Effect of Different Volumes on Pain Relief in Patient Receiving Fluoroscopic Guided Interlaminar Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection
|
|
|
- Chloe Cunningham
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pain Physician 2018; 21: ISSN Randomized Trial Effect of Different Volumes on Pain Relief in Patient Receiving Fluoroscopic Guided Interlaminar Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection Jeetinder Kaur Makkar, MD 1, Balbir Kumar, MD¹, Kajal Jain, MD 1, Saravdeep S. Dhutt, MS 2, YK Batra, MD 1, and Preet Mohinder Singh, MD 3 From: 1 Department of Anesthesia and Intensive care, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India; 2 Department of Orthopedics, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India; 3Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi Address Correspondence: Jeetinder Kaur Makkar, MD Department of Anesthesia and Intensive Care Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research Department of Anaesthesia Nehru Hospital, PGIMER, Sector 12, Chandigarh, India jeet1516@gmail.com Disclaimer: There was no external funding in the preparation of this manuscript. Conflict of interest: Each author certifies that he or she, or a member of his or her immediate family, has no commercial association (i.e., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted manuscript. Manuscript received: Revised manuscript received: Accepted for publication: Free full manuscript: Background: Epidural steroids injections (ESI) are frequently used to treat lumbar radicular pain. Although different volume have been used for interlaminar ESI in adults, there is no controlled trial comparing the effect of different volumes on pain relief for the same dose of steroid. Objective: To compare the effect of increase in volume of epidural drug on pain relief in lumbar ESI. Study design: Randomized double blind trial Settings: Pain OR of a tertiary care centre Methods: Sixty patients were randomly allocated to 1 of 3 groups: Group A (4 ml), Group B (6 ml), and Group C (8 ml). Pain was evaluated using visual analog scale (VAS) and improvement in disability using modified Oswestry Disability Questionnaire scores (MODQS) at 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks. Patients having less than 50% pain relief from baseline received an additional epidural injection of the same volume with a maximum of 3 injections at least 15 days apart. The primary objective of the study was incidence of patients attaining more than 50% pain relief at 6 months. Secondary outcome included MODQS and pattern of spread of iodinated contrast on fluoroscopy. Results: At the end of 6 months, there was no significant difference in the effective pain relief between the 3 groups (Group A-16/22 (72.7%), Group B-15/20 (75%), Group C-13/18 (72.2%); P = 0.98, chi- square test). All groups demonstrated a significant reduction in mean VAS scores. There was no significant intergroup difference in VAS sores and MODQS at all the time intervals. The pattern of contrast spread did not differ between the 3 groups. Limitation: Not a placebo controlled trial Conclusions: An increase in volume of the injectate from 4 ml to 8 ml did not increase the efficacy of interlaminar ESI. Key words: Epidural steroid, volume, low back pain, interlaminar: Pain Physician 2018; 21: Epidural steroid injections (ESI) are commonly used to treat chronic radicular low back pain secondary to disc herniation. Steroids act by inhibiting production of inflammatory markers (phospholipasea2) at the interface of the epidural space. Also they inhibit the occurrence of ectopic discharge from unmyelinated C fibers and relieve central sensitization (1,2).
2 Pain Physician: May/June 2018; 21: Several factors, like site of needle insertion, direction of bevel of the needle, speed of injection, epidural space contexture, age, weight, height, and volume of drug, might affect the distribution of the drug administered in the dorsal epidural space (3). The volume in which a drug is administered is a major factor in determining the range of spread of injected solution. Although different volumes have been used for interlaminar ESI in adults, only limited trials exist assessing the effect of volume on efficacy of interlaminar ESI (4,5). The aim of the present study was to compare therapeutic efficacy of the same dose of steroid in different volumes in patients receiving interlaminar ESI for lumbosacral radicular pain. Methods The institutional ethics committee approved this randomized double blind trial (NK 1098/MD/ dated , CTRI/2016/02/006675; registered on 24/02/2016). Fifty-eight patients between the ages of 30 to 60 years, with unilateral lumbosacral radicular pain for a minimum of 3 months duration, not responding to medications and physical therapies, were enrolled. Patients with lumbar canal stenosis, facet joint arthopathy, allergy to contrast or steroid, previous surgery on the lumbar spine, and those who received lumbar ESI in the past 3 months were excluded. Written informed consent was acquired. Patients were randomly divided into 1 of 3 groups using a computer generator random number sequence. Random numbers were kept in sealed envelopes and opened by an anesthesiologist uninvolved in the study. Group A received 80 mg of methylprednisolone acetate (MPA) with a total volume of 4 ml (2 ml of MPA + 2 ml of 2% lidocaine). Group B received the same dose of MPA with a total volume of 6 ml (2 ml of MPA + 2 ml of 2% lidocaine + 2 ml saline) and Group C with a total volume of 8 ml (2 ml of MPA + 2 ml of 2% lidocaine + 4 ml saline). One investigator performed the lumbar ESIs. Another investigator then followed the patient in a pain clinic. This investigator and patient were unaware of the group they had been assigned to. The intervertebral level for intervention was selected based on clinical examination and the results of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) study. The intervertebral level, which was maximally affected, was selected for intervention. Procedure All epidural injections were administered in the operating room (OR) in the prone position. An initial anteroposterior fluoroscopic image was obtained to identify the interalaminar space at the desired level of intervention. Local infiltration was done with 1% lidocaine down to the lamina. An 18-gauge Tuohy needle was inserted into the skin at this level aiming towards the base of the spinous process in the interalaminar space. Midline orientation of the needle was maintained between the 2 spinous processes. Once the needle touched the lower border of the lamina, the same was redirected into the epidural space using the loss-of-resistance to saline technique. The bevel of the needle was directed towards the symptomatic side. After a negative aspiration for blood and cerebrospinal fluid, 0.5 ml of iohexol dye (300 mg/ml), (Omnipaque, GE Healthcare, London, UK) was injected to confirm the epidural space. Following this, the equivalent volume of contrast, according to group assignment, was injected to evaluate for unilateral or bilateral spread. Lateral images were taken to see the ventral epidural spread, defined as presence of contrast along the posterior longitudinal ligament or abutting the posterior aspect of the contiguous vertebral body at the level of needle insertion, caudal spread, and segmental spread. The test drug (2 ml of MPA + 2 ml of 2% lidocaine in different volumes) was then injected into the epidural space according to the designated group. Total fluoroscopy time was recorded for each procedure. Assessment Assessment for pain relief and disability was done using the visual analog scale (VAS) from 0 (no pain) to 100 (maximum pain) and Modified Oswestry Disability Questionnaire (MODQ), respectively. Patients were also assessed for any postural headache, motor weakness, newly developed pain, paraplegia, or paresthesia. Primary and Secondary Outcomes The primary outcome of the study was to compare the effect of different volumes of lumbar ESI (4 ml, 6 ml, and 8 ml) on therapeutic efficacy in patients with lumbosacral radicular pain, defined as the number of patients attaining more than 50% pain relief at 6 month. Secondary objective measures were to study VAS scores, MODQ scores, and the pattern of spread of iodinated contrast on fluoroscopy. Follow-up All patients were followed for a period of 6 months at an interval of 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks. Patients who reported < 50% pain relief from baseline received an ad
3 Effect of Volume on Efficacy of Epidural Steroids ditional injection with the same approach and volume at least 15 days apart for a maximum of 3 injections. Those patients who reported > 50% pain relief received a subsequent epidural injection during the study period, only if pain increased to > 50% of baseline again. Statistical Analysis A sample size of 20 patients in each group was required based on a standard deviation (SD) of 2.5 at a power of 80% to detect a difference of 2 in mean VAS scores between baseline and at any follow-up period. Data were presented as mean + SD or median (range) with 95% confidence interval where necessary. Numerical variable were assessed for normality. Analysis of demographic data was done by student t- test and chi-square tests. Continuous data like VAS and MODQ were analyzed using 2 way repeated measures of analysis of variance (ANOVA), and with post hoc test when indicated. Categorical data (presence of anterior spread, perineural spread, and complication) were analyzed using chi-square test. Fig. 1. Flow of patients
4 Pain Physician: May/June 2018; 21: Table 1. Patients demographics and base line data in 3 groups. Group A (n = 22) Group B (n = 20) Group C (n = 18) Data expressed as mean ± SD, data analyzed using chi-square test, data analyzed using one way ANOVA, P value < 0.05 significant. P value Age (years) ± ± ± Gender Male Female 10 (45.5%) 12 (54.5%) 9 (45.0%) 11 (55.0%) 9 (50%) 9 (50.0%) Height (cm) ± ± ± Weight (kg) ± ± ± Baseline VAS 8.50 ± ± ± Table 2. Level of intervention in 3 groups. Level of intervention L3-L4 L4-L5 L5-S1 P value Group A (n = 22) 2 (9.1%) 14 (63.6%) 6 (27.3%) Group B (n = 20) 3 (15%) 13 (65.0%) 4 (20%) Group C (n = 18) 0 (0%) 10 (62.5%) 6 (37.5%) Data presented as numbers (percentages) and analyzed using chi-square test. Results Figure 1 shows the flow of patients. A total of 70 patients were included in this study. Four patients refused to give consent. Another 4 patients from group C were excluded due to breach in study protocol (noncompliance on follow-up and VAS could not be recorded). There was a loss to follow-up of one patient from group A and group B each after the first ESI. Data was analyzed for 60 patients. All 3 groups were comparable with respect to demographic data, duration of symptoms, level of disc herniation, baseline VAS, and MODQ (Table 1). The level of intervention was comparable in all 3 groups (Table 2). There was no statistically significant difference in the effectiveness of intervention among the 3 groups at the end of 6 months (Group A-16/22 (72.7%), Group B-15/20 (75%), Group C-13/18 (72.2%); P = 0.98, chisquare test). There was a significant reduction in mean VAS in each group compared to the baseline at various time intervals over the period of the 6 month follow-up. Repeated measure ANOVA revealed significant VAS time interaction within the 3 groups after epidural injection. However, there was no VAS group interaction. There was no significant difference in VAS sores between the 3 groups at any of the time intervals (Fig. 2). Intragroup analysis showed that there was statistically significant differences in MODQ reduction within the groups as compared to baseline at various points of time. On intergroup analysis, there was no significant difference in MODQ between the 3 groups over the period of 6 months (Fig. 3). The mean number of injections required for effective pain relief were comparable in all 3 groups (Group A 2.14 ± 0.834, Group B 1.90 ± 0.641; Group C 1.80 ± 0.77; t-test, P value = 0.375). There was no statistically significant difference in percentage of patients having ventral spread of contrast or perineural spread (Table 3). The intervention was given in the intervertebral space where maximum disc bulge was found. In case of more than one level disc herniation, the intervention was performed at the level corresponding with symptoms. The level of intervention was comparable in all 3 groups. The average number of vertebral segments of cephalic spread of contrast media in Group A was 2.82 ± 1.01, 2.29 ± 1.07, and 2.67 ± 1.16 for the first, second, and third ESI respectively. Cephalic spread in Group B was 2.95 ± 1.23, 3.06 ± 0.93, and 3.00 ± 0.71 for the first, second, and third ESI respectively. In Group C, the cephalic spread was 3.25 ± 1.39, 3.00 ± 0.95, and 3.33 ± 0.52 for the first, second, and third ESI. The average number of vertebral segments of caudal spread for Group A was 4.36 ± 1.71, 4.27 ± 1.79, and 3.33 ± 2.08 for the first, second, and third ESI. In Group B, the mean caudal spread was 4.30 ± 2.03, 4.00 ± 1.83, and 3.56 ± 246
5 Effect of Volume on Efficacy of Epidural Steroids Fig. 2. Line diagram showing mean visual analog scale in all the 3 groups at different time intervals. *represent P value 0.00 (< 0.05) within group as compare to base line at various interval (within group pairwise comparsion). Error bars represent standard deviation. Fig. 3. Line diagram showing mean MODQ score in all the 3 groups at various intervals. *Represent P value 0.00 (< 0.05) within group as compare to baseline, (pairwise comparison). Error bars represent standard deviation for the first, second, and third ESI. For Group C, the mean caudal spread was 3.93 ± 1.94, 5.08 ± 1.24, and 3.33 ± 0.52 for the first, second, and third ESI. There was no significant difference in segmental spread between groups. The bevel of the needle was directed towards the Table 3. Ventral spread in 3 groups. Ventral Spread Group A Group B Group C 1ST ESI 9/22 (38.5%) 8/20 (40%) 6/18 (33.3%) 2ND ESI 4/11(36.3%) 4/10 (40%) 3/7 (42.8%) 3RD ESI 3/7 (42.8%) 1/3 (33.5%) 2/7 (28.5%) Data expressed as number (percentage) and analyzed using chi-square tests
6 Pain Physician: May/June 2018; 21: side of pain to ensure unilateral spread. One hundred and three injections were done in total. Seventy-two patients had unilateral spread (69.9%). We did not meet any complications like intravascular injection, interathecal, or subdural injection. All of the patients were stable during and after the procedures. Discussion ESIs are used in combination with improved body mechanics and core muscle strengthening exercises to provide pain relief in patients with lumbar radicular pain. Optimal volume in which a steroid should be administered for lumbar ESI is debatable. Current literature suggests better pain relief with a higher volume. Several mechanisms have been proposed pertaining to this finding. Large volume leads to washing out of the inflammatory cytokines. It is also hypothesized that injecting larger volumes in the epidural space leads to lysis of neural adhesions by means of stretching along the dura and nerve roots (6,7). Further, added volume allows the lavage of epidural space, suppresses focus of ectopic discharge from the injured nerve, and enhances blood flow to the ischemic nerve roots (8). In the absence of any randomized control trial, Rabinovitch et al (9) conducted a systematic review in 2009 to study the correlation between the volume of lumbar ESI and pain relief. These authors found a statistically significant positive correlation between the volume and pain relief and concluded that injectate volume could be a variable determining the efficacy of epidural injection. Kim et al (10) injected a total of 50 ml in the caudal space at increments of 10 ml in 32 patients with chronic low back pain accompanied by radiculopathy. Fluoroscopic images were repeated after each 10 ml of contrast medium and drug. The authors found that the extent of spread was limited to mid and lower lumbar areas in the majority of the patients on injecting a volume of 10 ml. Further volume on subsequent injection did not increase the extent of spread. We expected to see a difference in extent of spread of contrast on using an epidural injectate volume less than 10 ml. Therefore we injected 3 different volumes of contrast at increments of 2 ml (i.e., 4, 6, and 8 ml). However, we found no difference in the extent of spread of contrast on using a volume injectate of less than 10 ml. This is probably because of the starling effect of the epidural space (11). Greater drug volumes may leak through sacral or lateral foramina in an attempt to maintain constant pressure whenever epidural space is filled over or above its capacity. This implies increasing leakage of drug from the epidural space with increasing volume. In a single prospective trial conducted to see the effect of different volumes, Chun et al (5) recently randomized 66 patients to receive lumbar transforaminal epidural injections with either a low-volume injectate (3 ml) or a high-volume injectate (8 ml). A higher percentage of patients achieved more than 50% pain relief at one month in the high volume group. However, post procedure epidurogram were not studied in this study. Also patients in the high volume injectate group received a larger dose of lidocaine. A total dose of lidocaine was kept constant in our study. Our decision to use 4 ml was based on the available literature on ESIs in the last 10 years, where maximum studies have used a volume ranging from 3 to 10 ml (12-14). We also wanted to evaluate whether doubling the volume to 8 ml would improve the spread and efficacy of lumbar ESIs. We used methylprednisolone, as clinical studies evaluating the efficacy of different types of steroid injections report variable results with nonparticulate steroids (15,16). Further, methylprednisolone is acceptable for interlaminar injections (17). Limitations Our study has few limitations. Firstly, it is not controlled with a placebo group. However, this is justifiable as involved patients had significant pain, and so it would be unethical to have a placebo group. Secondly, contrast and drug injected have different viscosities and may therefore have different epidural flow characteristics. We assumed the contrast flow to be parallel to the drug solution flow. Thirdly, we did not define the speed of injection. Only one study has reported a positive correlation between speed of injection and cranial spread of blockade. Injections performed at a rate of 1.2 ml/s using a Tuohy needle, resulted in a 4 segments greater spread of sensory blockade compared to an injection at a rate of 0.24 ml performed using an epidural catheter (18). In contrast, the same number of dermatomes blocked after 15 min of a rapid injection of mepivacaine 8 ml over 8 seconds versus 160 seconds (19). We did not use an infusion pump and high pressure tubing to control the speed of injection fearing that this would add another source of infection. Lastly, the number of patients analyzed were not the same in each groups
7 Effect of Volume on Efficacy of Epidural Steroids Conclusion To conclude, our study showed no significant dif- ference in pain relief on increasing the volume of drug in midline interlaminar approach. References 1. Wilkinson IM, Cohen SP. Epidural steroid injections. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2012; 16: Wilkinson I, Cohen SP. Epidural steroids for spinal pain and radiculopathy: A narrative, evidence-based review. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 2013; 26: Visser WA, Lee RA, Gielen MJ. Factors affecting the distribution of neural blockade by local anesthetics in epidural anaesthesia and a comparison of lumbar versus thoracic epidural anaesthesia. Anesth Analg 2008; 107: Lee SE, Joe HB, Park JH, Yi IK, Choi YH, Han KR. Distribution range of cervical interlaminar epidural injections: A comparative study with 2.5 ml, 5 ml, and 10 ml of contrast. Pain Physician 2013; 16: Chun EH, Park HS. Effect of high-volume injectate in lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injections: A randomized, active control trial. Pain Physician 2015; 18: Racz GB, Day MR, Heavner JE, Scott J. Lysis of epidural adhesions: The Racz technique. In: Waldman SD, editor. Pain Management. 2nd ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier Saunders; pp Lee JH, Moon J, Lee SH. Comparison of effectiveness according to different approaches of epidural steroid injection in lumbosacral herniated disk and spinal stenosis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil 2009; 22: Lee F, Jamison DE, Hurley R Cohen SP. Epidural lysis of adhesions. Korean J Pain 2014; 27: Rabinovitch DL, Peliowski A, Furlan AD. Influence of lumbar epidural injection volume on pain relief for radicular leg pain and/or low back pain. Spine J 2009; 9: Kim KM, Kim HS, Choi KH, Ahn WS. Cephalic spreading levels after volumetric caudal epidural injections in chronic low back pain. J Korean Med Sci 2001; 16: Kim YC, Lim YJ, Lee SC. Spreading pattern of epidurally administered contrast medium in rabbits. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1998; 42: Ackerman WE 3rd, Ahmad M. The efficacy of lumbar epidural steroid injections in patients with lumbar disc herniations. Anesth Analg 2007; 104: Carette S, Leclaire R, Marcoux S, Morin F, Blaise GA, St-Pierre A, Truchon R, Parent F, Levésque J, Bergeron V, Montminy P, Blanchette C. Epidural corticosteroid injections for sciatica due to herniated nucleus pulposus. N Engl J Med 1997; 336: Furman MB, Kothari G, Parikh, Anderson JG, Khawaja A.. Efficacy of fluoroscopically guided, contrast-enhanced lumbosacral interlaminar epidural steroid injections: A pilot study. Pain Med 2010; 11: Kim D, Brown J. Efficacy and safety of lumbar epidural dexamethasone versus methylprednisolone in the treatment of lumbar radiculopathy: A comparison of soluble versus particulate steroids. Clin J Pain 2011; 27: Makkar JK, Singh PM, Jain D Goudra B. Particulate vs non-particulate steroids for transforaminal epidural steroid injections: Systematic review and metaanalysis of the current literature. Pain Physician 2016; 19: Rathmell JP, Benzon HT, Dreyfuss P, Huntoon M, Wallace M, Baker R, Riew KD,Rosenquist RW, Aprill C, Rost NS, Buvanendran A, Kreiner DS, Bogduk N, Fourney DR, Fraifeld E, Horn S, Stone J, Vorenkamp K, Lawler G, Summers J, Kloth D,O Brien D Jr, Tutton S. Safeguards to prevent neurologic complications after epidural steroid injections: Consensus opinions from a multidisciplinary working group and national organizations. Anesthesiolog 2015; 122: Omote K, Namiki A, Iwasaki H. Epidural administration and analgesic spread: Comparison of injection with catheters and needles. J Anesth 1992; 6: Kanai A, Suzuki A, Hoka S. Rapid injection of epidural mepivacaine speeds the onset of nerve blockade. Can J Anaesth 2005; 52:
8
Won Kyoung Kwon, 1 Ah Na Kim, 2 Pil Moo Lee, 1 Cheol Hwan Park, 1 and Jae Hun Kim Background. 2. Materials and Methods
 Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 4158291, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4158291 Clinical Study Needle Tip Position and Bevel Direction Have No Effect in the Fluoroscopic Epidural
Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 4158291, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4158291 Clinical Study Needle Tip Position and Bevel Direction Have No Effect in the Fluoroscopic Epidural
Behnam Hosseini, Mohammad Hossein Ataei, Sirous Momenzadeh, Reza Jalili Khoshnood, Davood Ommi
 Original Article The comparison between steroid and hypertonic saline 10% with steroid in transforaminal epidural injection in patients with unilateral foraminal stenosis Behnam Hosseini, Mohammad Hossein
Original Article The comparison between steroid and hypertonic saline 10% with steroid in transforaminal epidural injection in patients with unilateral foraminal stenosis Behnam Hosseini, Mohammad Hossein
Effective Date: 1/1/2019 Section: MED Policy No: 391 Medical Policy Committee Approved Date: 6/17; 12/18
 Effective Date: 1/1/2019 Section: MED Policy No: 391 Medical Policy Committee Approved Date: 6/17; 12/18 1/1/2019 Medical Officer Date APPLIES TO: Medicare Only See Policy CPT/HCPCS CODE section below
Effective Date: 1/1/2019 Section: MED Policy No: 391 Medical Policy Committee Approved Date: 6/17; 12/18 1/1/2019 Medical Officer Date APPLIES TO: Medicare Only See Policy CPT/HCPCS CODE section below
Is Dexamethasone Epidural Injection Effective in Relieving Radicular Pain in an Adult Population?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 Is Dexamethasone Epidural Injection Effective
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 Is Dexamethasone Epidural Injection Effective
d EFFECTIVE DATE: POLICY LAST UPDATED:
 Medical Coverage Policy Epidural Injections for Pain Management d EFFECTIVE DATE: 04 01 2018 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 03 20 2018 OVERVIEW Epidural injections are generally performed to treat pain arising from
Medical Coverage Policy Epidural Injections for Pain Management d EFFECTIVE DATE: 04 01 2018 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 03 20 2018 OVERVIEW Epidural injections are generally performed to treat pain arising from
FDA Warnings and Safe Use Initiatives
 CDI Quality Institute Epidural Steroid Injection Guideline Thomas Gilbert, M.D., M.P.P., Damon Spitz, M.D., Blake Johnson, M.D., Kurt Schellhas, M.D. 6/8/15 working draft Over the last 15 years it has
CDI Quality Institute Epidural Steroid Injection Guideline Thomas Gilbert, M.D., M.P.P., Damon Spitz, M.D., Blake Johnson, M.D., Kurt Schellhas, M.D. 6/8/15 working draft Over the last 15 years it has
British Pain Society/Faculty of Pain Medicine (RCA) Consensus Statement on the use of Corticosteroids for Neuraxial Procedures in the UK.
 British Pain Society/Faculty of Pain Medicine (RCA) Consensus Statement on the use of Corticosteroids for Neuraxial Procedures in the UK. There has been international debate relating to the use of corticosteroids
British Pain Society/Faculty of Pain Medicine (RCA) Consensus Statement on the use of Corticosteroids for Neuraxial Procedures in the UK. There has been international debate relating to the use of corticosteroids
Evidence based Practice Changes Spinal Injections
 Evidence based Practice Changes Spinal Injections Kathryn Mueller, MD, MPH, FACOEM Professor, School of Public Health & Department of Physiatry - University of Colorado President - American College of
Evidence based Practice Changes Spinal Injections Kathryn Mueller, MD, MPH, FACOEM Professor, School of Public Health & Department of Physiatry - University of Colorado President - American College of
Epidural Steroid Injections for Back Pain
 Epidural Steroid Injections for Back Pain Policy Number: 2.01.94 Last Review: 12/2018 Origination: 12/2014 Next Review: 12/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage
Epidural Steroid Injections for Back Pain Policy Number: 2.01.94 Last Review: 12/2018 Origination: 12/2014 Next Review: 12/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage
Optimal Angle of Contralateral Oblique View in Cervical Interlaminar Epidural Injection Depending on the Needle Tip Position
 Pain Physician 2017; 20:E169-E175 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Study Optimal Angle of Contralateral Oblique View in Cervical Interlaminar Epidural Injection Depending on the Needle Tip Position Jun Young
Pain Physician 2017; 20:E169-E175 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Study Optimal Angle of Contralateral Oblique View in Cervical Interlaminar Epidural Injection Depending on the Needle Tip Position Jun Young
Comparative Efficacy of Levobupivacaine and Ropivacaine for Epidural Block in Outpatients with Degenerative Spinal Disease
 Pain Physician 2014; 17:525-529 ISSN 1533-3159 Prospective Trial Comparative Efficacy of Levobupivacaine and Ropivacaine for Epidural Block in Outpatients with Degenerative Spinal Disease Takashi Egashira,
Pain Physician 2014; 17:525-529 ISSN 1533-3159 Prospective Trial Comparative Efficacy of Levobupivacaine and Ropivacaine for Epidural Block in Outpatients with Degenerative Spinal Disease Takashi Egashira,
For purposes of this policy, a session is defined as all epidural or spinal procedures performed on a single calendar day.
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines LUMBAR EPIDURAL INJECTIONS (Lumbar/Sacral Interlaminar Epidural) (Lumbar/Sacral Transforaminal Epidural) Original Date: October 2015 Page 1 of 5 FOR
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines LUMBAR EPIDURAL INJECTIONS (Lumbar/Sacral Interlaminar Epidural) (Lumbar/Sacral Transforaminal Epidural) Original Date: October 2015 Page 1 of 5 FOR
Follow this and additional works at: Part of the Musculoskeletal Diseases Commons
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2016 Do Epidural Injections With Local Anesthetic
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2016 Do Epidural Injections With Local Anesthetic
Outcomes of Epidural Neuroplasty to Treat Lumbar Discogenic Pain- One-Year Follow-Up
 Chinese J. Pain 2009;19(1):08~16 Outcomes of Epidural Neuroplasty to Treat Lumbar Discogenic Pain- One-Year Follow-Up 1,4 3 2 2 1,4 Li Wei, Kung-Shing Lee, Man-Kit Siu, Yu-Ting Tai, Jia-Wei Lin, 1,4 1,4
Chinese J. Pain 2009;19(1):08~16 Outcomes of Epidural Neuroplasty to Treat Lumbar Discogenic Pain- One-Year Follow-Up 1,4 3 2 2 1,4 Li Wei, Kung-Shing Lee, Man-Kit Siu, Yu-Ting Tai, Jia-Wei Lin, 1,4 1,4
SPINE SECTION. Design. Prospective clinical study.
 bs_bs_banner Pain Medicine 2014; 15: 379 385 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. SPINE SECTION Original Research Article Caudal vs Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injections as Short-Term (6 Months) Pain Relief in
bs_bs_banner Pain Medicine 2014; 15: 379 385 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. SPINE SECTION Original Research Article Caudal vs Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injections as Short-Term (6 Months) Pain Relief in
The Correlation between Caudal Epidurogram and Low Back Pain
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2012 January; Vol. 25, No. 1: 22-27 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2012.25.1.22 The Correlation between Caudal Epidurogram and Low Back Pain
Original Article Korean J Pain 2012 January; Vol. 25, No. 1: 22-27 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2012.25.1.22 The Correlation between Caudal Epidurogram and Low Back Pain
Medical Affairs Policy
 Medical Affairs Policy Service: Back Pain Procedures-Epidural Injection (Caudal Epidural, Selective Nerve Root Block, Interlaminar, Transforaminal, Translaminar Epidural Injection) PUM 250-0015-1706 Medical
Medical Affairs Policy Service: Back Pain Procedures-Epidural Injection (Caudal Epidural, Selective Nerve Root Block, Interlaminar, Transforaminal, Translaminar Epidural Injection) PUM 250-0015-1706 Medical
Contractor Information. LCD Information. FUTURE Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Lumbar Epidural Injections (L33836)
 FUTURE Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Lumbar Epidural Injections (L33836) Please note: Future Effective Date. Contractor Information Contractor Name Noridian Healthcare Solutions, LLC opens in new
FUTURE Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Lumbar Epidural Injections (L33836) Please note: Future Effective Date. Contractor Information Contractor Name Noridian Healthcare Solutions, LLC opens in new
See Policy CPT/HCPCS CODE section below for any prior authorization requirements
 Effective Date: 7/1/2018 Section: MED Policy No: 123 Medical Officer 7/1/18 Date Technology Assessment Committee Approved Date: 10/10; 12/15 Medical Policy Committee Approved Date: 8/94; 7/96; 8/97; 4/98;
Effective Date: 7/1/2018 Section: MED Policy No: 123 Medical Officer 7/1/18 Date Technology Assessment Committee Approved Date: 10/10; 12/15 Medical Policy Committee Approved Date: 8/94; 7/96; 8/97; 4/98;
Concordant Provocation as a Prognostic Indicator During Interlaminar Lumbosacral Epidural Steroid Injections
 Pain Physician 2014; 17:247-253 ISSN 1533-3159 Randomized Trial Concordant Provocation as a Prognostic Indicator During Interlaminar Lumbosacral Epidural Steroid Injections Alexander H. Sinofsky, MD 1,
Pain Physician 2014; 17:247-253 ISSN 1533-3159 Randomized Trial Concordant Provocation as a Prognostic Indicator During Interlaminar Lumbosacral Epidural Steroid Injections Alexander H. Sinofsky, MD 1,
Nonsurgical Interventional Treatments for Spinal Pain Management
 Nonsurgical Interventional Treatments for Spinal Pain Management I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for nonsurgical interventional treatment for subacute and chronic spinal pain
Nonsurgical Interventional Treatments for Spinal Pain Management I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for nonsurgical interventional treatment for subacute and chronic spinal pain
MEDICAL HISTORY CHIRO PHYSICAL
 Overview of Spinal Injection Procedures Blake A. Johnson, MD, FACR 1 PATIENT MANAGEMENT EVALUATION TREATMENT P.T. MEDICAL CHIRO S SURGICAL Effective treatment requires a precise diagnosis! HISTORY PHYSICAL
Overview of Spinal Injection Procedures Blake A. Johnson, MD, FACR 1 PATIENT MANAGEMENT EVALUATION TREATMENT P.T. MEDICAL CHIRO S SURGICAL Effective treatment requires a precise diagnosis! HISTORY PHYSICAL
Spinal and Trigger Point Injections
 Spinal and Trigger Point Injections I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for nonsurgical interventional treatment for subacute and chronic spinal pain when determined to be medically
Spinal and Trigger Point Injections I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for nonsurgical interventional treatment for subacute and chronic spinal pain when determined to be medically
Transforaminal epidural steroid injection (TFESI) has gained
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Dexamethasone A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Dose-Response Trial Farshad M. Ahadian, MD,*Þ Kai McGreevy, MD,þ and Gerhard Schulteis, PhD* Background
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Dexamethasone A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Dose-Response Trial Farshad M. Ahadian, MD,*Þ Kai McGreevy, MD,þ and Gerhard Schulteis, PhD* Background
Clinical Study. Pain Physician 2018; 21:E181-E186 ISSN Younghoon Jeon, MD, PhD 1 and Saeyoung Kim, MD, PhD 2
 Pain Physician 2018; 21:E181-E186 ISSN 2150-1149 Clinical Study Detection of Intravascular Injection During Cervical Transforaminal Epidural Injection: A Comparison of Digital Subtraction Angiography and
Pain Physician 2018; 21:E181-E186 ISSN 2150-1149 Clinical Study Detection of Intravascular Injection During Cervical Transforaminal Epidural Injection: A Comparison of Digital Subtraction Angiography and
Technical Note NEEDLE TIP DEPTH ASSESSMENT ON FORAMINAL OBLIQUE FLUOROSCOPIC VIEWS DURING CERVICAL RADIOFREQUENCY NEUROTOMY.
 Technical Note Interventional Pain Management Reports ISSN 2575-9841 Volume 2, Number 4, pp127-131 2018, American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians NEEDLE TIP DEPTH ASSESSMENT ON FORAMINAL OBLIQUE
Technical Note Interventional Pain Management Reports ISSN 2575-9841 Volume 2, Number 4, pp127-131 2018, American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians NEEDLE TIP DEPTH ASSESSMENT ON FORAMINAL OBLIQUE
Effect of Cervical Interlaminar Epidural Steroid Injection: Analysis According to the Neck Pain Patterns and MRI Findings
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2016 April; Vol. 29, No. 2: 96-102 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2016.29.2.96 Effect of Cervical Interlaminar Epidural Steroid Injection:
Original Article Korean J Pain 2016 April; Vol. 29, No. 2: 96-102 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2016.29.2.96 Effect of Cervical Interlaminar Epidural Steroid Injection:
Medical Policy. MP Epidural Steroid Injections for Neck or Back Pain
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.94 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 7.01.87 Artificial Intervertebral Disc: Lumbar Spine 7.01.108 Artificial
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.94 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 7.01.87 Artificial Intervertebral Disc: Lumbar Spine 7.01.108 Artificial
Fluoroscopically-Guided Injections to Treat Kissing Spine Disease
 Pain Physician 2008; 11:549-554 ISSN 1533-3159 Case Report Fluoroscopically-Guided Injections to Treat Kissing Spine Disease Timothy J. Lamer, MD 1, Jeffrey M. Tiede, MD 2 and Douglas S. Fenton, MD 3 From:
Pain Physician 2008; 11:549-554 ISSN 1533-3159 Case Report Fluoroscopically-Guided Injections to Treat Kissing Spine Disease Timothy J. Lamer, MD 1, Jeffrey M. Tiede, MD 2 and Douglas S. Fenton, MD 3 From:
The goal of this article is to describe the. Alternative Approach To Needle Placement In Spinal Cord Stimulator Trial/Implantation.
 Pain Physician 2011; 14:45-53 ISSN 1533-3159 Technique Alternative Approach To Needle Placement In Spinal Cord Stimulator Trial/Implantation Jie Zhu, MD 1, Frank Falco, MD 1,2, C. Obi Onyewu, MD 1, Youssef
Pain Physician 2011; 14:45-53 ISSN 1533-3159 Technique Alternative Approach To Needle Placement In Spinal Cord Stimulator Trial/Implantation Jie Zhu, MD 1, Frank Falco, MD 1,2, C. Obi Onyewu, MD 1, Youssef
Clinical Policy Title: Spine pain epidural steroid injections
 Clinical Policy Title: Spine pain epidural steroid injections Clinical Policy Number: 03.03.04 Effective Date: March 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: January 10, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: June 5, 2018
Clinical Policy Title: Spine pain epidural steroid injections Clinical Policy Number: 03.03.04 Effective Date: March 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: January 10, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: June 5, 2018
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Epidural Steroid Injections for Back Pain File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: epidural_steroid_injections_for_back_pain 2/2016 4/2017 4/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Epidural Steroid Injections for Back Pain File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: epidural_steroid_injections_for_back_pain 2/2016 4/2017 4/2018
Confirmation with Epidurogram Necessary?
 Use of Fluoroscopy for Interlaminar Lumbar Epidural Injection: Is Confirmation with Epidurogram Necessary? Saeid Alemo, MD Department of Neurosurgery,Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia,Pennsylvania
Use of Fluoroscopy for Interlaminar Lumbar Epidural Injection: Is Confirmation with Epidurogram Necessary? Saeid Alemo, MD Department of Neurosurgery,Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia,Pennsylvania
PAIN MANAGEMENT CODES PRIOR AUTHORIZATION REQUIRED THROUGH EVICORE HEALTHCARE
 PAIN MANAGEMENT CODES PRIOR AUTHORIZATION REQUIRED THROUGH EVICORE HEALTHCARE The following CPT/HCPCS codes for pain management require prior authorization through evicore healthcare. In order to request
PAIN MANAGEMENT CODES PRIOR AUTHORIZATION REQUIRED THROUGH EVICORE HEALTHCARE The following CPT/HCPCS codes for pain management require prior authorization through evicore healthcare. In order to request
EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN
 EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN UnitedHealthcare Oxford Clinical Policy Policy Number: PAIN 019.21 T2 Effective Date: October 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
EPIDURAL STEROID AND FACET INJECTIONS FOR SPINAL PAIN UnitedHealthcare Oxford Clinical Policy Policy Number: PAIN 019.21 T2 Effective Date: October 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
DRAFT as posted for public comment 11/8/2016 to 8 a.m. 12/9/2016. HERC Coverage Guidance
 HEALTH EVIDENCE REVIEW COMMISSION (HERC) COVERAGE GUIDANCE: LOW BACK PAIN - CORTICOSTEROID INJECTIONS HERC Coverage Guidance Corticosteroid injections (including epidural, facet joint, medial branch, and
HEALTH EVIDENCE REVIEW COMMISSION (HERC) COVERAGE GUIDANCE: LOW BACK PAIN - CORTICOSTEROID INJECTIONS HERC Coverage Guidance Corticosteroid injections (including epidural, facet joint, medial branch, and
Outcome of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection According to the Severity of Lumbar Foraminal Spinal Stenosis
 Pain Physician 2018; 21:67-72 ISSN 1533-3159 Prospective Observational Study Outcome of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection According to the Severity of Lumbar Foraminal Spinal Stenosis Min Cheol
Pain Physician 2018; 21:67-72 ISSN 1533-3159 Prospective Observational Study Outcome of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection According to the Severity of Lumbar Foraminal Spinal Stenosis Min Cheol
22110 vertebral segment; cervical vertebral segment; thoracic vertebral segment; lumbar
 The following codes are authorized by Palladian Health for applicable product lines. Visit palladianhealth.com to request authorization and to access guidelines. Palladian Musculoskeletal Program Codes
The following codes are authorized by Palladian Health for applicable product lines. Visit palladianhealth.com to request authorization and to access guidelines. Palladian Musculoskeletal Program Codes
CLINICAL GUIDELINES. CMM-207: Epidural Adhesiolysis. Version Effective February 15, 2019
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES CMM-207: Version 1.0.2019 Effective February 15, 2019 Clinical guidelines for medical necessity review of speech therapy services. CMM-207: CMM-207.1: Definition 3 CMM-207.2: General
CLINICAL GUIDELINES CMM-207: Version 1.0.2019 Effective February 15, 2019 Clinical guidelines for medical necessity review of speech therapy services. CMM-207: CMM-207.1: Definition 3 CMM-207.2: General
Lumbar Disc Prolapse. Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan. Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon
 Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Epidural Analgesia in Labor - Whats s New
 Epidural Analgesia in Labor - Whats s New Wichelewski Josef 821 Selective neural blockade has many clinical applications in medicine but nowhere has its use been so well accepted than in the field of Obstetrics.
Epidural Analgesia in Labor - Whats s New Wichelewski Josef 821 Selective neural blockade has many clinical applications in medicine but nowhere has its use been so well accepted than in the field of Obstetrics.
Radiculopathy and lumbar pain icd 10 epidural injection
 Radiculopathy and lumbar pain icd 10 epidural injection The Borg System is 100 % Radiculopathy and lumbar pain icd 10 epidural injection 24-5-2016. 16 Intervertebral disc disorder with radiculopathy, lumbar
Radiculopathy and lumbar pain icd 10 epidural injection The Borg System is 100 % Radiculopathy and lumbar pain icd 10 epidural injection 24-5-2016. 16 Intervertebral disc disorder with radiculopathy, lumbar
Clinical Policy: Caudal or Interlaminar Epidural Steroid Injections
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: PA.CP.MP.164 Effective Date: 09/18 Last Review Date: 09/18 Coding Implications Revision Log Description Epidural steroid injections have been used for pain control in
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: PA.CP.MP.164 Effective Date: 09/18 Last Review Date: 09/18 Coding Implications Revision Log Description Epidural steroid injections have been used for pain control in
Clinical Policy: Selective Nerve Root Blocks and Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injections
 Clinical Policy: Selective Nerve Root Blocks and Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injections Reference Number: PA.CP.MP.165 Effective Date: 09/18 Last Review Date: 09/18 Coding Implications Revision Log
Clinical Policy: Selective Nerve Root Blocks and Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injections Reference Number: PA.CP.MP.165 Effective Date: 09/18 Last Review Date: 09/18 Coding Implications Revision Log
Improving the safety of transforaminal epidural steroid injections in the treatment of cervical radiculopathy.
 TRANSFORAMINAL NEEDLES Joseph Eldor, MD Pain Physician. 2011 May-Jun;14(3):285-93. Improving the safety of transforaminal epidural steroid injections in the treatment of cervical radiculopathy. Kloth DS,
TRANSFORAMINAL NEEDLES Joseph Eldor, MD Pain Physician. 2011 May-Jun;14(3):285-93. Improving the safety of transforaminal epidural steroid injections in the treatment of cervical radiculopathy. Kloth DS,
Background of Epidural Steroid Injections: Where Should We Go From Here?
 Background of Epidural Steroid Injections: Where Should We Go From Here? Ameet Nagpal, MD, MS, MEd Assistant Professor/Clinical, Department of Anesthesiology University of Texas Health Science Center at
Background of Epidural Steroid Injections: Where Should We Go From Here? Ameet Nagpal, MD, MS, MEd Assistant Professor/Clinical, Department of Anesthesiology University of Texas Health Science Center at
Vijay Singh, M.D Roosevelt Rd., Niagara, WI 54151
 Publications and Book Chapters Vijay Singh, M.D. 1601 Roosevelt Rd., Niagara, WI 54151 PUBLICATIONS Jul-Aug 2012 Jul-Aug 2012 Jul-Aug 2012 Jul-Aug 2012 Jul-Aug 2012 July 2012 July 2012 May-Jun 2012 May-Jun
Publications and Book Chapters Vijay Singh, M.D. 1601 Roosevelt Rd., Niagara, WI 54151 PUBLICATIONS Jul-Aug 2012 Jul-Aug 2012 Jul-Aug 2012 Jul-Aug 2012 Jul-Aug 2012 July 2012 July 2012 May-Jun 2012 May-Jun
Lumbar Retrodiscal Transforaminal Injection
 Pain Physician 2007; 10:501-510 ISSN 1533-3159 Technical Update Lumbar Retrodiscal Transforaminal Injection Joseph F. Jasper, MD From: Advanced Pain Medicine Physicians, Tacoma, WA. Dr. Jasper is Medical
Pain Physician 2007; 10:501-510 ISSN 1533-3159 Technical Update Lumbar Retrodiscal Transforaminal Injection Joseph F. Jasper, MD From: Advanced Pain Medicine Physicians, Tacoma, WA. Dr. Jasper is Medical
Clinical Policy Title: Spine pain epidural steroid injections
 Clinical Policy Title: Spine pain epidural steroid injections Clinical Policy Number: 03.03.04 Effective Date: March 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: January 10, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: July 20, 2017
Clinical Policy Title: Spine pain epidural steroid injections Clinical Policy Number: 03.03.04 Effective Date: March 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: January 10, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: July 20, 2017
EFFECTIVENESS OF ROOT BLOCK AND RADIOFREQUENCY IN PROLAPSE INTERVERTEBRAL DISC AND LUMBAR CANAL STENOSIS
 Indian J.Sci.Res. 4(2) : 205-209, 2013 ISSN : 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN : 2250-0138 (Online) EFFECTIVENESS OF ROOT BLOCK AND RADIOFREQUENCY IN PROLAPSE INTERVERTEBRAL DISC AND LUMBAR CANAL STENOSIS a1 b c
Indian J.Sci.Res. 4(2) : 205-209, 2013 ISSN : 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN : 2250-0138 (Online) EFFECTIVENESS OF ROOT BLOCK AND RADIOFREQUENCY IN PROLAPSE INTERVERTEBRAL DISC AND LUMBAR CANAL STENOSIS a1 b c
Lumbar epidural steroids injections have been a well
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy and Safety of Lumbar Epidural Dexamethasone Versus Methylprednisolone in the Treatment of Lumbar Radiculopathy A Comparison of Soluble Versus Particulate Steroids David Kim, MD
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy and Safety of Lumbar Epidural Dexamethasone Versus Methylprednisolone in the Treatment of Lumbar Radiculopathy A Comparison of Soluble Versus Particulate Steroids David Kim, MD
Distribution of Bupivacaine in Epidural Space
 Original Article Distribution of Bupivacaine in Epidural Space Hamid Haji Gholam Saryazdi 1, Gholamreza khalili 1, Reihanak Talakoub 1*, Masoud Shahbazi 1, Saeed Abbasi 1 Abstract Background: There is
Original Article Distribution of Bupivacaine in Epidural Space Hamid Haji Gholam Saryazdi 1, Gholamreza khalili 1, Reihanak Talakoub 1*, Masoud Shahbazi 1, Saeed Abbasi 1 Abstract Background: There is
HELPING THE OLDER ADULT PATIENT MANAGE CHRONIC PAIN: INTERVENTIONAL HIGH TECH INJECTIONS
 HELPING THE OLDER ADULT PATIENT MANAGE CHRONIC PAIN: INTERVENTIONAL HIGH TECH INJECTIONS Lawrence M. Kutz, DO The CORE Institute Learning Objectives: Explain to patients different potential treatment options
HELPING THE OLDER ADULT PATIENT MANAGE CHRONIC PAIN: INTERVENTIONAL HIGH TECH INJECTIONS Lawrence M. Kutz, DO The CORE Institute Learning Objectives: Explain to patients different potential treatment options
This supplement contains the following items:
 This supplement contains the following items: 1. Original protocol, final protocol, summary of changes 2. Original statistical analysis plan, final statistical analysis plan, summary of changes Original
This supplement contains the following items: 1. Original protocol, final protocol, summary of changes 2. Original statistical analysis plan, final statistical analysis plan, summary of changes Original
Contractor Information. Proposed/Draft LCD Information
 PROPOSED/DRAFT Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Surgery: Epidural Steroid Injections (DL34364) Please note: This is a Proposed/Draft policy. Proposed/Draft LCDs are works in progress that are available
PROPOSED/DRAFT Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Surgery: Epidural Steroid Injections (DL34364) Please note: This is a Proposed/Draft policy. Proposed/Draft LCDs are works in progress that are available
Variation In The Method Of Caudal Epidural Injection- A Regional Survey
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery Volume 5 Number 2 Variation In The Method Of Caudal Epidural Injection- A Regional Survey S Haque., J Gaskin., A Uguwoke, S Karmani Citation S Haque., J
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery Volume 5 Number 2 Variation In The Method Of Caudal Epidural Injection- A Regional Survey S Haque., J Gaskin., A Uguwoke, S Karmani Citation S Haque., J
Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections
 A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
Spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 06
 What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
Comparison of Epidural Methylprednisolone, Bupivacaine and Normal Saline Injection in Chronic Low Back Pain Due to Discal Hernia
 http://www.cjmb.org Open Access Original Article Crescent Journal of Medical and Biological Sciences Vol. 5, No., January 8, 57 6 eissn 48-9696 Comparison of Epidural Methylprednisolone, Bupivacaine and
http://www.cjmb.org Open Access Original Article Crescent Journal of Medical and Biological Sciences Vol. 5, No., January 8, 57 6 eissn 48-9696 Comparison of Epidural Methylprednisolone, Bupivacaine and
SpineFAQs. Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment
 SpineFAQs Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Neck pain is a common reason people visit their doctor. Neck pain typically doesn't start from a single injury. Instead, the problem usually develops over time
SpineFAQs Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Neck pain is a common reason people visit their doctor. Neck pain typically doesn't start from a single injury. Instead, the problem usually develops over time
Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at (sent 5/9/17) 1
 Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent 5/9/17) 1 Management of Lumbar Radiculopathy Associated with an Extruded L4 L5 disc and concurrent L5 S1 Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis
Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent 5/9/17) 1 Management of Lumbar Radiculopathy Associated with an Extruded L4 L5 disc and concurrent L5 S1 Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis
Transforaminal Endoscopic Decompression for a Giant Epidural Gas-Containing Pseudocyst: A Case Report and Literature Review
 Pain Physician 2017; 20:E445-E449 ISSN 2150-1149 Literature Review Transforaminal Endoscopic Decompression for a Giant Epidural Gas-Containing Pseudocyst: A Case Report and Literature Review Bin Zhu, MD,
Pain Physician 2017; 20:E445-E449 ISSN 2150-1149 Literature Review Transforaminal Endoscopic Decompression for a Giant Epidural Gas-Containing Pseudocyst: A Case Report and Literature Review Bin Zhu, MD,
Approaches to Low Back Pain
 Approaches to Low Back Pain NECOM/MaAOHN Annual Conference December 4, 2014 Moderator: John W. Burress, MD, MPH, FACOEM Panelists: Mark Crislip, MD Kathryn Mueller, MD, MPH, FACOEM Tony Tannoury, MD Donald
Approaches to Low Back Pain NECOM/MaAOHN Annual Conference December 4, 2014 Moderator: John W. Burress, MD, MPH, FACOEM Panelists: Mark Crislip, MD Kathryn Mueller, MD, MPH, FACOEM Tony Tannoury, MD Donald
Cervical intervertebral disc disease Degenerative diseases F 04
 Cervical intervertebral disc disease Degenerative diseases F 04 How is a herniated cervical intervertebral disc treated? Conservative treatment is generally sufficient for mild symptoms not complicated
Cervical intervertebral disc disease Degenerative diseases F 04 How is a herniated cervical intervertebral disc treated? Conservative treatment is generally sufficient for mild symptoms not complicated
Lumbar spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 08
 What is lumbar spinal canal stenosis? This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, and of the lateral recesses (recesssus laterales) and exit openings (foramina intervertebralia) for the
What is lumbar spinal canal stenosis? This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, and of the lateral recesses (recesssus laterales) and exit openings (foramina intervertebralia) for the
To: Manuel Suarez, M.D. Medical Director Neighborhood Health Plan Management Department 5757 Plaza Dr. Cyprus, CA Mailstop: CA
 To: Manuel Suarez, M.D. Medical Director Neighborhood Health Plan Management Department 5757 Plaza Dr. Cyprus, CA 30630 Mailstop: CA124-01290 Subject: Denial of Cervical Spinal Injection Procedures Dear
To: Manuel Suarez, M.D. Medical Director Neighborhood Health Plan Management Department 5757 Plaza Dr. Cyprus, CA 30630 Mailstop: CA124-01290 Subject: Denial of Cervical Spinal Injection Procedures Dear
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
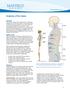 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
PERCUTANEOUS TREATMENT OF DISCOGENIC BACK PAIN WITH A PLASMA WAND
 PERCUTANEOUS TREATMENT OF DISCOGENIC BACK PAIN WITH A PLASMA WAND Caitlin Clark, B.A. and W. Craig Clark, M.D., Ph.D., FAANS, FACS, FICS INTRODUCTION In the United States, low back pain remains the fifth
PERCUTANEOUS TREATMENT OF DISCOGENIC BACK PAIN WITH A PLASMA WAND Caitlin Clark, B.A. and W. Craig Clark, M.D., Ph.D., FAANS, FACS, FICS INTRODUCTION In the United States, low back pain remains the fifth
Efficacy of epidural steroid injections in management of low back pain - a prospective study
 International Journal of Sciences & Applied Research www.ijsar.in Efficacy of epidural steroid injections in management of low back pain - a prospective study Vengamamba Tummala*, Nageswara Rao Lella,
International Journal of Sciences & Applied Research www.ijsar.in Efficacy of epidural steroid injections in management of low back pain - a prospective study Vengamamba Tummala*, Nageswara Rao Lella,
Accuracy of Live Fluoroscopy to Detect Intravascular Injection During Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Injections
 Original Article Korean J Pain Vol. 2, No., 2 pissn 25-959 / eissn 29-569 DOI:.44/kjp.2.2..8 Accuracy of Live Fluoroscopy to Detect Intravascular Injection During Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Injections
Original Article Korean J Pain Vol. 2, No., 2 pissn 25-959 / eissn 29-569 DOI:.44/kjp.2.2..8 Accuracy of Live Fluoroscopy to Detect Intravascular Injection During Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Injections
EFFICACY OF TRANSFORAMINAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION IN LUMBOSACRAL RADICULOPATHY
 EFFICACY OF TRANSFORAMINAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION IN LUMBOSACRAL RADICULOPATHY Saheel Majid 1, Dinesh K. Yadav 2, Suhail M. Vakil 3, Zameer Ali 4, Tauseef A. Bhat 5, Ayaz Ali 6, Shafaqat Rashid 7,
EFFICACY OF TRANSFORAMINAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION IN LUMBOSACRAL RADICULOPATHY Saheel Majid 1, Dinesh K. Yadav 2, Suhail M. Vakil 3, Zameer Ali 4, Tauseef A. Bhat 5, Ayaz Ali 6, Shafaqat Rashid 7,
Comments on Washington State Health Care Authority, HTA Program Key Questions for Spinal Injections
 American Society of Interventional ain hysicians " The Voice of Interventional ain Management " 81 Lakeview Drive, aducah, KY 42001 Tel.: (270) 554-9412; Fax : (270) 554-8987 E-mail:asipp@asipp.org August
American Society of Interventional ain hysicians " The Voice of Interventional ain Management " 81 Lakeview Drive, aducah, KY 42001 Tel.: (270) 554-9412; Fax : (270) 554-8987 E-mail:asipp@asipp.org August
Motor Weakness after Caudal Epidural Injection Using the Air-acceptance Test
 Case Report Korean J Pain 2013 July; Vol. 26, No. 3: 286-290 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.3.286 Motor Weakness after Caudal Epidural Injection Using the Air-acceptance
Case Report Korean J Pain 2013 July; Vol. 26, No. 3: 286-290 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.3.286 Motor Weakness after Caudal Epidural Injection Using the Air-acceptance
The main causes of cervical radiculopathy include degeneration, disc herniation, and spinal instability.
 SpineFAQs Cervical Radiculopathy Neck pain has many causes. Mechanical neck pain comes from injury or inflammation in the soft tissues of the neck. This is much different and less concerning than symptoms
SpineFAQs Cervical Radiculopathy Neck pain has many causes. Mechanical neck pain comes from injury or inflammation in the soft tissues of the neck. This is much different and less concerning than symptoms
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SPINAL INJECTIONS (EPIDURAL AND FACET INJECTIONS) FOR PAIN MANAGEMENT
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SPINAL INJECTIONS (EPIDURAL AND PAGE: 1 OF: 10 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SPINAL INJECTIONS (EPIDURAL AND PAGE: 1 OF: 10 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product
Nuances of Spinal Radiculopathy. James Mallows
 Nuances of Spinal Radiculopathy James Mallows Spinal dermatomes A dermatome is an area of skin that is mainly supplied by a single spinal nerve History of dermatomes Pioneering work by Sherrington (late
Nuances of Spinal Radiculopathy James Mallows Spinal dermatomes A dermatome is an area of skin that is mainly supplied by a single spinal nerve History of dermatomes Pioneering work by Sherrington (late
ESI - Utilization Review Case Presentation
 ESI - Utilization Review Case Presentation Request for ESI Hx & PE 31 y/o F parts warehouse stocker DOI: 2008 MOI: felt tightness in legs and shoulders reaching into a shelf to move a product from one
ESI - Utilization Review Case Presentation Request for ESI Hx & PE 31 y/o F parts warehouse stocker DOI: 2008 MOI: felt tightness in legs and shoulders reaching into a shelf to move a product from one
Therapeutic Exercise And Manual Therapy For Persons With Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Therapeutic Exercise And Manual Therapy For Persons With Lumbar Spinal Stenosis The program consisted of manual therapy twice per week (eg, soft tissue and neural The components of the Boot Camp Program
Therapeutic Exercise And Manual Therapy For Persons With Lumbar Spinal Stenosis The program consisted of manual therapy twice per week (eg, soft tissue and neural The components of the Boot Camp Program
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE/SERVICE/PHARMACEUTICAL
 Subject: Percutaneous Epidural Adhesiolysis for Chronic Low Back Pain (RACZ Procedure) Original Effective Date: 10/12/15 Policy Number: MCP-257 Revision Date(s): Review Date: 12/16/15, 12/14/16, 6/22/17
Subject: Percutaneous Epidural Adhesiolysis for Chronic Low Back Pain (RACZ Procedure) Original Effective Date: 10/12/15 Policy Number: MCP-257 Revision Date(s): Review Date: 12/16/15, 12/14/16, 6/22/17
Guideline Number: NIA_CG_301 Last Revised Date: March 2018 Responsible Department: Clinical Operations
 Magellan Healthcare Clinical guidelines PARAVERTEBRAL FACET JOINT INJECTIONS OR BLOCKS (no U/S) CPT Codes: Cervical Thoracic Region: 64490 (+ 64491, +64492) Lumbar Sacral Region: 64493 (+64494, +64495)
Magellan Healthcare Clinical guidelines PARAVERTEBRAL FACET JOINT INJECTIONS OR BLOCKS (no U/S) CPT Codes: Cervical Thoracic Region: 64490 (+ 64491, +64492) Lumbar Sacral Region: 64493 (+64494, +64495)
Blackburn with Darwen Clinical Commissioning Group and East Lancashire Clinical Commissioning Group. Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare
 Blackburn with Darwen Clinical Commissioning Group and East Lancashire Clinical Commissioning Group Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for Managing Back Pain Spinal /Facet Joint and Epidural
Blackburn with Darwen Clinical Commissioning Group and East Lancashire Clinical Commissioning Group Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for Managing Back Pain Spinal /Facet Joint and Epidural
Phillip Weidner, DO, DABA, BCPM May 20th, 2014
 Phillip Weidner, DO, DABA, BCPM May 20th, 2014 Introduction Comprehensive Pain Management Center Interventional therapies Epidural steroid injections Sacroiliac interventions Facet joint disease Who to
Phillip Weidner, DO, DABA, BCPM May 20th, 2014 Introduction Comprehensive Pain Management Center Interventional therapies Epidural steroid injections Sacroiliac interventions Facet joint disease Who to
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections
 A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections 2778 N. Webb Rd. Wichita, KS 67226 Phone: (316) 631-1600 Fax: (316) 631-1617 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections 2778 N. Webb Rd. Wichita, KS 67226 Phone: (316) 631-1600 Fax: (316) 631-1617 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
Interventional Pain. Judith Dunipace MD Board certified in Anesthesiology, Pain Management and Hospice and Palliative Care
 Interventional Pain Judith Dunipace MD Board certified in Anesthesiology, Pain Management and Hospice and Palliative Care IASP Definition of Pain Pain is an unpleasant sensory or emotional experience associated
Interventional Pain Judith Dunipace MD Board certified in Anesthesiology, Pain Management and Hospice and Palliative Care IASP Definition of Pain Pain is an unpleasant sensory or emotional experience associated
MEDICAL POLICY EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/15/13 REVISED DATE: 07/17/14, 06/18/15, 05/25/16, 05/18/17
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SPINAL INJECTIONS (EPIDURAL AND PAGE: 1 OF: 10 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product,
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SPINAL INJECTIONS (EPIDURAL AND PAGE: 1 OF: 10 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product,
Derya Burcu Hazer 1, Arsal Acarbaş 1, and Hans Eric Rosberg 2
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2018 April; Vol. 31, No. 2: 109-115 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2018.31.2.109 The outcome of epiduroscopy treatment in patients with chronic
Original Article Korean J Pain 2018 April; Vol. 31, No. 2: 109-115 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2018.31.2.109 The outcome of epiduroscopy treatment in patients with chronic
Degenerative Disease of the Spine
 Degenerative Disease of the Spine Introduction: I. Anatomy Talk Overview II. Overview of Disease Processes: A. Spondylosis B. Intervertebral Disc Disease III. Diagnosis IV. Therapy Introduction: Myelopathy
Degenerative Disease of the Spine Introduction: I. Anatomy Talk Overview II. Overview of Disease Processes: A. Spondylosis B. Intervertebral Disc Disease III. Diagnosis IV. Therapy Introduction: Myelopathy
INJECTION PROCEDURES
 INJECTION PROCEDURES GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS AND PREPARATION FOR THE INJECTION In general, injection procedures for the spine and some other parts of the body entail the use of live x- ray known as flouroscopy
INJECTION PROCEDURES GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS AND PREPARATION FOR THE INJECTION In general, injection procedures for the spine and some other parts of the body entail the use of live x- ray known as flouroscopy
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
Effect of epidural corticosteroid injection on magnetic resonance imaging findings
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2017 October; Vol. 30, No. 4: 281-286 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2017.30.4.281 Effect of epidural corticosteroid injection on magnetic resonance
Original Article Korean J Pain 2017 October; Vol. 30, No. 4: 281-286 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2017.30.4.281 Effect of epidural corticosteroid injection on magnetic resonance
A Novel Combination of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy and Epiduroscopic Laser Neural Decompression for Down-migrated Disc Herniation
 Pain Physician 2017; 20:E605-E609 ISSN 2150-1149 Case Report A Novel Combination of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy and Epiduroscopic Laser Neural Decompression for Down-migrated Disc Herniation
Pain Physician 2017; 20:E605-E609 ISSN 2150-1149 Case Report A Novel Combination of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy and Epiduroscopic Laser Neural Decompression for Down-migrated Disc Herniation
Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report
 Fujiwara et al. JA Clinical Reports (2017) 3:2 DOI 10.1186/s40981-016-0073-2 CASE REPORT Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report Open Access
Fujiwara et al. JA Clinical Reports (2017) 3:2 DOI 10.1186/s40981-016-0073-2 CASE REPORT Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report Open Access
Interventional Pain Management
 Origination: 5/21/08 Revised: 10/02/17 Annual Review: 11/02/17 Purpose: To provide interventional pain management clinical coordination criteria for the Medical Department staff to reference when making
Origination: 5/21/08 Revised: 10/02/17 Annual Review: 11/02/17 Purpose: To provide interventional pain management clinical coordination criteria for the Medical Department staff to reference when making
The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural Decompression between FBSS or Not
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2014 January; Vol. 27, No. 1: 63-67 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.63 The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural
Original Article Korean J Pain 2014 January; Vol. 27, No. 1: 63-67 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.63 The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural
Continuous Spinal Anaesthesia
 Continuous Spinal Anaesthesia Ph. Biboulet Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine, Lapeyronie University Hospital, Montpellier France CSA story : 1906 Dean 1944 Tuohy 1991 CSA revisited
Continuous Spinal Anaesthesia Ph. Biboulet Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine, Lapeyronie University Hospital, Montpellier France CSA story : 1906 Dean 1944 Tuohy 1991 CSA revisited
Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression and Fusion
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
