Phase II Results of an Intraocular Steroid Delivery System for Cataract Surgery
|
|
|
- Martina Gilmore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phase II Results of an Intraocular Steroid Delivery System for Cataract Surgery David F. Chang, MD, 1 Ivan H. Garcia, MD, 2 John D. Hunkeler, MD, 3 Thomas Minas, MD 4 Objective: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of an intraocular biodegradable polymer dexamethasone drug delivery system (DEX DDS) in treating postoperative inflammation after cataract surgery. Study Design: Multicenter, randomized, double-masked, parallel group study comparing two dose levels of the DEX DDS to concurrent placebo and no treatment control subjects. Participants: Ninety patients scheduled to undergo extracapsular cataract extraction with phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation participated in the study. Intervention: One or two DEX DDSs, each containing 60 g of dexamethasone, were placed in the posterior chamber after cataract surgery. Patients receiving the placebo received a DDS composed of the same matrix with no active drug. In vivo rabbit studies have determined that the DEX DDS releases dexamethasone into the anterior chamber (AC) for approximately 7 to 10 days. Main Outcome Measures: The AC cells and the AC flare were assessed over a 60-day postoperative period using slit-lamp examination by masked observers. The number and percent of patients in each treatment group requiring additional postoperative topical anti-inflammatory medication were compared. Results: Ninety patients were randomized into 4 treatment groups (30 to the 2 DEX DDS group, 30 to the 1 DEX DDS group, 15 to the placebo DDS group, and 15 to the no treatment group). The control patients required the addition of topical steroids as rescue medication more frequently and sooner than patients receiving DEX DDS (80% vs. 7% at week 2) (P 0.001). Patients receiving DEX DDS showed a significant reduction in postoperative inflammation as assessed by the combined AC cell and flare scores when compared to the control group from day 3 (P 0.002) through week 3. The DEX DDS was well tolerated. No clinically significant difference in any safety evaluations, including intraocular pressure, was seen between the DEX DDS-treated and control groups. Conclusion: The DEX DDS was safe and effective in suppressing postoperative inflammation after uncomplicated cataract surgery. Additional topical anti-inflammatory drops were not needed for most patients. Ophthalmology 1999;106: Perioperative anti-inflammatory medication for cataract surgery continues to be the standard of care. Untreated or protracted intraocular inflammation may cause increased and prolonged patient discomfort and may contribute to complications such as cystoid macular edema and secondary membrane. 1 3 Corticosteroids are effective in suppressing ocular inflammation and may be administered at the time of surgery via subconjunctival injection, collagen Originally received: September 25, Revision accepted: February 26, Manuscript no Altos Eye Physicians, Los Altos, California. 2 Omni Eye Specialists, Baltimore, Maryland. 3 Hunkeler Eye Centers, P.C., Kansas City, Missouri. 4 Arizona Ophthalmic Outpatient Surgery, LLC, Phoenix, Arizona. Presented in part at the American Academy of Ophthalmology annual meeting, New Orleans, Louisiana, November Supported by Oculex Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Sunnyvale, California. Dr. Hunkeler is an investor in Oculex Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and has received contract payments for research. None of the other authors has a proprietary interest in Oculex Pharmaceuticals or in the product discussed in this article. Reprint requests to David F. Chang, MD, 762 Altos Oaks Drive, Suite 1, Los Altos, CA shield, or eyedrops. 1 Because the therapeutic drug level achieved by these methods is of only short duration, topical steroid is usually continued for several weeks after surgery until the blood aqueous barrier is re-established. 4,5 Topical therapy is associated with the well-recognized problems of patient compliance. 6 For many patients, eyedrop instillation poses a significant inconvenience or concern. 7 A variable amount of physician or staff time is needed for patient instruction. For most topical steroids, optimal administration would consist of accurate cul-de-sac instillation, accompanied by punctal closure, of a properly shaken suspension at the appropriate frequency and interval. Even then, poor corneal penetration will limit the level of drug attainable within the anterior chamber (AC). 8 Oculex Pharmaceuticals (Sunnyvale, CA) has developed an intraocular drug delivery system (DDS) consisting of a biodegradable polymer matrix to which any variety of drugs can be bound. This small, 1-mm-long particle releases the drug continuously as it dissolves. The DDS can be designed so that the duration of drug delivery lasts for periods ranging from days to months. The first DDS product available for human clinical trials contains 60 g of microdispersed dexamethasone approximately the same amount of drug contained in a single drop 1172
2 Chang et al Intraocular Steroid Delivery System of dexamethasone 0.1% ophthalmic solution. Rabbit studies show that after direct placement within the AC, the DEX DDS continuously releases dexamethasone for approximately 7 to 10 days, after which the drug level falls to low or nondetectable levels (Oculex Pharmaceuticals, unpublished data). The Dexamethasone Drug Delivery System (DEX DDS) has been tested in a phase-i study involving six patients undergoing cataract surgery. The DEX DDS appeared to be effective in reducing postsurgical inflammation, and no clinically significant adverse safety problems related to the DEX DDS were seen. We report the results of a multicenter, randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled phase-ii clinical trial of the DEX DDS for postsurgical inflammation, in which patients received active treatment of one or two DEX DDS. Patients receiving either no treatment or a placebo DDS served as control subjects. Patients and Methods The DEX DDS is a white/off-white rod-shaped filament approximately 0.5 mm in diameter and 1.0 mm in length composed of dexamethasone in a biodegradable polymer matrix. It contains nominally 60 g of dexamethasone (United States Pharmacopeia). The placebo DDS is identical to the DEX DDS in both appearance and composition of the matrix but contains no dexamethasone. The protocol and informed consent forms were approved by the Institutional Review Board at each investigational site, and a written informed consent was obtained from participating patients. Male or female patients, at least 21 years old, and who required cataract extraction were eligible for the study. Only one eye per patient was eligible for treatment. Patients with a history of uveitis, concurrent anterior segment disease, or any intraoperative surgical complications were excluded from the study. Disqualifying surgical complications included hemorrhage, wound complications, flat AC, vitreous loss, and either posterior capsule rupture or zonular dehiscence. Ocular or systemic steroidal or nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medications were not allowed for the 2 weeks before surgery, on the day of surgery, or for the first 2 days after surgery. By postoperative day 3, the masked postoperative examiner could initiate any postoperative anti-inflammatory therapy deemed necessary for ocular inflammation that was failing to improve. Ocular antibiotics were permitted during the perioperative period. Intraoperative or postoperative medications to reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) were also permitted. After uncomplicated phacoemulsification intraocular lens surgery, 90 patients at 4 separate investigational sites were randomized in a 2:1 ratio into an active treatment group or a control group. The DEX DDS active treatment group consisted of two equalsized subgroups in which the patients received either one or two DEX DDSs at the conclusion of surgery. This allowed for comparison of the efficacy of the two different doses. The control group also consisted of two equal-sized subgroups. One subgroup received no treatment at the time of surgery, while the other subgroup received a placebo DDS containing no drug. Patient enrollment and randomization into one of the four subgroups did not occur until the completion of surgery. After removal of the viscoelastic, the DEX DDS or placebo DDS was inserted by the surgeon into the posterior chamber through the pupil at the 6-o clock position between the iris and the anterior surface of the intraocular lens. Although the DEX DDS would be effective when placed in the AC, positioning it behind the iris concealed the DDS from the postoperative slit-lamp examiner. In this manner, the postoperative examiners, who were separate individuals from the surgeons, were masked as to the presence or absence of the DDS. Surgeons were masked as to treatment assignment until the end of surgery. Patients were masked as to the treatment they received until the conclusion of the study. In addition to a preoperative baseline assessment, patients were examined on postoperative days 1, 3, 7, 14, 21, 30, and 60. Patients requiring further follow-up were seen on day 90. At each study visit, including baseline, an ocular examination was conducted that included best-corrected visual acuity, IOP, slit-lamp examination, and fundus examination. The patient s degree of pain, discomfort, photophobia, and lacrimation were graded. The degrees of conjunctival erythema, ciliary flush, corneal edema, AC cells, and AC flare were graded by slit-lamp examination. The AC cells were graded as: 0 no cells, 1 1 to 5 cells, 2 6 to 15 cells, 3 16 to 30 cells, 4 greater than 30 cells, and 5 hypopyon. The AC flare was graded as: 0 absent, 1 trace, 2 mild intensity, 3 moderate intensity, and 4 strong intensity. Any wound problems, iris pathology, adverse events, or concomitant medications were recorded and characterized. Statistical Methods All randomized patients were included in the analysis of efficacy data based on their original assigned treatment group. However, the analysis of safety data was based on patient s actual treatment received during the study. All data analyses were based on the actual observed data. A two-way analysis of variance model, which included treatment, center, and treatment-by-center interaction factors, was used for the analysis of AC cell and AC flare by study visit. Comparisons were made between the active treatment group (one and two DEX DDS subgroups, combined) and the control group (placebo DDS and no treatment subgroups, combined). The least-square mean and its standard error are presented. For the analysis of the data related to use of rescue medication, the Cochran Mantel Haenszel test for general association stratified by center was performed. The Z test for the difference in the proportion of patients without AC cell and flare between active and control groups was performed. A t test for paired data was used for the test of mean change in IOP or in visual acuity from baseline to follow-up visit within treatment group. A two-sample t test was used to make comparisons between active and control groups. All statistical tests are two-sided with a 0.05 significance level. Results Ninety patients requiring cataract surgery were randomized in a 2-to-1 ratio into active or control treatment groups at 4 study centers. Thirty patients were assigned to receive 2 DEX DDSs, 30 were assigned to receive 1 DEX DDS, 15 were assigned to receive a placebo DDS, and 15 were assigned to receive no treatment. One patient assigned to receive one DEX DDS actually received no treatment, while another patient assigned to receive a placebo DDS actually received two DEX DDSs. Eighty-nine patients completed the study. One patient who received a single DEX DDS withdrew from the study after the day-1 postoperative visit. Study treatment was unmasked in one patient when two DDSs were seen by the postoperative examiner. All treatment groups were similar in demographic characteristics and study eye (Table 1). The average age in the study population was 73 years (range, years). Among the 90 random- 1173
3 Ophthalmology Volume 106, Number 6, June 1999 Table 1. Demographics and Baseline Characteristics Two DEX DDSs One DEX DDS Placebo DDS No Treatment Total (n 90) P* Age (yrs) Mean (SD) 72 (11.0) 73 (7.8) 76 (5.4) 70 (10.4) 73 (9.2) (Range) (27, 85) (47, 90) (66, 83) (45, 83) (27, 90) Sex [n (%)] Male 10 (33.3) 11 (36.7) 8 (53.3) 10 (66.7) 39 (43.3) Female 20 (66.7) 19 (63.3) 7 (46.7) 5 (33.3) 51 (56.7) Race [n (%)] White 28 (93.3) 24 (80.0) 13 (86.7) 13 (86.7) 78 (86.7) Black 0 2 (6.7) 1 (6.7) 1 (6.7) 4 (4.4) Asian 2 (6.7) 4 (3.3) 1 (6.7) 1 (6.7) 8 (8.9) Treated eye [n (%)] OD 18 (60.0) 17 (56.7) 9 (60.0) 7 (46.7) 51 (56.7) OS 12 (40.0) 13 (43.3) 6 (40.0) 8 (53.3) 39 (43.3) * P values for the overall comparison among the four treatment groups were based on the F test of the Type III treatment factor from the ANOVA model including only the treatment factor (numerical data) or Fisher s exact test (categorical data). ized patients, 57% (51 of 90) of the patients were female, 87% (78 of 90) were white, and 57% (51 of 90) had surgery on their right eye. Although 65% (39 of 60) of the patients receiving the DEX DDS were female, compared to 40% (12 of 30) in the control group, this was not a statistically significant difference. Patients in the control groups (placebo or no treatment) required postoperative topical anti-inflammatory medication for the study eye (rescue medication) more frequently and sooner than did patients receiving DEX DDSs (Table 2). Rescue medications included corticosteroids such as dexamethasone and prednisolone acetate and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as diclofenac. Rescue medication was permitted at day 3 after surgery at the masked examiner s discretion. Forty-seven percent (14 of 30) of the control group patients received a topical anti-inflammatory at day 3 compared to only 3% (2 of 59) of the DEX DDS recipients. By week 2, 80% (24 of 30) of control group patients required a rescue medication compared to 7% (4 of 59) of the DEX DDS group patients. Rescue medication was prescribed for one additional DEX DDS patient at week 3 and for two additional DEX DDS patients at week 4. By the end of the 2-month study, 83% (25 of 30) of the control group patients and 12% (7 of 59) of the DEX DDS-treated patients had used rescue medications. The difference between the DEX DDS patients and the control group patients in use of rescue medications was statistically significant (P 0.001) at every postoperative visit from day 3 on. There was no significant difference in use of rescue medication between the patients who received one or two DEX DDSs or between the patients who received a placebo DDS compared to no treatment. The AC cells, the AC flare, and the combined sum of AC cell and flare were examined as measures of inflammation. For the majority of visits, there were no statistically significant differences in outcome for those patients receiving one versus those receiving two DEX DDSs (Table 3). There was also no difference between the two control subgroups when these parameters were compared (Table 3). Therefore, efficacy parameters from the combined active treatment groups (one DEX DDS and two DEX DDSs) and the combined control groups (placebo and no treatment) were compared (Table 4). Mean combined AC cell and flare scores were lower in the DEX DDS group than in the control group from day 3 through month 2. The DEX DDS group showed a statistically significant reduction in postoperative inflammation earlier than the control group, with mean combined AC cell and flare scores of 2.5 in the DEX DDS group compared to 3.8 in the control group at day 3 (P 0.002) (Table 4). This statistical superiority in effectiveness was maintained at weeks 1, 2, and 3. The greater improvement in the DEX DDS treatment group was seen despite the much higher proportion of patients using a rescue anti-inflammatory medication after day 3 in the control group. Achievement of a totally quiet AC occurred earlier and more frequently in the DEX DDS-treated patients compared with that of the control patients. Twenty-one percent (12 of 56) of patients receiving one or two DEX DDSs compared to 3% (1 of 30) of patients in the control groups had a combined AC cell and flare score of zero at week 1 (P 0.026) (Table 5). This difference continued through the end of the study, reaching statistical significance at weeks 2 and 3 as well. By the end of the study, 82% (46 of 56) of the DEX DDS recipients had no AC cell or flare compared to 66% (19 of 29) of the control patients (P 0.087), despite the fact that 83% of the control patients had received concomitant anti-inflammatory drops by this time. Mean AC cell scores alone were consistently lower in the DEX DDS groups than in the control groups from day 3 through month Table 2. Cumulative Anti-inflammatory Medication Usage for Study Eye by Visit: No. (%) of Patients Who Received Rescue Medication for the Study Eye Active One and Two DEX DDSs (n 59) Control Placebo DDS and No Treatment Day 3 2 (3) 14 (47) Week 1 3 (5) 22 (73) Week 2 4 (7) 24 (80) Week 3 5 (9) 25 (83) Month 1 7 (12) 25 (83) Month 2 7 (12) 25 (83) * P value for the test of treatment effect of categorical outcomes between active and control groups based on the CMH test for general association stratified by center. P* 1174
4 Chang et al Intraocular Steroid Delivery System Table 3. Analysis of Observed Anterior Chamber Cell and Flare by : Mean (SEM) of Anterior Chamber Cell and Flare Score* Active Groups Control Groups 2 DEX DDSs 1 DEX DDS P (2 DEX DDSs vs. 1 DEX DDS) Placebo DDS No Treatment P (placebo DDS vs no treatment) Day (0.3) 4.9 (0.3) (0.4) 4.3 (0.4) n Day (0.3) 2.8 (0.3) (0.4) 4.3 (0.5) n Week (0.3) 1.2 (0.3) (0.4) 3.6 (0.4) n Week (0.3) 0.8 (0.3) (0.5) 1.8 (0.5) n Week (0.2) 0.6 (0.2) (0.3) 1.6 (0.4) n Month (0.1) 0.3 (0.1) (0.2) 0.7 (0.2) n Month (0.1) 0.2 (0.1) (0.2) 0.6 (0.2) n * The mean and SEM (standard error of mean) were estimated from the ANOVA model that includes treatment, center, and treatment-by-center interaction factors. P value for the pairwise test of treatment effect of categorical outcomes two groups based on Type III analysis from the model described above. 2. The DEX DDS groups had significantly lower mean AC cells scores than the control groups at day 3 (P 0.022). This statistically significant difference was maintained at weeks 1, 2, and 3. The AC flare scores alone followed a similar pattern, with mean scores in the DEX DDS groups consistently lower than mean scores in the control groups from day 3 through month 2. A significant difference was seen between the DEX DDS and control groups at day 3 (P 0.001) and at week 1, week 2, and month 1. The DEX DDS-treated patients had significantly less conjunctival erythema and ciliary flush than did the control patients, beginning at day 1 (P for both parameters) and continuing Table 4. Analysis of Observed Anterior Chamber Cell and Flare: Mean (SEM) of Anterior Chamber Cell and Flare Score* Active 1 and 2 DEX DDSs (n 60) Control Placebo DDS and No Treatment Day (0.2) 4.2 (0.3) n Day (0.2) 3.8 (0.3) n Week (0.2) 3.2 (0.3) n Week (0.2) 2.1 (0.4) n Week (0.2) 1.5 (0.2) n Month (0.1) 0.6 (0.1) n Month (0.1) 0.5 (0.1) n * The mean and SEM (standard error of mean) were estimated from the ANOVA model that includes treatment, center and treatment by center interaction factors. P values for the test of treatment effect between two treatment groups were based on Type III analysis from the model described above. P through week 2. Significantly less discomfort (P 0.001), pain (P 0.006), photophobia (P 0.001), and lacrimation (P 0.045) were reported by the DEX DDS patients than the control patients at day 3. These statistical differences continued at least through week 1. The DEX DDS-treated patients showed similar or better outcomes than the control patients for the safety parameters of corneal status (normal/abnormal), corneal edema, fundus status (normal/ abnormal), visual acuity, and IOP. Less corneal edema was seen in the DEX DDS-treated patients (49 of 58, 85% with no edema) compared to the control patients (18 of 29, 62% with no edema) beginning at day 3. The difference in the degree of corneal edema was statistically significant at weeks 1 and 2 (both P 0.001). There was no significant difference between the DEX DDS and control groups in mean change from baseline in visual acuity, with all groups showing significantly improved visual acuity by day 3. Both the DEX DDS and control groups had a mean increase in IOP on day 1 after surgery (P and P 0.002, respectively). However, by day 3, both groups had a mean decrease in IOP Table 5. Patients with No Anterior Chamber Cell and Flare by Visit: No. (%) of Patients with No Anterior Chamber Cell and Flare Active 1 and 2 DEX DDSs (n 60) Control Placebo DDS and No Treatment Day 3 2/58 (3) 1/29 (3) Week 1 12/56 (21) 1/30 (3) Week 2 23/55 (42) 5/26 (19) Week 3 31/56 (55) 4/28 (14) Month 1 41/58 (71) 19/30 (63) Month 2 46/56 (82) 19/29 (66) * P values for the test of treatment effect between two combined treatment groups were based on the Z test for difference in proportions between two groups. P* 1175
5 Ophthalmology Volume 106, Number 6, June 1999 compared to baseline (P and P 0.001, respectively). Mean IOPs remained below baseline levels in both groups through the remainder of the study. Adverse events in the treated eye were seen in similar frequencies in the DEX DDS and control patients. Adverse events generally included symptoms related to the cataract surgery, such as posterior capsule opacity and eye discomfort. Discussion Although steroids are widely used in the treatment of postoperative inflammation after cataract surgery, there are few studies in the literature documenting the efficacy of this treatment. When this study was initiated, rimexolone (Vexol, Alcon) was the only steroid that had been proved efficacious over placebo by a randomized, prospective study and approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of postoperative inflammation. 9,10 For this reason, the DEX DDS was compared to inactive controls (a placebo DDS and untreated patients) to clearly show the efficacy of this system in suppressing postoperative inflammation. Dexamethasone is a corticosteroid that suppresses the inflammatory response to a variety of agents. 11 For the purpose of suppressing inflammation, topical application of corticosteroids can achieve a high therapeutic level in the conjunctiva and cornea. However, intraocular absorption of a topical preparation is low. In rabbit eyes, only 1.1% of 80 l of topically applied, radioactively labeled dexamethasone reached the AC after 15 minutes. 8 More than 90% of a topically applied ocular drug may be absorbed systemically by the nasal and gastric mucosa. 12 In addition, intraocular drug concentration fluctuates between applications with peak concentration reached approximately 1 hour after application. 13 Animal studies suggest that the 60 g of dexamethasone is released by the intraocular DEX DDS over a period of approximately 7 to 10 days (Oculex Pharmaceuticals, unpublished data). In two in vivo rabbit studies with the DEX DDS, dexamethasone in the AC reached a mean peak concentration of 0.63 to 2.1 g/ml on day 1 and a mean concentration of 0.10 to 0.36 g/ml on day 3 through day 9. Mean concentrations on day 11 were below 0.05 g/ml. In comparison, when two drops of 0.1% dexamethasone sodium phosphate (50 l) were applied to the rabbit eye, dexamethasone phosphate in the aqueous humor reached a maximum concentration of 0.5 g/ml at 2 hours after instillation (mean 0.19 g/ml), quickly decreasing to a mean concentration of 0.04 g/ml by 3 hours (Oculex Pharmaceuticals, unpublished data). A study in humans found that the peak concentration of dexamethasone alcohol in the aqueous humor was 31.0 ng/ml (0.031 g/ml) ½ to 2 hours after topical administration of 50 l. Mean concentrations decreased after this timepoint to a low of 3.1 ng/ml (0.003 g/ml) at 8 to 13 hours. 14 Because the DEX DDS is placed in the posterior chamber, the amount of drug needed to achieve a therapeutic level is small compared to eyedrops, and systemic effects are unlikely. Treatment with the DEX DDS was highly effective in early reduction and elimination of postoperative inflammation in this trial. The statistically significant improvement in mean combined AC cell and flare scores in the DEX DDS-treated group versus the control group began at day 3 and persisted through week 3. This difference was seen even though more than 80% of the control patients had received concomitant topical anti-inflammatory medications by week 3. After postoperative week 2, the mean AC cell and flare scores continued to be as low in the DEX DDS-treated patients as in the control patients, most of whom were taking topical anti-inflammatory medication. This suggests that rebound inflammation was not a frequent consequence of the relatively brief duration of drug delivery by the DEX DDS (7 10 days). The majority (93%, 55 of 59) of DEX DDS-treated patients did not require any other anti-inflammatory therapy by the week-2 postoperative visit. An additional 5% (3 of 59) of DEX DDS-treated patients started taking a topical steroid or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug at the third or fourth postoperative week. Because an insignificant intraocular level of dexamethasone would have been expected by this time, these few patients may have required more prolonged therapy for either persistent or rebound inflammation. The effectiveness of the DEX DDS may be explained by rabbit studies, which show that the intraocular DEX DDS is able to achieve a higher level of aqueous dexamethasone than is possible with topical administration. In contrast to a rapidly declining drug level within 3 hours after eyedrop instillation, a prolonged, continuous dexamethasone level is maintained by the DEX DDS in rabbits. Although this study was not designed to provide a direct comparison of intraocular DEX DDS versus topical dexamethasone delivery, a separate randomized, double-masked study conducted in Singapore has compared the DEX DDS with topical dexamethasone 0.1% for anti-inflammatory efficacy after cataract surgery. 15 In this study of 60 patients, AC flare, as measured with the Kowa FC500 Laser Flare Meter (Kowa Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), was lower in the DEX DDS group than in the topical steroid group at all postoperative visits. The difference was statistically significant from postoperative day 4 through day 30 (all P values 0.05). Mean slit-lamp AC cell and flare scores were also lower in the DEX DDS group at all postoperative visits, but the differences did not reach statistical significance. Additional larger studies comparing these two different delivery methods will be necessary to determine whether one treatment alternative is more efficacious than the other. The DEX DDS appears to be well tolerated. The most frequent adverse events were those commonly associated with cataract surgery, and no difference in frequency was seen between the DEX DDS and control groups. The transient increase in IOP seen in all treatment groups at day 1 was probably attributable to the use of viscoelastic during surgery. 16 The outcome of implanting this product in steroid responders has not yet been determined. Of particular interest would be the extent to which the short duration of drug administration might abate this potential problem. Whether used to administer antibiotic or anti-inflammatory medications, an ideal perioperative drug delivery sys- 1176
6 Chang et al Intraocular Steroid Delivery System tem for cataract surgery would have certain attributes. It would demonstrate superior efficacy by providing an adequately high and prolonged drug level at the desired site. It would be safe and would confine the drug action to the desired intraocular location, thereby avoiding systemic effect. It would be compatible with topical anesthesia and immediate vision. It would be short-acting enough to diminish the risks from side effects or allergy, but long-acting enough to obviate the necessity for postoperative topical therapy. Eliminating the need for patient self-medication would avoid problems with compliance and instruction. Further studies are warranted to confirm that the DEX DDS is able to provide some or all of these benefits. The concept of a biodegradable intraocular drug delivery system can be extended to many other drugs and potential ocular applications as well. A desirable companion product for intraocular surgery would be an antibiotic DDS for endophthalmitis prophylaxis. Such products could be especially important in third-world settings where topical medications might not otherwise be available after intraocular surgery. In conclusion, this multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-masked phase-ii study has shown both the efficacy and safety of the DEX DDS in the treatment of inflammation after uncomplicated cataract surgery. Although the comparative efficacy of the DEX DDS versus conventional topical steroid was not addressed by this study, this product did show the potential to substitute for topical steroids in the majority of patients undergoing uncomplicated cataract surgery. Decreasing or eliminating the need for postoperative anti-inflammatory drops would be a significant benefit to most patients and would reduce physician time otherwise spent on instructing and monitoring patients receiving topical therapy. References 1. Leopold IH. Nonsteroidal and steroidal anti-inflammatory agents. In: Sears ML, Tarkkanen A, eds. Surgical Pharmacology of the Eye. New York: Raven Press, 1985; Tennant JL. Cystoid maculopathy: prostaglandins in ophthalmology. In: Emery JM, ed. Current Concepts in Cataract Surgery. St. Louis: C.V. Mosby 1978; Apple DJ, Solomon KD, Tetz MR, et al. Posterior capsule opacification. Surv Ophthalmol 1992;37: Sanders DR, Kraff M. Steroidal and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Effect on postsurgical inflammation and blood- aqueous humor barrier breakdown. Arch Ophthalmol 1984; 102: Ferguson VMG, Spalton DJ. Recovery of the blood aqueous barrier after cataract surgery. Br J Ophthalmol 1991;75: Kass MA, Meltzer DW, Gordon M, et al. Compliance with topical pilocarpine treatment. Am J Ophthalmol 1986;101: Winfield AJ, Jessiman D, Williams A, Esakowitz L. A study of the causes of non-compliance by patients prescribed eyedrops. Br J Ophthalmol 1990;74: Ichigashira N, Yamaga N. Intraocular fate of dexamethasone disodium phosphate topically applied to the eyes of rabbits. Steroids 1978;32: Assil KK, Massry G, Lehmann R, et al. Control of ocular inflammation after cataract extraction with rimexolone 1% ophthalmic suspension. J Cataract Refract Surg 1997;23: Bron A, Denis P, Hoang Xuan TC, et al. The effects of Rimexolone 1% in postoperative inflammation after cataract extraction. A double-masked placebo-controlled study. Eur J Ophthalmol 1998;8: Dexamethasone. Reynolds JEF, ed. Martindale: the extra pharmacopoeia, 31st ed. London: Pharmaceutical Press, 1996; Bodor N. Designing safer ophthalmic drugs. In: van der Goot H, Domany G, Pallos L, Timmerman H, eds. Trends in Medicinal Chemistry 88. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers, 1989; Krupin T, Waltman SR, Becker B. Ocular penetration in rabbits of topically applied dexamethasone. Arch Ophthalmol 1974;92: Watson D, Noble MJ, Dutton GN, et al. Penetration of topically applied dexamethasone alcohol into human aqueous humor. Arch Ophthalmol 1988;106: Tan DTH, Chee S-P, Lim L, Lim ASM. Randomized clinical trial of a new dexamethasone delivery system (Surodex TM ) for treatment of post-cataract surgery inflammation. Ophthalmology 1999;106: Dada VK, Sindhu N, Sachdev MS. Postoperative intraocular pressure changes with use of different viscoelastics. Ophthalmic Surg 1994;25:
Role of Intracameral Dexamethasone in Preventing Immediate Postoperative Anterior Uveitis in Paediatric Cataract Extraction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of Intracameral Dexamethasone in Preventing Immediate Postoperative Anterior Uveitis in Paediatric Cataract Extraction CHAUDARY NASIR AHMAD, ASAD ASLAM KHAN, ZAHID SIDDIQUE, SHAKIL
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of Intracameral Dexamethasone in Preventing Immediate Postoperative Anterior Uveitis in Paediatric Cataract Extraction CHAUDARY NASIR AHMAD, ASAD ASLAM KHAN, ZAHID SIDDIQUE, SHAKIL
Medical Science. Research Paper. 2nd yr post graduate, Dept. Of Ophthalmology, SVS Medical College
 Dr. A.Narasimha Rao Dr. N.Deepika Dr. D.Chandrakanth Reddy Dr. M. Vijaya Ramaraju ABSTRACT KEYWORDS Research Paper Medical Science Comparative Evaluation of the Anti- Inflammatory Effect of Topical 1 %
Dr. A.Narasimha Rao Dr. N.Deepika Dr. D.Chandrakanth Reddy Dr. M. Vijaya Ramaraju ABSTRACT KEYWORDS Research Paper Medical Science Comparative Evaluation of the Anti- Inflammatory Effect of Topical 1 %
Optometric Postoperative Cataract Surgery Management
 Financial Disclosures Optometric Postoperative Cataract Surgery Management David Dinh, OD Oak Cliff Eye Clinic Dallas Eye Consultants March 10, 2015 Comanagement Joint cooperation between two or more specialists
Financial Disclosures Optometric Postoperative Cataract Surgery Management David Dinh, OD Oak Cliff Eye Clinic Dallas Eye Consultants March 10, 2015 Comanagement Joint cooperation between two or more specialists
Disorders of the. blood-aqueous barrier after. phacoemulsification in diabetic patients CLINICAL STUDY. Y Liu, L Luo, M He and X Liu
 (2004) 18, 900 904 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY Disorders of the blood-aqueous barrier after phacoemulsification in diabetic
(2004) 18, 900 904 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY Disorders of the blood-aqueous barrier after phacoemulsification in diabetic
Update on management of Anterior Uveitis
 Update on management of Anterior Uveitis Parthopratim Dutta Majumder Senior Consultant, Department of Uvea & Intraocular Inflammation Medical Research Foundation, Sankara Nethralaya ABCD of Treating a
Update on management of Anterior Uveitis Parthopratim Dutta Majumder Senior Consultant, Department of Uvea & Intraocular Inflammation Medical Research Foundation, Sankara Nethralaya ABCD of Treating a
PRECISION PROGRAM. Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide. Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique
 Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide PRECISION PROGRAM Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique Available at www.ozurdexprecisionprogram.com Provides step-by-step directions with
Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide PRECISION PROGRAM Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique Available at www.ozurdexprecisionprogram.com Provides step-by-step directions with
Cataract Surgery Co-Management
 Cataract Surgery Co-Management Phacoemulsification, Clear-Lens Extraction, and LensX INCLUSION CRITERIA: Significant visual complaints (decreased VA, increased glare, decreased Activities of Daily Living
Cataract Surgery Co-Management Phacoemulsification, Clear-Lens Extraction, and LensX INCLUSION CRITERIA: Significant visual complaints (decreased VA, increased glare, decreased Activities of Daily Living
nepafenac 1mg/mL eye drops, suspension (Nevanac ) SMC No. (813/12) Alcon Laboratories (UK) Ltd
 nepafenac 1mg/mL eye drops, suspension (Nevanac ) SMC No. (813/12) Alcon Laboratories (UK) Ltd 05 October 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
nepafenac 1mg/mL eye drops, suspension (Nevanac ) SMC No. (813/12) Alcon Laboratories (UK) Ltd 05 October 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
INVELTYS (loteprednol etabonate ophthalmic suspension) 1%, for topical ophthalmic use Initial U.S. Approval: 1998
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use INVELTYS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for INVELTYS. INVELTYS (loteprednol
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use INVELTYS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for INVELTYS. INVELTYS (loteprednol
Clinical Evaluation of the BunnyLens IOL
 Clinical Evaluation of the BunnyLens IOL Introduction: BunnyLens is a foldable Hydrophlic Acrylic IOL with four ear shaped haptic design. The lens design offers many advantages in terms of: 1. Centration
Clinical Evaluation of the BunnyLens IOL Introduction: BunnyLens is a foldable Hydrophlic Acrylic IOL with four ear shaped haptic design. The lens design offers many advantages in terms of: 1. Centration
Better ophthalmic surgery outcomes in recent years have created more Demanding Patients.
 By Alaa EL Zawawi Prof. of Ophthalmology Alexandria - Egypt Launch Better ophthalmic surgery outcomes in recent years have created more Demanding Patients. 1 NSAIDs can play a pivotal role in facilitating
By Alaa EL Zawawi Prof. of Ophthalmology Alexandria - Egypt Launch Better ophthalmic surgery outcomes in recent years have created more Demanding Patients. 1 NSAIDs can play a pivotal role in facilitating
Trabeculectomy combined with cataract extraction: a follow-up study
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1980, 64, 720-724 Trabeculectomy combined with cataract extraction: a follow-up study R. S. EDWARDS From the Birmingham and Midland Eye Hospital, Church Street, Birmingham
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1980, 64, 720-724 Trabeculectomy combined with cataract extraction: a follow-up study R. S. EDWARDS From the Birmingham and Midland Eye Hospital, Church Street, Birmingham
psivida Transforms into Commercial Stage Specialty BioPharmaceutical Company AAO October 25, 2018 NASDAQ: EYPT
 psivida Transforms into Commercial Stage Specialty BioPharmaceutical Company OIS @ AAO October 25, 2018 NASDAQ: EYPT Forward Looking SAFE HARBOR STATEMENTS UNDER THE PRIVATE SECURITIES LITIGATION REFORM
psivida Transforms into Commercial Stage Specialty BioPharmaceutical Company OIS @ AAO October 25, 2018 NASDAQ: EYPT Forward Looking SAFE HARBOR STATEMENTS UNDER THE PRIVATE SECURITIES LITIGATION REFORM
Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation
 Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation Masaru Inatani*, Hidenobu Tanihara, Takahito Muto*, Megumi Honjo*,
Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation Masaru Inatani*, Hidenobu Tanihara, Takahito Muto*, Megumi Honjo*,
Measure #192: Cataracts: Complications within 30 Days Following Cataract Surgery Requiring Additional Surgical Procedures
 Measure #192: Cataracts: Complications within 30 Days Following Cataract Surgery Requiring Additional Surgical Procedures 2012 PHYSICIAN QUALITY REPORTING OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
Measure #192: Cataracts: Complications within 30 Days Following Cataract Surgery Requiring Additional Surgical Procedures 2012 PHYSICIAN QUALITY REPORTING OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
84 Year Old with Rosacea
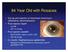 84 Year Old with Rosacea S/p tap and injection of intravitreal vancomycin, ceftazidime, dexamethasone Post-injection day#1 Va HM IOP 14 mmhg Post-injection week#3 BCVA 20/20-3 (plano +0.50 x 180) IOP 23
84 Year Old with Rosacea S/p tap and injection of intravitreal vancomycin, ceftazidime, dexamethasone Post-injection day#1 Va HM IOP 14 mmhg Post-injection week#3 BCVA 20/20-3 (plano +0.50 x 180) IOP 23
GLAUCOMA SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES
 SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES Introduction These are summary benchmarks for the Academy s Preferred Practice Pattern (PPP) guidelines. The Preferred Practice Pattern series
SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES Introduction These are summary benchmarks for the Academy s Preferred Practice Pattern (PPP) guidelines. The Preferred Practice Pattern series
Treatment of Uncontrolled Anterior Uveitis with 5- Fluorouracil: Case Series
 CASE STUDIES Treatment of Uncontrolled Anterior Uveitis with 5- Fluorouracil: Case Series Osama Mohammed Badeeb MD, FRCS(C), Ahmad Mohammed Bawazeer MD, FRCS(C) Department Of Ophthalmology, King Abdulaziz
CASE STUDIES Treatment of Uncontrolled Anterior Uveitis with 5- Fluorouracil: Case Series Osama Mohammed Badeeb MD, FRCS(C), Ahmad Mohammed Bawazeer MD, FRCS(C) Department Of Ophthalmology, King Abdulaziz
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
Abbreviated Drug Evaluation: Fluocinolone acetonide intravitreal implant (Retisert )
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Cataract Surgery in Patients with Uveitis
 Cataract Surgery in Patients with Uveitis Chris Kalogeropoulos MD, PhD, FEBO Professor of Ophthalmology Faculty of Medicine, University of Ioannina President of Hellenic Society for the Study of Ocular
Cataract Surgery in Patients with Uveitis Chris Kalogeropoulos MD, PhD, FEBO Professor of Ophthalmology Faculty of Medicine, University of Ioannina President of Hellenic Society for the Study of Ocular
The Biomedical Ocular Coil Drug delivery Comfort (OCDC) project
 The Biomedical Ocular Coil Drug delivery Comfort (OCDC) project Prof.dr. R.M.M.A. Nuijts (MUMC+) Dr. A. Dias (Eyegle BV) Prof.dr. R. Tuinier (TU/e) I. Schefman, BA (Eyegle BV) Dr. H. Theunissen (MVC, Part.
The Biomedical Ocular Coil Drug delivery Comfort (OCDC) project Prof.dr. R.M.M.A. Nuijts (MUMC+) Dr. A. Dias (Eyegle BV) Prof.dr. R. Tuinier (TU/e) I. Schefman, BA (Eyegle BV) Dr. H. Theunissen (MVC, Part.
CASE PRESENTATION. DR.Sravani 1 st yr PG Dept of Ophthalmology
 CASE PRESENTATION DR.Sravani 1 st yr PG Dept of Ophthalmology Name : X X X X X Age : 50yrs Sex : male Occupation : Farmer Residence : Mothkur CHIEF COMPLAINTS : - Diminision of vision in Right Eye since
CASE PRESENTATION DR.Sravani 1 st yr PG Dept of Ophthalmology Name : X X X X X Age : 50yrs Sex : male Occupation : Farmer Residence : Mothkur CHIEF COMPLAINTS : - Diminision of vision in Right Eye since
SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM
 Page 1 of 5 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM FML Liquifilm Sterile Eye Suspension COMPOSITION FML Liquifilm Sterile Eye Suspension contains: Fluorometholone 1,0 mg/ml Liquifilm
Page 1 of 5 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM FML Liquifilm Sterile Eye Suspension COMPOSITION FML Liquifilm Sterile Eye Suspension contains: Fluorometholone 1,0 mg/ml Liquifilm
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH. (Fluorometholone 0.1% Ophthalmic Suspension), USP. Corticosteroid
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH Pr Sandoz Fluorometholone (Fluorometholone 0.1% Ophthalmic Suspension), USP Corticosteroid Sandoz Canada Inc., Date of Revision: June 21, 2012 145 Jules-Léger Boucherville, QC, Canada
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH Pr Sandoz Fluorometholone (Fluorometholone 0.1% Ophthalmic Suspension), USP Corticosteroid Sandoz Canada Inc., Date of Revision: June 21, 2012 145 Jules-Léger Boucherville, QC, Canada
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA
 OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
Assisting in Ophthalmology. Copyright 2011, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Assisting in Ophthalmology Learning Objectives Define, spell, and pronounce the terms listed in the vocabulary. Apply critical thinking skills in performing patient assessment and care. Explain the differences
Assisting in Ophthalmology Learning Objectives Define, spell, and pronounce the terms listed in the vocabulary. Apply critical thinking skills in performing patient assessment and care. Explain the differences
CONTRAINDICATIONS None (4).
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DEXYCU safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DEXYCU. DEXYCU (dexamethasone
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DEXYCU safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DEXYCU. DEXYCU (dexamethasone
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
 Measure #192 (NQF 0564): Cataracts: Complications within 30 Days Following Cataract Surgery Requiring Additional Surgical Procedures National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR
Measure #192 (NQF 0564): Cataracts: Complications within 30 Days Following Cataract Surgery Requiring Additional Surgical Procedures National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR
THE CURRENT TREATMENT OF GLAUCOMA IS DIrected
 Three-Year Follow-up of the Tube Versus Trabeculectomy Study STEVEN J. GEDDE, JOYCE C. SCHIFFMAN, WILLIAM J. FEUER, LEON W. HERNDON, JAMES D. BRANDT, AND DONALD L. BUDENZ, ON BEHALF OF THE TUBE VERSUS
Three-Year Follow-up of the Tube Versus Trabeculectomy Study STEVEN J. GEDDE, JOYCE C. SCHIFFMAN, WILLIAM J. FEUER, LEON W. HERNDON, JAMES D. BRANDT, AND DONALD L. BUDENZ, ON BEHALF OF THE TUBE VERSUS
Cataract Surgery: Patient Information
 Cataract Surgery: Patient Information How do the Eyes Work? As light enters the eye, it first passes through the cornea the clear window of the eye. Because the cornea is curved, the light rays bend (refract).
Cataract Surgery: Patient Information How do the Eyes Work? As light enters the eye, it first passes through the cornea the clear window of the eye. Because the cornea is curved, the light rays bend (refract).
Secondary Intraocular Lens Implantation in University Hospital l, Kuala Lumpur
 Secondary Intraocular Lens Implantation in University Hospital l, Kuala Lumpur Fathilah Jaais, MRCOphth, Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya, Lembah Pantai, 50603 Kuala
Secondary Intraocular Lens Implantation in University Hospital l, Kuala Lumpur Fathilah Jaais, MRCOphth, Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya, Lembah Pantai, 50603 Kuala
INDICATIONS For steroid responsive inflammation of the palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva, cornea, and anterior segment of the eye globe.
 Page 1 of 5 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM PRED FORTE Sterile Eye Suspension COMPOSITION PRED FORTE Sterile Eye Suspension contains: Prednisolone acetate 10 mg/ml Preservative:
Page 1 of 5 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM PRED FORTE Sterile Eye Suspension COMPOSITION PRED FORTE Sterile Eye Suspension contains: Prednisolone acetate 10 mg/ml Preservative:
Comparison of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Dexamethasone and Diclofenac Sodium Eye Drops in Phacoemulsification
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Dexamethasone and Diclofenac Sodium Eye Drops in Phacoemulsification Muhammad Waseem and Sadia Humayun ABSTRACT Objective: To compare the effectiveness
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Dexamethasone and Diclofenac Sodium Eye Drops in Phacoemulsification Muhammad Waseem and Sadia Humayun ABSTRACT Objective: To compare the effectiveness
Subnormal Vision in Uneventful Cataract Surgery after 6 Weeks Hospital Based Study
 ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Subnormal Vision in Uneventful Cataract Surgery after 6 Weeks Hospital Based Study 1* 1 1 V. H. Karambelkar, Ankit Sharma, Viraj Pradhan 1 Department of Ophthalmology, Krishna
ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Subnormal Vision in Uneventful Cataract Surgery after 6 Weeks Hospital Based Study 1* 1 1 V. H. Karambelkar, Ankit Sharma, Viraj Pradhan 1 Department of Ophthalmology, Krishna
Role of Initial Preoperative Medical Management in Controlling Post-Operative Anterior Uveitis in Patients of Phacomorphic Glaucoma
 Original Article Role of Initial Preoperative Medical Management in Controlling Post-Operative Anterior Uveitis in Patients of Phacomorphic Glaucoma Irfan Qayyum Malik, M. Moin, A. Rehman, Mumtaz Hussain
Original Article Role of Initial Preoperative Medical Management in Controlling Post-Operative Anterior Uveitis in Patients of Phacomorphic Glaucoma Irfan Qayyum Malik, M. Moin, A. Rehman, Mumtaz Hussain
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title:Efficacy of 1% carboxymethylcellulose sodium for treating dry eye after phacoemulsification: results from a multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled study Authors:
Author's response to reviews Title:Efficacy of 1% carboxymethylcellulose sodium for treating dry eye after phacoemulsification: results from a multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled study Authors:
Audit of extracapsular cataract extraction and posterior chamber lens implantation as a routine treatment for age related cataract in east Africa
 Br J Ophthalmol 1999;83:897 901 897 Kikuyu Hospital, Kenya D Yorston London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London A Foster Correspondence to: Dr Allen Foster, London School of Hygiene and Tropical
Br J Ophthalmol 1999;83:897 901 897 Kikuyu Hospital, Kenya D Yorston London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London A Foster Correspondence to: Dr Allen Foster, London School of Hygiene and Tropical
WARNING LETTER. According to the Indications and Usage section of the FDA approved product labeling (PI):
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Rockville, MD 20857 TRANSMITTED BY FACSIMILE David E.I. Pyott President and Chief Executive Officer PO Box 19534
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Rockville, MD 20857 TRANSMITTED BY FACSIMILE David E.I. Pyott President and Chief Executive Officer PO Box 19534
COMPARISON BETWEEN 0.1% DICLOFENAC NATRIUM AND 0.1% DEXAMETHASONE EYEDROPS IN REDUCING CATARACT POSTOPERATIVE INFLAMMATION
 Folia Medica Indonesiana Vol. 42 No. 3 July September 2006 : 166-171 COMPARISON BETWEEN 0.1% DICLOFENAC NATRIUM AND 0.1% DEXAMETHASONE EYEDROPS IN REDUCING CATARACT POSTOPERATIVE INFLAMMATION Moestidjab
Folia Medica Indonesiana Vol. 42 No. 3 July September 2006 : 166-171 COMPARISON BETWEEN 0.1% DICLOFENAC NATRIUM AND 0.1% DEXAMETHASONE EYEDROPS IN REDUCING CATARACT POSTOPERATIVE INFLAMMATION Moestidjab
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Anterior Segment of the Eye File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: optical_coherence_tomography_(oct)_anterior_segment_of_the_eye
Corporate Medical Policy Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Anterior Segment of the Eye File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: optical_coherence_tomography_(oct)_anterior_segment_of_the_eye
Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma. Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4. Abstract
 Original article Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 4 Professor, Department of
Original article Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 4 Professor, Department of
Cronicon EC OPHTHALMOLOGY. Research Article Trephine Assisted Trabeculectomy Technique. Idrees* Introduction
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Research Article Idrees* Al Dara Hospital and Medical Center at Riyadh, Saudi Arabia *Corresponding Author: Dr Idrees, Al Dara Hospital and Medical Center at Riyadh,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Research Article Idrees* Al Dara Hospital and Medical Center at Riyadh, Saudi Arabia *Corresponding Author: Dr Idrees, Al Dara Hospital and Medical Center at Riyadh,
Clinical study of traumatic cataract and its management
 Clinical study of traumatic cataract and its management Original article Manjula Mangane, M.R. Pujari, Chethan N. Murthy Department of Ophthalmology, Basaweshwar Teaching and General Hospital, Gulbarga,
Clinical study of traumatic cataract and its management Original article Manjula Mangane, M.R. Pujari, Chethan N. Murthy Department of Ophthalmology, Basaweshwar Teaching and General Hospital, Gulbarga,
Relevant and Reliable Systematic Review Mapped to this Section. Relevance of Review to other sections of AAO PPP- 2011
 Table 1. American Academy for Ophthalmology s (AAO) Preferred Practice Patterns (PPP) Nonsurgical Hodge, 2005 Evid Rep Technol Assess (Summ). 2005 Jul;(117):1-6. Effects of omega- 3 fatty acids on eye
Table 1. American Academy for Ophthalmology s (AAO) Preferred Practice Patterns (PPP) Nonsurgical Hodge, 2005 Evid Rep Technol Assess (Summ). 2005 Jul;(117):1-6. Effects of omega- 3 fatty acids on eye
Vanderbilt Eye Institute
 Vanderbilt Eye Institute Joshua Ki Hu Vanderbilt Eye Institute Ophthalmology, PGY-4 DATE 05.30.08 Introduction Cataract surgery is one of the most commonly performed surgeries in the world, with over 1
Vanderbilt Eye Institute Joshua Ki Hu Vanderbilt Eye Institute Ophthalmology, PGY-4 DATE 05.30.08 Introduction Cataract surgery is one of the most commonly performed surgeries in the world, with over 1
INTRODUCTION J. DAWCZYNSKI, E. KOENIGSDOERFFER, R. AUGSTEN, J. STROBEL. Department of Ophthalmology, University Hospital Jena, Jena - Germany
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 3, 2007 / pp. 363-367 Anterior segment optical coherence tomography for evaluation of changes in anterior chamber angle and depth after intraocular lens
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 3, 2007 / pp. 363-367 Anterior segment optical coherence tomography for evaluation of changes in anterior chamber angle and depth after intraocular lens
Case History. Slit lamp exam: Clinical Pearls in the Management of Iritis. 2- injection: Irregular SPK and staining AC: grade 3 cell & flare
 Clinical Pearls in the Management of Iritis Paul Karpecki, OD, FAAO Corneal Services and Ocular Disease Research Koffler Vision Group-Lexington, KY 68 y.o. Caucasian female Complains of photophobia and
Clinical Pearls in the Management of Iritis Paul Karpecki, OD, FAAO Corneal Services and Ocular Disease Research Koffler Vision Group-Lexington, KY 68 y.o. Caucasian female Complains of photophobia and
sodium [2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl] acetate, a phenylacetic acid derivative CH 2 COONa
![sodium [2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl] acetate, a phenylacetic acid derivative CH 2 COONa sodium [2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl] acetate, a phenylacetic acid derivative CH 2 COONa](/thumbs/78/77533900.jpg) PRODUCT INFORMATION VOLTAREN * OPHTHA Eye Drop (diclofenac sodium) NAME OF THE MEDICINE Active ingredient: Chemical name: Molecular formula: C 14 H 10 Cl 2 NNaO 2 CAS number: 15307-79-6 Molecular weight:
PRODUCT INFORMATION VOLTAREN * OPHTHA Eye Drop (diclofenac sodium) NAME OF THE MEDICINE Active ingredient: Chemical name: Molecular formula: C 14 H 10 Cl 2 NNaO 2 CAS number: 15307-79-6 Molecular weight:
DRAFT CONSENSUS STATEMENT FOR COMMENT October
 DRAFT CONSENSUS STATEMENT FOR COMMENT October 9 2015 This statement was developed as a result of breakout group recommendations from the March 24, 2014 Developing Novel Endpoints for Premium IOLs Workshop
DRAFT CONSENSUS STATEMENT FOR COMMENT October 9 2015 This statement was developed as a result of breakout group recommendations from the March 24, 2014 Developing Novel Endpoints for Premium IOLs Workshop
 Traumatic Cataract Orbital Wall Fracture Vitreous Hemorrhage Optic Disc Hemorrhage a) Amblyopia b) Strabismus c) Trauma Playing with other children Sports Fire works BB gun Injecting needles .
Traumatic Cataract Orbital Wall Fracture Vitreous Hemorrhage Optic Disc Hemorrhage a) Amblyopia b) Strabismus c) Trauma Playing with other children Sports Fire works BB gun Injecting needles .
AUSTRALIAN PRODUCT INFORMATION FLAREX (FLUOROMETHOLONE ACETATE) EYE DROPS SUSPENSION
 AUSTRALIAN PRODUCT INFORMATION FLAREX (FLUOROMETHOLONE ACETATE) EYE DROPS SUSPENSION 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINE Fluorometholone acetate. 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION The active ingredient in
AUSTRALIAN PRODUCT INFORMATION FLAREX (FLUOROMETHOLONE ACETATE) EYE DROPS SUSPENSION 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINE Fluorometholone acetate. 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION The active ingredient in
Cataract Surgery by Phacoemulsification Surgical and Visual Outcome with Foldable and Non-Foldable Lenses
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Cataract Surgery by Phacoemulsification Surgical and Visual Outcome with Foldable and Non-Foldable Lenses Authors Dr. Chitra Pande 1,
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Cataract Surgery by Phacoemulsification Surgical and Visual Outcome with Foldable and Non-Foldable Lenses Authors Dr. Chitra Pande 1,
The Visian ICL Advantages
 The Visian ICL Advantages Many vision correction procedures promise an improved level of vision, but few vision correction alternatives offer the quality and features found with the Visian ICL. These include:
The Visian ICL Advantages Many vision correction procedures promise an improved level of vision, but few vision correction alternatives offer the quality and features found with the Visian ICL. These include:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. HIGH VOLUME CAMP SURGERIES A CLINICAL STUDY D. N. Prakash, K, Sathish, Sankalp Singh Sharma, Soujanya. K, Savitha Patil.
 HIGH VOLUME CAMP SURGERIES A CLINICAL STUDY D. N. Prakash, K, Sathish, Sankalp Singh Sharma, Soujanya. K, Savitha Patil. 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Ophthalmology, MMC & RI, Mysore, 2. Associate
HIGH VOLUME CAMP SURGERIES A CLINICAL STUDY D. N. Prakash, K, Sathish, Sankalp Singh Sharma, Soujanya. K, Savitha Patil. 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Ophthalmology, MMC & RI, Mysore, 2. Associate
Rama Vadapalli * 1, Vankadara Naga Suresh 2. Online Access and Article Informtaion. Original Research Article
 Original Research Article An Interventional Follow up Study to Determine the Effect of Nepafenac 0.1% in Macular thickness in Patients who had Undergone Cataract Surgery as Determined By OCT Rama Vadapalli
Original Research Article An Interventional Follow up Study to Determine the Effect of Nepafenac 0.1% in Macular thickness in Patients who had Undergone Cataract Surgery as Determined By OCT Rama Vadapalli
The role of perioperative nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs use in cataract surgery
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 18, Issue 1 Ser. 15 (January. 2019), PP 23-27 www.iosrjournals.org The role of perioperative nonsteroidal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 18, Issue 1 Ser. 15 (January. 2019), PP 23-27 www.iosrjournals.org The role of perioperative nonsteroidal
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME Flucon fluorometholone 0.1% Eye Drops Suspension 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ml of Flucon contains 1.0 mg of fluorometholone (0.1% w/v). Excipient
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME Flucon fluorometholone 0.1% Eye Drops Suspension 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ml of Flucon contains 1.0 mg of fluorometholone (0.1% w/v). Excipient
Quantified Measurement of Intraocular Inflammation after Phacoemulsification Cataract Surgery
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, December: 237-241, 14 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Quantified Measurement of Intraocular Inflammation after Phacoemulsification Cataract Surgery AYMAN M.
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, December: 237-241, 14 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Quantified Measurement of Intraocular Inflammation after Phacoemulsification Cataract Surgery AYMAN M.
PHARMACOLOGY Class: Ketorolac trometamol is a member of the pyrrolo-pyrolle group of non-steroidal antiinflammatory
 ACULAR Eye Drops NAME OF THE DRUG Non-proprietary name: ketorolac trometamol. Chemical Structure: Chemical Name: ( )-5-Benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid compound with 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol
ACULAR Eye Drops NAME OF THE DRUG Non-proprietary name: ketorolac trometamol. Chemical Structure: Chemical Name: ( )-5-Benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid compound with 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol
Anterior segment imaging
 Article Date: 11/1/2016 Anterior segment imaging AS OCT vs. UBM vs. endoscope; case based approaches BY BENJAMIN BERT, MD, FACS AND BRIAN FRANCIS, MD, MS Currently, numerous imaging modalities are available
Article Date: 11/1/2016 Anterior segment imaging AS OCT vs. UBM vs. endoscope; case based approaches BY BENJAMIN BERT, MD, FACS AND BRIAN FRANCIS, MD, MS Currently, numerous imaging modalities are available
FROM PRE-OP TO POST-OP, OPTIMIZE YOUR WORKFLOW WITH THE CATALYS SYSTEM MOBILE PATIENT BED.
 FROM PRE-OP TO POST-OP, OPTIMIZE YOUR WORKFLOW WITH THE CATALYS SYSTEM MOBILE PATIENT BED. PUSH THE LIMITS Imagine if your CATALYS System patient bed could: Optimize your productivity throughout the full
FROM PRE-OP TO POST-OP, OPTIMIZE YOUR WORKFLOW WITH THE CATALYS SYSTEM MOBILE PATIENT BED. PUSH THE LIMITS Imagine if your CATALYS System patient bed could: Optimize your productivity throughout the full
Iontophoresis Platform Safely and Effectively Delivers Dexamethasone to Manage Post Operative Inflammation and Pain Following Cataract Surgery.
 Poster #33516 Iontophoresis Platform Safely and Effectively Delivers Dexamethasone to Manage Post Operative Inflammation and Pain Following Cataract Surgery. JEFFREY H. LEVENSON, MD 1 (PRESENTING AUTHOR);
Poster #33516 Iontophoresis Platform Safely and Effectively Delivers Dexamethasone to Manage Post Operative Inflammation and Pain Following Cataract Surgery. JEFFREY H. LEVENSON, MD 1 (PRESENTING AUTHOR);
ISSN: (Paper) eissn: (Online) JOURNAL OF ADVANCED ACADEMIC RESEARCH (JAAR) April 2017
 Topical proparacaine vs combined topical-intracameral lidocaine anesthesia in phacoemulsification surgery with preoperative counseling about intraoperative visual fear Kiran Shakya 1, Sangita Shakya 2,
Topical proparacaine vs combined topical-intracameral lidocaine anesthesia in phacoemulsification surgery with preoperative counseling about intraoperative visual fear Kiran Shakya 1, Sangita Shakya 2,
Inadvertent trypan blue staining of posterior capsule during cataract surgery associated with "Argentinian flag" event
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2016 Inadvertent trypan blue staining of posterior capsule during cataract surgery associated with "Argentinian
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2016 Inadvertent trypan blue staining of posterior capsule during cataract surgery associated with "Argentinian
Complete Visual Rehabilitation in a Patient with No Light Perception after Surgical Management of a Penetrating Open-Globe Injury: A Case Report
 Published online: June 23, 2015 1663 2699/15/0062 0204$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Published online: June 23, 2015 1663 2699/15/0062 0204$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Cataracts in adults: management
 Cataracts in adults: management NICE guideline: short version Draft for consultation, May 0 This guideline covers managing cataracts in adults aged and over. It aims to improve care before, during and
Cataracts in adults: management NICE guideline: short version Draft for consultation, May 0 This guideline covers managing cataracts in adults aged and over. It aims to improve care before, during and
Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015
 Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015 Jimmy Lai Clinical Professor Department of Ophthalmology The University of Hong Kong 1 Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma PACG
Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015 Jimmy Lai Clinical Professor Department of Ophthalmology The University of Hong Kong 1 Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma PACG
D90 (27/10/2005) Final SmPC NL/H/653/01
 1/6 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MONOFREE DEXAMETHASON 1 mg/ml, eye drops, solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml solution contains 1 mg of dexamethasone phosphate as dexamethasone
1/6 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MONOFREE DEXAMETHASON 1 mg/ml, eye drops, solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml solution contains 1 mg of dexamethasone phosphate as dexamethasone
CONSENT FOR CATARACT SURGERY REQUEST FOR SURGICAL OPERATION / PROCEDURE AND ANAESTHETIC
 CONSENT FOR CATARACT SURGERY REQUEST FOR SURGICAL OPERATION / PROCEDURE AND ANAESTHETIC Your doctor has indicated that the condition of your eye appears stable and your cataract surgery and/or implantation
CONSENT FOR CATARACT SURGERY REQUEST FOR SURGICAL OPERATION / PROCEDURE AND ANAESTHETIC Your doctor has indicated that the condition of your eye appears stable and your cataract surgery and/or implantation
TOBAFLAM Eye Drops (Loteprednol etabonate 0.5% + Tobramycin 0.3%)
 Published on: 23 Sep 2014 TOBAFLAM Eye Drops (Loteprednol etabonate 0.5% + Tobramycin 0.3%) Composition Loteprednol Etabonate 5 mg (0.5% w/v) Tobramycin...3 mg (0.3% w/v) Benzalkonium Chloride.. 0.01%
Published on: 23 Sep 2014 TOBAFLAM Eye Drops (Loteprednol etabonate 0.5% + Tobramycin 0.3%) Composition Loteprednol Etabonate 5 mg (0.5% w/v) Tobramycin...3 mg (0.3% w/v) Benzalkonium Chloride.. 0.01%
Anterior Segment Cataract Surgery
 Current Use of Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs in the Treatment of Ocular Inflammation Related to Cataract Surgery Eric Donnenfeld Clinical Professor of Ophthalmology, New York University, New York,
Current Use of Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs in the Treatment of Ocular Inflammation Related to Cataract Surgery Eric Donnenfeld Clinical Professor of Ophthalmology, New York University, New York,
Chemical Names: Prednisolone acetate: 11ß,17,21-Trihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione 21-acetate.
 PRED-G (gentamicin and prednisolone acetate ophthalmic suspension, USP) 0.3%/1% sterile DESCRIPTION PRED-G sterile ophthalmic suspension is a topical anti-inflammatory/anti-infective combination product
PRED-G (gentamicin and prednisolone acetate ophthalmic suspension, USP) 0.3%/1% sterile DESCRIPTION PRED-G sterile ophthalmic suspension is a topical anti-inflammatory/anti-infective combination product
New Strategies to Prevent Posterior Capsule Opacification
 New Strategies to Prevent Posterior Capsule Opacification Heather Chandler, PhD chandler.111@osu.edu cornea aqueous humor lens capsule epithelium (LEC) lens fibres Cataracts any opacity of the crystalline
New Strategies to Prevent Posterior Capsule Opacification Heather Chandler, PhD chandler.111@osu.edu cornea aqueous humor lens capsule epithelium (LEC) lens fibres Cataracts any opacity of the crystalline
CONTRAINDICATIONS Active ocular infections (4).
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DEXTENZA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DEXTENZA. DEXTENZA (dexamethasone
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DEXTENZA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DEXTENZA. DEXTENZA (dexamethasone
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NEVANAC* safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NEVANAC. NEVANAC (nepafenac
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NEVANAC* safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NEVANAC. NEVANAC (nepafenac
Comparison of the Long-term Clinical Results of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Acrylic Intraocular Lenses
 Korean J Ophthalmol Vol. 19:29-33, 2005 Comparison of the Long-term Clinical Results of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Acrylic Intraocular Lenses Youngwoo Suh, MD 1, Chunghoon Oh, MD 2, Hyo-Myung Kim, MD,
Korean J Ophthalmol Vol. 19:29-33, 2005 Comparison of the Long-term Clinical Results of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Acrylic Intraocular Lenses Youngwoo Suh, MD 1, Chunghoon Oh, MD 2, Hyo-Myung Kim, MD,
SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM
 Page 1 of 5 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM FML-NEO Liquifilm Ophthalmic Suspension COMPOSITION FML-NEO Liquifilm Ophthalmic Suspension contains per ml: Fluorometholone 1,0
Page 1 of 5 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM FML-NEO Liquifilm Ophthalmic Suspension COMPOSITION FML-NEO Liquifilm Ophthalmic Suspension contains per ml: Fluorometholone 1,0
CHARTING THE NEW COURSE FOR MIGS
 CHARTING THE NEW COURSE FOR MIGS SEE WHAT S ON THE HORIZON CyPass Micro-Stent the next wave in micro-invasive glaucoma surgery. MICRO-INVASIVE GLAUCOMA SURGERY (MIGS) OFFERS A REVOLUTIONARY APPROACH TO
CHARTING THE NEW COURSE FOR MIGS SEE WHAT S ON THE HORIZON CyPass Micro-Stent the next wave in micro-invasive glaucoma surgery. MICRO-INVASIVE GLAUCOMA SURGERY (MIGS) OFFERS A REVOLUTIONARY APPROACH TO
An Injector s Guide to OZURDEX (dexamethasone intravitreal implant) 0.7 mg
 An Injector s Guide to OZURDEX (dexamethasone intravitreal implant) 0.7 mg This guide is intended to provide injectors with information on the recommended injection technique and the important risks related
An Injector s Guide to OZURDEX (dexamethasone intravitreal implant) 0.7 mg This guide is intended to provide injectors with information on the recommended injection technique and the important risks related
EYE TRAUMA: INCIDENCE
 Introduction EYE TRAUMA: INCIDENCE 2.5 million eye injuries per year in U.S. 40,000 60,000 of eye injuries lead to visual loss Introduction Final visual outcome of many ocular emergencies depends on prompt,
Introduction EYE TRAUMA: INCIDENCE 2.5 million eye injuries per year in U.S. 40,000 60,000 of eye injuries lead to visual loss Introduction Final visual outcome of many ocular emergencies depends on prompt,
Innovation In Ophthalmology
 Innovation In Ophthalmology INVELTYS TM Approval August 2018 Disclaimers and Notices This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform
Innovation In Ophthalmology INVELTYS TM Approval August 2018 Disclaimers and Notices This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform
A New Paradigm in NSAID Treatment
 V 5/6 pg Contents Common Uses of Ophthalmic NSAIDs A New Paradigm in NSAID History of (bromfenac ophthalmic solution).9% Efficacy of Phase III trials Pain data Post-Approval trials Pharmacokinetics, Penetration,
V 5/6 pg Contents Common Uses of Ophthalmic NSAIDs A New Paradigm in NSAID History of (bromfenac ophthalmic solution).9% Efficacy of Phase III trials Pain data Post-Approval trials Pharmacokinetics, Penetration,
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Pachymetry Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Pachymetry Professional Institutional Original Effective Date: March 11, 2004 Original Effective
Pachymetry Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Pachymetry Professional Institutional Original Effective Date: March 11, 2004 Original Effective
APPENDIX 1: SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. SPC for VEXOL Eye Drops, Suspension 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
 APPENDIX 1: SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS SPC for VEXOL Eye Drops, Suspension 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT VEXOL 1% (10 mg/ml) eye drops, suspension 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
APPENDIX 1: SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS SPC for VEXOL Eye Drops, Suspension 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT VEXOL 1% (10 mg/ml) eye drops, suspension 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity to any component of this product (4)
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use OMIDRIA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for OMIDRIA. OMIDRIA (phenylephrine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use OMIDRIA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for OMIDRIA. OMIDRIA (phenylephrine
FROM PRE-OP TO POST-OP, HELP OPTIMIZE YOUR WORKFLOW WITH THE CATALYS SYSTEM MOBILE PATIENT BED.
 FROM PRE-OP TO POST-OP, HELP OPTIMIZE YOUR WORKFLOW WITH THE CATALYS SYSTEM MOBILE PATIENT BED. PUSH THE LIMITS Imagine if your CATALYS System patient bed could: Optimize patient workflow throughout the
FROM PRE-OP TO POST-OP, HELP OPTIMIZE YOUR WORKFLOW WITH THE CATALYS SYSTEM MOBILE PATIENT BED. PUSH THE LIMITS Imagine if your CATALYS System patient bed could: Optimize patient workflow throughout the
Case History. The SEVEN HABITS of Highly Effective Anterior Uveitis Management. SLEx findings: SLEx corneal findings: y.o.
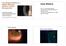 The SEVEN HABITS of Highly Effective Anterior Uveitis Management Case History! 68 y.o. Caucasian female of photophobia and blurred vision! As well as a headache over right eye for 2 days! Complains Paul
The SEVEN HABITS of Highly Effective Anterior Uveitis Management Case History! 68 y.o. Caucasian female of photophobia and blurred vision! As well as a headache over right eye for 2 days! Complains Paul
Critical Complication Wonderfully Managed by Vitreoretinal Surgeon
 Critical Complication Wonderfully Managed by Vitreoretinal Surgeon Prof. Dr. Sherif Embabi Consultant of ophthalmology Ain Shams univ. & Alwatany Eye Hospital, MD Dr. Remon Atef Ophthalmology specialist
Critical Complication Wonderfully Managed by Vitreoretinal Surgeon Prof. Dr. Sherif Embabi Consultant of ophthalmology Ain Shams univ. & Alwatany Eye Hospital, MD Dr. Remon Atef Ophthalmology specialist
Acute Eyes for ED. Enis Kocak. The Alfred Ophthalmology
 Acute Eyes for ED Enis Kocak The Alfred Ophthalmology The problem with eyes Things to cover Ocular anatomy Basic assessment Common presentations Eye first aid and procedures Ophthalmic emergencies What
Acute Eyes for ED Enis Kocak The Alfred Ophthalmology The problem with eyes Things to cover Ocular anatomy Basic assessment Common presentations Eye first aid and procedures Ophthalmic emergencies What
Glaucoma Surgical Treatments. Murray Fingeret, OD Justin Schweitzer, OD Joe Sowka, OD
 Glaucoma Surgical Treatments Murray Fingeret, OD Justin Schweitzer, OD Joe Sowka, OD Disclosures Murray Fingeret Consultant Bausch & Lomb, Alcon, Allergan Justin Schweitzer Allergan, Glaukos, Bausch and
Glaucoma Surgical Treatments Murray Fingeret, OD Justin Schweitzer, OD Joe Sowka, OD Disclosures Murray Fingeret Consultant Bausch & Lomb, Alcon, Allergan Justin Schweitzer Allergan, Glaukos, Bausch and
Sutureless Intrascleral Pocket Technique of Transscleral Fixation of Intraocular Lens in Previous Vitrectomized Eyes
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2014;28(2):181-185 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2014.28.2.181 Case Report Sutureless Intrascleral Pocket Technique of Transscleral Fixation of Intraocular
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2014;28(2):181-185 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2014.28.2.181 Case Report Sutureless Intrascleral Pocket Technique of Transscleral Fixation of Intraocular
SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4. PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM OZURDEX intravitreal implant
 Page 1 of 10 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM intravitreal implant COMPOSITION One intravitreal implant contains: Dexamethasone 700 μg Excipients: Ester terminated 50:50 poly
Page 1 of 10 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM intravitreal implant COMPOSITION One intravitreal implant contains: Dexamethasone 700 μg Excipients: Ester terminated 50:50 poly
New Zealand Data Sheet
 New Zealand Data Sheet Prednisolone-AFT 1% Prednisolone acetate (Ph Eur) 1% w/v ophthalmic suspension Presentation Prednisolone-AFT 1% is a milky white suspension in an eyedropper bottle for ophthalmic
New Zealand Data Sheet Prednisolone-AFT 1% Prednisolone acetate (Ph Eur) 1% w/v ophthalmic suspension Presentation Prednisolone-AFT 1% is a milky white suspension in an eyedropper bottle for ophthalmic
NICE guideline Published: 26 October 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng77
 Cataracts acts in adults: management NICE guideline Published: 26 October 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng77 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Cataracts acts in adults: management NICE guideline Published: 26 October 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng77 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
T.opically applied corticoids were shown to produce in man an increase in intraocular pressure, a reduction in outflow facility,
 Aqueous outflow facility in monkeys and the effect of topical corticoids Mansour F. Armaly The ocular effects of topically applied dexamethasone 21-phosphate and subconjunctivally administered methylprednisolone
Aqueous outflow facility in monkeys and the effect of topical corticoids Mansour F. Armaly The ocular effects of topically applied dexamethasone 21-phosphate and subconjunctivally administered methylprednisolone
Conjunctival displacement to the corneal side for oblique-parallel insertion in 25-gauge vitrectomy
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 18 no. 5, 2008 / pp. 848-851 SHORT COMMUNICATIONS & CASE REPORTS Conjunctival displacement to the corneal side for oblique-parallel insertion in 25-gauge vitrectomy
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 18 no. 5, 2008 / pp. 848-851 SHORT COMMUNICATIONS & CASE REPORTS Conjunctival displacement to the corneal side for oblique-parallel insertion in 25-gauge vitrectomy
Prabhu GR. Visual outcome of traumatic cataract in a tertiary care hospital, Tirupati.
 Jagannath C, Penchalaiah T, Swetha M, Prabhu GR. Visual outcome of traumatic cataract in a tertiary care hospital, Tirupati. Original Research Article Visual outcome of traumatic cataract in a tertiary
Jagannath C, Penchalaiah T, Swetha M, Prabhu GR. Visual outcome of traumatic cataract in a tertiary care hospital, Tirupati. Original Research Article Visual outcome of traumatic cataract in a tertiary
2/26/2017. Sameh Galal. M.D, FRCS Glasgow. Lecturer of Ophthalmology Research Institute of Ophthalmology
 Sameh Galal M.D, FRCS Glasgow Lecturer of Ophthalmology Research Institute of Ophthalmology No financial interest in the subject presented 1 Managing cataracts in children remains a challenge. Treatment
Sameh Galal M.D, FRCS Glasgow Lecturer of Ophthalmology Research Institute of Ophthalmology No financial interest in the subject presented 1 Managing cataracts in children remains a challenge. Treatment
THE OUTCOME OF EXTRACAPSULAR AND PHACOEMULSIFICATION CATARACT EXTRACTIONS
 JMBR: A Peer-review Journal of Biomedical Sciences June 2012, Vol. 11 No.1 pp 123-128 THE OUTCOME OF EXTRACAPSULAR AND PHACOEMULSIFICATION CATARACT EXTRACTIONS OSITA ME and YUEN SZ Abstract This study
JMBR: A Peer-review Journal of Biomedical Sciences June 2012, Vol. 11 No.1 pp 123-128 THE OUTCOME OF EXTRACAPSULAR AND PHACOEMULSIFICATION CATARACT EXTRACTIONS OSITA ME and YUEN SZ Abstract This study
