Table of Contents. 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders?
|
|
|
- Blanche McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Table of Contents 1. Introduction O 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders? P 3. Common types of work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders Q 4. Risk factors associated with work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders R 5. Occupational factors in relation to development of upper limb musculoskeletal disorders S 6. Symptoms T 7. Prevention U 8. Treatment NO 9. Assessment checklist for work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders NQ
3 1. Introduction Despite technological advancement and economic prosperity of our society, occupational musculoskeletal disorders are still prevalent in Hong Kong's work force. Work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders are particularly common, and tenosynovitis of hand and forearm are very usual in Hong Kong. You may have experienced upper limb musculoskeletal disorder to various degrees, including discomfort, pain, muscle soreness, cramp, numbness and tenderness in the shoulder, elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. The symptoms may not affect your daily activity or work, but if they persist and remain untreated, they will gradually deteriorate and develop occupational diseases. When an employee sustains upper limb musculoskeletal disorders in the course of employment, it not only affects the work performance, but also the activities of daily living are affected due to pain and restricted movement arising out of the injury. The worst situation may lead to incapacity of work. O
4 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders? Muscloskeletal system is the prime mover of our bodily movement. Muscle, skeleton, tendon and nerve are the key structures in mediating the maneuvers of various body positions in particular upper limb movement adopted in our daily activities. Work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders can be resulted from frequent, repetitive and forceful exertion on upper limb and improper posture adopted at work. Upper limbs refer to the following body parts: Shoulder, upper arm, elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers Upper limb musculoskeletal disorders include the following three types of injuries: 1. Muscle injury Work activities involving repetitive movement and forceful exertion require vigorous muscle contraction. Active pumping of muscular work promotes accumulation of metabolites which further initiates muscle fatigue and results in muscle soreness. Prolonged muscular work without adequate rest not only delays the recovery process in eliminating the metabolites, but cumulative effect of overusing muscles also assumes the cause of injuries. muscle tendon 2. Tendon injury Tendons are the connecting tissues which attach muscles to bones. Tendons are protected and lubricated by tendon sheath to enable smooth movement. Repetitive movement or forceful exertion would aggravate the sliding of tendon with tendon sheath or the bony part and cause inflammation or even shear injuries. 3. Nerve compression Nervous system is responsible for carrying messages within our body. It innervates muscle and kicks off movement, so that we can move our hands or feet. Nerve transmission can be restricted by increased pressure on nerve. It can be caused by the swelling of inflamed muscles or tendons around the nerve endings. Desensitization is one of the symptom of nerve compression. For severe nerve compression, it can result in muscle degeneration. P median nerve (normal) median nerve compressed by inflamed tendons
5 3. Common types of work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders Shoulder tendinitis Carpal tunnel syndrome Tenosynovitis of hand and forearm Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) 4. Risk factors associated with work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders Factor one Forceful exertion by hands, wrists or arms Forceful use of hand and forearm muscles to fit components into place Factor two Awkward posture, rapid and frequent movement Machine pacing to keep up packaging work with conveyor, chopping meat or playing musical instruments Q
6 Factor three Awkward and static posture Operating computer terminals, working as a cashier or assembling works of a production line Factor four Work for long periods without breaks or changes of activity No change to work routine or variation of tasks. Infrequent breaks or even no breaks Factor five No special arrangement for new employees New employees have to work full pace immediately they start the job No training is provided to new employees in risk of upper limb musculoskeletal disorders and ways that employees can reduce risk Factor six Poor environmental conditions Working in dim light, shadow or flickering light Working in cold or otherwise adverse conditions Working with vibrating tools R
7 5. Occupational factors in relation to development of upper limb musculoskeletal disorders Catering industry The job as a Chinese chef involves holding cooking utensils, throwing up a wok and barbecuing which require forceful exertion of hands, wrists and forearms. Personal and community services Hairdressers, beauticians, massage workers, washing and ironing workers, janitors, cashiers, paging operators all have to make a lot of repetitive movements with their hands and forearms. This can easily cause upper limb musculoskeletal disorders. Sedentary industry Operating display screen equipment requires sustained upper limb position and repetitive typing movements. Construction industry Bar bending, formwork, plastering, external wall and painting jobs involve awkward posture such as repetitive movements, bending of hands and reaching of upper limbs Operating vibrating hand tools such as concrete breaker and chain saw S
8 Manufacturing industry Assembling, packaging and stock management, etc. involve repetitive movements and gripping or holding items with force. Health care industry Health care workers require forceful and repetitive upper limb movement when treating or taking care of patients, which can easily cause musculoskeletal disorders of the upper limbs. The job characterized in the above mentioned industries require frequent upper limb movements. Forceful, rapid and repetitive upper limb movements together with awkward posture may lead to develop upper limb musculoskeletal disorders. Readers should pay attention to the work performed in your specific industry. If the work involves similar demand of upper limb movement, there may be a risk of upper limb musculoskeletal disorders. 6. Symptoms The on-set of musculoskeletal problem usually comes along with symptoms of pain and tingling. Because of local inflammation, swelling on the injured body parts as well as the burning sensation are identified. Other symptoms also include tenderness, muscle weakness and numbness. For the symptom of pain subsided persistently, our movement is limited to the pain free range of motion. Limited movement further put us to habituate a decreased range of motion and it can be easily turned into joint stiffness. T
9 7. Prevention The strategy to prevent upper limb musculoskeletal disorders is best achieved by managing the aspects of workplace health and safety and the coordination of medical rehabilitation program to facilitate return-to-work after injury. Prevention of upper limb musculoskeletal disorders at workplace can be effectively achieved by making effort in improving the engineering design of workstation, organization of work tasks and utilization of proper hand tools and equipment which are fit to the body built of workers. The followings are the common principles for prevention and modification: Modification of workplace design Utilize chairs, desks, working platforms with adjustable height to accommodate workers in different sizes; the best-fit-design for individuals can prevent awkward postures such as overstretching of forearm reach, wrist bending and twisting of trunk. Comfortable viewing distance at about mm First line on screen at just below eye level Screen at about right angle to line of sight Forearm at about right angle to arm Use wrist support if required Wrist keep straight or at most slightly inclined Backrest adjustable in height and tilt Adjustable seat height Rounded or scrolled edge seat pod Firm footrest if required For high repetition tasks, arrange those frequently used materials within the working zone which can be easily reached by workers; organized for convenience can avoid unnecessary twisting or over reaching. U
10 Use of hand tools Weight and grip of the hand tools should be suitable for workers. Wrists in neutral position, no bending up and down, when operating the hand tools. Use of hand tools that provide easy grip and save us from strenuous exertion in holding. Powered tool is preferred with minimal vibration. Use solid and light materials for packaging and making containers. The containers should have good coupling grip for carriage or lifting. Use of mechanical aids such as trolleys, conveyors are recommended whenever possible; mechanical aids assist carrying and moving heavy objects and reduce force required to lift. V
11 Organization of work tasks Convey materials, finished products, semi-finished products and parts automatically, or use automatic equipment as assistance. Avoid using manual handling. Organize rotation of job tasks to increase job variety; a mixture of job tasks minimizes chance of trapping into sustained posture or repetitive movement in one single task. If the job involves prolonged gripping of tools or repetitive and rapid movements, workers should be given enough rest time. Allow the new employees to build up their work rate sensibly as they gain experience. Rest and stretch Take adequate rest to recover from muscle fatigue. Take some short breaks in a day to stretch out as to improve blood circulation and promote adequate nutrient supply to those working muscle. NM
12 Self-care tips Avoid frequent activities in bending or twisting wrists, bending back and over reaching of upper arms. Not a single posture is a good posture. Try to move around from sitting to standing or vice versa in order to relieve muscle fatigue. Avoid repeating same task for prolonged period of time. Try to organize a mixture of work task to increase job diversity. Maintain proper lifting posture in manual handling operation and make use of mechanical aids to lift and carry heavy loads. Do seek for team lifting if the lifting task cannot be handled by one person. Arrange short breaks in a work shift which provides momentary relief. NN
13 8. Treatment Treatment options for musculoskeletal disorders are listed as follows. If further enquiries on medical treatment of individual case are needed, do always seek for professional advice from medical practitioners and therapists. Rest Rest is the simplest but essential way to relieve symptoms of discomforts. Bed rest gives the muscle a chance to recover from fatigue and restore energy for another day. Hot and cold packs To numb pain and decrease swelling, apply ice pack to the affected area; to relax sore muscles and increase circulation, apply heat pack right on the affected area. NO
14 Splinting Flexing or extending excessively worsens the symptoms substantially. Splints immobilize joint movement and help to stabilize the affected area in a neutral position. Physiotherapy Treatment modalities include using ultrasound, infrared and short wave. Mobilization exercises are prescribed in therapeutic means to speed up the healing process of musculoskeletal injuries. Medication and surgery Medications are taken to reduce swelling, inflammation and also ease compression on nerve. Medications prescribed by doctors include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and steroid drugs. Surgical option may be recommended if the symptoms cannot be treated solely by medication. If suitable preventive measures are not taken after medication treatment and recovery from the upper limb musculoskeletal disorders and persistently applying force with awkward posture for long periods, there may be high risk of recurrence of the problem in more serious condition. NP
15 9. Assessment checklist for work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders Assessment checklist for work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders Company / Department: Task : Assessor : Workstation : Worker : Date : Initial Assessment Does the job involve a lot of upper limb movement? Gripping Squeezing Frequent or Twisting forceful Reaching or awkward posture Moving objects (pushing, pulling, lifting)? Finger / Hand movement (keyboard work)? Are there any warning signs of workrelated upper limb musculoskeletal disorders? For example: Any actual cases of upper limb musculoskeletal disorders in this or similar work? Any complaints by workers, e.g. aches and pains in hands, wrists, arms, shoulder etc.? Any home-made, improvised changes to workstations or tools by workers? (e.g. handles cushioned or made longer) Tick your answer Yes========No Action required If all the answers are "NO", there is unlikely to have any work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders in your workplace. Review and reassess the task if the circumstances have significantly changed. If you have any ticks in the "YES" column, there may be a risk of workrelated upper limb musculoskeletal disorders in your workplace. Assessor should go on to carry out further assessment. NQ
16 Is risk Risk factors present Yes No Further Assessment Factor one: Need for a lot of force Does the job involve: - Strong force at the same time as awkward movements or posture, e.g. bent wrists, work with arms raised or fully extended? Forceful use of hand / forearm muscles? Trying to make do with ill-fitting components by forcing them into place? Repetitive and frequent tool operation, especially if squeezing, twisting, or hammering actions are required? Equipment suitable for the body built of the worker (e.g. height, arm length or size of hands, etc.)? Possible solutions Redesign workstation e.g. - reposition supply of components to reduce reaching required - move controls to more convenient position Redesign job, workstation or tools to avoid the overuse of the hand or forearm. Maintain tools, such as keeping the sharpness of knifes and lubricating the machine parts for ease of operation. Improve the quality of components; or Provide suitable tools for fitting. Replace domestic or DIY hand tools with tools designed for repetitive industrial use. Use suitable hand tools and equipment to achieve even distribution of force across hand rather than bent wrists. Use ergonomically designed equipment and hand tools that are suitable to the staff. Provide power tools to replace hand tools. Recommendation for action Factor two: Awkward posture, rapid and frequent movement Does the job involve: - Machine pacing (e.g. to keep up with conveyor)? Work that involves frequent repetition of movements? Awkward movements such as twisting or rotation of wrists, movements of wrist from side to side, very bent fingers and wrist, or hand or arm movements beyond a comfortable range? Pressure on employees to work fast, e.g. from piecework or bonus systems? Self-pacing is preferable Re-arrange work (e.g.: job rotation can reduce repetitive movements and give variety to the job.) Consider scope for automation or use of power tools. Redesign workstation, controls and shape of tool handles. Discuss with employees the feasibility of system change. Provide information and training in upper limb musculoskeletal disorders. NR
17 Is risk Risk factors present Yes No Factor three: Awkward and static posture Does the job involve: - Cramped body position and / or insufficient space to change posture? Arms stretched or overhead for long periods? Work at awkwardly high or low height (stooping, crouching or reaching up)? Poor posture for any other reason? (e.g. lack of knowledge or habitual problem among workers) Possible solutions Improve space available to worker. Provide adjustable chairs for workers who are above or below average height or shape. Move materials or control to more convenient position. Move materials or control to more convenient position. Provide information and training related to upper limb musculoskeletal disorders. Recommendation for action Factor four: Work for long periods without breaks or changes of activity Does the job involve: - No change to work routine or variation of tasks? Infrequent breaks or even no breaks? Worker not able to have short pauses when desired? Vary tasks to provide changes in activity. Provide adequate rest breaks. Ensure that breaks are taken, especially if work involves continuous effort such as holding tools, or rapidly repeated movements (e.g. typing). Re-design work to make short pauses possible. Factor five: No special arrangements for new employees Does the job involve: - People having to work at full pace immediately they start the job? No training in risk of upper limb musculoskeletal disorders and ways employees can reduce risks? Allow recruits to build up their work rate sensibly as they gain experience. Provide training in skills, posture, and warning symptoms for all those at risk. Factor six: Poor environmental conditions Is work carried out: - In dim light, shadow or flickering light? In cold or otherwise adverse conditions? With tools that vibrate? Provide better lighting so that workers do not have to adopt awkward posture to see properly. Cold (e.g. in handling frozen foods) may increase the risk of upper limb musculoskeletal disorders. If handling is unavoidable, provide suitable gloves and clothing for personal protection. Consider whether job can be done another way to avoid need for high vibration tools. Provide vibration-absorbing grip. Minimize vibration by proper maintenance. Source: HSE Upper Limb Disorders Assessing The Risk NS
18
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings. ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders. Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every
 According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
Ergonomics Glossary. Force The amount of physical effort a person uses to do a task.
 Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
Ergonomics. For additional assistance, contact the Occupational Safety office to schedule an evaluation.
 Ergonomics 1. Purpose: Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Safety and Risk and Risk Management (SRM) developed this program to improve the health and happiness of it s employees by assisting
Ergonomics 1. Purpose: Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Safety and Risk and Risk Management (SRM) developed this program to improve the health and happiness of it s employees by assisting
Session Objectives. Business & Legal Reports, Inc. 0903
 Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
Strains and Sprains. Signs and Symptoms of MSI
 Strains and Sprains Strains and sprains (known as musculoskeletal injuries) are the most common type of workrelated injury. Musculoskeletal injury (MSI) is a term used to describe an injury of the muscles,
Strains and Sprains Strains and sprains (known as musculoskeletal injuries) are the most common type of workrelated injury. Musculoskeletal injury (MSI) is a term used to describe an injury of the muscles,
Ergonomics. Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques (EOHSS)
 Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Ergonomics in Sonography
 Ergonomics in Sonography Marissa Pentico, MS, OT/L Duke Ergonomics Division Occupational and Environmental Safety Office Janet Ellis, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Duke Radiology Ultrasound What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics
Ergonomics in Sonography Marissa Pentico, MS, OT/L Duke Ergonomics Division Occupational and Environmental Safety Office Janet Ellis, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Duke Radiology Ultrasound What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics
Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03
 Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03 Working from home is becoming more of an option for employees today. The type of work usually entails working from the home computer work station.
Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03 Working from home is becoming more of an option for employees today. The type of work usually entails working from the home computer work station.
Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics
 Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics Targeting Risk Factors Definition of Risk Factors: Actions or conditions found to contribute to worker discomfort or development of Musculoskeletal Disorders MAIN RISK
Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics Targeting Risk Factors Definition of Risk Factors: Actions or conditions found to contribute to worker discomfort or development of Musculoskeletal Disorders MAIN RISK
How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck
 OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries. Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist
 Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist Agenda Musculoskeletal Injuries Risk factors Risk controls Tools and resources
Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist Agenda Musculoskeletal Injuries Risk factors Risk controls Tools and resources
The Ergonomic Alternative
 The Economics Of Ergonomics What Is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the field of study concerned with finding ways to keep people safe, comfortable, and productive while they perform tasks at work. We Refer
The Economics Of Ergonomics What Is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the field of study concerned with finding ways to keep people safe, comfortable, and productive while they perform tasks at work. We Refer
Department of Defense Ergonomics Working Group
 Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY
 CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY POLICY An ergonomics program is a systematic process that communicates information so that adequate and feasible solutions to ergonomic risks can be implemented to improve
CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY POLICY An ergonomics program is a systematic process that communicates information so that adequate and feasible solutions to ergonomic risks can be implemented to improve
Commonwealth Health Corporation NEXT
 Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Ergonomics in General Industry
 Ergonomics in General Industry Any job requires physical movement Some tasks may be repetitious and may require you to stand or sit for extended periods Jobs in the industrial environment can be physically
Ergonomics in General Industry Any job requires physical movement Some tasks may be repetitious and may require you to stand or sit for extended periods Jobs in the industrial environment can be physically
Risk Management Department. Office Ergonomics
 Risk Management Department Office 1 Introduction In order to prevent injuries, reduce stress and improve work productivity, APS has developed this training to provide you the knowledge to help yourself
Risk Management Department Office 1 Introduction In order to prevent injuries, reduce stress and improve work productivity, APS has developed this training to provide you the knowledge to help yourself
Reference Material Searched and Brought to you
 Reference Material Searched and Brought to you by While requesting for additional reference material, always mention Title and Reference of the document. Please ensure you provide your name, company email
Reference Material Searched and Brought to you by While requesting for additional reference material, always mention Title and Reference of the document. Please ensure you provide your name, company email
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis
 Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
Regulatory Requirements
 Safe Use of Display Screen Equipment The wide application of display screen equipment (DSE) to improve the quality of work and efficiency are commonly recognized in our daily life such as paper work, data
Safe Use of Display Screen Equipment The wide application of display screen equipment (DSE) to improve the quality of work and efficiency are commonly recognized in our daily life such as paper work, data
"INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
Element B9 / 2 Assessing Risks MSD s / Man Handling / Poor Posture
 Assessing Risks MSD s / Man Handling / Poor Posture Legal Requirements HASAWA Sec 2 (2) -. Use, handling, storage, transport of articles and substances MHSWR Assessments Manual Handling Operations (MHOR)
Assessing Risks MSD s / Man Handling / Poor Posture Legal Requirements HASAWA Sec 2 (2) -. Use, handling, storage, transport of articles and substances MHSWR Assessments Manual Handling Operations (MHOR)
Corporate Safety Manual. Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics
 Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
2/28/2017. EMC Insurance Companies Risk Improvement Department. Ergonomics for School Districts. Objectives. What is Ergonomics?
 Ergonomics for School Districts February 28, 2017 Dave Young, CSP EMC Insurance Companies Objectives Define ergonomics and its effect on the workplace Discuss ergonomic risk factors Review the preferred
Ergonomics for School Districts February 28, 2017 Dave Young, CSP EMC Insurance Companies Objectives Define ergonomics and its effect on the workplace Discuss ergonomic risk factors Review the preferred
Manual Handling/Manual Tasks Checklist
 Manual Handling/Manual Instruction: Complete for all manual tasks in consultation with workers undertaking the task. Date checklist completed Date for review Name of person completing checklist Position
Manual Handling/Manual Instruction: Complete for all manual tasks in consultation with workers undertaking the task. Date checklist completed Date for review Name of person completing checklist Position
Version February 2016
 Version 3.1 29 February 2016 Health and Safety Unit 1 Table of Contents 1. Setting up your computer workstation... 3 Step 1: Adjusting yourself to the correct height... 3 Step 2 Adjusting your Chair...
Version 3.1 29 February 2016 Health and Safety Unit 1 Table of Contents 1. Setting up your computer workstation... 3 Step 1: Adjusting yourself to the correct height... 3 Step 2 Adjusting your Chair...
Appendix A: Repetitive Motion Injuries (Cal/OSHA Standard)
 20.16.1 Appendix A: Repetitive Motion Injuries (Cal/OSHA Standard) 5110. Repetitive Motion Injuries. (a) Scope and application. This section shall apply to a job, process, operation where a repetitive
20.16.1 Appendix A: Repetitive Motion Injuries (Cal/OSHA Standard) 5110. Repetitive Motion Injuries. (a) Scope and application. This section shall apply to a job, process, operation where a repetitive
Ergonomic Education For Computer Workstations
 Ergonomic Education For Computer Workstations The University of Maryland Baltimore County s (UMBC) on-line ergonomic workstation tutorial is intended to provide you with the knowledge, skills, and educational
Ergonomic Education For Computer Workstations The University of Maryland Baltimore County s (UMBC) on-line ergonomic workstation tutorial is intended to provide you with the knowledge, skills, and educational
Repetitive Upper Limb Tasks. Introductions. ' Crown Copyright Health & Safety Laboratory. 1. Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist.
 Repetitive Upper Limb s Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist Introductions Sessions 1. Why repetitive upper limb tasks? 2. Common Upper Limb Disorders (ULD) and injuries? 3. 4. Introduction to the ART tool
Repetitive Upper Limb s Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist Introductions Sessions 1. Why repetitive upper limb tasks? 2. Common Upper Limb Disorders (ULD) and injuries? 3. 4. Introduction to the ART tool
"LABORATORY ERGONOMICS"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "LABORATORY ERGONOMICS" Part of the "LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES" Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow Outline of Major Points Covered in the "Laboratory Ergonomics"
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "LABORATORY ERGONOMICS" Part of the "LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES" Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow Outline of Major Points Covered in the "Laboratory Ergonomics"
Introduction to Ergonomics Ergonomics (er'gõ nom'iks):
 March 10 th 2009 Construction Ergonomics Introduction to ergonomics Risk factors of MSDs Solutions to minimize risk factors Q & A Resources Yutonah Bowes, Oregon OSHA Mark Noll, SAIF Corp. Kim Rhodes,
March 10 th 2009 Construction Ergonomics Introduction to ergonomics Risk factors of MSDs Solutions to minimize risk factors Q & A Resources Yutonah Bowes, Oregon OSHA Mark Noll, SAIF Corp. Kim Rhodes,
KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs
 KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs Funded by: With assistance from: WMSDs are preventable! 1 This training is dedicated to the memory of 2 GOALS OF THIS CLASS You will understand: What WMSDs
KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs Funded by: With assistance from: WMSDs are preventable! 1 This training is dedicated to the memory of 2 GOALS OF THIS CLASS You will understand: What WMSDs
Environmental Health & Safety
 Environmental Health & Safety Roene Fuller Occupational Therapist This guy needs more than a new chair! Socorro General Hospital Objectives What is ergonomics? Occupational risk factors How to sit properly
Environmental Health & Safety Roene Fuller Occupational Therapist This guy needs more than a new chair! Socorro General Hospital Objectives What is ergonomics? Occupational risk factors How to sit properly
Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness
 Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness PART 1 Objectives To gain an understanding of: What is ergonomics How cumulative trauma disorders develop Ergonomic risk factors Controlling risk factors To gain an
Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness PART 1 Objectives To gain an understanding of: What is ergonomics How cumulative trauma disorders develop Ergonomic risk factors Controlling risk factors To gain an
Ergonomics Checklist - Computer and General Workstations 1
 Ergonomics Checklist - Computer and General Workstations 1 Information to collect before conducting the Ergonomics Assessment 1. Evaluation Completed by 2. Date 3. Employee Name(s) observed 4. Department
Ergonomics Checklist - Computer and General Workstations 1 Information to collect before conducting the Ergonomics Assessment 1. Evaluation Completed by 2. Date 3. Employee Name(s) observed 4. Department
Office Ergonomics. Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer
 Office Ergonomics Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer Objectives Define Ergonomics & MSDs Identify Ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up workstations to minimize
Office Ergonomics Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer Objectives Define Ergonomics & MSDs Identify Ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up workstations to minimize
BOHS-Series. Series. Ergonomics Training Module
 BOHS-Series Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the
BOHS-Series Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the
OFFICE ERGONOMICS. Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh Ergonomics What is it? Why should I be interested? What do I need to know to help myself? Where can I get help?
OFFICE ERGONOMICS Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh Ergonomics What is it? Why should I be interested? What do I need to know to help myself? Where can I get help?
BOHS-Series. Ergonomics Training Module
 BOHS-Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the science
BOHS-Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the science
Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre
 Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre 1 No Disclosures 2 Musculoskeletal Injury (MSI) refers to damage
Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre 1 No Disclosures 2 Musculoskeletal Injury (MSI) refers to damage
Ergonomics 101: CREATING A PLAYBOOK FOR WORKSTATION ANALYSIS
 Ergonomics 101: CREATING A PLAYBOOK FOR WORKSTATION ANALYSIS Andy Litchfield Loss Prevention Consultant Gibson Presentation Objectives What Is Ergonomics? What Does OSHA Say? Identifying Problems Hierarchy
Ergonomics 101: CREATING A PLAYBOOK FOR WORKSTATION ANALYSIS Andy Litchfield Loss Prevention Consultant Gibson Presentation Objectives What Is Ergonomics? What Does OSHA Say? Identifying Problems Hierarchy
PERSONAL COMPUTER WORKSTATION CHECKLIST
 PERSONAL COMPUTER WORKSTATION CHECKLIST Last Revised: 6/26/17 A. Summary Use the following checklists to assess your own computer workstation. If you say No to any items within the lists, it may indicate
PERSONAL COMPUTER WORKSTATION CHECKLIST Last Revised: 6/26/17 A. Summary Use the following checklists to assess your own computer workstation. If you say No to any items within the lists, it may indicate
LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2955 LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2955 LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in
Display Screen Equipment Risk Assessment Workshop
 Display Screen Equipment Risk Assessment Workshop Objectives Hazard Identification Use of HSE checklist Provision of information Drawing conclusions from assessments Risk reduction and control. What is
Display Screen Equipment Risk Assessment Workshop Objectives Hazard Identification Use of HSE checklist Provision of information Drawing conclusions from assessments Risk reduction and control. What is
Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents
 Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents Introduction What is Office Ergonomics? 1 Goal of Office Ergonomics 1 What are Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)? 2 MSD Risk Factors 2 Office Ergonomics Guidelines
Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents Introduction What is Office Ergonomics? 1 Goal of Office Ergonomics 1 What are Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)? 2 MSD Risk Factors 2 Office Ergonomics Guidelines
This was good at the time - see ergoanalyst.com for the latest in manual tasks risk management
 Burgess-Limerick & Associates Ergonomics and Research Consultants ABN 84976421949 This was good at the time - see ergoanalyst.com for the latest in manual tasks risk management Procedure for Managing Injury
Burgess-Limerick & Associates Ergonomics and Research Consultants ABN 84976421949 This was good at the time - see ergoanalyst.com for the latest in manual tasks risk management Procedure for Managing Injury
INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM
 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in this program is presented in a definite order so that employees will see the relationships between the various groups of information
INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in this program is presented in a definite order so that employees will see the relationships between the various groups of information
Muscular Skeletal Disorders
 Alabama Department of REHABILITATION SERVICES "for Alabama's children and adults with disabilities" Muscular Skeletal Disorders Michael Papp, MSE Muscular Skeletal Disorders What are MSDs? Muscles Nerves
Alabama Department of REHABILITATION SERVICES "for Alabama's children and adults with disabilities" Muscular Skeletal Disorders Michael Papp, MSE Muscular Skeletal Disorders What are MSDs? Muscles Nerves
Beginning of Process: Development of the Office Ergonomics program.
 CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Office Ergonomics Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Office Ergonomics Program Purpose: To provide applicable suggestions and procedures that may be help reduce
CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Office Ergonomics Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Office Ergonomics Program Purpose: To provide applicable suggestions and procedures that may be help reduce
OFFICE WORKSTATION DESIGN
 No matter what industry you work in, computers are commonly used. Extended work with computers can lead to muscular fatigue and discomfort, usually in the back, arms, shoulders and neck. The risk of a
No matter what industry you work in, computers are commonly used. Extended work with computers can lead to muscular fatigue and discomfort, usually in the back, arms, shoulders and neck. The risk of a
OPNAVINST G 30 Dec 05
 Appendix 23-B Computer Workstation Checklist The computer workstation checklist is one method available for performing computer workstation assessments. The checklist is designed to be printed as two double-sided
Appendix 23-B Computer Workstation Checklist The computer workstation checklist is one method available for performing computer workstation assessments. The checklist is designed to be printed as two double-sided
ERGONOMICS. Risk Management
 ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS
 YOUR GUIDE TO DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Contents What is tendonitis and tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What is de Quervain s tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What treatment
YOUR GUIDE TO DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Contents What is tendonitis and tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What is de Quervain s tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What treatment
Ergonomics in the Laboratory
 instrumentation [management/administration and training generalist] Ergonomics in the Laboratory Terry Jo Gile, MT(ASCP)MA Ed From Gile and Associates, St Louis, MO Ergonomic disorders Work-site analysis
instrumentation [management/administration and training generalist] Ergonomics in the Laboratory Terry Jo Gile, MT(ASCP)MA Ed From Gile and Associates, St Louis, MO Ergonomic disorders Work-site analysis
Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist
 Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist What do you know about Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the study of designing equipment and devices that fit the human body,
Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist What do you know about Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the study of designing equipment and devices that fit the human body,
Adjust the chair height so that your feet rest comfortably on the floor, footrest or foot ring.
 Laboratory ergonomics Some tasks performed in research laboratories can lead to joint and muscle strains if done for prolonged periods. The following tips can help you to work effectively and reduce fatigue
Laboratory ergonomics Some tasks performed in research laboratories can lead to joint and muscle strains if done for prolonged periods. The following tips can help you to work effectively and reduce fatigue
Maine. Video Display Terminal Law. Training Program SAFE345
 Maine Video Display Terminal Law Training Program By the end of this presentation you will be able to: Identify the elements of the law Identify the training requirements Define ergonomics and its benefits
Maine Video Display Terminal Law Training Program By the end of this presentation you will be able to: Identify the elements of the law Identify the training requirements Define ergonomics and its benefits
Resources: Ergonomic/Musculoskeletal Hazards in Patient Handling. Sustained and/or Awkward Postures. Contact Stresses or Pressures
 Resources: Ergonomic/Musculoskeletal Hazards in Patient Handling Forceful Exertions Sustained and/or Awkward Postures Repetition Gripping Contact Stresses or Pressures High Risk Patient Handling Tasks
Resources: Ergonomic/Musculoskeletal Hazards in Patient Handling Forceful Exertions Sustained and/or Awkward Postures Repetition Gripping Contact Stresses or Pressures High Risk Patient Handling Tasks
13/02/2011. Ergonomics
 13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
BACK SPRAINS AND STRAINS FIRST AID FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES
 BACK SPRAINS AND STRAINS FIRST AID FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES This information sheet is designed to increase your awareness of factors that can contribute to the formation of Musculoskeletal Injuries
BACK SPRAINS AND STRAINS FIRST AID FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES This information sheet is designed to increase your awareness of factors that can contribute to the formation of Musculoskeletal Injuries
The Evolution of Human s? Objectives. Agenda. Defining Ergonomics. History of Ergonomics. Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer.
 Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer The Evolution of Human s? Presented By: Steve Grimmett Ergonomic Consultant Agenda Introduction to Ergonomics Form and Function of the Human Body Ergonomic Issues in
Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer The Evolution of Human s? Presented By: Steve Grimmett Ergonomic Consultant Agenda Introduction to Ergonomics Form and Function of the Human Body Ergonomic Issues in
260- OFFICE ERGONOMICS
 260.1 PURPOSE A. To provide some universally applicable suggestions and procedures that may be helpful when setting up an ergonomically correct work station in an office setting. 260.2 SCOPE A. This procedure
260.1 PURPOSE A. To provide some universally applicable suggestions and procedures that may be helpful when setting up an ergonomically correct work station in an office setting. 260.2 SCOPE A. This procedure
Courtesy of your source for the best ergonomic office furniture.
 Enjoy this free ergonomic evaluation form courtesy of Get Up Stand Up Desk Co., your online source for the best ergonomic office furniture at the best prices. We hope that this evaluation will help you
Enjoy this free ergonomic evaluation form courtesy of Get Up Stand Up Desk Co., your online source for the best ergonomic office furniture at the best prices. We hope that this evaluation will help you
Carpal tunnel syndrome
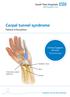 Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job
 Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job Job Site Analysis WorkRisk Analysis WorkTask Analysis WorkStation Analysis David Raptosh, MA, OTR/L Regional Director of WorkStrategies Job Site Analysis - Identify
Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job Job Site Analysis WorkRisk Analysis WorkTask Analysis WorkStation Analysis David Raptosh, MA, OTR/L Regional Director of WorkStrategies Job Site Analysis - Identify
EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow)
 EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow) Description Expected Outcome Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is the most common painful condition of the elbow. Inflammation and pain occur on the outer side
EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow) Description Expected Outcome Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is the most common painful condition of the elbow. Inflammation and pain occur on the outer side
Ergonomics Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa (515) Copyright
 2408 Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa 50011-3602 (515) 294-5359 www.ehs.iastate.edu Copyright Reviewed 2016 2 Ergonomics Directory of Service and Emergency Providers Services Environmental Health and Safety
2408 Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa 50011-3602 (515) 294-5359 www.ehs.iastate.edu Copyright Reviewed 2016 2 Ergonomics Directory of Service and Emergency Providers Services Environmental Health and Safety
Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design
 PPT Presentation page 1 Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design Presented by the NYS Public Employees Federation Paige Engelhardt PEF Health & Safety Trainer www.pef.org
PPT Presentation page 1 Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design Presented by the NYS Public Employees Federation Paige Engelhardt PEF Health & Safety Trainer www.pef.org
ERGONOMIC CHECKLIST. Area: Date of Survey: Assessors Name: BODY PART RISK FACTORS NECK/SHOULDER ELBOW HAND/WRIST Carpel tunnel
 ERGONOMIC CHECKLIST Area: Date of Survey: Assessors Name: Job Description Job Risk priority as per Risk Assessment ( X applicable column) H H-M M M-L L ERGONOMIC FACTORS Repetition BODY PART RISK FACTORS
ERGONOMIC CHECKLIST Area: Date of Survey: Assessors Name: Job Description Job Risk priority as per Risk Assessment ( X applicable column) H H-M M M-L L ERGONOMIC FACTORS Repetition BODY PART RISK FACTORS
Back Safety Healthcare #09-066
 Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
Office and Laboratory Ergonomics. WSU-TFREC Safety Training
 Office and Laboratory Ergonomics WSU-TFREC Safety Training What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the scientific study of human work Ergonomic principals adapt work to a specific person by designing tasks &
Office and Laboratory Ergonomics WSU-TFREC Safety Training What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the scientific study of human work Ergonomic principals adapt work to a specific person by designing tasks &
The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
Ergonomics and the Farm. Keri A. Gill-Smith, Physical Therapist
 Ergonomics and the Farm Keri A. Gill-Smith, Physical Therapist Farm Injury Rates Farming involves hard physical work Every day about 167 agricultural workers suffer a lost-work-time injury From 2008-2010,
Ergonomics and the Farm Keri A. Gill-Smith, Physical Therapist Farm Injury Rates Farming involves hard physical work Every day about 167 agricultural workers suffer a lost-work-time injury From 2008-2010,
Computer Ergonomics. Static Efforts
 Welcome to Essential WorkWellness online continuing education activities. Please be aware that this activity does not include a post test or certificate of completion. Simply read the article below to
Welcome to Essential WorkWellness online continuing education activities. Please be aware that this activity does not include a post test or certificate of completion. Simply read the article below to
Guidance Tool: Manual Handling
 Guidance Tool: Manual Handling Please tick the relevant boxes to ensure you follow the correct procedures. Manual Handling Risk Assessments completed for Hazardous Activities Employee made aware of the
Guidance Tool: Manual Handling Please tick the relevant boxes to ensure you follow the correct procedures. Manual Handling Risk Assessments completed for Hazardous Activities Employee made aware of the
A Patient s Guide to Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer s Elbow) William T. Grant, MD
 A Patient s Guide to Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer s Elbow) Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh,
A Patient s Guide to Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer s Elbow) Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh,
Ergonomic recommendations
 Page 1 Handling loads Awkward postures Recommendations are biological states that requires special protection During the entire process of gestation and breastfeeding, physiological, metabolic and psychological
Page 1 Handling loads Awkward postures Recommendations are biological states that requires special protection During the entire process of gestation and breastfeeding, physiological, metabolic and psychological
RIB FRACTURE. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms. Diagnosis
 RIB FRACTURE Explanation The heart and lungs are encased by the chest wall, which is composed of the ribs. The ribs must be flexible in order to allow movement during expansion and contraction. This movement
RIB FRACTURE Explanation The heart and lungs are encased by the chest wall, which is composed of the ribs. The ribs must be flexible in order to allow movement during expansion and contraction. This movement
ERGONOMICS in Office.
 ERGONOMICS in Office ก ก. ก What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics ก ก ก ก. ก ergonomic ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก Static vs Dynamic muscular effort ก ก vs. ก ก Dynamic Effort Static Effort What are the risks of ignoring
ERGONOMICS in Office ก ก. ก What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics ก ก ก ก. ก ergonomic ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก Static vs Dynamic muscular effort ก ก vs. ก ก Dynamic Effort Static Effort What are the risks of ignoring
Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness PART 2
 Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness PART 2 Identifying Risk Factors Remember Risk factors are actions or conditions found to contribute to worker discomfort or injury Cumulative Injury Risk Factors Four
Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness PART 2 Identifying Risk Factors Remember Risk factors are actions or conditions found to contribute to worker discomfort or injury Cumulative Injury Risk Factors Four
Safety Manual: Ergonomics. February 8, 2017
 Safety Manual: Ergonomics February 8, 2017 Overview 2.0 Ergonomics Introduction This Chapter provides a general overview of issues in the workplace and recommendations for reducing ergonomic injuries.
Safety Manual: Ergonomics February 8, 2017 Overview 2.0 Ergonomics Introduction This Chapter provides a general overview of issues in the workplace and recommendations for reducing ergonomic injuries.
Work Efficiently and Safely
 Work Efficiently and Safely Workstation Ergonomics 12 July 2017 Working Safely and Efficiently What is Covered? Apply Ergonomic Principles to 3 Develop Good Postures 4 Screen Positioning Guidelines 7 Focusing
Work Efficiently and Safely Workstation Ergonomics 12 July 2017 Working Safely and Efficiently What is Covered? Apply Ergonomic Principles to 3 Develop Good Postures 4 Screen Positioning Guidelines 7 Focusing
Dynamic Movement & Stress Reversals
 Resources: Hazard Control Options Equipment Work Heights Space Requirements Gripping Contact Stress Dynamic Movement & Stress Reversals Proper Body Mechanics According to Part 2 of the WSH Regulation,
Resources: Hazard Control Options Equipment Work Heights Space Requirements Gripping Contact Stress Dynamic Movement & Stress Reversals Proper Body Mechanics According to Part 2 of the WSH Regulation,
Office Ergonomics OSHA Resources. Risk Factors for Developing MSDs taken from OSHA voluntary guidelines. Mary Loughlin, OTR/L,CHT, CEAS
 Office Ergonomics Mary Loughlin, OTR/L,CHT, CEAS OSHA Occupational Safety and Health Administration November 2000 Federal OSHA published the Final Ergonomics Program Standard in the Federal Register. Effective
Office Ergonomics Mary Loughlin, OTR/L,CHT, CEAS OSHA Occupational Safety and Health Administration November 2000 Federal OSHA published the Final Ergonomics Program Standard in the Federal Register. Effective
The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person What is Ergonomics? By the end of this chapter, You will be able to: Demonstrate a general knowledge of office ergonomics Identify
OFFICE ERGONOMICS The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person What is Ergonomics? By the end of this chapter, You will be able to: Demonstrate a general knowledge of office ergonomics Identify
Vancouver. CoastalHealth. Promoting wellness. Ensuring care. Mary Pack Arthritis Program Occupational Therapy
 Vancouver CoastalHealth Promoting wellness. Ensuring care. Mary Pack Arthritis Program Occupational Therapy O.T. IVA-9 01 12005 PATIENT EDUCATION: JOINT PROTECTION AND ENERGY CONSERVATION The goals of
Vancouver CoastalHealth Promoting wellness. Ensuring care. Mary Pack Arthritis Program Occupational Therapy O.T. IVA-9 01 12005 PATIENT EDUCATION: JOINT PROTECTION AND ENERGY CONSERVATION The goals of
ERGONOMICS, BIOMECHANICS & MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDER- A REVIEW
 ERGONOMICS, BIOMECHANICS & MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDER- A REVIEW Md Shakibul Haque 1, Manoj Kumar ² 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Invertis University, Bareilly, U.P., (India) ABSTRACT Through
ERGONOMICS, BIOMECHANICS & MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDER- A REVIEW Md Shakibul Haque 1, Manoj Kumar ² 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Invertis University, Bareilly, U.P., (India) ABSTRACT Through
Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference.
 Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference. Thank you for your urge to grow and willingness to learn.
Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference. Thank you for your urge to grow and willingness to learn.
Ergonomics and Back Safety PPT-SM-BACKSFTY V.A.0.0
 Ergonomics and Back Safety 1 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomics Scientific study of equipment design for the purpose of improving efficiency, comfort and safety 2 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomic
Ergonomics and Back Safety 1 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomics Scientific study of equipment design for the purpose of improving efficiency, comfort and safety 2 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomic
Office Ergonomics: Best Practices and Results. Mike Lampl, MS, CPE Ohio Bureau of Workers Compensation (BWC)
 Office Ergonomics: Best Practices and Results Mike Lampl, MS, CPE Ohio Bureau of Workers Compensation (BWC) www.ohiobwc.com Analysis of Injury Data Nineteen organizations received safety grants to incorporate
Office Ergonomics: Best Practices and Results Mike Lampl, MS, CPE Ohio Bureau of Workers Compensation (BWC) www.ohiobwc.com Analysis of Injury Data Nineteen organizations received safety grants to incorporate
To educate employees that they share in the responsibility for their comfort and prevention of injury.
 It is the County of Fresno's policy to provide its employees with a safe and healthy workplace. This handbook reflects General Industry Safety guidelines for safe workstation arrangements for employees
It is the County of Fresno's policy to provide its employees with a safe and healthy workplace. This handbook reflects General Industry Safety guidelines for safe workstation arrangements for employees
Good display screen equipment (DSE) practice
 Health & Safety Services Good display screen equipment (DSE) practice If you normally use a computer for an hour or more a day, then the following guidance is for you Potential health problems Poor DSE
Health & Safety Services Good display screen equipment (DSE) practice If you normally use a computer for an hour or more a day, then the following guidance is for you Potential health problems Poor DSE
CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 WHAT IS CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME? SYMPTOMS Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most commonly occurring nerve compression in the upper body It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow The
WHAT IS CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME? SYMPTOMS Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most commonly occurring nerve compression in the upper body It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow The
TRAINING PACKAGE DISPLAY SCREEN EQUIPMENT (DSE) Any alphanumeric or graphic display screen, regardless of the display process involved
 TRAINING PACKAGE DISPLAY SCREEN EQUIPMENT (DSE) Any alphanumeric or graphic display screen, regardless of the display process involved Why? To Avoid ACHES AND PAINS - NECK, ARMS, WRISTS, LEGS & BACK (there
TRAINING PACKAGE DISPLAY SCREEN EQUIPMENT (DSE) Any alphanumeric or graphic display screen, regardless of the display process involved Why? To Avoid ACHES AND PAINS - NECK, ARMS, WRISTS, LEGS & BACK (there
Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc
 Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc Every job or task has unique physical and cognitive demands. Each person has unique physical attributes and abilities. www.prbembodychair.co.uk www.youandyourself.com
Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc Every job or task has unique physical and cognitive demands. Each person has unique physical attributes and abilities. www.prbembodychair.co.uk www.youandyourself.com
Preventing Work-related Injuries Among Sonographers
 Preventing Work-related Injuries Among Sonographers Carolyn T. Coffin, MPH, RDMS, RVT, RDCS, FSDMS Joan P. Baker, MSR, RDMS, RDCS, FSDMS Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WRMSD) have been reported
Preventing Work-related Injuries Among Sonographers Carolyn T. Coffin, MPH, RDMS, RVT, RDCS, FSDMS Joan P. Baker, MSR, RDMS, RDCS, FSDMS Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WRMSD) have been reported
Element 3: Musculoskeletal Hazards and Risk Control
 Work-Related Upper Limb Disorders Musculoskeletal disorders such as back pain and work-related upper limb disorder (WRULD) can result from repetitive tasks such as display screen equipment (DSE) use, checkout
Work-Related Upper Limb Disorders Musculoskeletal disorders such as back pain and work-related upper limb disorder (WRULD) can result from repetitive tasks such as display screen equipment (DSE) use, checkout
Human Factors and Ergonomics
 Human Factors and Ergonomics Short description This section of the HSEQ Manual provides awareness and guidance for Centennial employees and subcontractors in avoiding awkward work postures, excessive effort
Human Factors and Ergonomics Short description This section of the HSEQ Manual provides awareness and guidance for Centennial employees and subcontractors in avoiding awkward work postures, excessive effort
Dimensional Requirements. Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways.
 Dimensional Requirements Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings from MIL-HDBK 759. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings to
Dimensional Requirements Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings from MIL-HDBK 759. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings to
