Clinical Scoring System to Detect Malignant and Premalignant Vulval Lesions
|
|
|
- Tyrone Blake
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India (January February 2014) 64(1):41 46 DOI /s ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Scoring System to Detect Malignant and Premalignant Vulval Lesions Tyagi Shakun Tripathi Reva Batra Swaraj Received: 23 March 2011 / Accepted: 22 July 2011 / Published online: 1 September 2013 Ó Federation of Obstetric & Gynecological Societies of India 2013 Abstract Objective To construct a simple clinical scoring system for evaluation of vulval lesions that will be helpful in clinically detecting the premalignant or malignant lesions of vulva. Methods Seventy women referred for vulval examination at a tertiary care centre in north India were examined over a period of 2 years. Biopsy was performed in 66 consenting women. Association of high-grade vulval lesion with various clinical parameters such as age, duration of symptoms, presenting complaints, the presence of depigmentation, ulceration, hyperkeratosis, acetowhite changes on acetic acid application, asymmetrical distribution of the lesion, surface elevation on naked eye or colposcopy, induration on palpation and toluidine blue stain retention was studied. The significantly associated factors were assigned a value of 0 or 1 depending on whether they were present or absent. Score was then formulated for detection of high-grade lesion defined as moderate to severe dysplasia and early malignancy. Main outcome measures Histopathology. Results Out of the various parameters that were studied, duration of symptoms more than 6 months, hyperkeratosis, Tyagi S., Assistant Professsor Tripathi R., Director Professor Batra S., Director Professor Maulana Azad Medical College, Delhi, India Tyagi S. (&), Assistant Professsor C-501, Taj Apartments, Gazipur, Delhi , India tyagishakun@gmail.com asymmetrical distribution of the lesion, surface elevation on naked eye or colposcopy, induration on palpation and positive toluidine blue stain retention of the lesion were found to be significantly associated with a malignant or premalignant lesion. It was found that a score of equal to or greater than 3/6 was significantly associated with a malignant or premalignant lesion. Conclusion This simple scoring system has a potential to identify the high-grade lesions and can be used to identify the vulval lesion requiring a biopsy or further referral to higher centre. Keywords Score Introduction Vulva Preneoplastic lesion Malignancy Identification of lesion at high risk of malignant or premalignant change is priority in women presenting with any vulval lesion. In women with chronic non-neoplastic epithelial disorders such as lichen sclerosus, squamous hyperplasia and mild Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia (VIN) there is a need for long-term monitoring for development of malignant or premalignant changes as 3 6 % of patients with lichen sclerosus will develop invasive vulval carcinomas [1]. Role of colposcopy and colorimetric tests acetic acid and toluidine blue test, used as isolated tests in the diagnosis of vulvar disorders, has been questioned [2]. Utilization of
2 Tyagi et al. The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India (January February 2014) 64(1):41 46 multidisciplinary approach has been suggested for management of vulval lesions suggesting that the women with vulval lesions be examined by a person with interdisciplinary skills [3]. But it might not be possible for every primary or second line health facility to have trained staff with these facilities. In women with coloured skin chronic inflammation due to any reason leads to destruction of pigment cells resulting in depigmentation or hypopimentation which might be alarming to the patient as well as the gynaecologist not experienced in management of vulval lesions. Although the exact prevalence rates are not known, vulval intraepithelial lesions or early vulval carcinoma are not common clinical entities and not every gynaecologist will be comfortable in deciding whether biopsy needs to be taken or not. In this scenario, vulval biopsy and histopathtology examination of every lesion will be required unless a proper risk score to detect high-risk lesions is constructed. There have been no prospective studies in which clinical features of patients with vulval lesions have been studied individually or in combination for prediction of malignant or premaligmant lesion of vulva and a scoring system has been attempted. Therefore, the aim of this study was to determine the clinical associations of malignant and premalignant lesions of vulva (moderate to severe dysplasia and early invasive lesion) and to formulate a scoring system to differentiate the high-risk lesion from a low-risk lesion on clinical grounds so as to decide for biopsy and referral. Methodology The study was conducted at tertiary care hospital in northern India. Seventy women referred to or presenting directly to the outpatient clinic in view of vulval complaints or randomly detected vulval lesion were enrolled in the study. The study was reviewed and approved by the Departmental Review Board, the Head of the Institution and CSIR. Seventy women with mean age of 46.7 years Fig. 1 Pictures of carcinoma in situ vulva without toluidine blue Fig. 3 Another picture of carcinoma in situ Fig. 2 Pictures of carcinoma in situ vulva after toluidine blue Fig. 4 Picture of benign lesion: early lichen sclerosus 42
3 The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India (January February 2014) 64(1):41 46 Clinical Scoring System Table 1 Complaint at the time of presentation Presenting complaint Total Malignant/premalignant Benign N = 66 % N = 6 % N = 60 % Itching Itching and depigmentation Asymptomatic Depigmentation Follow-up vulvectomy for VIN/Ca vulva Vulval growth Pain Table 2 Duration of Symptoms Table 4 Histopathology report of the patients Duration Total Malignant/ premalignant Benign Histopathology Frequency N = 66 % N = 66 % N = 6 % N = 60 % More than 12 months months months Less than 3 months Squamuos cell carcinoma with invasion \5 mm Moderate to severe dysplasia Mild dysplasia Lichen sclerosus Squamous hyperplasia Plasma cell vulvitis Chronic inflammation Table 3 Age distribution Age (years) Total Malignant/premalignant Benign N = 66 % N = 6 % N = 60 % \ [ (SD 13.2) and range of (18 75 years) were initially enrolled into the study after informed consent. Women with acutely tender vulval lesions with duration of less than 2 weeks were not included so that cases of acute infective lesions were excluded. A thorough history was taken, followed by general physical and systemic examination. Vulva was thoroughly inspected for any lesions. After inspecting the vulva with naked eye under bright light, it was visualized using a colposcope. (Figs. 1, 3, 4) Acetic acid (5 %) was applied to vulva for a period of 3 min followed by naked eye and vulvoscopic examination for any acetowhite areas. Thereafter 1 % aqueous solution of Toluidine blue [4] was applied to the vulva including area from mons pubis to perianal area, bilateral labia majora, minora and introitus. The dye was allowed to stay over the area for 3 min, meanwhile colposcopic examination of cervix and vagina was performed. The dye was then sponged using 1 % acetic acid and areas of toluidine blue retention (Fig. 2) were observed. After washing off toluidine blue with acetic acid hyperkeratosis was viewed as areas retaining pale blue stain [5]. The vulva was viewed in detail by naked eye and under magnification for number and distribution of lesion, pigment change, ulcer, elevated area (surface topography), hyperkeratosis, extension over urethra, anal canal and vagina. The presence of induration on palpation along with naked eye examination was evaluated separately. At the end of the procedure 4-mm punch biopsy was performed under local anaesthesia. The biopsy specimen was formalin fixed and examined by an experienced pathologist. Clinical parameters: age, presenting complaints, duration of symptoms, asymmetrical distribution of the lesion, the presence of depigmentation, ulceration, hyperkeratosis, acetowhite changes after acetic acid application, surface elevation on naked eye or colposcopy, induration on palpation and toluidine blue stain retention were the characteristics that were studied for each woman. Association of clinical features with histopathology report of preneoplastic lesion and early malignancy was analysed. Statistical analysis was performed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (Version 15.0) with j 2 test or Fisher exact test as appropriate. A score was formulated using the factors which were significantly 43
4 Tyagi et al. The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India (January February 2014) 64(1):41 46 Table 5 Association of clinical features with histopathology report suggestive of malignant or premalignant lesion Risk factor Total no. of women positive for this factor Malignant/premalignant histopathology report Benign histopathology report P value Age [ Postmenopausal status Duration of symptoms more than 6 months (FE) Asymmetrical distribution of lesion (FE) Depigmentation (FE) Hyperkeratosis (FE) Ulceration (FE) Acetowhite changes with acetic acid (FE) Surface elevated on colposcopy (FE) Induration on palpation (FE) Toluidine test positive (FE) FE Fisher exact test Bold denote the statistically significant results associated with malignant or premalignant lesion. The performance of the test was evaluated using area under the ROC curve. Results Initially 70 women were enrolled for the study. Itching alone or in association with depigmentation was the most frequent symptom amongst the enrolled women present in 60 % of women (Table 1). In almost 50 % of women (Table 2) the complaints were of more than 6 months duration. The age distribution in the study population is shown in Table 3. In two women biopsy was not performed as the lesion appeared to improve on application of antifungal medication. Two more women refused biopsy after enrolment. These four women were excluded from the study and final analysis was performed for 66 women in whom biopsy was performed. The histopathology reports of the patient are shown in Table 4. In 91 % of women (60/ 66) the lesion was benign. Almost 17 % of women had mild, moderate or severe dysplasia or early invasive lesion on histopathology examination. Cases with moderate to severe dysplasia were classified as high-grade lesions. The cases of mild dysplasia were classified as benign lesions and managed conservatively on follow-up. They were not included in the high-grade lesion group as there is not enough evidence that these lesions will progress to invasive lesion [6]. Age, duration of symptoms, presenting complaints, asymmetrical distribution of the lesion, the presence of depigmentation, ulceration, hyperkeratosis, acetowhite area, surface elevation on naked eye or colposcopy, induration on palpation and toluidine blue stain retention were the factors that were statistically analysed for association with malignant or premalignant lesion. Age 44 more than 60 years, depigmentation, acetowhite change after application of acetic acid and ulceration were not significantly associated with high-grade lesion. The association of clinical features with premalignant or early neoplastic lesion is depicted in Table 5. A score of 6 was formulated by including the 6 clinical factors that were significantly associated with the high-grade lesions i.e. duration more than 6 months (P = 0.049), hyperkeratosis (P = 0.045), surface elevation (P = ), induration (P = ), positive toluidine blue staining (P = 0.04) and asymmetrical distribution of the lesion (0.000). A score of three or more was found to be significantly associated with high-grade lesion (P = ; Fisher exact test). The optimal cutoff point was found to be [3 with 100 % sensitivity and 91.7 % specificity and area under the curve 98.9 ± 1.1 % with P \ ROC is depicted in Fig. 5. Sensitivity ROC Curve Specificity Diagonal segments are produced by ties. Fig. 5 ROC for scores one to six for detection of malignant or premalignant lesion
5 The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India (January February 2014) 64(1):41 46 Clinical Scoring System Table 6 Score distribution according to histopathology result (malignant/premalignant histopathology report) and sensitivity/specificity of each score for detecting high-grade lesion Score Malignant/premalignant histopathology report Total Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) No Yes Discussion We have designed a scoring system for women with vulval lesion which has sensitivity and specificity for detecting vulval preneoplastic and early neoplastic lesions. Previously some of these factors have been reported to be associated with high-grade lesions but have never been incorporated in the form of a score. Duration of symptoms more than 6 months rules out symptoms due to infective condition. Excessive surface keratinisation, hyperkeratosis is seen by naked eye as a white, plaque-like area that is often strikingly white even without acetic acid application. In women with lichen sclerosus, with malignant/premalignant transformation are more likely to be associated with hyperkeratosis than in women without malignancy [7]. In our study hyperkeratosis is significantly associated with malignant/premalignant lesions in women with vulval lesions. Toluidine blue test has been studied by Joura et al. [4] and has been reported to have high negative predictive value. But another study gives conflicting reports with false positive rate of 26.9 % and false negative rate of 85.8 % [2]. Induration is a relatively subjective feature and has never been studied. But any chronic infiltrative lesion is likely to distort the epithelial and subepithelial architecture resulting in induration. Any surface elevation in an ominous sign reflecting an underlying cellular proliferation and HPV warts are the main differential in women with surface elevation in the vulval lesion. The presence of acetowhite area after application of 5 % acetic acid was not significantly associated with premalignant lesion in our study as opposed to cases of cervical premalignant lesion. Also, acetowhite changes in the vestibular and vulval areas have been documented to be normal vulval finding previously [8]. All these features found to be associated with high-grade lesions individually have low predictive value for vulval neoplasia. Therefore, we studied the combination of these features for evaluation of high-risk lesions and this score was formulated. For each score there was a certain probability to find or exclude a high-grade lesion. This has been summarised as sensitivity and specificity for high-grade lesions at different thresholds depicted in Table 6. No highgrade lesion had a total score of less than four. If the score was less than three then even mild dysplasia was ruled out. Thus in the current study biopsy could have been avoided in 50 % (33/66) of women without missing out on highgrade lesions. We would suggest that in patients with unifocal lesion having a score of 5/6 or more a wide local excision could have been attempted in the first place as the procedure could have been diagnostic as well as therapeutic for moderate to severe dysplasia and adequate sample could have been obtained to rule out invasive disease. This score needs to be validated in different and larger population. Conclusion This clinical grading of the lesion will prove to be more useful for facilities where easy referral to experts in vulval disorders is not available and there is not much experience in handling vulval lesions. This simple and effective tool can identify lesions with high malignant potential with the least invasive technique to decide for biopsy and referral. Repeated biopsies can also be avoided in patients following up for chronic non-neoplastic disorders of vulva and those who have been managed surgically in the past for neoplastic or preneoplastic lesion. Acknowledgment This study was conducted as part of Senior Research Associate Scheme funded by Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India. Dr Shashi Sharma s contribution towards statistical analysis is acknowledged. References 1. Maclean AB. Vulval cancer: prevention and screening. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2006;20:379Y Micheeletti L, Barbero, Trivelli MR, et al. Unreliability of toluidine blue test in the early diagnosis of vulvar neoplasia. Cervix LFGT. 1985;3:
6 Tyagi et al. The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India (January February 2014) 64(1): Micheletti L, Bogliatto F, Lynch PJ. Vulvoscopy: review of a diagnostic approach requiring clarification. J Reprod Med. 2008;53(3): Review. 4. Joura EA, Zeisler H, Lösch A, et al. Differentiating vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia from nonneoplastic epithelial disorders: the toluidine blue test. J Reprod Med. 1998;43(8): Singer A, Monaghan J, Quek SC, Deery ARS. Vulvar Intraepithelial Carcinoma. In: Singer A, Monaghan J, editors. Lower genital tract precancer-colposcopy, pathology and treatment. 2nd ed. Oxford: Blackwell Science; p Scurry J, Edward J, Wilkinson EJ. Review of terminology of precursors of vulvar squamous cell carcinoma. J Lower Genital Tract Dis. 2006;10(3): Jones RW, Sadler L, Grant S, et al. Clinically identifying women with vulvar lichen sclerosus at increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma. J Reprod Med. 2004;49:808Y van Beurden M, van der Vange N, de Craen AJ, et al. Normal findings in vulvar examination and vulvoscopy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1997;104(3):
Disorders of the vulva
 Vulval lesions Disorders of the vulva Terminology standardised by the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease(ISSVD) Classification 1.Nonneoplastic epithelial disorders of vulva Lichen
Vulval lesions Disorders of the vulva Terminology standardised by the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease(ISSVD) Classification 1.Nonneoplastic epithelial disorders of vulva Lichen
Treatment of Bowenoid and Basaloid Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia 2/3 with Imiquimod 5% Cream DO NOT DUPLICATE
 The Journal of Reproductive Medicine Treatment of Bowenoid and Basaloid Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia 2/3 with Imiquimod 5% Cream Claudia Marchitelli, M.D., Graciela Secco, M.D., Myriam Perrotta, M.D.,
The Journal of Reproductive Medicine Treatment of Bowenoid and Basaloid Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia 2/3 with Imiquimod 5% Cream Claudia Marchitelli, M.D., Graciela Secco, M.D., Myriam Perrotta, M.D.,
Postmenopausal Vulvar Pruritus - Colposcopic Diagnosis and Treatment
 Postmenopausal Vulvar Pruritus - Colposcopic Diagnosis and Treatment Pages with reference to book, From 315 To 317 A Bilge Sener, Neslihan C. Seckin, Oya Gokmen ( Departments of Menopause, Dr. Z.T.B. Women
Postmenopausal Vulvar Pruritus - Colposcopic Diagnosis and Treatment Pages with reference to book, From 315 To 317 A Bilge Sener, Neslihan C. Seckin, Oya Gokmen ( Departments of Menopause, Dr. Z.T.B. Women
VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD J M O R G A N
 VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD 2 0 1 8 J M O R G A N Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia VAIN I, II, III Incidence 0.1/100,000 women in US Mean age 50s (J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2009:18:1731) (J Obstet Gynaecol
VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD 2 0 1 8 J M O R G A N Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia VAIN I, II, III Incidence 0.1/100,000 women in US Mean age 50s (J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2009:18:1731) (J Obstet Gynaecol
Diseases of the vulva
 Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
The Case of Mrs. Virginia Jones* Asst. Professor Division of Gyne-Oncology University of British Columbia, Department of Gynecology Vancouver, Canada
 Case title: Case authors: Case synopsis: The Case of Mrs. Virginia Jones* Dr. Leslie A. Sadownik Asst. Professor Division of Gyne-Oncology University of British Columbia, Department of Gynecology Vancouver,
Case title: Case authors: Case synopsis: The Case of Mrs. Virginia Jones* Dr. Leslie A. Sadownik Asst. Professor Division of Gyne-Oncology University of British Columbia, Department of Gynecology Vancouver,
Summary. Accepted for publication 18 May Key words genital lichen planus, oral lichen planus, vulval lichen planus
 CLINICAL AND LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07480.x Prevalence of vulval lichen planus in a cohort of women with oral lichen planus: an interdisciplinary study P. Belfiore, O. Di
CLINICAL AND LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07480.x Prevalence of vulval lichen planus in a cohort of women with oral lichen planus: an interdisciplinary study P. Belfiore, O. Di
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
HOW TO DIAGNOSE VULVAR DISEASES:
 HOW TO DIAGNOSE VULVAR DISEASES: Diagnostic approach. Normal findings. Maria Sol Peremateu, MD A wide spectrum of benign, premalignant, and malignant lesions may occur on the vulva. Some of the disorders
HOW TO DIAGNOSE VULVAR DISEASES: Diagnostic approach. Normal findings. Maria Sol Peremateu, MD A wide spectrum of benign, premalignant, and malignant lesions may occur on the vulva. Some of the disorders
Clinical Guidance: Recommended Best Practices for Delivery of Colposcopy Services in Ontario Best Practice Pathway Summary
 Clinical Guidance: Recommended Best Practices for Delivery of Colposcopy Services in Ontario Best Practice Pathway Summary Glossary of Terms Colposcopy is the examination of the cervix, vagina and, in
Clinical Guidance: Recommended Best Practices for Delivery of Colposcopy Services in Ontario Best Practice Pathway Summary Glossary of Terms Colposcopy is the examination of the cervix, vagina and, in
Meet the ISSVD. President ISSVD. Jacob Bornstein, MD
 Meet the ISSVD Jacob Bornstein, MD President ISSVD Chairman, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Western Galilee Hospital Bar-Ilan University Faculty of Medicine Nahariya, Israel ISSVD Symposium: The
Meet the ISSVD Jacob Bornstein, MD President ISSVD Chairman, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Western Galilee Hospital Bar-Ilan University Faculty of Medicine Nahariya, Israel ISSVD Symposium: The
Evaluation of cervical cancer screening services in Minia Governorate, Egypt
 Evaluation of cervical cancer screening services in Minia Governorate, Egypt Dr. Ahmad Sameer Sanad Assistant professor Obstet. & Gynecol, Minia University Minia, Egypt Disclosures No financial relationships
Evaluation of cervical cancer screening services in Minia Governorate, Egypt Dr. Ahmad Sameer Sanad Assistant professor Obstet. & Gynecol, Minia University Minia, Egypt Disclosures No financial relationships
Associate Professor of Gyn. & Obs., Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Iran.
 Assessment of Visual Inspection with Acetic Acid (VIA) as a Screening Test for Cervical Neoplasia in Comparison with Cytologic Screening in Imam Khomeini Hospital F. Ghaemmaghami, MD Associate Professor
Assessment of Visual Inspection with Acetic Acid (VIA) as a Screening Test for Cervical Neoplasia in Comparison with Cytologic Screening in Imam Khomeini Hospital F. Ghaemmaghami, MD Associate Professor
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia
 Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia The terminology and pathology of VAIN are analogous to those of CIN (VAIN I-III). The main difference is that vaginal epithelium does not normally have crypts, so the
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia The terminology and pathology of VAIN are analogous to those of CIN (VAIN I-III). The main difference is that vaginal epithelium does not normally have crypts, so the
Advanced Training Skills Module August Vulval Disease
 Introduction Vulval Disease This module is designed to provide training in all aspects of vulval disease. Successful completion of the ATSM will equip an individual to develop this aspect of care in their
Introduction Vulval Disease This module is designed to provide training in all aspects of vulval disease. Successful completion of the ATSM will equip an individual to develop this aspect of care in their
LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES COLPOSCOPY RESULTS FORM L14
 LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES COLPOSCOPY RESULTS FORM L4 ID LABEL HERE ---> - - - VISIT #: FORM COMPLETED BY: VERSION DATE: 08/5/94 ANY MISSING OR INCOMPLETE TEST RESULTS MUST BE EXPLAINED ON THIS FORM.
LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES COLPOSCOPY RESULTS FORM L4 ID LABEL HERE ---> - - - VISIT #: FORM COMPLETED BY: VERSION DATE: 08/5/94 ANY MISSING OR INCOMPLETE TEST RESULTS MUST BE EXPLAINED ON THIS FORM.
Cervical Precancer: Evaluation and Management
 TAJ June 2002; Volume 15 Number 1 ISSN 1019-8555 The Journal of Teachers Association RMC, Rajshahi Review fam Cervical Precancer: Evaluation and Management SM Khodeza Nahar Begum 1 Abstract Carcinoma of
TAJ June 2002; Volume 15 Number 1 ISSN 1019-8555 The Journal of Teachers Association RMC, Rajshahi Review fam Cervical Precancer: Evaluation and Management SM Khodeza Nahar Begum 1 Abstract Carcinoma of
Treatment for Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia II/III Bowenoid or Basaloid with Imiquimod 5% cream.
 Treatment for Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia II/III Bowenoid or Basaloid with Imiquimod 5% cream. Authors: Marchitelli C; Secco G; Perrotta M; Lugones L; Pesce R; Testa R Claudia Marchitelli: Vulvar
Treatment for Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia II/III Bowenoid or Basaloid with Imiquimod 5% cream. Authors: Marchitelli C; Secco G; Perrotta M; Lugones L; Pesce R; Testa R Claudia Marchitelli: Vulvar
The use of CO2 laser for patients with Lichen sclerosus
 The use of CO2 laser for patients with Lichen sclerosus Dr. Christina Kuhler-Obbarius, Elisabeth Kunkel, Dr. Matthias Theden-Schow, Hamburg, Germany Our clinical center located in Hamburg includes eight
The use of CO2 laser for patients with Lichen sclerosus Dr. Christina Kuhler-Obbarius, Elisabeth Kunkel, Dr. Matthias Theden-Schow, Hamburg, Germany Our clinical center located in Hamburg includes eight
For many clinicians, the diagnosis of vulvar diseases
 2011 Terminology of the Vulva of the International Federation for Cervical Pathology and Colposcopy Jacob Bornstein, MD, MPA, 1 Mario Sideri, MD, 2 Silvio Tatti, MD, 3 Patrick Walker, MD, 4 Walter Prendiville,
2011 Terminology of the Vulva of the International Federation for Cervical Pathology and Colposcopy Jacob Bornstein, MD, MPA, 1 Mario Sideri, MD, 2 Silvio Tatti, MD, 3 Patrick Walker, MD, 4 Walter Prendiville,
Efficacy of cervical intrarepithelial neoplasia (CIN)
 The Ulster Medical Journal, Volume 72, No. 1, pp. 10-15, May 2003. Efficacy of cervical intrarepithelial neoplasia (CIN) treatment by cold coagulation A Zawislak, J H Price, H R McClelland, R G N Storey,
The Ulster Medical Journal, Volume 72, No. 1, pp. 10-15, May 2003. Efficacy of cervical intrarepithelial neoplasia (CIN) treatment by cold coagulation A Zawislak, J H Price, H R McClelland, R G N Storey,
WELL WOMAN CLINIC-SCREENING PROGRAM FOR CERVICAL CARCINOMAS G. J. Vani Padmaja 1
 WELL WOMAN CLINIC-SCREENING PROGRAM FOR CERVICAL CARCINOMAS G. J. Vani Padmaja 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: G. J. Vani Padmaja. Well Woman Clinic-Screening Program for Cervical Carcinomas. Journal of Evolution
WELL WOMAN CLINIC-SCREENING PROGRAM FOR CERVICAL CARCINOMAS G. J. Vani Padmaja 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: G. J. Vani Padmaja. Well Woman Clinic-Screening Program for Cervical Carcinomas. Journal of Evolution
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR Last Revision Date July 2015 1 Site Group: Gynecologic Cancer Vulvar Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR Last Revision Date July 2015 1 Site Group: Gynecologic Cancer Vulvar Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION
Vulval Intraepithelial Neoplasia (VIN)
 Vulval Intraepithelial Neoplasia (VIN) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is it? Vulval intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) is a condition where there are pre-cancerous cells in the skin of
Vulval Intraepithelial Neoplasia (VIN) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is it? Vulval intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) is a condition where there are pre-cancerous cells in the skin of
Clinically Microscopically Pathogenesis: autoimmune not lifetime
 Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Acceptable predictive accuracy of histopathology results by colposcopy done by Gynecology residents using Reid index
 DOI 10.1007/s00404-012-2569-y GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY Acceptable predictive accuracy of histopathology results by colposcopy done by Gynecology residents using Reid index Hadi Shojaei Fariba Yarandi Leila
DOI 10.1007/s00404-012-2569-y GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY Acceptable predictive accuracy of histopathology results by colposcopy done by Gynecology residents using Reid index Hadi Shojaei Fariba Yarandi Leila
3/25/2019. J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse
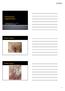 J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse 1 4 th most common GYN cancer 5% of malignancies of GYN type. 4850 new cases annually 1030 deaths Cigarette smoking Vulvar dystrophy (Lichen
J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse 1 4 th most common GYN cancer 5% of malignancies of GYN type. 4850 new cases annually 1030 deaths Cigarette smoking Vulvar dystrophy (Lichen
Epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia Elmar A. Joura
 Epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia Elmar A. Joura The incidence of human papilloma virus-related vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia is increasing worldwide. This is
Epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia Elmar A. Joura The incidence of human papilloma virus-related vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia is increasing worldwide. This is
The society for lower genital tract disorders since 1964.
 The society for lower genital tract disorders since 1964. Updated Consensus Guidelines for Managing Abnormal Cervical Cancer Screening Tests and Cancer Precursors American Society for and Cervical Pathology
The society for lower genital tract disorders since 1964. Updated Consensus Guidelines for Managing Abnormal Cervical Cancer Screening Tests and Cancer Precursors American Society for and Cervical Pathology
!"#$%&'(#)*$+&,$-&.#,$/#0()1-$ ),1')$2(%&,2#,%$%(0'#$34567$
 !"#$%&'(#)*$+&,$-&.#,$/#0()1-$ ),1')$2(%&,2#,%$%(0'#$34567$ Updated Consensus Guidelines for Managing Abnormal Cervical Cancer Screening Tests and Cancer Precursors American Society for and Cervical Pathology
!"#$%&'(#)*$+&,$-&.#,$/#0()1-$ ),1')$2(%&,2#,%$%(0'#$34567$ Updated Consensus Guidelines for Managing Abnormal Cervical Cancer Screening Tests and Cancer Precursors American Society for and Cervical Pathology
WOMEN S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES TREATMENT FORM FORM L16
 WOMEN S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES TREATMENT FORM FORM L16 ID LABEL HERE ---> - - - VISIT #: FORM COMPLETED BY: VERSION DATE: 05/01/95 ANY MISSING OR INCOMPLETE TEST RESULTS
WOMEN S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES TREATMENT FORM FORM L16 ID LABEL HERE ---> - - - VISIT #: FORM COMPLETED BY: VERSION DATE: 05/01/95 ANY MISSING OR INCOMPLETE TEST RESULTS
CASE 4 21/07/2017. Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix. Female 31. LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities
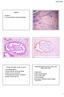 Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Department of Pathology, Kathmandu Medical College & Teaching Hospital, Sinamangal, Kathmandu, Nepal
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 4, Issue 20, 461-467 Original Article Correlation of PAP smear findings with clinical findings and cervical biopsy Pradhan B 1, Pradhan SB 2, Mital
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 4, Issue 20, 461-467 Original Article Correlation of PAP smear findings with clinical findings and cervical biopsy Pradhan B 1, Pradhan SB 2, Mital
Cervical cancer presentation
 Carcinoma of the cervix: Carcinoma of the cervix is the second commonest cancer among women worldwide, with only breast cancer occurring more commonly. Worldwide, cervical cancer accounts for about 500,000
Carcinoma of the cervix: Carcinoma of the cervix is the second commonest cancer among women worldwide, with only breast cancer occurring more commonly. Worldwide, cervical cancer accounts for about 500,000
Vaginal involvement in genital erosive lichen planus
 Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica. 2010; 89: 966 970 SHORT REPORT Vaginal involvement in genital erosive lichen planus ANNE LISE ORDING HELGESEN 1,2,3, PETTER GJERSVIK 3,4, PETER JEBSEN 5, ROLF KIRSCHNER
Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica. 2010; 89: 966 970 SHORT REPORT Vaginal involvement in genital erosive lichen planus ANNE LISE ORDING HELGESEN 1,2,3, PETTER GJERSVIK 3,4, PETER JEBSEN 5, ROLF KIRSCHNER
Vulvar Carcinoma. Definition: Cases should be classified as carsinoma of the vulva when the primary site growth is in the vulva Malignant melanoma sho
 Carcinoma Vulva & Vagina Subdivisi Onkologi Ginekologi Bagian Obgin FK USU Vulvar Carcinoma. Definition: Cases should be classified as carsinoma of the vulva when the primary site growth is in the vulva
Carcinoma Vulva & Vagina Subdivisi Onkologi Ginekologi Bagian Obgin FK USU Vulvar Carcinoma. Definition: Cases should be classified as carsinoma of the vulva when the primary site growth is in the vulva
Fluorescence Spectroscopy: A New Approach in Cervical Cancer
 DOI 10.1007/s13224-012-0298-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE : A New Approach in Cervical Cancer Pandey Kiran Pradhan Asima Agarwal Asha Bhagoliwal Ajay Agarwal Nidhi Received: 2 June 2008 / Accepted: 7 August 2012
DOI 10.1007/s13224-012-0298-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE : A New Approach in Cervical Cancer Pandey Kiran Pradhan Asima Agarwal Asha Bhagoliwal Ajay Agarwal Nidhi Received: 2 June 2008 / Accepted: 7 August 2012
LESION AT PACIFIC MEDICAL COLLEGE, UDAIPUR. 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, Pacific Medical college and hospital, Udaipur.
 International Journal of Medical Science and Education An official Publication of Association for Scientific and Medical Education (ASME) Original Research Article HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND CYTOLOGICAL ANALYSIS
International Journal of Medical Science and Education An official Publication of Association for Scientific and Medical Education (ASME) Original Research Article HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND CYTOLOGICAL ANALYSIS
Human Papillomavirus
 Human Papillomavirus Dawn Palaszewski, MD Assistant Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of February 18, 2018 9:40 am Dawn Palaszewski, MD Assistant Professor Department of Obstetrics and
Human Papillomavirus Dawn Palaszewski, MD Assistant Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of February 18, 2018 9:40 am Dawn Palaszewski, MD Assistant Professor Department of Obstetrics and
Becoming a colposcopist: Colposcope case studies
 Becoming a colposcopist: Colposcope case studies Seon-Kyung Lee, M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University Value of Colposcopy Cytology is an effective screening
Becoming a colposcopist: Colposcope case studies Seon-Kyung Lee, M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University Value of Colposcopy Cytology is an effective screening
Name of Policy: Speculoscopy
 Name of Policy: Speculoscopy Policy #: 095 Latest Review Date: September 2011 Category: Medicine/OB Gyn Policy Grade: C Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under Blue Cross
Name of Policy: Speculoscopy Policy #: 095 Latest Review Date: September 2011 Category: Medicine/OB Gyn Policy Grade: C Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under Blue Cross
SESSION J4. What's Next? Managing Abnormal PAPs in 2014
 37th Annual Advanced Practice in Primary and Acute Care Conference: October 9-11, 2014 2:45 SESSION J4 What's Next? Managing Abnormal PAPs in 2014 Session Description: Linda Eckert, MD Review current guidelines
37th Annual Advanced Practice in Primary and Acute Care Conference: October 9-11, 2014 2:45 SESSION J4 What's Next? Managing Abnormal PAPs in 2014 Session Description: Linda Eckert, MD Review current guidelines
Study Number: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period Study Design: Centres: Indication Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Colposcopy. Attila L Major, MD, PhD
 Colposcopy Attila L Major, MD, PhD Histology Colposcopy Cytology It has been estimated that annual Pap smear testing reduces a woman s chance of dying of cervical cancer from 4 in 1000 to about 5 in 10,000
Colposcopy Attila L Major, MD, PhD Histology Colposcopy Cytology It has been estimated that annual Pap smear testing reduces a woman s chance of dying of cervical cancer from 4 in 1000 to about 5 in 10,000
Article ID: WMC
 Article ID: WMC001971 2046-1690 Evaluation of Visual Inspection with Acetic Acid (Via) & Visual Inspection with Lugol's Iodine (Vili) as a Screening Tool for Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia in Comparison
Article ID: WMC001971 2046-1690 Evaluation of Visual Inspection with Acetic Acid (Via) & Visual Inspection with Lugol's Iodine (Vili) as a Screening Tool for Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia in Comparison
The Pap Smear Test. The Lebanese Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Women s health promotion series
 The Lebanese Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology Women s health promotion series The Pap Smear Test Since the Pap smear test started to be used the number of cases of cervical cancer was greatly reduced.
The Lebanese Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology Women s health promotion series The Pap Smear Test Since the Pap smear test started to be used the number of cases of cervical cancer was greatly reduced.
SENTINEL NODES FOR EARLY VULVAL CANCER:
 SENTINEL NODES FOR EARLY VULVAL CANCER: FEASIBILITY AND SAFETY IN A LOW RESOURCE SETTING LINDA ROGERS RCOG Congress 2017 None Declaration of Interests Vulval Cancer Rare 4% of all gynaecological malignancies
SENTINEL NODES FOR EARLY VULVAL CANCER: FEASIBILITY AND SAFETY IN A LOW RESOURCE SETTING LINDA ROGERS RCOG Congress 2017 None Declaration of Interests Vulval Cancer Rare 4% of all gynaecological malignancies
HCT Medical Policy. High-Resolution Anoscopy for Evaluation of Anal Lesions Policy # HCT109 Current Effective Date: 10/30/2014.
 HCT Medical Policy High-Resolution Anoscopy for Evaluation of Anal Lesions Policy # HCT109 Current Effective Date: 10/30/2014 Medical Policies are developed by HealthyCT to assist in administering plan
HCT Medical Policy High-Resolution Anoscopy for Evaluation of Anal Lesions Policy # HCT109 Current Effective Date: 10/30/2014 Medical Policies are developed by HealthyCT to assist in administering plan
Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia: Current concepts
 Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia: Current concepts L. Stewart Massad, M.D. Dept. of Obstetrics & Gynecology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO Disclosure I have no financial ties to
Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia: Current concepts L. Stewart Massad, M.D. Dept. of Obstetrics & Gynecology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO Disclosure I have no financial ties to
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Giant Acrochordon of Vulva
 Giant Madhusudan Dey, Reema Kumar, Raghu Sriram Department of Obstetric and Gynecology, Armed Forces Medical College, Pune, India Abstract Giant acrochordon or fibroepithelial stromal polyps usually occur
Giant Madhusudan Dey, Reema Kumar, Raghu Sriram Department of Obstetric and Gynecology, Armed Forces Medical College, Pune, India Abstract Giant acrochordon or fibroepithelial stromal polyps usually occur
Running head: EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE TWO-STEP DISCREPANCY
 Evidence-Based Medicine Two-Step Discrepancy 1 Running head: EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE TWO-STEP DISCREPANCY Evidence-Based Medicine Two-Step Discrepancy Julie Nelson Texas Woman s University Philosophy of
Evidence-Based Medicine Two-Step Discrepancy 1 Running head: EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE TWO-STEP DISCREPANCY Evidence-Based Medicine Two-Step Discrepancy Julie Nelson Texas Woman s University Philosophy of
Human Papillomavirus Induced Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions in Vulvar Lichen Planus
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Human Papillomavirus Induced Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions in Vulvar Lichen Planus Sigrid Regauer, MD, 1 Barbara Eberz, MD, 2 and Olaf Reich, MD 3 Objectives: Approximately
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Human Papillomavirus Induced Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions in Vulvar Lichen Planus Sigrid Regauer, MD, 1 Barbara Eberz, MD, 2 and Olaf Reich, MD 3 Objectives: Approximately
Appropriate Use of Cytology and HPV Testing in the New Cervical Cancer Screening Guidelines
 Appropriate Use of Cytology and HPV Testing in the New Cervical Cancer Screening Guidelines Tim Kremer, MD Ralph Anderson, MD 1 Objectives Describe the natural history of HPV particularly as it relates
Appropriate Use of Cytology and HPV Testing in the New Cervical Cancer Screening Guidelines Tim Kremer, MD Ralph Anderson, MD 1 Objectives Describe the natural history of HPV particularly as it relates
VULVAR CARCINOMA. Page 1 of 5
 VULVAR CARCINOMA EXAMPLE OF A VULVAR CARCINOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma arising in D-VIN Tumor in left labia major Left partial vaginectomy and sentinel lymph node
VULVAR CARCINOMA EXAMPLE OF A VULVAR CARCINOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma arising in D-VIN Tumor in left labia major Left partial vaginectomy and sentinel lymph node
LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES COLPOSCOPY RESULTS FORM L14
 LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES COLPOSCOPY RESULTS FORM L4 ID LABEL HERE ---> - - - VISIT #: FORM COMPLETED BY: VERSION DATE: 09/5/95 ANY MISSING OR INCOMPLETE TEST RESULTS MUST BE EXPLAINED ON THIS FORM.
LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES COLPOSCOPY RESULTS FORM L4 ID LABEL HERE ---> - - - VISIT #: FORM COMPLETED BY: VERSION DATE: 09/5/95 ANY MISSING OR INCOMPLETE TEST RESULTS MUST BE EXPLAINED ON THIS FORM.
Prevalence Of Precancerous Lesions Of The Uterine Cervix
 Prevalence Of Precancerous Lesions Of The Uterine Cervix 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Prevalence Of Precancerous Lesions Of INTRODUCTION. Gastric intestinal metaplasia is an intermediate precancerous gastric lesion
Prevalence Of Precancerous Lesions Of The Uterine Cervix 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Prevalence Of Precancerous Lesions Of INTRODUCTION. Gastric intestinal metaplasia is an intermediate precancerous gastric lesion
Pathology of the Cervix
 Pathology of the Cervix Thomas C. Wright Pathology of the Cervix Topics to Consider Burden of cervical cancer 1 Invasive Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer in world Second cause of cancer death in women Leading
Pathology of the Cervix Thomas C. Wright Pathology of the Cervix Topics to Consider Burden of cervical cancer 1 Invasive Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer in world Second cause of cancer death in women Leading
A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of 5-Fluorouracil for the Treatment of Cervicovaginal Human Papillomavirus
 Infectious Diseases in Obstetrics and Gynecology 7:186-189 (1999) (C) 1999 Wiley-Liss, Inc. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of 5-Fluorouracil for the Treatment of Cervicovaginal Human
Infectious Diseases in Obstetrics and Gynecology 7:186-189 (1999) (C) 1999 Wiley-Liss, Inc. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of 5-Fluorouracil for the Treatment of Cervicovaginal Human
Cervical Dysplasia and HPV
 Cervical Dysplasia and HPV J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse HPV Double stranded DNA virus The HPV infect epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes Highest risk
Cervical Dysplasia and HPV J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse HPV Double stranded DNA virus The HPV infect epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes Highest risk
SIMULTANEOUS SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMAS OF THE LOWER FEMALE GENITAL TRACT
 SIMULTANEOUS SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMAS OF THE LOWER FEMALE GENITAL TRACT Mark H. Stoler, M.D. University of Virginia Health System INTRODUCTION For the average woman the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma
SIMULTANEOUS SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMAS OF THE LOWER FEMALE GENITAL TRACT Mark H. Stoler, M.D. University of Virginia Health System INTRODUCTION For the average woman the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma
Vulva Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma
 Vulva Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Ethnicity Unknown AboriginalTorres
Vulva Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Ethnicity Unknown AboriginalTorres
Eradicating Mortality from Cervical Cancer
 Eradicating Mortality from Cervical Cancer Michelle Berlin, MD, MPH Vice Chair, Obstetrics & Gynecology Associate Director, Center for Women s Health June 2, 2009 Overview Prevention Human Papilloma Virus
Eradicating Mortality from Cervical Cancer Michelle Berlin, MD, MPH Vice Chair, Obstetrics & Gynecology Associate Director, Center for Women s Health June 2, 2009 Overview Prevention Human Papilloma Virus
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 11 Page November 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i11.10 Acetic acid Visualisation of Cervix as
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i11.10 Acetic acid Visualisation of Cervix as
Investigation of 100 consecutive negative cone biopsies
 British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology January 1997, Vol. 104, pp. 100-104 Investigation of 100 consecutive negative cone biopsies *Pouran Golbang Research Fellow and Consultant (Gynaecology), **James
British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology January 1997, Vol. 104, pp. 100-104 Investigation of 100 consecutive negative cone biopsies *Pouran Golbang Research Fellow and Consultant (Gynaecology), **James
Asymptomatic Undiagnosed Lichen Sclerosus
 Asymptomatic Undiagnosed Lichen Sclerosus Lynette J. Margesson MD FRCPC Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Surgery(Dermatology) Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Lebanon, NH, USA Disclosures
Asymptomatic Undiagnosed Lichen Sclerosus Lynette J. Margesson MD FRCPC Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Surgery(Dermatology) Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Lebanon, NH, USA Disclosures
What are the symptoms of a vulval skin condition?
 Information for you Published in December 2013 Skin conditions of the vulva About this information This information is for you if you want to know about skin conditions affecting the vulva. If you are
Information for you Published in December 2013 Skin conditions of the vulva About this information This information is for you if you want to know about skin conditions affecting the vulva. If you are
Vulval intraepithelial neoplasia: clinical review
 Genitourin Med 1987;63:147-152 Review article Vulval intraepithelial neoplasia: clinical review Nomenclature Preinvasive neoplasia ofthe vulva has been recognised for over 75 years, but terminology to
Genitourin Med 1987;63:147-152 Review article Vulval intraepithelial neoplasia: clinical review Nomenclature Preinvasive neoplasia ofthe vulva has been recognised for over 75 years, but terminology to
Colposcopic Evaluation Of Patients With Abnormal Cervical Cytology And Its Histopathological Corelation An Original Article
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics Volume 18 Number 1 Colposcopic Evaluation Of Patients With Abnormal Cervical Cytology And Its Histopathological Corelation An Original Article
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics Volume 18 Number 1 Colposcopic Evaluation Of Patients With Abnormal Cervical Cytology And Its Histopathological Corelation An Original Article
Learning Objectives. What is HPV? Incidence in the U.S. 5/22/2013. Human papillomavirus Infections
 Human papillomavirus Infections Anne Rompalo, MD, ScM Professor of Medicine Learning Objectives By the end of the presentation the participants will be able to: Describe the role of persistent HPV infection
Human papillomavirus Infections Anne Rompalo, MD, ScM Professor of Medicine Learning Objectives By the end of the presentation the participants will be able to: Describe the role of persistent HPV infection
HPV infections and potential outcomes
 CONTENTS Preface by Silvia de Sanjosé... 33 Preface by Jacob Bornstein... 37 Author s note... 39 Acknowledgments... 45 CHAPTER 1 HPV infections and potential outcomes HPV: What it is, where it is and what
CONTENTS Preface by Silvia de Sanjosé... 33 Preface by Jacob Bornstein... 37 Author s note... 39 Acknowledgments... 45 CHAPTER 1 HPV infections and potential outcomes HPV: What it is, where it is and what
MEDICAL POLICY EFFECTIVE DATE: 12/20/12 REVISED DATE: 11/21/13, 10/16/14 SUBJECT: HIGH RESOLUTION ANOSCOPY
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics
 International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Treatment of Cervical Precancerous Lesions using Thermocoagulation(Cold Coagulation) and Cryotherapy General Principles All high grade CIN should be
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Treatment of Cervical Precancerous Lesions using Thermocoagulation(Cold Coagulation) and Cryotherapy General Principles All high grade CIN should be
1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal
 Diseases of cervix I. Inflammations 1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal squamous mucosa
Diseases of cervix I. Inflammations 1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal squamous mucosa
Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(1): 80-84
 80 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(1): 80-84 Letter to the Editor Assessing the Effectiveness of a Cervical Cancer Screening Program in a Hospital-based Study* YANG Yi1, LANG Jing He1, WANG You Fang1, CHENG
80 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(1): 80-84 Letter to the Editor Assessing the Effectiveness of a Cervical Cancer Screening Program in a Hospital-based Study* YANG Yi1, LANG Jing He1, WANG You Fang1, CHENG
Comparison between Pap smear and visual inspection with acetic acid in screening of premalignant cervical intraepithelial lesion and
 International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Sokkary HH. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Jan;6(1):54-59 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789 DOI:
International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Sokkary HH. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Jan;6(1):54-59 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789 DOI:
How might we implement screening for anal cancer in HIV-positive patients?
 Objective How might we implement screening for anal cancer in HIV-positive patients? Identify the elements required to set up an anal cancer screening and prevention program J. Michael Berry, MD Associate
Objective How might we implement screening for anal cancer in HIV-positive patients? Identify the elements required to set up an anal cancer screening and prevention program J. Michael Berry, MD Associate
Medicine OPEN. Diagnostic Accuracy Study. 1. Introduction
 Diagnostic Accuracy Study Medicine OPEN Clinical analysis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia with vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia Yue He, MD, Qun Zhao, PhD, Yu-Ning Geng, MD, Shu-Li Yang, MD, Cheng-Hong
Diagnostic Accuracy Study Medicine OPEN Clinical analysis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia with vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia Yue He, MD, Qun Zhao, PhD, Yu-Ning Geng, MD, Shu-Li Yang, MD, Cheng-Hong
HPV-related papillomatous-condylomatous lesions in female anogenital area
 HPV-related papillomatous-condylomatous lesions in female anogenital area Theo Panoskaltsis MD, FRCOG, CCST (UK) Epidemiology Anal cancer is increasing in both men and women Groups at risk: - HIV (+)
HPV-related papillomatous-condylomatous lesions in female anogenital area Theo Panoskaltsis MD, FRCOG, CCST (UK) Epidemiology Anal cancer is increasing in both men and women Groups at risk: - HIV (+)
CORRELATION OF PAP SMEAR AND COLPOSCOPIC FINDING OF CERVIX WITH HISTOPATHOLGIOCAL REPORT IN A GROUP OF PATIENT ATTENDING IN A TERTIARY HOSPITAL
 CORRELATION OF PAP SMEAR AND COLPOSCOPIC FINDING OF CERVIX WITH HISTOPATHOLGIOCAL REPORT IN A GROUP OF PATIENT ATTENDING IN A TERTIARY HOSPITAL PARVIN S 1, KABIR N 2, LIPE YS 3, NASREEN K 4, ALAM KMN 5
CORRELATION OF PAP SMEAR AND COLPOSCOPIC FINDING OF CERVIX WITH HISTOPATHOLGIOCAL REPORT IN A GROUP OF PATIENT ATTENDING IN A TERTIARY HOSPITAL PARVIN S 1, KABIR N 2, LIPE YS 3, NASREEN K 4, ALAM KMN 5
Int. J. Life. Sci. Scienti. Res., 2(3): (ISSN: ) Impact Factor 2.4 MAY Research Article (Open access)
 Int. J. Life. Sci. Scienti. Res., 2(3): -279-284 (ISSN: 2455-1716) Impact Factor 2.4 MAY-2016 Research Article (Open access) Detection of Abnormal Cervical Cytology by Papanicolaou Stained (PAP) Smears
Int. J. Life. Sci. Scienti. Res., 2(3): -279-284 (ISSN: 2455-1716) Impact Factor 2.4 MAY-2016 Research Article (Open access) Detection of Abnormal Cervical Cytology by Papanicolaou Stained (PAP) Smears
Your Colposcopy Visit
 Introduction Welcome to the colposcopy clinic. This booklet tells you about. The colposcopy examination.. Tests that are done in the colposcopy clinic.. What these tests look for Take a few minutes to
Introduction Welcome to the colposcopy clinic. This booklet tells you about. The colposcopy examination.. Tests that are done in the colposcopy clinic.. What these tests look for Take a few minutes to
Information about your HANS assessment, HPV and AIN
 Information about your HANS assessment, HPV and AIN Incorporating hospital and community health services, teaching and research This booklet has been written for people attending the Homerton anal neoplasia
Information about your HANS assessment, HPV and AIN Incorporating hospital and community health services, teaching and research This booklet has been written for people attending the Homerton anal neoplasia
High-grade vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia: can we be selective about who we treat?
 DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.12223 www.bjog.org Gynaecological oncology High-grade vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia: can we be selective about who we treat? N Ratnavelu, a A Patel, a AD Fisher, a K Galaal,
DOI: 10.1111/1471-0528.12223 www.bjog.org Gynaecological oncology High-grade vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia: can we be selective about who we treat? N Ratnavelu, a A Patel, a AD Fisher, a K Galaal,
Management that provides continuity of care for women
 Management that provides continuity of care for women If women are diagnosed with reproductive tract infection, prompt treatment should be instituted according to the WHO guidelines. Though it may be preferred
Management that provides continuity of care for women If women are diagnosed with reproductive tract infection, prompt treatment should be instituted according to the WHO guidelines. Though it may be preferred
WOMEN'S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY GYNECOLOGICAL EXAM FORM 8
 WOMEN'S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY GYNECOLOGICAL EXAM FORM 8 AFFIX ID LABEL HERE ---> PARTICIPANT ID: (Enter number here only if ID label is not available) - - - WIHS STUDY VISIT #: FORM VERSION: 04/01/99 EXAMINER'S
WOMEN'S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY GYNECOLOGICAL EXAM FORM 8 AFFIX ID LABEL HERE ---> PARTICIPANT ID: (Enter number here only if ID label is not available) - - - WIHS STUDY VISIT #: FORM VERSION: 04/01/99 EXAMINER'S
Cervical Testing and Results Management. An Evidenced-Based Approach April 22nd, Debora Bear, MSN, MPH
 Cervical Testing and Results Management An Evidenced-Based Approach April 22nd, 2010 Debora Bear, MSN, MPH Assistant Medical Director for Planned Parenthood of New Mexico, Inc. Burden of cervical cancer
Cervical Testing and Results Management An Evidenced-Based Approach April 22nd, 2010 Debora Bear, MSN, MPH Assistant Medical Director for Planned Parenthood of New Mexico, Inc. Burden of cervical cancer
SCAN Gynaecological Group. Clinical Management Protocols vulval cancer
 SE Scotland Cancer Network SCAN Gynaecological Group Clinical Management Protocols vulval cancer 2009 www.scan.scot.nhs.uk August 2001 updated annually, most recently INTRODUCTION The South East Scotland
SE Scotland Cancer Network SCAN Gynaecological Group Clinical Management Protocols vulval cancer 2009 www.scan.scot.nhs.uk August 2001 updated annually, most recently INTRODUCTION The South East Scotland
ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION. Tajossadat Allameh 1, Somayeh Khanjani 2, Fereshteh Mohammadizadeh 3*, Elaheh Refaei 4. sions.
 Open Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 213, 3, 341-346 http://dx.doi.org/.4236/ojog.213.363 Published Online May 213 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojog/) OJOG Diagnostic of the combination of TruScreen
Open Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 213, 3, 341-346 http://dx.doi.org/.4236/ojog.213.363 Published Online May 213 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojog/) OJOG Diagnostic of the combination of TruScreen
Cytology and Surgical Pathology of Gynecologic Neoplasms
 Cytology and Surgical Pathology of Gynecologic Neoplasms Current Clinical Pathology ANTONIO GIORDANO, MD, PHD SERIES EDITOR For further titles published in this series, go to http://www.springer.com/springer/series/7632
Cytology and Surgical Pathology of Gynecologic Neoplasms Current Clinical Pathology ANTONIO GIORDANO, MD, PHD SERIES EDITOR For further titles published in this series, go to http://www.springer.com/springer/series/7632
ORIGINAL ARTICLE COLPOSCOPIC FINDINGS IN UNHEALTHY CERVIX AND ITS COMPARISON WITH CYTOLOGY AND HISTOPATHOLOGY
 COLPOSCOPIC FINDINGS IN UNHEALTHY CERVIX AND ITS COMPARISON WITH CYTOLOGY AND HISTOPATHOLOGY N. Gopal 1, Prashant. S. Joshi 2, Ravindra Pukale 3, Shamashoor 4. 1. Professor, Department of Obstetrics &
COLPOSCOPIC FINDINGS IN UNHEALTHY CERVIX AND ITS COMPARISON WITH CYTOLOGY AND HISTOPATHOLOGY N. Gopal 1, Prashant. S. Joshi 2, Ravindra Pukale 3, Shamashoor 4. 1. Professor, Department of Obstetrics &
Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect
 Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect For women with vulvar cancer What is the vulva? The vulva is the external (outside) part of the female genitals. The vulva includes the outer and inner lip, the clitoris,
Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect For women with vulvar cancer What is the vulva? The vulva is the external (outside) part of the female genitals. The vulva includes the outer and inner lip, the clitoris,
Faculty Pap Smear Guidelines: Family Planning Update 2008 Part Two
 Faculty Pap Smear Guidelines: Family Planning Update 2008 Part Two Seshu P. Sarma, MD, FAAP Emory University Regional Training Center Atlanta, Georgia Produced by the Alabama Department of Public Health
Faculty Pap Smear Guidelines: Family Planning Update 2008 Part Two Seshu P. Sarma, MD, FAAP Emory University Regional Training Center Atlanta, Georgia Produced by the Alabama Department of Public Health
Profile Of Cervical Smears Cytology In Western Region Of Saudi Arabia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics Volume 1 Number 2 Profile Of Cervical Smears Cytology In Western Region Of Saudi Arabia I Mansoor Citation I Mansoor. Profile Of Cervical Smears
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics Volume 1 Number 2 Profile Of Cervical Smears Cytology In Western Region Of Saudi Arabia I Mansoor Citation I Mansoor. Profile Of Cervical Smears
WOMEN S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES COLPOSCOPY RESULTS FORM L14
 WOMEN S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES COLPOSCOPY RESULTS FORM L4 ID LABEL HERE ---> - - - VISIT #: FORM COMPLETED BY: VERSION DATE: 0 / 0 / 6 ANY MISSING OR INCOMPLETE TEST RESULTS
WOMEN S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES COLPOSCOPY RESULTS FORM L4 ID LABEL HERE ---> - - - VISIT #: FORM COMPLETED BY: VERSION DATE: 0 / 0 / 6 ANY MISSING OR INCOMPLETE TEST RESULTS
AgNOR Count and its Correlation with Colposcopy in Suspicious Cervix
 DOI 10.1007/s13224-012-0300-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Count and its Correlation with Colposcopy in Suspicious Cervix Goyal Ritu Mohi Kaur Manjit Bal Singh Manjit Received: 15 December 2009 / Accepted: 7 August
DOI 10.1007/s13224-012-0300-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Count and its Correlation with Colposcopy in Suspicious Cervix Goyal Ritu Mohi Kaur Manjit Bal Singh Manjit Received: 15 December 2009 / Accepted: 7 August
Use of Schiller s test versus Pap smear to increase detection rate of cervical dysplasias
 International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Ramaraju HE et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2016 May;5(5):1446-1450 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789
International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Ramaraju HE et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2016 May;5(5):1446-1450 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789
Pap Smears Pelvic Examinations Well Woman Examinations. When should you have them performed???
 Pap Smears Pelvic Examinations Well Woman Examinations. When should you have them performed??? Arlene Evans-DeBeverly, PA-C Copyright 2012 There are always ongoing changes in gynecology, including the
Pap Smears Pelvic Examinations Well Woman Examinations. When should you have them performed??? Arlene Evans-DeBeverly, PA-C Copyright 2012 There are always ongoing changes in gynecology, including the
LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES COLPOSCOPY RESULTS FORM L14
 LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES COLPOSCOPY RESULTS FORM L4 ID LABEL HERE ---> - - - VISIT #: FORM COMPLETED BY: VERSION DATE: 0/0/0 ANY MISSING OR INCOMPLETE TEST RESULTS MUST BE EXPLAINED ON THIS FORM.
LABORATORY - PELVIC EXAM STUDIES COLPOSCOPY RESULTS FORM L4 ID LABEL HERE ---> - - - VISIT #: FORM COMPLETED BY: VERSION DATE: 0/0/0 ANY MISSING OR INCOMPLETE TEST RESULTS MUST BE EXPLAINED ON THIS FORM.
