BACK PAIN AMONGST SCHOOLCHILDREN AND ASSOCIATED RISK FACTORS
|
|
|
- Melvyn Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BACK PAIN AMONGST SCHOOLCHILDREN AND ASSOCIATED RISK FACTORS Sam Murphy, Peter Buckle & Dave Stubbs Robens Centre for Health Ergonomics This study set out to identify the role of ergonomic and other factors in new episodes of disabling back pain in schoolchildren and to develop methods to access potential risk factors of schoolchildren and evaluate their relationship with subsequent symptomology. It has been shown that a strong predictor of having future back pain is a previous history of such symptoms. The self-report questionnaire ascertained demographic characteristics, back pain history, school and leisure activities, school bag and furniture details, common childhood complaints and psychological factors. The prevalence of back pain was ascertained using a body map. Descriptive results are presented then the results of a multivariate analysis are presented and discussed. Introduction This study set out to identify the role of ergonomic and other factors in episodes of disabling back pain in schoolchildren and to access potential risk factors of schoolchildren and evaluate their relationship with subsequent symptomology. It has been shown that a strong predictor of having future back pain is a previous history of such symptoms (Troup et al 1987). A large portion of adults suffers report a first onset of back pain in their early teenage years or in their twenties (Papageorgiou et al 1996). Recent studies have highlighted the high prevalence of back pain that exists among schoolchildren (Burton et al 1996; Mikkelsson et al 1997; Watson et al 2002; Murphy 2003). Several authors have reported a relationship between back pain and school bag weight (Viry et al 1999; Grimmer & Williams, 2000; Whittfield et al 2001). A greater understanding of the risk factors associated with the onset of spinal pain is important before well targeted preventative action can be taken with the aim of controlling and/or reducing back pain amongst children. Methods Twelve schools in Surrey, England took part in a cross-sectional survey. A self-report questionnaire (Watson et al 2002; Murphy 2003) ascertained demographic characteristics, back pain history, school and leisure activities, school bag and furniture, common childhood complaints and psychological factors. The prevalence of back pain in the last seven days and last month was established using a body map (Kuorinka et al 1987). Children were measured for height and weight. The weight of the school bag was also measured. Details regarding school furniture were ascertained by the Chair Feature Checklist (Shackel et al 1969), which provided information about furniture suitability and comfort. The checklist had previously been modified for use of children age years (Murphy 2003). Common childhood complaints were considered by asking children how many days in the last month they had suffered from headache, stomachache and sore throats. Psychosocial factors were assessed using the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) (Goodman 1997), which provided coverage of young people s behaviours, emotions and relationships. The SDQ questions provided scores on hyperactivity, emotional symptoms, conduct problems, peer problems and pro-social scales. Recoding of the posture of children (sub-sample of n=66). in real time in the classroom was made using the Portable Ergonomic Observation method (Fransson-Hall et al 1995) and developed for use in the classroom by Murphy et al (2003). Results Six hundred and seventy nine responded (response rate 97%) with 343 males and 336 females. The mean age was 12.8 (SD 0.9). The mean body mass index was 19 (SD 3.38). Neck, upper back and low back pain (see table 1). Most of those with neck pain rated the pain as medium, 24% with 13% of children in a lot of pain when at it s worst. Almost 30% of children had upper back pain in the last month and 17 % had upper back pain in the last week. Just over 30% of children had low back pain in the last month and 20% had low back pain in the last week. Approximately 22% reported low back pain for 1 day or more in the last month (table 1). Almost 12% reported medium pain and 8% reported a lot of pain when at it s worst.
2 Table 1. Spinal pain Neck pain N % Last month Last week day or more Upper back pain N % Last month Last week day or more Low back pain N % Last month Last week day or more Ever History of low back pain. Sixty percent of children had a family member who suffered from low back pain Mother 20%, Father 21% and Mother and Father 9%. Twenty three percent reported experiencing a previous injury to their lower back. More than half of the children reported having low back pain at some stage prior to the study. PEO observations. A sub-sample of children (n=66) had their sitting postures monitored in real time in normal lessons. The results of the PEO observations are reported in detail elsewhere (Murphy et al 2003). To summarise the following variables were found to be significantly associated with musculosketal pain in the last week and month. Static posture was significantly associated with neck pain in the last week and upper back pain in the last week and month. Long lesson length was significantly associated with low back pain reported in the last month. Flexed trunk posture and flexed neck posture were both significantly associated with low back pain in the last week. A high percentage of time spent working at the desk, which, occurred when the trunk was flexed, was also significantly associated with low back pain in the last week. Statistical analysis. The outcome definition used for multivariate analysis was low back pain (in a specific area identified on a pain drawing) lasting one day or more. This definition was also used for neck and upper back pain. The definition of a back pain case was that used by the University of Manchester (Papageorgiou et al 1995 and Watson et al 2002) to examine existing pain. Finally children were asked if they had ever experienced low back pain. Variables that achieved significance levels of (p<0.05) in univariate analysis (controlling for age and gender) were entered into each of the multivariate models to establish factors that were independently associated with each area of pain. Logistic regression was used to access the relationship between one dependent variable and several independent variables. The study was cross-sectional and therefore may identify associations but not causality between exposure and disease Neck pain. too low was associated with double the reporting of neck pain. 1 2 days in the last month was associated with more than double the reporting and headache 3 31 days in the last month was associated with more than a threefold increase in reporting. Having a family member with low back pain was associated with an increased reporting of approximately 60% and having had treatment for a musculosketal disorder was associated with double reporting of neck pain (table 3). Table 3. Neck pain and associated factors Don t know Too low 0.004** Too high days 1 2 days 0.001** days 0.000** Family with LBP 0.01** Treatment 0.000** Upper back pain. A bag weight of between 3.4 and 4.45 kg on the day of the study was associated with double the reporting of upper back pain. Sometimes experiencing difficulties with homework more than a threefold increase in reporting and those who did experience difficulties had more than a fivefold increase in reporting upper back pain. Twisting the back for more than 10 minutes during the lesson was associated with double the reporting. Chair high too low was associated with double the reporting. 1 2 days in the last month was associated with approximately a threefold increase in the reporting and headache 3 31 days in the last month was associated with approximately a fivefold increase in the reporting. Having previous treatment for a musculosketal disorder was associated with more than double the reporting of upper back pain (table 4). Table 4. Upper back pain Bag weight kg *
3 Homework dif Sometimes 0.003** Yes 0.008** minutes minutes ** Don t know Too low 0.01* Too high days 1 2 days 0.004** days 0.000** Treatment (MSDs) 0.000** Low back pain. Twisting the back for more than 10 minutes during the lesson was associated with an increased reporting of low back pain of approximately 90%. too low was associated with double the reporting. Backrest too high was associated with a fivefold increase in reporting days in the last month was associated with approximately a threefold increase in the reporting. Having stomach ache 1 2 days in the last month associated with an increased reporting of 80% and having stomach ache 3 31 days in the last month was associated with double the reporting. Having a previous accident involving any body part was associated with double the reporting of low back pain (table 5). Table 5. Low back pain 0-10 minutes minutes * Don t know Too low 0.005** Too high Backrest position Don t know Too low Too high 0.000** days 1-2 days 0.03* days 0.01* Accident 0.006** Low back pain ever. Twisting the back for 0-10 minutes during the lesson was associated with an increased reporting of approximately 60% and twisting the back for more than 10 minutes during the lesson was associated with an increased reporting of low back pain of approximately 90%. Backrest position too low, headache 1-2 days in the last month an abnormal score on the Emotion questions were all associated with an increased reporting of 70% and headache 3-31 days in the last month was associated with approximately a threefold increase in the reporting. Sore throat 1-2 days in the last month was associated with double the reporting and sore throat 3-31 days in the last month was associated with an increased reporting of approximately 80%. Again older children had an increased reporting of 50% and having a family member with low back pain was associated with an increased reporting of approximately 60%. Having a low back injury was associated with more than double the reporting of low back pain (table 6). Table 6. Low back pain ever 0-10 minutes 0.03* minutes ** Backrest position Don t know Too low 0.01* Too high Emotion rmal Borderline Abnormal 0.02* days 1-2 days 0.01* days 0.000** Sore throat 0 days 1-2 days 0.001** days 0.01* Age 0.000** Family with LBP 0.01* Low back injury 0.000** Discussion The strongest association in this crosssectional survey was observed between neck, upper back and low back pain and common childhood complaints, namely headaches and sore throat. Jones et al (2003) recently concluded that the reporting of back symptoms was related to childhood somatic symptoms. Mikkelsson et al (1997) found that 30.5% of children in their study reported headache at least once a week compared with 54% of children who also reported musculoskeletal pain, while Brattberg & Wickman (1992) found pupils with back pain and headache reported more stomach ache than those who had no such symptoms. This suggests that factors influencing the reporting of pain symptoms among children needs to be
4 thoroughly understood when interpreting the issues surrounding back pain. The present study found that further relationships existed between back pain and emotional symptoms. Balague et al (1995) found psychological factors to be significantly associated with reported non-specific low back pain and the medical care sought for it. Psychological variables were strongly associated with low back pain in the last week and month (Murphy 2003) suggesting that psychological variables may have an influence at the onset of pain. Of the physical factors assessed in this study, characteristics of the school furniture were found to have the strongest relationship with pain., backrest height and backrest position were all associated with pain. Children may have to adopt flexed or static postures for prolonged periods increasing muscular fatigue in the neck and back. was significantly associated with pain at all three spinal areas suggesting that children have problems with the height of school chairs. Salminen et al (1992) reported similar findings and surmised that a low school desk placed the back into a forward leaning position and thus under load, which could be a possible contributing factor to low back pain. Parcells et al (1999) made the observation that the variability that exists among pre-adolescent aged children means it is very unlikely that furniture of fixed dimension will fit the majority of students. In addition to the potential anthropometric mismatch, it is possible that children do not use the furniture in the way it was designed to be used. The observations of children using PEO showed that they rarely used the backrest of the chair (Murphy et al 2003). Storr- Paulsen and Aagaard-Henson (1994) found that children spent only half of their time spent sitting making use of the backrest. It is possible that the chair design encourages the adoption of compromised posture or else behavioural issues influence the way in which the chair is used. While several authors have reported a relationship between back pain and school bag weight (Viry et al 1999; Grimmer & Williams, 2000) the findings in this study were inconclusive. There was a significant relationship between having a medium weight school bag and upper back pain. Interestingly, it is worth noting that most of the children carrying the heaviest bags went to schools that performed well in Government performance league tables. There was no significant relationship between activity and pain although other studies have found such relationships. While the benefits of exercise are clear the literature recommends exercising some caution to prevent the growing spine from being over exposed to excessive loads. Children who had a family with low back pain reported significantly more neck pain and low back pain ever. Children who had had treatment for musculoskeletal pain regardless of the area treated reported more neck and upper back pain. Future research must attempt to better understand psychological and familial risk factors, and interactions that may exist between them to ascertain their relative importance and predictive ability. While it may be possible to influence physical risk factors in the school environment, it is important that psychological factors are also included in a preventative strategy aimed at reducing the occurrence of back pain amongst school children. There are also serious implications for the future workforce with many young adults entering the workplace with neck and back pain already present. References Balagué, F., Skovron, M.L., rdin, M., Dutoit, G. & Waldburger, M Low back pain in school children: A study of familial and psychological factors. Spine 20: Brattberg, G. & Wickman, V Prevalence of back pain and headache in Swedish school children: A questionnaire survey. The Pain Clinic 5: Burton, A.K., Clark, R.D., McClune, T.D. & Tillotson, K.M The natural history of low back pain in adolescents. Spine 21: Fransson-Hall, C., Gloria, R., Kilbom, A., Winkel, J., Karlqvist, L. & Wiktorin, C A portable ergonomic observation method (PEO) for computerized on-line recording of postures and manual handling. Applied Ergonomics 26: Goodman, R The Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire: A research note. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 38: Grimmer, K. & Williams, M Gender-age environmental associates of adolescent low back pain. Applied Ergonomics 31: Jones et al (2003) University of Manchester (In press). Kuorinka, I., Jonsson, B., Kilbom, A., Vinterberg, H., Sorensen, F.B., Andersson, G. & Jorgensen, K Standardized rdic questionnaires for the analysis of musculoskeletal symptoms. Applied Ergonomics 18: Mikkelsson M, Salminen JJ and Kautiainen H (1997). n-specific musculoskeletal pain in preadolescents. Prevalence and 1-year persistence. Pain 73: Murphy S (2003). PhD Thesis, University of Surrey. Murphy, S.D. & Buckle, P The occurrence of back pain in schoolchildren and the risk factors in schools: Can they be measured? The triennial Congress of the International Ergonomics Association and 44th meeting of the Human Factors and Ergonomic Society, July 29-August 4 San Diego, California: Papageorgiou, A.C., Croft, P.R., Thomas, E., Ferry, S., Jayson, M.I.V. & Silman, A.J Influence of previous pain experience on the episode incidence of
5 low back pain: results from the South Manchester Back Pain Study. Pain 66: Parcells, R.N., Stommel, M. & Hubbard, R.P Mismatch of Classroom Furniture and Student Body Dimensions: Empirical Findings and Health Implications. Journal of Adolescent Health 24: Salminen, J.J., Pentti, J. & Terho, P Low back pain and disability in 14-year-old schoolchildren. Acta Paediatric 81: Shackel, B., Chidsey, K.D. & Shipley, P The assessment of chair comfort. Ergonomics 12: Storr-Paulsen, A. & Aagaard-Hensen, J The Working Positions of School children. Applied Ergonomics 25 (1): Troup, J.D.G., Foreman, T.K., Baxter, C.E. & Brown, D The perception of back pain and the role of psychophysical tests of lifting capacity. Spine 12: Viry, P., Creveuil, C. & Marcelli, C n-specific back pain in children: a search for associated factors in 14-year-old schoolchildren. Revue du Rhumatisme 66: Watson, K.D., Papageorgiou, A.C., Jones, T.J., Taylor, S., Symmons, D.P.M., Silman, A.J. & Macfarlane, G.J Low back pain in schoolchildren: occurrence and characteristics. Pain 97: Whittfield, J., Legg, S.J. & Hedderley, D.I The weight and use of schoolbags in New Zealand secondary schools. Ergonomics 44:
Clare Haselgrove 1, Leon Straker 1, Anne Smith 1, Peter O Sullivan 1, Mark Perry 1 and Nick Sloan 2. Introduction
 Haselgrove et al: Adolescent spinal pain and school bags Perceived school bag load, duration of carriage, and method of transport to school are associated with spinal pain in adolescents: an observational
Haselgrove et al: Adolescent spinal pain and school bags Perceived school bag load, duration of carriage, and method of transport to school are associated with spinal pain in adolescents: an observational
Back pain in Portuguese schoolchildren: prevalence and risk factors
 Back pain in Portuguese schoolchildren: prevalence and risk factors Maria J. Trigueiro1,2, Leandro Massada2, Rui Garganta2 1 Occupational Therapy Department, Superior School of Health Sciences, Polytechnic
Back pain in Portuguese schoolchildren: prevalence and risk factors Maria J. Trigueiro1,2, Leandro Massada2, Rui Garganta2 1 Occupational Therapy Department, Superior School of Health Sciences, Polytechnic
Functional Tools Pain and Activity Questionnaire
 Job dissatisfaction (Bigos, Battie et al. 1991; Papageorgiou, Macfarlane et al. 1997; Thomas, Silman et al. 1999; Linton 2001), fear avoidance and pain catastrophizing (Ciccone and Just 2001; Fritz, George
Job dissatisfaction (Bigos, Battie et al. 1991; Papageorgiou, Macfarlane et al. 1997; Thomas, Silman et al. 1999; Linton 2001), fear avoidance and pain catastrophizing (Ciccone and Just 2001; Fritz, George
A school-based survey of recurrent non-speci c low-back pain prevalence and consequences in children 1
 HEALTH EDUCATION RESEARCH Vol.19 no.3 2004 Theory & Practice Pages 284±289 A school-based survey of recurrent non-speci c low-back pain prevalence and consequences in children 1 M. A. Jones 1,2,6, G. Stratton
HEALTH EDUCATION RESEARCH Vol.19 no.3 2004 Theory & Practice Pages 284±289 A school-based survey of recurrent non-speci c low-back pain prevalence and consequences in children 1 M. A. Jones 1,2,6, G. Stratton
... Introduction. Methods. Maria J. Trigueiro 1,2, Leandro Massada 2, Rui Garganta 2. Sample
 ... European Journal of Public Health, Vol. 23, No. 3, 499 503 ß The Author 2012. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Public Health Association. All rights reserved. doi:10.1093/eurpub/cks105
... European Journal of Public Health, Vol. 23, No. 3, 499 503 ß The Author 2012. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Public Health Association. All rights reserved. doi:10.1093/eurpub/cks105
General practice. Role of mechanical and psychosocial factors in the onset of forearm pain: prospective population based study.
 Role of mechanical and psychosocial factors in the onset of forearm pain: prospective population based study Gary J Macfarlane, Isabelle M Hunt, Alan J Silman Unit of Chronic Disease Epidemiology, School
Role of mechanical and psychosocial factors in the onset of forearm pain: prospective population based study Gary J Macfarlane, Isabelle M Hunt, Alan J Silman Unit of Chronic Disease Epidemiology, School
Smart Health Training & Services SISA General Meeting August 2013
 Smart Health Training & Services SISA General Meeting August 2013 Introduction Most of us look at sitting as safe and restful thing to do. But It s not just that we sit, it s HOW we sit and for HOW LONG.
Smart Health Training & Services SISA General Meeting August 2013 Introduction Most of us look at sitting as safe and restful thing to do. But It s not just that we sit, it s HOW we sit and for HOW LONG.
How Posture and Equipment Setup Can Influence Comfort/Discomfort
 How Posture and Equipment Setup Can Influence Comfort/Discomfort Scott Openshaw Erin Taylor Allsteel Inc. Kevin Costello United States Ergonomics Overview Discuss objectives Explain the study and data
How Posture and Equipment Setup Can Influence Comfort/Discomfort Scott Openshaw Erin Taylor Allsteel Inc. Kevin Costello United States Ergonomics Overview Discuss objectives Explain the study and data
School Bag Usage, Postural and Behavioral Habits and Its Effect on Back Pain Occurrence Among School Children
 American Journal of Nursing Science 2017; 6(3): 218-231 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajns doi: 10.11648/j.ajns.20170603.20 ISSN: 2328-5745 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5753 (Online) School Bag Usage,
American Journal of Nursing Science 2017; 6(3): 218-231 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajns doi: 10.11648/j.ajns.20170603.20 ISSN: 2328-5745 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5753 (Online) School Bag Usage,
TRAINING PACKAGE DISPLAY SCREEN EQUIPMENT (DSE) Any alphanumeric or graphic display screen, regardless of the display process involved
 TRAINING PACKAGE DISPLAY SCREEN EQUIPMENT (DSE) Any alphanumeric or graphic display screen, regardless of the display process involved Why? To Avoid ACHES AND PAINS - NECK, ARMS, WRISTS, LEGS & BACK (there
TRAINING PACKAGE DISPLAY SCREEN EQUIPMENT (DSE) Any alphanumeric or graphic display screen, regardless of the display process involved Why? To Avoid ACHES AND PAINS - NECK, ARMS, WRISTS, LEGS & BACK (there
Original article Scand J Work Environ Health 1999;25(3): doi: /sjweh.431
 Downloaded from www.sjweh.fi on March 03, 2014 Original article Scand J Work Environ Health 1999;25(3):246-254 doi:10.5271/sjweh.431 Evaluation of questionnaire-based information on previous physical work
Downloaded from www.sjweh.fi on March 03, 2014 Original article Scand J Work Environ Health 1999;25(3):246-254 doi:10.5271/sjweh.431 Evaluation of questionnaire-based information on previous physical work
Do pain problems in young school children persist into early adulthood? A 13-year follow-up
 European Journal of Pain 8 (2004) 187 199 www.europeanjournalpain.com Do pain problems in young school children persist into early adulthood? A 13-year follow-up Gunilla Brattberg a,b, * a Department of
European Journal of Pain 8 (2004) 187 199 www.europeanjournalpain.com Do pain problems in young school children persist into early adulthood? A 13-year follow-up Gunilla Brattberg a,b, * a Department of
Prevalance of Neck Pain in Computer Users
 Original Article Prevalance of Neck Pain in Computer Users Faiza Sabeen, 1 Muhammad Salman Bashir, 2 Syed Imtiaz Hussain, 3 Sarah Ehsan 4 Abstract Prolonged use of computers during daily work activities
Original Article Prevalance of Neck Pain in Computer Users Faiza Sabeen, 1 Muhammad Salman Bashir, 2 Syed Imtiaz Hussain, 3 Sarah Ehsan 4 Abstract Prolonged use of computers during daily work activities
Moving and Handling Guidance
 NIPEC/19/03 (replacing NIPEC/14/21) NORTHERN IRELAND PRACTICE AND EDUCATION COUNCIL FOR NURSING AND MIDWIFERY Moving and Handling Guidance February 2019 Review date: April 2021 Centre House 79 Chichester
NIPEC/19/03 (replacing NIPEC/14/21) NORTHERN IRELAND PRACTICE AND EDUCATION COUNCIL FOR NURSING AND MIDWIFERY Moving and Handling Guidance February 2019 Review date: April 2021 Centre House 79 Chichester
ERGONOMIC STUDY ON THE VARIER MOVE CHAIR
 ERGONOMIC STUDY ON THE VARIER MOVE CHAIR TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVE... 3 INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVE... 3 METHODOLOGY... 5 METHODOLOGY... 5 1A) INFORMATION FOR USERS...5 1A) INFORMATION
ERGONOMIC STUDY ON THE VARIER MOVE CHAIR TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVE... 3 INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVE... 3 METHODOLOGY... 5 METHODOLOGY... 5 1A) INFORMATION FOR USERS...5 1A) INFORMATION
Commonwealth Health Corporation NEXT
 Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Flexion and Rotation of the Trunk and Lifting at Work Are Risk Factors for Low Back Pain
 Flexion and Rotation of the Trunk and Lifting at Work Are Risk Factors for Low Back Pain Results of a Prospective Cohort Study Wilhelmina E. Hoogendoorn, MSc,* Paulien M. Bongers, PhD,* Henrica C.W. de
Flexion and Rotation of the Trunk and Lifting at Work Are Risk Factors for Low Back Pain Results of a Prospective Cohort Study Wilhelmina E. Hoogendoorn, MSc,* Paulien M. Bongers, PhD,* Henrica C.W. de
Short term influence of mechanical factors on regional musculoskeletal pain: a study of new workers from 12 occupational groups
 374 Arthritis Research Campaign Epidemiology Unit, School of Epidemiology and Health Sciences, The Medical School, University of Manchester, Manchester M13 9PT, UK E S Nahit G J Macfarlane C M Pritchard
374 Arthritis Research Campaign Epidemiology Unit, School of Epidemiology and Health Sciences, The Medical School, University of Manchester, Manchester M13 9PT, UK E S Nahit G J Macfarlane C M Pritchard
OFFICE ERGONOMICS. Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh Ergonomics What is it? Why should I be interested? What do I need to know to help myself? Where can I get help?
OFFICE ERGONOMICS Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh Ergonomics What is it? Why should I be interested? What do I need to know to help myself? Where can I get help?
Basic Ergonomics for Logistics and Transport Operations. DR NG WEE TONG Mb.ChB, MMED (OM), Dip Av Med, Dip Geri Med
 Basic Ergonomics for Logistics and Transport Operations DR NG WEE TONG Mb.ChB, MMED (OM), Dip Av Med, Dip Geri Med Types of Ergonomics 3 main types: Physical Concerned with human anatomical, anthropometric,
Basic Ergonomics for Logistics and Transport Operations DR NG WEE TONG Mb.ChB, MMED (OM), Dip Av Med, Dip Geri Med Types of Ergonomics 3 main types: Physical Concerned with human anatomical, anthropometric,
Back Problems Due To Heavy Backpacks in School Children
 IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS) Volume X, Issue X (May. - Jun. 2013), PP 01-00 e-issn: 2279-0837, p-issn: 2279-0845. www.iosrjournals.org Back Problems Due To Heavy Backpacks
IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS) Volume X, Issue X (May. - Jun. 2013), PP 01-00 e-issn: 2279-0837, p-issn: 2279-0845. www.iosrjournals.org Back Problems Due To Heavy Backpacks
EFFECT OF THE CRITICAL ERGONOMICS PARAMETERS ON DOMESTIC CHAIRS FOR COMFORT USING THE HUMAN BASED PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT SOFTWARE
 EFFECT OF THE CRITICAL ERGONOMICS PARAMETERS ON DOMESTIC CHAIRS FOR COMFORT USING THE HUMAN BASED PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT SOFTWARE Hasan EFE 1, Ali KASAL 2, Halil KILIÇ 2, Can ÖZCAN 3 1 Gazi University, Faculty
EFFECT OF THE CRITICAL ERGONOMICS PARAMETERS ON DOMESTIC CHAIRS FOR COMFORT USING THE HUMAN BASED PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT SOFTWARE Hasan EFE 1, Ali KASAL 2, Halil KILIÇ 2, Can ÖZCAN 3 1 Gazi University, Faculty
Page 1 of 5. Figure A
 Introduction Around May of 2002 some of my students and myself came up with an idea that was of a redesign and improvement approach to the Ergonomics of a Computer Designer s workspace and placement specifications
Introduction Around May of 2002 some of my students and myself came up with an idea that was of a redesign and improvement approach to the Ergonomics of a Computer Designer s workspace and placement specifications
WORK POSTURE AND PREVALENCE OF MUSCULOSKELETAL SYMPTOMS AMONG WOMEN IN PACKING ACTIVITIES OF
 IJCRR Vol 05 issue 17 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 20/05/13 Revised on: 24/06/13 Accepted on: 19 /07/13 WORK POSTURE AND PREVALENCE OF MUSCULOSKELETAL SYMPTOMS AMONG WOMEN IN PACKING
IJCRR Vol 05 issue 17 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 20/05/13 Revised on: 24/06/13 Accepted on: 19 /07/13 WORK POSTURE AND PREVALENCE OF MUSCULOSKELETAL SYMPTOMS AMONG WOMEN IN PACKING
Development of Ergonomics Guidelines for Improved Sitting Postures in the Classroom among Malaysian University Students
 American Journal of Applied Sciences Original Research Paper Development of Ergonomics Guidelines for Improved Sitting Postures in the Classroom among Malaysian University Students Poh Kiat Ng, Kian Siong
American Journal of Applied Sciences Original Research Paper Development of Ergonomics Guidelines for Improved Sitting Postures in the Classroom among Malaysian University Students Poh Kiat Ng, Kian Siong
Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety. 5th Edition
 Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety 5th Edition Summary Ergonomics deals with the compatibility between workers and their work. Work is made up of the work environment, workstations,
Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety 5th Edition Summary Ergonomics deals with the compatibility between workers and their work. Work is made up of the work environment, workstations,
Poor sitting posture and a heavy schoolbag as contributors to musculoskeletal pain in children: an ergonomic school education intervention program
 Journal of Pain Research open access to scientific and medical research Open Access Full Text Article Poor sitting posture and a heavy schoolbag as contributors to musculoskeletal pain in children: an
Journal of Pain Research open access to scientific and medical research Open Access Full Text Article Poor sitting posture and a heavy schoolbag as contributors to musculoskeletal pain in children: an
Impact of Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders on Egyptian Pediatric Physical Therapists: One-Year Follow-Up Study
 Trends in Applied Sciences Research 10 (3): 175-182, 2015 ISSN 1819-3579 / DOI: 10.3923/tasr.2015.175.182 2015 Academic Journals Inc. Impact of Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders on Egyptian Pediatric
Trends in Applied Sciences Research 10 (3): 175-182, 2015 ISSN 1819-3579 / DOI: 10.3923/tasr.2015.175.182 2015 Academic Journals Inc. Impact of Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders on Egyptian Pediatric
Hampstead Hill School Health and Safety Policy: Display Screen Equipment
 All Hampstead Hill School Policies are always to be read and considered in conjunction with Equal Opportunities, Race Equality and Inclusion Policies. This Policy of Hampstead Hill School applies to all
All Hampstead Hill School Policies are always to be read and considered in conjunction with Equal Opportunities, Race Equality and Inclusion Policies. This Policy of Hampstead Hill School applies to all
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 06 Page June 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i6.61 Low Back Pain among Dentists Authors Alka
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i6.61 Low Back Pain among Dentists Authors Alka
Acknowledgements. Illness Behavior A cognitive and behavioral phenomenon. Seeking medical care. Communicating pain to others
 Acknowledgements Parent Training to Address Pediatric Functional Abdominal Pain: A Researcher s Perspective Dr. Kim Swanson National Institutes of Health Rona L. Levy, MSW, PhD, MPH Professor and Director
Acknowledgements Parent Training to Address Pediatric Functional Abdominal Pain: A Researcher s Perspective Dr. Kim Swanson National Institutes of Health Rona L. Levy, MSW, PhD, MPH Professor and Director
EVALUATION OF RISK FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH WORK-RELATED MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS OF UPPER LIMBS EXTREMITY AMONG PRESS WORKERS
 EVALUATION OF RISK FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH WORK-RELATED MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS OF UPPER LIMBS EXTREMITY AMONG PRESS WORKERS Mohammad Pourmahabadian 1, Kamal Azam 2 ABSTRACT Objective: Exposure assessment
EVALUATION OF RISK FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH WORK-RELATED MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS OF UPPER LIMBS EXTREMITY AMONG PRESS WORKERS Mohammad Pourmahabadian 1, Kamal Azam 2 ABSTRACT Objective: Exposure assessment
Ergonomic recommendations
 Page 1 Handling loads Awkward postures Recommendations are biological states that requires special protection During the entire process of gestation and breastfeeding, physiological, metabolic and psychological
Page 1 Handling loads Awkward postures Recommendations are biological states that requires special protection During the entire process of gestation and breastfeeding, physiological, metabolic and psychological
Ergonomics. Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques (EOHSS)
 Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
An Ergonomics Study on Assembly Line Workstation Design
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 8 (11): 1195-1201, 2011 ISSN 1546-9239 2011 Science Publications An Ergonomics Study on Assembly Line Workstation Design 1 Baba Md Deros, 1 Nor Kamaliana Khamis, 2
American Journal of Applied Sciences 8 (11): 1195-1201, 2011 ISSN 1546-9239 2011 Science Publications An Ergonomics Study on Assembly Line Workstation Design 1 Baba Md Deros, 1 Nor Kamaliana Khamis, 2
Agir avec mon dos. Mon dos en tête. Agir avec mon dos. Back-pain. Evolution. Back-pain. Radiology. Non-specific back pain. Context.
 Back-pain Context Agir avec mon dos un programme de prévention du mal de dos à l attention des collaborateurs des institutions médico-thérapeutiques du canton de Genève Dominique Monnin Physiothérapeute
Back-pain Context Agir avec mon dos un programme de prévention du mal de dos à l attention des collaborateurs des institutions médico-thérapeutiques du canton de Genève Dominique Monnin Physiothérapeute
The best way to deal with back pain
 The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain Back pain is common and can be very painful but, serious or permanent damage is rare. The Facts Most back pain is not due to any
The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain Back pain is common and can be very painful but, serious or permanent damage is rare. The Facts Most back pain is not due to any
A case-control study of Naval rehabilitation patients assessing levels of psychological strain, susceptibility factors and workplace stressors.
 A case-control study of Naval rehabilitation patients assessing levels of psychological strain, susceptibility factors and workplace stressors. Dr Lachlan Mackay Brown Rehabilitation in HM Forces 3 tier
A case-control study of Naval rehabilitation patients assessing levels of psychological strain, susceptibility factors and workplace stressors. Dr Lachlan Mackay Brown Rehabilitation in HM Forces 3 tier
The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person What is Ergonomics? By the end of this chapter, You will be able to: Demonstrate a general knowledge of office ergonomics Identify
OFFICE ERGONOMICS The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person What is Ergonomics? By the end of this chapter, You will be able to: Demonstrate a general knowledge of office ergonomics Identify
Ergonomic Risk Factors associated with Muscuslokeletal Disorders in Computer Workstation
 Ergonomic Risk Factors associated with Muscuslokeletal Disorders in Computer Workstation Mohd Nasrull Abdol Rahman* Ibrahim Masood Nur Farahanim Awalludin Mohd Fahrul Hassan Department of Material and
Ergonomic Risk Factors associated with Muscuslokeletal Disorders in Computer Workstation Mohd Nasrull Abdol Rahman* Ibrahim Masood Nur Farahanim Awalludin Mohd Fahrul Hassan Department of Material and
Spinal Biomechanics & Sitting Posture
 Spinal Biomechanics & Sitting Posture Sitting: weight of the body is transferred to a supporting area 1.Main Contact points (seat) Ischial tuberosities Soft tissues 2. Secondary contact points (other)
Spinal Biomechanics & Sitting Posture Sitting: weight of the body is transferred to a supporting area 1.Main Contact points (seat) Ischial tuberosities Soft tissues 2. Secondary contact points (other)
Downloaded from on October 02, Scand J Work Environ Health 1996;22(4):
 Downloaded from www.sjweh.fi on October 02, 2018 Original article Scand J Work Environ Health 1996;22(4):251-259 doi:10.5271/sjweh.139 Validity of self-reported physical work load in epidemiologic studies
Downloaded from www.sjweh.fi on October 02, 2018 Original article Scand J Work Environ Health 1996;22(4):251-259 doi:10.5271/sjweh.139 Validity of self-reported physical work load in epidemiologic studies
Outline Are You Getting Hurt? Ergonomic for Fitness Professionals
 Outline Are You Getting Hurt? Ergonomic for Fitness Professionals Mike Bracko, Ed.D. CSCS, FACSM Fitness Educator / Sports Physiologist drbrackofitness@aol.com Outline 1. What is Ergonomics? 2. How Does
Outline Are You Getting Hurt? Ergonomic for Fitness Professionals Mike Bracko, Ed.D. CSCS, FACSM Fitness Educator / Sports Physiologist drbrackofitness@aol.com Outline 1. What is Ergonomics? 2. How Does
The Benefits of Pelvic Stabilization
 The Benefits of Pelvic Stabilization ERGONOMIC CRITERIA FOR THE DESIGN OF THE AERON CHAIR A work chair should preserve natural spinal alignment, even in upright postures. Reclining postures help to maintain
The Benefits of Pelvic Stabilization ERGONOMIC CRITERIA FOR THE DESIGN OF THE AERON CHAIR A work chair should preserve natural spinal alignment, even in upright postures. Reclining postures help to maintain
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis
 Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
Everything You Need to Know About Ergonomics
 Everything You Need to Know About Ergonomics What is Ergonomics? The study of people in their workplace using his/her workspace in the most efficient manner with the least risk of injury. (Purdue University,
Everything You Need to Know About Ergonomics What is Ergonomics? The study of people in their workplace using his/her workspace in the most efficient manner with the least risk of injury. (Purdue University,
The Effectiveness of BackHealth Technology
 The Effectiveness of BackHealth Technology Back injuries are the single largest health problem in the workplace, affecting as many as 35 percent of the work force and accounting for about 25 percent of
The Effectiveness of BackHealth Technology Back injuries are the single largest health problem in the workplace, affecting as many as 35 percent of the work force and accounting for about 25 percent of
THE EMOTIONAL AND BEHAVIOURAL HEALTH OF ABORIGINAL CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE
 Chapter THE EMOTIONAL AND BEHAVIOURAL HEALTH OF ABORIGINAL CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE Summary......................................................... 5 Mental health and social and emotional wellbeing..................
Chapter THE EMOTIONAL AND BEHAVIOURAL HEALTH OF ABORIGINAL CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE Summary......................................................... 5 Mental health and social and emotional wellbeing..................
Interrelations of risk factors and low back pain in scavolders
 Occup Environ Med 2001;58:597 603 597 Department of Public Health, Erasmus University Rotterdam, PO Box 1738, 3000 DR Rotterdam, The Netherlands L A M Elders A Burdorf Occupational Health Service, Maetis
Occup Environ Med 2001;58:597 603 597 Department of Public Health, Erasmus University Rotterdam, PO Box 1738, 3000 DR Rotterdam, The Netherlands L A M Elders A Burdorf Occupational Health Service, Maetis
Sheffield Hallam University. MODULE LEADER Helen Batty NOTIONAL STUDY Tutor-led Tutor-directed Self-directed Total Hours
 MODULE DESCRIPTOR TITLE Rehabilitation of functional movement SI MODULE CODE 66-5881-00L CREDITS 10 LEVEL 5 JACS CODE B160 SUBJECT GROUP Physiotherapy DEPARTMENT Health and Wellbeing MODULE LEADER Helen
MODULE DESCRIPTOR TITLE Rehabilitation of functional movement SI MODULE CODE 66-5881-00L CREDITS 10 LEVEL 5 JACS CODE B160 SUBJECT GROUP Physiotherapy DEPARTMENT Health and Wellbeing MODULE LEADER Helen
Assessing the Prevalence of Recurrent Neck and Shoulder Pain in Korean High School Male Students: A Cross-sectional Observational Study
 Original Article Korean J Pain 202 July; Vol. 25, No. 3: 6-67 pissn 2005-959 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/0.3344/kjp.202.25.3.6 Assessing the Prevalence of Recurrent Neck and Shoulder Pain in Korean
Original Article Korean J Pain 202 July; Vol. 25, No. 3: 6-67 pissn 2005-959 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/0.3344/kjp.202.25.3.6 Assessing the Prevalence of Recurrent Neck and Shoulder Pain in Korean
SURVEY AMONG SCHOOL-AGED CHILDREN WITH
 4. MAGYAR BIOMECHANIKAI KONFERENCIA A-1 SURVEY AMONG SCHOOL-AGED CHILDREN WITH ULTRASOUND-BASED MOTION ANALYZING SYSTEM AT TWO PRIMARY SCHOOLS IN SZOLNOK Mária Takács 1, Ervin Rudner 2, Ildikó Juhász 2,
4. MAGYAR BIOMECHANIKAI KONFERENCIA A-1 SURVEY AMONG SCHOOL-AGED CHILDREN WITH ULTRASOUND-BASED MOTION ANALYZING SYSTEM AT TWO PRIMARY SCHOOLS IN SZOLNOK Mária Takács 1, Ervin Rudner 2, Ildikó Juhász 2,
Avoid the Dreaded Tech-Neck - How to Correct Posture Issues As A Result of Extended Mobile Device and Laptop Use
 Page Title Avoid the Dreaded Tech-Neck - How To Correct Posture Issues As A Result of Extended Mobile Device and Laptop Use Meta Description Extended use each day on a laptop or mobile device can cause
Page Title Avoid the Dreaded Tech-Neck - How To Correct Posture Issues As A Result of Extended Mobile Device and Laptop Use Meta Description Extended use each day on a laptop or mobile device can cause
Analysis of the functional biomechanics of different chair types during esports activity
 Analysis of the functional biomechanics of different chair types during esports activity Final Report December 2017 Dr. Frank Emrich Scientific Consultant Biomechanics & Ergonomics 1 Introduction The esports
Analysis of the functional biomechanics of different chair types during esports activity Final Report December 2017 Dr. Frank Emrich Scientific Consultant Biomechanics & Ergonomics 1 Introduction The esports
Spinal pain in adolescents: prevalence, incidence, and course: a school-based two-year prospective cohort study in 1,300 Danes aged 11 13
 Aartun et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:187 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Spinal pain in adolescents: prevalence, incidence, and course: a school-based two-year prospective cohort study in
Aartun et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:187 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Spinal pain in adolescents: prevalence, incidence, and course: a school-based two-year prospective cohort study in
CBIA Ergonomic Conference Office Environments December 8 th, 2016
 Loss Control & Risk Management Approach to Control Ergonomic Risks CBIA Ergonomic Conference Office Environments December 8 th, 2016 Course Outline Controlling Ergonomics In Office Environments 1. Experience
Loss Control & Risk Management Approach to Control Ergonomic Risks CBIA Ergonomic Conference Office Environments December 8 th, 2016 Course Outline Controlling Ergonomics In Office Environments 1. Experience
Element B9 / 2 Assessing Risks MSD s / Man Handling / Poor Posture
 Assessing Risks MSD s / Man Handling / Poor Posture Legal Requirements HASAWA Sec 2 (2) -. Use, handling, storage, transport of articles and substances MHSWR Assessments Manual Handling Operations (MHOR)
Assessing Risks MSD s / Man Handling / Poor Posture Legal Requirements HASAWA Sec 2 (2) -. Use, handling, storage, transport of articles and substances MHSWR Assessments Manual Handling Operations (MHOR)
Trial non randomizzato sul mal di schiena tra video terminalisti
 CONVEGNO EBP e Lavoro : La Prevenzione efficace dei rischi e danni da lavoro FIRENZE - 23-24 ottobre 2008 Trial non randomizzato sul mal di schiena tra video terminalisti Relatore: Prof. Paolo Pillastrini
CONVEGNO EBP e Lavoro : La Prevenzione efficace dei rischi e danni da lavoro FIRENZE - 23-24 ottobre 2008 Trial non randomizzato sul mal di schiena tra video terminalisti Relatore: Prof. Paolo Pillastrini
Body Mechanics and Safe Patient Handling
 Body Mechanics and Safe Patient Handling Body Mechanics means using the body in an efficient and careful way involves good posture, balance, and using your strongest and largest muscles for work good body
Body Mechanics and Safe Patient Handling Body Mechanics means using the body in an efficient and careful way involves good posture, balance, and using your strongest and largest muscles for work good body
Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03
 Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03 Working from home is becoming more of an option for employees today. The type of work usually entails working from the home computer work station.
Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03 Working from home is becoming more of an option for employees today. The type of work usually entails working from the home computer work station.
Ergonomics: Optimizing human well-being & system performance
 Ergonomics: Optimizing human well-being & system performance Protecting your back is not a luxury When you re healthy you can participate and enjoy life Leisure activities-enjoy going for a run Household
Ergonomics: Optimizing human well-being & system performance Protecting your back is not a luxury When you re healthy you can participate and enjoy life Leisure activities-enjoy going for a run Household
Rapid Entire Body Assessment (REBA)
 Applied Ergonomics 31 (2000) 201}205 Technical note Rapid Entire Body Assessment (REBA) Sue Hignett *,Lynn McAtamney Ergonomist, Nottingham City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG5 1PB, UK Director,
Applied Ergonomics 31 (2000) 201}205 Technical note Rapid Entire Body Assessment (REBA) Sue Hignett *,Lynn McAtamney Ergonomist, Nottingham City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG5 1PB, UK Director,
The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person What is Ergonomics? By the end of this training program learners will be able to: Demonstrate a general knowledge of office ergonomics
OFFICE ERGONOMICS The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person What is Ergonomics? By the end of this training program learners will be able to: Demonstrate a general knowledge of office ergonomics
THE FREQUENCY OF RESTRICTED RANGE OF MOVEMENT IN INDIVIDUALS WITH SELF-REPORTED SHOULDER PAIN: RESULTS FROM A POPULATION-BASED SURVEY
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:1137-1141 THE FREQUENCY OF RESTRICTED RANGE OF MOVEMENT IN INDIVIDUALS WITH SELF-REPORTED SHOULDER PAIN: RESULTS FROM A POPULATION-BASED SURVEY D. P. POPE, P. R.
British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:1137-1141 THE FREQUENCY OF RESTRICTED RANGE OF MOVEMENT IN INDIVIDUALS WITH SELF-REPORTED SHOULDER PAIN: RESULTS FROM A POPULATION-BASED SURVEY D. P. POPE, P. R.
Good Working Positions
 Good Working Positions To understand the best way to set up a computer workstation, it is helpful to understand the concept of neutral body positioning. This is a comfortable working posture in which your
Good Working Positions To understand the best way to set up a computer workstation, it is helpful to understand the concept of neutral body positioning. This is a comfortable working posture in which your
Factors Associated With Work Ability in Patients Undergoing Surgery for Cervical Radiculopathy
 Factors Associated With Work Ability in Patients Undergoing Surgery for Cervical Radiculopathy Eunice Ng, Venerina Johnston, Johanna Wibault, Hakan Lofgren, Asa Dedering, Birgitta Öberg, Peter Zsigmond
Factors Associated With Work Ability in Patients Undergoing Surgery for Cervical Radiculopathy Eunice Ng, Venerina Johnston, Johanna Wibault, Hakan Lofgren, Asa Dedering, Birgitta Öberg, Peter Zsigmond
A Method for Non-experts in Assessing Exposure to Risk Factors for Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders ERIN
 Short Communication A Method for Non-experts in Assessing Exposure to Risk Factors for Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders ERIN Yordán RODRÍGUEZ 1 *, Silvio VIÑA 1 and Ricardo MONTERO 2 1 Deparment
Short Communication A Method for Non-experts in Assessing Exposure to Risk Factors for Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders ERIN Yordán RODRÍGUEZ 1 *, Silvio VIÑA 1 and Ricardo MONTERO 2 1 Deparment
Lecture 3: Workplace Design Physical work
 Lecture 3: Workplace Design Physical work ENVD 5380 Human Factors/Ergonomics in Environmental Design By Su-Jeong Hwang Shin, Ph.D. Physical work Occupational injuries About 25 % of all occupational injuries
Lecture 3: Workplace Design Physical work ENVD 5380 Human Factors/Ergonomics in Environmental Design By Su-Jeong Hwang Shin, Ph.D. Physical work Occupational injuries About 25 % of all occupational injuries
THE DEVELOPMENT OF ACTION LEVELS FOR THE QUICK EXPOSURE CHECK (QEC) SYSTEM
 THE DEVELOPMENT OF ACTION LEVELS FOR THE QUICK EXPOSURE CHECK (QEC) SYSTEM Robert Brown 1 and Guangyan Li 2 1 University of Sunderland, Sunderland, SR1 3SD UK 2 Human Engineering Limited Shore House, 68
THE DEVELOPMENT OF ACTION LEVELS FOR THE QUICK EXPOSURE CHECK (QEC) SYSTEM Robert Brown 1 and Guangyan Li 2 1 University of Sunderland, Sunderland, SR1 3SD UK 2 Human Engineering Limited Shore House, 68
Stooped. Squatting Postures. Workplace. and. in the. July 29 30, 2004 Oakland, California, USA CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
 CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS Stooped and Squatting Postures in the Workplace July 29 30, 2004 Oakland, California, USA Center for Occupational and Environmental Health n University of California: Berkeley n
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS Stooped and Squatting Postures in the Workplace July 29 30, 2004 Oakland, California, USA Center for Occupational and Environmental Health n University of California: Berkeley n
Feel Better. Stanford University ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE. USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better.
 Feel Better. PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better. Stanford University Your workspace should respond to your changing needs, helping you eliminate uncomfortable
Feel Better. PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better. Stanford University Your workspace should respond to your changing needs, helping you eliminate uncomfortable
Strengths and Difficulties
 Strengths and Difficulties Name of Child: Completed by: Relationship to child: Date: Copyright ISBN 0 11 322426 5 STRENGTHS AND DIFFICULTIES 1 19. Fuller discussion is vital for several reasons. Firstly,
Strengths and Difficulties Name of Child: Completed by: Relationship to child: Date: Copyright ISBN 0 11 322426 5 STRENGTHS AND DIFFICULTIES 1 19. Fuller discussion is vital for several reasons. Firstly,
Staff Information Leaflet
 Posture Staff Information Leaflet This leaflet is designed to give you an understanding of posture and some advice on what you can do to help yourself. If your symptoms persist you should seek advice from
Posture Staff Information Leaflet This leaflet is designed to give you an understanding of posture and some advice on what you can do to help yourself. If your symptoms persist you should seek advice from
SUMMARY AND DISCUSSION
 Risk factors for the development and outcome of childhood psychopathology SUMMARY AND DISCUSSION Chapter 147 In this chapter I present a summary of the results of the studies described in this thesis followed
Risk factors for the development and outcome of childhood psychopathology SUMMARY AND DISCUSSION Chapter 147 In this chapter I present a summary of the results of the studies described in this thesis followed
Ergonomics Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa (515) Copyright
 2408 Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa 50011-3602 (515) 294-5359 www.ehs.iastate.edu Copyright Reviewed 2016 2 Ergonomics Directory of Service and Emergency Providers Services Environmental Health and Safety
2408 Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa 50011-3602 (515) 294-5359 www.ehs.iastate.edu Copyright Reviewed 2016 2 Ergonomics Directory of Service and Emergency Providers Services Environmental Health and Safety
The story retold. Performance. Remastered from the castors up
 Aeron Chairs The story retold While its iconic form has remained largely unchanged, the Aeron chair has been remastered from the castors up to meet the needs of today s work. With the help of original
Aeron Chairs The story retold While its iconic form has remained largely unchanged, the Aeron chair has been remastered from the castors up to meet the needs of today s work. With the help of original
The relationship between early life stress and psychopathology: a network approach
 9 th Annual Research Conference 2017 The relationship between early life stress and psychopathology: a network approach Healy C, Clarke M, Kelleher I & Cannon M Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland Current
9 th Annual Research Conference 2017 The relationship between early life stress and psychopathology: a network approach Healy C, Clarke M, Kelleher I & Cannon M Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland Current
Chapter 13. Body Mechanics. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 13 Body Mechanics Body Mechanics Body mechanics means using the body in an efficient and careful way. It involves good posture, balance, and using your strongest and largest muscles for work. 2
Chapter 13 Body Mechanics Body Mechanics Body mechanics means using the body in an efficient and careful way. It involves good posture, balance, and using your strongest and largest muscles for work. 2
Department of Public Health and Community Medicine, Al-Azhar Faculty of Medicine, Nasr city, Cairo, Egypt 2
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Public Health Volume 2012, Article ID 294895, 6 pages doi:10.5402/2012/294895 Research Article Prognostic Factors of Short-Term Outcome of Low Back Pain in
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Public Health Volume 2012, Article ID 294895, 6 pages doi:10.5402/2012/294895 Research Article Prognostic Factors of Short-Term Outcome of Low Back Pain in
SAMPLE. Osteopathy and Back pain a safe and effective approach
 Osteopathy and Back pain a safe and effective approach Back pain will affect 8 out of 10 people at some point in their life - mild or severe, acute or chronic. Common causes of back pain include: heavy
Osteopathy and Back pain a safe and effective approach Back pain will affect 8 out of 10 people at some point in their life - mild or severe, acute or chronic. Common causes of back pain include: heavy
Many dental hygiene professionals realize that undiagnosed. Elbow Room
 00 Elbow Room Free-motion elbow supports could be a key to reducing musculoskeletal disorders among dental hygienists. Many dental hygiene professionals realize that undiagnosed and untreated injuries
00 Elbow Room Free-motion elbow supports could be a key to reducing musculoskeletal disorders among dental hygienists. Many dental hygiene professionals realize that undiagnosed and untreated injuries
The Efficacy of Exercise as an Intervention to Treat Recurrent Nonspecific Low Back Pain in Adolescents
 Pediatric Exercise Science, 2007, 19, 349-359 2007 Human Kinetics, Inc. The Efficacy of Exercise as an Intervention to Treat Recurrent Nonspecific Low Back Pain in Adolescents Michelle Jones, Gareth Stratton,
Pediatric Exercise Science, 2007, 19, 349-359 2007 Human Kinetics, Inc. The Efficacy of Exercise as an Intervention to Treat Recurrent Nonspecific Low Back Pain in Adolescents Michelle Jones, Gareth Stratton,
Driving (for work or fun) Can Contribute to the Development of Repetitive Strain Injuries:
 Driving (for work or fun) Can Contribute to the Development of Repetitive Strain Injuries: Driving in a vehicle for long distances can contribute to lower and upper back and neck pain, poor circulation
Driving (for work or fun) Can Contribute to the Development of Repetitive Strain Injuries: Driving in a vehicle for long distances can contribute to lower and upper back and neck pain, poor circulation
ERGOWATCH: A NEW MANUAL HANDLING MANAGEMENT TOOL. Gary Dennis and Rod Barrett
 JAN 2000 ERGOWATCH: A NEW MANUAL HANDLING MANAGEMENT TOOL Gary Dennis and Rod Barrett School of Physiotherapy and Exercise Science Griffith University, Queensland, Australia Email: G.Dennis@mailbox.gu.edu.au
JAN 2000 ERGOWATCH: A NEW MANUAL HANDLING MANAGEMENT TOOL Gary Dennis and Rod Barrett School of Physiotherapy and Exercise Science Griffith University, Queensland, Australia Email: G.Dennis@mailbox.gu.edu.au
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 9-9571 Original Research Article Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression among Patients with Chronic Lumbar Spondylosis NP Singh 1,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 9-9571 Original Research Article Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression among Patients with Chronic Lumbar Spondylosis NP Singh 1,
Stay healthy and happy at work with advice from the Chartered Society of Physiotherapy
 Stay healthy and happy at work with advice from the Chartered Society of Physiotherapy Employment plays a big part in keeping you healthy just going out to work is good for you, both physically and mentally.
Stay healthy and happy at work with advice from the Chartered Society of Physiotherapy Employment plays a big part in keeping you healthy just going out to work is good for you, both physically and mentally.
DRAFT. The best way to deal with back pain
 Services provided by Essex Parntership University NHS Foundation Trust and West Essex NHS Clinical Commissioning Group niversity The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain
Services provided by Essex Parntership University NHS Foundation Trust and West Essex NHS Clinical Commissioning Group niversity The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain
Effects of SEL education on children s socio-emotional competencies across Europe: results of EAP_SEL project
 Effects of SEL education on children s socio-emotional competencies across Europe: results of EAP_SEL project Charli Eriksson (professor emeritus, School of Health Sciences, Örebro University, Sweden)
Effects of SEL education on children s socio-emotional competencies across Europe: results of EAP_SEL project Charli Eriksson (professor emeritus, School of Health Sciences, Örebro University, Sweden)
The best way to deal with back pain
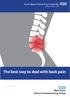 The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain Back pain is common and can be very painful but, serious or permanent damage is rare. The Facts Most back pain is not due to any
The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain Back pain is common and can be very painful but, serious or permanent damage is rare. The Facts Most back pain is not due to any
Identifying and Coping with Adolescent Anxiety
 University of Vermont ScholarWorks @ UVM Family Medicine Block Clerkship, Student Projects College of Medicine 2014 Identifying and Coping with Adolescent Anxiety Merima Ruhotina University of Vermont
University of Vermont ScholarWorks @ UVM Family Medicine Block Clerkship, Student Projects College of Medicine 2014 Identifying and Coping with Adolescent Anxiety Merima Ruhotina University of Vermont
A B S T R A C T. Title : PHYSICAL FITNESS ACTIVITIES FOR ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PUPILS OF MATACON ELEMENTARY SCHOOL
 A B S T R A C T Title : PHYSICAL FITNESS ACTIVITIES FOR ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PUPILS OF MATACON ELEMENTARY SCHOOL Researcher : DOMAGSANG, Ariel B. Type of Document ; Unpublished Thesis SUMMARY This study dealt
A B S T R A C T Title : PHYSICAL FITNESS ACTIVITIES FOR ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PUPILS OF MATACON ELEMENTARY SCHOOL Researcher : DOMAGSANG, Ariel B. Type of Document ; Unpublished Thesis SUMMARY This study dealt
Dimensional Requirements. Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways.
 Dimensional Requirements Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings from MIL-HDBK 759. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings to
Dimensional Requirements Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings from MIL-HDBK 759. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings to
Table of Contents. 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders?
 Table of Contents 1. Introduction O 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders? P 3. Common types of work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders Q 4. Risk factors associated with
Table of Contents 1. Introduction O 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders? P 3. Common types of work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders Q 4. Risk factors associated with
FORCES AND MOMENTS AT THE L41L5 VERTEBRAL LEVEL WHILE FORWARD BENDING IN A SUPPORTED POSTURE
 FORCES AND MOMENTS AT THE L41L5 VERTEBRAL LEVEL WHILE FORWARD BENDING IN A SUPPORTED POSTURE Daniel J. Wilson, Jennie L. Gorham, and Kimberly M. Hickey University of Missouri-Columbia, Columbia, MO, 65212
FORCES AND MOMENTS AT THE L41L5 VERTEBRAL LEVEL WHILE FORWARD BENDING IN A SUPPORTED POSTURE Daniel J. Wilson, Jennie L. Gorham, and Kimberly M. Hickey University of Missouri-Columbia, Columbia, MO, 65212
Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc
 Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc Every job or task has unique physical and cognitive demands. Each person has unique physical attributes and abilities. www.prbembodychair.co.uk www.youandyourself.com
Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc Every job or task has unique physical and cognitive demands. Each person has unique physical attributes and abilities. www.prbembodychair.co.uk www.youandyourself.com
PATIENT NAME DATE CONSULTATION QUESTIONNAIRE
 CONSULTATION QUESTIONNAIRE 1. What is your major symptom? 2. What does this prevent you from doing or enjoying? 3. If this is a recurrence, when was the first time you noticed this problem? How did it
CONSULTATION QUESTIONNAIRE 1. What is your major symptom? 2. What does this prevent you from doing or enjoying? 3. If this is a recurrence, when was the first time you noticed this problem? How did it
Prevalance of musculoskeletal disorders among sugarcane workers A cross sectional study
 Original article: Prevalance of musculoskeletal disorders among sugarcane workers A cross sectional study 1Miss. SmitaYashvantVasave, 2 Dr. Deepak B. Anap 1Physiotherapy Student, 2 Associate Professor
Original article: Prevalance of musculoskeletal disorders among sugarcane workers A cross sectional study 1Miss. SmitaYashvantVasave, 2 Dr. Deepak B. Anap 1Physiotherapy Student, 2 Associate Professor
WORK RELATED MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS AMONG PREPARATORY SCHOOL TEACHERS IN EGYPT
 Egyptian Journal of Occupational Medicine, 2017; 41 (1) : 115-126 WORK RELATED MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS AMONG PREPARATORY SCHOOL TEACHERS IN EGYPT By 1 El Gendy M and 2 Korish MM 1 Department of Basic
Egyptian Journal of Occupational Medicine, 2017; 41 (1) : 115-126 WORK RELATED MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS AMONG PREPARATORY SCHOOL TEACHERS IN EGYPT By 1 El Gendy M and 2 Korish MM 1 Department of Basic
Choosing the right Office Chair
 Choosing the right Office Chair Choosing the Right Ergonomic Office Chair Working in an office typically involves spending a great deal of time sitting in an office chair a position that adds stress to
Choosing the right Office Chair Choosing the Right Ergonomic Office Chair Working in an office typically involves spending a great deal of time sitting in an office chair a position that adds stress to
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017, 2469 2474 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) WORK POSTURE ASSESSMENT OF TAILORS BY RULA AND REBA ANALYSIS Upasana and Deepa
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017, 2469 2474 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) WORK POSTURE ASSESSMENT OF TAILORS BY RULA AND REBA ANALYSIS Upasana and Deepa
