Chronic Childhood Constipation Is Associated with Impaired Quality of Life: A Case-Controlled Study
|
|
|
- Joan Perry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 41:56 60 Ó July 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia Chronic Childhood Constipation Is Associated with Impaired Quality of Life: A Case-Controlled Study Nader N. Youssef, Annette L. Langseder, Barbara J. Verga, Richard L. Mones, and Joel R. Rosh Center for Pediatric Functional Gastrointestinal and Motility Disorders, Goryeb Children s Hospital, Atlantic Health System Morristown, New Jersey ABSTRACT Objective: The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of chronic constipation on children s quality of life. Methods: From October 2002 to November 2003, 224 children (140 male, 84 female, aged years) and 224 parents were evaluated by a health related quality of life tool during initial outpatient consultation. Children with constipation (n = 80) were compared with controls with inflammatory bowel disease (n = 42), controls with gastroesophageal reflux disease (n = 56), and with healthy children (n = 46). Results: Children with constipation had lower quality of life scores than did those with inflammatory bowel disease (70 versus 84; P, 0.05), gastroesophageal reflux disease (70 versus 80; P, 0.05), and healthy children (70 versus 88; P, 0.05). Children with constipation reported lower physical scores than did inflammatory bowel disease patients (75 versus 85; P, 0.02), gastroesophageal reflux disease patients (75 versus 85; P, 0.05), or healthy children (75 versus 87; P, 0.05). Parents of children with constipation reported lower scores than did their children (61 versus 70; P, 0.05). Children with constipation had longer duration of symptoms than did the controls with inflammatory bowel disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease (43.8 months versus 14.2 months; P, 0.001). Prolonged duration of symptoms for children with constipation correlated with lower parent-reported scores (P, 0.002). Conclusions: At initial evaluation, children with constipation have a lower quality of life than do children with inflammatory bowel disease or gastroesophageal reflux disease. Self-reported lower scores may be a reflection of impaired physical ability. Parental perceptions of low quality of life are probably impacted by the duration of their child s symptoms and by family members with similar complaints. Practitioners should be aware of the high level of parental concern and the relatively low self-reported and parent-reported quality of life in children with chronic constipation as they plan therapy. JPGN 41:56 60, Key Words: Constipation Children Quality of life. Ó 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins INTRODUCTION Chronic constipation is one of the most common conditions encountered in general pediatric and pediatric gastroenterology offices and is associated with a great deal of underappreciated morbidity (1). Chronic stool retention can contribute to recurrent abdominal pain and urinary tract pathology (2). Fecal soiling occurs in 1.5% to 7.5% of school children 6 to 12 years of age (3). Constipation may contribute significantly to abdominal pain complaints in adolescence (4). The symptoms of chronic abdominal pain and fecal soiling may cause psychosocial difficulties, disruption of peer relationships Received October 4, 2004; accepted April 8, Address correspondence and reprint requests to Nader N. Youssef, Center for Pediatric Functional Gastrointestinal and Motility Disorders, Goryeb Children s Hospital, Atlantic Health System, 100 Madison Avenue Box -82, Morristown, NJ ( nader.youssef@ahsys. org). Supported in part by the Joseph P. and Marguerite Goryeb research endowment to the Center for Pediatric Functional Gastrointestinal and Motility Disorders. and familial stress (5 7). Long-term follow-up studies indicate that chronic constipation and associated complaints persist into adulthood in one third of patients (8). Children with constipation may appear quiet, withdrawn, embarrassed and angry during medical evaluation compared with children with other chronic gastrointestinal disorders (9,10). Denial of the symptoms is common in constipated children (11). Despite these published observations, there have been no formal studies comparing the quality of life of children with chronic constipation and their families with children having other chronic gastrointestinal conditions and their families. SUBJECTS AND METHODS After informed consent was obtained, the PedsQLä (Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory) was administered by a research coordinator in a consecutive fashion at a tertiary pediatric care center to children and their parents in the waiting room as they were registering for their initial evaluation (12,13). The PedsQLä, a health related quality of life tool, was administered before any encounter with the physician (13). The inventory uses 56
2 CHRONIC CHILDHOOD CONSTIPATION AND IMPAIRED QOL 57 generic core scales derived both from child self-reports and parent proxy reports. The PedsQLä has been validated in children as young as 5 years of age. The 23-item PedsQLä generic core scales encompass physical (eight items), emotional (five items), social (five items), and school functioning (five items). A 5-point response scale is used (0 = never a problem; 4 = almost always a problem). Items are reverse scored and linearly transformed to a zero to 100 scale (0 = 100, 1 = 75, 2 = 50, 3 = 25, 4 = 0) with higher scores indicating better health-related quality of life. The PedsQLä was read to children under age 7 by the research coordinator. Parents and their children completed the PedsQLä separately. Separate reports are used because child self-reports are based on perceptions of internal states, whereas parent reports reflect the child s observable behaviors. It is often the parent s perception of a child s health status that influences health care use. Study Population All study patients were children presenting to a pediatric tertiary care center for evaluation of gastrointestinal complaints. Eligibility criteria for entry were a) age 5 to 18 years b) no organic cause of constipation, c) no reported attention deficit disorder, d) no reported cognitive delay and e) good comprehension of the English language. Additional healthy control subjects were recruited from a community-based general pediatric office where they were reporting for routine physical examinations or receiving care for minor acute medical problems. Criteria for chronic constipation included difficulty passing stools for.3 months (straining, grunting, stool getting stuck ) and passage of fewer than 3 stools per week (14). During the study, 52 new patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) were identified in our center. Ten of these patients already had an established diagnosis at the time of their initial visit to our center and had been referred for further evaluation and treatment. These 10 patients were not offered inclusion in the study. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) was defined as biopsy-proven inflammation of the esophagus associated with upper gastrointestinal symptoms. Outcomes The primary outcome measure of the study was quality of life in children with chronic constipation (the CONS group) for more than 3 months compared with healthy controls and children with other chronic gastrointestinal disorders with symptoms for more than 3 months. A secondary outcome measure included parental assessment of their child s quality of life. Additional outcome measures were the differences in perception in PedsQLä between children and their parents. Data Analysis Gender, age, and standard error differences among patient groups (CONS, IBD, GERD and healthy controls) were analyzed by x 2 test. Total quality of life scores were compared using independent sample t tests. All P values are two sided with P, 0.05 being considered as statistically significant. The Institution Review Board of Atlantic Health System approved the study. RESULTS From October 2002 to November 2003, 224 children (140 male, 84 female, aged years) and 224 parents completed the PedsQLä before the completion of their initial evaluation. Results from children with chronic constipation (CONS, n = 80) and parents were compared with control patients lacking evidence of chronic constipation. Included as controls were 42 children with IBD, 56 children with GERD and 46 healthy controls. The groups were similar in race, parental marital status and socioeconomic status. The associated gastrointestinal symptoms of the study population and their duration are listed in Table 1. There was abdominal pain in 89% and fecal soiling in 29% of the CONS children. Family history of constipation was found in 40.2% of CONS versus 8.9% of controls (P, 0.05). Fifty-eight percent of CONS children had received no previous treatment for their symptoms despite their chronicity. Only 8% were receiving any treatment at time of evaluation. In the age groups evaluated, urinary incontinence was present in 3 of the 80 CONS patients. No case of Hirschsprung disease was subsequently diagnosed in any CONS patient. TABLE 1. Demographics of patient population CONS IBD GERD HC N Age (years) Gender (% male) 67% 45% 52% 48% Symptom duration (months) NA Abdominal pain 89% 64% 51% 4% Vomiting 4% 11% 40% 3% Heartburn 2% 20% 65% 5% Nausea 10% 22% 74% 4% Weight loss 2% 18% 3% 2% Pain with defecation 58% 17% 3% 5% Stools,3/week 100% 11% 5% 5% Stools.3/day 0% 28% 11% 11% Stool in underwear 29% 4% 2% 0% CONS, chronic constipation; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; GERD, gastroesophageal reflux disease; HC, healthy controls; NA, not applicable.
3 58 YOUSSEF ET AL. Primary Outcome Table 2 shows the patient self reported and parent proxy scores on the PedsQLä. CONS children had lower mean quality of life self-reported score (70) than children with IBD (84, P, 0.05), GERD (80, P, 0.05), and healthy controls (88, P, 0.05) (Fig. 1). CONS children reported lower mean physical score (75) than children with IBD (85, P, 0.02), GERD (85, P, 0.05), and healthy controls (87, P, 0.05). There was no difference in quality of life between CONS children with or without fecal soiling (70 versus 74, P = not significant) (Fig. 1). In the subgroup of children with soiling; there was no difference between the scores of those with and without abdominal pain (69 versus 74, P = not significant). Secondary Outcomes CONS parents reported overall lower mean quality of life scores compared to their own children s self reported scores (61 versus 70, P, 0.05) (Table 2). Parents of all children with abdominal pain reported lower mean perceived emotional score for their children compared to healthy control parents. The mean score of healthy controls was 83 compared to 55 in CONS (P, 0.001), 64 in GERD (P, 0.05) and 65 in IBD (P, 0.05). In addition, CONS parents reported the lower mean emotional score (55) than GERD (64, P, 0.02) and IBD (65, P, 0.02). CONS parents reported lower perceived mean social score (67) compared to IBD parents (78, P, 0.02), GERD parents (88, P, 0.001) and healthy control parents (93, P, 0.001). Duration of symptoms for CONS children was associated with lower mean parent reported scores (P, 0.002) (Fig. 2). DISCUSSION Health-related quality of life is an important outcome in clinical trials, clinical improvement strategies and population-based health assessment (15). In this study, children with chronic constipation had a lower self-reported quality of life than children with symptoms of IBD and GERD at time of initial evaluation. The impaired quality of life was not limited to patients but was also reported by their parents. In our study there was no difference in mean overall quality of life score between children with and without fecal soiling. This refuted our suspicion that fecal soiling would be a leading factor in lower self-reported scores. Years of abdominal pain and painful defecation reported by 89% of CONS children may have been the factors leading to the impaired of quality of life as reflected in the lower self-reported physical scores, which contained questions regarding ache or hurt. In contrast, only 50% to 66% of children with IBD and GERD reported abdominal pain at initial evaluation, with a much shorter duration of symptoms. Although constipation is felt to be one of the most stigmatizing and least socially acceptable conditions in childhood and has been associated with lowered self-esteem (7), we found no differences in emotional scores between the children with and without soiling. This is possibly because the PedsQLä is a generic measure of overall pediatric health (16 18). It is not designed as a specific gauge for intestinal disease. A more sensitive instrument may have appreciated differences. Parents of constipated children reported lower perceived emotional and social scores for their children compared to parents of healthy children and those with TABLE 2. Scale scores for different diagnostic categories on the PedsQLä CONS GERD IBD HC Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Child self-report Total 70.4* (12.2) 79.9 (14.0) 83.8 (13.2) 87.7 (14.7) Physical 75.3 (16.6) 84.7 (14.7) 84.6 (14.3) 86.8 (16.8) Emotional 80.3 (13.1) 83 (15.1) 78.1 (16.5) 88.6 (19.7) Social 68.4 (12.3) 72.3 (13.2) 71.2 (13.9) 75.7 (18.7) School 67.8 (13.6) 68.1 (12.2) 73.5 (13.6) 75.6 (22.0) Parent report Total 60.6 (18.4) 76.6 (12.3) 77.4 (12.4) 80.7 (15.1) Physical 76.9 (14.8) 83.9 (13.3) 81.5 (11.5) 78.1 (14.0) Emotional 55.2 k (21.2) 63.9 (16.4) 65 (12.2) 82.8 (18.4) Social 66.6{ (16.7) 87.5 (14.2) 77.5 (14.7) 93.2 (16.7) School 72.2 (15.8) 73.9 (15.1) 74.5 (12.1) 68.9 (15.8) CONS, chronic constipation; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; GERD, gastroesophageal reflux disease; HC, healthy controls. * lower score than all children. lower score than all children. lower score than their own children. lower score than healthy control parents. k lower score than GER and IBD parents. { lower score than all parents.
4 CHRONIC CHILDHOOD CONSTIPATION AND IMPAIRED QOL 59 FIG. 1. (A) Total Quality of Life scores in all children; (B) Total Quality of Life scores in constipated children with or without soiling. ns, not significant. other chronic gastrointestinal diseases. As the families had been dealing with constipation for more than 3-1/2 years, chronicity may be responsible for the low scores given by parents. Another factor contributing to the lowered parental perceptions of their children s quality of life may be the strong family history of constipation among the constipated children. Parents may have been influenced by their own experiences when completing the quality of life questionnaire, as 40% percent had a history of constipation themselves. Our control children with IBD rated their quality of life as highly as healthy controls. Akobeng et al have reported on the negative impact that Crohn s disease has on children (19). In their study, lowered quality of life in children with Crohn s disease was attributed to depressive symptoms while on steroid therapy, fatigue, pain, unpleasant investigations and lack of understanding of Crohn s disease among friends, teachers, and medical professionals. In fact, their study focus group meetings revealed that children with Crohn s disease initially denied any effect on their lives at all (19). In our study, children s quality of life was measured at a point before a final diagnosis and before investigations and therapies had begun. Timing thus may explain the self-reported results by children. Symptoms present before referral may have been considered minor and consistent with recurrent viral illness. Conversely, parents of children with IBD did appreciate the effect on quality of life, as their scores were lower than those reported by parents of healthy controls. It should be emphasized that our study defined chronic constipation as difficulty passing stools for.3 months with straining, grunting, or stool getting stuck and passage of stools,3 times/week. Whether our observations would be confirmed with a shorter duration of symptoms is unknown. Further limitations include lack of a control group with similar duration of symptoms to the CONS group. In this study the controls with IBD and GERD had a mean duration of symptoms that was greater than 1 year. Duration of symptoms included the time elapsed from initial symptoms and first evaluation by a primary care physician to the time they were referred to the pediatric gastroenterologist. It is not rare that there is a significant delay between the time the family first presents to the general physician and the time the complaint is referred to a gastroenterologist. Additional factors that may explain the prolonged duration of symptoms reported in our CONS patients include early-onset constipation, painful defecation, treatments involving anal manipulation, coercive toilet training practices and social stressors, all of which could lead to stool withholding and stool retention (20 22). In summary, children with chronic constipation report an associated lower quality of life, both self reported and by parental assessment, compared with children with symptoms of IBD and GERD at time of initial evaluation to a pediatric gastroenterology office. Lower self-reported quality of life scores by children may be a reflection of associated abdominal pain and painful defecation. Lower perceptions by parents are most likely attributable to the duration of symptoms and family experience with constipation. Recognition of the lowered quality of life in these children and high level of parental concern should recommend more prompt management. REFERENCES FIG. 2. Effect of duration of symptoms on parents reported quality of life scores for their children with constipation. 1. Loening-Baucke V. Chronic constipation in children. Gastroenterology 1993;105: Motta ME, Silva GA. Signs and symptoms associated with chronic constipation [in Portuguese]. J Pediatr (Rio J) 2000;76: Loening-Baucke V. Factors determining outcome in children with chronic constipation and fecal soiling. Gut 1989;30: Hyams JS, Burke G, Davis PM, Rzepski B, Andrulonis PA. Abdominal pain and irritable bowel syndrome in adolescents: a community-based study. J Pediatr 1996;129:220 6.
5 60 YOUSSEF ET AL. 5. Levine MD, Bakow H. Children with encopresis: a study of treatment outcome. Pediatrics 1976;58: Bornstein P, Balleweg B, McLellarn RW, et al. The bathroom game: A systemic program for the elimination of encopretic behavior. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry 1983;14: Bellman, M. Studies on encopresis. Acta Pediatr Scand 1966;56: S van Ginkel R, Reitsma J, Buller H, van Wijk MK, Taminiau JA, Benninga MA. Childhood constipation: Longitudinal follow-up beyond puberty Gastroenterology 2003;125: Goh J, Byrne PJ, McDonald G, Stephens R, Keeling P. Severe juvenile chronic constipation. Ir Med J 2001;94: Dawson P, Griffith K, Boeke K. Combined medical and psychological treatment for hospitalized children with encopresis. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 1990;20: Streeter BL. Teenage constipation: case study. Gastroenterol Nurs 2002:25: Varni JW, Seid M, Rode CA. The PedsQL: measurement model for the pediatric quality of life inventory. Med Care 1999;2: Varni JW, Seid M, Kurtin PS. PedsQL 4.0: reliability and validity of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory version 4.0 generic core scales in healthy and patient populations. Med Care 2001;8: Rasquin-Weber A, Hyman PE, Cucchiara S, et al. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders. Gut 1999;45 (suppl 2)SII Treurniet HF, Essink-Bot ML, Mackenbach JP. van der Maas PJ. Health-related quality of life: an indicator of quality of care? Qual Life Res 1997;6: Seid M, Varni JW, Kurtin PS. Measuring quality of care for vulnerable children: challenges and conceptualization of a pediatric outcome measure of quality. Am J Med Qual 2000;15: Varni JW, Burwinkle TM, Seid M, Skarr D. The PedsQL 4.0 as a pediatric population health measure: feasibility, reliability, and validity. Ambul Pediatr 2003;6: Schwimmer JB, Burwinkle TM, Varni JW. Health related quality of life of severely obese children and adolescents. JAMA 2003;289: Akobeng AK, Suresh-Babu MV, Firth D, Miller V, Mir P, Thomas AG. Quality of life in children with Crohn s disease: a pilot study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1999;28:S Brooks RC, Copen RM, Cox DJ, Morris J, Borowitz S, Sutphen J. Review of the treatment literature for encopresis, functional constipation, and stool-toileting refusal. Ann Behav Med 2000;22: Borowitz SM, Cox DJ, Tam A, Ritterband LM, Sutphen JL, Penberthy JK. Precipitants of constipation during early childhood. J Am Board Fam Pract 2003;16: Fishman L, Rappaport L, Schonwald A, Nurko S. Early constipation and toilet training in children with encopresis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2002;34:385 8.
Constipation in childhood is characterized by a low defecation frequency in combination with either involuntary loss of
 USE OF ROME II CRITERIA IN CHILDHOOD DEFECATION DISORDERS: APPLICABILITY IN CLINICAL AND RESEARCH PRACTICE WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL, MD, JAROM HEIJMANS, HUGO S. A. HEIJMANS, MD, PHD, JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,MD,PHD,
USE OF ROME II CRITERIA IN CHILDHOOD DEFECATION DISORDERS: APPLICABILITY IN CLINICAL AND RESEARCH PRACTICE WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL, MD, JAROM HEIJMANS, HUGO S. A. HEIJMANS, MD, PHD, JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,MD,PHD,
Quality of Life and Psychiatric Comorbidity in Children and Adolescents with Functional Constipation: A Case-Control Study
 Govaresh/ Vol. 21, No.3, Autumn 2016; 194-199. Quality of Life and Psychiatric Comorbidity in Children and Adolescents with Functional Constipation: A Case-Control Study Hamidreza Kianifar 1, Paria Hebrani
Govaresh/ Vol. 21, No.3, Autumn 2016; 194-199. Quality of Life and Psychiatric Comorbidity in Children and Adolescents with Functional Constipation: A Case-Control Study Hamidreza Kianifar 1, Paria Hebrani
Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol. glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide, lactulose. treatment of functional constipation in children
 Original article Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide and lactulosein treatment of functional constipation in children Hossein Saneian 1, Neda Mostofizadeh 2 1 Assistant
Original article Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide and lactulosein treatment of functional constipation in children Hossein Saneian 1, Neda Mostofizadeh 2 1 Assistant
The involuntary loss of feces in the underwear after. Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence.
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 26;4:67 72 Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, RIJK VAN GINKEL,* HANS A.
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 26;4:67 72 Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, RIJK VAN GINKEL,* HANS A.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Behavioral therapy for functional constipation in childhood: health-related quality of life, emotional and behavior problems & parental child-rearing attitudes van
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Behavioral therapy for functional constipation in childhood: health-related quality of life, emotional and behavior problems & parental child-rearing attitudes van
Chronic constipation, often accompanied by encopresis. Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty. Patients and Methods
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2003;125:357 363 Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty RIJK VAN GINKEL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, HANS A. BÜLLER, MICHIEL P. VAN WIJK,* JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,* and
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2003;125:357 363 Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty RIJK VAN GINKEL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, HANS A. BÜLLER, MICHIEL P. VAN WIJK,* JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,* and
190 Index Case studies, abdominal pain, 2 Crohn s disease, 2 3, cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS), 2 fecal incontinence (FI), 2 medical c
 Index Abdominal pain, case study, 2 Achalasia, 75 Acupuncture 108 American Academy of Pediatrics, 49 Anxiety, 8 9, 98 Autism, GI disorders and, 25 27 BASC. See Behavior Assessment System for Children (BASC)
Index Abdominal pain, case study, 2 Achalasia, 75 Acupuncture 108 American Academy of Pediatrics, 49 Anxiety, 8 9, 98 Autism, GI disorders and, 25 27 BASC. See Behavior Assessment System for Children (BASC)
Constipation in children
 Search date August 2003 Gregory Rubin QUESTIONS Effects of treatments...397 395 INTERVENTIONS CONSTIPATION Trade off between benefits and harms Cisapride with or without magnesium oxide*...397 Unknown
Search date August 2003 Gregory Rubin QUESTIONS Effects of treatments...397 395 INTERVENTIONS CONSTIPATION Trade off between benefits and harms Cisapride with or without magnesium oxide*...397 Unknown
Measuring Health-Related Quality of Life With the Parental Opinions of Pediatric Constipation Questionnaire
 Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 40(8), 2015, 814 824 doi: 10.1093/jpepsy/jsv028 Advance Access Publication Date: 2 April 2015 Original Research Article Measuring Health-Related Quality of Life With the
Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 40(8), 2015, 814 824 doi: 10.1093/jpepsy/jsv028 Advance Access Publication Date: 2 April 2015 Original Research Article Measuring Health-Related Quality of Life With the
The Effects of Increased Dietary Fiber on School- Aged Children s Quality of Life
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs College of Health and Human Sciences Honors Program Undergraduate Theses College of Health and Human Sciences Honors Program 5-2013 The Effects of Increased Dietary Fiber
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs College of Health and Human Sciences Honors Program Undergraduate Theses College of Health and Human Sciences Honors Program 5-2013 The Effects of Increased Dietary Fiber
Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands
 Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Constipation 0-10% >10-20% >20-30% >30-40% Mugie SM, et al. Best Pract & Res Clin Gastroenterol
Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Constipation 0-10% >10-20% >20-30% >30-40% Mugie SM, et al. Best Pract & Res Clin Gastroenterol
Diarrhea may be: Acute (short-term, usually lasting several days), which is usually related to bacterial or viral infections.
 Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 4 August 2010; 595-601 Original article Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy Sanguansak Rerksuppaphol a, Lakkana Rerksuppaphol b
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 4 August 2010; 595-601 Original article Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy Sanguansak Rerksuppaphol a, Lakkana Rerksuppaphol b
Assessment of health-related quality of life in children with functional defecation disorders
 21-57/6/82-6/421 Jornal de Pediatria Copyright 26 by Sociedade Brasileira de Pediatria doi:1.2223/jped.153 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of health-related quality of life in children with functional defecation
21-57/6/82-6/421 Jornal de Pediatria Copyright 26 by Sociedade Brasileira de Pediatria doi:1.2223/jped.153 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of health-related quality of life in children with functional defecation
Constipation is a common disorder in children,
 The Effect of Anorectal Manometry on the Outcome of Treatment in Severe Childhood Constipation: A Randomized, Controlled Trial Rijk van Ginkel, MD*; Hans A. Büller, PhD ; Guy E. Boeckxstaens, PhD ; Roos
The Effect of Anorectal Manometry on the Outcome of Treatment in Severe Childhood Constipation: A Randomized, Controlled Trial Rijk van Ginkel, MD*; Hans A. Büller, PhD ; Guy E. Boeckxstaens, PhD ; Roos
Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka
 Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka Shaman Rajindrajith 1, Niranga Manjuri Devanarayana 2, Sachith Mettananda 3, Priyantha Perera 1, Sanofer
Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka Shaman Rajindrajith 1, Niranga Manjuri Devanarayana 2, Sachith Mettananda 3, Priyantha Perera 1, Sanofer
Constipation and Soiling: Integrated Models of Care
 Constipation and Soiling: Integrated Models of Care Rose Schroedl, PhD Department of Pediatric Psychology and Neuropsychology No financial disclosures or conflicts of interest Constipation and Fecal Incontinence
Constipation and Soiling: Integrated Models of Care Rose Schroedl, PhD Department of Pediatric Psychology and Neuropsychology No financial disclosures or conflicts of interest Constipation and Fecal Incontinence
BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS
 BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS BI-PED PROJECT (BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: PEDIATRICS) Emotional Health Committee Maryland Chapter American Academy of Pediatrics David Bromberg M.D. Overview: Encopresis is diagnosed
BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS BI-PED PROJECT (BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: PEDIATRICS) Emotional Health Committee Maryland Chapter American Academy of Pediatrics David Bromberg M.D. Overview: Encopresis is diagnosed
Abdominal massage for the treatment of idiopathic constipation in children with profound learning disabilities: a single case study design
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Abdominal massage for the treatment of idiopathic constipation in children with profound learning disabilities: a single case study design Lucy Moss, Melanie Smith, Sarah Wharton and Annette
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Abdominal massage for the treatment of idiopathic constipation in children with profound learning disabilities: a single case study design Lucy Moss, Melanie Smith, Sarah Wharton and Annette
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
C onstipation is a common problem in children, accounting
 723 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognosis of constipation: clinical factors and colonic transit time F de Lorijn, M P van Wijk, J B Reitsma, R van Ginkel, J A J M Taminiau, M A Benninga... See end of article for
723 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognosis of constipation: clinical factors and colonic transit time F de Lorijn, M P van Wijk, J B Reitsma, R van Ginkel, J A J M Taminiau, M A Benninga... See end of article for
Entrustable Professional Activity
 Entrustable Professional Activity 1. Title: Care for infants, children, and adolescents with common outpatient GI, liver/biliary, pancreatic and nutritional issues 2. Description of Activity Pediatric
Entrustable Professional Activity 1. Title: Care for infants, children, and adolescents with common outpatient GI, liver/biliary, pancreatic and nutritional issues 2. Description of Activity Pediatric
Depressive symptoms in children with chronic gastrointestinal disorders
 bs_bs_banner Pediatrics International (2014) 56, 583 587 doi: 10.1111/ped.12335 Original Article Depressive symptoms in children with chronic gastrointestinal disorders Subhashini Jayanath, 1 Way Seah
bs_bs_banner Pediatrics International (2014) 56, 583 587 doi: 10.1111/ped.12335 Original Article Depressive symptoms in children with chronic gastrointestinal disorders Subhashini Jayanath, 1 Way Seah
Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation
 Pediatr Radiol (2010) 40:1789 1793 DOI 10.1007/s00247-010-1725-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation Fredericus T. Kokke & Judith S. Sittig & Annemiek de Bruijn
Pediatr Radiol (2010) 40:1789 1793 DOI 10.1007/s00247-010-1725-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation Fredericus T. Kokke & Judith S. Sittig & Annemiek de Bruijn
High Prevalence of Nausea in Children With Pain-Associated Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: Are Rome Criteria Applicable?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: GASTROENTEROLOGY High Prevalence of Nausea in Children With Pain-Associated Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: Are Rome Criteria Applicable? Katja Kovacic, Sara Williams, B U.K. Li,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE: GASTROENTEROLOGY High Prevalence of Nausea in Children With Pain-Associated Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: Are Rome Criteria Applicable? Katja Kovacic, Sara Williams, B U.K. Li,
Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children
 R E S E A R C H P A P E R Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children VIKRANT KHANNA*, UJJAL PODDAR AND SURENDER KUMAR YACHHA From the Departments of Pediatric Gastroenterology and
R E S E A R C H P A P E R Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children VIKRANT KHANNA*, UJJAL PODDAR AND SURENDER KUMAR YACHHA From the Departments of Pediatric Gastroenterology and
IBS - Definition. Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by:
 IBS - Definition Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by: 3500 3000 No. of Publications 2500 2000 1500 1000 Irritable Bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome 500 0 1968-1977 1978-1987
IBS - Definition Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by: 3500 3000 No. of Publications 2500 2000 1500 1000 Irritable Bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome 500 0 1968-1977 1978-1987
Reliability and Validity of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory Generic Core Scales, Multidimensional Fatigue Scale, and Cancer Module
 2090 The PedsQL in Pediatric Cancer Reliability and Validity of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory Generic Core Scales, Multidimensional Fatigue Scale, and Cancer Module James W. Varni, Ph.D. 1,2
2090 The PedsQL in Pediatric Cancer Reliability and Validity of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory Generic Core Scales, Multidimensional Fatigue Scale, and Cancer Module James W. Varni, Ph.D. 1,2
Weekly Prevalence of Symptoms USA vs. Colombia
 THE OVERLAP BETWEEN INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE AND FUNCTIONAL GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS: CHALLENGES AND TREATMENT IMPLICATIONS Miguel Saps, MD Professor of Pediatrics, Ohio State University Director of
THE OVERLAP BETWEEN INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE AND FUNCTIONAL GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS: CHALLENGES AND TREATMENT IMPLICATIONS Miguel Saps, MD Professor of Pediatrics, Ohio State University Director of
Evaluation of a Standard Protocol for Retentive Encopresis: A Replication
 Journal of Pediatric Psychology. Vol. 22, No. 5, 1997, pp. 619-633 Evaluation of a Standard Protocol for Retentive Encopresis: A Replication Lori J. Stark, 1 Lisa C. Opipari, Deidre L. Donaldson, Michael
Journal of Pediatric Psychology. Vol. 22, No. 5, 1997, pp. 619-633 Evaluation of a Standard Protocol for Retentive Encopresis: A Replication Lori J. Stark, 1 Lisa C. Opipari, Deidre L. Donaldson, Michael
TREATMENT SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION
 SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION One of the most common functional GI disorders
SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION One of the most common functional GI disorders
Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT
 Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study is to find out if there is any relationship between
Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study is to find out if there is any relationship between
Gastroenterology. Certification Examination Blueprint. Purpose of the exam
 Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
There are clues to help to decide if the bellyache is a medical problem:
 Bellyaches in Children Pediatric and Adolescent Gastrointestinal Motility & Pain Program Department of Pediatrics, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, Louisiana By: Paul Hyman,
Bellyaches in Children Pediatric and Adolescent Gastrointestinal Motility & Pain Program Department of Pediatrics, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, Louisiana By: Paul Hyman,
E ncopresis in childhood and adolescence is a disabling condition that can result in
 Short-Term Treatment of Children With Encopresis GARY FIREMAN, PH.D. HAROLD S. KOPLEWICZ, M.D. To examine the effectiveness of a short-term behavioral treatment of encopresis, 52 encopretic children were
Short-Term Treatment of Children With Encopresis GARY FIREMAN, PH.D. HAROLD S. KOPLEWICZ, M.D. To examine the effectiveness of a short-term behavioral treatment of encopresis, 52 encopretic children were
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
Usefulness of Assessment of Stool Form by the Modified Bristol Stool Form Scale in Primary Care Pediatrics
 pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 https://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2018.21.2.93 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2018 April 21(2):93-100 Original Article PGHN Usefulness of Assessment of Stool Form by the
pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 https://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2018.21.2.93 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2018 April 21(2):93-100 Original Article PGHN Usefulness of Assessment of Stool Form by the
American Pediatric Surgical Nurses Association 111 Deer Lake Rd., Suite 100 Deerfield, IL 60015
 An Innovative Program for Children with Dysfunctional Elimination Kimberly S. Jarczyk, M.S.N., C.P.N.P. Pediatric Continence Program Nemours Children s Clinic Jacksonville, Florida Disclosure Information
An Innovative Program for Children with Dysfunctional Elimination Kimberly S. Jarczyk, M.S.N., C.P.N.P. Pediatric Continence Program Nemours Children s Clinic Jacksonville, Florida Disclosure Information
Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up
 1400 Gut 1993; 34:1400-1404 Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up Department of Pediatrics, University of Iowa, USA V Loening-Baucke Correspondence
1400 Gut 1993; 34:1400-1404 Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up Department of Pediatrics, University of Iowa, USA V Loening-Baucke Correspondence
Management of GI Issues in Duchenne. Kent Williams, MD Assistant Professor Nationwide Children s Hospital Columbus Ohio
 Management of GI Issues in Duchenne Kent Williams, MD Assistant Professor Nationwide Children s Hospital Columbus Ohio Objectives Current GI recommendations What is known and not known Case Presentation:
Management of GI Issues in Duchenne Kent Williams, MD Assistant Professor Nationwide Children s Hospital Columbus Ohio Objectives Current GI recommendations What is known and not known Case Presentation:
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University
 CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
Recurrent abdominal pain and consulting behaviour among children in a rural community in Malaysia
 University of Malaya From the SelectedWorks of Christopher Boey Chiong Meng March, 2001 Recurrent abdominal pain and consulting behaviour among children in a rural community in Malaysia Christopher Boey
University of Malaya From the SelectedWorks of Christopher Boey Chiong Meng March, 2001 Recurrent abdominal pain and consulting behaviour among children in a rural community in Malaysia Christopher Boey
Human Anatomy rectum
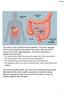 rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. What Is IBS?
 1 What Is IBS? At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is the abbreviation that doctors use for irritable bowel syndrome, often when they are talking about people with IBS. We will
1 What Is IBS? At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is the abbreviation that doctors use for irritable bowel syndrome, often when they are talking about people with IBS. We will
Bowel control is an important
 Continuing Nursing Education Objectives and posttest can be found on page 113. Encopresis: A Medical and Family Approach Deborah Padgett Coehlo Bowel control is an important developmental milestone for
Continuing Nursing Education Objectives and posttest can be found on page 113. Encopresis: A Medical and Family Approach Deborah Padgett Coehlo Bowel control is an important developmental milestone for
Gastrointestinal Society 2016 SURVEY RESULTS
 Gastrointestinal Society 2016 SURVEY RESULTS Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) The GI (Gastrointestinal) Society represents Canadians living with gastrointestinal diseases and disorders including those who
Gastrointestinal Society 2016 SURVEY RESULTS Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) The GI (Gastrointestinal) Society represents Canadians living with gastrointestinal diseases and disorders including those who
Bowel cancer risk in the under 50s. Greg Rubin Professor of General Practice and Primary Care
 Bowel cancer risk in the under 50s Greg Rubin Professor of General Practice and Primary Care Prevalence of GI problems in the consulting population Thompson et al, Gut 2000 Number of patients % of patients
Bowel cancer risk in the under 50s Greg Rubin Professor of General Practice and Primary Care Prevalence of GI problems in the consulting population Thompson et al, Gut 2000 Number of patients % of patients
Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation in childhood
 Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017) 43:24 DOI 10.1186/s13052-017-0334-3 RESEARCH Open Access Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation
Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017) 43:24 DOI 10.1186/s13052-017-0334-3 RESEARCH Open Access Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation
PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions
 PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions Departman Tarih Prof. A. Melih OZEL, MD Department of Gastroenterology Anadolu Medical Center Hospital Gebze Kocaeli - TURKEY Presentation plan 15 min. Introduction
PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions Departman Tarih Prof. A. Melih OZEL, MD Department of Gastroenterology Anadolu Medical Center Hospital Gebze Kocaeli - TURKEY Presentation plan 15 min. Introduction
FAMILY THERAPY OR FAMILY BASED INTERVENTION FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WHO SUFFER FROM PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title FAMILY THERAPY OR FAMILY BASED INTERVENTION FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WHO SUFFER FROM PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Disease State Psychiatry Indicator Classification Disease
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title FAMILY THERAPY OR FAMILY BASED INTERVENTION FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WHO SUFFER FROM PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Disease State Psychiatry Indicator Classification Disease
Validation of a Four-Graded Scale for Severity of Heartburn in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Volume 11 Number 4 2008 VALUE IN HEALTH Validation of a Four-Graded Scale for Severity of Heartburn in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ola Junghard, PhD, 1 Ingela Wiklund, PhD
Volume 11 Number 4 2008 VALUE IN HEALTH Validation of a Four-Graded Scale for Severity of Heartburn in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ola Junghard, PhD, 1 Ingela Wiklund, PhD
The Pediatric Cardiac Quality of Life Inventory (PCQLI)
 The Pediatric Cardiac Quality of Life Inventory (PCQLI) A disease-specific measure of health-related quality of life for children and adolescents with congenital or acquired heart disease A brief user
The Pediatric Cardiac Quality of Life Inventory (PCQLI) A disease-specific measure of health-related quality of life for children and adolescents with congenital or acquired heart disease A brief user
Diagnostic dilemmas and results of treatment for
 36 Department of Paediatrics, Free University Hospital, PO Box 757, 17 MB Amsterdam, The Netherlands CW Keuzenkamp-Jansen CJ Fijnvandraat CMF Kneepkens AC Douwes Correspondence and reprint requests to:
36 Department of Paediatrics, Free University Hospital, PO Box 757, 17 MB Amsterdam, The Netherlands CW Keuzenkamp-Jansen CJ Fijnvandraat CMF Kneepkens AC Douwes Correspondence and reprint requests to:
Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2009; Vol 19 (No 3), Pp:255-261 Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation Hasan Karami* 1, MD; Mohammad Khademloo 2,
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2009; Vol 19 (No 3), Pp:255-261 Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation Hasan Karami* 1, MD; Mohammad Khademloo 2,
Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence
 The UNC Center for Functional GI & Motility Disorders www.med.unc.edu/ibs Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence Olafur S. Palsson, Psy.D. Associate Professor of Medicine UNC Center for
The UNC Center for Functional GI & Motility Disorders www.med.unc.edu/ibs Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence Olafur S. Palsson, Psy.D. Associate Professor of Medicine UNC Center for
IBS: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria
 IBS: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria William D. Chey, MD Professor of Medicine University of Michigan What is the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptom based
IBS: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria William D. Chey, MD Professor of Medicine University of Michigan What is the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptom based
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Managing IBD at the extremes of age: Transitioning Teens
 Oxford Inflammatory Bowel Disease & Hepatology MasterClass Managing IBD at the extremes of age: Transitioning Teens Dr RM Beattie Consultant Paediatric Gastroenterologist Southampton Challenges in the
Oxford Inflammatory Bowel Disease & Hepatology MasterClass Managing IBD at the extremes of age: Transitioning Teens Dr RM Beattie Consultant Paediatric Gastroenterologist Southampton Challenges in the
2017 NEEDS ASSESSMENT SURVEY
 2017 NEEDS ASSESSMENT SURVEY Quick Overview: Educational Topic Findings The online 2017 Needs Assessment survey was programmed through SurveyMonkey and a personalized request to complete the questionnaire
2017 NEEDS ASSESSMENT SURVEY Quick Overview: Educational Topic Findings The online 2017 Needs Assessment survey was programmed through SurveyMonkey and a personalized request to complete the questionnaire
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Associated with
 Table1: Rome III and Rome IV diagnostic criteria for IBS, functional constipation and functional dyspepsia. Rome III diagnostic criteria 1,2 Rome IV diagnostic criteria 3,4 Diagnostic criteria for IBS
Table1: Rome III and Rome IV diagnostic criteria for IBS, functional constipation and functional dyspepsia. Rome III diagnostic criteria 1,2 Rome IV diagnostic criteria 3,4 Diagnostic criteria for IBS
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction (BBD) Naida Kalloo, MD Pediatric Urology Children s National
 Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction (BBD) Naida Kalloo, MD Pediatric Urology Children s National What is Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction? Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and bowel movement disorders Majority
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction (BBD) Naida Kalloo, MD Pediatric Urology Children s National What is Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction? Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and bowel movement disorders Majority
Measurement of colonic transit time with the Transit-Pellets TM method
 Measurement of colonic transit time with the Transit-Pellets TM method Measurement of colonic transit time is an important investigation in clinical gastroenterology. The measurement is indicated particularly
Measurement of colonic transit time with the Transit-Pellets TM method Measurement of colonic transit time is an important investigation in clinical gastroenterology. The measurement is indicated particularly
PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions
 PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions Departman Tarih Prof. A. Melih OZEL, MD Department of Gastroenterology Anadolu Medical Center Hospital Gebze Kocaeli - TURKEY Presentation plan 15 min. Introduction
PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions Departman Tarih Prof. A. Melih OZEL, MD Department of Gastroenterology Anadolu Medical Center Hospital Gebze Kocaeli - TURKEY Presentation plan 15 min. Introduction
Disclosures. GI Motility Disorders. Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome None Disclosures Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington 6 th Asian Health Symposium
Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome None Disclosures Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington 6 th Asian Health Symposium
Patient-reported Outcomes
 3 Patient-reported Outcomes Ingela Wiklund Key points Many gastrointestinal diseases are symptomdriven, so the patient s perspective is particularly important in this area. Patient-reported outcomes (PROs)
3 Patient-reported Outcomes Ingela Wiklund Key points Many gastrointestinal diseases are symptomdriven, so the patient s perspective is particularly important in this area. Patient-reported outcomes (PROs)
CHAPTER V. Summary and Recommendations. policies, including uniforms (Behling, 1994). The purpose of this study was to
 HAPTER V Summary and Recommendations The current belief that fashionable clothing worn to school by students influences their attitude and behavior is the major impetus behind the adoption of stricter
HAPTER V Summary and Recommendations The current belief that fashionable clothing worn to school by students influences their attitude and behavior is the major impetus behind the adoption of stricter
Evaluation of the Pediatric Crohn Disease Activity Index: A Prospective Multicenter Experience
 Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 41:416 421 Ó October 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia Evaluation of the Pediatric Crohn Disease Activity Index: A Prospective Multicenter
Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 41:416 421 Ó October 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia Evaluation of the Pediatric Crohn Disease Activity Index: A Prospective Multicenter
Bloating, Flatulence, and
 A 45-Year-Old Man With Recurrent Abdominal Pain, Bloating, Flatulence, and Intermittent Loose Stools Anthony J. Lembo, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, GI Motility Laboratory
A 45-Year-Old Man With Recurrent Abdominal Pain, Bloating, Flatulence, and Intermittent Loose Stools Anthony J. Lembo, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, GI Motility Laboratory
Hot Topics In Nutrition & IBD January 6, Kate Vance, RD Wael N. Sayej, MD
 Hot Topics In Nutrition & IBD January 6, 2018 Kate Vance, RD Wael N. Sayej, MD Nutrients of Focus Calories Calcium Vitamin D Iron Nutritional Treatment in IBD Improve nutritional status As primary therapy
Hot Topics In Nutrition & IBD January 6, 2018 Kate Vance, RD Wael N. Sayej, MD Nutrients of Focus Calories Calcium Vitamin D Iron Nutritional Treatment in IBD Improve nutritional status As primary therapy
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Behavioral therapy for functional constipation in childhood: health-related quality of life, emotional and behavior problems & parental child-rearing attitudes van
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Behavioral therapy for functional constipation in childhood: health-related quality of life, emotional and behavior problems & parental child-rearing attitudes van
Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate.
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
The pediatric Rome IV criteria: what s new?
 Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology ISSN: 1747-4124 (Print) 1747-4132 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/ierh20 The pediatric Rome IV criteria: what s new? Ilan J.N. Koppen,
Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology ISSN: 1747-4124 (Print) 1747-4132 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/ierh20 The pediatric Rome IV criteria: what s new? Ilan J.N. Koppen,
Quality of life in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease in an Iranian population
 Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2013 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE Quality of life in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2013 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE Quality of life in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST
 COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST Paediatric Gastroenterology : Referral Base Common problems Feeding difficulties in infancy Recurrent
COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST Paediatric Gastroenterology : Referral Base Common problems Feeding difficulties in infancy Recurrent
The 2012 SAGE Wait Time Program: Survey of Access to GastroEnterology in Canada Can J Gastroenterol 2013;27:83-9.
 The 2012 SAGE Wait Time Program: Survey of Access to GastroEnterology in Canada Can J Gastroenterol 2013;27:83-9. Desmond Leddin MB, David Armstrong MD, Mark Borgaonkar MD, Ronald J Bridges MD, Carlo A
The 2012 SAGE Wait Time Program: Survey of Access to GastroEnterology in Canada Can J Gastroenterol 2013;27:83-9. Desmond Leddin MB, David Armstrong MD, Mark Borgaonkar MD, Ronald J Bridges MD, Carlo A
Constipation is a common and distressing pediatric problem, with a prevalence ranging from 7% to 30% in both western
 Lactobacillus reuteri (DSM 17938) in Infants with Functional Chronic Constipation: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study Paola Coccorullo, MD, Caterina Strisciuglio, MD, Massimo Martinelli,
Lactobacillus reuteri (DSM 17938) in Infants with Functional Chronic Constipation: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study Paola Coccorullo, MD, Caterina Strisciuglio, MD, Massimo Martinelli,
Randomised controlled trial of biofeedback training in persistent encopresis with anismus
 Arch Dis Child 1998;79:131 135 131 Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics Unit, Melbourne University Department of Paediatrics, Royal Children s Hospital, Parkville Victoria, Australia 3052 T Nolan Department
Arch Dis Child 1998;79:131 135 131 Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics Unit, Melbourne University Department of Paediatrics, Royal Children s Hospital, Parkville Victoria, Australia 3052 T Nolan Department
Quality of life in pediatric heart transplant recipients: A comparison with children with and without heart disease
 http://www.jhltonline.org Quality of life in pediatric heart transplant recipients: A comparison with children with and without heart disease Karen Uzark, PhD, CPNP, a Lisa Griffin, BSN, CCTC, b Rose Rodriguez,
http://www.jhltonline.org Quality of life in pediatric heart transplant recipients: A comparison with children with and without heart disease Karen Uzark, PhD, CPNP, a Lisa Griffin, BSN, CCTC, b Rose Rodriguez,
Long-Term Bowel Symptoms Following Corrective Surgery
 HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Children s Hospital Medical Center, Boston Ma Long-Term Bowel Symptoms Following Corrective Surgery
HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Children s Hospital Medical Center, Boston Ma Long-Term Bowel Symptoms Following Corrective Surgery
Constipation in Children. Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG*
 1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 Education-Family Physician Corner Constipation in Children Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG* Constipation in pediatrics age group is frequently
1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 Education-Family Physician Corner Constipation in Children Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG* Constipation in pediatrics age group is frequently
PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: GASTROENTEROLOGY/GYNECOLOGY/PSYCHIATRY/ RHEUMATOLOGY
 PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: GASTROENTEROLOGY/GYNECOLOGY/PSYCHIATRY/ RHEUMATOLOGY San Juan, Puerto Rico The Ritz-Carlton, San Juan March 15 18, 2018 Thursday, March 15th: 7:30 am 8:00
PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: GASTROENTEROLOGY/GYNECOLOGY/PSYCHIATRY/ RHEUMATOLOGY San Juan, Puerto Rico The Ritz-Carlton, San Juan March 15 18, 2018 Thursday, March 15th: 7:30 am 8:00
from Bowel Control Problems twitter.com/voicesforpfd
 BREAK FREE from Bowel Control Problems POP Quiz THE NUMBER OF PEOPLE IN THE UNITED STATES WITH BOWEL CONTROL PROBLEMS: A. 6 million B. 12 million C. 18 million BOWEL CONTROL PROBLEMS Nearly 18 million
BREAK FREE from Bowel Control Problems POP Quiz THE NUMBER OF PEOPLE IN THE UNITED STATES WITH BOWEL CONTROL PROBLEMS: A. 6 million B. 12 million C. 18 million BOWEL CONTROL PROBLEMS Nearly 18 million
Current Treatment of Childhood Constipation
 Ann Nestlé [Engl] 2007;65:73 79 DOI: 10.1159/000101716 O livia Liem a, b Carlo Di Lorenzo b Jan A.J.M. Taminiau a Hayat M. Mousa b Marc A. Benninga a a Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition,
Ann Nestlé [Engl] 2007;65:73 79 DOI: 10.1159/000101716 O livia Liem a, b Carlo Di Lorenzo b Jan A.J.M. Taminiau a Hayat M. Mousa b Marc A. Benninga a a Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition,
Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders. TERRAGASTRO - Good health starts in the gut
 Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASE Referred to as gastrointestinal diseases, they are common disorders which affect the esophagus,
Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASE Referred to as gastrointestinal diseases, they are common disorders which affect the esophagus,
Childhood constipation: new insights in testing, treatment and cost Liem, O.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Childhood constipation: new insights in testing, treatment and cost Liem, O. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Liem, O. (2010). Childhood
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Childhood constipation: new insights in testing, treatment and cost Liem, O. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Liem, O. (2010). Childhood
Patient Interview Form
 Page 1 of 5 Orange Coast Memorial Office: 18111 Brookhurst Ave. Suite 5200, Fountain Valley, CA 92708 * Tel: (714) 962-7705 * Fax: (714) 861-4552 www.unitedgi.com Patient Interview Form Patient Information
Page 1 of 5 Orange Coast Memorial Office: 18111 Brookhurst Ave. Suite 5200, Fountain Valley, CA 92708 * Tel: (714) 962-7705 * Fax: (714) 861-4552 www.unitedgi.com Patient Interview Form Patient Information
Validated questionnaire on diagnosis and symptom severity for functional constipation in the Chinese population
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22: 483 488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02621.x Validated questionnaire on diagnosis and symptom severity for functional constipation in the Chinese population A. O. O.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22: 483 488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02621.x Validated questionnaire on diagnosis and symptom severity for functional constipation in the Chinese population A. O. O.
Managing Defecation Disorders in Children
 A SUPPLEMENT TO Internal Medicine News Managing Defecation Disorders in Children Perspectives on Constipation and Encopresis: Current Issues and New Findings Infant Dyschezia and Functional Constipation
A SUPPLEMENT TO Internal Medicine News Managing Defecation Disorders in Children Perspectives on Constipation and Encopresis: Current Issues and New Findings Infant Dyschezia and Functional Constipation
Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome among Medical Students and Interns in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
 Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome among Medical Students and Interns in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia Mohammed Y Hasosah 1*, Samer A Alamri 2, Faisal A Al-Husayni 2, Rakan M. Aljedaani 2, Mohammad A Zwawy
Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome among Medical Students and Interns in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia Mohammed Y Hasosah 1*, Samer A Alamri 2, Faisal A Al-Husayni 2, Rakan M. Aljedaani 2, Mohammad A Zwawy
Anorectal Diagnostic Overview
 Anorectal Diagnostic Overview 11-25-09 3.11.2010 2009 2010 Anorectal Manometry Overview Measurement of pressures and the annotation of rectal sensation throughout the rectum and anal canal to determine:
Anorectal Diagnostic Overview 11-25-09 3.11.2010 2009 2010 Anorectal Manometry Overview Measurement of pressures and the annotation of rectal sensation throughout the rectum and anal canal to determine:
Health related quality of life in children with autism spectrum disorder in Bangladesh
 related quality of life in children with autism spectrum disorder in Bangladesh Farhana Safa and Md. Nazrul Islam Department of Public, American International University-Bangladesh (AIUB) Original Article
related quality of life in children with autism spectrum disorder in Bangladesh Farhana Safa and Md. Nazrul Islam Department of Public, American International University-Bangladesh (AIUB) Original Article
Additive Benefits of Laxative, Toilet Training, and Biofeedback Therapies in the Treatment of Pediatric Encopresis 1
 Journal of Pediatric Psychology, Vol. 21, No. 5, 1996, pp. 659-670 Additive Benefits of Laxative, Toilet Training, and Biofeedback Therapies in the Treatment of Pediatric Encopresis 1 Daniel J. Cox, 2
Journal of Pediatric Psychology, Vol. 21, No. 5, 1996, pp. 659-670 Additive Benefits of Laxative, Toilet Training, and Biofeedback Therapies in the Treatment of Pediatric Encopresis 1 Daniel J. Cox, 2
parts induction and development of self consciousness, defense mechanisms, unavoidable
 2. LITERATURE REVIEW A study investigating the symptomatology of abnormal appearance using written accounts of 54 patients with various facial abnormalities revealed a similar pattern which can be divided
2. LITERATURE REVIEW A study investigating the symptomatology of abnormal appearance using written accounts of 54 patients with various facial abnormalities revealed a similar pattern which can be divided
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
Health related quality of life assessment in Pakistani paediatric cancer patients using PedsQL TM 4.0 generic core scale and PedsQL cancer module
 Chaudhry and Siddiqui Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2012, 10:52 RESEARCH Open Access Health related quality of life assessment in Pakistani paediatric cancer patients using PedsQL TM 4.0 generic
Chaudhry and Siddiqui Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2012, 10:52 RESEARCH Open Access Health related quality of life assessment in Pakistani paediatric cancer patients using PedsQL TM 4.0 generic
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a ... PRESENTATION... Defining and Diagnosing Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 ... PRESENTATION... Defining and Diagnosing Irritable Bowel Syndrome Based on a presentation by Marvin M. Schuster, MD Presentation Summary Approximately 20% of the general population has irritable bowel
... PRESENTATION... Defining and Diagnosing Irritable Bowel Syndrome Based on a presentation by Marvin M. Schuster, MD Presentation Summary Approximately 20% of the general population has irritable bowel
Pediatric Gastroenterology Referral Guidelines
 Suggested Pre-Referral Workup This is a general suggestion of possible testing to confirm a suspected diagnosis. Although referrals will be accepted without the suggested work up being complete, to ensure
Suggested Pre-Referral Workup This is a general suggestion of possible testing to confirm a suspected diagnosis. Although referrals will be accepted without the suggested work up being complete, to ensure
