Chronic (nonulcerative) colitis (CC)
|
|
|
- Randell Rich
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chronic (nonulcerative) colitis (CC) Chronic (nonulcerative) colitis (CC) - a chronic nonspecific polyetiological disease of colon, morphologically characterized by the development of inflammatory-dystrophic changes (with prevalence of either inflammatory or dystrophic), and with long-term flow - atrophic changes in the mucous membrane of entire colon or its parts and colon dysfunction. In the literature of our country, the notions of "enteritis" and "colitis" used to be united into one diagnosis (chronic enterocolitis with primary lesion of a certain intestinal part). Recently, enteritis and colitis are considered as separate, though still connected nosologies. In occidental literature and MSKH-10 the notions of "enteritis" and "colitis" have slightly different meaning. There are infectious (acute, with a known infectious agent) and non-infectious enteritis and colitis (K50-K52). Among non-infectious enteritis and colitis are: Non-infectious inflammatory diseases of intestines: Crohn's disease ( regional enteritis) - K50, ulcerative colitis - K51. Other non-infectious gastroenteritis and colitis (K52),: a) postradiational (after irradiation) b) toxic (cause of intoxication must be specified) c) allergic and nutritional (caused by allergies to food components) d) eosinophilic, e) ischemic f) other of specified ("microscopic colitis" - collagen, lymphocytic) and unspecified origin. In the literature of our country CE and CC include other conditions (see Etiological moments) "Unified clinical and statistical classification of digestive system diseases" (Ministry of Health of Ukraine, 2004) is an attempt to reconcile the MSKH 10 data and needs of the clinic on problem of chronic colitis: Chronic colitis K52 Etiology: E1 - nutritional K.52.2 E2 - postinfectious
2 E3 - parasitic E4 - allergic K.52.2 E5 - toxic K.52.1 E6 - radiation K.52.0 E7 - mechanical E8 - pseudomembranous Functional bowel condition: Q1 - hypomotor Q2 hypermotor Phase process: F1 exacerbation F2 remission Stages of CC etiopathogenesis Undergone acute intestinal and chronic long-lasting infections Genetically conditioned factors Parasitic diseases Ionizing radiation Toxic substances and certain medicaments Primary diseases of other digestive organs and some other systems Diet and nutritional quality disturbance- alimentary factors - dysbacteriosis; - immune reaction changes (local) + allergy; - undertreated chronic infections and parasitic helminthic invasion; - dysfunction of gastrointestinal endocrine system; - fermentopathies Large intestine changes: - inflammatory; - dystrophic;
3 - dysgenerative; - atrophic Intestinal function disorder: - motor; - secretory Extraintestinal disturbances (not evident as a rule) Classification of chronic colitis: Etiology: Characteristic: I.Primary colitis Infectious (postinfectious) Alimentary Toxic Allergic Postradiational II.Secondary At other digestive organ diseases and ischemic colitis (at mesenteric veins pathology) A. Anatomical and morphological: 1. Total CC (pancolitis) 2. Segmental CC: I. By localization: - right-side (typhlitis); - transversitis; - angulitis; - Left-sided (sigmoiditis, proctitis, proctosigmoiditis). II. By morphological features (depth of lesion): 1. Superficial CC 2. Atrophic CC B. Clinical: 1. Exacerbation 2. Remission I. The clinical phase of disease: II. By severity of flow: 1. light (I degree)
4 2. moderate (II degree) 3. severe (III degree) III. By complications: - solar plexitis (ganglionitis); - mesadenitis; - pericolitis; - bowel obstruction; - coprostasis; - dysbacteriosis (if it is a result of colitis) C. Functional: I. The nature of motility disorder: - hypermotor; - hypomotor; - mixed dyskinesia II. Presence of transport disorder (hyposecretion of ions and water, reducing of their reabsorption) III. Mucus secretion disorder: - hypersecretion; - hyposecretion - (transport of ions, H2O and mucus secretion in functional characteristics are indicated rarely) Clinic picture of chronic (non-ulcerative) colitis Typical clinical syndromes at CC: - pain syndrome; -dyskinetic syndrome; - dyspeptic syndrome; - asthenoneurotic syndrome Diagnostic criteria of chronic colitis: 1. Complaints; 2. History (etiological factors identifying); 3. Dyskinetic syndrome (changes in gut motility and tone); 4. Instrumental methods of study (detection of organic and functional changes in colon): - colonoscopy, - proctoscopy with mucous membrane biopsy; - radiological methods
5 5. Laboratory methods of study: - coproscopy-basic analysis; - dysbacteriosis analysis and (if it is detected) - antibiotic susceptibility ; - additional complete urine and blood analysis urine amylase, blood biochemistry Differential diagnostics of chronic enteritis and chronic colitis: Signs Chronic enteritis Chronic (nonulcerous) colitis 1. Pain Of bursting character, around the navel, 3-4 hours after eating, sometimes worsens after stool Down the colon, depending on process localization, of various character (dull, aching, bursting, cramp-like), 7-8 hours after eating or immediately after it (as a result of gastrointestinal reflex), temporarily decrease after stool 2. Constipations Not typical Sometimes 3. Tenesmus absent typical 4. Diarrhea 6-8 times a day, rarely 2-3 times, usually in second part of day, in the evening, defecation does not bring relief polyfecalia, fatty stool without blood 5. Palpation Painfullness in the navel area, Porges point, Obraztsov symptom ( loud rumbling in blind gut area) 6. General changes as disorders of protein, carbohydrate, lipid metabolism, electrolyte balance, level of vitamins 10 times or more a day after eating, especially after breakfast, sometimes early in the morning ( alarm clock symptom ). Pain increasing before defecation an decreasing after it. Small stool volume, semiformed, liquid or semiliquid, with mucus, bloodstreaked stool Painfullness, spasm or dilatation of certain colon part Unexpressed (happen mainly with dysbacteriosis of III-IV stage joining) 7. Weight loss In most patients Not typical 8. Biochemical indices typical Not typical changes 9. Stool micro- and macroscopy large volume stool ( polyfecalia ) Small volume stool inflammatory elements in Inflammatory changes syndrome ( mucus,
6 10.D-xylose test 11.Instrumental methods of study stool are not typical steatorrhea ( mainly by fatty acids, soaps), amylorrhea, creatorrhea D-xylose absorption decreasing Signs of organic and functional changes in duodenum Principles of chronic non-ulcerative colitis treatment: I. Diet II. Drug therapy: - antibiotic therapy and normalization of intestinal microflora; - normalization of intestine motor function and - correction of stool disorder; - treatment of evident allergic reactions; - local treatment of proctosigmoiditis; - stabilizers of intestinal epithelium membranes - enzymes III. Phytotherapy IV. Physiotherapy Preparations, which influence on gut organisms leukocytes, inflammatory elements in stool) Steatorrhea, creatorrhea, amylorrhea are not typical Without changes Organic and functional changes in colon Antibiotics - drugs of primary fungous origin that have antagonistic effect both on pathogenic and normal microflora Eubiotics - preparations of various (synthetic and microbiologic) origin, affecting the pathogenic microflora without significant negative influence on normal intestinal microflora. To eubiotics belong preparations with mentioned characteristics, which, however, do not include in their composition normal intestinal microflora and its substances. Probiotics preparations containing normal intestinal microflora and/or products of its activity or processing: Linex, Symbiter laktovit, Bifi form and other. Prebiotics preparations of various (mainly carbohydrate) origin, that promote growth and/or activity of probiotic bacteria, lactulose, inulin, pectin, vitamin B15. Synbiotics -preparations containing components of both probiotic and prebiotic actions. Preparations for intestinal function normalization 1. Drugs that increase the viscosity of gut contents: a) astringent and coating drugs: 0,5 g of tanalbin 3 times a day before meals;
7 0,5 g of bismuth nitrate 3 times a day, 30 minutes before meal, 1 tab. of de nol 4 times a day; 0,5 g of calcium carbonate 3 times a day, 30 minutes before meal b) adsorbents: 2 tab. of activated charcoal 3 times a day for 3-5 days; 1 tbsp to ½ -1 cup of water of polipefan (in granules) 3 times a day before meal for 5-7 days; enterosgel according to scheme; 1 packet of smecta to 100 ml of water 2-3 times a day for 5-7 days; 1-2 tab. of kaopektat 2-3 times a day; 2 tab. of sabsimplex (simethicone) 3 times a day after meal; espumizan; 1-2 tsp of bilignin 3 times a day before meal 2. Drugs that slow passage of intestinal contents and gut motility: a) at hypertensive-hyperkinetic dyskinesia with pain syndrome: myotropic spasmolytics (1 tab. of no-shpa 3 times a day, 2 ml of papaverine 2 times a day intramuscularly) ; selective antagonists of calcium channels in gastrointestinal tract: 1-2 drops of dicetel (pinaverium-bromide) 3 times a day; 1 tab. of riabal or spazmomen 3 times a day; M- cholinergic antagonist: 0,3-0,5 ml of 0.1% atropine subcutaneously ; 1 ml of 0.2% platifillin subcutaneously ; 1 tab. of buscopan, duspatalin 3 times a day b) prokinetics (regulate intestinal motility, depending on the body's needs): 1-2 tab. (10-20 mg) of mosapryd (mosyd) itopryd (primer, ganaton)3 times a day 30 minutes before meal; 1 tab. (100 mg) of trimebutin (debrydat, trymebudat) 3 times a day or 1 amp. of 1% solution intramuscularly 2-3 times a day ; metoclopramide (cerukal) and domperidone (motilium) are ineffective. They are used with absence of mentioned prokinetics and concomitant pathology of gastroduodenal area 1 tab.(10 mg) 3 times a day or intramuscularly; c) opioid drugs - with more severe and prolonged diarrhea (at CE are used rarely): ml of codeine; reasek (combined drug, atropine sulfate + diphenoxylate hydrochloride) - starting dose - up to 4 tablets, repeated dose 2 tablets after 6 hours, then, if necessary, 1-2 tab. 3 times a day;
8 0,004 g (2 capsules) of loperamide (Imodium) at acute diarrhea, then 0,002 grams (1 capsule) after every liquid stool, but not more than 6 capsules per day. Drugs for treatment of constipation a) drugs for inhibiting of water and sodium reabsorption in guts and secretion stimulating: -drugs with antraglycosides (1-2 tab. of ramnil in the evening, buckthorn extract, senadexin, tysasen in similar doses, 1-2 packets of regulax in the evening); -diphenylmethane derivatives (0,1 g of phenolphthalein 2-3 times a day; 1-3 dragee or suppositories of bisakodyl in the evening); g of castor oil (or 15 capsules) for 30 minutes; -salt means (2 tsp of Carlsbad salt, salt "Barbara» with 0,5 l of warm water, ½ cup 2-3 times a day; drops of guttalax (pikolax, laksygal) in the evening. c) drugs that increase volume of intestinal contents (1 tab. of laminaryd 3 times a day after meal, 1-3 tbsp of lactulose (normaze) a day, brans, etc.); c) agents that soften stool: 1-2 tsp of fatty oils (almond, olive, vaseline, etc.) 1-2 times a day Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) - a functional intestinal disorder which lasts 3 or more months at least 3 days per month. It is characterized by recurrent abdominal pain and/or discomfort in the abdomen, and at least two following features - change of stool frequency, change of stool shape, relief after defecation. IBS refers to functional intestinal disorders (according to Roman criteria of III revision, 2006), which also include functional bloating, functional constipation, functional diarrhea and nonspecific functional intestinal disorder. An important role in etiology of the disease have genetic predisposition, psychological peculiarities of a patient (congenital and acquired), psycho-traumatic factors. Other risk factors: alimentary; previous acute intestinal infections; primary chronic diseases of the digestive system (peptic ulcer, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, hepatitis, etc.). gynecological and other dyshormonal disorders; diseases of the spinal lower parts;
9 any debilitating disease; intestinal microflora disorder (dysbacteriosis) postoperative adhesions in the abdomen Pathogenetic factors: various disorders of intestinal tone and motility; increased sensitivity of intestine receptors to stretching; visceral hyperalgesia, which is formed following the so-called sensitizing factors (see risk factors); general dysfunctional neurovegetative disorders Classification of IBS according to the Roman criteria III (2006) 1. IBS with constipation - hard or lumpy feces at least in 25% of cases 2. IBS with diarrhea - watery or liquid frequent feces at least in 25% of cases 3. Mixed IBS alternation of constipation (hard feces) with diarrhea (watery feces) 4. Nonspecific IBS no stool frequency disturbances, possible stool consistency disorders, prevalence of pain syndrome and meteorism Basic (local, intestinal) symptoms: Abdominal pain of variable location, character and intensity, which temporarily decreases after defecation and appears (increase) after emotional or physical stress, sometimes after eating; Change in frequency (constipation, diarrhea) and consistency (hard, liquid) of stool; Defecation disturbances (difficulties, imperative or uncomplete bowel emptying feeling ); Mucus in feces; Bloating, feeling of fullness and abdominal murmurs, tenesmus. Other (general, extraintestinal) symptoms: Anxiety, constant worry; Mood lability ; Rapid fatigability; Spasmodic headache (sometimes migraine-like); Sleep disturbance;
10 Often -cancerophobia Objectively painfulness during intestinal loops palpation (more often - spasmodic) Diagnostic criteria of IBS: 1. Clinical and medical history: - typical intestinal and extraintestinal complaints now and in history; - inconsistency between complaints and real condition; - at objective examination - signs of emotional lability, locally intestine painfulness during palpation 2. Laboratory and instrumental data: - light (usually) or moderate dysbiosis in feces analysis; no helminth eggs, signs of inflammation, maldigestion; - changes of thyroid and sex hormones level, other indices,as a rule, are without significant changes or depend on the primary background pathology; - absence of intestinal mucous membrane organic changes during instrumental studies (colonoscopy, passage, irrigoscopy) and histological examination of biopsy samples Treatment of IBS 1. General measures: a) eliminating of stressful situations; b) psychological correction (psychotherapy, autogenic training, explanation of causes and developing mechanisms of existing intestinal disorders, keeping a diary of changes in health, etc.). c) sufficient sleep; d) keeping fit (regular physical exercises), regular outdoor walks; e) recommendations of nutrition correction: - with prevalence of diarrhea and pain limitation of fatty, fried food, pickles, sweets, fizzy drinks, coffee, alcohol, food that increase gas production (milk, cabbage, beans, etc.); - with prevalence of hypotonic constipations - a high in cellulose, bran diet 2. Drug therapy - depends on the clinical course of IBS: a) IBS with diarrhea - antidiarrheal agents (2-4 mg of loperamide up to 3-5 days, enterosgel, medicinal plants of astringent action);
11 b) IBS with constipation various laxatives (1-2 sachets of mukofalk 1-4 times a day, ml of lactulose 1-2 times a day, 1-2 sachets of endofalk,etc.), prokinetics (mosapryd, itopryd), prebiotics (in addition to lactulose also pectins, alginates); c) with abdominal pains (any variant of IBS, including nonspecific) - antispasmodics (no-shpa, riabal, duspatalin, platifillin, etc.), selective calcium antagonists (dicetel), prokinetics, central acting drugs (antidepressants, benzodiazepines, sedative herbs, etc.).
1. 2.
 Enteropathies (EP) 1. 2. Enzymopathies (2): - Genetic factors Parasitic invasion Radiation Toxic substances incl. medicines Primary diseases of other organs and/or systems Diet and nutritional quality
Enteropathies (EP) 1. 2. Enzymopathies (2): - Genetic factors Parasitic invasion Radiation Toxic substances incl. medicines Primary diseases of other organs and/or systems Diet and nutritional quality
Protectives and Adsorbents. Inorganic chemistry Course 1 Third year Assist. Lecturer Ahlam A. Shafeeq MSc. Pharmaceutical chemistry
 Protectives and Adsorbents Inorganic chemistry Course 1 Third year 2016-2017 Assist. Lecturer Ahlam A. Shafeeq MSc. Pharmaceutical chemistry Protectives and Adsorbents This group of gastrointestinal agents
Protectives and Adsorbents Inorganic chemistry Course 1 Third year 2016-2017 Assist. Lecturer Ahlam A. Shafeeq MSc. Pharmaceutical chemistry Protectives and Adsorbents This group of gastrointestinal agents
Irritable Bowel Disease. Dr. Alexandra Ilnyckyj MD
 Irritable Bowel Disease Dr. Alexandra Ilnyckyj MD Exactly what is IBS? Common condition affecting mostly women Symptoms are variable but they reflect altered gut movement (motility) and sensation Commonly
Irritable Bowel Disease Dr. Alexandra Ilnyckyj MD Exactly what is IBS? Common condition affecting mostly women Symptoms are variable but they reflect altered gut movement (motility) and sensation Commonly
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Now. George M. Logan, MD Friday, May 5, :35 4:05 PM
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Now George M. Logan, MD Friday, May 5, 2017 3:35 4:05 PM Dr. Logan indicated no potential conflict of interest to this presentation. He does not intend to discuss any unapproved/investigative
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Now George M. Logan, MD Friday, May 5, 2017 3:35 4:05 PM Dr. Logan indicated no potential conflict of interest to this presentation. He does not intend to discuss any unapproved/investigative
Antidiarrheals Antidiarrheal
 Antidiarrheals Major factors in diarrhea Increased motility of the GI tract. Decreased absorption of fluid. Antidiarrheal drugs include: Antimotility agents. Adsorbents. Drugs that modify fluid and electrolyte
Antidiarrheals Major factors in diarrhea Increased motility of the GI tract. Decreased absorption of fluid. Antidiarrheal drugs include: Antimotility agents. Adsorbents. Drugs that modify fluid and electrolyte
Lower Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406
 Lower Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Lower GI Tract A&P Small Intestine Anatomy Duodenum, jejunum, ileum Maximum surface area for digestion and absorption Specialized enterocytes from stem cells of crypts
Lower Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Lower GI Tract A&P Small Intestine Anatomy Duodenum, jejunum, ileum Maximum surface area for digestion and absorption Specialized enterocytes from stem cells of crypts
Drugs Affecting the Gastrointestinal System. Antidiarrheal and Laxatives
 Drugs Affecting the Gastrointestinal System Antidiarrheal and Laxatives Diarrhea Abnormal frequent passage of loose stools or Abnormal passage of stools with increased frequency, fluidity, and weight,
Drugs Affecting the Gastrointestinal System Antidiarrheal and Laxatives Diarrhea Abnormal frequent passage of loose stools or Abnormal passage of stools with increased frequency, fluidity, and weight,
Digestion: Small and Large Intestines Pathology
 Digestion: Small and Large Intestines Pathology Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one onone relationship with a qualified health
Digestion: Small and Large Intestines Pathology Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one onone relationship with a qualified health
Diarrhea may be: Acute (short-term, usually lasting several days), which is usually related to bacterial or viral infections.
 Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
The Role of Food in the Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
 The Role of Food in the Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders H. Vahedi, MD. Gastroentrologist Associate professor of medicine DDRI 92.4.27 vahedi@ams.ac.ir Disorder Sub-category A. Oesophageal disorders
The Role of Food in the Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders H. Vahedi, MD. Gastroentrologist Associate professor of medicine DDRI 92.4.27 vahedi@ams.ac.ir Disorder Sub-category A. Oesophageal disorders
Why does my stomach hurt? Exploring irritable bowel syndrome
 Why does my stomach hurt? Exploring irritable bowel syndrome By Flavio M. Habal, MD, PhD, FRCPC Case In this article: 1. What is IBS? A 45-year-old female is referred to your office with recurrent 2. How
Why does my stomach hurt? Exploring irritable bowel syndrome By Flavio M. Habal, MD, PhD, FRCPC Case In this article: 1. What is IBS? A 45-year-old female is referred to your office with recurrent 2. How
Chapter 34. Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
 What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)? Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a health issue found in your intestines (gut). IBS can cause symptoms such as: Belly pain. Cramping. Gas. Bloating (or swelling)
What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)? Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a health issue found in your intestines (gut). IBS can cause symptoms such as: Belly pain. Cramping. Gas. Bloating (or swelling)
IBS - Definition. Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by:
 IBS - Definition Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by: 3500 3000 No. of Publications 2500 2000 1500 1000 Irritable Bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome 500 0 1968-1977 1978-1987
IBS - Definition Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by: 3500 3000 No. of Publications 2500 2000 1500 1000 Irritable Bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome 500 0 1968-1977 1978-1987
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) has a variety of symptoms, most commonly cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Symptoms can vary from person to person,
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) has a variety of symptoms, most commonly cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Symptoms can vary from person to person,
Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders. TERRAGASTRO - Good health starts in the gut
 Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASE Referred to as gastrointestinal diseases, they are common disorders which affect the esophagus,
Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASE Referred to as gastrointestinal diseases, they are common disorders which affect the esophagus,
Is one of the most common chronic disorders. causing patients to seek medical treatment.
 ILOs After this lecture you should be able to : Define IBS Identify causes and risk factors of IBS Determine the appropriate therapeutic options for IBS Is one of the most common chronic disorders causing
ILOs After this lecture you should be able to : Define IBS Identify causes and risk factors of IBS Determine the appropriate therapeutic options for IBS Is one of the most common chronic disorders causing
IBS. Patient INFO. A Guide to Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Patient INFO IBS A Guide to Irritable Bowel Syndrome The information provided by the AGA Institute is not medical advice and should not be considered a replacement for seeing a medical professional. About
Patient INFO IBS A Guide to Irritable Bowel Syndrome The information provided by the AGA Institute is not medical advice and should not be considered a replacement for seeing a medical professional. About
Digestion. Text. What You Don t Know Can Hurt You!
 Digestion Text What You Don t Know Can Hurt You! Digestive Problems Approximately 36.5 million visits annually to ambulatory care facilities due to the diseases of the digestive system Over 4 million ulcers
Digestion Text What You Don t Know Can Hurt You! Digestive Problems Approximately 36.5 million visits annually to ambulatory care facilities due to the diseases of the digestive system Over 4 million ulcers
Nursing Principles & Skills II. Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction
 Nursing Principles & Skills II Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction Bowel Sounds Definitionthe noise or sounds made by the peristaltic waves of the intestinal muscle contracting and relaxing Bowel
Nursing Principles & Skills II Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction Bowel Sounds Definitionthe noise or sounds made by the peristaltic waves of the intestinal muscle contracting and relaxing Bowel
more intense treatments are needed to get rid of the infection.
 What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? Clostridium difficile, or C. diff for short, is an infection from a bacterium that can grow in your intestines and cause bad GI symptoms. The main risk of getting
What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. Diff)? Clostridium difficile, or C. diff for short, is an infection from a bacterium that can grow in your intestines and cause bad GI symptoms. The main risk of getting
Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,2 Lotronex (alosetron) a Indication For women with severe diarrheapredominant irritable
Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,2 Lotronex (alosetron) a Indication For women with severe diarrheapredominant irritable
An Approach to Abdominal Pain
 An Approach to Abdominal Pain objectives Should know the different types of abd pain Is acute or chronic? Hx taking skills with knowing the key questions Important abdominal pain signs A good differential
An Approach to Abdominal Pain objectives Should know the different types of abd pain Is acute or chronic? Hx taking skills with knowing the key questions Important abdominal pain signs A good differential
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 What I need to know about Irritable Bowel Syndrome NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know
What I need to know about Irritable Bowel Syndrome NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know
Certain genes passed on from parent to child increase the risk of developing Crohn's disease, if the right trigger occurs.
 Topic Page: Crohn's disease Definition: Crohn's disease from Benders' Dictionary of Nutrition and Food Technology Chronic inflammatory disease of the bowel, commonly the terminal ileum, of unknown aetiology,
Topic Page: Crohn's disease Definition: Crohn's disease from Benders' Dictionary of Nutrition and Food Technology Chronic inflammatory disease of the bowel, commonly the terminal ileum, of unknown aetiology,
Fecal incontinence causes 196 epidemiology 8 treatment 196
 Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Crohn's Disease. What causes Crohn s disease? What are the symptoms?
 Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
SIBO
 SIBO What is it? Small Intestinal Bowel Overgrowth A chronic bacterial infection of the small intestine Caused by bad bacteria such as E Coli and Clostridium migrating to the small intestine There is not
SIBO What is it? Small Intestinal Bowel Overgrowth A chronic bacterial infection of the small intestine Caused by bad bacteria such as E Coli and Clostridium migrating to the small intestine There is not
5. Which component of the duodenal contents entering the stomach causes the most severe changes to gastric mucosa:
 Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University
 CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
Chronic diarrhea. Dr.Nasser E.Daryani Professor of Tehran Medical University
 1 Chronic diarrhea Dr.Nasser E.Daryani Professor of Tehran Medical University Timing Acute diarrhea: 4 weeks Definitions Derived from Greek
1 Chronic diarrhea Dr.Nasser E.Daryani Professor of Tehran Medical University Timing Acute diarrhea: 4 weeks Definitions Derived from Greek
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 The Digestive System
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. What Is IBS?
 1 What Is IBS? At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is the abbreviation that doctors use for irritable bowel syndrome, often when they are talking about people with IBS. We will
1 What Is IBS? At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is the abbreviation that doctors use for irritable bowel syndrome, often when they are talking about people with IBS. We will
Ever wonder what s really happening on the inside?
 For Practitioners Ever wonder what s really happening on the inside? Are your patients suffering from diarrhea, constipation, bloating, gas or indigestion? Rocky Mountain Analytical is now offering Gut-Well
For Practitioners Ever wonder what s really happening on the inside? Are your patients suffering from diarrhea, constipation, bloating, gas or indigestion? Rocky Mountain Analytical is now offering Gut-Well
Gastroporesis or Leaky Gut
 Dr Wendy Wells 8595 E Bell Rd D101 Scottsdale, AZ 85260 (480) 607-0299 Gastroporesis or Leaky Gut From the mouth to anus is an enfolding of our skin. As you know, our skin contains a layer of cells and
Dr Wendy Wells 8595 E Bell Rd D101 Scottsdale, AZ 85260 (480) 607-0299 Gastroporesis or Leaky Gut From the mouth to anus is an enfolding of our skin. As you know, our skin contains a layer of cells and
Digestive Health Symptomatic Relief Suggestions
 Digestive Health Symptomatic Relief Suggestions Here are a list of suggestions in case you end up with constipation, bloating and stomach pain, diarrhea and/or indigestion/acid reflux. These are some great
Digestive Health Symptomatic Relief Suggestions Here are a list of suggestions in case you end up with constipation, bloating and stomach pain, diarrhea and/or indigestion/acid reflux. These are some great
Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Mustafa Giaffer March 2017
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Mustafa Giaffer March 2017 Introduction First described in 1771. 50% of patients present
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Mustafa Giaffer March 2017 Introduction First described in 1771. 50% of patients present
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
Constipation An Overview. Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment
 CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
What to eat when you have Short Bowel Syndrome
 What to eat when you have Short Bowel Syndrome What is Short Bowel Syndrome? Your bowel is an organ, shaped like a long tube, and is made up of the small and large bowel. The small bowel is about 15 to
What to eat when you have Short Bowel Syndrome What is Short Bowel Syndrome? Your bowel is an organ, shaped like a long tube, and is made up of the small and large bowel. The small bowel is about 15 to
CHRONIC DIARRHEA DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) DEFINITION: *LOOSE, WATERY STOOLS *MORE THAN 3 TIMES A DAY *FOR MORE THAN 4 WEEKS
 DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (403) 270-7479 CHRONIC DIARRHEA DEFINITION: *LOOSE, WATERY STOOLS *MORE THAN 3 TIMES A DAY *FOR MORE
DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (403) 270-7479 CHRONIC DIARRHEA DEFINITION: *LOOSE, WATERY STOOLS *MORE THAN 3 TIMES A DAY *FOR MORE
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Emetics, Antiemetics, and Antidiarrheals. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Emetics, Antiemetics, and Antidiarrheals. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Given one
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Emetics, Antiemetics, and Antidiarrheals. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Given one
4) Irritable Bowel Syndrome - Dr. Shaikhani. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Burden. Diagnosis
 4) Irritable Bowel Syndrome - Dr. Shaikhani Epidemiology A common disorder, with a 7% prevalence. Women are 1.5 times more likely to be affected than men, most commonly between ages 20-40 years. Onset
4) Irritable Bowel Syndrome - Dr. Shaikhani Epidemiology A common disorder, with a 7% prevalence. Women are 1.5 times more likely to be affected than men, most commonly between ages 20-40 years. Onset
Chapter 41. Media Directory. Lower Digestive Tract. Constipation (continued) Constipation
 Chapter 41 Drugs for Bowel Disorders and Other Gastrointestinal Conditions Slide 43 Media Directory Tegaserod Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Lower Digestive Tract Figure
Chapter 41 Drugs for Bowel Disorders and Other Gastrointestinal Conditions Slide 43 Media Directory Tegaserod Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Lower Digestive Tract Figure
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 6 April 2011
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 6 April 2011 METEOXANE, capsules B/60 (CIP code: 306 693-3) Applicant: IPRAD Simethicone Hydrated phloroglucinol ATC
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 6 April 2011 METEOXANE, capsules B/60 (CIP code: 306 693-3) Applicant: IPRAD Simethicone Hydrated phloroglucinol ATC
Advancing gastroenterology, improving patient care
 American College of Gastroenterology Advancing gastroenterology, improving patient care Note to Visitors: A fully updated ACG Systematic Review on the Management of Chronic Idiopathic Constipation and
American College of Gastroenterology Advancing gastroenterology, improving patient care Note to Visitors: A fully updated ACG Systematic Review on the Management of Chronic Idiopathic Constipation and
DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION
 Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Christina Tennyson, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology
 Diarrhea Christina Tennyson, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Columbia University DIARRHEA Symptom: stool frequency, liquidity Sign: > 200-250 g/day Acute Chronic Time
Diarrhea Christina Tennyson, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Columbia University DIARRHEA Symptom: stool frequency, liquidity Sign: > 200-250 g/day Acute Chronic Time
Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems
 Chapter 20 Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems Objectives Explain uses of diet therapy in gastrointestinal disturbances Identify foods allowed and disallowed in therapeutic diets discussed Adapt normal
Chapter 20 Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems Objectives Explain uses of diet therapy in gastrointestinal disturbances Identify foods allowed and disallowed in therapeutic diets discussed Adapt normal
2/26/2009. Diarrhea. Christina Tennyson, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Columbia University
 Diarrhea Christina Tennyson, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Columbia University 1 Symptom: Sign: DIARRHEA stool frequency, liquidity > 200-250 g/day Acute Chronic Time
Diarrhea Christina Tennyson, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Columbia University 1 Symptom: Sign: DIARRHEA stool frequency, liquidity > 200-250 g/day Acute Chronic Time
The Secrets of your Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
 The Secrets of your Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Dr Simon Greenfield Consultant Gastroenterologist Spire Harpenden Hospital Pinehill Hospital, Hitchin QE2 Hospital, Welwyn Garden Lister Hospital, Stevenage
The Secrets of your Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Dr Simon Greenfield Consultant Gastroenterologist Spire Harpenden Hospital Pinehill Hospital, Hitchin QE2 Hospital, Welwyn Garden Lister Hospital, Stevenage
Algorithms & Information Sheets
 Minor Ailment Scheme Algorithms & Information Sheets Acute Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is an increased frequency, fluidity or volume of the bowel movements with the passage of soft and watery stools as compared
Minor Ailment Scheme Algorithms & Information Sheets Acute Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is an increased frequency, fluidity or volume of the bowel movements with the passage of soft and watery stools as compared
The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders What are functional GI disorders?
 The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders Christine B. Dalton, PA-C Douglas A. Drossman, MD and Kellie Bunn, PA-C What are functional GI
The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders Christine B. Dalton, PA-C Douglas A. Drossman, MD and Kellie Bunn, PA-C What are functional GI
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Functional gastrointestinal disorders Definition A variable combination of chronic or recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms (attributed to the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, biliary
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Functional gastrointestinal disorders Definition A variable combination of chronic or recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms (attributed to the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, biliary
Constipation an Old Friend. Presented by Dr. Keith Harris
 Constipation an Old Friend Presented by Dr. Keith Harris Irregularity and the Tricks of the Trade." CONSTIPATION What is constipation? INFREQUENT BOWEL MOVEMENTS DIFFICULTY DURING DEFECATION SENSATION
Constipation an Old Friend Presented by Dr. Keith Harris Irregularity and the Tricks of the Trade." CONSTIPATION What is constipation? INFREQUENT BOWEL MOVEMENTS DIFFICULTY DURING DEFECATION SENSATION
Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory
 Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Sumner Brooks, MPH, RDN, LD March 11, 2017 Objectives Identify factors that may alter nutritional status in IBD Understand the role of diet and nutrition
Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Sumner Brooks, MPH, RDN, LD March 11, 2017 Objectives Identify factors that may alter nutritional status in IBD Understand the role of diet and nutrition
fever a persistent unexplained change in bowel habit in somebody over 50 years of age a family history of bowel or ovarian cancer.
 If you have had these symptoms for some time, if they come and go but never completely go away, then go and see your doctor. In practice, IBS is a diagnosis of exclusion. There is no test or marker that
If you have had these symptoms for some time, if they come and go but never completely go away, then go and see your doctor. In practice, IBS is a diagnosis of exclusion. There is no test or marker that
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2)
 NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 22 June 2011
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 22 June 2011 SPASFON, film-coated tablets B/30 (CIP code: 309 860-8) SPASFON, suppositories B/10 (CIP code: 309 861-4)
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 22 June 2011 SPASFON, film-coated tablets B/30 (CIP code: 309 860-8) SPASFON, suppositories B/10 (CIP code: 309 861-4)
Diverticular Disease Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.
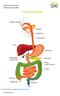 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
MOVICOL HALF PI December MOVICOL-Half. Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Potassium 5.4 mmol/l. Bicarbonate 17 mmol/l
 MOVICOL -Half Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Product Name: Product Description: MOVICOL-Half Each sachet of MOVICOL-Half contains: Macrogol 3350 6.563 g Sodium chloride 175.4 mg Sodium bicarbonate
MOVICOL -Half Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Product Name: Product Description: MOVICOL-Half Each sachet of MOVICOL-Half contains: Macrogol 3350 6.563 g Sodium chloride 175.4 mg Sodium bicarbonate
Microbiome GI Disorders
 Microbiome GI Disorders Prof. Ram Dickman Neurogastroenterology Unit Rabin Medical Center Israel 1 Key Points Our gut microbiota Were to find them? Symbiosis or Why do we need them? Dysbiosis or when things
Microbiome GI Disorders Prof. Ram Dickman Neurogastroenterology Unit Rabin Medical Center Israel 1 Key Points Our gut microbiota Were to find them? Symbiosis or Why do we need them? Dysbiosis or when things
Irritable Bowel. Syndrome. Health Promotion Service
 The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
Fecal microbial transplantation
 Version 09/16 Consent Form For Fecal microbial transplantation Fecal transplant is an operation in which liquid produced from a healthy human being (as per a survey questionnaire and blood and feces tests)
Version 09/16 Consent Form For Fecal microbial transplantation Fecal transplant is an operation in which liquid produced from a healthy human being (as per a survey questionnaire and blood and feces tests)
IBS Irritable Bowel syndrome Therapeutics II PHCL 430
 Salman Bin AbdulAziz University College Of Pharmacy IBS Irritable Bowel syndrome Therapeutics II PHCL 430 Email:- ahmedadel.pharmd@gmail.com Ahmed A AlAmer PharmD R.S is 32-year-old woman experiences intermittent
Salman Bin AbdulAziz University College Of Pharmacy IBS Irritable Bowel syndrome Therapeutics II PHCL 430 Email:- ahmedadel.pharmd@gmail.com Ahmed A AlAmer PharmD R.S is 32-year-old woman experiences intermittent
PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions
 PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions Departman Tarih Prof. A. Melih OZEL, MD Department of Gastroenterology Anadolu Medical Center Hospital Gebze Kocaeli - TURKEY Presentation plan 15 min. Introduction
PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions Departman Tarih Prof. A. Melih OZEL, MD Department of Gastroenterology Anadolu Medical Center Hospital Gebze Kocaeli - TURKEY Presentation plan 15 min. Introduction
STRESS AND THE HEALTH OF THE BODY
 Slide 1 STRESS AND THE HEALTH OF THE BODY Slide 2 What is Stress It is a physical response that occurs in our body when we are stressed Physiologically, it is a series of actions in the body that are regulated
Slide 1 STRESS AND THE HEALTH OF THE BODY Slide 2 What is Stress It is a physical response that occurs in our body when we are stressed Physiologically, it is a series of actions in the body that are regulated
Saliva & Feces analysis
 Saliva & Feces analysis Saliva analysis What is Saliva? Watery substance present in humans and animals and secreted by salivary glands and aids in digestion It is a filtrate of plasma Contains electrolytes,
Saliva & Feces analysis Saliva analysis What is Saliva? Watery substance present in humans and animals and secreted by salivary glands and aids in digestion It is a filtrate of plasma Contains electrolytes,
X-ray (Radiography) - Lower GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Lower GI Tract Lower gastrointestinal tract radiography or lower GI uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy and a barium-based contrast material to
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Lower GI Tract Lower gastrointestinal tract radiography or lower GI uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy and a barium-based contrast material to
Primary Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Primary Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Instructor, Division of Gastroenterology Current Concepts in Drug Therapy CME Course April 23, 2015 Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Primary Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Instructor, Division of Gastroenterology Current Concepts in Drug Therapy CME Course April 23, 2015 Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
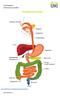 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
Irritable bowel syndrome in adults
 Irritable bowel syndrome in adults NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised Welcome In February 2008, NICE published a clinical guideline on
Irritable bowel syndrome in adults NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised Welcome In February 2008, NICE published a clinical guideline on
Bloating. There are many causes of bloating, including: diet, irritable bowel syndrome, lactose intolerance, reflux, and constipation.
 1 of 5 1/5/2017 9:23 AM From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Bloating is any abnormal general swelling, or increase in diameter of the abdominal area. [1] As a symptom, the patient feels a full and tight
1 of 5 1/5/2017 9:23 AM From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Bloating is any abnormal general swelling, or increase in diameter of the abdominal area. [1] As a symptom, the patient feels a full and tight
A patient s guide to the. management of constipation following surgery
 A patient s guide to the management of constipation following surgery This leaflet has been designed to give you more information about using laxatives after your surgery. What is constipation? After your
A patient s guide to the management of constipation following surgery This leaflet has been designed to give you more information about using laxatives after your surgery. What is constipation? After your
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation. Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class
 Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Lesson 1. Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Clinical Evaluation of CHRONIC DIARRHEA. By Dr. Mohamed El-Awady
 Clinical Evaluation of CHRONIC DIARRHEA By Dr. Mohamed El-Awady Definition Stool weight of more than 300 gm / 24 h more than 4 weeks (Feldman et al 2002) CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION 1) Large-Volume Versus
Clinical Evaluation of CHRONIC DIARRHEA By Dr. Mohamed El-Awady Definition Stool weight of more than 300 gm / 24 h more than 4 weeks (Feldman et al 2002) CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION 1) Large-Volume Versus
PainReliefSciences.com 1
 PainReliefSciences.com 1 Copyright 2016 NutriFrontier Limited All rights reserved Published by Kevin Richardson. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted
PainReliefSciences.com 1 Copyright 2016 NutriFrontier Limited All rights reserved Published by Kevin Richardson. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted
PERSISTENT DIARRHOEA. IAP UG Teaching slides
 PERSISTENT DIARRHOEA 1 DEFINITION Prolongation of acute diarrhoea / dysentery for more than 14 days Generally associated with weight loss. 2 PROTRACTED DIARRHOEA Prolongation of acute diarrhoea or dysentery
PERSISTENT DIARRHOEA 1 DEFINITION Prolongation of acute diarrhoea / dysentery for more than 14 days Generally associated with weight loss. 2 PROTRACTED DIARRHOEA Prolongation of acute diarrhoea or dysentery
Tana's Habitat - Vim and Vigor - They Don t Call Them High Bars For Nothin
 http://www.tanashabitat.com/vim/0404151of6.asp Do you have a tummy ache that ver seems to go away? Do you wish your gu would just calm down and let you live your life? If so, you re not alo. You may suffer
http://www.tanashabitat.com/vim/0404151of6.asp Do you have a tummy ache that ver seems to go away? Do you wish your gu would just calm down and let you live your life? If so, you re not alo. You may suffer
Small-Bowel and colon Transit. Mahsa Sh.Nezami October 2016
 Small-Bowel and colon Transit Mahsa Sh.Nezami October 2016 Dyspeptic symptoms related to dysmotility originating from the small bowel or colon usually include : Abdominal pain Diarrhea Constipation However,
Small-Bowel and colon Transit Mahsa Sh.Nezami October 2016 Dyspeptic symptoms related to dysmotility originating from the small bowel or colon usually include : Abdominal pain Diarrhea Constipation However,
Ulcerative Colitis. ulcerative colitis usually only affects the colon.
 Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
Dulcolax 5 mg, film-coated tablets
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Dulcolax 5 mg, film-coated tablets BISACODYL This leaflet is a copy of the Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflet for a medicine, which
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Dulcolax 5 mg, film-coated tablets BISACODYL This leaflet is a copy of the Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflet for a medicine, which
You are not alone. Feeling Bloated?
 Feeling Bloated? You are not alone. Feeling Bloated? Bloating during pregnancy is a common symptom, that starts around 11 weeks and likely to continue throughout your pregnancy. H 3C H H 3C H O CH 3 H
Feeling Bloated? You are not alone. Feeling Bloated? Bloating during pregnancy is a common symptom, that starts around 11 weeks and likely to continue throughout your pregnancy. H 3C H H 3C H O CH 3 H
Pharmacology. Drugs that Affect the Gastrointestinal System
 Pharmacology Drugs that Affect the Gastrointestinal System Topics Peptic Ulcer Disease Constipation Diarrhea Emesis Digestion Peptic Ulcer Disease Factors that Increase Acidity Factors that Protect Against
Pharmacology Drugs that Affect the Gastrointestinal System Topics Peptic Ulcer Disease Constipation Diarrhea Emesis Digestion Peptic Ulcer Disease Factors that Increase Acidity Factors that Protect Against
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Causes and Treatments
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Causes and Treatments Oh heck. Gas, bloating, alternating constipation and diarrhea, food cravings and abdominal pain. Your symptoms may be significant and cause you embarrassment
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Causes and Treatments Oh heck. Gas, bloating, alternating constipation and diarrhea, food cravings and abdominal pain. Your symptoms may be significant and cause you embarrassment
IBS CLOSED REFERRAL STATUS: Dear Dr.,
 Name: PHN/ULI: DOB: RHRN: RefMD: Dr. RefMD Fax: RefDate: Date Today: CONFIRMATION: TRIAGE CATEGORY: REFERRAL STATUS: Dear Dr., Referral Received Enhanced Primary Care Pathway CLOSED IBS The clinical and
Name: PHN/ULI: DOB: RHRN: RefMD: Dr. RefMD Fax: RefDate: Date Today: CONFIRMATION: TRIAGE CATEGORY: REFERRAL STATUS: Dear Dr., Referral Received Enhanced Primary Care Pathway CLOSED IBS The clinical and
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Diagnosis and Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) For the Primary Care Provider
 Diagnosis and Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) For the Primary Care Provider Elizabeth Coss, MD General Gastroenterologist Audie Murphy Veterans Hospital UT Health This presentation does not
Diagnosis and Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) For the Primary Care Provider Elizabeth Coss, MD General Gastroenterologist Audie Murphy Veterans Hospital UT Health This presentation does not
DOWNLOAD OR READ : IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME ONE DISEASE SEVERAL OR NONE PERSPECTIVES IN DIGESTIVE DISEASES VOL 5 PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME ONE DISEASE SEVERAL OR NONE PERSPECTIVES IN DIGESTIVE DISEASES VOL 5 PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 irritable bowel syndrome one disease several or none perspectives
DOWNLOAD OR READ : IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME ONE DISEASE SEVERAL OR NONE PERSPECTIVES IN DIGESTIVE DISEASES VOL 5 PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 irritable bowel syndrome one disease several or none perspectives
First Name. Profession. Weight lbs. Weight 1 year ago lbs. Min. Adult Weight lbs. at age Maximum Weight lbs. at age
 Date Time Dietary consultation involves a health profile whose purpose is not to establish a diagnosis, but rather to determine a client's health status in order to guide his or her weight loss plan. A
Date Time Dietary consultation involves a health profile whose purpose is not to establish a diagnosis, but rather to determine a client's health status in order to guide his or her weight loss plan. A
Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels.
 Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels. Abscess A localised collection of pus in a cavity that is formed by the decay of diseased
Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels. Abscess A localised collection of pus in a cavity that is formed by the decay of diseased
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Dr Rex J Polson 17 th January 2018 Overview Description of the condition Discussion of symptoms and investigations that may be required Discussion of management and treatment
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Dr Rex J Polson 17 th January 2018 Overview Description of the condition Discussion of symptoms and investigations that may be required Discussion of management and treatment
Chronic Diarrhea in Dogs
 Chronic Diarrhea in Dogs Basics OVERVIEW A change in the frequency, consistency, and volume of bowel movement (feces) for more than 3 weeks Can be either small bowel (small intestine) diarrhea, large bowel
Chronic Diarrhea in Dogs Basics OVERVIEW A change in the frequency, consistency, and volume of bowel movement (feces) for more than 3 weeks Can be either small bowel (small intestine) diarrhea, large bowel
Chapter 5: Common Digestive Problems from The Kansas State University Human Nutrition (HN 400) Flexbook by Brian Lindshield is in the public domain
 Chapter 5: Common Digestive Problems from The Kansas State University Human Nutrition (HN 400) Flexbook by Brian Lindshield is in the public domain in the United States. 5 Common Digestive Problems Before
Chapter 5: Common Digestive Problems from The Kansas State University Human Nutrition (HN 400) Flexbook by Brian Lindshield is in the public domain in the United States. 5 Common Digestive Problems Before
Second term/
 Second term/ 2015-2016 L. 1 Dr Mohammed AL-Zobaidy Learning objectives GIT pharmacology After completing this chapter the student will be able to: Recognise pathophysiological factors implicated in acid-peptic
Second term/ 2015-2016 L. 1 Dr Mohammed AL-Zobaidy Learning objectives GIT pharmacology After completing this chapter the student will be able to: Recognise pathophysiological factors implicated in acid-peptic
Diarrhoea. Myeloma Infosheet Series. Symptoms and complications. Infoline:
 Diarrhoea This Infosheet explains what diarrhoea is, what causes it in myeloma patients, what the symptoms of it are, how it is treated and some tips for self-management. What is diarrhoea? Diarrhoea is
Diarrhoea This Infosheet explains what diarrhoea is, what causes it in myeloma patients, what the symptoms of it are, how it is treated and some tips for self-management. What is diarrhoea? Diarrhoea is
Digestion Assessment Scorecard
 Name Digestion Assessment Age Height Weight Based upon your health profile for the past 30 days, please select the appropriate number, from '0-3' on all questions (0 as least/never/no and 3 as most/always/yes).
Name Digestion Assessment Age Height Weight Based upon your health profile for the past 30 days, please select the appropriate number, from '0-3' on all questions (0 as least/never/no and 3 as most/always/yes).
ROLE OF THE GUT BACTERIA
 ROLE OF THE GUT BACTERIA Our Good Bacteria In a perfect world, we would all have a proper ratio of good bacteria And what could this proper ratio do for us? The knowledge of the connections between our
ROLE OF THE GUT BACTERIA Our Good Bacteria In a perfect world, we would all have a proper ratio of good bacteria And what could this proper ratio do for us? The knowledge of the connections between our
