ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر. Zaid. Th. Jaber
|
|
|
- Kristian McDonald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber
2 Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis. 4- mention the Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis. 5-microscopic and macroscopic pics of atherosclerosis. 6- the outcome of atherosclerosis.
3 normal The 3 concentric layers-intima, media and adventitia-are most clearly defined in the larger vessels particularly arteries. Arteries consist of: 1. Intima. 2. Internal elastic lamina. 3. Media. 4. External elastic lamina. 5. Adventitia. The basic constituents of the wall are: 1. Endothelial cells. 2. Smooth muscle cells. 3. Extracellular matrix (ECM), including elastin, collagen and glycosaminoglycans.
4
5
6
7
8
9 Normal coronary artery
10 Definition of atherosclerosis is a slowly progressive inflammatory disorder of the arterial wall. Hardening of arteries. In which the walls of arteries thicken; stiffen; And loose their elastisty.
11 Atherosclerosis is a dominant pattern of arteriosclerosis. It primarily affects elastic and large to medium sized muscular arteries : 1-abdominal oarta 2- coronary artery 3- popliteal artery 4- carotid artery 5- circle of willis.
12 Risk factors
13 Pathophysiology
14
15 Theories: 1- Endothelial injury 2- Thrombogenic 3- C.pneumoniae
16 The pathogenesis of Ath. remains unexplained, but endothelial damage (and chlamydia infection?,) could be the primary event and the reaction to it may eventually lead to plaque formation (response to injury hypothesis;!). Plaques usually develop at sites of high mechanical stress (vessel bifurcation); in this way also hypertension becomes a risk factor. Among the reactions are an increased lipid uptake in the vessel wall as well as adhesion of monocytes and thrombocytes helped by HoCys. The monocytes penetrate into the intima and are transformed into macrophages.these liberate reactive O2 radicals, especially the superoxide anion
17 O2 (also helped by HoCys), which have a general damaging effect on endothelial cells and inactivate endothelium-formed NO on its way to the endothelium and the vascular musculature: NO + O2! ONOO. This results in the loss of NO action, namely inhibition of platelet and monocyte adhesion to the endothelium as well as antiproliferative and vasodilating effects on the vascular musculature. The latter favor spasms Even in the early stages of Ath., O2 radicalsmodify by oxidation of those LDLs that have entered the endothelium. Oxidized LDLs damage the endothelium and there induce the expression of adhesion molecules which allow vessel musculature to proliferate.
18 Oxidation also results in altered binding of LDLs. They can no longer be recognized by ApoB 100 receptors (!p. 246ff.), but rather by so-called scavenger receptors that are contained in large amounts within the macrophages. Consequently, these now phagocytize large amounts of LDLs and are transformed into sedentary foam cells (!C9). Lipoprotein(a) can be oxidized and phagocytized in a similar fashion. Simultaneously, chemotactic factors of monocytes and thrombocytes trigger the migration of smooth muscle cells from the media into the intima (!C6). Here they are stimulated to proliferate by PDGF and other growth-promoting factors (from macrophages, thrombocytes, damaged endothelium, and the muscle cells themselves). They, too, are transformed into foam cells by uptake of oxidized LDLs (!C10). They form an extracellular matrix (collagen, elastin, proteoglycans) that also contributes to atheroma formation.
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35 Atherosclerotic plaque
36 Atherosclerosis with severe narrowing of the lumen & area of calcification at the lower right
37 Atheromatous plaque with recent thrombosis
38 Atheroma at high magnification : numerous foam cells & cholesterol clefts
39
40
41 The consequences of plaque deposition are narrowing of the lumen that can lead to ischemia. Coronary heart disease as well as chronic occlusive arterial disease of the limbs with painful ischemia on exercise (intermittent claudication) are examples of this. Other consequences of plaque formation are stiffening of the vessel wall (calcification), thrombus formation that obstructs the residual lumen and can cause peripheral emboli (e.g., cerebral infarction, stroke) as well as bleeding into the plaques (additional narrowing by the haematoma) and the vessel wall. Thus weakened, the wall may be stretched (aneurysm; see below) and even rupture, with dangerous bleeding into the surrounding tissues, for example, from the aorta (see below) or cerebral vessels (massive intracerebral bleeding, stroke.
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51 Reference 1-Robbins and Cotran PATHOLOGIC BASIS OF DISEASE. 2-Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology 2000 Thieme 3- Davidson_ Principles_and_Practice_of_Medicine_21 st 4- diagnosis.com 5- Nature. Macmillan Magazines, London/UK
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Blood Vessels. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease
 Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
Dyslipidemia Endothelial dysfunction Free radicals Immunologic
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
Invited Review. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
Observe the effects of atherosclerosis on the coronary artery lumen
 Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
Part 1 Risk Factors and Atherosclerosis. LO1. Define the Different Forms of CVD
 Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
THE BLOOD VESSELS. Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department.
 THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein
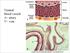 Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
INFLAMM-O-WARS ACTIVITY 4B. Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis. Student Activity Page 4B. Introduction. Background A LOOK AT ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Student Activity Page 4B Introduction Chances are that every one in your class knows somebody who has had a heart attack, but how many really understand what
Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Student Activity Page 4B Introduction Chances are that every one in your class knows somebody who has had a heart attack, but how many really understand what
HEART HEALTH WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Fatty deposits can narrow and harden the artery
 WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS FIGURE 1 Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory process where cholesterol is deposited in the wall of arteries and
WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS FIGURE 1 Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory process where cholesterol is deposited in the wall of arteries and
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial
 An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
Atherosclerosis. Be able to discuss pathology and complications of ischemic heart diseases with special emphasis on myocardial infarction.
 Atherosclerosis Objectives: () Understand the pathogenesis and clinical consequences of atherosclerosis. () Be able to discuss pathology and complications of ischemic heart diseases with special emphasis
Atherosclerosis Objectives: () Understand the pathogenesis and clinical consequences of atherosclerosis. () Be able to discuss pathology and complications of ischemic heart diseases with special emphasis
Cardiac Ischemia (is-kē-mē-uh)
 Chapter 21 Cardiac Ischemia (is-kē-mē-uh) By: Alejandra & Lindsay I. Cardiac Ischemia =the most common cause of death in Western Culture ~35% of deaths. -Suddenly from acute coronary occlusion or fibrillation
Chapter 21 Cardiac Ischemia (is-kē-mē-uh) By: Alejandra & Lindsay I. Cardiac Ischemia =the most common cause of death in Western Culture ~35% of deaths. -Suddenly from acute coronary occlusion or fibrillation
Complications of Diabetes mellitus. Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015
 Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease. Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
 Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System
 Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System Piryaei May 2011 Circulatory System Heart Blood Vessels Macrovasculature (More than 0.1mm) Elastic Artery Muscular (Distributing) Artery Large Arteriol Small Vein Muscular
Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System Piryaei May 2011 Circulatory System Heart Blood Vessels Macrovasculature (More than 0.1mm) Elastic Artery Muscular (Distributing) Artery Large Arteriol Small Vein Muscular
Fourth Practical Pathology. Circulatory disturbances
 Fourth Practical Pathology Circulatory disturbances 12.12.2018 1 Organ: Lung (40X, low power) 1) The blood capillaries within the alveolar septa are engorged with blood 2) Pinkish proteinaceous fluid,
Fourth Practical Pathology Circulatory disturbances 12.12.2018 1 Organ: Lung (40X, low power) 1) The blood capillaries within the alveolar septa are engorged with blood 2) Pinkish proteinaceous fluid,
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the
 The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
Prevalence of Coronary Artery Disease: A Tertiary Care Hospital Based Autopsy Study
 Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism
 Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
Acute coronary syndrome. Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA
 Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
1 Functions of endothelial cells include all the following EXCEPT. 2 Response to vascular injury is characterised by
 airns ase Hospital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 Functions of endothelial cells include all the following XPT Formation of von-willebrand factor Formation of collagen and proteoglycans Formation of
airns ase Hospital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 Functions of endothelial cells include all the following XPT Formation of von-willebrand factor Formation of collagen and proteoglycans Formation of
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD
 Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Approach to the Patient with (suspected) Arterial Insufficiency Related Ulceration
 Approach to the Patient with (suspected) Arterial Insufficiency Related Ulceration Elisa C. Taffe, MD, CWSP Vascular Medicine Medical Director Allegheny General Advanced Wound Healing and Lymphedema Center
Approach to the Patient with (suspected) Arterial Insufficiency Related Ulceration Elisa C. Taffe, MD, CWSP Vascular Medicine Medical Director Allegheny General Advanced Wound Healing and Lymphedema Center
According to the etiology, edema may be:
 What is edema? Edema : It refers to the accumulation of excess liquid in the interstitial (extracellular) spaces of a tissue or in pre-existing cavities. It may affect any organ, but most often it appears
What is edema? Edema : It refers to the accumulation of excess liquid in the interstitial (extracellular) spaces of a tissue or in pre-existing cavities. It may affect any organ, but most often it appears
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock. Richard A. McPherson, M.D.
 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
Vascular biology of atherosclerosis
 Chapter 1 Vascular biology of atherosclerosis Peter F. Bodary, Daniel T. Eitzman Introduction The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis has been the subject of thousands of articles published over the past several
Chapter 1 Vascular biology of atherosclerosis Peter F. Bodary, Daniel T. Eitzman Introduction The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis has been the subject of thousands of articles published over the past several
Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases
 Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases Trends in egg consumption in U.S. and the reason A. Egg Consumption: - 403 in 1945-234 in 1993 (176 Table eggs, 58 Processed eggs) - 256 in
Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases Trends in egg consumption in U.S. and the reason A. Egg Consumption: - 403 in 1945-234 in 1993 (176 Table eggs, 58 Processed eggs) - 256 in
Atherothrombosis And Coronary Artery Disease
 Atherothrombosis And Coronary Artery Disease 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Atherothrombosis And Coronary Artery Disease Risk factors for coronary artery disease (CAD) were not formally established until the initial
Atherothrombosis And Coronary Artery Disease 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Atherothrombosis And Coronary Artery Disease Risk factors for coronary artery disease (CAD) were not formally established until the initial
KEY COMPONENTS. Metabolic Risk Cardiovascular Risk Vascular Inflammation Markers
 CardioMetabolic Risk Poor blood sugar regulation and unhealthy triglyceride and lipoprotein levels often present long before the diagnosis of type 2 Diabetes. SpectraCell s CardioMetabolic and Pre-Diabetes
CardioMetabolic Risk Poor blood sugar regulation and unhealthy triglyceride and lipoprotein levels often present long before the diagnosis of type 2 Diabetes. SpectraCell s CardioMetabolic and Pre-Diabetes
ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION. Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret
 ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret Outline Inflammation in CVDs the evidence Basic Science in Cardiovascular inflammation: The Main players Inflammation as
ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret Outline Inflammation in CVDs the evidence Basic Science in Cardiovascular inflammation: The Main players Inflammation as
THROMBOSIS. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan
 THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
Glutamate and Heart Disease
 Glutamate and Heart Disease By Linda Emmanuel Today, heart disease is the #1 killer of Americans, even more than cancer. There are two ways to get heart disease, but they both have the same common denominator
Glutamate and Heart Disease By Linda Emmanuel Today, heart disease is the #1 killer of Americans, even more than cancer. There are two ways to get heart disease, but they both have the same common denominator
Atherosclerosis, inflammation and leukotrienes
 Review. Ingvill Ellertsen, Marcelo H. Petri, Magnus Bäck Atherosclerosis, inflammation and leukotrienes Michael Quarterly 2011;8:514 22. Atherosclerosis, which is a chronic inflammatory disease that leads
Review. Ingvill Ellertsen, Marcelo H. Petri, Magnus Bäck Atherosclerosis, inflammation and leukotrienes Michael Quarterly 2011;8:514 22. Atherosclerosis, which is a chronic inflammatory disease that leads
Blood Vessel Disorders
 Blood Vessel Disorders Objectives: Hyperlipidemia Arterioschlerosis Disorders associated with arteries Disorders associated with veins Hypertension and hypotension Part 1: Diseases Associated with Arterial
Blood Vessel Disorders Objectives: Hyperlipidemia Arterioschlerosis Disorders associated with arteries Disorders associated with veins Hypertension and hypotension Part 1: Diseases Associated with Arterial
Arterial Diseases & Grafts What Can Go Wrong and How to Fix It
 Arterial Diseases & Grafts What Can Go Wrong and How to Fix It Lecture #9 Ref: Harloff, Jan, Are Biomaterials the Limiting Factor in the Progress of Arterial Prosthesis? Termpaper, BE 512, introduction
Arterial Diseases & Grafts What Can Go Wrong and How to Fix It Lecture #9 Ref: Harloff, Jan, Are Biomaterials the Limiting Factor in the Progress of Arterial Prosthesis? Termpaper, BE 512, introduction
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview)
 Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Ischemic heart disease
 Ischemic heart disease Introduction In > 90% of cases: the cause is: reduced coronary blood flow secondary to: obstructive atherosclerotic vascular disease so most of the time it is called: coronary artery
Ischemic heart disease Introduction In > 90% of cases: the cause is: reduced coronary blood flow secondary to: obstructive atherosclerotic vascular disease so most of the time it is called: coronary artery
Pathology of Cardiovascular Interventions. Body and Disease 2011
 Pathology of Cardiovascular Interventions Body and Disease 2011 Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis Intervention Goals: Acute Coronary Syndromes: Treat plaque rupture and thrombosis Significant Disease: Prevent
Pathology of Cardiovascular Interventions Body and Disease 2011 Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis Intervention Goals: Acute Coronary Syndromes: Treat plaque rupture and thrombosis Significant Disease: Prevent
Plaque Imaging: What It Can Tell Us. Kenneth Snyder, MD, PhD L Nelson Hopkins MD FACS Elad Levy MD MBA FAHA FACS Adnan Siddiqui MD PhD
 Plaque Imaging: What It Can Tell Us Kenneth Snyder, MD, PhD L Nelson Hopkins MD FACS Elad Levy MD MBA FAHA FACS Adnan Siddiqui MD PhD Buffalo Disclosure Information FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE: Research and consultant
Plaque Imaging: What It Can Tell Us Kenneth Snyder, MD, PhD L Nelson Hopkins MD FACS Elad Levy MD MBA FAHA FACS Adnan Siddiqui MD PhD Buffalo Disclosure Information FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE: Research and consultant
Vascular Biology Anatomy and Function of Blood Vessels in Health Fig. 1.1 Endothelial Function Three Layers of Arteries
 1 Vascular Biology Scott Kinlay, MBBS, PhD, FACC, FRACP Vascular Biology applies to processes affecting arteries, veins, and other blood vessels. This chapter will focus on the physiology and pathophysiology
1 Vascular Biology Scott Kinlay, MBBS, PhD, FACC, FRACP Vascular Biology applies to processes affecting arteries, veins, and other blood vessels. This chapter will focus on the physiology and pathophysiology
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
 Diseases of the cardiovascular system 心血管系统疾病 Zhengrong Mao PhD,Associate Prof. maozr@zju.edu.cn Pathology and pathophysiology Department Zhejiang University School of Medicine Diseases of the cardiovascular
Diseases of the cardiovascular system 心血管系统疾病 Zhengrong Mao PhD,Associate Prof. maozr@zju.edu.cn Pathology and pathophysiology Department Zhejiang University School of Medicine Diseases of the cardiovascular
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Blood Vessel Structure
 Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
PoS(FISBH2006)019. Imaging Vulnerable Plaque A radionuclide approach. H. William Strauss, M.D. 1
 A radionuclide approach H. William Strauss, M.D. 1 Section of Nuclear Medicine, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10021 United States E-mail: straussh@mskcc.org Frontiers in Imaging
A radionuclide approach H. William Strauss, M.D. 1 Section of Nuclear Medicine, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10021 United States E-mail: straussh@mskcc.org Frontiers in Imaging
Fibromuscular Dysplasia. Miranda Forrest Baker College
 Fibromuscular Dysplasia Miranda Forrest Baker College Overview Case Study Patient Information Exam Images Findings FMD Types Signs and Symptoms Treatment Case Study Patient Information Female 57 years
Fibromuscular Dysplasia Miranda Forrest Baker College Overview Case Study Patient Information Exam Images Findings FMD Types Signs and Symptoms Treatment Case Study Patient Information Female 57 years
Arteriosclerosis. I/AAAAAAAACes/jTiOFGWrWZI/s1600/angina+aterosklerosis.jpg
 Arteriosclerosis http://1.bp.blogspot.com/_smg3fxietuk/s96rjr9ewa I/AAAAAAAACes/jTiOFGWrWZI/s1600/angina+aterosklerosis.jpg Definition of Arteriosclerosis Arteriosclerosis is a general term for several
Arteriosclerosis http://1.bp.blogspot.com/_smg3fxietuk/s96rjr9ewa I/AAAAAAAACes/jTiOFGWrWZI/s1600/angina+aterosklerosis.jpg Definition of Arteriosclerosis Arteriosclerosis is a general term for several
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROMES
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROMES Brian R. Holroyd, MD, FACEP, FRCPC Professor and Director, Division of Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton,
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROMES Brian R. Holroyd, MD, FACEP, FRCPC Professor and Director, Division of Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton,
Introduction. Risk factors of PVD 5/8/2017
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
Misrepair mechanism in the development of atherosclerotic plaques
 Misrepair mechanism in the development of atherosclerotic plaques Jicun Wang-Michelitsch 1 *, Thomas M Michelitsch 2 1 Department of Medicine, Addenbrooke's Hospital, University of Cambridge, UK (Work
Misrepair mechanism in the development of atherosclerotic plaques Jicun Wang-Michelitsch 1 *, Thomas M Michelitsch 2 1 Department of Medicine, Addenbrooke's Hospital, University of Cambridge, UK (Work
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
 BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
Understanding Cholesterol
 Understanding Cholesterol Dr Mike Laker Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT This book is intended not as a substitute for personal
Understanding Cholesterol Dr Mike Laker Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT This book is intended not as a substitute for personal
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART. I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine
 HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine Acute myocardial infarction coagulative necrosis subendocardialy 2 hyperemic layer 3 normal myocard 4 epicard Acute myocardial
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine Acute myocardial infarction coagulative necrosis subendocardialy 2 hyperemic layer 3 normal myocard 4 epicard Acute myocardial
Functional vascular disorders
 Functional vascular disorders Raynaud s phenomenon Raynaud s phenomenon Refers to Intermittent,bilateral attacks of ischemia of the fingers or toes, and sometimes ears or nose. It clinically manifests
Functional vascular disorders Raynaud s phenomenon Raynaud s phenomenon Refers to Intermittent,bilateral attacks of ischemia of the fingers or toes, and sometimes ears or nose. It clinically manifests
Cardiovascular System and Health. Chapter 15
 Cardiovascular System and Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death in U.S. Claims 1 life every 43 seconds Often, the first sign is a fatal heart attack Death Rates #1 CVD #2 Cancer
Cardiovascular System and Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death in U.S. Claims 1 life every 43 seconds Often, the first sign is a fatal heart attack Death Rates #1 CVD #2 Cancer
Case Presentation VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Vasculitis
 Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Cardiovascular Pathology
 Cardiovascular Pathology Duration: 03 Weeks (15 days) Concepts Objectives Activity Time Department Comments 3/SBM-3/01 Introduction to ischaemia, infarction, thrombosis stenosis / occlusion, embolism Atherosclerosis
Cardiovascular Pathology Duration: 03 Weeks (15 days) Concepts Objectives Activity Time Department Comments 3/SBM-3/01 Introduction to ischaemia, infarction, thrombosis stenosis / occlusion, embolism Atherosclerosis
INTRODUCTORY TEXT BOX
 INTRODUCTORY TEXT BOX Diagnostic Partners provides a range of onsite, in-office cardiac and vascular diagnostic testing services. From Resting Echocardiograms to Abdominal Aorta scans, each study is performed
INTRODUCTORY TEXT BOX Diagnostic Partners provides a range of onsite, in-office cardiac and vascular diagnostic testing services. From Resting Echocardiograms to Abdominal Aorta scans, each study is performed
Pathology of Vulnerable Plaque Angioplasty Summit 2005 TCT Asia Pacific, Seoul, April 28-30, 2005
 Pathology of Vulnerable Plaque Angioplasty Summit 25 TCT Asia Pacific, Seoul, April 28-3, 25 Renu Virmani, MD CVPath, A Research Service of the International Registry of Pathology Gaithersburg, MD Plaque
Pathology of Vulnerable Plaque Angioplasty Summit 25 TCT Asia Pacific, Seoul, April 28-3, 25 Renu Virmani, MD CVPath, A Research Service of the International Registry of Pathology Gaithersburg, MD Plaque
Lab 2 CVS pathology بالتأكيد
 Lab 2 CVS pathology أعزائي الطلبة هذه الورقة تحتوي فقط عىل ما قيل عن هذه الصور زيادة عن النظري وأي معلومة ذكرت في النظري وتكررت في العمىلي لن تجدوها مذكورة هنا ولكنكم مطالبون بمعرفتها بالتأكيد The aortic
Lab 2 CVS pathology أعزائي الطلبة هذه الورقة تحتوي فقط عىل ما قيل عن هذه الصور زيادة عن النظري وأي معلومة ذكرت في النظري وتكررت في العمىلي لن تجدوها مذكورة هنا ولكنكم مطالبون بمعرفتها بالتأكيد The aortic
Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis
 Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology 2008 Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis The purpose of this exercise is to allow students to recapitulate issues discussed throughout the course which
Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology 2008 Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis The purpose of this exercise is to allow students to recapitulate issues discussed throughout the course which
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System This system comprises both the blood and lymphatic vascular system. Blood vascular system is composed from; The heart: an organ whose function is to pump the blood. The arteries:
The Circulatory System This system comprises both the blood and lymphatic vascular system. Blood vascular system is composed from; The heart: an organ whose function is to pump the blood. The arteries:
Thrombosis and emboli. Peter Nagy
 Thrombosis and emboli Peter Nagy A thrombus is any solid object developing from the blood in vivo within the vascular system or heart. Thrombosis is hemostasis in the wrong place. Major components, forms:
Thrombosis and emboli Peter Nagy A thrombus is any solid object developing from the blood in vivo within the vascular system or heart. Thrombosis is hemostasis in the wrong place. Major components, forms:
VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation
 VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Athérosclérose - Plaque Physiopathologie, Evaluation
 Athérosclérose - Plaque Physiopathologie, Evaluation Dr Philippe GAROT Institut Cardiovasculaire Paris Sud MASSY-QUINCY www.rcf-icps.com Mécanisme cellulaire Constitution de la plaque d athérome Monocytes
Athérosclérose - Plaque Physiopathologie, Evaluation Dr Philippe GAROT Institut Cardiovasculaire Paris Sud MASSY-QUINCY www.rcf-icps.com Mécanisme cellulaire Constitution de la plaque d athérome Monocytes
Histopathology: chronic inflammation
 Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
10/8/2018. Lecture 9. Cardiovascular Health. Lecture Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor
 Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Blood Vessel Mechanics
 Blood Vessel Mechanics Ying Zheng, Ph.D. Department of Bioengineering BIOEN 326 11/01/2013 Blood Vessel Structure A Typical Artery and a Typical Vein Pressure and Blood Flow Wall stress ~ pressure Poiseuille
Blood Vessel Mechanics Ying Zheng, Ph.D. Department of Bioengineering BIOEN 326 11/01/2013 Blood Vessel Structure A Typical Artery and a Typical Vein Pressure and Blood Flow Wall stress ~ pressure Poiseuille
AN EARLY WARNING SYSTEM FOR CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
 AN EARLY WARNING SYSTEM FOR CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE Good for your patients. Good for your practice. Using the AngioDefender system to complement your patients care routine enables you to: Improve your patient
AN EARLY WARNING SYSTEM FOR CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE Good for your patients. Good for your practice. Using the AngioDefender system to complement your patients care routine enables you to: Improve your patient
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry
 Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
SENIOR PDHPE WORKSHEET Health Priorities in Australia
 SENIOR PDHPE WORKSHEET Health Priorities in Australia NAME ORGANISATION DATE INSTRUCTIONS 1. Make sure you read the bold text in boxes throughout the worksheet as they contain important information These
SENIOR PDHPE WORKSHEET Health Priorities in Australia NAME ORGANISATION DATE INSTRUCTIONS 1. Make sure you read the bold text in boxes throughout the worksheet as they contain important information These
Cho et al., 2009 Journal of Cardiology (2009), 54:
 Endothelial Dysfunction, Increased Carotid Artery Intima-media Thickness and Pulse Wave Velocity, and Increased Level of Inflammatory Markers are Associated with Variant Angina Cho et al., 2009 Journal
Endothelial Dysfunction, Increased Carotid Artery Intima-media Thickness and Pulse Wave Velocity, and Increased Level of Inflammatory Markers are Associated with Variant Angina Cho et al., 2009 Journal
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 23 : Vessels and Circulation 23-1 Blood Vessels An efficient style of transport for oxygen, nutrients, and waste products to and from body tissues.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 23 : Vessels and Circulation 23-1 Blood Vessels An efficient style of transport for oxygen, nutrients, and waste products to and from body tissues.
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Tracking a Killer Molecule
 Tracking a Killer Molecule Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA www.mercodia.com Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA products Product Catalog No Kit size Oxidized LDL ELISA 10-1143-01 96 wells Oxidized LDL competitive
Tracking a Killer Molecule Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA www.mercodia.com Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA products Product Catalog No Kit size Oxidized LDL ELISA 10-1143-01 96 wells Oxidized LDL competitive
Lipoprotein Particle Profile
 Lipoprotein Particle Profile 50% of people at risk for HEART DISEASE are not identified by routine testing. Why is LPP Testing The Most Comprehensive Risk Assessment? u Provides much more accurate cardiovascular
Lipoprotein Particle Profile 50% of people at risk for HEART DISEASE are not identified by routine testing. Why is LPP Testing The Most Comprehensive Risk Assessment? u Provides much more accurate cardiovascular
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Chapter 21 Peripheral circulation and Regulation
 Chapter 21 Peripheral circulation and Regulation I. Blood vessel structure A. Blood flows from large arteries to small capillaries 1. Large arteries contain large amounts of elastic tissue and little smooth
Chapter 21 Peripheral circulation and Regulation I. Blood vessel structure A. Blood flows from large arteries to small capillaries 1. Large arteries contain large amounts of elastic tissue and little smooth
2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid
 Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Imaging Overview for Vulnerable Plaque: Data from IVUS Trial and An Introduction to VH-IVUS Imgaging
 Imaging Overview for Vulnerable Plaque: Data from IVUS Trial and An Introduction to VH-IVUS Imgaging Gary S. Mintz,, MD Cardiovascular Research Foundation New York, NY Today, in reality, almost everything
Imaging Overview for Vulnerable Plaque: Data from IVUS Trial and An Introduction to VH-IVUS Imgaging Gary S. Mintz,, MD Cardiovascular Research Foundation New York, NY Today, in reality, almost everything
2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Cerebral Vascular Diseases. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
Until recently, atherosclerosis was
 Heart 2000;83:247 252 CORONARY DISEASE Atherogenesis: current understanding of the causes of atheroma Peter L Weissberg School of Clinical Medicine, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK Correspondence
Heart 2000;83:247 252 CORONARY DISEASE Atherogenesis: current understanding of the causes of atheroma Peter L Weissberg School of Clinical Medicine, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK Correspondence
Distribution of type IV collagen, laminin, nidogen and fibronectin in the haemodynamically stressed vascular wall
 Histol Histopath (1 990) 5: 161-1 67 Histology and Histopathology Distribution of type IV collagen, laminin, nidogen and fibronectin in the haemodynamically stressed vascular wall Reinhold Kittelberger,
Histol Histopath (1 990) 5: 161-1 67 Histology and Histopathology Distribution of type IV collagen, laminin, nidogen and fibronectin in the haemodynamically stressed vascular wall Reinhold Kittelberger,
IV. Cerebrovascular diseases
 IV. Cerebrovascular diseases - Cerebrovascular disease denotes brain disorders caused by pathologic processes involving the blood vessels. - The three main pathogenic mechanisms are: 1. Thrombotic occlusion
IV. Cerebrovascular diseases - Cerebrovascular disease denotes brain disorders caused by pathologic processes involving the blood vessels. - The three main pathogenic mechanisms are: 1. Thrombotic occlusion
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
Londonderry,+Northern+Ireland,+BT47+6SB+ *Corresponding+author+
 Computational+Modelling+of+Atherosclerosis+ + Andrew+Parton 1,+Victoria+McGilligan 1,+Maurice+O Kane 2,+Francina+R+ Baldrick 1,+Steven+Watterson 1* + + 1 Northern+Ireland+Centre+for+Stratified+Medicine,+Ulster+University,+CLTRIC,+Altnagelvin+Hospital+
Computational+Modelling+of+Atherosclerosis+ + Andrew+Parton 1,+Victoria+McGilligan 1,+Maurice+O Kane 2,+Francina+R+ Baldrick 1,+Steven+Watterson 1* + + 1 Northern+Ireland+Centre+for+Stratified+Medicine,+Ulster+University,+CLTRIC,+Altnagelvin+Hospital+
Objectives. Acute Coronary Syndromes; The Nuts and Bolts. Overview. Quick quiz.. How dose the plaque start?
 Objectives Acute Coronary Syndromes; The Nuts and Bolts Michael P. Gulseth, Pharm. D., BCPS Pharmacotherapy II Spring 2006 Compare and contrast pathophysiology of unstable angina (UA), non-st segment elevation
Objectives Acute Coronary Syndromes; The Nuts and Bolts Michael P. Gulseth, Pharm. D., BCPS Pharmacotherapy II Spring 2006 Compare and contrast pathophysiology of unstable angina (UA), non-st segment elevation
Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system
 1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
