Cases in employees. Cases. Day of onset (July)
|
|
|
- Mariah Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cases in employees Cases Day of onset (July)
2 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors Day of onset (July)
3 Secondary attack rate Cases in household members X 100 Total number of household members
4 Epidemiology: the study of diseases in populations Epidemic: an unusual occurrence (a significant increase in incidence above baseline) Epidemiologist: someone who studies epidemics.
5 An Epidemic of an Unknown Disease Place: the Oakland County, Michigan, Health Department Time: July 1 Problem: acute febrile illness in most of the employees of the health department As an EIS officer at the CDC, you are sent to investigate the outbreak.
6 Incubation periods < 24 hours Staphylococcal food poisoning chemical toxins 1-3 days influenza Shigellosis 1-3 weeks whooping cough psittacosis Mycoplasma pneumonia
7 You and two other EIS officers arrive on the scene and begin work in the building on Saturday, July 6. You continue working through the weekend. On Tuesday evening, all of you become ill with the syndrome. The air conditioning system had been turned off over the weekend and turned on again Monday morning.
8 Secondary Attack Rates High Influenza Measles, mumps, chickenpox Diphtheria Low Meningitis Pneumococcal pneumonia Hansen's Disease
9 Symptom Malaise Myalgia Fever Chills Headache Cough Dizziness Nausea Chest pain Joint pain Sore or dry throat Abdominal pain Confusion Bizarre dreams Irritability Number with symptom % with symptom
10 Bacterial species isolated from water at the base of the evaporative condenser Corynebacterium sp. Bacillus sp. Pseudomonas sp. Flavobacterium sp. Pseudomonas stuzeri Pseudomonas maltophilia Which organism caused the outbreak?
11 Find the defect in the air conditioning system Place smoke bombs in the system, follow the smoke. Place guinea pigs in the system, look for illness. Inspect the system, look for leaks. Culture the water, ducts, etc.
12 Establish the microbial etiology Culture the ill guinea pigs. Test the guinea pigs (real and human) for rises in antibody titers toward likely pathogens. Compare antibody titers in ill and well persons. Freeze down the samples and wait.
13 1976. An outbreak of severe pneumonia among participants in the National Convention of the American Legion, Philadelphia, PA A newly-recognized cause of human disease, Legionella pneumophila, was discovered. Using the correct culture techniques, L. pneumophila was isolated from the guinea pig tissues stored at CDC from the Michigan outbreak. Both the ill employees and EIS officers had significant antibody titers to L. pneumophila.
14 Diseases caused by L. pneumophila Legionnaire's Disease pneumonia, often fatal Pontiac Fever influenza-like illness, rarely fatal The same microbe causes both kinds of disease. The reasons for the differences are still not completely understood.
15 Antibacterial drugs: sites of action β-lactams Vancomycin Erythromycin Aminoglycosides Quinolones Cell wall mrna-ribosome complex DNA (supercoiled)
16 Peptidoglycan M M M M G M G M G peptide crosslink G G G Chains of sugars
17 G G M M G Ala Glu Lys - Ala Ala (- Gly -) 5 - Ala - Ala Glu Lys A peptide cross-link. The arrow shows the bond created by the transpeptidase (penicillin-binding protein). G and M are sugar molecules.
18 Ala - Ala - Lys Gly - Gly - Gly- PENICILLIN
19 G G M M G Ala Glu Lys - Ala Ala (- Gly -) 5 G Ala Glu Lys Ala Ala Vancomycin covers the Ala - Ala at the end of the peptide chain, preventing it from forming the cross-link.
20 Penicillin G S CH3 CH3 C N CH O COOH R - N - CH - CH C β-lactam ring bond cleaved by both transpeptidase and penicillinase
21 Antibiotics and Antibiotic- resistant Bacteria How antibiotics work Penicillins Vancomycin How bacteria become resistant to antibiotics Penicillins Vancomycin How antibiotic resistance spreads Some things we can do
22 Mechanisms of action Inhibit cell wall synthesis Penicillins, vancomycin Inhibit protein synthesis Erythromycins, aminoglycosides Inhibit DNA synthesis sulfonamides, quinolones An effective antimicrobial drug must inhibit or kill the microbe without harming the host. Selectivity.
23 How antibiotics work: 2 examples Beta-lactams Penicillin G Methicillin, nafcillin, cloxacillin Cephalosporins Vancomycin
24 Bacterial resistance to antibiotics Enzymes that destroy the drug Beta-lactamases destroy beta-lactams Altered target site Transpeptidase mutations: MRSA Peptidoglycan mutation: VRE Decreased cell wall permeability Increased antibiotic efflux
25 How antibiotic resistance spreads ("selection pressures") Use of antibiotics in agriculture Livestock, plants Environments with intensive antibiotic use Hospitals, nursing homes Day care centers Unnecessary use in medicine Uncontrolled usage Unnecessary prescribing
26 What we can do Decrease indiscriminate uses of antibiotics Develop better vaccines for preventing otitis media, pneumonia, other infections now treated with antibiotics Improve surveillance worldwide Develop new antimicrobial drugs and promote intelligent usage
Legionnaires Disease Q&A (General) (Source: OSHA) (4/29/10)
 Legionnaires Disease Q&A (General) (Source: OSHA) (4/29/10) Q. What is Legionnaires Disease? A. Legionnaires disease is a common name for one of the several illnesses caused by Legionella bacteria. Legionnaires
Legionnaires Disease Q&A (General) (Source: OSHA) (4/29/10) Q. What is Legionnaires Disease? A. Legionnaires disease is a common name for one of the several illnesses caused by Legionella bacteria. Legionnaires
Bacteria & Viruses. Biology Science Department
 Bacteria & Viruses What do you already know? What are the differences between viruses and bacteria? Are all bacteria harmful? When you get a cold, should you take an antibiotic to help you get better?
Bacteria & Viruses What do you already know? What are the differences between viruses and bacteria? Are all bacteria harmful? When you get a cold, should you take an antibiotic to help you get better?
Antibacterials and Antivirals
 Structure of a Bacterium: Antibacterials and Antivirals Capsule: protective layer made up of proteins, sugars and lipids Cell wall: provides the bacteria with its shape and structure Cell membrane: permeable
Structure of a Bacterium: Antibacterials and Antivirals Capsule: protective layer made up of proteins, sugars and lipids Cell wall: provides the bacteria with its shape and structure Cell membrane: permeable
Communicable Disease & Immunization
 Communicable Disease & Immunization Ingham County Health Surveillance Book 2016 Communicable Disease & Immunization - 1 Communicable Disease & Immunization T he control of communicable disease and immunization,
Communicable Disease & Immunization Ingham County Health Surveillance Book 2016 Communicable Disease & Immunization - 1 Communicable Disease & Immunization T he control of communicable disease and immunization,
Warm Up. What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease?
 Warm Up What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease? Infectious Diseases Chapter 14 Lesson 1: Types of Infectious Disease Infectious Diseases An infectious disease
Warm Up What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease? Infectious Diseases Chapter 14 Lesson 1: Types of Infectious Disease Infectious Diseases An infectious disease
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate
 Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Infection, Detection, Prevention...
 Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Legionnella. You can t t see it but you can catch it. Dr Charmaine Gauci MD, MSc, PhD Head of Disease Surveillance Unit
 Legionnella You can t t see it but you can catch it Dr Charmaine Gauci MD, MSc, PhD Head of Disease Surveillance Unit Legionella infections First documented outbreak name from 221 cases of pneumonia occurred
Legionnella You can t t see it but you can catch it Dr Charmaine Gauci MD, MSc, PhD Head of Disease Surveillance Unit Legionella infections First documented outbreak name from 221 cases of pneumonia occurred
Streptococcus Pneumoniae
 Streptococcus Pneumoniae (Invasive Pneumococcal Disease) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report by mail or by electronic
Streptococcus Pneumoniae (Invasive Pneumococcal Disease) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report by mail or by electronic
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics. Question No. 1 of 10. Question. Feedback. Question
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics No. 1 of 10 1. An effective chemotherapeutic drug should have. (A) Low therapeutic index (B) More toxicity (C) Selective toxicity (D) Mutation inducing properties
Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics No. 1 of 10 1. An effective chemotherapeutic drug should have. (A) Low therapeutic index (B) More toxicity (C) Selective toxicity (D) Mutation inducing properties
Development of C sporins. Beta-lactam antibiotics - Cephalosporins. Second generation C sporins. Targets - PBP s
 Beta-lactam antibiotics - Cephalosporins Development of C sporins Targets - PBP s Activity - Cidal - growing organisms (like the penicillins) Principles of action - Affinity for PBP s Permeability properties
Beta-lactam antibiotics - Cephalosporins Development of C sporins Targets - PBP s Activity - Cidal - growing organisms (like the penicillins) Principles of action - Affinity for PBP s Permeability properties
Kathleen Arrington, RN Kankakee County Health Department
 Kathleen Arrington, RN Kankakee County Health Department Current Pertussis Statistics Year Reported Cases* 2000 7,867 2001 7,580 2002 9,771 2003 11,647 2004 25,827 2005 25,616 2006 15,632 2007 10,454
Kathleen Arrington, RN Kankakee County Health Department Current Pertussis Statistics Year Reported Cases* 2000 7,867 2001 7,580 2002 9,771 2003 11,647 2004 25,827 2005 25,616 2006 15,632 2007 10,454
What is Legionnaires' disease?
 Understanding Legionnaires disease: A Fact Sheet For Workers Organization(s): New York Committee for Occupational Safety and Health Other languages: Spanish Summary Statement: This NYCOSH fact sheet is
Understanding Legionnaires disease: A Fact Sheet For Workers Organization(s): New York Committee for Occupational Safety and Health Other languages: Spanish Summary Statement: This NYCOSH fact sheet is
Presented. April 22nd 1986
 J. LEGIONNAIRES' DISEASE Presented at ALBERTA Public Works, Supply and Services Property Management Division Water Treatment Coordinators' Meeting Edmonton, Alberta April 22nd 1986 by G.F. Yuzwa, P.Eng.
J. LEGIONNAIRES' DISEASE Presented at ALBERTA Public Works, Supply and Services Property Management Division Water Treatment Coordinators' Meeting Edmonton, Alberta April 22nd 1986 by G.F. Yuzwa, P.Eng.
Vaccines for Children
 Vaccines for Children 12 24 old Our goal is to offer your family the best care possible, which includes making sure your child is up to date on all vaccines. DTaP (Diptheria, Tetanus, Pertussis) Vaccine
Vaccines for Children 12 24 old Our goal is to offer your family the best care possible, which includes making sure your child is up to date on all vaccines. DTaP (Diptheria, Tetanus, Pertussis) Vaccine
Infectious Diseases through Viruses. Obj. 3.c. & 3.g.
 Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Overview Existing, Emerging, and Re-Emerging Communicable Diseases
 Overview Existing, Emerging, and Re-Emerging Communicable Diseases Many communicable diseases have existed with us since the beginning of time. Communicable diseases, which are infections we catch from
Overview Existing, Emerging, and Re-Emerging Communicable Diseases Many communicable diseases have existed with us since the beginning of time. Communicable diseases, which are infections we catch from
Issues Abx request. Sneezing w/ post- nasal d/c & redness mucous membranes Throat. Chest px w/ coughing, difficulty breathing
 Week 5 Magic Bullets URTI + Pneumonia Presenting Sx Cough, sore throat & runny nose Aches & pains all over Shivers & fevers Respiratory Viruses Viruses causing flu Influenza A/B/C (orthomyxovirus) Respiratory
Week 5 Magic Bullets URTI + Pneumonia Presenting Sx Cough, sore throat & runny nose Aches & pains all over Shivers & fevers Respiratory Viruses Viruses causing flu Influenza A/B/C (orthomyxovirus) Respiratory
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani
 RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nasopharynx Oropharynx Respiratory Tract Infections
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nasopharynx Oropharynx Respiratory Tract Infections
Local Public Health Department. Communicable diseases Environmental health Chronic diseases Emergency preparedness Special programs
 Susan I. Gerber, MD Local Public Health Department Communicable diseases Environmental health Chronic diseases Emergency preparedness Special programs Public Health Reporting Ground Zero Local government
Susan I. Gerber, MD Local Public Health Department Communicable diseases Environmental health Chronic diseases Emergency preparedness Special programs Public Health Reporting Ground Zero Local government
Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia. Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali
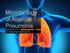 Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali Pneumonia P n e u m o n i a i s a n infection of the lungs that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Atypical! Pneumonia Symptoms. X-ray
Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali Pneumonia P n e u m o n i a i s a n infection of the lungs that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Atypical! Pneumonia Symptoms. X-ray
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Vancomycin. A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci.
 Vancomycin A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci. Used IV in treating endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant
Vancomycin A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci. Used IV in treating endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant
Acute respiratory illness This is a disease that typically affects the airways in the nose and throat (the upper respiratory tract).
 Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
2017 Vaccine Preventable Disease Summary
 2017 Vaccine Preventable Disease Summary Prepared 12251 James Street Holland, MI 49424 www.miottawa.org/healthdata October 2018 2017 Summary of Vaccine Preventable Diseases in Ottawa County This is a detailed
2017 Vaccine Preventable Disease Summary Prepared 12251 James Street Holland, MI 49424 www.miottawa.org/healthdata October 2018 2017 Summary of Vaccine Preventable Diseases in Ottawa County This is a detailed
Pneumococcal Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining around the brain and spinal cord. Most severe cases
 Pneumococcal Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining around the brain and spinal cord. Most severe cases are caused by bacteria. Pneumococcal bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae) are the
Pneumococcal Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining around the brain and spinal cord. Most severe cases are caused by bacteria. Pneumococcal bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae) are the
UNDERSTANDING THE CORRECT ANSWERS immunize.ca
 UNDERSTANDING THE CORRECT ANSWERS Understanding the correct answers Question 1: Vaccination is... (information adapted from Your Child s Best Shot, 3rd edition, page 10) Vaccination (or immunization) is
UNDERSTANDING THE CORRECT ANSWERS Understanding the correct answers Question 1: Vaccination is... (information adapted from Your Child s Best Shot, 3rd edition, page 10) Vaccination (or immunization) is
Immune System Review. 1. State one way white blood cells protect the body from foreign microbes.
 Name Immune System Review Date 1. State one way white blood cells protect the body from foreign microbes. 2. Cells of the immune system are able to respond to the presence of invading organisms because
Name Immune System Review Date 1. State one way white blood cells protect the body from foreign microbes. 2. Cells of the immune system are able to respond to the presence of invading organisms because
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology
 RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Anatomy of the Respiratory System Respiratory Infections Respiratory tract can be divided into: Upper Respiratory Tract (URT): Sinuses Nasopharynx,.
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Anatomy of the Respiratory System Respiratory Infections Respiratory tract can be divided into: Upper Respiratory Tract (URT): Sinuses Nasopharynx,.
Chapter 14. Bugs that Resist Drugs
 Chapter 14 Bugs that Resist Drugs See website Learning Objectives Important Terminology Power point- posted after chapter is completed What happened to Carlos Don, Rebecca Lohsen, Ricky Lannetti? Carlos
Chapter 14 Bugs that Resist Drugs See website Learning Objectives Important Terminology Power point- posted after chapter is completed What happened to Carlos Don, Rebecca Lohsen, Ricky Lannetti? Carlos
Vaccines. Bacteria and Viruses:
 1 Immunity Resistance to or protection against a specific disease; {power to resist infection. Every day, bacteria, viruses and other germs attack our bodies. But we usually don t get sick. That s because
1 Immunity Resistance to or protection against a specific disease; {power to resist infection. Every day, bacteria, viruses and other germs attack our bodies. But we usually don t get sick. That s because
Respiratory tract infections. Krzysztof Buczkowski
 Respiratory tract infections Krzysztof Buczkowski Etiology Viruses Rhinoviruses Adenoviruses Coronaviruses Influenza and Parainfluenza Viruses Respiratory Syncitial Viruses Enteroviruses Etiology Bacteria
Respiratory tract infections Krzysztof Buczkowski Etiology Viruses Rhinoviruses Adenoviruses Coronaviruses Influenza and Parainfluenza Viruses Respiratory Syncitial Viruses Enteroviruses Etiology Bacteria
 Reducing Legionella Risk What is Legionella? Legionella Species Biofilm stable structures and breeding grounds Where does Legionella live? Non-potable Water Shower Aerosol Cooling Tower Aerosol Infectivity
Reducing Legionella Risk What is Legionella? Legionella Species Biofilm stable structures and breeding grounds Where does Legionella live? Non-potable Water Shower Aerosol Cooling Tower Aerosol Infectivity
FACTS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH)
 FACTS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) General Questions About Pertussis What is pertussis? Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person sneezes or coughs
FACTS ABOUT PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH) General Questions About Pertussis What is pertussis? Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a contagious illness that is spread when an infected person sneezes or coughs
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care. Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK
 Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Polio, Hib and Hepatitis B vaccine for babies and children
 Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Polio, Hib and Hepatitis B vaccine for babies and children This leaflet tells you about the DTaP/IPV/Hib/ HepB vaccine, also known as 6 in 1 as it protects against six diseases,
Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Polio, Hib and Hepatitis B vaccine for babies and children This leaflet tells you about the DTaP/IPV/Hib/ HepB vaccine, also known as 6 in 1 as it protects against six diseases,
A. Children born in 1942 B. Children born in 1982 C. Children born in 2000 D. Children born in 2010
 Who do you think received the most immunologic components in vaccines? Development of which vaccine slowed after the invention of antibiotics? A. Children born in 1942 B. Children born in 1982 C. Children
Who do you think received the most immunologic components in vaccines? Development of which vaccine slowed after the invention of antibiotics? A. Children born in 1942 B. Children born in 1982 C. Children
STRUCTURE OF COMMONLY USED PENICILLINS
 PENICILLINS Alice Prince I. CHEMISTRY A basic structure of penicillins consists of a nucleus with three components: a thiazolidine ring, a β-lactam ring and a side chain. The side chain determines, in
PENICILLINS Alice Prince I. CHEMISTRY A basic structure of penicillins consists of a nucleus with three components: a thiazolidine ring, a β-lactam ring and a side chain. The side chain determines, in
Chapter 17. Infectious Diseases
 Chapter 17 Infectious Diseases Lesson 1 What is an infectious disease? Infectious disease Is any disease that is caused by an agent that can be passed from one living thing to another. Disease causing
Chapter 17 Infectious Diseases Lesson 1 What is an infectious disease? Infectious disease Is any disease that is caused by an agent that can be passed from one living thing to another. Disease causing
2016 Vaccine Preventable Disease Summary
 2016 Vaccine Preventable Disease Summary 12251 James Street Holland, MI 49424 www.miottawa.org/healthdata Prepared October 2017 2016 Summary of Vaccine Preventable Diseases (VPDs) Reported to Ottawa County
2016 Vaccine Preventable Disease Summary 12251 James Street Holland, MI 49424 www.miottawa.org/healthdata Prepared October 2017 2016 Summary of Vaccine Preventable Diseases (VPDs) Reported to Ottawa County
Blood Borne Pathogens. November 2010
 Blood Borne Pathogens November 2010 Objectives Meet requirements of OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 OSHA Blood Borne Pathogens Post Test Routes of Transmission Types of Pathogens BSI / PPE Common Diseases
Blood Borne Pathogens November 2010 Objectives Meet requirements of OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 OSHA Blood Borne Pathogens Post Test Routes of Transmission Types of Pathogens BSI / PPE Common Diseases
Medical Interventions- Unit 1 Study Guide (Due Dec. 15 th!)
 Medical Interventions- Unit 1 Study Guide (Due Dec. 15 th!) Name: Lesson 1.1 1. Define medical intervention. What are 3 medical interventions that Sue Smith would have encountered during her infection
Medical Interventions- Unit 1 Study Guide (Due Dec. 15 th!) Name: Lesson 1.1 1. Define medical intervention. What are 3 medical interventions that Sue Smith would have encountered during her infection
Topic 7 - Commonality
 II. Organism Topic 7 - Commonality From Viruses to Bacteria to Genetic Engineering Prebiotic Period Refers to before life Early Earth contained little O 2 O 2 prevents complex molecules Complex organic
II. Organism Topic 7 - Commonality From Viruses to Bacteria to Genetic Engineering Prebiotic Period Refers to before life Early Earth contained little O 2 O 2 prevents complex molecules Complex organic
Influenza Fact Sheet
 What is influenza? Influenza, also known as the flu, is caused by a virus that affects the nose, throat, bronchial airways, and lungs. There are two types of flu that affect humans, types A and B. Influenza
What is influenza? Influenza, also known as the flu, is caused by a virus that affects the nose, throat, bronchial airways, and lungs. There are two types of flu that affect humans, types A and B. Influenza
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Hamed Al Zoubi
 number 8 Done by م ها أبو عجمي ة Corrected by Mamoon Alqtamin Doctor Hamed Al Zoubi The last page includes definitions for the underlined asterisked words *, You can skip Extra notes, Enjoy! A Brief Introduction
number 8 Done by م ها أبو عجمي ة Corrected by Mamoon Alqtamin Doctor Hamed Al Zoubi The last page includes definitions for the underlined asterisked words *, You can skip Extra notes, Enjoy! A Brief Introduction
Influenza can cause: fever, sore throat, cough, headache, chills, muscle aches
 Influenza Vaccine: What You Need to Know From the U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Immunization Program 1. Why get vaccinated? Influenza is
Influenza Vaccine: What You Need to Know From the U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Immunization Program 1. Why get vaccinated? Influenza is
BODY DEFENCES AGAINST DISEASE AND THE ROLE OF VACCINES
 BODY DEFENCES AGAINST DISEASE AND THE ROLE OF VACCINES Topic 3 This topic links in with MICROBES (from unit 1) 1. What are the 3 types of microbes? 2. Which microbe do antibiotics destroy? 3. What microbe
BODY DEFENCES AGAINST DISEASE AND THE ROLE OF VACCINES Topic 3 This topic links in with MICROBES (from unit 1) 1. What are the 3 types of microbes? 2. Which microbe do antibiotics destroy? 3. What microbe
COUNSELING CARDS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS
 www.calcuttakids.org info@calcuttakids.org COUNSELING CARDS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS For Community Health Workers Created by Calcutta Kids, May 2012 COUNSELING POINTS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS Sheet 1 Tuberculosis Sheet
www.calcuttakids.org info@calcuttakids.org COUNSELING CARDS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS For Community Health Workers Created by Calcutta Kids, May 2012 COUNSELING POINTS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS Sheet 1 Tuberculosis Sheet
SPECIFIC DISEASE EXCLUSION GUIDELINES FOR CHILDCARE
 See individual fact sheets for exclusion and other information on the diseases listed below. Bed Bugs Acute Bronchitis (Chest Cold)/Bronchiolitis Campylobacteriosis Until fever is gone (without the use
See individual fact sheets for exclusion and other information on the diseases listed below. Bed Bugs Acute Bronchitis (Chest Cold)/Bronchiolitis Campylobacteriosis Until fever is gone (without the use
VACCINATION. DR.FATIMA ALKHALEDY M.B.Ch.B;F.I.C.M.S/C.M.
 VACCINATION DR.FATIMA ALKHALEDY M.B.Ch.B;F.I.C.M.S/C.M. IMMUNIZATION Immunization is defined as the procedure by which the body is prepared to fight against a specific disease. It is used to induce the
VACCINATION DR.FATIMA ALKHALEDY M.B.Ch.B;F.I.C.M.S/C.M. IMMUNIZATION Immunization is defined as the procedure by which the body is prepared to fight against a specific disease. It is used to induce the
bacteria review 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria?
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria? 5. How do human diseases caused by bacteria and diseases caused by viruses react to antibiotics? A. ribosome B. cytoplasm C. cell
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria? 5. How do human diseases caused by bacteria and diseases caused by viruses react to antibiotics? A. ribosome B. cytoplasm C. cell
2. How might a person find more information about a vaccine? 3. Why should some people not get the MMR vaccine?
 Vaccines & Herd Immunity Text adapted from http://www.vaccines.gov/basics/index.html and http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/body/herd-immunity.html [Retrieved Feb 2015] PART A: INDEPENDENT READING. On your own,
Vaccines & Herd Immunity Text adapted from http://www.vaccines.gov/basics/index.html and http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/body/herd-immunity.html [Retrieved Feb 2015] PART A: INDEPENDENT READING. On your own,
Preventing Legionella Transmission An Environmental Health View
 Preventing Legionella Transmission An Environmental Health View April 25, 2013 Erin Reinsborough Environmental Health Specialist Mission Statement Together with the Halton community, the Health Department
Preventing Legionella Transmission An Environmental Health View April 25, 2013 Erin Reinsborough Environmental Health Specialist Mission Statement Together with the Halton community, the Health Department
Pathogens of the Respiratory System
 Pathogens of the Respiratory System Chapter 21, Pages 531-567 1. Respiratory System Introduction A. Anatomy (Pages 532-534) i. Upper Respiratory Track a. Nasal Hairs b. Paranasal Sinuses c. Nasal Chonchae
Pathogens of the Respiratory System Chapter 21, Pages 531-567 1. Respiratory System Introduction A. Anatomy (Pages 532-534) i. Upper Respiratory Track a. Nasal Hairs b. Paranasal Sinuses c. Nasal Chonchae
gram neg.(semisynthetic) Bacteria Drugs that inhibit cell wall synthesis Drug Action Organisms Comments Spectrum of Action Mycobacterium
 Mickey Dufilho s Drugs and Bugs Revised 10/10/15 Bacteria Drugs that Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis Drug Action Spectrum of Action Comments Spectrum of Action Bacitracin Beta-Lactam antibiotics Penicillin
Mickey Dufilho s Drugs and Bugs Revised 10/10/15 Bacteria Drugs that Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis Drug Action Spectrum of Action Comments Spectrum of Action Bacitracin Beta-Lactam antibiotics Penicillin
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT
 THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 25, 2018 0800 EDT NH-HAN 20180825 Cluster of Legionella pneumophila Pneumonia (Legionnaire
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 25, 2018 0800 EDT NH-HAN 20180825 Cluster of Legionella pneumophila Pneumonia (Legionnaire
Infection Control Manual Residential Care Part 3 Infection Control Standards IC6: Additional Precautions
 IC6: 0110 Appendix I Selection Table Infection Control Manual esidential Care IC6: Additional Legend: outine Practice * reportable to Public Health C - Contact ** reportable by Lab D - Droplet A - Airborne
IC6: 0110 Appendix I Selection Table Infection Control Manual esidential Care IC6: Additional Legend: outine Practice * reportable to Public Health C - Contact ** reportable by Lab D - Droplet A - Airborne
WHO Technical Consultation on the severity of disease caused by the new influenza A (H1N1) virus infections
 WHO Technical Consultation on the severity of disease caused by the new influenza A (H1N1) virus infections Original short summary posted 6 May 2009. Revised full report posted May 9 2009. On 5 May 2009
WHO Technical Consultation on the severity of disease caused by the new influenza A (H1N1) virus infections Original short summary posted 6 May 2009. Revised full report posted May 9 2009. On 5 May 2009
Influenza. Giovanni Maciocia
 Influenza Giovanni Maciocia Zhang Zhong Jing (about 150-219AD) Ye Tian Shi (1667-1746) Wu Ju Tong (1758-1836) 1. WESTERN MEDICINE VIEW a) INFLUENZA INFLUENZA IN CHINESE MEDICINE Epidemiologists predict
Influenza Giovanni Maciocia Zhang Zhong Jing (about 150-219AD) Ye Tian Shi (1667-1746) Wu Ju Tong (1758-1836) 1. WESTERN MEDICINE VIEW a) INFLUENZA INFLUENZA IN CHINESE MEDICINE Epidemiologists predict
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections OTITIS MEDIA Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear. There are more than 709 million cases of otitis media worldwide each year; half of these cases occur in
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections OTITIS MEDIA Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear. There are more than 709 million cases of otitis media worldwide each year; half of these cases occur in
2014/2015 Ottawa County Influenza Surveillance Summary
 214/215 Ottawa County Influenza Surveillance Summary Time Period: October 1, 211 to March 31, 215 Michigan Disease Surveillance System (MDSS) MDSS data in Table 1 indicates that there were no new laboratory
214/215 Ottawa County Influenza Surveillance Summary Time Period: October 1, 211 to March 31, 215 Michigan Disease Surveillance System (MDSS) MDSS data in Table 1 indicates that there were no new laboratory
Wasatch School District Guidelines for Student Exclusion and Readmission
 Wasatch School District Guidelines for Student Exclusion and Readmission Condition Chicken pox (Varicella) Colds, Sore Throat, or a Persistent Cough Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Diarrhea (An increased number
Wasatch School District Guidelines for Student Exclusion and Readmission Condition Chicken pox (Varicella) Colds, Sore Throat, or a Persistent Cough Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Diarrhea (An increased number
CAP: general principles Respiratory infections Community acquired pneumonia: a review of common pathogens
 CAP: general principles Respiratory infections Community acquired pneumonia: a review of common pathogens Natalie Neu, MD Presentation Etiology Specific organisms and pneumonia Streptococcus pneumoniae
CAP: general principles Respiratory infections Community acquired pneumonia: a review of common pathogens Natalie Neu, MD Presentation Etiology Specific organisms and pneumonia Streptococcus pneumoniae
Pneumococcal Disease and Pneumococcal Vaccines
 Pneumococcal Disease and Epidemiology and Prevention of - Preventable Diseases Note to presenters: Images of vaccine-preventable diseases are available from the Immunization Action Coalition website at
Pneumococcal Disease and Epidemiology and Prevention of - Preventable Diseases Note to presenters: Images of vaccine-preventable diseases are available from the Immunization Action Coalition website at
Legionnaires Disease: Epidemiology and Outbreak Investigation
 Legionnaires Disease: Epidemiology and Outbreak Investigation Ellen Laine, JD, MPH Emerging Infections Unit Infectious Disease Epidemiology, Prevention and Control Division History of Legionnaires Disease
Legionnaires Disease: Epidemiology and Outbreak Investigation Ellen Laine, JD, MPH Emerging Infections Unit Infectious Disease Epidemiology, Prevention and Control Division History of Legionnaires Disease
Objective 3 Viruses & Bacteria genetic material capsule Pili DNA
 Objective 3 Viruses & Bacteria 1. Compare the structure and functions of viruses to cells and describe the role of viruses in causing diseases and conditions such as acquired immune deficiency syndrome,
Objective 3 Viruses & Bacteria 1. Compare the structure and functions of viruses to cells and describe the role of viruses in causing diseases and conditions such as acquired immune deficiency syndrome,
Medical Interventions- Unit 1 Study Guide (Due Dec. 16 th!)
 Medical Interventions- Unit 1 Study Guide (Due Dec. 16 th!) Name: Lesson 1.1 1. Define medical intervention. What are 3 medical interventions that Sue Smith would have encountered during her infection
Medical Interventions- Unit 1 Study Guide (Due Dec. 16 th!) Name: Lesson 1.1 1. Define medical intervention. What are 3 medical interventions that Sue Smith would have encountered during her infection
INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases)
 INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases) 1. Agent: Influenza viruses A, B, and C. Only influenza A and B are of public health concern since they are responsible for epidemics. 2. Identification:
INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases) 1. Agent: Influenza viruses A, B, and C. Only influenza A and B are of public health concern since they are responsible for epidemics. 2. Identification:
UNION COUNTY 2017 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT
 UNION COUNTY 7 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious disease for January 7 December 7. TABLE OF CONTENTS Annual Communicable Diseases... 3 Communicable
UNION COUNTY 7 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious disease for January 7 December 7. TABLE OF CONTENTS Annual Communicable Diseases... 3 Communicable
Module 2: Vaccines and drugs: similarities and differences
 Module 2: Vaccines and drugs: similarities and differences Vaccine PV Fellowship WHO Collaborating Centre for Advocacy and Training in Pharmacovigilance Accra, Ghana 7 th 18 th September 2015 Learning
Module 2: Vaccines and drugs: similarities and differences Vaccine PV Fellowship WHO Collaborating Centre for Advocacy and Training in Pharmacovigilance Accra, Ghana 7 th 18 th September 2015 Learning
PUBLIC HEALTH SIGNIFICANCE SEASONAL INFLUENZA AVIAN INFLUENZA SWINE INFLUENZA
 INFLUENZA DEFINITION Influenza is an acute highly infectious viral disease characterized by fever, general and respiratory tract catarrhal manifestations. Influenza has 3 Types Seasonal Influenza Avian
INFLUENZA DEFINITION Influenza is an acute highly infectious viral disease characterized by fever, general and respiratory tract catarrhal manifestations. Influenza has 3 Types Seasonal Influenza Avian
Preventing & Controlling the Spread of Infection
 Preventing & Controlling the Spread of Infection Contributors: Alice Pong M.D., Hospital Epidemiologist Chris Abe, R.N., Senior Director Ancillary and Support Services Objectives Review the magnitude of
Preventing & Controlling the Spread of Infection Contributors: Alice Pong M.D., Hospital Epidemiologist Chris Abe, R.N., Senior Director Ancillary and Support Services Objectives Review the magnitude of
Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets
 Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets www.biochemj.org/bj/330/0581/bj3300581.htm Professor Vassie Ware Bioscience in the 21 st Century November 5, 2012 PERSPECTIVE Widespread use of antibiotics after
Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets www.biochemj.org/bj/330/0581/bj3300581.htm Professor Vassie Ware Bioscience in the 21 st Century November 5, 2012 PERSPECTIVE Widespread use of antibiotics after
R 8451 CONTROL OF COMMUNICABLE DISEASE. 1. Teachers will be trained to detect communicable diseases in pupils by recognizing the symptoms of disease.
 R 8451/page 1 of 5 M R 8451 CONTROL OF COMMUNICABLE DISEASE A. Detection of Communicable Diseases 1. Teachers will be trained to detect communicable diseases in pupils by recognizing the symptoms of disease.
R 8451/page 1 of 5 M R 8451 CONTROL OF COMMUNICABLE DISEASE A. Detection of Communicable Diseases 1. Teachers will be trained to detect communicable diseases in pupils by recognizing the symptoms of disease.
8.L.1 Practice Questions
 Name: Date: 1. Why should antibiotics be given to a person who is ill with a bacterial disease like strep throat, but not to a person who has a viral disease like flu?. ntibiotics kill bacteria but not
Name: Date: 1. Why should antibiotics be given to a person who is ill with a bacterial disease like strep throat, but not to a person who has a viral disease like flu?. ntibiotics kill bacteria but not
Antibiotic Consumption in the Community in Ireland REPORT FOR First Half of 2013
 Antibiotic Consumption in the Community in Ireland REPORT FOR First Half of 2013 1 Summary: Community Antibiotic Use The rate for Quarter 1 of 2013 (1 st January to 31 st March) was 27.4 Defined Daily
Antibiotic Consumption in the Community in Ireland REPORT FOR First Half of 2013 1 Summary: Community Antibiotic Use The rate for Quarter 1 of 2013 (1 st January to 31 st March) was 27.4 Defined Daily
Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines.
 Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines. Why vaccines matter. Thanks to widespread vaccination programs, several diseases that can infect our children have been eliminated. But
Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines. Why vaccines matter. Thanks to widespread vaccination programs, several diseases that can infect our children have been eliminated. But
Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines.
 Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines. Why vaccines matter. Thanks to widespread vaccination programs, several diseases that can infect our children have been eliminated. But
Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines. Why vaccines matter. Thanks to widespread vaccination programs, several diseases that can infect our children have been eliminated. But
People do not always agree about the use of antibiotics in food production.
 Q1. Read the passage about antibiotics. People do not always agree about the use of antibiotics in food production. If we put low doses of antibiotics in feed for animals such as cattle and sheep, it helps
Q1. Read the passage about antibiotics. People do not always agree about the use of antibiotics in food production. If we put low doses of antibiotics in feed for animals such as cattle and sheep, it helps
Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple)
 Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple) 1. Your Baby s First Vaccines: What You Need to Know Babies get six vaccines between birth and 6 months of age. These vaccines protect your
Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple) 1. Your Baby s First Vaccines: What You Need to Know Babies get six vaccines between birth and 6 months of age. These vaccines protect your
Vaccination and Immunity
 Vaccination and Immunity Eric A. Utt, PhD Director, Worldwide Science Policy Pfizer Inc California Immunization Coalition Summit 2012 Completing the Circle: Ensuring Adult & Adolescent Vaccination for
Vaccination and Immunity Eric A. Utt, PhD Director, Worldwide Science Policy Pfizer Inc California Immunization Coalition Summit 2012 Completing the Circle: Ensuring Adult & Adolescent Vaccination for
Lesson 3: Immunizations
 K-W-L Graphic Organizer K (Know) What do you know about W (Want) What do you want to know about L (Learned) What did you learn about Glossary 1. antibodies: proteins created by the immune system to fight
K-W-L Graphic Organizer K (Know) What do you know about W (Want) What do you want to know about L (Learned) What did you learn about Glossary 1. antibodies: proteins created by the immune system to fight
Outbreak of travel-associated Legionnaires' disease Palmanova, Mallorca (Spain), September October Main conclusions and options for response
 RAPID RISK ASSESSMENT Outbreak of travel-associated Legionnaires' disease Palmanova, Mallorca (Spain), September October 2017 23 October 2017 Main conclusions and options for response An increase in Legionnaires
RAPID RISK ASSESSMENT Outbreak of travel-associated Legionnaires' disease Palmanova, Mallorca (Spain), September October 2017 23 October 2017 Main conclusions and options for response An increase in Legionnaires
EPIDEMIOLOGY SURVEILLANCE REPORT Northeast Region. Namitha Reddy Regional Coordinator North/Central West Region
 EPIDEMIOLOGY SURVEILLANCE REPORT Northeast Region Namitha Reddy Regional Coordinator North/Central West Region 1 This report is for use by Public Health Officials only and not for public distribution.
EPIDEMIOLOGY SURVEILLANCE REPORT Northeast Region Namitha Reddy Regional Coordinator North/Central West Region 1 This report is for use by Public Health Officials only and not for public distribution.
Other β-lactam. A. Carbapenems:
 A. Carbapenems: Other β-lactam Carbapenems are synthetic β-lactam antibiotics Differ in structure from the penicillins in that the sulfur atom of the thiazolidine ring. Imipenem, meropenem, doripenem,
A. Carbapenems: Other β-lactam Carbapenems are synthetic β-lactam antibiotics Differ in structure from the penicillins in that the sulfur atom of the thiazolidine ring. Imipenem, meropenem, doripenem,
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines August Pneumococcal Disease, Invasive (IPD)
 August 2011 Pneumococcal Disease, Invasive (IPD) Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition August
August 2011 Pneumococcal Disease, Invasive (IPD) Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition August
Diphtheria. Vaccine Preventable Childhood Diseases. General information
 Diphtheria General information Caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheria. Transmission is most often person-to-person spread via respiratorydroplets. The word diphtheria comes from Greek and means
Diphtheria General information Caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheria. Transmission is most often person-to-person spread via respiratorydroplets. The word diphtheria comes from Greek and means
Respiratory tract anatomy Respiratory infections Community acquired pneumonia: a review of common pathogens
 Respiratory tract anatomy Respiratory infections Community acquired pneumonia: a review of common pathogens Natalie Neu, MD Community acquired pneumonia: CAP 5.6 million cases annually #1 cause of death
Respiratory tract anatomy Respiratory infections Community acquired pneumonia: a review of common pathogens Natalie Neu, MD Community acquired pneumonia: CAP 5.6 million cases annually #1 cause of death
Which Diseases Should My Child Be Protected Against?
 What is Immunization? Immunization is a process that helps your body fight off diseases caused by certain viruses and bacteria. One way for you to be immunized is to receive a vaccine. What is a Vaccine?
What is Immunization? Immunization is a process that helps your body fight off diseases caused by certain viruses and bacteria. One way for you to be immunized is to receive a vaccine. What is a Vaccine?
SPECIFIC DISEASE EXCLUSION FOR SCHOOLS
 SPECIFIC DISEASE EXCLUSION FOR SCHOOLS See individual fact sheets for more information on the diseases listed below. Bed Bugs Acute Bronchitis (Chest Cold)/Bronchiolitis Campylobacteriosis Until fever
SPECIFIC DISEASE EXCLUSION FOR SCHOOLS See individual fact sheets for more information on the diseases listed below. Bed Bugs Acute Bronchitis (Chest Cold)/Bronchiolitis Campylobacteriosis Until fever
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
Chapter 12 Preventing Infection
 Chapter 12 Preventing Infection Infection is a major safety and health hazard. Minor infections cause acute illnesses and some infections are serious and can cause death. Microbe/microorganism is a small
Chapter 12 Preventing Infection Infection is a major safety and health hazard. Minor infections cause acute illnesses and some infections are serious and can cause death. Microbe/microorganism is a small
Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent. 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens
 Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent Consider: 1) the host 2) the site of infection 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens 4) the likelihood that these pathogens are resistant to antimicrobial agents
Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent Consider: 1) the host 2) the site of infection 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens 4) the likelihood that these pathogens are resistant to antimicrobial agents
Current and Emerging Legionella Diagnostics
 Current and Emerging Legionella Diagnostics Nicole Wolter Centre for Respiratory Diseases and Meningitis (CRDM) National Institute for Communicable Diseases nicolew@nicd.ac.za 7 th FIDSSA Conference, Cape
Current and Emerging Legionella Diagnostics Nicole Wolter Centre for Respiratory Diseases and Meningitis (CRDM) National Institute for Communicable Diseases nicolew@nicd.ac.za 7 th FIDSSA Conference, Cape
Haemophilus influenzae
 Haemophilus influenzae type b Severe bacterial infection, particularly among infants During late 19th century believed to cause influenza Immunology and microbiology clarified in 1930s Haemophilus influenzae
Haemophilus influenzae type b Severe bacterial infection, particularly among infants During late 19th century believed to cause influenza Immunology and microbiology clarified in 1930s Haemophilus influenzae
TABLE OF CONTENTS. In what way can this educational material help me? Why are vaccinations important? Who needs vaccinations?
 www.promovax.eu TABLE OF CONTENTS A B C D E F G H In what way can this educational material help me? Why are vaccinations important? Who needs vaccinations? Which diseases do vaccines prevent? Are vaccinations
www.promovax.eu TABLE OF CONTENTS A B C D E F G H In what way can this educational material help me? Why are vaccinations important? Who needs vaccinations? Which diseases do vaccines prevent? Are vaccinations
Class 9 th Why do we fall ill?
 Class 9 th Why do we fall ill? Health: health is a state of physical, mental and social well being. The health of all individuals is dependent on their physical environment, social environment, and their
Class 9 th Why do we fall ill? Health: health is a state of physical, mental and social well being. The health of all individuals is dependent on their physical environment, social environment, and their
INFECTIOUS DISEASES IN THE LONG TERM CARE FACILITY
 INFECTIOUS DISEASES IN THE LONG TERM CARE FACILITY The following is a list of the most common infectious diseases that are to be found in the long term care facility. Precautions are recommended and the
INFECTIOUS DISEASES IN THE LONG TERM CARE FACILITY The following is a list of the most common infectious diseases that are to be found in the long term care facility. Precautions are recommended and the
