageal carcinoma? Per oral endoscopic myotomy, endocytoscopy and carcinogenesis. BMC Gastroenterology :22.
Duke Masters of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Orlando, FL. September 17, Session VI: Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery: Miscellaneous
 Duke Masters of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Orlando, FL September 17, 2016 Session VI: Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery: Miscellaneous NOTES and POEM James D. Luketich MD, FACS Henry T. Bahnson
Duke Masters of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Orlando, FL September 17, 2016 Session VI: Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery: Miscellaneous NOTES and POEM James D. Luketich MD, FACS Henry T. Bahnson
A Novel Endoscopic Treatment for Achalasia Is the POEM mightier than the sword?
 A Novel Endoscopic Treatment for Achalasia Is the POEM mightier than the sword? Pavlos Kaimakliotis, MD Department of Gastroenterology Lahey Hospital and Medical Center Assistant Professor of Medicine
A Novel Endoscopic Treatment for Achalasia Is the POEM mightier than the sword? Pavlos Kaimakliotis, MD Department of Gastroenterology Lahey Hospital and Medical Center Assistant Professor of Medicine
POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS DISCLAIMER CODING INFORMATION REFERENCES POLICY HISTORY
 Original Issue Date (Created): November 26, 2013 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): November 26, 2013 Effective Date: April 1, 2014 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS
Original Issue Date (Created): November 26, 2013 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): November 26, 2013 Effective Date: April 1, 2014 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS
How I Do It? Per-oral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) Ping-hong ZHOU, MD. Endoscopy Center, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University, Shanghai, China
 How I Do It? Per-oral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) Ping-hong ZHOU, MD Endoscopy Center, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University, Shanghai, China The 2 nd World Congress on CONTROVERSIES IN GASTROENTEROLOGY Prof.
How I Do It? Per-oral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) Ping-hong ZHOU, MD Endoscopy Center, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University, Shanghai, China The 2 nd World Congress on CONTROVERSIES IN GASTROENTEROLOGY Prof.
Early and long term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in a large patient series
 594 Early and long term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in a large patient series KEN OHNITA 1, HAJIME ISOMOTO 1, SABURO SHIKUWA 2, HIROYUKI YAJIMA 1, HITOMI MINAMI
594 Early and long term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in a large patient series KEN OHNITA 1, HAJIME ISOMOTO 1, SABURO SHIKUWA 2, HIROYUKI YAJIMA 1, HITOMI MINAMI
Management of the Difficult Patient with Type 3 Achalasia. Steven R. DeMeester Professor and Clinical Scholar Department of Surgery
 Management of the Difficult Patient with Type 3 Achalasia Steven R. DeMeester Professor and Clinical Scholar Department of Surgery Achalasia Treatment Concepts Disease leads to non-relaxing LES and loss
Management of the Difficult Patient with Type 3 Achalasia Steven R. DeMeester Professor and Clinical Scholar Department of Surgery Achalasia Treatment Concepts Disease leads to non-relaxing LES and loss
Abstract CASE REPORT. Sha Shi, Kuangi Fu, Xin-Qian Dong, Yu-Jing Hao, Sen-Lin Li
 Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i2.99 World J Gastrointest Endosc 2017 February 16; 9(2): 99-104 ISSN 1948-5190 (online) CASE REPORT Combination of concurrent endoscopic
Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i2.99 World J Gastrointest Endosc 2017 February 16; 9(2): 99-104 ISSN 1948-5190 (online) CASE REPORT Combination of concurrent endoscopic
Description. Section: Medicine Effective Date: January 15, 2015 Subsection: Original Policy Date: December 6, 2013 Subject: Page: 1 of 7
 Last Review Status/Date: December 2014 Page: 1 of 7 Description Esophageal achalasia is characterized by prolonged occlusion of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and reduced peristaltic activity, making
Last Review Status/Date: December 2014 Page: 1 of 7 Description Esophageal achalasia is characterized by prolonged occlusion of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and reduced peristaltic activity, making
Oesophageal Disorders
 Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Achalasia: Classic View
 Achalasia: Dilate, Botox, Knife or POEM Prateek Sharma, MD Kansas University School of Medicine Achalasia: Classic View 1 Diagnosis of Achalasia Endoscopy may be normal in as many as 44% Upper GI series
Achalasia: Dilate, Botox, Knife or POEM Prateek Sharma, MD Kansas University School of Medicine Achalasia: Classic View 1 Diagnosis of Achalasia Endoscopy may be normal in as many as 44% Upper GI series
Delayed Perforation Occurring after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Early Gastric Cancer
 CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2015;48:251-255 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.3.251 Open Access Delayed Perforation Occurring after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2015;48:251-255 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.3.251 Open Access Delayed Perforation Occurring after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD
 Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus
 Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
What s New in the Management of Esophageal Disease
 What s New in the Management of Esophageal Disease Philip O. Katz, MD Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College
What s New in the Management of Esophageal Disease Philip O. Katz, MD Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks
 Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Case Report The Rise of Tunnel Endoscopic Surgery: A Case Report and Literature Review
 Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 847640, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/847640 Case Report The Rise of Tunnel Endoscopic Surgery: A Case Report and Literature Review Mingyan
Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 847640, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/847640 Case Report The Rise of Tunnel Endoscopic Surgery: A Case Report and Literature Review Mingyan
Barrett s Esophagus. Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI
 Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Philip Chiu Associate Professor Department of Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong
 Application of Chromoendoscopy, NBI and AFI in Esophagus why, who, and how? Philip Chiu Associate Professor Department of Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong Cancer of
Application of Chromoendoscopy, NBI and AFI in Esophagus why, who, and how? Philip Chiu Associate Professor Department of Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong Cancer of
Per-oral Endoscopic Myotomy
 POEM With the Flexible Scope as a Treatment for Achalasia and Zenker's Diverticulum Abraham Mathew, MD, MSc Professor of Medicine Penn State College of Medicine Penn State Hershey Medical Center Per-oral
POEM With the Flexible Scope as a Treatment for Achalasia and Zenker's Diverticulum Abraham Mathew, MD, MSc Professor of Medicine Penn State College of Medicine Penn State Hershey Medical Center Per-oral
Comparison of the Outcomes of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia According to Manometric Subtype
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 11, No. 5, September 2017, pp. 642-647 ORiginal Article Comparison of the Outcomes of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia According to Manometric Subtype Won Hee Kim 1, Joo Young
Gut and Liver, Vol. 11, No. 5, September 2017, pp. 642-647 ORiginal Article Comparison of the Outcomes of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia According to Manometric Subtype Won Hee Kim 1, Joo Young
New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus
 New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Prateek Sharma, MD Key Clinical Management Points: Endoscopic recognition of a columnar lined distal esophagus is crucial
New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Prateek Sharma, MD Key Clinical Management Points: Endoscopic recognition of a columnar lined distal esophagus is crucial
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Achalasia: Initial Results of a Korean Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2013;46:161-167 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2013.46.2.161 Open Access Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Achalasia:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2013;46:161-167 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2013.46.2.161 Open Access Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Achalasia:
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD. Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd
 ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
Vital staining and Barrett s esophagus
 Marcia Irene Canto, MD, MHS Baltimore, Maryland Vital staining or chromoendoscopy refers to staining of endoscopic tissue or topical application of chemical stains or pigments to alter tissue appearances
Marcia Irene Canto, MD, MHS Baltimore, Maryland Vital staining or chromoendoscopy refers to staining of endoscopic tissue or topical application of chemical stains or pigments to alter tissue appearances
Efficacy and safety of endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial cancer of the cervical esophagus
 Original article Efficacy and safety of endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial cancer of the cervical esophagus Authors Toshiro Iizuka 1, 2,DaisukeKikuchi 1,ShuHoteya 1, Yoshiaki Kajiyama 2,MitsuruKaise
Original article Efficacy and safety of endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial cancer of the cervical esophagus Authors Toshiro Iizuka 1, 2,DaisukeKikuchi 1,ShuHoteya 1, Yoshiaki Kajiyama 2,MitsuruKaise
B Barrett neoplasia, early, endoscopic mucosal resection of, in Europe, 297
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, treatment of, history of, 258 259 Achalasia myotomy, 270 Adenocarcinomas, endoscopic management of, in Asia, 289 290 B Barrett neoplasia,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, treatment of, history of, 258 259 Achalasia myotomy, 270 Adenocarcinomas, endoscopic management of, in Asia, 289 290 B Barrett neoplasia,
Treating Achalasia. When to consider surgery and New options for therapy
 Treating Achalasia When to consider surgery and New options for therapy James B. Wooldridge,Jr., MD Ochsner Medical Center Senior Staff Surgeon General, Laparoscopic, and Bariatric Surgery Disclosures
Treating Achalasia When to consider surgery and New options for therapy James B. Wooldridge,Jr., MD Ochsner Medical Center Senior Staff Surgeon General, Laparoscopic, and Bariatric Surgery Disclosures
Primary Achalasia : POEM Vs Heller's Myotomy AMOL BAPAYE MD (MS ), FAS GE
 Primary Achalasia : POEM Vs Heller's Myotomy AMOL BAPAYE MD (MS ), FAS GE SHIVANAND DESAI CENTER FOR DIG EST IVE DISOR DERS DEENANAT H MANGESHKAR HOSPITAL & R ESEAR C H C ENTER, PUNE, INDIA What is Achalasia
Primary Achalasia : POEM Vs Heller's Myotomy AMOL BAPAYE MD (MS ), FAS GE SHIVANAND DESAI CENTER FOR DIG EST IVE DISOR DERS DEENANAT H MANGESHKAR HOSPITAL & R ESEAR C H C ENTER, PUNE, INDIA What is Achalasia
34th Annual Toronto Thoracic Surgery Refresher Course
 34th Annual Toronto Thoracic Surgery Refresher Course TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR ACHALASIA Dr. Carmine Simone Director, Intensive Care Unit Head, Division of Critical Care Departments of Medicine and Surgery
34th Annual Toronto Thoracic Surgery Refresher Course TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR ACHALASIA Dr. Carmine Simone Director, Intensive Care Unit Head, Division of Critical Care Departments of Medicine and Surgery
AGA SECTION. Gastroenterology 2016;150:
 Gastroenterology 2016;150:1026 1030 April 2016 AGA Section 1027 Procedural intervention (3) Upper endoscopy indications 3 6 Non-response of symptoms to a 4 8 week empiric trial of twice-daily PPI Troublesome
Gastroenterology 2016;150:1026 1030 April 2016 AGA Section 1027 Procedural intervention (3) Upper endoscopy indications 3 6 Non-response of symptoms to a 4 8 week empiric trial of twice-daily PPI Troublesome
Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology
 Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology GERD is defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus DeVault et al. Am J
Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology GERD is defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus DeVault et al. Am J
Achalasia: Inject, Dilate, or Surgery?
 Achalasia: Inject, Dilate, or Surgery? John E. Pandolfino, MD, MSCI, FACG Professor of Medicine Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Northwestern
Achalasia: Inject, Dilate, or Surgery? John E. Pandolfino, MD, MSCI, FACG Professor of Medicine Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Northwestern
A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES. Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus
 A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus CASE DESCRIPTION 63yo, F, single, attending nurse. PMH includes T2DM (Sitagliptin/Metformin), Hyperlipidemia
A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus CASE DESCRIPTION 63yo, F, single, attending nurse. PMH includes T2DM (Sitagliptin/Metformin), Hyperlipidemia
잭해머식도를경구내시경근절개술로치료한 1 예
 Korean J Gastroenterol Vol. 64 No. 6, 370-374 http://dx.doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.64.6.370 pissn 1598-9992 eissn 2233-6869 CASE REPORT 잭해머식도를경구내시경근절개술로치료한 1 예 고원진, 이병무, 박원영, 김진녕, 조준형, 이태희, 홍수진 1, 조주영 순천향대학교서울병원소화기병센터,
Korean J Gastroenterol Vol. 64 No. 6, 370-374 http://dx.doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.64.6.370 pissn 1598-9992 eissn 2233-6869 CASE REPORT 잭해머식도를경구내시경근절개술로치료한 1 예 고원진, 이병무, 박원영, 김진녕, 조준형, 이태희, 홍수진 1, 조주영 순천향대학교서울병원소화기병센터,
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for the Treatment of Achalasia in a 10-Year-Old Male Patient
 18 Case Report THIEME Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for the Treatment of Achalasia in a 10-Year-Old Male Patient Jörg Filser 1 Anke Dick 2 Thomas Meyer 1 Christoph-Thomas Germer 1 Burkard H.A. von Rahden
18 Case Report THIEME Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for the Treatment of Achalasia in a 10-Year-Old Male Patient Jörg Filser 1 Anke Dick 2 Thomas Meyer 1 Christoph-Thomas Germer 1 Burkard H.A. von Rahden
Radiology. Gastrointestinal. Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact. Farooq P. Agha
 Gastrointest Radiol 9:9%103 (1984) Gastrointestinal Radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1984 Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact Farooq P. Agha Department of Radiology,
Gastrointest Radiol 9:9%103 (1984) Gastrointestinal Radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1984 Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact Farooq P. Agha Department of Radiology,
Professor, Department of Endoscopic Diagnostic and Therapeutics, Chiba University School of Medicine
 Gastrointestinal Diseases Esophageal Disorders JMAJ 47(): 41 47, 24 Teruo KOUZU Professor, Department of Endoscopic Diagnostic and Therapeutics, Chiba University School of Medicine Abstract: Recent trends
Gastrointestinal Diseases Esophageal Disorders JMAJ 47(): 41 47, 24 Teruo KOUZU Professor, Department of Endoscopic Diagnostic and Therapeutics, Chiba University School of Medicine Abstract: Recent trends
History. Prevalence at Endoscopy. Prevalence and Reflux Sx. Prevalence at Endoscopy. Barrett s Esophagus: Controversy and Management
 Barrett s Esophagus: Controversy and Management History Norman Barrett (1950) Chronic Peptic Ulcer of the Oesophagus and Oesophagitis Allison and Johnstone (1953) The Oesophagus Lined with Gastric Mucous
Barrett s Esophagus: Controversy and Management History Norman Barrett (1950) Chronic Peptic Ulcer of the Oesophagus and Oesophagitis Allison and Johnstone (1953) The Oesophagus Lined with Gastric Mucous
EGD. John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008
 EGD John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008 Different Ways to do an EGD Which scope? Pediatric, regular, jumbo EGD endoscope or pediatric colonoscope Transnasal vs. transoral insertion Sedation
EGD John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008 Different Ways to do an EGD Which scope? Pediatric, regular, jumbo EGD endoscope or pediatric colonoscope Transnasal vs. transoral insertion Sedation
Ablation for Barrett s Esophagus: Burn or Freeze
 Ablation for Barrett s Esophagus: Burn or Freeze John R. Saltzman MD Director of Endoscopy Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Disclosures No relevant disclosures
Ablation for Barrett s Esophagus: Burn or Freeze John R. Saltzman MD Director of Endoscopy Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Disclosures No relevant disclosures
Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행
 Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행 JGCA classification - Japanese Gastric Cancer Association - Type 0 superficial polypoid, flat/depressed, or excavated tumors Type 1 polypoid carcinomas, usually attached
Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행 JGCA classification - Japanese Gastric Cancer Association - Type 0 superficial polypoid, flat/depressed, or excavated tumors Type 1 polypoid carcinomas, usually attached
Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 560712, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/560712 Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach Shigeo
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 560712, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/560712 Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach Shigeo
How to treat early gastric cancer? Endoscopy
 How to treat early gastric cancer? Endoscopy Presented by Pierre H. Deprez Institution Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc, Brussels Université catholique de Louvain 2 3 4 5 6 Background Diagnostic or therapeutic
How to treat early gastric cancer? Endoscopy Presented by Pierre H. Deprez Institution Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc, Brussels Université catholique de Louvain 2 3 4 5 6 Background Diagnostic or therapeutic
Achalasia is a rare disease with an annual incidence estimated REVIEWS. Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:1020 1024 REVIEWS Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia BOUDEWIJN F. KESSING, ALBERT J. BREDENOORD, and ANDRÉ J. P. M. SMOUT
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:1020 1024 REVIEWS Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia BOUDEWIJN F. KESSING, ALBERT J. BREDENOORD, and ANDRÉ J. P. M. SMOUT
Gastroesophageal reflux disease Principles of GERD treatment Treatment of reflux diseases GERD
 Esophagus Anatomy/Physiology Gastroesophageal reflux disease Principles of GERD treatment Treatment of reflux diseases GERD Manometry Question 50 years old female with chest pain and dysphagia. Manometry
Esophagus Anatomy/Physiology Gastroesophageal reflux disease Principles of GERD treatment Treatment of reflux diseases GERD Manometry Question 50 years old female with chest pain and dysphagia. Manometry
Hong Kong Society of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons CLINICAL MEETING 29 NOV 2012
 Hong Kong Society of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons CLINICAL MEETING 29 NOV 2012 Esophageal Leiomyoma Introduction Case presentation Operative video Discussion Esophageal Leiomyoma Benign tumors of the
Hong Kong Society of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons CLINICAL MEETING 29 NOV 2012 Esophageal Leiomyoma Introduction Case presentation Operative video Discussion Esophageal Leiomyoma Benign tumors of the
Sreeni Jonnalagadda, MD., FASGE Professor of Medicine, UMKC Director of Interventional Endoscopy Saint Luke s Hospital, Kansas City
 Sreeni Jonnalagadda, MD., FASGE Professor of Medicine, UMKC Director of Interventional Endoscopy Saint Luke s Hospital, Kansas City Peptic stricture Shtki Schatzki s ring Esophageal cancer Radiation therapy
Sreeni Jonnalagadda, MD., FASGE Professor of Medicine, UMKC Director of Interventional Endoscopy Saint Luke s Hospital, Kansas City Peptic stricture Shtki Schatzki s ring Esophageal cancer Radiation therapy
Barrett s Esophagus. lining of the lower esophagus that bears his name (i.e., Barrett's esophagus). We now
 Shamika Johnson Anatomy & Physiology 206 April 20, 2010 Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s Esophagus? Norman Barrett was a pathologist. In 1950, he described an abnormality in the lining of the lower
Shamika Johnson Anatomy & Physiology 206 April 20, 2010 Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s Esophagus? Norman Barrett was a pathologist. In 1950, he described an abnormality in the lining of the lower
Clinical analysis of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection in treating esophageal submucosal tumors.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9231-9235 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Clinical analysis of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection in treating esophageal submucosal tumors. Fu Xinjuan 1,2, Shi
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9231-9235 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Clinical analysis of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection in treating esophageal submucosal tumors. Fu Xinjuan 1,2, Shi
THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia. Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone. Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital
 THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital Objectives Definitions Common causes Investigations Treatment options Anatomy
THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital Objectives Definitions Common causes Investigations Treatment options Anatomy
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Gregory G. Ginsberg, M.D.
 Radiofrequency Ablation for Barrett s Esophagus with HGD Gregory G. Ginsberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine Abramson Cancer Center Gastroenterology Division Executive
Radiofrequency Ablation for Barrett s Esophagus with HGD Gregory G. Ginsberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine Abramson Cancer Center Gastroenterology Division Executive
Case Scenario 1. The patient has now completed his neoadjuvant chemoradiation and has been cleared for surgery.
 Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Endoscopic Management of Perforations
 Endoscopic Management of Perforations Gregory G. Ginsberg, MD Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine Gastroenterology Division Executive Director of Endoscopic Services
Endoscopic Management of Perforations Gregory G. Ginsberg, MD Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine Gastroenterology Division Executive Director of Endoscopic Services
Digestive Disease Center Showa University Northern Yokohama Hospital Since 2001
 Digestive Disease Center Showa University Northern Yokohama Hospital Since 21 As a core hospital of the community, and as a leading international institution for research and education Website http://www.showa-ddc.com/
Digestive Disease Center Showa University Northern Yokohama Hospital Since 21 As a core hospital of the community, and as a leading international institution for research and education Website http://www.showa-ddc.com/
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
A prospective analysis of GERD after POEM on anterior myotomy
 Surg Endosc (2016) 30:2496 2504 DOI 10.1007/s00464-015-4507-0 and Other Interventional Techniques A prospective analysis of GERD after POEM on anterior myotomy Hironari Shiwaku 1 Haruhiro Inoue 2 Takamitsu
Surg Endosc (2016) 30:2496 2504 DOI 10.1007/s00464-015-4507-0 and Other Interventional Techniques A prospective analysis of GERD after POEM on anterior myotomy Hironari Shiwaku 1 Haruhiro Inoue 2 Takamitsu
Helicobacter pylori Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Mucosal Incision and Forceps Biopsy for Reliable Tissue Sampling of Gastric Subepithelial Tumors
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2017;50:64-68 https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.094 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Mucosal Incision and Forceps Biopsy for Reliable Tissue Sampling of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2017;50:64-68 https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.094 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Mucosal Incision and Forceps Biopsy for Reliable Tissue Sampling of
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks
 Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks Ali A. Siddiqui, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Interventional Endoscopy Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia, PA When Do You Suspect a Luminal
Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks Ali A. Siddiqui, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Interventional Endoscopy Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia, PA When Do You Suspect a Luminal
Traction-assisted colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection using clip and line: a feasibility study
 E51 Traction-assisted colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection using clip and line: a feasibility study Authors Institution Yasushi Yamasaki, Yoji Takeuchi, Noriya Uedo, Minoru Kato, Kenta Hamada, Kenji
E51 Traction-assisted colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection using clip and line: a feasibility study Authors Institution Yasushi Yamasaki, Yoji Takeuchi, Noriya Uedo, Minoru Kato, Kenta Hamada, Kenji
References. GI Biopsies. What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD
 What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath
 Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Eosinophilic esophagitis Incidence of eosinophilic gastritis is increasing. Symptoms: food impaction and dysphagia. Histology: infiltration
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Eosinophilic esophagitis Incidence of eosinophilic gastritis is increasing. Symptoms: food impaction and dysphagia. Histology: infiltration
Metachronous Esophageal Cancer and Colon Cancer Treated by Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
 CASE REPORT Metachronous Esophageal Cancer and Colon Cancer Treated by Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Chun-Chao Chang, Chia-Lang Fang, Horng-Yuan Lou, Ching-Ruey Hsieh, Sheng-Hsuan Chen* Most cases of esophageal
CASE REPORT Metachronous Esophageal Cancer and Colon Cancer Treated by Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Chun-Chao Chang, Chia-Lang Fang, Horng-Yuan Lou, Ching-Ruey Hsieh, Sheng-Hsuan Chen* Most cases of esophageal
Diagnosis of colorectal lesions with a novel endocytoscopic classification a pilot study
 Original article 869 Diagnosis of colorectal lesions with a novel endocytoscopic classification a pilot study Authors S-E Kudo 1, K. Wakamura 1, N. Ikehara 1,Y.Mori 1, H. Inoue 1, S. Hamatani 2 Institutions
Original article 869 Diagnosis of colorectal lesions with a novel endocytoscopic classification a pilot study Authors S-E Kudo 1, K. Wakamura 1, N. Ikehara 1,Y.Mori 1, H. Inoue 1, S. Hamatani 2 Institutions
Radiofrequency Ablation: Stepwise circumferential and focal RFA of Barrett s s esophagus using the HALO System
 Radiofrequency Ablation: Stepwise circumferential and focal RFA of Barrett s s esophagus using the HALO System Used abbreviations BE: Barrett s esophagus EC: Early cancer ER: Endoscopic resection HGD:
Radiofrequency Ablation: Stepwise circumferential and focal RFA of Barrett s s esophagus using the HALO System Used abbreviations BE: Barrett s esophagus EC: Early cancer ER: Endoscopic resection HGD:
EMR, ESD and Beyond. Peter Draganov MD. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida
 EMR, ESD and Beyond Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated by Endoscopy
EMR, ESD and Beyond Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated by Endoscopy
Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
 Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Alina M.Boeriu 1, Daniela E.Dobru 1, Simona Mocan 2 1) Department of Gastroenterology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy;
Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Alina M.Boeriu 1, Daniela E.Dobru 1, Simona Mocan 2 1) Department of Gastroenterology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy;
Clearance mechanisms of the aperistaltic esophagus. The pump-gun hypothesis.
 Gut Online First, published on December 14, 2005 as 10.1136/gut.2005.085423 Clearance mechanisms of the aperistaltic esophagus. The pump-gun hypothesis. Radu Tutuian 1, Daniel Pohl 1, Donald O Castell
Gut Online First, published on December 14, 2005 as 10.1136/gut.2005.085423 Clearance mechanisms of the aperistaltic esophagus. The pump-gun hypothesis. Radu Tutuian 1, Daniel Pohl 1, Donald O Castell
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Esophageal Achalasia
 Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Esophageal Achalasia Policy Number: 2.01.91 Last Review: 3/2018 Origination: 3/2018 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Esophageal Achalasia Policy Number: 2.01.91 Last Review: 3/2018 Origination: 3/2018 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Achalasia is diagnosed by showing dysfunction of lower
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2013;11:131 137 ALIMENTARY TRACT A Comparison of Symptom Severity and Bolus Retention With Chicago Classification Esophageal Pressure Topography Metrics in Patients
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2013;11:131 137 ALIMENTARY TRACT A Comparison of Symptom Severity and Bolus Retention With Chicago Classification Esophageal Pressure Topography Metrics in Patients
Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia Difficulty
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia Difficulty
Nakamura et al. BMC Cancer (2016) 16:743 DOI /s y
 Nakamura et al. BMC Cancer (2016) 16:743 DOI 10.1186/s12885-016-2787-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Natural history of superficial head and neck squamous cell carcinoma under scheduled follow-up endoscopic
Nakamura et al. BMC Cancer (2016) 16:743 DOI 10.1186/s12885-016-2787-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Natural history of superficial head and neck squamous cell carcinoma under scheduled follow-up endoscopic
Diagnosis and Management of Achalasia: Past, Present, & Future
 Diagnosis and Management of Achalasia: Past, Present, & Future Kyle A. Perry, MD, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery Division of General & Gastrointestinal Surgery The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Diagnosis and Management of Achalasia: Past, Present, & Future Kyle A. Perry, MD, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery Division of General & Gastrointestinal Surgery The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy
 Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
Feasibility of endoscopic mucosa-submucosa clip closure method (with video)
 Feasibility of endoscopic mucosa-submucosa clip closure method (with video) Authors Toshihiro Nishizawa 1, Shigeo Banno 2, Satoshi Kinoshita 1,HidekiMori 2, Yoshihiro Nakazato 3,YuichiroHirai 2,Yoko Kubosawa
Feasibility of endoscopic mucosa-submucosa clip closure method (with video) Authors Toshihiro Nishizawa 1, Shigeo Banno 2, Satoshi Kinoshita 1,HidekiMori 2, Yoshihiro Nakazato 3,YuichiroHirai 2,Yoko Kubosawa
Geisinger Clinic Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant
 Geisinger Clinic Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Nonformula Grant Overview The Geisinger Clinic received $1,000,000 in nonformula funds for the
Geisinger Clinic Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Nonformula Grant Overview The Geisinger Clinic received $1,000,000 in nonformula funds for the
Treatment of long-segment Barrett s adenocarcinoma by complete circular endoscopic submucosal dissection: a case report
 Kaneko et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2018) 18:16 DOI 10.1186/s12876-018-0743-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Treatment of long-segment Barrett s adenocarcinoma by complete circular endoscopic submucosal dissection:
Kaneko et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2018) 18:16 DOI 10.1186/s12876-018-0743-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Treatment of long-segment Barrett s adenocarcinoma by complete circular endoscopic submucosal dissection:
Ten Initial Cases of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Esophageal Motility Disorders at Okayama University Hospital
 Original Article http ://escholarship.lib.okayama-u.ac.jp/amo/ Ten Initial Cases of Peroral Endoscopic yotomy for Treatment of Esophageal otility Disorders at Okayama University Hospital Yuusaku Sugihara
Original Article http ://escholarship.lib.okayama-u.ac.jp/amo/ Ten Initial Cases of Peroral Endoscopic yotomy for Treatment of Esophageal otility Disorders at Okayama University Hospital Yuusaku Sugihara
Combined Experience of Two European Centers
 Minimally Invasive Surgery for Achalasia: Combined Experience of Two European Centers Garzi A, Valla JS*, Molinaro F, Amato G, Messina M. Unit of Pediatric Surgery, University of Siena (Italy) *Lenval
Minimally Invasive Surgery for Achalasia: Combined Experience of Two European Centers Garzi A, Valla JS*, Molinaro F, Amato G, Messina M. Unit of Pediatric Surgery, University of Siena (Italy) *Lenval
THE NORMAL HUMAN ESOPHAGEAL MUCOSA: A HISTOLOGICAL REAPPRAISAL
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 68:40-44, 1975 Copyright 1975 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 68, No.1 Printed in U.S.A. THE NORMAL HUMAN ESOPHAGEAL MUCOSA: A HISTOLOGICAL REAPPRAISAL WILFRED M. WEINSTEIN, M.D., EARL
GASTROENTEROLOGY 68:40-44, 1975 Copyright 1975 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 68, No.1 Printed in U.S.A. THE NORMAL HUMAN ESOPHAGEAL MUCOSA: A HISTOLOGICAL REAPPRAISAL WILFRED M. WEINSTEIN, M.D., EARL
Factors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Early Colorectal Neoplasms: A Single Center Clinical Experience in China
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2015;48:405-410 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.5.405 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Factors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Early Colorectal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2015;48:405-410 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.5.405 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Factors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Early Colorectal
Marc F. Catalano, MD, FACG, FACP, AGAF, FASGE Professor of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology The
 Marc F. Catalano, MD, FACG, FACP, AGAF, FASGE Professor of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology The University of Texas, McGovern Medical School Review the
Marc F. Catalano, MD, FACG, FACP, AGAF, FASGE Professor of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology The University of Texas, McGovern Medical School Review the
Pharynx and esophagus atlas
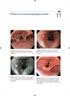 163 Pharynx and esophagus atlas 11 Figure 11.1 High resolution white light image of normal vocal cords (NYU School of Medicine). Figure 11.2 Small nodule on arytenoid and cyst on vocal cord (Erasmus University
163 Pharynx and esophagus atlas 11 Figure 11.1 High resolution white light image of normal vocal cords (NYU School of Medicine). Figure 11.2 Small nodule on arytenoid and cyst on vocal cord (Erasmus University
Perspective on Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia: Zhongshan Experience
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 9, No. 2, March 2015, pp. 152-158 Review Perspective on Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia: Zhongshan Experience Quan-Lin Li and Ping-Hong Zhou Endoscopy Center and Endoscopy
Gut and Liver, Vol. 9, No. 2, March 2015, pp. 152-158 Review Perspective on Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia: Zhongshan Experience Quan-Lin Li and Ping-Hong Zhou Endoscopy Center and Endoscopy
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy
 Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments 1.1 Cancer reporting: Biopsies
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments 1.1 Cancer reporting: Biopsies
Table 2.9. Case control studies of helicobacter pylori infection and oesophageal adenocarcinoma
 Characteristics of Characteristics of controls Detection Chow et al (1998) 1993-1995 129 of newly diagnosed oesophageal/gastric cardia (OGC) adenocarcinoma. 224 population controls selected by random digit
Characteristics of Characteristics of controls Detection Chow et al (1998) 1993-1995 129 of newly diagnosed oesophageal/gastric cardia (OGC) adenocarcinoma. 224 population controls selected by random digit
MP Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treatment of Esophageal Achalasia
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.91 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.38 Transesophageal Endoscopic Therapies for Gastroesophageal Reflux
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.91 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.38 Transesophageal Endoscopic Therapies for Gastroesophageal Reflux
A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma. in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis. of Lymph Node Metastasis
 Kitakanto Med J 2002 ; 52 : 189-193 189 A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis of Lymph Node Metastasis Susumu Kawate,' Susumu Ohwada,'
Kitakanto Med J 2002 ; 52 : 189-193 189 A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis of Lymph Node Metastasis Susumu Kawate,' Susumu Ohwada,'
Review Article Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for the Treatment of Achalasia: An Analysis
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Volume 2013, Article ID 389596, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/389596 Review Article Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for the Treatment of Achalasia: An Analysis
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Volume 2013, Article ID 389596, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/389596 Review Article Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for the Treatment of Achalasia: An Analysis
01/26/2010 GENERAL SURGERY ABSITE ANATOMY ANATOMY. Yvonne M. Carter, MD Georgetown University Medical Center. Layers. mucosa. squamous epithelium
 GENERAL SURGERY ABSITE REVIEW: ESOPHAGUS Yvonne M. Carter, MD Georgetown University Medical Center ANATOMY Layers mucosa muscle squamous epithelium columnar epithelium (distal 2cm) inner = circular outer
GENERAL SURGERY ABSITE REVIEW: ESOPHAGUS Yvonne M. Carter, MD Georgetown University Medical Center ANATOMY Layers mucosa muscle squamous epithelium columnar epithelium (distal 2cm) inner = circular outer
Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia
 Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia Ralf Kiesslich I. Medical Department Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany Cumulative cancer risk in ulcerative colitis 0.5-1.0%
Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia Ralf Kiesslich I. Medical Department Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany Cumulative cancer risk in ulcerative colitis 0.5-1.0%
Two electrosurgical endo-knives for endoscopic submucosal dissection of colorectal superficial neoplasms: a prospective randomized study
 Two electrosurgical endo-knives for endoscopic submucosal dissection of colorectal superficial neoplasms: a prospective randomized study Authors Yuusaku Sugihara 1,KeitaHarada 2, Yoshiro Kawahara 2, Daisuke
Two electrosurgical endo-knives for endoscopic submucosal dissection of colorectal superficial neoplasms: a prospective randomized study Authors Yuusaku Sugihara 1,KeitaHarada 2, Yoshiro Kawahara 2, Daisuke
Clinicopathological Characteristics of Superficial Type
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, 1995, Vol. 2, pp. 99-105 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1995 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, 1995, Vol. 2, pp. 99-105 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1995 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in
Image Analysis of Magnifying Endoscopy for Differentiation between Early Gastric Cancers and Gastric Erosions
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 297 306, September 2017 Original Image Analysis of Magnifying Endoscopy for Differentiation between Early Gastric Cancers and Gastric Erosions Shotaro HANAMURA, Kuniyo GOMI,
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 297 306, September 2017 Original Image Analysis of Magnifying Endoscopy for Differentiation between Early Gastric Cancers and Gastric Erosions Shotaro HANAMURA, Kuniyo GOMI,
Gland ducts and multilayered epithelium in mucosal biopsies from gastroesophageal-junction region are useful in characterizing esophageal location
 Diseases of the Esophagus (2005) 18, 87 92 2005 ISDE Blackwell Publishing, Ltd. Original article Gland ducts and multilayered epithelium in mucosal biopsies from gastroesophageal-junction region are useful
Diseases of the Esophagus (2005) 18, 87 92 2005 ISDE Blackwell Publishing, Ltd. Original article Gland ducts and multilayered epithelium in mucosal biopsies from gastroesophageal-junction region are useful
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) & Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD)
 Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) & Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) Minimally Invasive Polyp Removal IE-02700-Understanding EMR and ESD Brochure_R3.indd 1 Occasionally, a polyp that infiltrates
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) & Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) Minimally Invasive Polyp Removal IE-02700-Understanding EMR and ESD Brochure_R3.indd 1 Occasionally, a polyp that infiltrates
