An electronic pressure-meter nociception paw test for mice
|
|
|
- Jordan Fletcher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (24) 37: Mouse paw pressure-meter test ISSN 1-879X 41 An electronic pressure-meter nociception paw test for mice T.M. Cunha, W.A. Verri Jr., G.G. Vivancos, I.F. Moreira, S. Reis, C.A. Parada, F.Q. Cunha and S.H. Ferreira Departamento de Farmacologia, Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto, Universidade de São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, SP, Brasil Correspondence S.H. Ferreira Departamento de Farmacologia FMRP, USP Av. Bandeirantes, Ribeirão Preto, SP Brasil Fax: Research supported by CNPq, CAPES, FAPESP and PRONEX. These authors contributed equally to this study. Received June 2, 23 Accepted December 8, 23 Abstract The aim of the present investigation was to describe and validate an electronic mechanical test for quantification of the inteity of inflammatory nociception in mice. The electronic pressure-meter test coists of inducing the animal hindpaw flexion reflex by poking the plantar region with a polypropylene pipette tip adapted to a hand-held force traducer. This method was compared to the classical von Frey filaments test in which pressure inteity is automatically recorded after the nociceptive hindpaw flexion reflex. The electronic pressure-meter and the von Frey filaments were used to detect time versus treatment interactio of carrageenininduced hypernociception. In two separate experiments, the electronic pressure-meter was more seitive than the von Frey filaments for the detection of the increase in nociception (hypernociception) induced by small doses of carrageenin (3 µg). The electronic pressure-meter detected the antinociceptive effect of noteroidal drugs in a dose-dependent manner. Indomethacin administered intraperitoneally ( mg/kg) or intraplantarly (3-3 µg/ paw) prevented the hyperseitive effect of carrageenin (1 µg/ paw). The electronic pressure-meter also detected the hypernociceptive effect of prostaglandin E 2 (PGE 2 ; 1-1 ng) in a dosedependent manner. The hypernociceptive effect of PGE 2 (1 ng) was blocked by dipyrone (1 and 32 µg/paw) but not by intraplantar administration of indomethacin (3 µg/paw). The present results validate the use of the electronic pressure-meter as more seitive than the von Frey filaments in mice. Furthermore, it is an objective and quantitative nociceptive test for the evaluation of the peripheral antinociceptive effect of anti-inflammatory analgesic drugs, which inhibit prostaglandin synthesis (indomethacin) or directly block the ongoing hypernociception (dipyrone). Key words Hyperalgesia Nociception Indomethacin Dipyrone von Frey filaments Introduction The type and site of application of a nociceptive stimulus, the seitivity to analgesic drugs, as well as a typical innate behavioral respoe (end-point) characterize nociceptive tests. There is a growing coeus in the literature that mice are the animals of choice for experimental studies, including immunological, physiopathological and inflammatory studies, because bioengineered specific reagents, such as recombinant cytokines and monoclonal antibodies, are available mainly for this species. Moreover, mice
2 42 T.M. Cunha et al. are also used for the generation of tragenic and knockout animals for different molecules, including immune and inflammatory mediators, and also for their specific receptors (1). The most popular test for the investigation of nociception in this animal species is the writhing test (2), quantified by the frequency of abdominal cotrictio induced by inflammatory stimuli (i.e., acetic acid and zymosan). The tail flick and the formalin paw tests have also been exteively used (2). Although the writhing test is quite seitive for detection of analgesic compounds, its therapeutic predictivity is inferior to the classical Randall and Selitto nociceptive test in rats (2). However, with the tests (except for the classical Randall and Selitto test), it is rather difficult to determine if an analgesic is causing antinociception by blocking the seitization or by the activation of the nociceptors, phenomena that characterize inflammatory pain, which has a quite different mechanism. Seitization of the nociceptors (hypernociception) is a metabotropic event involving at least the stimulation of the camp/pka/ca 2 or the phospholipase/pkc/ Ca 2 pathways (3-8). In recent years, the classical von Frey filaments test (9) has become popular among the mechanical tests used for rats and mice (1,11). This mechanical test has an advantage over the writhing test and formalin test in mice because it distinguishes between the two components of inflammatory pain, i.e., seitization and activation of the nociceptor. In the present study, we standardized and evaluated an electronic version of the von Frey filaments test for mice. An electronic pressure-meter test has been described for use in huma and rats (12,13). We induced an inflammatory process and seitized the paws of mice with different doses of carrageenin and prostaglandin E 2 (PGE 2 ), respectively, to compare the seitivity of the von Frey filaments and the electronic pressuremeter tests. We also used paws treated with carrageenin or with PGE 2 to compare the seitivity of the tests in detecting the analgesic action of indomethacin, a cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor or dipyrone, a direct-acting anti-hyperalgesic drug (14-1). Material and Methods Animals The experiments were performed on 25-3-g Swiss mice (University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, SP, Brazil) housed in the animal care facility of the School of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto and taken to the testing room at least 1 h before the experiment. Food and water were available ad libitum. All behavioral testing was performed between 9: am and 4: pm. The mice were used only once. Animal care and handling procedures were in accordance with the International Association for Study of Pain (IASP) guidelines on the use of animals in pain research. Efforts were made to minimize the number of animals used and their suffering. von Frey filaments and electronic pressuremeter paw tests for mice In a quiet room, mice were placed in acrylic cages (12 x 1 x 17 cm high) with a wire grid floor 15-3 min before testing. During this adaptation period, the paws were poked 2-3 times. Before paw stimulation, the animals were quiet, without exploratory movements or defecation and not resting on their paws. In these experiments, we used either a series of von Frey filaments (Stoelting, Chicago, IL, USA) with logarithmically incremental stiffness (-1.17 to.74 log of force, g) or a pressure-meter which coisted of a handheld force traducer fitted with a.5 mm 2 polypropylene tip (electronic von Frey anesthesiometer, IITC Inc., Life Science Itruments, Woodland Hills, CA, USA) (see accompanying paper, Ref. 17). The investiga-
3 Mouse paw pressure-meter test 43 tor was trained to apply the filaments or the polypropylene tip perpendicularly to the central area of the hindpaw with a gradual increase in pressure. A tilted mirror below the grid provided a clear view of the animal s hindpaw. The test coisted of poking a hindpaw to provoke a flexion reflex followed by a clear flinch respoe after paw withdrawal. Each one of the von Frey filaments was applied for approximately 3-4 s to induce the end-point reflex. Testing was initiated with the filament handle marked 4.31, a value corresponding to.31 log of force (g) which is in the middle of the filament series. The respoe to this filament defined if a series of weaker or stronger filaments would be tested. The weakest filament able to elicit a respoe was taken to be the mechanical threshold (g). The results are reported as the log of force (g) calculated by subtracting the value of the measurements (log of force) after treatment from that of the first measurement for the von Frey test (before treatment). In the electronic pressure-meter test the inteity of the stimulus was automatically recorded when the paw was withdrawn. The maximal force applied was 18 g. The stimulation of the paw was repeated until the animal presented two similar measurements. If the results were incoistent (great difference in the baseline respoe compared to the other animals of the experiment), another animal was used. The results are reported as the withdrawal threshold (g) which was calculated by subtracting the values obtained after the treatments from the first measurement (before treatment). Drugs Dipyrone and PGE 2 were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). Carrageenin was obtained from FMC Corporation (Philadelphia, PA, USA), and indomethacin from Prodome Química e Farmacêutica (São Paulo, SP, Brazil). Carrageenin and dipyrone were diluted in sterile saline. A stock solution of PGE 2 was prepared in 1% ethanol, and further dilutio were made in saline; the final concentration of ethanol was 1%. Indomethacin was diluted in.1 M Tris-HCl buffer, ph 8.. Tris-HCl buffer alone was used for the control groups. Drug administration For local administration, drugs were injected subcutaneously into the plantar region of the hindpaws. A hypodermic 2-G needle was ierted into the skin of the second footpad (to avoid back flow) and the tip of the needle was introduced until the central area of the hindpaw, in the same place where filaments or the tip of the pressure-meter were applied. A volume of 25 µl was administered. For systemic treatment, drugs were injected intraperitoneally in a volume of 2 µl. Doses were calculated based on animal weight. Statistical analysis Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare the groups and doses over all times. The factors analyzed were treatments, time and time vs treatment interaction. When a significant time vs treatment interaction was detected, one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey test was performed for each time in order to distinguish dose effects. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test was also used for dose-respoe curves for a single time point. Results with P <.5 were coidered to be significant. Results Comparison of the seitivity for the detection of carrageenin-induced mechanical hypernociception by the electronic pressuremeter and the von Frey filaments tests Figure 1 shows that the carrageenin-
4 44 T.M. Cunha et al. induced hypernociception was detected by both the electronic pressure-meter (panel A; 1, 3, 1 and 3 µg/paw) and the classical von Frey filaments (panel B; 3, 1 and 3 µg/paw) tests. There was a significant increase in paw hypernociception with a time versus treatment interaction (ANOVA). The hypernociception induced by a low dose of carrageenin (3 µg/paw) was detected by the electronic pressure-meter but not by the von Frey filaments as a significant effect. Detection of the local and systemic effects of indomethacin on the carrageenin-induced hypernociception by the electronic pressuremeter test The systemic (panel A) and local (panel Figure 1. Time course of the hypernociception induced by intraplantar injectio of carrageenin (Cg) in mice detected with the electronic pressuremeter (A) and von Frey filaments (B). Saline was injected intraplantarly in the control group. The results are reported as the mean ± SEM for 4-5 animals per group and are representative of two separate experiments. P <.5 indicates a significant difference between time-points indicated by the brackets. = noignificant (two-way ANOVA and one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey test). Inteity of hypernociception ( withdrawal threshold, g) A Saline 1 µg Cg 3 µg Cg 1 µg Cg 3 µg Cg Time after injection (h) B 2 1 Inteity of hypernociception ( log force, g) Figure 2. Effect of indomethacin on carrageenin-induced hypernociception in mice measured with the electronic pressuremeter. Animals were pretreated with indomethacin 3 min before intraplantar injection of carrageenin (1 µg). Indomethacin was injected intraperitoneally (A, systemic, 1.8, 5 and 15 µg/kg) or subcutaneously into the mouse paw (B, local, 3, 1 and 3 µg/paw or contralateral (cl) paw, 1 and 3 µg/paw). Tris-HCl buffer (Tris) was injected in the control groups. The bars indicate the withdrawal threshold 3 h after carrageenin administration. The results are reported as the mean ± SEM for 5 animals per group and are representative of two separate experiments. P <.5 compared to control (Tris) (one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey test). Inteity of hypernociception ( withdrawal threshold, g) Systemic Local A B Tris Tris cl 3 3 cl Indomethacin (mg/kg) Indomethacin (µg/paw) Carrageenin (1 µg/paw)
5 Mouse paw pressure-meter test 45 B) inhibitory effects of indomethacin on the hypernociception induced by carrageenin (1 µg) is shown in Figure 2. Both systemic (1.8, 5 and 15 mg/kg, intraperitoneally) and local (3, 1 and 3 µg/paw) administration of indomethacin produced a dose-dependent (ANOVA) blockade of the hypernociceptive state induced by carrageenin (1 µg/paw). Although the local administration of indomethacin at a dose of 3 µg/paw had a systemic effect on carrageenin-induced hypernociception, the dose of 1 µg/paw had only a local effect since it was not able to inhibit the carrageenin-induced hypernociception in the contralateral paw. Dose-respoe curve for the hypernociception induced by intraplantar injection of PGE 2 in mice and its blockade by dipyrone but not by indomethacin The electronic pressure-meter was able to detect the statistically significant intraplantar effect of the three doses of PGE 2 (1, 3 and 1 ng; Figure 3, ANOVA). Paw hypernociception tended to increase with time (particularly with small doses) and there was a significant interaction between time and the different treatments (Figure 3A, ANOVA). Dipyrone (8, 1 and 32 µg; Figure 3C), but not indomethacin (Figure 3B), inhibited the PGE 2 -induced (1 ng) hypernociception in a dose-dependent manner (ANOVA). Discussion In the present study, we have used the word hypernociception (increased nociception) to describe the behavioral respoe induced by the application of von Frey filaments or the electronic pressure-meter. The terms allodynia and hyperalgesia describe distinct nociceptive symptoms in man (18,19). von Frey filaments have been used to measure increased experimental nociceptor seitivity referred to as allodynia or hyperalgesia by different investigators. In Inteity of hypernociception ( withdrawal treshold, g) Prostaglandin E 2 Indomethacin Dipyrone A B C Sal 1 ng 3 ng 1 ng Time after injection (h) Tris 5 Tris 3 Sal Systemic (mg/kg) Local (µg/paw) Local (µg/paw) Prostaglandin E 2 (1 ng/paw) Figure 3. Dose-respoe curve for the hypernociception induced by intraplantar injection of prostaglandin E 2 (PGE 2 ) in mice and its blockade by dipyrone but not by indomethacin measured with the electronic pressuremeter. Panel A shows the time course of the PGE 2 -induced hypernociception at the doses of 1, 3 and 1 ng/ paw. In Panel B, dipyrone (8, 1 and 32 µg/paw) or saline (Sal) was injected 2 h after PGE 2 (1 ng). In Panel C, pretreatment with indomethacin (3 µg) or Tris-HCl buffer (Tris) was performed 3 min before injection of the hyperseitizing agent. Measurements were made 3 h after PGE 2 in A and B. The results are reported as the mean ± SEM for 4-5 animals per group and are representative of two separate experiments. P <.5 indicates a significant difference between points (A, two-way ANOVA and one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey test); P <.5 compared to control (Sal or Tris; B and C, one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey test).
6 4 T.M. Cunha et al. fact, so far there is no demotration that these symptoms describe different second messenger events in the inflammatory respoe. The use of the terms hyperseitivity or hyperexcitability was also avoided because they have specific meanings in immunology and electrophysiology, respectively. We evaluated the efficacy of the electronic pressure-meter to detect nociceptor hypernociception in mice. This commercially available itrument (electronic von Frey) is similar to that successfully used to quantify neuropathic allodynia (13) and inflammatory hypernociception in rats (17). The electronic method has several advantages over the classical von Frey filaments: a) reduction of the number of attempts required to evaluate the nociceptive threshold; b) elimination of the problems of filament standardization; c) stimulation of areas of equal size (the area varies with the diameter of the von Frey filaments), d) the end-point is automatically recorded (12,2). Carrageenin-induced hypernociception could be detected in the inflamed paws of the mice by poking the paws with the von Frey filaments and the electronic pressure-meter. The electronic pressure-meter detected hypernociception as early as 1 h after the injection of carrageenin at the lower doses, which was not detected by the von Frey filaments. The usefulness of the electronic pressure-meter for the study of analgesics in mice was demotrated with indomethacin and dipyrone. Indomethacin is a COX inhibitor and dipyrone has specific antinociceptive effects on PGE 2 -induced hypernociception, which are not shared by COX inhibitors. The activation of the arginine-nocgmp pathway contributes to dipyrone-induced spinal and peripheral analgesia (14) via opening of K ATP-seitive channels (15). The electronic pressure-meter detected the systemic and local antinociceptive effects of a standard COX inhibitor, indomethacin, in a dose-dependent manner. The electronic test differentiated among increasing doses of PGE 2 although no time discrimination between 1 and 5 h after administration was observed. In general, hypernociception tended to be more intee at later times. Although indomethacin (as expected) showed no local effect on PGE 2 -induced hypernociception, dipyrone showed a dose-dependent antinociceptive effect. Thus, this technique is capable of differentiating between drugs that prevent the development of hypernociception (blockade of carrageenin hypernociception) and those which directly antagonize ongoing hypernociception, i.e., dipyrone. A clear dissociation in time between the hypernociceptive and the nociceptive stimuli, an easily defined and recorded end-point induced by the nociceptive stimulus, and the ability to differentiate between different classes of peripheral analgesics are essential characteristics of a useful test for the development of new analgesics as well as for the investigation of inflammatory pain mechanisms. In the present investigation, we showed that the electronic pressure-meter test in mice fulfills all of these basic conditio. Acknowledgments We wish to thank Iramirton Figuerêdo Moreira and Simone Reis, summer visiting students (Academia Brasileira de Ciências) for their assistance, and Ieda Regina dos Santos Schivo and Sérgio Roberto Rosa for excellent technical support. The authors also want to express their gratitude to Prof. Francisco Silveira Guimarães for useful advice about statistical analysis.
7 Mouse paw pressure-meter test 47 Referentes 1. Mogil JS & Grisel JE (1998). Tragenic studies of pain. Pain, 77: Le Bars D, Gozariu M & Cadden SW (21). Animal models of nociception. Pharmacological Reviews, 53: Taiwo YO & Levine JD (1989). Contribution of guanine nucleotide regulatory protei to prostaglandin hyperalgesia in the rat. Brain Research, 492: Cunha FQ, Teixeira MM & Ferreira SH (1999). Pharmacological modulation of secondary mediator systems - cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP - on inflammatory hyperalgesia. British Journal of Pharmacology, 127: Ferreira SH & Nakamura M (1979). I-Prostaglandin hyperalgesia: a camp/ca 2 dependent process. Prostaglandin, 18: Lynn B & O Shea NR (1998). Inhibition of forskolin-induced seitization of frog skin nociceptors by the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A antagonist H-29. Brain Research, 78: Taniguchi K, Shinjo K, Mizutani M, Shimada K, Ishikawa T, Menniti FS & Nagahisa A (1997). Anti-nociceptive activity of CP-11,, NMDA receptor NR2B subunit antagonist. British Journal of Pharmacology, 122: Coderre TJ (1992). Contribution of protein kinase C to central seitisation and persistent pain following tissue injury. Neuroscience Letters, 14: von Frey M (189). Untersuchunger über die Sinnesfunctionen der mechlichen Haut. Bandes der Abhandlungen der mathematischphysischen Classe der Königl. Sächsischen Gesellschaft der Wissechaften, 23: Prado WA, Schiavon VF & Cunha FQ (22). Dual effect of local application of nitric oxide donors in a model of incision pain in rats. European Journal of Pharmacology, 441: Shimoyama M, Tanaka K, Hasue F & Shimoyama N (22). A mouse model of neuropathic cancer pain. Pain, 99: Jeen K, Andsersen HO, Olesen J & Lindblom U (198). Pressure-pain threshold in human temporal region. Evaluation of a new pressure algometer. Pain, 25: Möller KÄ, Johason B & Berg OG (1998). Assessing mechanical allodynia in the rat paw with a new electronic algometer. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 84: Lorenzetti BB & Ferreira SH (199). Activation of the arginine-nitric oxide pathway in primary seory neuro contributes to dypironeinduced spinal and peripheral analgesia. Inflammation Research, 45: Alves D & Duarte I (22). Involvement of ATP-seitive K() channels in the peripheral antinociceptive effect induced by dipyrone. European Journal of Pharmacology, 24: Ferreira SH, Moncada S & Vane JR (1973). Prostaglandi and the mechanism of analgesia produced by aspirin-like drugs. British Journal of Pharmacology, 49: Vivancos GG, Verri Jr WA, Cunha TM, Schivo IRS, Parada CA, Cunha FQ & Ferreira SH (24). An electronic pressure-meter nociception paw test for rats. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 37: Onttonen T & Pertovaara A (2). The mechanical antihyperalgesic effect of intrathecally administered MPV-242, a novel alpha2- adrenoceptor agonist, in a rat model of postoperative pain. Anesthesiology, 92: Vrinten DH, Gispen WH, Groen GJ & Adan RA (2). Antagonism of the melanocortin system reduces cold and mechanical allodynia in mononeuropathic rats. Journal of Neuroscience, 2: Greepan JD & Taylor D (199). Thresholds for the perception of sharpness and mechanical pain. Pain, 5 (Suppl): S313.
enhances nociceptive responses in rats
 Brazilian Chronic intrathecal Journal of Medical cannulation and Biological Research (2000) 33: 949-956 ISSN 0100-879X 949 Chronic intrathecal cannulation enhances nociceptive responses in rats F.R.C.
Brazilian Chronic intrathecal Journal of Medical cannulation and Biological Research (2000) 33: 949-956 ISSN 0100-879X 949 Chronic intrathecal cannulation enhances nociceptive responses in rats F.R.C.
A cascade of cytokines mediates mechanical inflammatory hypernociception in mice. Methods
 A cascade of cytokines mediates mechanical inflammatory hypernociception in mice T. M. Cunha*, W. A. Verri, Jr.*, J. S. Silva, S. Poole, F. Q. Cunha*, and S. H. Ferreira* Departments of *Pharmacology and
A cascade of cytokines mediates mechanical inflammatory hypernociception in mice T. M. Cunha*, W. A. Verri, Jr.*, J. S. Silva, S. Poole, F. Q. Cunha*, and S. H. Ferreira* Departments of *Pharmacology and
Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior
 Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 103 (2013) 678 683 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pharmbiochembeh
Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 103 (2013) 678 683 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pharmbiochembeh
Role of complement C5a in mechanical inflammatory hypernociception: potential use of C5a receptor antagonists to control inflammatory pain
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2008) 153, 1043 1053 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 1188/08 $30.00 www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Role of complement C5a in mechanical inflammatory
British Journal of Pharmacology (2008) 153, 1043 1053 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 1188/08 $30.00 www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Role of complement C5a in mechanical inflammatory
ONLINE. F.M. Teixeira*, L.L. Castro*, R.T. Ferreira, P.A. Pires, F.A. Vanderlinde and M.A. Medeiros
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research Online Provisional Version ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research Online Provisional Version ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully
Atropine and ODQ antagonize tetanic fade induced by L-arginine in cats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1277-1283 Antagonism of tetanic fade induced by NO ISSN 0-879X 1277 Atropine and ODQ antagonize tetanic fade induced by L-arginine in cats
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1277-1283 Antagonism of tetanic fade induced by NO ISSN 0-879X 1277 Atropine and ODQ antagonize tetanic fade induced by L-arginine in cats
Streptozotocin-induced mechanical hypernociception is not dependent on hyperglycemia
 Brazilian STZ-induced Journal hypernociception of Medical and does Biological not depend Research on hyperglycemia (2009) 42: 197-206 ISSN 0100-879X 197 Streptozotocin-induced mechanical hypernociception
Brazilian STZ-induced Journal hypernociception of Medical and does Biological not depend Research on hyperglycemia (2009) 42: 197-206 ISSN 0100-879X 197 Streptozotocin-induced mechanical hypernociception
NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions as Related to Analgesia and Tolerance
 Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S7 Proceedings Supplement NDMA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions
Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S7 Proceedings Supplement NDMA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
Pharmacological Evidence for the Role of Nitric Oxide-cGMP in Antinociception
 Pharmacological Evidence for the Role of Nitric Oxide-cGMP in Antinociception Ehab S. EL Desoky, MD, PhD* Ihab A. Fouad, PhD *Pharmacology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University, Assiut, Egypt
Pharmacological Evidence for the Role of Nitric Oxide-cGMP in Antinociception Ehab S. EL Desoky, MD, PhD* Ihab A. Fouad, PhD *Pharmacology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University, Assiut, Egypt
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat. Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons Hawon Cho, Young Duk Yang, Jesun Lee, Byeongjoon Lee, Tahnbee Kim Yongwoo Jang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons Hawon Cho, Young Duk Yang, Jesun Lee, Byeongjoon Lee, Tahnbee Kim Yongwoo Jang,
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and. widespread hyperalgesia
 Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Bradykinin B 1 and B 2 receptors, tumour necrosis factor a and in ammatory hyperalgesia
 British Journal of Pharmacology (1999) 126, 649 ± 656 ã 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp Bradykinin B 1 and B 2 receptors, tumour necrosis
British Journal of Pharmacology (1999) 126, 649 ± 656 ã 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp Bradykinin B 1 and B 2 receptors, tumour necrosis
Coding of facial expressions of pain in the laboratory mouse
 nature methods Coding of facial expressions of pain in the laboratory mouse Dale J Langford 1, Andrea L Bailey 1, Mona Lisa Chanda 1, Sarah E Clarke 1, Tanya E Drummond 1, Stephanie Echols 2, Sarah Glick
nature methods Coding of facial expressions of pain in the laboratory mouse Dale J Langford 1, Andrea L Bailey 1, Mona Lisa Chanda 1, Sarah E Clarke 1, Tanya E Drummond 1, Stephanie Echols 2, Sarah Glick
Anti-hyperalgesic effect of systemic magnesium sulfate in carrageenan-induced inflammatory pain in rats: influence of the nitric oxide pathway
 Magnesium Research 214; 27 (2): 77-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anti-hyperalgesic effect of systemic magnesium sulfate in carrageenan-induced inflammatory pain in rats: influence of the nitric oxide pathway Dragana
Magnesium Research 214; 27 (2): 77-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anti-hyperalgesic effect of systemic magnesium sulfate in carrageenan-induced inflammatory pain in rats: influence of the nitric oxide pathway Dragana
Preclinical evaluation of pain in endometriosis
 receptor antagonism reduces peripheral and central hyperalgesia in a preclinical mouse model of endometriosis Erin Greaves, Andrew W Horne, Helen Jerina, arta ikolajczak, Lisa Hilferty, Rory itchell, Sue
receptor antagonism reduces peripheral and central hyperalgesia in a preclinical mouse model of endometriosis Erin Greaves, Andrew W Horne, Helen Jerina, arta ikolajczak, Lisa Hilferty, Rory itchell, Sue
NOSH-Aspirin (NBS-1120), a Dual Nitric Oxide and Hydrogen Sulfide-Releasing Hybrid, Reduces Inflammatory Pain
 City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works Publications and Research City College of New York 2015 NOSH-Aspirin (NBS-1120), a Dual Nitric Oxide and Hydrogen Sulfide-Releasing Hybrid, Reduces
City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works Publications and Research City College of New York 2015 NOSH-Aspirin (NBS-1120), a Dual Nitric Oxide and Hydrogen Sulfide-Releasing Hybrid, Reduces
Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical Allodynia in a Rat Model of Postoperative Pain
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2013 April; Vol. 26, No. 2: 125-129 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.2.125 Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical
Original Article Korean J Pain 2013 April; Vol. 26, No. 2: 125-129 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.2.125 Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical
TRP modulators based on glycine and mono-, bicyclic terpenoids synthesis and pharmacological properties
 TRP modulators based on glycine and mono-, bicyclic terpenoids synthesis and pharmacological properties Mariia Nesterkina*and Iryna Kravchenko I.I. Mechnikov dessa National University, 2 Dvorjanskaya st.,
TRP modulators based on glycine and mono-, bicyclic terpenoids synthesis and pharmacological properties Mariia Nesterkina*and Iryna Kravchenko I.I. Mechnikov dessa National University, 2 Dvorjanskaya st.,
Analgesic Activity of Sathikkai Podi- a Siddha Drug
 Research Article Analgesic Activity of Sathikkai Podi- a Siddha Drug K. Kanagavalli 1, P. Kavitha 2, J. Anbu 3, P. Sathiya Rajeswaran 4 and P. Parthiban 5 1 UG Maruthuvam Department. 2 PG Scholar final
Research Article Analgesic Activity of Sathikkai Podi- a Siddha Drug K. Kanagavalli 1, P. Kavitha 2, J. Anbu 3, P. Sathiya Rajeswaran 4 and P. Parthiban 5 1 UG Maruthuvam Department. 2 PG Scholar final
Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior
 Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 98 (2011) 188 195 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pharmbiochembeh Granulocyte-Colony
Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 98 (2011) 188 195 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pharmbiochembeh Granulocyte-Colony
Effects of a neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on lipopolysaccharide-induced fever
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (999) 3: 38-387 Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and thermoregulation ISSN 000-879X 38 Effects of a neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on lipopolysaccharide-induced
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (999) 3: 38-387 Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and thermoregulation ISSN 000-879X 38 Effects of a neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on lipopolysaccharide-induced
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Synthesis and Evaluation of Antiallodynic and Anticonvulsant Activity of Novel Amide and Urea Derivatives of Valproic Acid Analogues Dan Kaufmann, Meir Bialer, $, Jakob Avi Shimshoni,
Supporting Information Synthesis and Evaluation of Antiallodynic and Anticonvulsant Activity of Novel Amide and Urea Derivatives of Valproic Acid Analogues Dan Kaufmann, Meir Bialer, $, Jakob Avi Shimshoni,
Pharmacologyonline 1: (2009)
 ANTINOCICEPTIVE ACTIVITY OF TADALAFIL AND ADRENERGIC AGENTS IN THE WRITHING TEST IN MICE Patel S 1, Shah J 1, Mistry K 1, Contractor R 1, Nagda C 1, Patel V 2 1 Indukaka Ipcowala College of Pharmacy, Beyond
ANTINOCICEPTIVE ACTIVITY OF TADALAFIL AND ADRENERGIC AGENTS IN THE WRITHING TEST IN MICE Patel S 1, Shah J 1, Mistry K 1, Contractor R 1, Nagda C 1, Patel V 2 1 Indukaka Ipcowala College of Pharmacy, Beyond
Potentiation of antinociceptive effect of NSAIDs by a specific lipooxygenase inhibitor, acetyl 11-keto-beta boswellic acid
 Indian Journal of Experimental Biology Vol. 44, February 2006, pp. 128-132 Potentiation of antinociceptive effect of NSAIDs by a specific lipooxygenase inhibitor, acetyl 11-keto-beta boswellic acid Mahendra
Indian Journal of Experimental Biology Vol. 44, February 2006, pp. 128-132 Potentiation of antinociceptive effect of NSAIDs by a specific lipooxygenase inhibitor, acetyl 11-keto-beta boswellic acid Mahendra
Social Modulation of Pain as Evidence for Empathy in Mice. Introduction
 Social Modulation of Pain as Evidence for Empathy in Mice Dale J. Langford, Sara E. Crager, Zarrar Shehzad, Shad B. Smith, Susana G. Sotocinal, Jeremy S. Levenstadt, Mona Lisa Chanda, Daniel J. Levitin,
Social Modulation of Pain as Evidence for Empathy in Mice Dale J. Langford, Sara E. Crager, Zarrar Shehzad, Shad B. Smith, Susana G. Sotocinal, Jeremy S. Levenstadt, Mona Lisa Chanda, Daniel J. Levitin,
The evaluation of analgesic effects of simvastatin, pravastatin and atorvastatin in hot plate test
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences The evaluation of analgesic effects of simvastatin, pravastatin and atorvastatin in hot plate test M. KESIM, M. KADIOGLU, M. OKUYAN*, E. MUCI, I.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences The evaluation of analgesic effects of simvastatin, pravastatin and atorvastatin in hot plate test M. KESIM, M. KADIOGLU, M. OKUYAN*, E. MUCI, I.
Evaluation of electromyographic activity and heart rate responses to isometric exercise. The role played by muscular mass and type
 Brazilian Electromyography Journal of and Medical heart and rate Biological responses Research to isometric (1999) exercise 32: 115-120 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 115 Evaluation of electromyographic
Brazilian Electromyography Journal of and Medical heart and rate Biological responses Research to isometric (1999) exercise 32: 115-120 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 115 Evaluation of electromyographic
Supplementary information to. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reversed Morphine Tolerance and Opioid-induced Hyperalgesia
 Supplementary information to Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reversed Morphine Tolerance and Opioid-induced Hyperalgesia Zhen Hua 1,2 *, LiPing Liu 1 *, Jun Shen 1, Katherine Cheng 1, Aijun Liu 1, Jing Yang 1,
Supplementary information to Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reversed Morphine Tolerance and Opioid-induced Hyperalgesia Zhen Hua 1,2 *, LiPing Liu 1 *, Jun Shen 1, Katherine Cheng 1, Aijun Liu 1, Jing Yang 1,
Calibrated Forceps: A Sensitive and Reliable Tool for Pain and Analgesia Studies
 The Journal of Pain, Vol 7, No 1 (January), 2006: pp 32-39 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Calibrated Forceps: A Sensitive and Reliable Tool for Pain and Analgesia Studies Oliva Erendira Luis-Delgado,
The Journal of Pain, Vol 7, No 1 (January), 2006: pp 32-39 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Calibrated Forceps: A Sensitive and Reliable Tool for Pain and Analgesia Studies Oliva Erendira Luis-Delgado,
Continuous Wound Infusion and Postoperative Pain Current status?
 Continuous Wound Infusion and Postoperative Pain Current status? Pr Patricia Lavand homme Department of Anesthesiology St Luc Hospital University Catholic of Louvain Medical School Brussels, Belgium Severe
Continuous Wound Infusion and Postoperative Pain Current status? Pr Patricia Lavand homme Department of Anesthesiology St Luc Hospital University Catholic of Louvain Medical School Brussels, Belgium Severe
Pharmacological and histopathological study of cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis - comparison of the effects of dexamethasone and Mesna
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1211-1215 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1211 Pharmacological and histopathological study of cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1211-1215 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1211 Pharmacological and histopathological study of cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis
IK01400: non-opioid preclinical drug candidate for pain treatment
 IK01400: non-opioid preclinical drug candidate for pain treatment Introduction Bio-Link presents a valuable licensing opportunity for the development of novel nonopioid drug candidates to manage acute
IK01400: non-opioid preclinical drug candidate for pain treatment Introduction Bio-Link presents a valuable licensing opportunity for the development of novel nonopioid drug candidates to manage acute
Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
 University of Kentucky From the SelectedWorks of Renee R. Donahue 2001 Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
University of Kentucky From the SelectedWorks of Renee R. Donahue 2001 Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy
 Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy David Kendall & Bengt von Mentzer; PharmNovo AB/UK Alex Conibear & Eamonn Kelly, University of Bristol Junaid Asghar,
Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy David Kendall & Bengt von Mentzer; PharmNovo AB/UK Alex Conibear & Eamonn Kelly, University of Bristol Junaid Asghar,
Defense reaction induced by a metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist microinjected into the dorsal periaqueductal gray of rats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 3: 1533-1537 Behavioral effects of injected into PAG ISSN 1-79X Short Communication 1533 Defense reaction induced by a metabotropic glutamate
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 3: 1533-1537 Behavioral effects of injected into PAG ISSN 1-79X Short Communication 1533 Defense reaction induced by a metabotropic glutamate
The peripheral antinociceptive e ect induced by morphine is associated with ATP-sensitive K + channels
 (2000) 129, 110 ± 114 ã 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/bjp The peripheral antinociceptive e ect induced by morphine is associated with ATP-sensitive
(2000) 129, 110 ± 114 ã 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/bjp The peripheral antinociceptive e ect induced by morphine is associated with ATP-sensitive
Spinal Glia and Proinflammatory Cytokines Mediate Mirror-Image Neuropathic Pain in Rats
 1026 The Journal of Neuroscience, February 1, 2003 23(3):1026 1040 Spinal Glia and Proinflammatory Cytokines Mediate Mirror-Image Neuropathic Pain in Rats Erin D. Milligan, 1 Carin Twining, 1 Marucia Chacur,
1026 The Journal of Neuroscience, February 1, 2003 23(3):1026 1040 Spinal Glia and Proinflammatory Cytokines Mediate Mirror-Image Neuropathic Pain in Rats Erin D. Milligan, 1 Carin Twining, 1 Marucia Chacur,
Thigmotactic responses in an open-field
 Brazilian Thigmotaxis Journal in the of open-field Medical and Biological Research (2008) 41: 135-140 ISSN 0100-879X 135 Thigmotactic responses in an open-field M.R. Lamprea 1, F.P. Cardenas 2, J. Setem
Brazilian Thigmotaxis Journal in the of open-field Medical and Biological Research (2008) 41: 135-140 ISSN 0100-879X 135 Thigmotactic responses in an open-field M.R. Lamprea 1, F.P. Cardenas 2, J. Setem
Infusions of AP5 into the basolateral amygdala impair the formation, but not the expression, of step-down inhibitory avoidance
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2) 33: 829-834 Amygdaloid NMDA receptors and fear memory ISSN 1-879X 829 Infusions of AP5 into the basolateral amygdala impair the formation, but not
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2) 33: 829-834 Amygdaloid NMDA receptors and fear memory ISSN 1-879X 829 Infusions of AP5 into the basolateral amygdala impair the formation, but not
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation
 Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Gabapentin Antinociception in Mice with Acute Herpetic Pain Induced by Herpes Simplex Virus Infection
 0022-3565/01/2962-270 275$3.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 296, No. 2 Copyright 2001 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 3229/880565
0022-3565/01/2962-270 275$3.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 296, No. 2 Copyright 2001 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 3229/880565
ONLINE. Key words: Tramadol; Tramadol-N-oxide; Rats; Peripheral nerves; Local anesthesia; Analgesia
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research Online Provisional Version ISSN 0100-879X This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research Online Provisional Version ISSN 0100-879X This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full
Evaluation of Gabapentin and S-( )-3-Isobutylgaba in a Rat Model of Postoperative Pain
 0022-3565/97/2823-1242$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 282, No. 3 Copyright 1997 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
0022-3565/97/2823-1242$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 282, No. 3 Copyright 1997 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
Microglial Inhibition Influences XCL1/XCR1 Expression and Causes Analgesic Effects in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Neuropathy
 Microglial Inhibition Influences XCL1/XCR1 Expression and Causes Analgesic Effects in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Magdalena Zychowska, M.D., Ewelina Rojewska, Ph.D., Anna Piotrowska, M.D., Grzegorz
Microglial Inhibition Influences XCL1/XCR1 Expression and Causes Analgesic Effects in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Magdalena Zychowska, M.D., Ewelina Rojewska, Ph.D., Anna Piotrowska, M.D., Grzegorz
Effects of meperidine or saline on thermal, mechanical and electrical nociceptive thresholds in cats
 Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia, 2008, 35, 543 547 doi:10.1111/j.1467-2995.2008.00419.x SHORT COMMUNICATION Effects of meperidine or saline on thermal, mechanical and electrical nociceptive thresholds
Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia, 2008, 35, 543 547 doi:10.1111/j.1467-2995.2008.00419.x SHORT COMMUNICATION Effects of meperidine or saline on thermal, mechanical and electrical nociceptive thresholds
Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in the rat
 Cheppudira et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2016) 16:73 DOI 10.1186/s12871-016-0242-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in
Cheppudira et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2016) 16:73 DOI 10.1186/s12871-016-0242-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in
Participation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in experimental neuropathic pain induced by sciatic nerve transection
 ISSN 0100-879X Volume 43 (04) 325-408 April 2010 BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES AND CLINICAL INVESTIGATION Braz J Med Biol Res, March 2010, Volume 43(4) 367-376 Participation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in
ISSN 0100-879X Volume 43 (04) 325-408 April 2010 BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES AND CLINICAL INVESTIGATION Braz J Med Biol Res, March 2010, Volume 43(4) 367-376 Participation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in
Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2010, 2(5): 358-362 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2010, 2(5): 358-362 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Sensory Assessment of Regional Analgesia in Humans
 REVIEW ARTICLE Dennis M. Fisher, M.D., Editor-in-Chief Anesthesiology 2000; 93:1517 30 2000 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Sensory Assessment of Regional
REVIEW ARTICLE Dennis M. Fisher, M.D., Editor-in-Chief Anesthesiology 2000; 93:1517 30 2000 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Sensory Assessment of Regional
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/325/5941/760/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Spinal Endocannabinoids and CB 1 Receptors Mediate C-Fiber Induced Heterosynaptic Pain Sensitization Alejandro J. Pernía-Andrade,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/325/5941/760/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Spinal Endocannabinoids and CB 1 Receptors Mediate C-Fiber Induced Heterosynaptic Pain Sensitization Alejandro J. Pernía-Andrade,
Materials and Methods
 Anesthesiology 2004; 100:1258 62 2004 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Spinal Adenosine Receptor Activation Reduces Hypersensitivity after Surgery by a Different
Anesthesiology 2004; 100:1258 62 2004 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Spinal Adenosine Receptor Activation Reduces Hypersensitivity after Surgery by a Different
Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase Type 1 and 2 Enzyme by Aqueous Extract of Elaeagnus Angustifolia in Mice
 Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase Type 1 and 2 Enzyme by Aqueous Extract of Elaeagnus Angustifolia in Mice Shahedeh Farahbakhsh 1, Sedigheh Arbabian 1, Fatemeh Emami 1, Banafsheh Rastegar Moghadam 1, Hassan
Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase Type 1 and 2 Enzyme by Aqueous Extract of Elaeagnus Angustifolia in Mice Shahedeh Farahbakhsh 1, Sedigheh Arbabian 1, Fatemeh Emami 1, Banafsheh Rastegar Moghadam 1, Hassan
Factors influencing the Aspergillus fumigatus survival into the host mediated by the calcineurin pathway
 Factors influencing the Aspergillus fumigatus survival into the host mediated by the calcineurin pathway Gustavo H. Goldman Universidade de São Paulo, Brazil Calcineurin is a calmodulin/ca +2 dependent
Factors influencing the Aspergillus fumigatus survival into the host mediated by the calcineurin pathway Gustavo H. Goldman Universidade de São Paulo, Brazil Calcineurin is a calmodulin/ca +2 dependent
TESTS AND MODELS OF NOCICEPTION AND PAIN IN RODENTS
 Neuroscience 211 (2012) 39 50 REVIEW TESTS AND MODELS OF NOCICEPTION AND PAIN IN RODENTS M. BARROT* Institut des Neurosciences Cellulaires et Intégratives, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique,
Neuroscience 211 (2012) 39 50 REVIEW TESTS AND MODELS OF NOCICEPTION AND PAIN IN RODENTS M. BARROT* Institut des Neurosciences Cellulaires et Intégratives, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique,
TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH SECTION
 Pain Medicine 2011; 12: 923 941 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH SECTION Original Research Article Intravenous Injection of Leconotide, an Omega Conotoxin: Synergistic Antihyperalgesic Effects
Pain Medicine 2011; 12: 923 941 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH SECTION Original Research Article Intravenous Injection of Leconotide, an Omega Conotoxin: Synergistic Antihyperalgesic Effects
Dezocine Antagonizes Morphine Analgesia upon Simultaneous Administration in Rodent Models of Acute Nociception
 Pain Physician 2017; 20:E401-E409 ISSN 2150-1149 Animal Study Dezocine Antagonizes Morphine Analgesia upon Simultaneous Administration in Rodent Models of Acute Nociception Na-Na Li, MS 1, Ya-Qin Huang,
Pain Physician 2017; 20:E401-E409 ISSN 2150-1149 Animal Study Dezocine Antagonizes Morphine Analgesia upon Simultaneous Administration in Rodent Models of Acute Nociception Na-Na Li, MS 1, Ya-Qin Huang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 METHODS Mice and rats. Behavioural experiments were performed in male and female 7 12 week old mice or in male 7 10 week old Wistar rats. Permissions for the animal experiments have been obtained from
METHODS Mice and rats. Behavioural experiments were performed in male and female 7 12 week old mice or in male 7 10 week old Wistar rats. Permissions for the animal experiments have been obtained from
Centrally Mediated Anti-Hyperalgesic and Anti-Allodynic Effect of Tolperisone in Spared Nerve Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain
 Centrally Mediated Anti-Hyperalgesic and Anti-Allodynic Effect of Tolperisone in Spared Nerve Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain Keyur S Patel *, Punam D Sachdeva Department of Pharmacology, A.R.College
Centrally Mediated Anti-Hyperalgesic and Anti-Allodynic Effect of Tolperisone in Spared Nerve Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain Keyur S Patel *, Punam D Sachdeva Department of Pharmacology, A.R.College
Routine post-weaning handling of rats prevents isolation rearing-induced deficit in prepulse inhibition
 Routine Brazilian handling Journal of prevents Medical PPI and deficit Biological in isolated Research rats (2005) 38: 1691-1696 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1691 Routine post-weaning handling of
Routine Brazilian handling Journal of prevents Medical PPI and deficit Biological in isolated Research rats (2005) 38: 1691-1696 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1691 Routine post-weaning handling of
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor
 Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
Social transfer of pain in mice
 NEUROPSYCHOLOGY Social transfer of pain in mice Monique L. Smith, 1 Caroline M. Hostetler, 1 Mary M. Heinricher, 1,2 Andrey E. Ryabinin 1 * A complex relationship exists between the psychosocial environment
NEUROPSYCHOLOGY Social transfer of pain in mice Monique L. Smith, 1 Caroline M. Hostetler, 1 Mary M. Heinricher, 1,2 Andrey E. Ryabinin 1 * A complex relationship exists between the psychosocial environment
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Central and Peripheral Analgesia Mediated by the Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibitor Neostigmine in the Rat Inflamed Knee Joint Model
 Central and Peripheral Analgesia Mediated by the Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibitor Neostigmine in the Rat Inflamed Knee Joint Model H. Buerkle, MD, M. Boschin, MS, M. A. E. Marcus, MD, G. Brodner, MD, Pm,
Central and Peripheral Analgesia Mediated by the Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibitor Neostigmine in the Rat Inflamed Knee Joint Model H. Buerkle, MD, M. Boschin, MS, M. A. E. Marcus, MD, G. Brodner, MD, Pm,
Arthritis is a very common medical condition estimated to affect around. seven million people in the UK. However, it is not a single disease but comes
 Chapter 6: Antiarthritic activity of cultured mycelium of Volvariella volvacea 6.1. Introduction Arthritis is a very common medical condition estimated to affect around seven million people in the UK.
Chapter 6: Antiarthritic activity of cultured mycelium of Volvariella volvacea 6.1. Introduction Arthritis is a very common medical condition estimated to affect around seven million people in the UK.
ACTIVITY USING RATS A METHOD FOR THE EVALUATION OF ANALGESIC. subject and a variety of stimuli employed. In the examination of new compounds
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1946), 1, 255. A METHOD FOR THE EVALUATION OF ANALGESIC ACTIVITY USING RATS BY 0. L. DAVIES, J. RAVENT6S, AND A. L. WALPOLE From Imperial Chemical Industries, Ltd., Biological Laboratories,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1946), 1, 255. A METHOD FOR THE EVALUATION OF ANALGESIC ACTIVITY USING RATS BY 0. L. DAVIES, J. RAVENT6S, AND A. L. WALPOLE From Imperial Chemical Industries, Ltd., Biological Laboratories,
Abstract. R. Roesler 1, J. Quevedo 1, C. Rodrigues 1, M. Madruga 1, M.R.M. Vianna 1 and M.B.C. Ferreira 2
 Brazilian Amygdaloid Journal non-nmda of Medical receptors and Biological and memory Research expression (1999) 32: 349-353 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 349 Increased training prevents the impairing
Brazilian Amygdaloid Journal non-nmda of Medical receptors and Biological and memory Research expression (1999) 32: 349-353 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 349 Increased training prevents the impairing
Animal models of fibromyalgia
 DeSantana et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy REVIEW Animal models of fibromyalgia Josimari M DeSantana 1,2,3, Kamilla ML da Cruz 3 and Kathleen A Sluka 4* Abstract Animal models of disease states are
DeSantana et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy REVIEW Animal models of fibromyalgia Josimari M DeSantana 1,2,3, Kamilla ML da Cruz 3 and Kathleen A Sluka 4* Abstract Animal models of disease states are
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Schlosburg et al. 10.1073/pnas.1219159110 SI Materials and Methods: Quantification of Heroin Metabolites Sample Collection. Trunk blood was collected in a 1:1 ratio with acetate
Supporting Information Schlosburg et al. 10.1073/pnas.1219159110 SI Materials and Methods: Quantification of Heroin Metabolites Sample Collection. Trunk blood was collected in a 1:1 ratio with acetate
LONG-TERM postoperative pain follows many common
 Prolonged Suppression of Postincisional Pain by a Slow-release Formulation of Lidocaine Chi-Fei Wang, M.D.,* Carlo Pancaro, M.D., Peter Gerner, M.D., Gary Strichartz, Ph.D. ABSTRACT Background: Postoperative
Prolonged Suppression of Postincisional Pain by a Slow-release Formulation of Lidocaine Chi-Fei Wang, M.D.,* Carlo Pancaro, M.D., Peter Gerner, M.D., Gary Strichartz, Ph.D. ABSTRACT Background: Postoperative
Analgesic effects of the COX-2 inhibitor parecoxib on surgical pain through suppression of spinal ERK signaling
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 275-279, 2013 Analgesic effects of the COX-2 inhibitor parecoxib on surgical pain through suppression of spinal ERK signaling YA-JING GUO 1, XU-DAN SHI 2, DI FU
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 275-279, 2013 Analgesic effects of the COX-2 inhibitor parecoxib on surgical pain through suppression of spinal ERK signaling YA-JING GUO 1, XU-DAN SHI 2, DI FU
Effect of chronic oral administration of a low dose of captopril on sodium appetite of hypothyroid rats. Influence of aldosterone treatment
 Brazilian Sodium appetite Journal of in Medical hypothyroid and rats Biological Research (21) 34: 47-411 ISSN 1-879X Short Communication 47 Effect of chronic oral administration of a low dose of captopril
Brazilian Sodium appetite Journal of in Medical hypothyroid and rats Biological Research (21) 34: 47-411 ISSN 1-879X Short Communication 47 Effect of chronic oral administration of a low dose of captopril
Intravenous dipyrone for the acute treatment of episodic tension-type headache. A randomized, placebocontrolled,
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2002) 35: 1139-1145 Dipyrone in the treatment of episodic tension-type headache ISSN 0100-879X 1139 Intravenous dipyrone for the acute treatment of
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2002) 35: 1139-1145 Dipyrone in the treatment of episodic tension-type headache ISSN 0100-879X 1139 Intravenous dipyrone for the acute treatment of
A Series of D-Amino Acid Oxidase Inhibitors Specifically Prevents and Reverses Formalin-Induced Tonic Pain in Rats
 0022-3565/11/3361-282 293$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 336, No. 1 Copyright 2011 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 172353/3653734
0022-3565/11/3361-282 293$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 336, No. 1 Copyright 2011 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 172353/3653734
Modulatory Role of Morphine and Gabapentin as Anti-inflammatory Agents Alone and on Coadministration. Edema
 American Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics Original Article Modulatory Role of Morphine and Gabapentin as Anti-inflammatory Agents Alone and on Coadministration with Diclofenac in Rat Paw
American Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics Original Article Modulatory Role of Morphine and Gabapentin as Anti-inflammatory Agents Alone and on Coadministration with Diclofenac in Rat Paw
Opioidergic orofacial antinociception induced by electroacupuncture at acupoint St36
 St36 Brazilian acupoint Journal of stimulation Medical and induces Biological opioidergic Research (2008) orofacial 41: 621-626 antinociception ISSN 0100-879X 621 Opioidergic orofacial antinociception
St36 Brazilian acupoint Journal of stimulation Medical and induces Biological opioidergic Research (2008) orofacial 41: 621-626 antinociception ISSN 0100-879X 621 Opioidergic orofacial antinociception
Atorvastatin inhibits inflammatory hypernociception
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2006) 149, 14 22 & 2006 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 1188/06 $30.00 www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Atorvastatin inhibits inflammatory hypernociception
British Journal of Pharmacology (2006) 149, 14 22 & 2006 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 1188/06 $30.00 www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Atorvastatin inhibits inflammatory hypernociception
MOLECULAR PAIN. Josée Guindon 1,3*, Liting Deng 1,2,3, Baochang Fan 1, Jim Wager-Miller 1 and Andrea G Hohmann 1,2,3*
 Guindon et al. Molecular Pain 2014, 10:56 MOLECULAR PAIN RESEARCH Open Access Optimization of a cisplatin model of chemotherapyinduced peripheral neuropathy in mice: use of vitamin C and sodium bicarbonate
Guindon et al. Molecular Pain 2014, 10:56 MOLECULAR PAIN RESEARCH Open Access Optimization of a cisplatin model of chemotherapyinduced peripheral neuropathy in mice: use of vitamin C and sodium bicarbonate
Spinal Cord Injury Pain. Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018
 Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
 72..83 British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:1.1111/j.1476-5381.21.895.x www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPERbph_895 Cooperative role of tumour necrosis factor-a, interleukin-1b and neutrophils in a novel
72..83 British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:1.1111/j.1476-5381.21.895.x www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPERbph_895 Cooperative role of tumour necrosis factor-a, interleukin-1b and neutrophils in a novel
Glycine-gated ion channels Converging mechanism and therapeutic potentials
 Glycine-gated ion channels Converging mechanism and therapeutic potentials Li Zhang Laboratory for Integrative Neuroscience, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, National Institutes of Health,
Glycine-gated ion channels Converging mechanism and therapeutic potentials Li Zhang Laboratory for Integrative Neuroscience, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, National Institutes of Health,
A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch
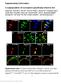 Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE André Luiz de Souza Grava 1, Luiz Fernando Ferrari 2, Carlos Amílcar Parada 3, Helton Luiz Aparecido Defino 4 ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the hyperalgesia and histological abnormalities
ORIGINAL ARTICLE André Luiz de Souza Grava 1, Luiz Fernando Ferrari 2, Carlos Amílcar Parada 3, Helton Luiz Aparecido Defino 4 ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the hyperalgesia and histological abnormalities
Effects of autacoid inhibitors and of an antagonist on malaria infection in mice
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2004) 37: 1199-1204 Autacoids in malarial prophylaxis ISSN 0100-879X 1199 Effects of autacoid inhibitors and of an antagonist on malaria infection
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2004) 37: 1199-1204 Autacoids in malarial prophylaxis ISSN 0100-879X 1199 Effects of autacoid inhibitors and of an antagonist on malaria infection
Special Issue on Pain and Itch
 Special Issue on Pain and Itch Title: Recent Progress in Understanding the Mechanisms of Pain and Itch Guest Editor of the Special Issue: Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Chronic pain is a major health problem world-wide.
Special Issue on Pain and Itch Title: Recent Progress in Understanding the Mechanisms of Pain and Itch Guest Editor of the Special Issue: Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Chronic pain is a major health problem world-wide.
Antinociception and the New COX Inhibitors: Research Approaches and Clinical Perspectives
 CNS Drug Reviews Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 227 252 2003 Neva Press, Branford, Connecticut Antinociception and the New COX Inhibitors: Research Approaches and Clinical Perspectives Juan F. Herrero, E. Alfonso
CNS Drug Reviews Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 227 252 2003 Neva Press, Branford, Connecticut Antinociception and the New COX Inhibitors: Research Approaches and Clinical Perspectives Juan F. Herrero, E. Alfonso
Laboratory Reports Anti-allodynic effects of oral COX-2 selective inhibitor on postoperative pain in the rat
 354 Laboratory Reports Anti-allodynic effects of oral COX-2 selective inhibitor on postoperative pain in the rat Tatsuo Yamamoto MD, Yoshihiko Sakashita MD, Natsuko Nozaki-Taguchi MD Purpose: To examine
354 Laboratory Reports Anti-allodynic effects of oral COX-2 selective inhibitor on postoperative pain in the rat Tatsuo Yamamoto MD, Yoshihiko Sakashita MD, Natsuko Nozaki-Taguchi MD Purpose: To examine
The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function in vitro
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1998) 31: 811-818 L-arginine on airway smooth muscle ISSN -879X 811 The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1998) 31: 811-818 L-arginine on airway smooth muscle ISSN -879X 811 The effect of L-arginine on guinea-pig and rabbit airway smooth muscle function
Peripheral Antinociception by Carbamazepine in an Inflammatory Mechanical Hyperalgesia Model in the Rat: a New Target for Carbamazepine?
 J Pharmacol Sci 100, 310 314 (2006) Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 2006 The Japanese Pharmacological Society Short Communication Peripheral Antinociception by Carbamazepine in an Inflammatory Mechanical
J Pharmacol Sci 100, 310 314 (2006) Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 2006 The Japanese Pharmacological Society Short Communication Peripheral Antinociception by Carbamazepine in an Inflammatory Mechanical
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Neuropharmacology. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 August 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Neuropharmacology. 2013 August ; 71: 1 9. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.03.009. The nitroxyl donor, Angeli s salt, inhibits inflammatory
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Neuropharmacology. 2013 August ; 71: 1 9. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.03.009. The nitroxyl donor, Angeli s salt, inhibits inflammatory
Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice.
 Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D.,
Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D.,
SEX DIFFERENCES IN OPIOID ANTINOCICEPTION: MODULATION BY THE N- METHYL-D-ASPARTATE SYSTEM. Lisa Madonia Lomas
 SEX DIFFERENCES IN OPIOID ANTINOCICEPTION: MODULATION BY THE N- METHYL-D-ASPARTATE SYSTEM Lisa Madonia Lomas A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in
SEX DIFFERENCES IN OPIOID ANTINOCICEPTION: MODULATION BY THE N- METHYL-D-ASPARTATE SYSTEM Lisa Madonia Lomas A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in
Diabetic Complications Consortium
 Diabetic Complications Consortium Application Title: Cathepsin S inhibition and diabetic neuropathy Principal Investigator: Nigel A Calcutt 1. Project Accomplishments: We investigated the efficacy of cathepsin
Diabetic Complications Consortium Application Title: Cathepsin S inhibition and diabetic neuropathy Principal Investigator: Nigel A Calcutt 1. Project Accomplishments: We investigated the efficacy of cathepsin
Thermal and Mechanical Hyperalgesia
 Focus Thermal and Mechanical Hyperalgesia A Distinct Role for Different Excitatory Amino Acid Receptors and Signal Transduction Pathways? s. T. Metier There are three steps in the revelation of any truth:
Focus Thermal and Mechanical Hyperalgesia A Distinct Role for Different Excitatory Amino Acid Receptors and Signal Transduction Pathways? s. T. Metier There are three steps in the revelation of any truth:
05. Pain and Nociception Neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury: A possible role of endothelin ET A and ET B receptors.
 05. Pain and Nociception 05.001 Neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury: A possible role of endothelin ET A and ET B receptors. Forner S, Martini AC, Rae GA UFSC Farmacologia Introduction: Traumatic
05. Pain and Nociception 05.001 Neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury: A possible role of endothelin ET A and ET B receptors. Forner S, Martini AC, Rae GA UFSC Farmacologia Introduction: Traumatic
NORLAND AVENUE PHARMACY PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING FOR PAIN MANAGEMENT
 NOVEMBER 2011 NORLAND AVENUE PHARMACY PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING N ORLANDA VENUEP HARMACY. COM We customize individual prescriptions for the specific needs of our patients. INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Sciatic Pain
NOVEMBER 2011 NORLAND AVENUE PHARMACY PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING N ORLANDA VENUEP HARMACY. COM We customize individual prescriptions for the specific needs of our patients. INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Sciatic Pain
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016)
 International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) Analgesic Contrast of Diverse Administrations of Botulinum Neurotoxin A (BoTN/A) Using Rat Neuropathic Pain Model Qiong-Fang YANG1,3,
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) Analgesic Contrast of Diverse Administrations of Botulinum Neurotoxin A (BoTN/A) Using Rat Neuropathic Pain Model Qiong-Fang YANG1,3,
Visceral Pain-Related Anxiety: Role of Glucocorticoids
 Visceral Pain-Related Anxiety: Role of Glucocorticoids Brent Myers, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry University of Cincinnati Center for Neuroscience University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center Irritable
Visceral Pain-Related Anxiety: Role of Glucocorticoids Brent Myers, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry University of Cincinnati Center for Neuroscience University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center Irritable
Role of bradykinin in postprandial hypotension in humans
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 777-781 Postprandial bradykinin release ISSN 0100-879X 777 Role of bradykinin in postprandial hypotension in humans S. Tumilero 1, L. Gallo
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 777-781 Postprandial bradykinin release ISSN 0100-879X 777 Role of bradykinin in postprandial hypotension in humans S. Tumilero 1, L. Gallo
