IDENTIFICATION AND PREDICTION OF CORONARY HEART DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH APOLIPOPROTEIN LEVELS
|
|
|
- Alban Patterson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page31 Available Online through IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 IDENTIFICATION AND PREDICTION OF CORONARY HEART DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH APOLIPOPROTEIN LEVELS Sreenivasan R S 1*, Kavitha A 1, Anusa A R 1, Krishna Moorthy P 2, Renganathan N G 3 1. DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE AND HUMANITIES, VELTECH MULTITECH DR.RANGARAJAN DR.SAKUNTHALA ENGINEERING COLLEGE, 2. DEPARTMENT OF BIO-ENGINEERING, BHARATH UNIVERSITY, 3. DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE AND HUMANITIES, VELTECH DR.RR & DR.SR TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, CHENNAI, INDIA. *Corresponding Author E.mail: rssvasan1973@yahoo.co.in, rssvasan1973@rediffmail.com Research Article RECEIVED ON ACCEPTED ON ABSTRACT Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) is the leading cause of deaths in the developed and developing countries. CHD is always due to atherosclerosis. A number of risk factors have been reported for atherosclerosis. Of these, the major risk factors are high cholesterol level, hypertension, smoking and diabetes mellitus. Fifteen patients with coronary heart disease were chosen for the study. Blood samples were collected from the overnight fast CHD patients and the levels of lipid profile were analyzed and were compared to the age and sex matched normal persons. In the result, increased levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, VLDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol and moderately elevated levels of HDL-cholesterol were seen. While in apoproteins, increased level of Apo-B and decreased level of Apo-A 1 and lowered Apo-A 1 /Apo-B ratio were seen in CHD patients, when compared to the normal subjects. Increased cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol and decreased HDL cholesterol are considered to be high risk factor for CHD. These conventional lipid profiles were used to identify the CHD. The measurement of apolipoprotein-a 1 and B may be more useful in the identification and prediction of CHD. Therefore, conclude that the quantization of apolipoproteins is superior to the traditional lipid profile in the identification and prediction of CHD. KEYWORDS: Apolipoprotein-A 1, apolipoprotein-b, cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, triglycerides. Introduction Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) is the leading cause in most industrialized countries, accounting for one out of every two deaths in the United States. Disorders of the lipid transport system resulting from complex interactions among nutritional environmental and generic factors. It has been proposed low density lipoproteins (LDL) cause cholesterol deposition in the arterial wall whereas high density lipoproteins (HDL) promote effect of cholesterol from this site. The low levels of HDL and/or high levels of LDL have been associated with increased risk of CHD. Atherosclerosis, a disease literally means hardening of the arteries and accumulation of lipids characterizing the typical lesions. It is the principal cause of death in western world, a progressive process that begins in childhood with clinical manifestations in middle to late adulthood 1. Arteries like the aorta, coronary and the cerebral are the prime International Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (ISSN: )
2 Page32 IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 targets with myocardial infarction and cerebral infarction, which are major consequences. In small arteries, atheromos are occlusive, comprising ischemic injury, while in large arteries; they are destructive, favoring thrombosis. Many lesions are dense and fibrous while others containing large amount of lipids and necrotic debris 2, 3. By reducing the lumen of coronary arteries, atherosclerosis causes an absolute decrease in myocardial perfusion in the vasal state. Fatty streaks develop as circulating monocytes migrates into intima, taking oxidized LDL from plasma, becoming lipid larden foam cells. A nature plaque contains a core of extracellular lipid surrounded by smooth muscle cells separated from lumen by collagen rich thick-cap. Such plaques may ruptures; allowing blood which disrupts the arterial walls comprising thrombosis and local vasospasm, further causing acute coronary syndromes 4. A reduction in the oxygen carrying capacity of the blood, as in extremely severe anemia, is a rare cause of myocardial ischemia. When there is decreased in the supply of blood to the heart, thus resulting in heart attack and cell death 5. Hypercholestrolemia,hypertriglyceride mia and other abnormalities in lipid metabolism contribute a major risk factor. The most striking association is with elevated levels of LDL and VLDL containing 70% of cholesterol in the blood 6. Smoking is the dominant cause of atherosclerosis in women mainly increasing the degree of aortic and coronary atherosclerosis 7. Two fold increases is seen in incidence of myocardial infarction in diabetes than non-diabetic. Obesity is an independent risk factor which is associated with hypertension, diabetes and physical inactivity. Regular physical activity shown to reduce risk for CHD by increasing HDL-cholesterol, lowering BP and reducing blood clotting etc 8. Increase in age and male sex is the risk factors which cannot be corrected. Expression of anger affects CHD risk because of increased cardiovascular reactivity 9. Blood concentrations of antioxidant affect the susceptibility of LDL and lipoprotein-a to oxidation, may increase atherosclerosis risk, when decreased. Hyperhomocystinuria has been established as an independent risk factor for coronary vascular disease etc. High levels of fibrinogen, coagulation factor VII increases the risk for CHD 10. Lipoproteins are conjugated protein, consists of a lipid core of mainly non-polar or hydrophobic triglyceride, cholesterol ester and free fatty acid surrounded by a single layer of polar or hydrophilic phospholipid and cholesterol molecules 11. Apolipoprotein is the protein part, which characterize the lipoprotein. The amount and the nature of the apolipoprotein vary with that of lipoprotein. Apolipoprotein carry out several important roles like enzyme co-factors, lipid transfer proteins, solubility of lipid molecules and ligand for interaction with lipoprotein receptors in tissues. Table 1: Structure and Functions of Different Classes of Apoproteins Apoprotein Lipoprotein Function Apo-A 1 HDL and CM Activator of LCAT Apo-A 2 HDL & CM Inhibitor of LCAT Apo-B 100 LDL, VLDL & IDL Acts as ligand for LDL receptor Apo-B 48 CM & CM reminants Synthesized in intestine Apo-C VLDL, LDL & IDL Apo-C 1 activator of LCAT Apo-D Subfraction of HDL Apo-C 2 activator of lipoprotein lipase May acts as lipid transfer protein
3 Page33 IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 Apo-E VLDL, HDL & CM Cholesterol transportation Increase in LDL, IDL and -VLDL lead to atherosclerosis. The most common lipoprotein abnormalities like hyperlipidemia and hyperlipoproteinemia lead to accumulation of excessive lipids. While in apoproteins, increased levels of Apo-B and decreased level of Apo-A 1 have been associated with increased risk for atherosclerosis. It has been postulated for many years that apolipoproteins mainly Apo-A 1 and Apo-B could be better predictors than lipids for CHD. It is the main lipid found in the blood, bile and brain tissues. It is also one of the most important steroids of the body and is a precursor of many steroid hormones. Two thirds of cholesterol present in the blood is esterified. The liver metabolizes the cholesterol and it is transported in the blood stream by lipoproteins. Increased levels are found in hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidemia, hypothyroidism, uncontrolled diabetes, nephritic syndrome and cirrhosis. Decreased levels are found in malabsorption, malnutrition, hyperthyroidism, and anemia and liver diseases. Triglycerides (TG) are a family of lipids absorbed from the diet and produced endogenously from carbohydrate. Measurement of triglycerides is important in the diagnosis and management of hyperlipidemia. These diseases can be genetic or secondary to other disorders including nephrosis, diabetes mellitus and endocrine disturbances. Elevation of triglycerides has been identified as a risk factor for atherosclerotic disease. Cholesterol distribution in the different fractions of lipoproteins i.e. HDL, LDL, VLDL and chylomicron (CM) are of particular interest in understanding the metabolic status and risk of various diseases like artherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, etc. Lower levels of HDLcholesterol are associated with higher risks of atherosclerosis i.e. deposition of cholesterol in cells of blood vessels and complications like hypertension, coronary heart disease related to it. Coronary heart disease and stroke (e.g. myocardial infarction) are the leading cause of deaths in the industrialized countries. CHD is always due to atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the accumulation of fatty deposits in arteries, thus leads to coronary artery disease. Research indicates number of risk factors for CHD. These includes age, sex, hypertension, family history, lipid disorders, diabetes mellitus, smoking, high cholesterol level, haemostatic variables, sudden life style, obesity and poly unsaturated fatty acid deficiency. Conventional lipid profile cholesterol, HDL, LDL, TG, VLDL levels are used to identifying risk factor for CHD. Increased cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol arid decreased HDL-cholesterol is considered to be a high risk factor for CHD. However in certain cases the conventional lipid fractions particularly LDL and HDL levels do not recognize CHD. Recently quantation of apolipoproteins specifically Apo- A 1 and Apo-B has been suggested to be a more specific and a sensitive marker for profiling individual CHD risk than corresponding levels of lipoprotein fractions. Apo-B is a carrier protein for LDL-cholesterol; Apo-A 1 is a carrier protein for HDL-cholesterol. Therefore the present study analysis apolipoprotein levels in people with CHD. The main objectives of the present study are to review various etiological factors in the development of atherosclerosis and CHD, analysis the conventional lipid profile - cholesterol, TG, HDL, LDL and VLDL in CHD patients and controls, analysis the levels of Apo-A 1 and Apo-B and to correlate the levels of Apo-A 1 and Apo-B with CHD.
4 Page34 IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 Materials and Methods 2.1 Subjects and Samples The subjects taken for the study of altered cholesterol, TGL, HDL, LDL were coronary heart disease. Blood samples were collected from fifteen newly diagnosed CHD patients from Vel R.S. Medical College and Hospital, Avadi, Chennai. These samples of patients were compared with normal individual blood of the same sex and age. Blood was collected from 15 normal individual persons and used as controls. Both controls and patients were ranging in age from years. Blood were collected by fasting sample in a tube serum was separated by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 15 min. 2.2 Estimation of Cholesterol The serum cholesterol levels were estimated by Ziakiti s-zak and Boyle method. Plasma was treated with ferric chloride acetic acid reagent to precipitate the protein. The protein free supernatant was treated with concentrated H 2 SO 4. A reddish purple color was developed which was measured at 560nm using a suitable standard and a reagent blank. Take 0.2m1 of serum in a 15ml glass stopper centrifuge tube. Added 9.8m1 of working ferric chloride acetic acid reagent mixed well and allowed to stand for 15 mins and centrifuged. Take 0.5m1 of supernatant and added 3ml of concentrated sulphuric acid, added 1ml of ferric chloride acetic acid reagent. Make up the working standard solution to 6ml with ferric acetic acid reagent. To all the tubes, added 3ml of concentrated sulphuric acid and mixed well. Measured the color which developed was read at 560nm after 15 mins. The results were expressed as mg/dl. 2.3 Estimation of HDL-cholesterol The HDL-cholesterol was estimated by Wybenga and Pileggi method. In hot acidic medium, cholesterol oxidize ferric ion to a colored complex which can be measured at 830nm was directly proportional to the cholesterol concentration. Serum 0.2ml was taken in the test tube and added 0.2ml of the HDL reagent, mixed well for 15 mins and centrifuged separated the clear supernatant and estimated the cholesterol level of the supernatant. Series of the test tubes were taken and marked them as blank, standard, test as 1, 2, 3 respectively. 5ml of the cholesterol reagent was pipette out into the series of three tubes. Then add the HDL reagent into the first tube and second tube in the level of 0.2m1 respectively. Then supernatant 0.2ml was added into the third tube considered as test cholesterol standard reagent (20 mg/dl). 0.02ml was added to the second test tube which was considered as a standard. First tube was considered as a blank. Mixed well and immediately kept in boiling water bath for 90 seconds then cooled. After cooling the given color developed was read at 530nm against blank HDL. The results were expressed as mg/dl. 2.4 Estimation of Triglycerides Triglycerides were estimated by enzymatic method. Increased levels of triglycerides well commonly found in hyperlipoproteinemia, nephrotic syndrome, coronary heart disease, hyperthyroidism, liver disorders and diabetes mellitus. Dissolve one enzyme vial with 10ml buffer. Series of three test tubes were taken and marked as 1,2,3 for the preparation of blank. Into the first tube, 0.05m1 of distilled water was added 1ml of reconstituted reagent was added to the same tube. To the second test tube, 0.05m1 of standard solution was added and 1ml of reconstituted reagent was added to that tube. Serum 0.05ml was added to the third tube and added 1ml of the reconstituted reagent. This was considered as test. All these tubes considered reagents were mixed and incubated for 10 mins at 37 C. After
5 Page35 IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 exactly 10 mins incubation, 2m1 of distilled water was added to all these tubes. The color developed in the tube was read at 560nm after 30 mins. The results were expressed as mg/dl. 2.5 Estimation of Apolipoprotein A 1 The apolipoprotein-a 1 was estimated by immuno turbidimetric method. The apolipoproteins contained in the human serum form immune complexes with their corresponding antibodies. The concentrations are determined by turbidimetry assay. The results are evaluated using reference curve prepared with the aid of dilution of calibrator. The control and sample are diluted manually or automatically with saline solution (0.9% NaCl). Diluted antiserum Apo-A 1:41 with buffer solution. The working reagent is stable for 2 weeks at 2-8 C. Diluted samples and controls 1:21 with saline solution. To 20 l of diluted calibrator, control and sample is pipette out with 1ml of working reagent. Mixed and incubated for 10 mins at 37 C. Read at 340nm against blank. The results were expressed in mg/dl. 2.6 Estimation of Apolipoprotein-B The apolipoprotein-b was estimated by immuno turbidimetric method. The apolipoprotein contained in the human serum form immune complexes with their corresponding antibodies. The concentrations are determined by turbidimetry assay. The results are evaluated using a reference curve prepared with the aid of solution of calibrator. Diluted antiserum Apo-B 1:41 with buffer solution. The working reagent is stable for 2 weeks at 2-8 C. Diluted sample and control 1:15 with saline. Dilute the calibrator with saline. To 20 ml of diluted calibrator, control and sample is pipette out with 1ml of working reagent. Mixed and incubated for 10 mins at 37 C. Read at 340nm against blank. The results were expressed in mg/dl. 2.7 Statistical Analysis All the quantitative measurements were made on each patient and normal. The values are expressed as Mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was done by student t test and the p values to assess the statistical significance of the changes, observed in CHD patients as compared to controls. Results and Discussions The present study analyzed the lipid profile in 15 CHD patients. The results were compared with an equal number of age and sex matched normal subjects. Table 2 shows the case history of the normal and CHD subjects. Table 3 shows the plasma levels of total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol and LDLcholesterol in normal and CHD subjects. Table 4 shows the levels of triglyceride and VLDL cholesterol in normal and CHD patients. Table 5 shows the levels of apolipoproteins and their ratio in the normal and CHD subjects. The present study focused the relation between the conventional lipid profile along with lipoproteins and CHD. Lipid profile - cholesterol, TG including lipoproteins Apo-A 1 and Apo-B were analyzed in 15 persons who were diagnosed as CHD patients. The results were compared with an equal number of 15 male, age matched normal subjects. The levels of total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL-cholesterol and VLDLcholesterol were significantly increased in plasma of CHD patients as compared to normal. The levels of HDL-cholesterol were moderately increased. The concentration of apolipoprotein-a 1 was significantly decreased while apolipoprotein-b is increased significantly in the plasma of CHD patients as compared to the normal. The Apo-A 1 /Apo-B ratio was found to be significantly reduced in CHD patients as compared to normal subjects. Several epidemiological studies have confirmed that
6 Page36 IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 Coronary heart disease (CHD) has associated with lipid abnormalities. The reduction of total and LDL-cholesterol and an increase of HDL-cholesterol reduce the risk of CHD. Table 2: Case Histories of the Subjects Investigated General Characteristics Normal Abnormal Total number of subjects Sex Age Type of habits 15 Male Male Cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption Table 3: Plasma Levels of Total Cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol in Normal and CHD Patients Parameters Normal CHD Patients Total cholesterol * HDL-cholesterol LDL-cholesterol * Data represents Mean SD from 15 subjects in each group * Significantly different from normal (p<0.001) Moderately different from normal (p<0.001)
7 Page37 IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 Fig.1: Plasma Levels of Total Cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol 300 and LDL-cholesterol in Normal and CHD Patients Total Cholesterol Normal HDL-cholesterol LDL-cholesterol CHD Patients Table 4: Levels of Triglyceride and VLDL-cholesterol in Normal and CHD Patients Parameters Normal CHD Patients Triglycerides * VLDL cholesterol * Data represents Mean SD from 15 subjects in each group * Significantly different from normal (p<0.001)
8 Page38 IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 Fig.2: Levels of Triglyceride and VLDL-cholesterol in Normal and CHD Patients Triglycerides VLDL cholesterol Normal CHD Patients Table 5: Plasma Levels of Apolipoproteins in Normal and CHD Patients Parameters Normal CHD Patients Apolipoprotein A * Apolipoprotein B * Apo-A 1 /Apo-B * Data represents Mean SD from 15 subjects in each group Significantly different from normal (p<0.001)
9 Page39 IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 Fig.3: Plasma Levels of Apolipoprotein in Apolipoprotein A 1 Normal and CHD Patients Apolipoprotein B Apo-A 1 /Apo-B Normal CHD Patients Besides dietary factors, the plasma cholesterol level is affected by a number of factors and depends upon the presence of specific receptors on cell surface. The plasma levels of cholesterol reflect the level of lipoproteins LDL and HDL. LDL is cholesterol rich and accounts for the most of the cholesterol in the plasma. The plasma concentration of LDL is determined by the rate of uptake by LDL receptors. Cholesterol accumulation in liver may leads to reduction of LDL receptor in number and hence by increase plasma LDL level 12. Cigarette smoking is known to increase total cholesterol and decrease HDLcholesterol 7. Secondary increase in plasma total cholesterol due to chronic alcoholism has been reported. Most of the patients investigated were known to be smokers and alcohol drinkers. Therefore our reports have agreement with these risk factors to CHD. Increased levels of plasma LDL-cholesterol and Apo-B are risk factors for atherosclerosis. The critical role of LDL in atherosclerosis has been confirmed in genetically altered mice. The mechanism is that normal LDL does not cause foam cell formation when incubated, but when LDL undergoes lipid peroxidation result in the formation of cholesterol laden foam cells. In addition to these, oxidized LDL acts in the vessel wall to stimulate the secretion of cytokines, growth factors by endothelial cells, smooth cells and monocyte derived macrophages. The consequence is attachment of more monocytes to the lesions and proliferation of smooth muscle cells which synthesise and secrete increased amount of matrix such as collagen. Although mice are resistance to atherosclerosis, increased plasma levels of reminants of lipoproteins or LDL leads to atherosclerosis in these species. In contrast to atherogenic Apo-B lipoprotein, the Apo-A containing lipoprotein HDL, appear to be antiatherogenic. HDL cholesterol levels are as strong indicator of protection of CHD, as LDLcholesterol levels are indicators of risk. HDL mediated reverse cholesterol transport from peripheral tissue to liver is thought to be the
10 Page40 IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 primary mechanism by which HDL protects from atherosclerosis. In rare cases, low plasma HDL is due to a genetic deficiency of one of the structural components of HDL, such as Apo-A but low HDL levels usually, the secondary constituents of increased plasma levels of VLDL and IDL(CM and its reminants)[13]. Elevated levels of TG and VLDL were observed in the present study. TG make up the bulk of the VLDL 55% to 85% by weight and the size of the VLDL is determined by the TG available,hence very large TG rich VLDL is secreted in state of caloric excess in diabetes mellitus and with alcohol consumption. Small VLDL is secreted when fewer TG are available. The role of VLDL in atherogenesis is uncertain. The major reason for this uncertainity is due to the inverse relationship between elevated levels of TG rich lipoproteins and reduced levels of antiatherogenic HDL cholesterol. Hypertriglyceridemia, may not be directly atherogenic but the surrogate of other lipoprotein abnormalities 14. The concentration of Apo-A 1 was decreased significantly and Apo- B was increased in all CHD patients as compared to normal. Recent reports suggest that apolipoprotein-a 1 may be better diagnosis of CHD than cholesterol levels and low ratio of apolipoprotein-a 1 and B may be best predictor 15. Further, Apo-A 1 levels have been found to be more useful in identifying patients with CHD than HDL 16, 17. In our study, the result showed increased HDL level with decreased Apo-A 1 in CHD patients as compared to normal subjects. Apo-B is a carrier protein for LDL-cholesterol. Apo-B has seen increased in the following states like nephrotic syndrome, pregnancy, biliary obstruction, cigarette smoking and haemodialysis, while decreased in abetalipoproteinemia, estrogen therapy, liver disease, exercise, drug therapy and infections. Apo-A 1 is a major carrier protein of HDLcholesterol, increases during pregnancy, exercise, alcohol consumption and estrogen therapy and decreased by fish-eye disease, familial LCAT deficiency, infection, cholestasis, cigarette smoking, and diabetes and drug therapy. Recent studies have revealed that decreased levels of Apo-B and subsequently increased level of HDL-cholesterol are directly associated with angiographic reduction and favorable clinical outcome 15. Research further showed that patients with CHD exists a group with normal LDLcholesterol but with high concentrations of Apo-B. Measurement of LDL-cholesterol does not recognize the coronary in these individuals. Therefore, Apo-B has been shown to be a more reliable indicator of risk. Therefore Apo-B measurement can be useful in identifying patients at increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease could otherwise go unidentified by the traditional lipoprotein profile 18. The Apo-A 1 and Apo-B ratio of all CHD patients lowered significantly as compared to normal. Studies have shown that Apo- A 1 /Apo-B ratio distinguishes unequivocal between patients with and those without CHD. Therefore, apolipoprotein-a and B studies are superior to conventional total cholesterol or LDL, and HDL cholesterol studies for identifying the risk of CHD. Acknowledgement Authors sincerely thank Dr.R.Rangarajan, Chairman, Dr.Sakunthala Rangarajan, Vice-Chairman, VELTECH Group of Educational Institutions and Dr.K.Siddappa Naidu, Principal, VELTECH MULTITECH Dr.Rangarajan Dr.Sakunthala Engineering College, Chennai for their unremitting encouragement and valuable advices for publishing this paper successfully.
11 Page41 IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 References 1.Alexander, R.W., Inflammation and coronary artery disease. New Engl. J. Med., 331: 468 9, (1994). 2.Tipping, P.G., Hancock, W.W., Production of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 by macrophages from human atheromatous plaques. Am. J. Pathol., 138: , (1991). 3.Galea, J., Armstrong, J.A., Gadsdon, P.A., Interleukin-1 in coronary arteries of patients with ischemic heart disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 16: , (1996). 4.Danesh. J., Whincup. P., Walker. M., Low grade inflammation and coronary heart disease: Prospective study and updated meta-analyses. Basic Med. J., 321: , (2000). 5.Ridker, P.M., Rifai, N., Pfeffer, M.A., Inflammation, pravastatin and the risk of coronary events after myocardial infarction in patients with average cholesterol levels. Circulation, 98: , (1998). 6.Osborne, J.A., Cardiovascular effects of acute hypercholesterolemia in rabbits: Reversal with lovastatin treatment. J. Clin. Investigation, 83: , (1989). and atherosclerosis. Lancet Infect. Disease, 2: 11 7, (2002). 11.Brown, G., Regression of CAD as a result of intensive lipid lowering therapy in men with high levels of apolipoprotein-b. New Engl. J. Med., 223: 19-24, (1990). 12.Freigang, S., Horkko, S., Miller, E., Witztum, J.L., Palinski, W., Immunization of LDL receptor-deficient mice with homologous malondialdehyde-modified and native LDL reduces progression of atherosclerosis by mechanism other than induction of high titers of antibodies to oxidative neoepitopes. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 18: , (1998). 13.Francis, S.E., Camp, N.J., Dewberry, R.M., Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene polymorphism and coronary artery disease. Circulation, 99: , (1999). 14.Eisenberg, S., Metabolism of apolipoproteins and lipoproteins. Curr. Opin. Lipidology, 1: , (1990). 15.Maciejko, J.J., Holmes, D.R., Kottke, B.A., Zinzrneister, A.R., Dinh, D.M., Mao, S.J.J., Apolipoprotein-A as a marker of angiographically assessed CAD. New Engl. J. Med., 309: 385-9, (1983). 7.Pugalendi, K.V., Ramakrishna, S., Blood cholesterol and HDL-cholesterol in cigarette smokers. Ind. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 35: , (1991). 8.Burstein, M., Scholnick, H.P., Mortin, R., Cholesterol in high density lipoprotein: Using Mg 2+ /PTA. J. Lipid Res., 19: 583-6, (1970). 9.Ernst, E., Plasma fibrinogen - an independent cardiovascular risk factor. J. Intern. Med., 227: , (1996). 10.Leinonen, M., Saikku, P., Evidence for infectious agents in cardiovascular disease 16.Smith, J.D., Trogan, E., Ginsberg, M., Grigaux, C., Tian, J., Miyata, M., Decreased atherosclerosis in mice deficient in both macrophage colony-stimulating factor and apolipoprotein-e. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 92: , (1995). 17.Whitman, S.C., Ravisankar, P., Elam, H., Daugherty, A., Exogenous interferonenhances atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein- E. Am. J. Pathol., 157: , (2000). 18.Pohorecky, S., Interaction of alcohol and stress at the cardiovascular level. Alcohol, 7: , (1990).
12 Page42 IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 *Address for the Correspondence: Dr.R.S.Sreenivasan, Department of Chemistry, VELTECH MULTITECH Dr.Rangarajan Dr.Sakunthala Engineering College, Chennai ,INDIA. Contact Phone Number: E.mail: rssvasan1973@yahoo.co.in, rssvasan1973@rediffmail.com
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders
 Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
PLASMA LIPOPROTEINS AND LIPIDS DETERMINATION OF PLASMA CHOLESTEROL AND TRIGLICERIDE LEVEL
 PLASMA LIPOPROTEINS AND LIPIDS DETERMINATION OF PLASMA CHOLESTEROL AND TRIGLICERIDE LEVEL Lipids are characterized by low polarity and limited solubility in water. Their plasma concentration is about 500-600
PLASMA LIPOPROTEINS AND LIPIDS DETERMINATION OF PLASMA CHOLESTEROL AND TRIGLICERIDE LEVEL Lipids are characterized by low polarity and limited solubility in water. Their plasma concentration is about 500-600
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
Part 1 Risk Factors and Atherosclerosis. LO1. Define the Different Forms of CVD
 Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry
 Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
BCH 447. Triglyceride Determination in Serum
 BCH 447 Triglyceride Determination in Serum Introduction: Triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and are hydrolyzed by lipase to glycerol and free fatty acids. Triglyceride determinations when performed
BCH 447 Triglyceride Determination in Serum Introduction: Triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and are hydrolyzed by lipase to glycerol and free fatty acids. Triglyceride determinations when performed
Dyslipidemia Endothelial dysfunction Free radicals Immunologic
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis. Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk
 The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview)
 Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Apolipoprotein B (APOB or ApoB) are the primary apolipoproteins of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer "bad cholesterol"
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Apolipoprotein B (APOB or ApoB) are the primary apolipoproteins of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer "bad cholesterol"
Triglyceride determination
 Triglyceride determination Introduction: - Triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and are hydrolyzed to glycerol and free fatty acids (by lipase) - Triglyceride determinations when performed in conjunction
Triglyceride determination Introduction: - Triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and are hydrolyzed to glycerol and free fatty acids (by lipase) - Triglyceride determinations when performed in conjunction
determination of Triglyceride in Serum Amal Alamri
 determination of Triglyceride in Serum Amal Alamri Triglyceride are fatty acid esters of glycerol,and are the main lipids in the diet. They broken down(by lipase) in the small intestine to a mixture of
determination of Triglyceride in Serum Amal Alamri Triglyceride are fatty acid esters of glycerol,and are the main lipids in the diet. They broken down(by lipase) in the small intestine to a mixture of
Chapter (5) Etiology of Low HDL- Cholesterol
 Chapter (5) Etiology of Low HDL- Cholesterol The aim of this chapter is to summarize the different etiological factors mainly the role of life-style and different disease conditions contributing to the
Chapter (5) Etiology of Low HDL- Cholesterol The aim of this chapter is to summarize the different etiological factors mainly the role of life-style and different disease conditions contributing to the
Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by. Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam
 Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Hyperlipidemia. Prepared by : Muhannad Mohammed Supervisor professor : Dr. Ahmed Yahya Dallalbashi
 Hyperlipidemia Prepared by : Muhannad Mohammed Supervisor professor : Dr. Ahmed Yahya Dallalbashi Outline The story of lipids Definition of hyperlipidemia Classification of hyperlipidemia Causes of hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia Prepared by : Muhannad Mohammed Supervisor professor : Dr. Ahmed Yahya Dallalbashi Outline The story of lipids Definition of hyperlipidemia Classification of hyperlipidemia Causes of hyperlipidemia
Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL
 Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL Sung-Joon Lee, PhD Division of Food Science Institute of Biomedical Science and Safety Korea University Composition of Lipoproteins:
Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL Sung-Joon Lee, PhD Division of Food Science Institute of Biomedical Science and Safety Korea University Composition of Lipoproteins:
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD
 Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 05 Page May 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i5.193 Lipid Profile as Early Predictor of Complication
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i5.193 Lipid Profile as Early Predictor of Complication
Lipids Testing
 Previously Listed as Edit 12 190.23 - Lipids Testing Lipoproteins are a class of heterogeneous particles of varying sizes and densities containing lipid and protein. These lipoproteins include cholesterol
Previously Listed as Edit 12 190.23 - Lipids Testing Lipoproteins are a class of heterogeneous particles of varying sizes and densities containing lipid and protein. These lipoproteins include cholesterol
Hypertriglyceridemia, Inflammation, & Pregnancy
 Hypertriglyceridemia, Inflammation, & Pregnancy Richard L. Nemiroff, MD, FACOG, NLA Professor, Clinical Gynecology Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA Disclosure of
Hypertriglyceridemia, Inflammation, & Pregnancy Richard L. Nemiroff, MD, FACOG, NLA Professor, Clinical Gynecology Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA Disclosure of
Human LDL ELISA Kit. Innovative Research, Inc.
 Human LDL ELISA Kit Catalog No: IRKTAH2582 Lot No: SAMPLE INTRODUCTION Human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transports cholesterol from the liver to tissues where it is incorporated into cell membranes.
Human LDL ELISA Kit Catalog No: IRKTAH2582 Lot No: SAMPLE INTRODUCTION Human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transports cholesterol from the liver to tissues where it is incorporated into cell membranes.
Lipids digestion and absorption, Biochemistry II
 Lipids digestion and absorption, blood plasma lipids, lipoproteins Biochemistry II Lecture 1 2008 (J.S.) Triacylglycerols (as well as free fatty acids and both free and esterified cholesterol) are very
Lipids digestion and absorption, blood plasma lipids, lipoproteins Biochemistry II Lecture 1 2008 (J.S.) Triacylglycerols (as well as free fatty acids and both free and esterified cholesterol) are very
Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia
 Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Lipoproteins Metabolism
 Lipoproteins Metabolism LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this Lecture, the student should be able to describe: What are Lipoproteins? Describe Lipoprotein Particles. Composition of Lipoproteins. The chemical
Lipoproteins Metabolism LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this Lecture, the student should be able to describe: What are Lipoproteins? Describe Lipoprotein Particles. Composition of Lipoproteins. The chemical
Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system
 1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
 Acetyl CoA HMG CoA Mevalonate (C6) Dimethylallyl Pyrophosphate isopentenyl Pyrophosphate (C5) Geranyl Pyrophosphate (C10) FarnesylPyrophosphate (C15) Squalene (C30) Lanosterol (C30) 7 Dehydrocholesterol
Acetyl CoA HMG CoA Mevalonate (C6) Dimethylallyl Pyrophosphate isopentenyl Pyrophosphate (C5) Geranyl Pyrophosphate (C10) FarnesylPyrophosphate (C15) Squalene (C30) Lanosterol (C30) 7 Dehydrocholesterol
Tracking a Killer Molecule
 Tracking a Killer Molecule Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA www.mercodia.com Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA products Product Catalog No Kit size Oxidized LDL ELISA 10-1143-01 96 wells Oxidized LDL competitive
Tracking a Killer Molecule Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA www.mercodia.com Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA products Product Catalog No Kit size Oxidized LDL ELISA 10-1143-01 96 wells Oxidized LDL competitive
Hypertriglyceridemia. Ara Metjian, M.D. Resident s Report 20 December 2002
 Hypertriglyceridemia Ara Metjian, M.D. Resident s Report 20 December 2002 Review of Lipids Chylomicrons (CM): Dietary lipids absorbed through the GI tract are assembled intracellularly into CM. Very Low
Hypertriglyceridemia Ara Metjian, M.D. Resident s Report 20 December 2002 Review of Lipids Chylomicrons (CM): Dietary lipids absorbed through the GI tract are assembled intracellularly into CM. Very Low
KEY COMPONENTS. Metabolic Risk Cardiovascular Risk Vascular Inflammation Markers
 CardioMetabolic Risk Poor blood sugar regulation and unhealthy triglyceride and lipoprotein levels often present long before the diagnosis of type 2 Diabetes. SpectraCell s CardioMetabolic and Pre-Diabetes
CardioMetabolic Risk Poor blood sugar regulation and unhealthy triglyceride and lipoprotein levels often present long before the diagnosis of type 2 Diabetes. SpectraCell s CardioMetabolic and Pre-Diabetes
Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins
 Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins - Cholesterol: It is a sterol which is found in all eukaryotic cells and contains an oxygen (as a hydroxyl group OH) on Carbon number
Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins - Cholesterol: It is a sterol which is found in all eukaryotic cells and contains an oxygen (as a hydroxyl group OH) on Carbon number
Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui
 Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Lipoproteins a Lipids are insoluble in plasma. In order to be transported they are combined with specific proteins to form lipoproteins: Clusters of proteins and lipids.
Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Lipoproteins a Lipids are insoluble in plasma. In order to be transported they are combined with specific proteins to form lipoproteins: Clusters of proteins and lipids.
Cholesterol, Heart Attack and Stroke. Dr Tai E Shyong Consultant Department of Endocrinology Singapore General Hospital
 Cholesterol, Heart Attack and Stroke Dr Tai E Shyong Consultant Department of Endocrinology Singapore General Hospital Outline Why are we interested in cholesterol What is a heart attack and how does it
Cholesterol, Heart Attack and Stroke Dr Tai E Shyong Consultant Department of Endocrinology Singapore General Hospital Outline Why are we interested in cholesterol What is a heart attack and how does it
High density lipoprotein metabolism
 High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر. Zaid. Th. Jaber
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein
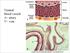 Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness. Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
ATP III (Adult Treatment Panel III) CLASSIFICATION C IN ADULTS
 LABORATORY AND RISK FACTORS OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS S R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty RISK FACTORS FOR CHD Clinical Risk Factors Laboratory Risk Factors MAJOR CLINICAL RISK
LABORATORY AND RISK FACTORS OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS S R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty RISK FACTORS FOR CHD Clinical Risk Factors Laboratory Risk Factors MAJOR CLINICAL RISK
Nutrition & Wellness for Life 2012 Chapter 6: Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Effect of mixed diet on lipid fractions levels in Coronary Heart diseases in adults of western Maharashtra region of India.
 Effect of mixed diet on lipid fractions levels in Coronary Heart diseases in adults of western Maharashtra region of India. nervous system frequency provokes transient cerebral Dr.Javed Bakas Mulla, Dept.
Effect of mixed diet on lipid fractions levels in Coronary Heart diseases in adults of western Maharashtra region of India. nervous system frequency provokes transient cerebral Dr.Javed Bakas Mulla, Dept.
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease
 Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema
 The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema Dept Cardiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden,
The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema Dept Cardiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden,
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
ESTIMATION OF LECITHIN CHOLESTROL ACYL TRANSFERASE ACTIVITY AND HIGH DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN CHOLESTROL IN TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
 ESTIMATION OF LECITHIN CHOLESTROL ACYL TRANSFERASE ACTIVITY AND HIGH DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN CHOLESTROL IN TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS *Tahmeen Jameel 1 and Syed Mahmood Ahmed 2 1 Department of Biochemistry,
ESTIMATION OF LECITHIN CHOLESTROL ACYL TRANSFERASE ACTIVITY AND HIGH DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN CHOLESTROL IN TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS *Tahmeen Jameel 1 and Syed Mahmood Ahmed 2 1 Department of Biochemistry,
Lipids Testing
 190.23 - Lipids Testing Lipoproteins are a class of heterogeneous particles of varying sizes and densities containing lipid and protein. These lipoproteins include cholesterol esters and free cholesterol,
190.23 - Lipids Testing Lipoproteins are a class of heterogeneous particles of varying sizes and densities containing lipid and protein. These lipoproteins include cholesterol esters and free cholesterol,
Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (MDA-LDL Quantitation), General
 Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (MDA-LDL Quantitation), General For the detection and quantitation of human OxLDL in plasma, serum or other biological fluid samples Cat. No. KT-959 For Research Use Only.
Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (MDA-LDL Quantitation), General For the detection and quantitation of human OxLDL in plasma, serum or other biological fluid samples Cat. No. KT-959 For Research Use Only.
Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD INTRODUCTION
 2 Hyperlipidemia Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION RISK CATEGORIES AND TARGET LDL-CHOLESTEROL TREATMENT OF LDL-CHOLESTEROL SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS OLDER AND YOUNGER ADULTS ADDITIONAL
2 Hyperlipidemia Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION RISK CATEGORIES AND TARGET LDL-CHOLESTEROL TREATMENT OF LDL-CHOLESTEROL SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS OLDER AND YOUNGER ADULTS ADDITIONAL
Estimation of glucose in blood serum
 Estimation of glucose in blood serum Enzymatic estimation of glucose uses a reagent containing two enzymes and a chromogen. Glucose oxidase catalyses the oxidation of glucose to gluconolactone with the
Estimation of glucose in blood serum Enzymatic estimation of glucose uses a reagent containing two enzymes and a chromogen. Glucose oxidase catalyses the oxidation of glucose to gluconolactone with the
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
Chapter 18. Diet and Health
 Chapter 18 Diet and Health Risk Factors and Chronic Diseases Interrelationships among Chronic Diseases Chronic Disease Heart Disease and Stroke Hypertension Cancer Diabetes The Formation of Plaques in
Chapter 18 Diet and Health Risk Factors and Chronic Diseases Interrelationships among Chronic Diseases Chronic Disease Heart Disease and Stroke Hypertension Cancer Diabetes The Formation of Plaques in
1. Most of your blood cholesterol is produced by: a. your kidneys b. your liver c. your pancreas d. food consumption (Your liver)
 I. TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE OF CHOLESTEROL Choose the correct answer. 1. Most of your blood cholesterol is produced by: a. your kidneys b. your liver c. your pancreas d. food consumption (Your liver) 2. Only
I. TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE OF CHOLESTEROL Choose the correct answer. 1. Most of your blood cholesterol is produced by: a. your kidneys b. your liver c. your pancreas d. food consumption (Your liver) 2. Only
Invited Review. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Lipoprotein Particle Profile
 Lipoprotein Particle Profile 50% of people at risk for HEART DISEASE are not identified by routine testing. Why is LPP Testing The Most Comprehensive Risk Assessment? u Provides much more accurate cardiovascular
Lipoprotein Particle Profile 50% of people at risk for HEART DISEASE are not identified by routine testing. Why is LPP Testing The Most Comprehensive Risk Assessment? u Provides much more accurate cardiovascular
Inspired Functional Ingredients to Innovate and Differentiate Your Brand. Products by Ecovatec Solutions Inc.
 Inspired Functional Ingredients to Innovate and Differentiate Your Brand Products by Ecovatec Solutions Inc. High Density Lipopeptides (HDL p ) High Density Lipopeptides (HDL p ) High density lipoproteins
Inspired Functional Ingredients to Innovate and Differentiate Your Brand Products by Ecovatec Solutions Inc. High Density Lipopeptides (HDL p ) High Density Lipopeptides (HDL p ) High density lipoproteins
13/09/2012. Dietary fatty acids. Triglyceride. Phospholipids:
 CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES (CVD) and NUTRITION Major cause of morbidity & mortality in Canada & other developed countries e.g., majority of approved health claims on food labels relate to lowering CVD Relation
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES (CVD) and NUTRITION Major cause of morbidity & mortality in Canada & other developed countries e.g., majority of approved health claims on food labels relate to lowering CVD Relation
Disclosures. Background 1 What is Known MENOPAUSE, ESTROGENS, AND LIPOPROTEIN PARTICLES. Background 2 What is Not Known 10/2/2017
 Disclosures MENOPAUSE, ESTROGENS, AND LIPOPROTEIN PARTICLES Grants: NIH, Quest Diagnostics Consultant: Quest Diagnostics Merck Global Atherosclerosis Advisory Board Ronald M. Krauss, Children s Hospital
Disclosures MENOPAUSE, ESTROGENS, AND LIPOPROTEIN PARTICLES Grants: NIH, Quest Diagnostics Consultant: Quest Diagnostics Merck Global Atherosclerosis Advisory Board Ronald M. Krauss, Children s Hospital
The apolipoprotein story
 Atherosclerosis Supplements 7 (2006) 23 27 The apolipoprotein story Frank M. Sacks a,b, a Department of Nutrition, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, MA, USA b Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical
Atherosclerosis Supplements 7 (2006) 23 27 The apolipoprotein story Frank M. Sacks a,b, a Department of Nutrition, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, MA, USA b Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical
THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF LIPID DISORDERS
 THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF LIPID DISORDERS Hormonal regulation INSULIN lipid synthesis, lipolysis CORTISOL lipolysis GLUCAGON lipolysis GROWTH HORMONE lipolysis CATECHOLAMINES lipolysis LEPTIN catabolism
THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF LIPID DISORDERS Hormonal regulation INSULIN lipid synthesis, lipolysis CORTISOL lipolysis GLUCAGON lipolysis GROWTH HORMONE lipolysis CATECHOLAMINES lipolysis LEPTIN catabolism
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF THE MINOR RESEARCH PROJECT Submitted to UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION
 1 A STUDY ON THE EFFECT OF DIET & LIFE STYLE ON THE INCIDENCE OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE IN MODERATELY DRINKING EX MILITARY MEN IN PATHANAMTHITTA DISTRICT. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF THE MINOR RESEARCH PROJECT
1 A STUDY ON THE EFFECT OF DIET & LIFE STYLE ON THE INCIDENCE OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE IN MODERATELY DRINKING EX MILITARY MEN IN PATHANAMTHITTA DISTRICT. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF THE MINOR RESEARCH PROJECT
Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY
 MCC-006 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00269 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will be multiple
MCC-006 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00269 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will be multiple
Free Glycerol Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 Product Manual Free Glycerol Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number STA-398 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Glycerol is the backbone of Triglycerides
Product Manual Free Glycerol Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number STA-398 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Glycerol is the backbone of Triglycerides
Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions
 Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions What Are Lipids? Lipids Diverse group of molecules that are insoluble in water Fats The lipid content of diets and foods 1 Lipids in Body Cells and Tissues Types of
Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions What Are Lipids? Lipids Diverse group of molecules that are insoluble in water Fats The lipid content of diets and foods 1 Lipids in Body Cells and Tissues Types of
CHAPTER FORTY FIVE ENDOGENOUS LIPID TRANSPORT PATHWAY: VLDL AND IDL
 CHAPTER FORTY FIVE ENDOGENOUS LIPID TRANSPORT PATHWAY: VLDL AND IDL You will notice that the endogenous pathway is very similar to the exogenous pathway What is the average daily amount of triacylglycerol
CHAPTER FORTY FIVE ENDOGENOUS LIPID TRANSPORT PATHWAY: VLDL AND IDL You will notice that the endogenous pathway is very similar to the exogenous pathway What is the average daily amount of triacylglycerol
Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia
 Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Study of relationship of serum Lipid Profile and etiological factors of Ischaemic Heart Diseases
 Original article: Study of relationship of serum Lipid Profile and etiological factors of Ischaemic Heart Diseases Dr Abhijit Nikam, Dr Sonu Yadav, Dr Vivek Chiddarwar, Dr A L Kakrani Dept of Medicine,
Original article: Study of relationship of serum Lipid Profile and etiological factors of Ischaemic Heart Diseases Dr Abhijit Nikam, Dr Sonu Yadav, Dr Vivek Chiddarwar, Dr A L Kakrani Dept of Medicine,
THE EFFECT OF VITAMIN-C THERAPY ON HYPERGLYCEMIA, HYPERLIPIDEMIA AND NON HIGH DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN LEVEL IN TYPE 2 DIABETES
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2013 Varikasuvu Seshadri Reddy et al., 2013 Review Article ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 2, No. 1, January 2013 2013 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved THE EFFECT OF VITAMIN-C
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2013 Varikasuvu Seshadri Reddy et al., 2013 Review Article ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 2, No. 1, January 2013 2013 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved THE EFFECT OF VITAMIN-C
Learning Objectives. Cholesterol and Lipids in Kids: It s a Matter of the Heart. Is Atherosclerosis a Pediatric Disease?
 Scott J. Soifer, MD Professor and Vice Chair Department of Pediatrics University of California, San Francisco UCSF Benioff Children s Hospital Cholesterol and Lipids in Kids: It s a Matter of the Heart
Scott J. Soifer, MD Professor and Vice Chair Department of Pediatrics University of California, San Francisco UCSF Benioff Children s Hospital Cholesterol and Lipids in Kids: It s a Matter of the Heart
How would you manage Ms. Gold
 How would you manage Ms. Gold 32 yo Asian woman with dyslipidemia Current medications: Simvastatin 20mg QD Most recent lipid profile: TC = 246, TG = 100, LDL = 176, HDL = 50 What about Mr. Williams? 56
How would you manage Ms. Gold 32 yo Asian woman with dyslipidemia Current medications: Simvastatin 20mg QD Most recent lipid profile: TC = 246, TG = 100, LDL = 176, HDL = 50 What about Mr. Williams? 56
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease. Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
 Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Topic 11. Coronary Artery Disease
 Topic 11 Coronary Artery Disease Lipid metabolism http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/health/7372495.stm Sterol Metabolism and Coronary Artery Disease Big Picture: Exogenous Cholesterol and Fat Metabolism Fats-Triglycerides
Topic 11 Coronary Artery Disease Lipid metabolism http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/health/7372495.stm Sterol Metabolism and Coronary Artery Disease Big Picture: Exogenous Cholesterol and Fat Metabolism Fats-Triglycerides
Dr G R Letchuman. Clogged by Cholesterol
 Dr G R Letchuman Clogged by Cholesterol Main message Cholesterol management is all about reducing risk of CV events vs the side effects, hassle and cost of drugs News that it is no longer important to
Dr G R Letchuman Clogged by Cholesterol Main message Cholesterol management is all about reducing risk of CV events vs the side effects, hassle and cost of drugs News that it is no longer important to
Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) ELISA Kit
 Product Manual Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) ELISA Kit Catalog Number STA-616 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cholesterol is a lipid sterol
Product Manual Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) ELISA Kit Catalog Number STA-616 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cholesterol is a lipid sterol
The Role of Fats. Fat provides flavour and texture to foods. Fat contributes to making us feel satiated because
 The Role of Fats Fat provides flavour and texture to foods. Fat contributes to making us feel satiated because Fats are more energy dense than carbohydrates or protein Fats take longer to digest Emulsion
The Role of Fats Fat provides flavour and texture to foods. Fat contributes to making us feel satiated because Fats are more energy dense than carbohydrates or protein Fats take longer to digest Emulsion
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012
 LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
DYSLIPIDEMIA PHARMACOLOGY. University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D
 DYSLIPIDEMIA PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Know normal cholesterol levels Understand what the role
DYSLIPIDEMIA PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Know normal cholesterol levels Understand what the role
PPAR history of research
 PPAR Rubens, 1640 PPAR history of research number of publications 3000 2000 1000 0 till now: : 16 296 publications 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 year liver, brown adipocytes, kidney, heart, skeletal muscles,
PPAR Rubens, 1640 PPAR history of research number of publications 3000 2000 1000 0 till now: : 16 296 publications 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 year liver, brown adipocytes, kidney, heart, skeletal muscles,
Fats and Other Lipids
 Fats and Other Lipids Chapter 6 Chapter 6: Fats and other Lipids 1 6.1 Understanding Lipids Lipids include: 1. Fatty acids 2. Triglycerides 3. Phospholipids 4. Cholesterol Oil and Water Don t Mix Because
Fats and Other Lipids Chapter 6 Chapter 6: Fats and other Lipids 1 6.1 Understanding Lipids Lipids include: 1. Fatty acids 2. Triglycerides 3. Phospholipids 4. Cholesterol Oil and Water Don t Mix Because
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
Inflammation and and Heart Heart Disease in Women Inflammation and Heart Disease
 Inflammation and Heart Disease in Women Inflammation and Heart Disease What is the link between een inflammation and atherosclerotic disease? What is the role of biomarkers in predicting cardiovascular
Inflammation and Heart Disease in Women Inflammation and Heart Disease What is the link between een inflammation and atherosclerotic disease? What is the role of biomarkers in predicting cardiovascular
Lipid Concentration And The Extent Of Their Peroxidation In Nigerian Hypertensives
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 8 Number 1 Lipid Concentration And The Extent Of Their Peroxidation In Nigerian Hypertensives P Igbinaduwa, B Igbinaduwa, I Oforofuo Citation P Igbinaduwa,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 8 Number 1 Lipid Concentration And The Extent Of Their Peroxidation In Nigerian Hypertensives P Igbinaduwa, B Igbinaduwa, I Oforofuo Citation P Igbinaduwa,
Topic 1: Lifestyle, Health and Risk
 alevelbiology.co.uk Topic 1: Lifestyle, Health and Risk SPECIFICATION Many animals have a heart and circulation (mass transport to overcome limitations of diffusion in meeting the requirements of organisms).
alevelbiology.co.uk Topic 1: Lifestyle, Health and Risk SPECIFICATION Many animals have a heart and circulation (mass transport to overcome limitations of diffusion in meeting the requirements of organisms).
Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona,
 Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona, Jamaica At the end of this presentation the participant
Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona, Jamaica At the end of this presentation the participant
Plasma fibrinogen level, BMI and lipid profile in type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypertension
 World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
The 10 th International & 15 th National Congress on Quality Improvement in Clinical Laboratories
 The 10 th International & 15 th National Congress on Quality Improvement in Clinical Laboratories Cardiac biomarkers in atherosclerosis Najma Asadi MD-APCP Ross and Colleagues in 1973: Response to Injury
The 10 th International & 15 th National Congress on Quality Improvement in Clinical Laboratories Cardiac biomarkers in atherosclerosis Najma Asadi MD-APCP Ross and Colleagues in 1973: Response to Injury
Observe the effects of atherosclerosis on the coronary artery lumen
 Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
ARE YOU AT RISK OF A HEART ATTACK OR STROKE? Understand How Controlling Your Cholesterol Reduces Your Risk
 ARE YOU AT RISK OF A HEART ATTACK OR STROKE? Understand How Controlling Your Cholesterol Reduces Your Risk CONSIDER YOUR HEART HEALTH: REDUCE YOUR CHOLESTEROL Uncontrolled or continuous high cholesterol
ARE YOU AT RISK OF A HEART ATTACK OR STROKE? Understand How Controlling Your Cholesterol Reduces Your Risk CONSIDER YOUR HEART HEALTH: REDUCE YOUR CHOLESTEROL Uncontrolled or continuous high cholesterol
Understanding Cholesterol and Triglycerides
 MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Understanding Cholesterol and Triglycerides About This Kit Along with cigarette smoking, high blood pressure, physical
MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Understanding Cholesterol and Triglycerides About This Kit Along with cigarette smoking, high blood pressure, physical
LDL (Human) ELISA Kit
 LDL (Human) ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA3864 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use This immunoassay kit allows for the specific measurement of human low density lipoprotein, LDL concentrations in cell culture supernates,
LDL (Human) ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA3864 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use This immunoassay kit allows for the specific measurement of human low density lipoprotein, LDL concentrations in cell culture supernates,
Cholesterol and its transport. Alice Skoumalová
 Cholesterol and its transport Alice Skoumalová 27 carbons Cholesterol - structure Cholesterol importance A stabilizing component of cell membranes A precursor of bile salts A precursor of steroid hormones
Cholesterol and its transport Alice Skoumalová 27 carbons Cholesterol - structure Cholesterol importance A stabilizing component of cell membranes A precursor of bile salts A precursor of steroid hormones
Antihyperlipidemic Drugs
 Antihyperlipidemic Drugs Lipid disorders: Disorders of lipid metabolism are manifest by elevation of the plasma concentrations of the various lipid and lipoprotein fractions (total and LDL cholesterol,
Antihyperlipidemic Drugs Lipid disorders: Disorders of lipid metabolism are manifest by elevation of the plasma concentrations of the various lipid and lipoprotein fractions (total and LDL cholesterol,
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients
 2012 international Conference on Diabetes and metabolism (ICDM) Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients Nan Hee Kim, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University
2012 international Conference on Diabetes and metabolism (ICDM) Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients Nan Hee Kim, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University
Investigations on the mechanism of hypercholesterolemia observed in copper deficiency in rats
 J. Biosci., Vol. 12, Number 2, June 1987, pp. 137 142. Printed in India. Investigations on the mechanism of hypercholesterolemia observed in copper deficiency in rats P. VALSALA and P. A. KURUP Department
J. Biosci., Vol. 12, Number 2, June 1987, pp. 137 142. Printed in India. Investigations on the mechanism of hypercholesterolemia observed in copper deficiency in rats P. VALSALA and P. A. KURUP Department
Acute coronary syndrome. Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA
 Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Study of serum Lipid Profile patterns of Indian population in young Ischaemic Heart Disease
 Original article: Study of serum Lipid Profile patterns of Indian population in young Ischaemic Heart Disease Dr Sonu Yadav, Dr Abhijit Nikam, Dr Vivek Chiddarwar, Dr A L Kakrani Department of Medicine,
Original article: Study of serum Lipid Profile patterns of Indian population in young Ischaemic Heart Disease Dr Sonu Yadav, Dr Abhijit Nikam, Dr Vivek Chiddarwar, Dr A L Kakrani Department of Medicine,
OxiSelect Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (OxPL-LDL Quantitation)
 Product Manual OxiSelect Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (OxPL-LDL Quantitation) Catalog Number STA-358 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Lipoproteins are submicroscopic
Product Manual OxiSelect Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (OxPL-LDL Quantitation) Catalog Number STA-358 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Lipoproteins are submicroscopic
Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both
 Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both Lluís Masana Vascular Medicine and Metabolism Unit. Sant Joan University Hospital. IISPV. CIBERDEM Rovira i Virgili
Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both Lluís Masana Vascular Medicine and Metabolism Unit. Sant Joan University Hospital. IISPV. CIBERDEM Rovira i Virgili
