Trigger finger, or stenosing tenosynovitis, Corticosteroid Injections in the Treatment of Trigger Finger: A Level I and II Systematic Review
|
|
|
- Caren Hensley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Corticosteroid Injections in the Treatment of Trigger Finger: A Level I and II Systematic Review Sheryl B. Fleisch, BS Kurt P. Spindler, MD Donald H. Lee, MD Ms. Fleisch is Medical Student, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN. Dr. Spindler is Professor and Vice Chairman, Department of Orthopaedics/Sports Medicine, Vanderbilt Orthopaedic Institute, Nashville. Dr. Lee is Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Vanderbilt Orthopaedic Institute. None of the following authors has received anything of value from or owns stock in a commercial company or institution related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article: Ms. Fleisch, Dr. Spindler, and Dr. Lee. Reprint requests: Dr. Lee, Vanderbilt Orthopaedic Institute, Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 3200, st Avenue, Nashville, TN J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2007;15: Copyright 2007 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Abstract Trigger finger is a tendinitis (stenosing tenosynovitis) with multiple management approaches. We conducted an evidencebased medicine systematic review of level I and II prospective randomized controlled trials to determine the effectiveness of injection in managing trigger finger. MEDLINE, Cochrane database, and secondary references were reviewed to locate all English-language prospective randomized controlled trials evaluating trigger finger treatment. Four studies using injectable s were identified, based on the following inclusion criteria: all were prospective randomized controlled trials of adults with >85% follow-up. This review indicates that the incidence of trigger finger is greatest in women (75%), with an average patient age range of 52 to 62 years. Combined analysis of these four studies shows that injections are effective in 57% of patients. Trigger finger, or stenosing tenosynovitis, is a condition in which the flexor tendon is prohibited from gliding through the tendon sheath because of thickening of the synovial sheath over the tendon. 1 As a result, digital movement is impaired, and the affected digit locks in either flexion (the most common position) or extension, causing pain and swelling. Trigger digit pathology can be associated with occupations involving lifting or gripping, but it also is associated with disease states, such as rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes mellitus. 2 Trigger finger has a reported incidence of 28 cases per 100,000 subjects annually, or a risk of 2.6% over a lifetime. 3 A survey of 516 patients treated between 1975 and 1994 indicated that 61% of trigger fingers occurred in women. 4 Multiple approaches are available for managing trigger finger. Splinting, s (either single or multiple injections), percutaneous surgery, and open surgery are all established means of treatment. The many published articles that address methods of managing trigger finger are predominantly retrospective and are confounded by significant bias. A survey of the available literature without regard to evidence-based medicine (EBM) showed that splinting was effective in relieving trigger finger in 55% to 66% of patients. 5,6 A single injection of relieved symptoms in 47% to 87% of patients with trigger finger No data are available on recurrence of trigger finger symptoms with splinting. However, the recurrence of trigger finger with injec- 166 Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
2 Sheryl B. Fleisch, BS, et al tion can be 27% in just 1 year, 12 suggesting that injection, although useful, may not provide long-term relief. According to Newport et al, 13 each additional injection resulted in decreased efficacy. Despite the lack of an EBM review on the efficacy of injection in the management of trigger finger, injection has been widely accepted as firstline treatment. 8,9,14-16 When splinting and/or injections fail, surgery is recommended. 14,15 Non- EBM literature indicates that surgical procedures (open and percutaneous) have a success rate of 89% to 100% Thus, there is a need to determine whether EBM supports the use of injection as first-line treatment of trigger finger. A systematic EBM review of level I and II studies is required to determine the most appropriate management for trigger finger, noting that multiple management options, coupled with variable success rates, especially for injections, have been proposed. We sought prospective randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that would meet the EBM criteria. 20 By relying on the highest levels of evidence, bias is reduced, and clinicians can feel more confident about executing change in their clinical practice. Our goal in this study was twofold. First, we wanted to determine whether sufficient EBM data exist to adequately determine whether injections are effective in managing trigger finger. Second, we wanted to analyze the EBM data that do exist to determine whether EBM supports injection of in the treatment of patients with trigger finger. This EBM systematic review identified and analyzed four level I and II RCTs. 8-10,21 These studies were culled from an extensive review of the medical literature on the treatment available for trigger finger. Methods Only prospective RCTs (level I and II) were reviewed because this type of study provides the highest level of reliable evidence. 20 MEDLINE and Cochrane database searches, coupled with a secondary search of the references of selected articles, were performed to identify all Englishlanguage clinical papers assessing treatment options for trigger finger from January 1966 through January Key words used in the literature search were trigger finger, stenosing tenosynovitis, tenosynovitis, stenosing tendovaginitis, and tendon entrapment. Of 56 total trigger finger studies identified, only four met specific criteria for RCTs using injectable s. Fifty of the remaining articles were excluded because they were not RCTs (many were retrospective reviews of data). Two studies were excluded that met all of the inclusion criteria because they compared efficacy of surgical procedures rather than injection efficacy. Other criteria required for inclusion in this review were that the study must be prospective, must have at least 85% follow-up, and must include only adults, the latter because disease pathology and treatment is reportedly different in children. 13,22 Because of the paucity of RCTs on trigger finger, studies stated as using randomized techniques were included despite a lack of precise definition of the exact randomization methods used. Further, because of their small sample size (<50 patients), two included studies 8,9 are level II, as defined by the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (American edition) criteria. 23 The four RCTs included in this systematic analysis were reviewed using a worksheet developed by an orthopaedics, biostatistics, and health services research center at a university-based medical center. 24 Use of this worksheet allowed for efficient organization of articles reviewed, including hypotheses, results, and potential sources of bias. Results were analyzed for specific treatment, age, sex, inclusion and exclusion criteria, percentage of digits at follow-up, digit being studied, method of randomization, time to follow-up, outcomes of each study, and statistical significance. Data from each study were organized and presented in tabular form. Reproducibility between studies was assessed to identify similar comparative information between the RCTs. The treatment methods included in each study, along with the sex and mean age of participants, are summarized in Table 1. The details of inclusion and exclusion criteria, as well as methods of randomization and follow-up, are summarized in Table 2. The success rate of injections in the treatment of trigger finger is analyzed and compared in Table 3. Results Demographics Mean reported patient age range was 52 to 62 years (Table 1). Interestingly, more women were enrolled than men, with women accounting for 75% of this EBM study population. The preponderance of women in these RCTs validates previous, lesser controlled studies 4 that suggested that most trigger finger patients are women. Duration of follow-up after injection was highly variable among these studies, ranging from 1 month to 27 months. Prior symptoms also were variable: Lambert et al 8 enrolled only individuals who had trigger finger lasting longer than 3 months. The other three studies 9,10,21 did not specify the number of months an individual must have had trigger finger to be included in the study. Patients with comorbidities such as diabetes and rheumatoid disease were omitted from most studies, 8,9,21 although Maneerit et al 10 allowed inclusion of diabetic patients (Table 2). Volume 15, Number 3, March
3 Corticosteroid Injections in the Treatment of Trigger Finger Table 1 Prospective Randomized Controlled Trials by Type and Demographic Sex Study Journal Year Country Treatment Male Female Total No. of Digits Mean Age in Years (Range) Murphy et al 9 Surgery (Am) 1995 United States Corticosteroid (NR) Placebo (NR) Lambert et al 8 Surgery (Br) 1992 England Corticosteroid (22-56) Placebo (30-76) Maneerit et al 10 * Surgery (Br) 2003 Thailand Percutaneous release with Corticosteroid alone (31-68) (31-76) Taras et al 21 Surgery (Am) 1998 United States Intrasheath Subcutaneous (NR) (NR) Total * 127 patients initially included, with sex determination indicated only for the 125 patients at follow-up 95 patients with involvement of 107 digits NR = not reported Study Design Study design was analyzed for each trial, including percentage of follow-up, percentage of thumbs versus fingers, method of randomization, and blinding methods (Table 2). Patient population ranged from 24 to 127 patients across the four RCTs. Murphy et al 9 and Lambert et al 8 had the smallest patient populations, with 24 and 41 patients, respectively. Although both studies were RCTs, their small patient populations may have induced a type II error (low power) into the outcome. 20 All studies 8-10,21 had >95% follow-up, which minimizes exclusion bias or systemic differences between groups because of inadequate follow-up. 25 Maneerit et al 10 included trigger finger patients with involvement solely in thumbs. The remaining three studies 8,9,21 included patients with predominant finger, rather than thumb, involvement. Fingers accounted for 67% to 77% of the patient population in these studies. Because the thumb and the finger have intrinsically different anatomic properties, the vast difference in the number of thumbs and fingers studied in each report may potentially contribute to exclusion bias and may affect the results. 26 Corticosteroid Injection Only two studies 8,9 specifically analyzed the effect of injection versus placebo. Maneerit et al 10 compared the success rate of injection with that of percutaneous surgical release in combination with injection. Taras et al 21 compared the efficacy of placing a injection into the subcutaneous tissue versus directly into the tendon sheath. The combined results of the four RCTs 8-10,21 indicate that surgical percutaneous release with injection relieved 91% of triggering, injection alone relieved 57% of triggering, and placebo relieved 17% of symptoms (Table 3). Despite intrinsic differences between each RCT, three of these studies 8-10 reported statistically significant data (P < 0.05). The Taras et al 21 study did not achieve statistical significance (β < 0.08) because of the low power of the study. Despite differences in the type of 168 Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
4 Sheryl B. Fleisch, BS, et al Table 2 Study Design Study No. of Treatment Groups Intervention Inclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria No. of Digits at Follow-up (%) Thumb vs Fingers Average Method of Follow-up Randomization (mos) Murphy 2 Corticosteroid et al 9 vs placebo NR Lambert 2 Corticosteroid >3 mos et al 8 vs placebo TF/thumb Maneerit et al 10 2 Percutaneous release with Trigger thumb, grade 2-4, diabetes vs alone Taras NR et al 21 vs subcutaneous injection RA, IDDM, previous tendon laceration or TF injection RA, IDDM, eczema, concurrent infection, injection in the past 3 mos Trauma, carpal tunnel syndrome TF>6mos, IDDM/ NIDDM, systemic connective tissue disease 24/24 (100) 39/41 (95) 125/127 (98) 107/107 (100) 33% Fingers, 67% 29% Fingers, 71% 100% 23% Fingers, 77% Sealed envelopes 4 NR 1 NR 23 Medical record number: odd file number received subcutaneous injection, even file number received intrasheath injection 27 IDDM = insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, NIDDM = non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, NR = not reported, RA = rheumatoid arthritis, TF = trigger finger used, our meta-analysis of these four studies showed that injection was useful in relieving trigger finger in 57% of patients. Complications from all of the aforementioned interventions were minimal. Discussion Evidence-based Evaluation of Bias Selection bias occurs when patients are selected for a particular intervention group based on different variables that could affect the outcome of the study. 20 Two studies 9,21 used randomization techniques that could be prone to selection bias: 20 medical record number 21 and, if improperly performed, sealed envelopes. 9 The remaining two studies 8,10 did not mention method of randomization. Despite potential selection bias in the four RCTs, all were included in this systematic review because of the scarcity of level I and II studies available for analysis. Besides selection and exclusion bias, detection bias occurs when examiners are not blinded to the intervention. Only two studies 8,9 were double-blind, such that the intervention and examination were performed by different clinicians and the examiner did not know which intervention was performed on which individual. The remaining two studies 10,21 did not report whether their studies were blinded. The number of thumbs and fingers included in each study and the different types and doses of also could contribute to bias. Outcome Measures The outcome measures used in the four EBM studies 8-10,21 were highly variable, thus providing no consistent evaluation technique for trigger finger. A more uniform scale is needed to measure resolution of trigger finger symptoms based on pain and mobility before and after interven- Volume 15, Number 3, March
5 Corticosteroid Injections in the Treatment of Trigger Finger Table 3 Results of Corticosteroid Versus Placebo Success (No. of Patients) Study Pain Type of Corticosteroid Corticosteroid Placebo Percutaneous Release With Corticosteroid Difference P value* Murphy et al 9 Lambert et al 8 Maneerit et al 10 Subjectively graded by patient before and after injection Patients kept a diary of pain experienced Visual analog pain scale 1 ml betamethasone sodium phosphate + 3mL1% lidocaine 0.5 ml methylprednisolone acetate ml 1% lidocaine 1 ml triamcinolone acetonide ml 1% lidocaine hydrochloride Taras et al 21 NR 1 ml betamethasone sodium phosphate ml 1.0% lidocaine 64% (9/14) 20% (2/10) 60% (12/20) 47% (28/60) Total 57% (115/201) 15% (3/20) NA 91% (59/65) NA 44% <0.02 NA 44% < % % NA NA NA NS, NR (66/107) 17% (5/30) 91% (59/65) * Determined by chi-square test Number of successful injections/total number of patients injected Corticosteroid injections were administered in either the intrasheath or subcutaneous compartment, with no significant difference between the two. NA = not applicable, NR = not reported, NS = not significant (lack of significance was attributed to low power [β < 0.8]) tion. Three of the four studies used variable subjective nonstandard rating scales; 8,9,21 Maneerit et al 10 used a trigger grading scale that was not explicitly explained. Three tools may improve outcome measures for the treatment of trigger finger: (1) a classification system for diagnosing trigger finger severity, 2,27 (2) a visual analog pain scale for measuring pain intensity, and (3) a goniometer for measuring total active motion as a quantification of digit mobility. Standard systems for evaluating trigger finger would permit a more confident assessment of the efficacy of a procedure, thus enabling better comparison of clinical outcomes in future RCTs. Summary This EBM review indicates that trigger finger is most prevalent in women aged 52 to 62 years, which supports previous non-ebm data. 4 Furthermore, although injection is widely used in the treatment of trigger finger, there is a paucity of well-controlled EBM studies evaluating its effectiveness. Only two of the studies in this systematic review specifically compared injection with placebo. 8,9 Maneerit et al 10 compared injection with percutaneous release in combination with injection, while Taras et al 21 compared subcutaneous injection with intrasheath injection. EBM analysis of these four RCTs demonstrates that injection provided relief in 57% of patients. These results contrast with those of non-ebm studies, which indicated that injection may be useful in up to 87% of patients Nevertheless, these recent EBM data are consistent with older non-ebm studies that recommended intervention as a first-line treatment option for trigger finger. Corticosteroid injections continue to be recommended because the procedure is relatively simple and because more than half of patients experience relief after injection, thus obviating the need for 170 Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
6 Sheryl B. Fleisch, BS, et al surgical intervention. Despite providing the best evidence available, the RCTs analyzed in this review used questionable methods of randomization, two studies exhibited a lack of examiner blinding, 10,21 and two studies had limited duration of follow-up (<2 years). 8,9 Future RCTs are needed that incorporate both pharmacologic and surgical interventions. We also strongly recommend the establishment and use of a more universal rating scale (classification system, visual analog scale, mobility assessment test) so that efficacy of trigger finger management can be better evaluated using EBM principles. Acknowledgment The authors thank Cameron T. Atkinson for technical assistance, Lynn S. Cain for editorial assistance, and each of the authors of the four excellent studies reviewed. This work was funded entirely by the Vanderbilt Sports Medicine Research Fund. Additional Resource CME Course: Managing Complicated Hand and Wrist Problems. Course Directors: Mark E. Baratz, MD, and Mark S. Cohen, MD. May 11-12, 2007, Rosemont, IL: mastcaldb/cmedetails.cfm?recor dnum=2106 References Evidence-based Medicine: Level I/II randomized prospective trials are references 8-10 and 21. Reference 2 is expert opinion. Citation numbers printed in bold type indicated references published within the past 5 years. 1. Saldana MJ: Trigger digits: Diagnosis and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2001;9: Wolfe SW: Tenosynovitis, in Green DP, Hotchkiss RN, Pederson WC, Wolfe SW (eds): Green s Operative Hand Surgery, ed 5. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone, 2005, Strom L: Trigger finger in diabetes. J Med Soc N J 1977;74: Kasdan ML, Leis VM, Lewis K, Kasdan AS: Trigger finger: Not always work related. J Ky Med Assoc 1996;94: Patel MR, Bassini L: Trigger fingers and thumb: When to splint, inject, or operate. J Hand Surg [Am] 1992;17: Patel MR, Moradia VJ: Percutaneous release of trigger digit with and without cortisone injection. J Hand Surg [Am] 1997;22: Marks MR, Gunther SF: Efficacy of cortisone injection in treatment of trigger fingers and thumbs. J Hand Surg [Am] 1989;14: Lambert MA, Morton RJ, Sloan JP: Controlled study of the use of local steroid injection in the treatment of trigger finger and thumb. J Hand Surg [Br] 1992;17: Murphy D, Failla JM, Koniuch MP: Steroid versus placebo injection for trigger finger. J Hand Surg [Am] 1995;20: Maneerit J, Sriworakun C, Budhraja N, Nagavajara P: Trigger thumb: Results of a prospective randomised study of percutaneous release with steroid injection versus steroid injection alone. J Hand Surg [Br] 2003;28: Freiberg A, Mulholland RS, Levine R: Nonoperative treatment of trigger fingers and thumbs. J Hand Surg [Am] 1989;14: Anderson B, Kaye S: Treatment of flexor tenosynovitis of the hand ( trigger finger ) with s: A prospective study of the response to local injection. Arch Intern Med 1991;151: Newport ML, Lane LB, Stuchin SA: Treatment of trigger finger by steroid injection. J Hand Surg [Am] 1990;15: Nimigan AS, Ross DC, Gan BS: Steroid injections in the management of trigger fingers. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2006;85: Akhtar S, Bradley MJ, Quinton DN, Burke FD: Management and referral for trigger finger/thumb. BMJ 2005; 331: Benson LS, Ptaszek AJ: Injection versus surgery in the treatment of trigger finger. J Hand Surg [Am] 1997;22: Gilberts EC, Beekman WH, Stevens HJ, Wereldsma JC: Prospective randomized trial of open versus percutaneous surgery for trigger digits. J Hand Surg [Am] 2001;26: Lorthioir J Jr: Surgical treatment of trigger-finger by a subcutaneous method. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1958; 40: Lyu SR: Closed division of the flexor tendon sheath for trigger finger. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1992;74: Mayer D: Essential Evidence-Based Medicine. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, Taras JS, Raphael JS, Pan WT, Movagharnia F, Sotereanos DG: Corticosteroid injections for trigger digits: Is intrasheath injection necessary? J Hand Surg [Am] 1998;23: Fahey JJ, Bollinger JA: Trigger-finger in adults and children. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1954;36: Wright JG, Swiontkowski MF, Heckman JD: Introducing levels of evidence to the journal. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003;85: Spindler KP, Kuhn JE, Dunn W, Matthews CE, Harrell FE Jr, Dittus RS: Reading and reviewing the orthopaedic literature: A systematic, evidence-based medicine approach. JAmAcadOrthopSurg2005;13: Greenhalgh T: How to Read a Paper: The Basics of Evidence Based Medicine. London, England: British Medical Journal Publishing Group, Moriya K, Uchiyama T, Kawaji Y: Comparison of the surgical outcomes for trigger finger and trigger thumb: Preliminary results. Hand Surg 2005; 10: Eastwood DM, Gupta KJ, Johnson DP: Percutaneous release of the trigger finger: An office procedure. J Hand Surg [Am] 1992;17: Volume 15, Number 3, March
Sonographic findings in trigger fingers and outcome of sonographic guided injection
 Sonographic findings in trigger fingers and outcome of sonographic guided injection Poster No.: C-1239 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: R. Faschingbauer, F. Guerra, M. Kaserer, M. C.
Sonographic findings in trigger fingers and outcome of sonographic guided injection Poster No.: C-1239 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: R. Faschingbauer, F. Guerra, M. Kaserer, M. C.
The Efficacy of Steroid Injection in the Treatment of Trigger Finger
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:263-268 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.4.263 The Efficacy of Steroid Injection in the Treatment of Trigger Finger Benan M. Dala-Ali, MBBS, Amir
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:263-268 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.4.263 The Efficacy of Steroid Injection in the Treatment of Trigger Finger Benan M. Dala-Ali, MBBS, Amir
eplasty: Vol. 8 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique
 eplasty: Vol. 8 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine, University of Louisville,
eplasty: Vol. 8 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine, University of Louisville,
Percutaneous trigger finger release Pandey BK, Sharma S, Manandhar RR, Pradhan RL, Lakhey S, Rijal KP
 Original Article Percutaneous trigger finger release Pandey BK, 1, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kathmandu Medical College Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Trigger Þ nger is
Original Article Percutaneous trigger finger release Pandey BK, 1, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kathmandu Medical College Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Trigger Þ nger is
Ultrasound-Guided First Annular Pulley Injection for Trigger Finger
 Article Ultrasound-Guided First Annular Pulley Injection for Trigger Finger Marko Bodor, MD, Tiffany Flossman Objective. The purpose of this study was to develop an ultrasound-guided first annular (A1)
Article Ultrasound-Guided First Annular Pulley Injection for Trigger Finger Marko Bodor, MD, Tiffany Flossman Objective. The purpose of this study was to develop an ultrasound-guided first annular (A1)
Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique
 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L. Zeineh, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine,
Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L. Zeineh, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine,
Safe Treatment of Trigger Thumb With Longitudinal Anatomic Landmarks
 Safe Treatment of Trigger Thumb With Longitudinal Anatomic Landmarks Ron Hazani, MD, Josh Elston, BS, Ryan D. Whitney, BS, Jeremiah Redstone, MD, Saeed Chowdhry, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division
Safe Treatment of Trigger Thumb With Longitudinal Anatomic Landmarks Ron Hazani, MD, Josh Elston, BS, Ryan D. Whitney, BS, Jeremiah Redstone, MD, Saeed Chowdhry, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Surgical Correction of Trigger Finger GM Ref: GM038 Version: 1.1 (6 June 2018)
 Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Surgical Correction of Trigger Finger GM Ref: GM038 Version: 1.1 (6 June 2018) Commissioning Statement Surgical Correction of Trigger Finger Policy Exclusions
Greater Manchester EUR Policy Statement on: Surgical Correction of Trigger Finger GM Ref: GM038 Version: 1.1 (6 June 2018) Commissioning Statement Surgical Correction of Trigger Finger Policy Exclusions
TRIGGER DIGIT, OR stenosing tenosynovitis, isa
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Multiple Pulley Rupture Following Corticosteroid Injection for Trigger Digit: Case Report Cassie Gyuricza, MD, Eva Umoh, BA, Scott W. Wolfe, MD We report a case of pulley rupture following
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Multiple Pulley Rupture Following Corticosteroid Injection for Trigger Digit: Case Report Cassie Gyuricza, MD, Eva Umoh, BA, Scott W. Wolfe, MD We report a case of pulley rupture following
NHS Fylde and Wyre Clinical Commissioning Group. Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare. Policy for surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
 NHS Fylde and Wyre Clinical Commissioning Group Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome 1 Introduction 1.1 This document is part of a suite
NHS Fylde and Wyre Clinical Commissioning Group Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome 1 Introduction 1.1 This document is part of a suite
Trigger Finger: Comparative Study between Corticosteroid Injection and Percutaneous Release
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 Trigger Finger: Comparative Study between Corticosteroid Injection and Percutaneous Release V Singh, S Chong, S Marriapan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 Trigger Finger: Comparative Study between Corticosteroid Injection and Percutaneous Release V Singh, S Chong, S Marriapan Citation
Trigger finger: etiology, evaluation, and treatment
 Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med (2008) 1:92 96 DOI 10.1007/s12178-007-9012-1 Trigger finger: etiology, evaluation, and treatment Al Hasan Makkouk Æ Matthew E. Oetgen Æ Carrie R. Swigart Æ Seth D. Dodds Published
Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med (2008) 1:92 96 DOI 10.1007/s12178-007-9012-1 Trigger finger: etiology, evaluation, and treatment Al Hasan Makkouk Æ Matthew E. Oetgen Æ Carrie R. Swigart Æ Seth D. Dodds Published
Corticosteroid injections for the treatment of hand and wrist disorders in general practice Peters-Veluthamaningal, Cyriac
 University of Groningen Corticosteroid injections for the treatment of hand and wrist disorders in general practice Peters-Veluthamaningal, Cyriac IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
University of Groningen Corticosteroid injections for the treatment of hand and wrist disorders in general practice Peters-Veluthamaningal, Cyriac IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley.
 TRIGGER DIGITS Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley. Abstract Primary stenosing tenosynovitis is usually idiopathic
TRIGGER DIGITS Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley. Abstract Primary stenosing tenosynovitis is usually idiopathic
Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb
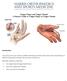 Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb Introduction Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the movement of the tendons as they bend the
Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb Introduction Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the movement of the tendons as they bend the
British Society for Surgery of the Hand Evidence for Surgical Treatment (BEST)
 British Society for Surgery of the Hand Evidence for Surgical Treatment (BEST) Topic: Evidence based management of adult trigger digits Date of publication: October 2016 Date of anticipated review: October
British Society for Surgery of the Hand Evidence for Surgical Treatment (BEST) Topic: Evidence based management of adult trigger digits Date of publication: October 2016 Date of anticipated review: October
Overuse Injuries of the Upper Extremity. Overuse Injuries 7/23/2018. Peadiatric Overuse Sports Injuries. Al Hess, MD
 Overuse Injuries of the Upper Extremity Al Hess, MD 7/21/2018 1 Overuse Injuries Everything? Not Trauma, infection, tumor, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis Onset of pain associated with repetitive
Overuse Injuries of the Upper Extremity Al Hess, MD 7/21/2018 1 Overuse Injuries Everything? Not Trauma, infection, tumor, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis Onset of pain associated with repetitive
ACPOMIT Conference 2013 Workshop: Hand and Wrist
 ACPOMIT Conference 2013 Workshop: Hand and Wrist Sarah Turner, MCSP, Clinical Specialist in Hand Therapy Grad Dip Injection Therapy Workshop! Trigger Finger! OA 1 st CMC joint! De Quervain s Tenosynovitis!
ACPOMIT Conference 2013 Workshop: Hand and Wrist Sarah Turner, MCSP, Clinical Specialist in Hand Therapy Grad Dip Injection Therapy Workshop! Trigger Finger! OA 1 st CMC joint! De Quervain s Tenosynovitis!
ComparisonoftheShortTermTreatmentOutcomeamongWatchfulWaitingandSolubleandInsolubleCorticosteroidInjectionsinIdiopathicTriggerFinger
 : H Orthopedic and Musculoskeletal System Volume 16 Issue 1 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618
: H Orthopedic and Musculoskeletal System Volume 16 Issue 1 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618
Sonographic Appearance of Trigger Fingers
 Article Sonographic Appearance of Trigger Fingers Henri Guerini, MD, Eric Pessis, MD, Nicolas Theumann, MD, Janine-Sophie Le Quintrec, MD, Raphaël Campagna, MD, PhD, Alain Chevrot, MD, PhD, Antoine Feydy,
Article Sonographic Appearance of Trigger Fingers Henri Guerini, MD, Eric Pessis, MD, Nicolas Theumann, MD, Janine-Sophie Le Quintrec, MD, Raphaël Campagna, MD, PhD, Alain Chevrot, MD, PhD, Antoine Feydy,
Original Article. Methylprednisolone Acetate Injection Plus Casting Versus Casting Alone for the Treatment of de Quervain s Tenosynovitis
 Original Article Methylprednisolone Acetate Injection Plus Casting Versus Casting Alone for the Treatment of de Quervain s Tenosynovitis Seyed Abdolhossein Mehdinasab MD 1, Seyed Amirmohammad Alemohammad
Original Article Methylprednisolone Acetate Injection Plus Casting Versus Casting Alone for the Treatment of de Quervain s Tenosynovitis Seyed Abdolhossein Mehdinasab MD 1, Seyed Amirmohammad Alemohammad
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS. Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran
 TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
Trigger Finger Release
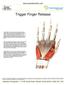 Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2
 Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Common Hand Conditions SHAMIM UMARJI MA (Oxon) FRCS (Tr & Orth) CONSULTANT TRAUMA & ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON
 Common Hand Conditions SHAMIM UMARJI MA (Oxon) FRCS (Tr & Orth) CONSULTANT TRAUMA & ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON Common Hand Conditions Carpal tunnel syndrome Dupuytren s Disease Ganglia Trigger Digits De Quervain
Common Hand Conditions SHAMIM UMARJI MA (Oxon) FRCS (Tr & Orth) CONSULTANT TRAUMA & ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON Common Hand Conditions Carpal tunnel syndrome Dupuytren s Disease Ganglia Trigger Digits De Quervain
Stenosing flexor tenosynovitis (trigger finger) is
 An Original Study Recalcitrant Trigger Finger Managed With Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Resection Sohail N. Husain, MD, Sylvan E. Clarke, MD, Glenn A. Buterbaugh, MD, and Joseph E. Imbriglia, MD Abstract
An Original Study Recalcitrant Trigger Finger Managed With Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Resection Sohail N. Husain, MD, Sylvan E. Clarke, MD, Glenn A. Buterbaugh, MD, and Joseph E. Imbriglia, MD Abstract
Andrew L Terrono, MD Chief Hand Surgery Service NEBH Clinical Professor Orthopaedics Tufts University. May 2 & 3, 2016
 Andrew L Terrono, MD Chief Hand Surgery Service NEBH Clinical Professor Orthopaedics Tufts University Work Related Workshop WorkInjuries Related Injuries Workshop Exertional??? Webster- precipitated by
Andrew L Terrono, MD Chief Hand Surgery Service NEBH Clinical Professor Orthopaedics Tufts University Work Related Workshop WorkInjuries Related Injuries Workshop Exertional??? Webster- precipitated by
International Journal of Orthopaedics Sciences 2017; 3(2): Dr. Rakesh Chand Meena and Dr. Sudhir Kumar Yadav
 2017; 3(2): 779-783 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 779-783 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 22-02-2017 Accepted: 23-03-2017 Dr. Rakesh Chand Meena Rajasthan, India Dr. Sudhir Kumar Yadav Rajasthan
2017; 3(2): 779-783 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 779-783 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 22-02-2017 Accepted: 23-03-2017 Dr. Rakesh Chand Meena Rajasthan, India Dr. Sudhir Kumar Yadav Rajasthan
Injection Treatment of Trigger Finger in Patients with Previous Injection Resistant Trigger Finger
 Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Yale Medicine Thesis Digital Library School of Medicine 9-29-2010 Injection Treatment of Trigger Finger in Patients with Previous
Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Yale Medicine Thesis Digital Library School of Medicine 9-29-2010 Injection Treatment of Trigger Finger in Patients with Previous
Results Of Tenosynovectomy And Intralesional Steroid In The Management Of Trigger Fingers
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Results Of Tenosynovectomy And Intralesional Steroid In The Management Of Trigger Fingers A Ogbemudia, A Bafor, E Edomwonyi Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Results Of Tenosynovectomy And Intralesional Steroid In The Management Of Trigger Fingers A Ogbemudia, A Bafor, E Edomwonyi Citation
To study the role of ultrasonography in diagnosis, management and prevention of incomplete surgical release in patient s of de Quervain s disease
 2017; 3(4): 344-348 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(4): 344-348 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 18-08-2017 Accepted: 20-09-2017 Dr. Tilak Rommel Pinto Dr. Harsharaj K Dr. Anston Vernon Braggs Department
2017; 3(4): 344-348 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(4): 344-348 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 18-08-2017 Accepted: 20-09-2017 Dr. Tilak Rommel Pinto Dr. Harsharaj K Dr. Anston Vernon Braggs Department
Treatment of De Quervain's Syndrome with ultrasound (US)- guided infiltration of steroids and hyaluronic acid
 Treatment of De Quervain's Syndrome with ultrasound (US)- guided infiltration of steroids and hyaluronic acid Poster No.: C-2052 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Turturici 1, E.
Treatment of De Quervain's Syndrome with ultrasound (US)- guided infiltration of steroids and hyaluronic acid Poster No.: C-2052 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Turturici 1, E.
Are Indians more prone for De Quervains tendinitis?
 Original article: Are Indians more prone for De Quervains tendinitis? *Manoj M Kulkarni 1, A Ashok 2 *1 Asst. Prof, Dept of Anatomy, SBKS Medical Institute & Research Center, Piparia, Vadodara, Gujarat,
Original article: Are Indians more prone for De Quervains tendinitis? *Manoj M Kulkarni 1, A Ashok 2 *1 Asst. Prof, Dept of Anatomy, SBKS Medical Institute & Research Center, Piparia, Vadodara, Gujarat,
Occupational therapy for rheumatoid arthritis (Review)
 Steultjens EEMJ, Dekker JJ, Bouter LM, Schaardenburg DD, Kuyk MAMAH, Van den Ende ECHM This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The
Steultjens EEMJ, Dekker JJ, Bouter LM, Schaardenburg DD, Kuyk MAMAH, Van den Ende ECHM This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The
Corticosteroid injections for the treatment of hand and wrist disorders in general practice Peters-Veluthamaningal, Cyriac
 University of Groningen Corticosteroid injections for the treatment of hand and wrist disorders in general practice Peters-Veluthamaningal, Cyriac IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
University of Groningen Corticosteroid injections for the treatment of hand and wrist disorders in general practice Peters-Veluthamaningal, Cyriac IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
US-guided steroid and hyaluronic acid infiltration for the treatment of hand and wrist tenosynovitis: Preliminary experience
 US-guided steroid and hyaluronic acid infiltration for the treatment of hand and wrist tenosynovitis: Preliminary experience Poster No.: C-2342 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal
US-guided steroid and hyaluronic acid infiltration for the treatment of hand and wrist tenosynovitis: Preliminary experience Poster No.: C-2342 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal
CIC Edizioni Internazionali. Percutaneous trigger finger release with an MS64 scalpel. Original article. Introduction. Summary
 Original article Percutaneous trigger finger release with an MS64 scalpel Damián Mifsut-Miedes 1 Alfonso A. Valverde Navarro 2 Juan Moreno Rivelles 3 1 Department of Surgery, University of Valencia; Hospital
Original article Percutaneous trigger finger release with an MS64 scalpel Damián Mifsut-Miedes 1 Alfonso A. Valverde Navarro 2 Juan Moreno Rivelles 3 1 Department of Surgery, University of Valencia; Hospital
eplasty: Vol. 8 Anatomic Landmarks for the First Dorsal Compartment
 eplasty: Vol. 8 Anatomic Landmarks for the First Dorsal Compartment Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Damon Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, University of Louisville School of Medicine,
eplasty: Vol. 8 Anatomic Landmarks for the First Dorsal Compartment Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Damon Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, University of Louisville School of Medicine,
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Carpal tunnel syndrome results from the pinching or entrapping of the median nerve in the underside of the wrist. The actual pathology in most cases is due to either a decrease in
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Carpal tunnel syndrome results from the pinching or entrapping of the median nerve in the underside of the wrist. The actual pathology in most cases is due to either a decrease in
Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
 Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014 Nov;93(11 Suppl 3):S108-21. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000115. Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014 Nov;93(11 Suppl 3):S108-21. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000115. Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
Comparison of the results of open
 1131 Original Article Singapore Med.1 27; 48 (12) : Comparison of the results of open carpal tunnel release and KnifeLight carpal tunnel release Yeo K Q, Yeo E M N Yeo Orthopaedic Centre, Mount Elizabeth
1131 Original Article Singapore Med.1 27; 48 (12) : Comparison of the results of open carpal tunnel release and KnifeLight carpal tunnel release Yeo K Q, Yeo E M N Yeo Orthopaedic Centre, Mount Elizabeth
Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity. Mark Tait MD
 Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity Mark Tait MD Tendonitis History Pain and swelling (any tendon, any location) Overuse Physical examination findings Localized swelling Pain with resistance
Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity Mark Tait MD Tendonitis History Pain and swelling (any tendon, any location) Overuse Physical examination findings Localized swelling Pain with resistance
Name: McGillivary, Gary R. 1 CURRICULUM VITAE Lecturer, Dalhousie University School of Nursing, Outpost Nursing Program
 Name: McGillivary, Gary R. 1 CURRICULUM VITAE Name: Gary R. McGillivary, M.D. Revised: October 1, 2012 Office Address: Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Emory Orthopaedic and Spine Center 59 Executive
Name: McGillivary, Gary R. 1 CURRICULUM VITAE Name: Gary R. McGillivary, M.D. Revised: October 1, 2012 Office Address: Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Emory Orthopaedic and Spine Center 59 Executive
Effectiveness of Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Lateral Epicondylosis
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2012, 21, 83-88 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. Effectiveness of Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Lateral Epicondylosis Kelli R. Snyder and Todd A. Evans Clinical Scenario
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2012, 21, 83-88 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. Effectiveness of Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Lateral Epicondylosis Kelli R. Snyder and Todd A. Evans Clinical Scenario
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet. Under review. Page 1
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a common problem which affects the hand and wrist. Symptoms are caused
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a common problem which affects the hand and wrist. Symptoms are caused
Recommendations for Optimal Care of the Fragility Fracture Patient to Reduce the Risk of Future Fracture
 Recommendations for Optimal Care of the Fragility Fracture Patient to Reduce the Risk of Future Fracture Mary L. Bouxsein, PhD, John Kaufman, MD, Laura Tosi, MD, Steven Cummings, MD, Joseph Lane, MD, and
Recommendations for Optimal Care of the Fragility Fracture Patient to Reduce the Risk of Future Fracture Mary L. Bouxsein, PhD, John Kaufman, MD, Laura Tosi, MD, Steven Cummings, MD, Joseph Lane, MD, and
Disclosure. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 11/9/15
 Michael S. Bednar, M.D. Chief, Hand Surgery Professor, Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehab Loyola University - Chicago Disclosure No conflicts for this talk Carpal Tunnel Syndrome AKA Corporal tunnel
Michael S. Bednar, M.D. Chief, Hand Surgery Professor, Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehab Loyola University - Chicago Disclosure No conflicts for this talk Carpal Tunnel Syndrome AKA Corporal tunnel
Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives
 NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives POLICY TRAIL AND VERSION CONTROL SHEET: Policy Reference:
NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives POLICY TRAIL AND VERSION CONTROL SHEET: Policy Reference:
1 Comprehensive Orthopaedic Review Hand and Wrist Tendinopathies Bernard F. Hearon, MD September 2, de Quervain Disorder Fritz de Quervain,
 1 Comprehensive Orthopaedic Review Hand and Wrist Tendinopathies Bernard F. Hearon, MD September 2, 2016 2 de Quervain Disorder Fritz de Quervain, Swiss surgeon, 1895 Stenosing tendinosis, 1st dorsal compartment
1 Comprehensive Orthopaedic Review Hand and Wrist Tendinopathies Bernard F. Hearon, MD September 2, 2016 2 de Quervain Disorder Fritz de Quervain, Swiss surgeon, 1895 Stenosing tendinosis, 1st dorsal compartment
Interesting Case Series. The Recurrent Motor Branch of the Median Nerve
 Interesting Case Series The Recurrent Motor Branch of the Median Nerve Jeon Cha, Blair York, and John Tawfik The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney Eye Hospital, Sydney, Australia Correspondence:
Interesting Case Series The Recurrent Motor Branch of the Median Nerve Jeon Cha, Blair York, and John Tawfik The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney Eye Hospital, Sydney, Australia Correspondence:
Orthopaedic Section of the APTA Grant Program Annual Progress Report Form
 Orthopaedic Section of the APTA Grant Program Annual Progress Report Form Date: 9/21/2015 Name of Investigators: Name of Grant: Shane McClinton, Timothy Flynn, Bryan Heiderscheit Comparison of Usual Podiatric
Orthopaedic Section of the APTA Grant Program Annual Progress Report Form Date: 9/21/2015 Name of Investigators: Name of Grant: Shane McClinton, Timothy Flynn, Bryan Heiderscheit Comparison of Usual Podiatric
Workshop: Cochrane Rehabilitation 05th May Trusted evidence. Informed decisions. Better health.
 Workshop: Cochrane Rehabilitation 05th May 2018 Trusted evidence. Informed decisions. Better health. Disclosure I have no conflicts of interest with anything in this presentation How to read a systematic
Workshop: Cochrane Rehabilitation 05th May 2018 Trusted evidence. Informed decisions. Better health. Disclosure I have no conflicts of interest with anything in this presentation How to read a systematic
Occupational therapy guidelines for conditions in which the metacarpophalangeal joints could be splinted in extension
 Occupational therapy guidelines for conditions in which the metacarpophalangeal joints could be splinted in extension Elani Muller Corrianne van Velze Tania Buys 24 May 2018 Introduction MP joints should
Occupational therapy guidelines for conditions in which the metacarpophalangeal joints could be splinted in extension Elani Muller Corrianne van Velze Tania Buys 24 May 2018 Introduction MP joints should
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES
 JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES. Revision Surgery after percutaneous release of the A1 pulley for surgical treatment of trigger finger: An unusual case and brief review of literature.
JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES. Revision Surgery after percutaneous release of the A1 pulley for surgical treatment of trigger finger: An unusual case and brief review of literature.
Study selection Study designs of evaluations included in the review Diagnosis.
 Diagnosis and treatment of worker-related musculoskeletal disorders of the upper extremity: epicondylitis Chapell R, Bruening W, Mitchell M D, Reston J T, Treadwell J R Authors' objectives The objectives
Diagnosis and treatment of worker-related musculoskeletal disorders of the upper extremity: epicondylitis Chapell R, Bruening W, Mitchell M D, Reston J T, Treadwell J R Authors' objectives The objectives
OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT
 375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Introduction Interventional procedures overview of needle fasciotomy for Dupuytren s contracture This overview has been prepared
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Introduction Interventional procedures overview of needle fasciotomy for Dupuytren s contracture This overview has been prepared
Workplace Hand Injuries & Disorders: Evaluation and Treatments. Hervey L. Kimball MD, MS Hand Surgical Associates Occupational Medicine Center
 Workplace Hand Injuries & Disorders: Evaluation and Treatments Hervey L. Kimball MD, MS Hand Surgical Associates Occupational Medicine Center Outline Hand Anatomy and Function Workplace injuries & Case
Workplace Hand Injuries & Disorders: Evaluation and Treatments Hervey L. Kimball MD, MS Hand Surgical Associates Occupational Medicine Center Outline Hand Anatomy and Function Workplace injuries & Case
It s All Relative: How Presentation of Information To Patients Influences Their Decision-Making
 MUMJ Original Research 15 ORIGINAL RESEARCH It s All Relative: How Presentation of Information To Patients Influences Their Decision-Making Mohit Bhandari, MD, MSc Vikas Khera, BSc Jaydeep K. Moro, MD
MUMJ Original Research 15 ORIGINAL RESEARCH It s All Relative: How Presentation of Information To Patients Influences Their Decision-Making Mohit Bhandari, MD, MSc Vikas Khera, BSc Jaydeep K. Moro, MD
ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES
 ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES OAAPN October 20, 2016 David H. Sohn, JD MD Chief, Shoulder and Sports Medicine University of Toledo Medical Center When to aspirate? To rule out infection
ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES OAAPN October 20, 2016 David H. Sohn, JD MD Chief, Shoulder and Sports Medicine University of Toledo Medical Center When to aspirate? To rule out infection
Effect of Local Corticosteroid Injection of the Hand and Wrist on Blood Glucose in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus
 Effect of Local Corticosteroid Injection of the Hand and Wrist on Blood Glucose in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus Louis W. Catalano III, MD; Steven Z. Glickel, MD; O. Alton Barron, MD; Richard Harrison,
Effect of Local Corticosteroid Injection of the Hand and Wrist on Blood Glucose in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus Louis W. Catalano III, MD; Steven Z. Glickel, MD; O. Alton Barron, MD; Richard Harrison,
Role of evidence from observational studies in the process of health care decision making
 Role of evidence from observational studies in the process of health care decision making Jan van der Meulen Health Services Research Unit London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine Clinical Effectiveness
Role of evidence from observational studies in the process of health care decision making Jan van der Meulen Health Services Research Unit London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine Clinical Effectiveness
Appraising the Literature Overview of Study Designs
 Chapter 5 Appraising the Literature Overview of Study Designs Barbara M. Sullivan, PhD Department of Research, NUHS Jerrilyn A. Cambron, PhD, DC Department of Researach, NUHS EBP@NUHS Ch 5 - Overview of
Chapter 5 Appraising the Literature Overview of Study Designs Barbara M. Sullivan, PhD Department of Research, NUHS Jerrilyn A. Cambron, PhD, DC Department of Researach, NUHS EBP@NUHS Ch 5 - Overview of
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Concord Orthopaedics 264 Pleasant Street Concord, NH 03301 Phone: 6032243368 Fax: 6032287268 marketing.copa@concordortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Concord Orthopaedics 264 Pleasant Street Concord, NH 03301 Phone: 6032243368 Fax: 6032287268 marketing.copa@concordortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Carpal Tunnel Release
 Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures
 Journal of the Accident and Medical Practitioners Association (JAMPA) 2006; Vol. 3 (No. 1) Accident and Medical Practitioners Association, New Zealand Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures Sarah Cooper, MBChB
Journal of the Accident and Medical Practitioners Association (JAMPA) 2006; Vol. 3 (No. 1) Accident and Medical Practitioners Association, New Zealand Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures Sarah Cooper, MBChB
Short-term Versus Long-term Outcomes After Open or Percutaneous Release for Trigger Thumb
 Short-term Versus Long-term Outcomes After Open or for Trigger Thumb Hui-Kuang Huang, MD; Jung-Pan Wang, MD, PhD; Chin-Jung Lin, MD; Yi-Chao Huang, MD; Tung-Fu Huang, MD; Ming-Chau Chang, MD abstract Good
Short-term Versus Long-term Outcomes After Open or for Trigger Thumb Hui-Kuang Huang, MD; Jung-Pan Wang, MD, PhD; Chin-Jung Lin, MD; Yi-Chao Huang, MD; Tung-Fu Huang, MD; Ming-Chau Chang, MD abstract Good
Acute Services Division. Information for patients. Carpal Tunnel. Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary
 Acute Services Division Information for patients Carpal Tunnel Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary Introduction Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) can cause the symptoms of pain, pins and needles
Acute Services Division Information for patients Carpal Tunnel Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary Introduction Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) can cause the symptoms of pain, pins and needles
West Suffolk Hospital
 For staff use only: Patient Details: First names: Hospital no: (Use hospital identification label) West Suffolk Hospital Patient information leaflet Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 2-3 Patient agreement to investigation
For staff use only: Patient Details: First names: Hospital no: (Use hospital identification label) West Suffolk Hospital Patient information leaflet Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 2-3 Patient agreement to investigation
Results. NeuRA Hypnosis June 2016
 Introduction may be experienced as an altered state of consciousness or as a state of relaxation. There is no agreed framework for administering hypnosis, but the procedure often involves induction (such
Introduction may be experienced as an altered state of consciousness or as a state of relaxation. There is no agreed framework for administering hypnosis, but the procedure often involves induction (such
APPLYING EVIDENCE-BASED METHODS IN PSYCHIATRY JOURNAL CLUB: HOW TO READ & CRITIQUE ARTICLES
 University of Miami Scholarly Repository Faculty Research, Publications, and Presentations Department of Health Informatics 7-26-2017 APPLYING EVIDENCE-BASED METHODS IN PSYCHIATRY JOURNAL CLUB: HOW TO
University of Miami Scholarly Repository Faculty Research, Publications, and Presentations Department of Health Informatics 7-26-2017 APPLYING EVIDENCE-BASED METHODS IN PSYCHIATRY JOURNAL CLUB: HOW TO
Demographic Trends and Complication Rates in Arthroscopic Elbow Surgery
 Demographic Trends and Complication Rates in Arthroscopic Elbow Surgery Natalie L. Leong 1 *, Jeremiah R. Cohen 1, Elizabeth Lord 1, Jeffrey C. Wang 2, David R. McAllister 1, and Frank A. Petrigliano 1
Demographic Trends and Complication Rates in Arthroscopic Elbow Surgery Natalie L. Leong 1 *, Jeremiah R. Cohen 1, Elizabeth Lord 1, Jeffrey C. Wang 2, David R. McAllister 1, and Frank A. Petrigliano 1
Clinical Case Report Competition
 Massage Therapists Association of B.C. Clinical Case Report Competition West Coast College of Massage Therapy June, 2009 Honourable Mention Janet Lee The Effects of Massage Therapy in Pain Management of
Massage Therapists Association of B.C. Clinical Case Report Competition West Coast College of Massage Therapy June, 2009 Honourable Mention Janet Lee The Effects of Massage Therapy in Pain Management of
Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment
 Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment Link to guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ bedfordshire-and-hertfordshire-priorities-forum Dupuytren's contracture - clinical presentation for patients History Examination
Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment Link to guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ bedfordshire-and-hertfordshire-priorities-forum Dupuytren's contracture - clinical presentation for patients History Examination
Inflammation Is Present In De Quervain s Disease- a Correlation Study Between Biochemical And Histopathological Evaluation
 Inflammation Is Present In De Quervain s Disease- a Correlation Study Between Biochemical And Histopathological Evaluation Hsu Kai-Lan 1, KUO YAO-LUNG 2, WU PO-TING 1, JOU I-MING 1. 1 National Cheng Kung
Inflammation Is Present In De Quervain s Disease- a Correlation Study Between Biochemical And Histopathological Evaluation Hsu Kai-Lan 1, KUO YAO-LUNG 2, WU PO-TING 1, JOU I-MING 1. 1 National Cheng Kung
Comparison of Roll Stitch Technique and Core Suture Technique for Extensor Tendon Repair at the Metacarpophalangeal Joint level
 Trauma Mon. 2016 February; 21(1): e24563. Published online 2016 February 6. doi: 10.5812/traumamon.24563 Research Article Comparison of Roll Stitch Technique and Core Suture Technique for Extensor Tendon
Trauma Mon. 2016 February; 21(1): e24563. Published online 2016 February 6. doi: 10.5812/traumamon.24563 Research Article Comparison of Roll Stitch Technique and Core Suture Technique for Extensor Tendon
Overview of Study Designs in Clinical Research
 Overview of Study Designs in Clinical Research Systematic Reviews (SR), Meta-Analysis Best Evidence / Evidence Guidelines + Evidence Summaries Randomized, controlled trials (RCT) Clinical trials, Cohort
Overview of Study Designs in Clinical Research Systematic Reviews (SR), Meta-Analysis Best Evidence / Evidence Guidelines + Evidence Summaries Randomized, controlled trials (RCT) Clinical trials, Cohort
The Philadelphia Panel evidence-based clinical
 SPECIAL ARTICLE Managing musculoskeletal complaints with rehabilitation therapy: Summary of the Philadelphia Panel evidence-based clinical practice guidelines on musculoskeletal rehabilitation interventions
SPECIAL ARTICLE Managing musculoskeletal complaints with rehabilitation therapy: Summary of the Philadelphia Panel evidence-based clinical practice guidelines on musculoskeletal rehabilitation interventions
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Mashad University of Medical Sciences, Mashad, Iran
 Arch Iranian Med 2003; 6 (3): 196 199 ORIGINAL ARTICLE INJECTION OF METHYLPREDNISOLONE AND LIDOCAINE IN THE TREATMENT OF MEDIAL EPICONDYLITIS: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL Mahmood Bahari MD, Mohammad Gharehdaghi
Arch Iranian Med 2003; 6 (3): 196 199 ORIGINAL ARTICLE INJECTION OF METHYLPREDNISOLONE AND LIDOCAINE IN THE TREATMENT OF MEDIAL EPICONDYLITIS: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL Mahmood Bahari MD, Mohammad Gharehdaghi
Wrist and Hand Complaints
 Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Trigger Finger: Incidence in Children and Adults and the Possibility of a Predisposition in Certain Age Groups
 Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 0001-6470 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort19 Trigger Finger: Incidence in Children and Adults and the Possibility of a Predisposition
Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 0001-6470 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort19 Trigger Finger: Incidence in Children and Adults and the Possibility of a Predisposition
HOW TO DEVELOP A RESEARCH PROTOCOL
 Research and Evidence Based Medicine Committee 2010-2011 HOW TO DEVELOP A RESEARCH PROTOCOL Evidence-Based Medicine The conscientious, explicit, and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions
Research and Evidence Based Medicine Committee 2010-2011 HOW TO DEVELOP A RESEARCH PROTOCOL Evidence-Based Medicine The conscientious, explicit, and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions
Traumatic brain injury
 Introduction It is well established that traumatic brain injury increases the risk for a wide range of neuropsychiatric disturbances, however there is little consensus on whether it is a risk factor for
Introduction It is well established that traumatic brain injury increases the risk for a wide range of neuropsychiatric disturbances, however there is little consensus on whether it is a risk factor for
Systematic Review of Diagnostic Utility and Therapeutic Effectiveness of Thoracic Facet Joint Interventions
 Pain Physician 2008; 11:611-629 ISSN 1533-3159 Systematic Review Systematic Review of Diagnostic Utility and Therapeutic Effectiveness of Thoracic Facet Joint Interventions Sairam Atluri, MD 1, Sukdeb
Pain Physician 2008; 11:611-629 ISSN 1533-3159 Systematic Review Systematic Review of Diagnostic Utility and Therapeutic Effectiveness of Thoracic Facet Joint Interventions Sairam Atluri, MD 1, Sukdeb
We performed a prospective, randomised trial on
 LOCAL CORTICOSTEROID INJECTION VERSUS CYRIAX-TYPE PHYSIOTHERAPY FOR TENNIS ELBOW J. A. N. VERHAAR, G. H. I. M. WALENKAMP, H. VAN MAMEREN, A. D. M. KESTER, A. J. VAN DER LINDEN From the University Hospital,
LOCAL CORTICOSTEROID INJECTION VERSUS CYRIAX-TYPE PHYSIOTHERAPY FOR TENNIS ELBOW J. A. N. VERHAAR, G. H. I. M. WALENKAMP, H. VAN MAMEREN, A. D. M. KESTER, A. J. VAN DER LINDEN From the University Hospital,
Elastic bandage vs. neoprene thumb stabilizer splint in acute De Quervain s tenosynovitis
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 5 No. 2 April 2011; 263-267 Technical report (original) DOI: 10.5372/1905-7415.0502.035 Elastic bandage vs. neoprene thumb stabilizer splint in acute De Quervain s tenosynovitis
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 5 No. 2 April 2011; 263-267 Technical report (original) DOI: 10.5372/1905-7415.0502.035 Elastic bandage vs. neoprene thumb stabilizer splint in acute De Quervain s tenosynovitis
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
Results. NeuRA Treatments for dual diagnosis August 2016
 Introduction Many treatments have been targeted to improving symptom severity for people suffering schizophrenia in combination with substance use problems. Studies of dual diagnosis often investigate
Introduction Many treatments have been targeted to improving symptom severity for people suffering schizophrenia in combination with substance use problems. Studies of dual diagnosis often investigate
NeuRA Obsessive-compulsive disorders October 2017
 Introduction (OCDs) involve persistent and intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive actions (compulsions). The DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition) defines
Introduction (OCDs) involve persistent and intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive actions (compulsions). The DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition) defines
Journal of Biostatistics and Epidemiology
 Journal of Biostatistics and Epidemiology Original Article Usage of statistical methods and study designs in publication of specialty of general medicine and its secular changes Swati Patel 1*, Vipin Naik
Journal of Biostatistics and Epidemiology Original Article Usage of statistical methods and study designs in publication of specialty of general medicine and its secular changes Swati Patel 1*, Vipin Naik
Problem solving therapy
 Introduction People with severe mental illnesses such as schizophrenia may show impairments in problem-solving ability. Remediation interventions such as problem solving skills training can help people
Introduction People with severe mental illnesses such as schizophrenia may show impairments in problem-solving ability. Remediation interventions such as problem solving skills training can help people
Is Phlogenzym Effective in Reducing Moderate to Severe Osteoarthritis Pain in Adults?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2013 Is Phlogenzym Effective in Reducing Moderate
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2013 Is Phlogenzym Effective in Reducing Moderate
Interesting Case Series. Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression
 Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
Getting Evidence into Clinical Practice: Musculoskeletal Research Facilitation Group (CAT Group) Date: June 2017
 Specific Question: In adults with chronic shoulder pain is a nerve ablation procedure (for the suprascapular nerve) as effective in reducing pain, in the long term compared with usual care? Clinical bottom
Specific Question: In adults with chronic shoulder pain is a nerve ablation procedure (for the suprascapular nerve) as effective in reducing pain, in the long term compared with usual care? Clinical bottom
Musculoskeletal corticosteroid use:
 Musculoskeletal corticosteroid use: Types, Indications, Contraindications, Equivalent doses, Frequency of use and Adverse effects. Dr Jide Olubaniyi MBBS, FRCR Dr Sean Crowther MB BCh, MRCS, FRCR Dr Sukhvinder
Musculoskeletal corticosteroid use: Types, Indications, Contraindications, Equivalent doses, Frequency of use and Adverse effects. Dr Jide Olubaniyi MBBS, FRCR Dr Sean Crowther MB BCh, MRCS, FRCR Dr Sukhvinder
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY
 8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
