enhances nociceptive responses in rats
|
|
|
- Claud Hubbard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brazilian Chronic intrathecal Journal of Medical cannulation and Biological Research (2000) 33: ISSN X 949 Chronic intrathecal cannulation enhances nociceptive responses in rats F.R.C. Almeida, I.R.S. Schivo, B.B. Lorenzetti and S.H. Ferreira Departamento de Farmacologia, Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto, Universidade de São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, SP, Brasil Correspondence S.H. Ferreira Departamento de Farmacologia FMRP, USP Av. Bandeirantes, Ribeirão Preto, SP Brasil Fax: Research supported by FAPESP and CNPq. The present address of F.R.C. Almeida is Departamento de Bioquímica e Farmacologia, CCS, UFPI, Teresina, PI, Brasil, and that of B.B. Lorenzetti is Departamento de Farmacologia, Setor de Ciências Biológicas, UFPR, Curitiba, PR, Brasil. Received November 25, 1999 Accepted May 3, 2000 Abstract Key words Hyperalgesia Spinal sensitization Intrathecal cannulation Nociceptive response Inflammation Introduction
2 950 F.R.C. Almeida et al. Material and Methods Animals Drugs Chronic intrathecal cannulation Direct intrathecal administration
3 Chronic intrathecal cannulation 951 Nociceptive methods Histopathological analysis of spinal cord slices Results
4 952 F.R.C. Almeida et al. Intensity of hyperalgesia (D reaction time, s) A B C Nv Sh Cg (µg, ipl ) PGE 2 (ng, ipl ) Figure 2 - Effect of indomethacin on the intensity of PGE 2 hyperalgesia in chronically cannulated (, triangles), sham-operated (Sh, squares) and naive (Nv, circles) animals. Indomethacin was administered via an intrathecal (it) cannula (panel A), directly into the subarachnoid space (panel B) or systemically (ip, panel C) 30 min before intraplantar injection of PGE 2 (10 ng/paw). Each point represents the mean reaction time (s) ± SEM of 5-13 animals per group measured 3 h after the hyperalgesic challenge. The data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan s test (asterisks indicate significant differences for each dose, P<0.05). Nv Sh Sh Nv Figure 1 - Comparison of the intensity of mechanical hyperalgesia in response to increasing doses of carrageenin (Cg) or PGE 2 in chronically cannulated (, triangles), naive (Nv, circles) and sham-operated (Sh, squares) rats. The intensity of hyperalgesia was measured 1 h (panel A) and 3 h (panel B) after the different doses of carrageenin ( µg, intraplantar (ipl )). Panel C shows the intensity of hyperalgesia measured 3 h after an ipl injection of PGE 2 (5-100 ng/ml). The data (mean ± SEM for five animals per group) were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan s test. P<0.05 compared to Nv and Sh animals. Intensity of hyperalgesia (D reaction time, s) A B C Nv Sh Nv Sh Via cannula Direct Systemic Indomethacin (µg, it) Indomethacin (mg/kg, ip)
5 Chronic intrathecal cannulation 953 Mean number of flinches Mean number of flinches Discussion Nv Sh Nv Sh Nv Sh 0.3% 1% 5% Formalin (first phase) Direct (Nv) Direct () Via cannula () A B C C IND C IND C IND 5% Formalin (second phase) Figure 3 - Differences in the intensity of response of chronically cannulated (), naive (Nv) and sham-operated (Sh) rats during phase 1 of the formalin test. Formalin was administered at different doses of 0.3, 1, and 5%. Each bar is the mean ± SEM number of flinches of 6-12 animals, measured for 10 min after the nociceptive stimulus. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan s test. P<0.05 compared to normal or Sh animals. Figure 4 - Inhibitory effect of indomethacin on the increased response of the second phase (10-60 min) of the 5% formalin test in cannulated () animals. Panels A and B show the effects of direct injections of indomethacin (IND, 10 µg/10 µl) administered 30 min before subcutaneous injection of formalin to naive (Nv) and animals. Panel C shows the effect of IND administration through a cannula. The controls (C) received 10 µl of Tris-buffer. The bars represent the mean ± SEM number of flinches of the injected paw of 9-12 animals per group. The asterisks indicate significant differences (P<0.01 and P<0.001, unpaired Student t-test).
6 954 F.R.C. Almeida et al. Figure 5 - Comparison of cannulated (), naive (Nv) and sham (Sh) animals in terms of withdrawal latencies of carrageenin (Cg)-inflamed rat paws in response to thermal stimulation. The bars represent groups injected with different doses of carrageenin (intraplantar, ipl ). C is the control group injected with saline. The results are the mean ± SEM percent ratio between carrageenin-injected and control paws 1 h after injection of the stimulus in 5-13 animals per group. Data were analyzed by ANOVA followed by Duncan s test. The asterisks indicate significant differences between Nv and animals (P<0.05). Latency of injected paw/control (%) Nv Sh NvSh Nv Sh NvSh C Cg (µg, ipl )
7 Chronic intrathecal cannulation 955
8 956 F.R.C. Almeida et al. References 1. Yaksh TL & Rudy TA (1976). Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiology and Behavior, 17: Yaksh TL & Rudy TA (1976). Analgesia mediated by a direct spinal action of narcotics. Science, 192: Malmberg AB & Yaksh TL (1993). Pharmacology of the spinal action of ketorolac, morphine, ST-91, U50488H, and L-PIA on the formalin test and an isobolographic analysis of the NSAID interaction (see comments). Anesthesiology, 79: Malmberg AB & Yaksh TL (1995). Cyclooxygenase inhibition and the spinal release of prostaglandin E2 and amino acids evoked by paw formalin injection: a microdialysis study in unanesthetized rats. Journal of Neuroscience, 15: Malmberg AB & Yaksh TL (1995). The effect of morphine on formalin-evoked behaviour and spinal release of excitatory amino acids and prostaglandin E2 using microdialysis in conscious rats. British Journal of Pharmacology, 114: Akerman B, Rosell S & Folkers K (1982). Intrathecal (D-Pro2, D-Trp7,9)-SP elicits hypoalgesia and motor blockade in the rat and antagonizes noxious responses induced by substance P. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica, 114: Yamamoto T & Yaksh TL (1993). Effects of intrathecal strychnine and bicuculline on nerve compression-induced thermal hyperalgesia and selective antagonism by MK-801. Pain, 54: Chaplan SR, Pogrel JW & Yaksh TL (1994). Role of voltage-dependent calcium channel subtypes in experimental tactile allodynia. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 269: Ramwell PW, Shaw JE & Jessup R (1966). Spontaneous and evoked release of prostaglandins from frog spinal cord. American Journal of Physiology, 211: Ferreira SH (1983). Peripheral and central analgesia. In: Bonica JJ, Lindblom U & Iggor A (Editors), Advances in Pain Research and Therapy. Raven Press, New York. 11. Taiwo YO & Levine JD (1986). Indomethacin blocks central nociceptive effects of PGF2 alpha. Brain Research, 373: Minami T, Uda R, Horiguchi S, Ito S, Hyodo M & Hayaishi O (1994). Allodynia evoked by intrathecal administration of prostaglandin E2 to conscious mice. Pain, 57: Malmberg AB & Yaksh TL (1992). Antinociceptive actions of spinal nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents on the formalin test in the rat. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 263: Malmberg AB & Yaksh TL (1992). Hyperalgesia mediated by spinal glutamate or substance P receptor blocked by spinal cyclooxygenase inhibition. Science, 257: Ferreira SH, Lorenzetti BB & Correa FM (1978). Central and peripheral antialgesic action of aspirin-like drugs. European Journal of Pharmacology, 53: Serpell MG, DeLeo JA, Coombs DW, Colburn RW, Twitchell BB, Willenbring S & Fromm C (1993). Intrathecal catheterization alone reduces autotomy after sciatic cryoneurolysis in the rat. Life Sciences, 53: Papir-Kricheli D, Frey J, Laufer R, Gilon C, Chorev M, Selinger Z & Devor M (1987). Behavioural effects of receptor-specific substance P agonists. Pain, 31: Mestre C, Pelissier T, Fialip J, Wilcox G & Eschalier A (1994). A method to perform direct transcutaneous intrathecal injection in rats. Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology Methods, 32: Wheeler-Aceto H, Porreca F & Cowan A (1990). The rat paw formalin test: comparison of noxious agents. Pain, 40: Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C & Joris J (1988). A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain, 32: Ferreira SH, Nakamura M & Abreu Castro MS (1978). The hyperalgesic effects of prostacyclin and prostaglandin E2. Prostaglandins, 16: Long JB, Mobley WC & Holaday JW (1988). Neurological dysfunction after intrathecal injection of Dynorphin A (1-13) in the rat. I. Injection procedures modify pharmacological responses. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 246: Stevens CW & Yaksh TL (1986). Dynorphin A and related peptides administered intrathecally in the rat: A search for putative kappa opiate receptor activity. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 238: Bianchi M, Dib B & Panerai AE (1998). Interleukin-1 and nociception in the rat. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 53: Castro MSA & Ferreira SH (1979). Cell migration and hyperalgesia: A paradoxical effect of endotoxin. In: Weissmann G, Samuelsson B & Paoletti R (Editors), Advances in Inflammation Research. Raven Press, New York. 26. Ferreira SH & Lorenzetti BB (1994). Glutamate spinal retrograde sensitization of primary sensory neurons associated with nociception. Neuropharmacology, 33: Ferreira SH & Lorenzetti BB (1996). Intrathecal administration of prostaglandin E2 causes sensitization of the primary afferent neuron via the spinal release of glutamate. Inflammation Research, 45: Coderre TJ, Katz J, Vaccarino AL & Melzack R (1993). Contribution of central neuroplasticity to pathological pain: review of clinical and experimental evidence. Pain, 52:
An electronic pressure-meter nociception paw test for mice
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (24) 37: 41-47 Mouse paw pressure-meter test ISSN 1-879X 41 An electronic pressure-meter nociception paw test for mice T.M. Cunha, W.A. Verri Jr., G.G.
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (24) 37: 41-47 Mouse paw pressure-meter test ISSN 1-879X 41 An electronic pressure-meter nociception paw test for mice T.M. Cunha, W.A. Verri Jr., G.G.
Bradykinin B 1 and B 2 receptors, tumour necrosis factor a and in ammatory hyperalgesia
 British Journal of Pharmacology (1999) 126, 649 ± 656 ã 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp Bradykinin B 1 and B 2 receptors, tumour necrosis
British Journal of Pharmacology (1999) 126, 649 ± 656 ã 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp Bradykinin B 1 and B 2 receptors, tumour necrosis
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
Streptozotocin-induced mechanical hypernociception is not dependent on hyperglycemia
 Brazilian STZ-induced Journal hypernociception of Medical and does Biological not depend Research on hyperglycemia (2009) 42: 197-206 ISSN 0100-879X 197 Streptozotocin-induced mechanical hypernociception
Brazilian STZ-induced Journal hypernociception of Medical and does Biological not depend Research on hyperglycemia (2009) 42: 197-206 ISSN 0100-879X 197 Streptozotocin-induced mechanical hypernociception
ONLINE. F.M. Teixeira*, L.L. Castro*, R.T. Ferreira, P.A. Pires, F.A. Vanderlinde and M.A. Medeiros
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research Online Provisional Version ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research Online Provisional Version ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully
Standardization of a fluorimetric assay for the determination of tissue angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in rats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research () 33: 755-76 ACE activity in rat tissue samples ISSN -879X 755 Standardization of a fluorimetric assay for the determination of tissue angiotensin-converting
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research () 33: 755-76 ACE activity in rat tissue samples ISSN -879X 755 Standardization of a fluorimetric assay for the determination of tissue angiotensin-converting
Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior
 Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 103 (2013) 678 683 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pharmbiochembeh
Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 103 (2013) 678 683 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pharmbiochembeh
Evaluation of Gabapentin and S-( )-3-Isobutylgaba in a Rat Model of Postoperative Pain
 0022-3565/97/2823-1242$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 282, No. 3 Copyright 1997 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
0022-3565/97/2823-1242$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 282, No. 3 Copyright 1997 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
Atropine and ODQ antagonize tetanic fade induced by L-arginine in cats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1277-1283 Antagonism of tetanic fade induced by NO ISSN 0-879X 1277 Atropine and ODQ antagonize tetanic fade induced by L-arginine in cats
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1277-1283 Antagonism of tetanic fade induced by NO ISSN 0-879X 1277 Atropine and ODQ antagonize tetanic fade induced by L-arginine in cats
Materials and Methods
 Anesthesiology 2004; 100:1258 62 2004 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Spinal Adenosine Receptor Activation Reduces Hypersensitivity after Surgery by a Different
Anesthesiology 2004; 100:1258 62 2004 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Spinal Adenosine Receptor Activation Reduces Hypersensitivity after Surgery by a Different
Central and Peripheral Analgesia Mediated by the Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibitor Neostigmine in the Rat Inflamed Knee Joint Model
 Central and Peripheral Analgesia Mediated by the Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibitor Neostigmine in the Rat Inflamed Knee Joint Model H. Buerkle, MD, M. Boschin, MS, M. A. E. Marcus, MD, G. Brodner, MD, Pm,
Central and Peripheral Analgesia Mediated by the Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibitor Neostigmine in the Rat Inflamed Knee Joint Model H. Buerkle, MD, M. Boschin, MS, M. A. E. Marcus, MD, G. Brodner, MD, Pm,
Pain Pathways. Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH
 Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
Gabapentin Antinociception in Mice with Acute Herpetic Pain Induced by Herpes Simplex Virus Infection
 0022-3565/01/2962-270 275$3.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 296, No. 2 Copyright 2001 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 3229/880565
0022-3565/01/2962-270 275$3.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 296, No. 2 Copyright 2001 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 3229/880565
NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions as Related to Analgesia and Tolerance
 Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S7 Proceedings Supplement NDMA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions
Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S7 Proceedings Supplement NDMA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions
Effect of COX-1 and COX-2 Inhibition on Induction and Maintenance of Carrageenan-Evoked Thermal Hyperalgesia in Rats 1
 0022-3565/98/2853-1031$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 285, No. 3 Copyright 1998 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
0022-3565/98/2853-1031$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 285, No. 3 Copyright 1998 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics
 279 International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics Available online at Print ISSN: 2278 2648 Online ISSN: 2278-2656 IJRPP Volume 2 Issue 1 2013 Research article Protective effect
279 International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics Available online at Print ISSN: 2278 2648 Online ISSN: 2278-2656 IJRPP Volume 2 Issue 1 2013 Research article Protective effect
A study on analgesic effect of Caryophyllus aromaticus by formalin test in albino rats
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 2 Issue 1 January 2013 PP.28-35 A study on analgesic effect of Caryophyllus aromaticus
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 2 Issue 1 January 2013 PP.28-35 A study on analgesic effect of Caryophyllus aromaticus
Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in the rat
 Cheppudira et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2016) 16:73 DOI 10.1186/s12871-016-0242-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in
Cheppudira et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2016) 16:73 DOI 10.1186/s12871-016-0242-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in
Intrathecal lidocaine elevates prostaglandin E 2 levels in cerebrospinal fluid: a microdialysis study in freely moving rats
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 101 (5): 716 22 (2008) doi:10.1093/bja/aen243 Advance Access publication August 20, 2008 Intrathecal lidocaine elevates prostaglandin E 2 levels in cerebrospinal fluid: a
British Journal of Anaesthesia 101 (5): 716 22 (2008) doi:10.1093/bja/aen243 Advance Access publication August 20, 2008 Intrathecal lidocaine elevates prostaglandin E 2 levels in cerebrospinal fluid: a
d-methadone Is Antinociceptive in the Rat Formalin Test 1
 0022-3565/97/2832-0648$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 283, No. 2 Copyright 1997 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
0022-3565/97/2832-0648$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 283, No. 2 Copyright 1997 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase Type 1 and 2 Enzyme by Aqueous Extract of Elaeagnus Angustifolia in Mice
 Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase Type 1 and 2 Enzyme by Aqueous Extract of Elaeagnus Angustifolia in Mice Shahedeh Farahbakhsh 1, Sedigheh Arbabian 1, Fatemeh Emami 1, Banafsheh Rastegar Moghadam 1, Hassan
Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase Type 1 and 2 Enzyme by Aqueous Extract of Elaeagnus Angustifolia in Mice Shahedeh Farahbakhsh 1, Sedigheh Arbabian 1, Fatemeh Emami 1, Banafsheh Rastegar Moghadam 1, Hassan
BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS American Neurological Association Published by Wiley-Liss, Inc., through Wiley Subscription Services
 BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS Gene Transfer of Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Reduces Neuropathic Pain Shuanglin Hao, MD, PhD, 1 Marina Mata, MD, 1 Darren Wolfe, PhD, 2 Joseph C. Glorioso, PhD, 2 and David J. Fink,
BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS Gene Transfer of Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Reduces Neuropathic Pain Shuanglin Hao, MD, PhD, 1 Marina Mata, MD, 1 Darren Wolfe, PhD, 2 Joseph C. Glorioso, PhD, 2 and David J. Fink,
Materials and Methods
 Anesthesiology 2002; 97:1263 73 2002 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Gabapentin and Pregabalin Can Interact Synergistically with Naproxen to Produce Antihyperalgesia
Anesthesiology 2002; 97:1263 73 2002 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Gabapentin and Pregabalin Can Interact Synergistically with Naproxen to Produce Antihyperalgesia
Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical Allodynia in a Rat Model of Postoperative Pain
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2013 April; Vol. 26, No. 2: 125-129 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.2.125 Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical
Original Article Korean J Pain 2013 April; Vol. 26, No. 2: 125-129 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.2.125 Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 METHODS Mice and rats. Behavioural experiments were performed in male and female 7 12 week old mice or in male 7 10 week old Wistar rats. Permissions for the animal experiments have been obtained from
METHODS Mice and rats. Behavioural experiments were performed in male and female 7 12 week old mice or in male 7 10 week old Wistar rats. Permissions for the animal experiments have been obtained from
GABA B Receptor Agonist Baclofen Has Non-Specific Antinociceptive Effect in the Model of Peripheral Neuropathy in the Rat
 Physiol. Res. 3: 31-3, GABA B Receptor Agonist Baclofen Has Non-Specific Antinociceptive Effect in the Model of Peripheral Neuropathy in the Rat M. FRANĚK, Š. VACULÍN, R. ROKYTA Department of Normal, Pathological
Physiol. Res. 3: 31-3, GABA B Receptor Agonist Baclofen Has Non-Specific Antinociceptive Effect in the Model of Peripheral Neuropathy in the Rat M. FRANĚK, Š. VACULÍN, R. ROKYTA Department of Normal, Pathological
A Series of D-Amino Acid Oxidase Inhibitors Specifically Prevents and Reverses Formalin-Induced Tonic Pain in Rats
 0022-3565/11/3361-282 293$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 336, No. 1 Copyright 2011 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 172353/3653734
0022-3565/11/3361-282 293$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 336, No. 1 Copyright 2011 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 172353/3653734
San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001
 PAIN San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001 CONGENITAL INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional)
PAIN San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001 CONGENITAL INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional)
Modulatory Role of Morphine and Gabapentin as Anti-inflammatory Agents Alone and on Coadministration. Edema
 American Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics Original Article Modulatory Role of Morphine and Gabapentin as Anti-inflammatory Agents Alone and on Coadministration with Diclofenac in Rat Paw
American Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics Original Article Modulatory Role of Morphine and Gabapentin as Anti-inflammatory Agents Alone and on Coadministration with Diclofenac in Rat Paw
Role of bradykinin in postprandial hypotension in humans
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 777-781 Postprandial bradykinin release ISSN 0100-879X 777 Role of bradykinin in postprandial hypotension in humans S. Tumilero 1, L. Gallo
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 777-781 Postprandial bradykinin release ISSN 0100-879X 777 Role of bradykinin in postprandial hypotension in humans S. Tumilero 1, L. Gallo
PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus. MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive
 PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive MEASUREMENT OF PAIN: A BIG PROBLEM Worst pain ever
PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive MEASUREMENT OF PAIN: A BIG PROBLEM Worst pain ever
Zinc and water intake in rats: investigation of adrenergic and opiatergic central mechanisms
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1217-1222 Opioid and zinc interplay in isoproterenol-induced drinking ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1217 Zinc and water intake in rats:
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1217-1222 Opioid and zinc interplay in isoproterenol-induced drinking ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1217 Zinc and water intake in rats:
Yan-Ping Chen, Shao-Rui Chen, and Hui-Lin Pan
 0022-3565/05/3152-696 703$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 315, No. 2 Copyright 2005 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 91314/3054541
0022-3565/05/3152-696 703$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 315, No. 2 Copyright 2005 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 91314/3054541
Update on the Neurophysiology of Pain Transmission and Modulation: Focus on the NMDA-Receptor
 S2 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Proceedings Supplement NMDA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia Update on the Neurophysiology of Pain Transmission
S2 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Proceedings Supplement NMDA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia Update on the Neurophysiology of Pain Transmission
Tonic Descending Facilitation from the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla Mediates Opioid-Induced Abnormal Pain and Antinociceptive Tolerance
 The Journal of Neuroscience, January 1, 2001, 21(1):279 286 Tonic Descending Facilitation from the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla Mediates Opioid-Induced Abnormal Pain and Antinociceptive Tolerance Todd
The Journal of Neuroscience, January 1, 2001, 21(1):279 286 Tonic Descending Facilitation from the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla Mediates Opioid-Induced Abnormal Pain and Antinociceptive Tolerance Todd
Local administration of 9 -tetrahydrocannabinol attenuates capsaicin-induced thermal nociception in rhesus monkeys: a peripheral cannabinoid action
 Psychopharmacology (1999) 143:322 326 Springer-Verlag 1999 RAPID COMMUNICATION Mei-Chuan Ko James H. Woods Local administration of 9 -tetrahydrocannabinol attenuates capsaicin-induced thermal nociception
Psychopharmacology (1999) 143:322 326 Springer-Verlag 1999 RAPID COMMUNICATION Mei-Chuan Ko James H. Woods Local administration of 9 -tetrahydrocannabinol attenuates capsaicin-induced thermal nociception
A cascade of cytokines mediates mechanical inflammatory hypernociception in mice. Methods
 A cascade of cytokines mediates mechanical inflammatory hypernociception in mice T. M. Cunha*, W. A. Verri, Jr.*, J. S. Silva, S. Poole, F. Q. Cunha*, and S. H. Ferreira* Departments of *Pharmacology and
A cascade of cytokines mediates mechanical inflammatory hypernociception in mice T. M. Cunha*, W. A. Verri, Jr.*, J. S. Silva, S. Poole, F. Q. Cunha*, and S. H. Ferreira* Departments of *Pharmacology and
ONLINE. Key words: Tramadol; Tramadol-N-oxide; Rats; Peripheral nerves; Local anesthesia; Analgesia
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research Online Provisional Version ISSN 0100-879X This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research Online Provisional Version ISSN 0100-879X This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full
Non-opioidergic mechanism mediating morphine-induced. antianalgesia in the mouse spinal cord. Hsiang-En Wu, Jonathan Thompson, Han-Sen Sun,
 JPET This Fast article Forward. has not been Published copyedited on and formatted. March 3, The 2004 final version as DOI:10.1124/jpet.104.065334 may differ from this version. JPET #65334 Non-opioidergic
JPET This Fast article Forward. has not been Published copyedited on and formatted. March 3, The 2004 final version as DOI:10.1124/jpet.104.065334 may differ from this version. JPET #65334 Non-opioidergic
Pain. Types of Pain. Types of Pain 8/21/2013
 Pain 1 Types of Pain Acute Pain Complex combination of sensory, perceptual, & emotional experiences as a result of a noxious stimulus Mediated by rapidly conducting nerve pathways & associated with increased
Pain 1 Types of Pain Acute Pain Complex combination of sensory, perceptual, & emotional experiences as a result of a noxious stimulus Mediated by rapidly conducting nerve pathways & associated with increased
Centrally Mediated Anti-Hyperalgesic and Anti-Allodynic Effect of Tolperisone in Spared Nerve Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain
 Centrally Mediated Anti-Hyperalgesic and Anti-Allodynic Effect of Tolperisone in Spared Nerve Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain Keyur S Patel *, Punam D Sachdeva Department of Pharmacology, A.R.College
Centrally Mediated Anti-Hyperalgesic and Anti-Allodynic Effect of Tolperisone in Spared Nerve Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain Keyur S Patel *, Punam D Sachdeva Department of Pharmacology, A.R.College
Special Issue on Pain and Itch
 Special Issue on Pain and Itch Title: Recent Progress in Understanding the Mechanisms of Pain and Itch Guest Editor of the Special Issue: Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Chronic pain is a major health problem world-wide.
Special Issue on Pain and Itch Title: Recent Progress in Understanding the Mechanisms of Pain and Itch Guest Editor of the Special Issue: Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Chronic pain is a major health problem world-wide.
Opioidergic orofacial antinociception induced by electroacupuncture at acupoint St36
 St36 Brazilian acupoint Journal of stimulation Medical and induces Biological opioidergic Research (2008) orofacial 41: 621-626 antinociception ISSN 0100-879X 621 Opioidergic orofacial antinociception
St36 Brazilian acupoint Journal of stimulation Medical and induces Biological opioidergic Research (2008) orofacial 41: 621-626 antinociception ISSN 0100-879X 621 Opioidergic orofacial antinociception
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation
 Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Analgesics, pain and tolerance: The St John s discussion
 EDITORIAL Analgesics, pain and tolerance: The St John s discussion Four of the articles in the present issue of Pain Research & Management discuss preclinical issues relevant to understanding the changes
EDITORIAL Analgesics, pain and tolerance: The St John s discussion Four of the articles in the present issue of Pain Research & Management discuss preclinical issues relevant to understanding the changes
Axotomy increases NADPH-diaphorase activity in the dorsal root ganglia and lumbar spinal cord of the turtle Trachemys dorbigni
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 489-493 NADPH-d after peripheral axotomy in the turtle ISSN 0100-879X 489 Axotomy increases NADPH-diaphorase activity in the dorsal root
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 489-493 NADPH-d after peripheral axotomy in the turtle ISSN 0100-879X 489 Axotomy increases NADPH-diaphorase activity in the dorsal root
Interaction among NMDA receptor-, NMDA glycine site- and AMPA receptor antagonists in spinally mediated analgesia
 LABORATORY INVESTIGATION 693 Tomoki Nishiyama MD PhD Interaction among NMDA receptor-, NMDA glycine site- and AMPA receptor antagonists in spinally mediated analgesia Purpose: The NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate)
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION 693 Tomoki Nishiyama MD PhD Interaction among NMDA receptor-, NMDA glycine site- and AMPA receptor antagonists in spinally mediated analgesia Purpose: The NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate)
Materials and Methods
 Anesthesiology 2003; 98:203 8 2003 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Intrathecal Lidocaine Reverses Tactile Allodynia Caused by Nerve Injuries and Potentiates
Anesthesiology 2003; 98:203 8 2003 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Intrathecal Lidocaine Reverses Tactile Allodynia Caused by Nerve Injuries and Potentiates
Diabetic Complications Consortium
 Diabetic Complications Consortium Application Title: Cathepsin S inhibition and diabetic neuropathy Principal Investigator: Nigel A Calcutt 1. Project Accomplishments: We investigated the efficacy of cathepsin
Diabetic Complications Consortium Application Title: Cathepsin S inhibition and diabetic neuropathy Principal Investigator: Nigel A Calcutt 1. Project Accomplishments: We investigated the efficacy of cathepsin
Supraspinal contributions to hyperalgesia
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 96, pp. 7687 7692, July 1999 Colloquium Paper This paper was presented at the National Academy of Sciences colloquium The Neurobiology of Pain, held December 11 13, 1998,
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 96, pp. 7687 7692, July 1999 Colloquium Paper This paper was presented at the National Academy of Sciences colloquium The Neurobiology of Pain, held December 11 13, 1998,
Infusions of AP5 into the basolateral amygdala impair the formation, but not the expression, of step-down inhibitory avoidance
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2) 33: 829-834 Amygdaloid NMDA receptors and fear memory ISSN 1-879X 829 Infusions of AP5 into the basolateral amygdala impair the formation, but not
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2) 33: 829-834 Amygdaloid NMDA receptors and fear memory ISSN 1-879X 829 Infusions of AP5 into the basolateral amygdala impair the formation, but not
Pharmacological Evidence for the Role of Nitric Oxide-cGMP in Antinociception
 Pharmacological Evidence for the Role of Nitric Oxide-cGMP in Antinociception Ehab S. EL Desoky, MD, PhD* Ihab A. Fouad, PhD *Pharmacology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University, Assiut, Egypt
Pharmacological Evidence for the Role of Nitric Oxide-cGMP in Antinociception Ehab S. EL Desoky, MD, PhD* Ihab A. Fouad, PhD *Pharmacology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University, Assiut, Egypt
Antisense mrna for NPY-Y 1 receptor in the medial preoptic area increases prolactin secretion
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1161-1165 NPY-Y 1 receptors in the MPOA and PRL secretion ISSN 0100-879X 1161 Antisense mrna for NPY-Y 1 receptor in the medial preoptic
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1161-1165 NPY-Y 1 receptors in the MPOA and PRL secretion ISSN 0100-879X 1161 Antisense mrna for NPY-Y 1 receptor in the medial preoptic
Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
 University of Kentucky From the SelectedWorks of Renee R. Donahue 2001 Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
University of Kentucky From the SelectedWorks of Renee R. Donahue 2001 Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice.
 Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D.,
Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D.,
Sensory Assessment of Regional Analgesia in Humans
 REVIEW ARTICLE Dennis M. Fisher, M.D., Editor-in-Chief Anesthesiology 2000; 93:1517 30 2000 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Sensory Assessment of Regional
REVIEW ARTICLE Dennis M. Fisher, M.D., Editor-in-Chief Anesthesiology 2000; 93:1517 30 2000 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Sensory Assessment of Regional
Analgesic effects of the COX-2 inhibitor parecoxib on surgical pain through suppression of spinal ERK signaling
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 275-279, 2013 Analgesic effects of the COX-2 inhibitor parecoxib on surgical pain through suppression of spinal ERK signaling YA-JING GUO 1, XU-DAN SHI 2, DI FU
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 275-279, 2013 Analgesic effects of the COX-2 inhibitor parecoxib on surgical pain through suppression of spinal ERK signaling YA-JING GUO 1, XU-DAN SHI 2, DI FU
Animal models of fibromyalgia
 DeSantana et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy REVIEW Animal models of fibromyalgia Josimari M DeSantana 1,2,3, Kamilla ML da Cruz 3 and Kathleen A Sluka 4* Abstract Animal models of disease states are
DeSantana et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy REVIEW Animal models of fibromyalgia Josimari M DeSantana 1,2,3, Kamilla ML da Cruz 3 and Kathleen A Sluka 4* Abstract Animal models of disease states are
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat. Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons Hawon Cho, Young Duk Yang, Jesun Lee, Byeongjoon Lee, Tahnbee Kim Yongwoo Jang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons Hawon Cho, Young Duk Yang, Jesun Lee, Byeongjoon Lee, Tahnbee Kim Yongwoo Jang,
GABA B MEDIATED ANALGESIA IN TONIC PAIN IN MONKEYS
 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1993; 37(3): 189-193 GABA B MEDIATED ANALGESIA IN TONIC PAIN IN MONKEYS RATNA SHARMA, RASHMI MATHUR AND USHA NAYAR Department of Physiology, All India Institute ofmedical Sciences,
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1993; 37(3): 189-193 GABA B MEDIATED ANALGESIA IN TONIC PAIN IN MONKEYS RATNA SHARMA, RASHMI MATHUR AND USHA NAYAR Department of Physiology, All India Institute ofmedical Sciences,
Journal of Biomedical Science
 Journal of Biomedical Science BioMed Central Research Antinociceptive actions of honokiol and magnolol on glutamatergic and inflammatory pain Yi-Ruu Lin 1, Hwei-Hsien Chen 1, Yu-Chin Lin 2, Chien-Hsin
Journal of Biomedical Science BioMed Central Research Antinociceptive actions of honokiol and magnolol on glutamatergic and inflammatory pain Yi-Ruu Lin 1, Hwei-Hsien Chen 1, Yu-Chin Lin 2, Chien-Hsin
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016)
 International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) Analgesic Contrast of Diverse Administrations of Botulinum Neurotoxin A (BoTN/A) Using Rat Neuropathic Pain Model Qiong-Fang YANG1,3,
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) Analgesic Contrast of Diverse Administrations of Botulinum Neurotoxin A (BoTN/A) Using Rat Neuropathic Pain Model Qiong-Fang YANG1,3,
Inhibition of Inflammatory Pain by Activating B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Signal Pathway in Nociceptive Sensory Neurons
 The Journal of Neuroscience, August 11, 2010 30(32):10927 10938 10927 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Inhibition of Inflammatory Pain by Activating B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Signal Pathway in Nociceptive
The Journal of Neuroscience, August 11, 2010 30(32):10927 10938 10927 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Inhibition of Inflammatory Pain by Activating B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Signal Pathway in Nociceptive
A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch
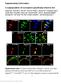 Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
University of Colorado-Boulder
 University of Colorado-Boulder Activated Glia as Culprits in Opposing Opioid Analgesia & Driving Tolerance, Dependence & Reward: Role of a Non-classical Non-classical Opioid Receptor Linda R. Watkins Psychology
University of Colorado-Boulder Activated Glia as Culprits in Opposing Opioid Analgesia & Driving Tolerance, Dependence & Reward: Role of a Non-classical Non-classical Opioid Receptor Linda R. Watkins Psychology
Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture the student should be familiar with: 1. The relationship between nociception
Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture the student should be familiar with: 1. The relationship between nociception
Effect of chronic oral administration of a low dose of captopril on sodium appetite of hypothyroid rats. Influence of aldosterone treatment
 Brazilian Sodium appetite Journal of in Medical hypothyroid and rats Biological Research (21) 34: 47-411 ISSN 1-879X Short Communication 47 Effect of chronic oral administration of a low dose of captopril
Brazilian Sodium appetite Journal of in Medical hypothyroid and rats Biological Research (21) 34: 47-411 ISSN 1-879X Short Communication 47 Effect of chronic oral administration of a low dose of captopril
Spinal Cord Injury Pain. Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018
 Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
The biochemical origin of pain: The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response: Inflammatory profile of pain syndromes
 The biochemical origin of pain: The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response: Inflammatory profile of pain syndromes 1 Medical Hypothesis 2007, Vol. 69, pp. 1169 1178 Sota Omoigui
The biochemical origin of pain: The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response: Inflammatory profile of pain syndromes 1 Medical Hypothesis 2007, Vol. 69, pp. 1169 1178 Sota Omoigui
Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior
 Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 98 (2011) 188 195 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pharmbiochembeh Granulocyte-Colony
Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 98 (2011) 188 195 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pharmbiochembeh Granulocyte-Colony
Original Article Upregulation of neuregulin-1 reverses signs of neuropathic pain in rats
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(9):5916-5921 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001263 Original Article Upregulation of neuregulin-1 reverses signs of neuropathic pain in rats Guojun Wang 1,2*, Dawei Dai
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(9):5916-5921 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001263 Original Article Upregulation of neuregulin-1 reverses signs of neuropathic pain in rats Guojun Wang 1,2*, Dawei Dai
Dezocine Antagonizes Morphine Analgesia upon Simultaneous Administration in Rodent Models of Acute Nociception
 Pain Physician 2017; 20:E401-E409 ISSN 2150-1149 Animal Study Dezocine Antagonizes Morphine Analgesia upon Simultaneous Administration in Rodent Models of Acute Nociception Na-Na Li, MS 1, Ya-Qin Huang,
Pain Physician 2017; 20:E401-E409 ISSN 2150-1149 Animal Study Dezocine Antagonizes Morphine Analgesia upon Simultaneous Administration in Rodent Models of Acute Nociception Na-Na Li, MS 1, Ya-Qin Huang,
Mechanism of Pain Production
 Mechanism of Pain Production Pain conducting nerve fibers are small myelinated (A-delta) or unmyelinated nerve fibers (C-fibers). Cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or sensory ganglia of
Mechanism of Pain Production Pain conducting nerve fibers are small myelinated (A-delta) or unmyelinated nerve fibers (C-fibers). Cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or sensory ganglia of
PLATELET-ACTIVATING FACTOR AFFECTS NOCICEPTION IN RATS AT CEREBRAL SITES OF ACTION
 PLATELET-ACTIVATING FACTOR AFFECTS NOCICEPTION IN RATS AT CEREBRAL SITES OF ACTION Lisa A. Teather 1,2 & Richard J. Wurtman 1 1 Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
PLATELET-ACTIVATING FACTOR AFFECTS NOCICEPTION IN RATS AT CEREBRAL SITES OF ACTION Lisa A. Teather 1,2 & Richard J. Wurtman 1 1 Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
The peripheral antinociceptive e ect induced by morphine is associated with ATP-sensitive K + channels
 (2000) 129, 110 ± 114 ã 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/bjp The peripheral antinociceptive e ect induced by morphine is associated with ATP-sensitive
(2000) 129, 110 ± 114 ã 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/bjp The peripheral antinociceptive e ect induced by morphine is associated with ATP-sensitive
Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia
 University of New England DUNE: DigitalUNE Nurse Anesthesia Capstones School of Nurse Anesthesia 3-2015 Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia Lisa Nieder University of New England Follow this and additional works
University of New England DUNE: DigitalUNE Nurse Anesthesia Capstones School of Nurse Anesthesia 3-2015 Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia Lisa Nieder University of New England Follow this and additional works
A Single Trial of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Reduces Chronic Neuropathic Pain Following Median Nerve Injury in Rats
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2014, 232, 207-214Upper-Limb TENS Reduces Neuropathic Pain 207 A Single Trial of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Reduces Chronic Neuropathic Pain Following Median Nerve
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2014, 232, 207-214Upper-Limb TENS Reduces Neuropathic Pain 207 A Single Trial of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Reduces Chronic Neuropathic Pain Following Median Nerve
Defense reaction induced by a metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist microinjected into the dorsal periaqueductal gray of rats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 3: 1533-1537 Behavioral effects of injected into PAG ISSN 1-79X Short Communication 1533 Defense reaction induced by a metabotropic glutamate
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 3: 1533-1537 Behavioral effects of injected into PAG ISSN 1-79X Short Communication 1533 Defense reaction induced by a metabotropic glutamate
A role for uninjured afferents in neuropathic pain
 Acta Physiologica Sinica, October 25, 2008, 60 (5): 605-609 http://www.actaps.com.cn 605 Review A role for uninjured afferents in neuropathic pain Richard A. Meyer 1,2,3,*, Matthias Ringkamp 1 Departments
Acta Physiologica Sinica, October 25, 2008, 60 (5): 605-609 http://www.actaps.com.cn 605 Review A role for uninjured afferents in neuropathic pain Richard A. Meyer 1,2,3,*, Matthias Ringkamp 1 Departments
Available online at
 Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 37, no. 4, 2007 349 Effects of Intrathecal Injection of Prednisolone Acetate on Expression of NR2B Subunit and nnos
Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 37, no. 4, 2007 349 Effects of Intrathecal Injection of Prednisolone Acetate on Expression of NR2B Subunit and nnos
Virtually everyone has experienced pain in one
 Transfer of Advances in Sciences into Dental Education Recent Insights into Brainstem Mechanisms Underlying Craniofacial Pain Barry J. Sessle, B.D.S., M.D.S., B.Sc., Ph.D., F.R.S.C., D.Sc. (honorary) Abstract:
Transfer of Advances in Sciences into Dental Education Recent Insights into Brainstem Mechanisms Underlying Craniofacial Pain Barry J. Sessle, B.D.S., M.D.S., B.Sc., Ph.D., F.R.S.C., D.Sc. (honorary) Abstract:
Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy
 Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy David Kendall & Bengt von Mentzer; PharmNovo AB/UK Alex Conibear & Eamonn Kelly, University of Bristol Junaid Asghar,
Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy David Kendall & Bengt von Mentzer; PharmNovo AB/UK Alex Conibear & Eamonn Kelly, University of Bristol Junaid Asghar,
suppressed by endogenous opioid peptides. This opioid-mediated inhibition seems to Leicestershire LE12 5RD
 Journal of Physiology (1992), 449, pp. 493-501 493 With 3 figures Printed in Great Britain OPIOIDERGIC INHIBITION OF FLEXOR AND EXTENSOR REFLEXES IN THE RABBIT BY R. W. CLARKE, FIONA J. GALLOWAY, J. HARRIS,
Journal of Physiology (1992), 449, pp. 493-501 493 With 3 figures Printed in Great Britain OPIOIDERGIC INHIBITION OF FLEXOR AND EXTENSOR REFLEXES IN THE RABBIT BY R. W. CLARKE, FIONA J. GALLOWAY, J. HARRIS,
Participation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in experimental neuropathic pain induced by sciatic nerve transection
 ISSN 0100-879X Volume 43 (04) 325-408 April 2010 BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES AND CLINICAL INVESTIGATION Braz J Med Biol Res, March 2010, Volume 43(4) 367-376 Participation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in
ISSN 0100-879X Volume 43 (04) 325-408 April 2010 BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES AND CLINICAL INVESTIGATION Braz J Med Biol Res, March 2010, Volume 43(4) 367-376 Participation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in
Glial activation in the rostroventromedial medulla promotes descending facilitation to mediate inflammatory hypersensitivity
 European Journal of Neuroscience European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 30, pp. 229 241, 2009 doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06813.x NEUROSYSTEMS Glial activation in the rostroventromedial medulla promotes
European Journal of Neuroscience European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 30, pp. 229 241, 2009 doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06813.x NEUROSYSTEMS Glial activation in the rostroventromedial medulla promotes
The Effect of Intrathecal Gabapentin on Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Rats Induced by Spinal Nerve Ligation
 J Korean Med Sci 2002; 17: 225-9 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences The Effect of Intrathecal Gabapentin on Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Rats Induced
J Korean Med Sci 2002; 17: 225-9 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences The Effect of Intrathecal Gabapentin on Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Rats Induced
TITLE PAGE. Effects of intrathecal SNC80, a delta receptor ligand, on nociceptive threshold and
 JPET Fast This article Forward. has not Published been copyedited on and August formatted. 26, The 2013 final version as DOI:10.1124/jpet.113.206573 may differ from this version. TITLE PAGE Effects of
JPET Fast This article Forward. has not Published been copyedited on and August formatted. 26, The 2013 final version as DOI:10.1124/jpet.113.206573 may differ from this version. TITLE PAGE Effects of
Acute Inhibition of Ca 2 /Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II Reverses Experimental Neuropathic Pain in Mice
 0022-3565/09/3302-650 659$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 330, No. 2 Copyright 2009 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 152165/3499060
0022-3565/09/3302-650 659$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 330, No. 2 Copyright 2009 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 152165/3499060
Evaluation of electromyographic activity and heart rate responses to isometric exercise. The role played by muscular mass and type
 Brazilian Electromyography Journal of and Medical heart and rate Biological responses Research to isometric (1999) exercise 32: 115-120 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 115 Evaluation of electromyographic
Brazilian Electromyography Journal of and Medical heart and rate Biological responses Research to isometric (1999) exercise 32: 115-120 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 115 Evaluation of electromyographic
Central lead administration inhibits water intake and sodium appetite in rats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (999) : -8 Lead and central control of water intake and sodium appetite ISSN -89X Short Communication Central lead administration inhibits water intake
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (999) : -8 Lead and central control of water intake and sodium appetite ISSN -89X Short Communication Central lead administration inhibits water intake
What it Takes to be a Pain
 What it Takes to be a Pain Pain Pathways and the Neurophysiology of pain Dennis S. Pacl, MD, FACP, FAChPM Austin Palliative Care/ Hospice Austin A Definition of Pain complex constellation of unpleasant
What it Takes to be a Pain Pain Pathways and the Neurophysiology of pain Dennis S. Pacl, MD, FACP, FAChPM Austin Palliative Care/ Hospice Austin A Definition of Pain complex constellation of unpleasant
Central and peripheral sites of action for CB 2 receptor mediated analgesic activity in chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain models in rats
 8.. British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:./j.76-8..6.x www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPERbph_6 Central and peripheral sites of action for CB receptor mediated analgesic activity in chronic inflammatory
8.. British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:./j.76-8..6.x www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPERbph_6 Central and peripheral sites of action for CB receptor mediated analgesic activity in chronic inflammatory
LACK OF A CEILING EFFECT FOR INTRATHECAL BUPRENORPHINE ON C FIBRE MEDIATED SOMATOSYMPATHETIC REFLEXES
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 1993; 71: 528-533 LACK OF A CEILING EFFECT FOR INTRATHECAL BUPRENORPHINE ON C FIBRE MEDIATED SOMATOSYMPATHETIC REFLEXES C. WANG, M. K. CHAKRABARTI AND J. G. WHITWAM SUMMARY
British Journal of Anaesthesia 1993; 71: 528-533 LACK OF A CEILING EFFECT FOR INTRATHECAL BUPRENORPHINE ON C FIBRE MEDIATED SOMATOSYMPATHETIC REFLEXES C. WANG, M. K. CHAKRABARTI AND J. G. WHITWAM SUMMARY
Abstract. R. Roesler 1, J. Quevedo 1, C. Rodrigues 1, M. Madruga 1, M.R.M. Vianna 1 and M.B.C. Ferreira 2
 Brazilian Amygdaloid Journal non-nmda of Medical receptors and Biological and memory Research expression (1999) 32: 349-353 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 349 Increased training prevents the impairing
Brazilian Amygdaloid Journal non-nmda of Medical receptors and Biological and memory Research expression (1999) 32: 349-353 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 349 Increased training prevents the impairing
PAIN & ANALGESIA. often accompanied by clinical depression. fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue, etc. COX 1, COX 2, and COX 3 (a variant of COX 1)
 Pain - subjective experience associated with detection of tissue damage ( nociception ) acute - serves as a warning chronic - nociception gone bad often accompanied by clinical depression fibromyalgia,
Pain - subjective experience associated with detection of tissue damage ( nociception ) acute - serves as a warning chronic - nociception gone bad often accompanied by clinical depression fibromyalgia,
Introduction. Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive
 642 The Journal of Neuroscience, January 21, 2004 24(3):642 651 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Changes in the Effect of Spinal Prostaglandin E 2 during Inflammation: Prostaglandin E (EP1 EP4) Receptors in
642 The Journal of Neuroscience, January 21, 2004 24(3):642 651 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Changes in the Effect of Spinal Prostaglandin E 2 during Inflammation: Prostaglandin E (EP1 EP4) Receptors in
Role of complement C5a in mechanical inflammatory hypernociception: potential use of C5a receptor antagonists to control inflammatory pain
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2008) 153, 1043 1053 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 1188/08 $30.00 www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Role of complement C5a in mechanical inflammatory
British Journal of Pharmacology (2008) 153, 1043 1053 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 1188/08 $30.00 www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Role of complement C5a in mechanical inflammatory
Role of CaMKIIα Leading to Inflammatory and. Neuropathic Pain
 Role of CaMKIIα Leading to Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain BY YAN CHEN M.S. (Biology), Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2004 B.S. (Biology), Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2002 THESIS Submitted
Role of CaMKIIα Leading to Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain BY YAN CHEN M.S. (Biology), Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2004 B.S. (Biology), Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2002 THESIS Submitted
