Mechanical Properties of the Cochlea. Reading: Yost Ch. 7
|
|
|
- Chastity Mathews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mechanical Properties of the Cochlea CF Reading: Yost Ch. 7
2 The Cochlea Inner ear contains auditory and vestibular sensory organs. Cochlea is a coiled tri-partite tube about 35 mm long. Basilar membrane, supporting the Organ of Corti, runs along entire length of cochlea. Its mechanical properties change as a function of distance from the stapes: designed to analyze frequency components in complex sounds. Hair cells receptors in Organ of Corti of two types: inner (single row) and outer (3/4 rows) Stereocilia are rigid rods interconnected on their flanks, and at their tips. Tip links critical to transduction.
3 Traveling Wave Stapes vibration generates pressure waves in fluids of cochlea. Pressure waves generate vibrations of the basilar membrane that propagate from base to apex along the basilar membrane as a traveling wave (von Békesy 1961) BM vibrates at the same frequency as the simple sound stimulus wherever the basilar membrane is set in motion by the TW. Amplitude of the TW differs at different locations, depending on frequency and amplitude (acoustic energy) of the stimulus.
4 Traveling Wave Motion The vibratory motion of the basilar membrane is a traveling wave. A traveling wave moves longitudinally from one place (stapes) to another place (helicotrema) (like that in a rope with the far end free) Top (a): snapshot of basilar membrane model showing instantaneous vibration pattern and shape of traveling wave (as seen from the side). Bottom (b): More accurate view of pattern, with membrane attached at sides. Note that different regions of membrane are out of phase, with a greater phase difference ahead of the peak of the wavefront (apical) than behind it (basal). Base Apex
5 Envelope of Traveling Wave For a given traveling wave, basilar membrane displacement changes as a function of distance from apex to base. If a line is drawn through the points of maximum displacement for a specific traveling wave, then the resulting curve is called the envelope of the traveling wave. Numbered curves: freeze-frames of TW for a sustained pure tone stimulus taken at different instants in time. Different locations along the membrane displaced in opposite directions (called a local phase difference). For pure tone stimulus, the TW envelope shows a single maximum of displacement.
6 Traveling wave peak shifts from base to apex as stimulus frequency is varied from high to low (von Bekesy 1947). TW for low frequencies stretches over a long distance, can vibrate nearly entire basilar membrane if sound sufficiently intense. TW for high frequencies more confined, only stimulates the base. Place Theory
7 Why do Sounds Generate a TW? Each point along the basilar membrane that is set in motion vibrates at the same frequency as the stimulus. However, different frequencies will cause maximum vibration amplitude at different points and times along the membrane. A number of factors vary along the length of the cochlea. In particular, moving from base to apex: BM width increases (higher mass) BM becomes thinner (less stiffness) Stereocilia get longer (higher mass, less stiffness). These changes reduce the resonant frequency of the basilar membrane with distance from the stapes (F r a s/m), and thus increase time to peak response.
8 Complex sounds create complex traveling wave patterns, with multiple vibration maxima. Pattern of excitation provides information about Frequency Amplitude Temporal variation Complex Sounds Note that due to the traveling wave, low frequency components of a sound are transduced after high frequency components... The TW introduces temporal distortions (absolute time and relative phase delays)! Envelope of basilar membrane displacement to 50 Hz or 100 Hz alone, and combined as F 0 and F 1 of a harmonic series.
9 Mechanical Tuning in Organ of Corti Mechanical tuning of any point along BM resembles bandpass filter, with a steep high-frequency roll-off, and a shallow lowfrequency roll-off. Mechanical tuning curves Characteristic frequency (CF): Frequency at which the sound level reaches a minimum to obtain a criterion displacement for that position on the BM Thus, the organ of Corti topographically decomposes the spectrum of the sound with frequency-selective bandpass filters (channels). CF Iso-sensitivity curve of basilar membrane plotted as equal-displacement function re 19 Ångstroms ( 1.9 x 10-8 cm) CF = 8350 Hz.
10 Basilar Membrane Nonlinearity The higher the stimulus level, the greater the amplitude of basilar membrane displacement. Displacement of BM is not linear as a function of stimulus level near the peak of the TW. Consequence: Near CF, range of BM motion is less than the range of sound levels, i.e. the dynamic range shows compressive non-linearity. Compressive nonlinearity generates distortion products (e.g., harmonics, difference tones). Input-output ( transfer ) function: BM velocity vs sound level. (CF =9000 Hz)
11 Mechanical Excitation of Hair Cells TM OHCs Traveling wave causes up-and-down motion of basilar membrane and tectorial membrane (at same frequency as stimulus). IHCs Displacement sets up transverse shearing force that deflects hair cell stereocilia. Kiang 1984 BM after Wada 2002
12 Mechanical Excitation: Outer Hair Cells Tips of OHC stereocilia are embedded in tectorial membrane. BM pivots around inner pillar cell attachment to spiral lamina when stimulated. Stereocilia deflected by mechanical shearing: tectorial membrane pushes and pulls as hair cells move back and forth. Geisler 1998
13 Mechanical Excitation: Inner Hair Cells Model of putative fluid shearing mechanism of stereocilia bundle deflection and excitation in IHCs. Geisler 1998
14 Summary Excitation of inner ear gives rise to traveling wave along the basilar membrane, due to longitudinal changes in the basilar membrane (principally, compliance stiffness) Changes in sound frequency shift the location of the traveling wave peak along the basilar membrane, creating a place code for frequency (tonotopy). Hair cells are stimulated by basilar membrane traveling wave(s): they are mechanically tuned to a single CF according to their location on the BM; and the amplitude of their vibration is related to stimulus level. CF
Structure, Energy Transmission and Function. Gross Anatomy. Structure, Function & Process. External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer Ear
 Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear
 ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 30. Organ of Corti
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 30 Waves, waves, waves. Organ of Corti Tectorial membrane Sits on top Inner hair cells Outer hair cells The microphone for the brain 1 Hearing Perceptually,
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 30 Waves, waves, waves. Organ of Corti Tectorial membrane Sits on top Inner hair cells Outer hair cells The microphone for the brain 1 Hearing Perceptually,
HST 721 Lecture 4: Mechanics, electromotility and the cochlear amplifier
 HST 721 Lecture 4: Mechanics, electromotility and the cochlear amplifier 1 Cochlear Mechanics: Measures of Basilar Membrane Motion 2 Cochlear Mechanics: Measures of Basilar Membrane Motion Bekesy s experiments
HST 721 Lecture 4: Mechanics, electromotility and the cochlear amplifier 1 Cochlear Mechanics: Measures of Basilar Membrane Motion 2 Cochlear Mechanics: Measures of Basilar Membrane Motion Bekesy s experiments
Hearing Sound. The Human Auditory System. The Outer Ear. Music 170: The Ear
 Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear. Tamara Smyth, Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016
 Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear. Week 5. The peripheral auditory system: The ear as a signal processor
 Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear Week 5 The peripheral auditory system: The ear as a signal processor Think of this set of organs 2 as a collection of systems, transforming sounds to be sent to
Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear Week 5 The peripheral auditory system: The ear as a signal processor Think of this set of organs 2 as a collection of systems, transforming sounds to be sent to
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
Innervation of the Cochlea. Reading: Yost Ch. 8
 Innervation of the Cochlea Reading: Yost Ch. 8 Fine Structure of the Organ of Corti Auditory Nerve Auditory nerve (AN) is a branch of the VIII th cranial nerve (other branch is vestibular). AN is composed
Innervation of the Cochlea Reading: Yost Ch. 8 Fine Structure of the Organ of Corti Auditory Nerve Auditory nerve (AN) is a branch of the VIII th cranial nerve (other branch is vestibular). AN is composed
Auditory System. Barb Rohrer (SEI )
 Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Intro to Audition & Hearing
 Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function.
 Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, Auditory system. http:
 Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, 2018 Auditory system http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html The physics of sound Measuring sound intensity We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities,
Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, 2018 Auditory system http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html The physics of sound Measuring sound intensity We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities,
Lecture 6 Hearing 1. Raghav Rajan Bio 354 Neurobiology 2 January 28th All lecture material from the following links unless otherwise mentioned:
 Lecture 6 Hearing 1 All lecture material from the following links unless otherwise mentioned: 1. http://wws.weizmann.ac.il/neurobiology/labs/ulanovsky/sites/neurobiology.labs.ulanovsky/files/uploads/purves_ch12_ch13_hearing
Lecture 6 Hearing 1 All lecture material from the following links unless otherwise mentioned: 1. http://wws.weizmann.ac.il/neurobiology/labs/ulanovsky/sites/neurobiology.labs.ulanovsky/files/uploads/purves_ch12_ch13_hearing
What does it mean to analyze the frequency components of a sound? A spectrogram such as that shown here is the usual display of frequency components
 1 2 3 4 What does it mean to analyze the frequency components of a sound? A spectrogram such as that shown here is the usual display of frequency components as a function of time here during the production
1 2 3 4 What does it mean to analyze the frequency components of a sound? A spectrogram such as that shown here is the usual display of frequency components as a function of time here during the production
Auditory System Feedback
 Feedback Auditory System Feedback Using all or a portion of the information from the output of a system to regulate or control the processes or inputs in order to modify the output. Central control of
Feedback Auditory System Feedback Using all or a portion of the information from the output of a system to regulate or control the processes or inputs in order to modify the output. Central control of
SOLUTIONS Homework #3. Introduction to Engineering in Medicine and Biology ECEN 1001 Due Tues. 9/30/03
 SOLUTIONS Homework #3 Introduction to Engineering in Medicine and Biology ECEN 1001 Due Tues. 9/30/03 Problem 1: a) Where in the cochlea would you say the process of "fourier decomposition" of the incoming
SOLUTIONS Homework #3 Introduction to Engineering in Medicine and Biology ECEN 1001 Due Tues. 9/30/03 Problem 1: a) Where in the cochlea would you say the process of "fourier decomposition" of the incoming
Receptors / physiology
 Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
SPHSC 462 HEARING DEVELOPMENT. Overview Review of Hearing Science Introduction
 SPHSC 462 HEARING DEVELOPMENT Overview Review of Hearing Science Introduction 1 Overview of course and requirements Lecture/discussion; lecture notes on website http://faculty.washington.edu/lawerner/sphsc462/
SPHSC 462 HEARING DEVELOPMENT Overview Review of Hearing Science Introduction 1 Overview of course and requirements Lecture/discussion; lecture notes on website http://faculty.washington.edu/lawerner/sphsc462/
What is the effect on the hair cell if the stereocilia are bent away from the kinocilium?
 CASE 44 A 53-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of feeling like the room is spinning, dizziness, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, and fullness in both ears. He states
CASE 44 A 53-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of feeling like the room is spinning, dizziness, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, and fullness in both ears. He states
Can You Hear Me Now?
 An Introduction to the Mathematics of Hearing Department of Applied Mathematics University of Washington April 26, 2007 Some Questions How does hearing work? What are the important structures and mechanisms
An Introduction to the Mathematics of Hearing Department of Applied Mathematics University of Washington April 26, 2007 Some Questions How does hearing work? What are the important structures and mechanisms
Sound. Audition. Physics of Sound. Properties of sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition. Sound. Physics of Sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Acoustics Research Institute
 Austrian Academy of Sciences Acoustics Research Institute Modeling Modelingof ofauditory AuditoryPerception Perception Bernhard BernhardLaback Labackand andpiotr PiotrMajdak Majdak http://www.kfs.oeaw.ac.at
Austrian Academy of Sciences Acoustics Research Institute Modeling Modelingof ofauditory AuditoryPerception Perception Bernhard BernhardLaback Labackand andpiotr PiotrMajdak Majdak http://www.kfs.oeaw.ac.at
Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism
 Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism Objectives (1) Anatomy of the inner ear Functions of the cochlear and vestibular systems Three compartments within the cochlea and membranes
Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism Objectives (1) Anatomy of the inner ear Functions of the cochlear and vestibular systems Three compartments within the cochlea and membranes
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I. Professor Dave Furness Keele University
 Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of these lectures Introduction to gross anatomy of the cochlea Focus (1) on
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of these lectures Introduction to gross anatomy of the cochlea Focus (1) on
MECHANISM OF HEARING
 MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium!
 Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! Chapter 17 Part 2 Special Senses! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium!
 Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
HEARING AND PSYCHOACOUSTICS
 CHAPTER 2 HEARING AND PSYCHOACOUSTICS WITH LIDIA LEE I would like to lead off the specific audio discussions with a description of the audio receptor the ear. I believe it is always a good idea to understand
CHAPTER 2 HEARING AND PSYCHOACOUSTICS WITH LIDIA LEE I would like to lead off the specific audio discussions with a description of the audio receptor the ear. I believe it is always a good idea to understand
Acoustics, signals & systems for audiology. Psychoacoustics of hearing impairment
 Acoustics, signals & systems for audiology Psychoacoustics of hearing impairment Three main types of hearing impairment Conductive Sound is not properly transmitted from the outer to the inner ear Sensorineural
Acoustics, signals & systems for audiology Psychoacoustics of hearing impairment Three main types of hearing impairment Conductive Sound is not properly transmitted from the outer to the inner ear Sensorineural
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 29. Hearing
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception
 Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception Overview of Questions What is it that makes sounds high pitched or low pitched? How do sound vibrations inside the ear lead to the perception
Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception Overview of Questions What is it that makes sounds high pitched or low pitched? How do sound vibrations inside the ear lead to the perception
Sound and Hearing. Decibels. Frequency Coding & Localization 1. Everything is vibration. The universe is made of waves.
 Frequency Coding & Localization 1 Sound and Hearing Everything is vibration The universe is made of waves db = 2log(P1/Po) P1 = amplitude of the sound wave Po = reference pressure =.2 dynes/cm 2 Decibels
Frequency Coding & Localization 1 Sound and Hearing Everything is vibration The universe is made of waves db = 2log(P1/Po) P1 = amplitude of the sound wave Po = reference pressure =.2 dynes/cm 2 Decibels
The Structure and Function of the Auditory Nerve
 The Structure and Function of the Auditory Nerve Brad May Structure and Function of the Auditory and Vestibular Systems (BME 580.626) September 21, 2010 1 Objectives Anatomy Basic response patterns Frequency
The Structure and Function of the Auditory Nerve Brad May Structure and Function of the Auditory and Vestibular Systems (BME 580.626) September 21, 2010 1 Objectives Anatomy Basic response patterns Frequency
The frequency analysis of the cochlea a review of Nobili et al (1998) and Ruggero et al (1992)
 The frequency analysis of the cochlea a review of Nobili et al (1998) and Ruggero et al (1992) by Pedro da Fonseca (pedrofon@mail.telepac.pt) Neuroscience course Presented in 17.12.99 to professor STEPHEN
The frequency analysis of the cochlea a review of Nobili et al (1998) and Ruggero et al (1992) by Pedro da Fonseca (pedrofon@mail.telepac.pt) Neuroscience course Presented in 17.12.99 to professor STEPHEN
A truly remarkable aspect of human hearing is the vast
 AUDITORY COMPRESSION AND HEARING LOSS Sid P. Bacon Psychoacoustics Laboratory, Department of Speech and Hearing Science, Arizona State University Tempe, Arizona 85287 A truly remarkable aspect of human
AUDITORY COMPRESSION AND HEARING LOSS Sid P. Bacon Psychoacoustics Laboratory, Department of Speech and Hearing Science, Arizona State University Tempe, Arizona 85287 A truly remarkable aspect of human
Printable version - Hearing - OpenLearn - The Open University
 Skip to content Accessibility Sign in Contact Search the OU The Open University Study at the OU Research at the OU OU Community About the OU Hearing Printable page generated Saturday, 12 November 2011,
Skip to content Accessibility Sign in Contact Search the OU The Open University Study at the OU Research at the OU OU Community About the OU Hearing Printable page generated Saturday, 12 November 2011,
Improving the diagnostic power of otoacoustic emissions. Arturo Moleti Physics Department University of Roma Tor Vergata
 Improving the diagnostic power of otoacoustic emissions Arturo Moleti Physics Department University of Roma Tor Vergata The human ear Ear canal: resonant cavity Middle ear: impedance adapter and pressure
Improving the diagnostic power of otoacoustic emissions Arturo Moleti Physics Department University of Roma Tor Vergata The human ear Ear canal: resonant cavity Middle ear: impedance adapter and pressure
Processing of sounds in the inner ear
 Processing of sounds in the inner ear Sripriya Ramamoorthy Associate Professor, IIT Bombay WiSSAP 2018 Cochlea converts sound into electrical signals [Picture courtesy of Northwestern University] von Bekesy
Processing of sounds in the inner ear Sripriya Ramamoorthy Associate Professor, IIT Bombay WiSSAP 2018 Cochlea converts sound into electrical signals [Picture courtesy of Northwestern University] von Bekesy
Music and Hearing in the Older Population: an Audiologist's Perspective
 Music and Hearing in the Older Population: an Audiologist's Perspective Dwight Ough, M.A., CCC-A Audiologist Charlotte County Hearing Health Care Centre Inc. St. Stephen, New Brunswick Anatomy and Physiology
Music and Hearing in the Older Population: an Audiologist's Perspective Dwight Ough, M.A., CCC-A Audiologist Charlotte County Hearing Health Care Centre Inc. St. Stephen, New Brunswick Anatomy and Physiology
Modelling the micromechanics of the cochlea in Femlab
 Modelling the micromechanics of the cochlea in Femlab R.R.J.J. van Doorn DCT 27.7 Traineeship report Coach(es): Supervisor: Prof. S.J. Elliott Prof. P. Gardonio Prof. H. Nijmeijer Technische Universiteit
Modelling the micromechanics of the cochlea in Femlab R.R.J.J. van Doorn DCT 27.7 Traineeship report Coach(es): Supervisor: Prof. S.J. Elliott Prof. P. Gardonio Prof. H. Nijmeijer Technische Universiteit
AUDL GS08/GAV1 Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear. Pitch & Binaural listening
 AUDL GS08/GAV1 Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear Pitch & Binaural listening Review 25 20 15 10 5 0-5 100 1000 10000 25 20 15 10 5 0-5 100 1000 10000 Part I: Auditory frequency selectivity Tuning
AUDL GS08/GAV1 Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear Pitch & Binaural listening Review 25 20 15 10 5 0-5 100 1000 10000 25 20 15 10 5 0-5 100 1000 10000 Part I: Auditory frequency selectivity Tuning
Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics
 9 Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics Click Chapter to edit 9 Hearing: Master title Physiology style and Psychoacoustics The Function of Hearing What Is Sound? Basic Structure of the Mammalian Auditory
9 Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics Click Chapter to edit 9 Hearing: Master title Physiology style and Psychoacoustics The Function of Hearing What Is Sound? Basic Structure of the Mammalian Auditory
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH
 College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
Required Slide. Session Objectives
 Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Sound Waves. Sensation and Perception. Sound Waves. Sound Waves. Sound Waves
 Sensation and Perception Part 3 - Hearing Sound comes from pressure waves in a medium (e.g., solid, liquid, gas). Although we usually hear sounds in air, as long as the medium is there to transmit the
Sensation and Perception Part 3 - Hearing Sound comes from pressure waves in a medium (e.g., solid, liquid, gas). Although we usually hear sounds in air, as long as the medium is there to transmit the
Human Acoustic Processing
 Human Acoustic Processing Sound and Light The Ear Cochlea Auditory Pathway Speech Spectrogram Vocal Cords Formant Frequencies Time Warping Hidden Markov Models Signal, Time and Brain Process of temporal
Human Acoustic Processing Sound and Light The Ear Cochlea Auditory Pathway Speech Spectrogram Vocal Cords Formant Frequencies Time Warping Hidden Markov Models Signal, Time and Brain Process of temporal
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Deafness and hearing impairment
 Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Hearing and Balance 1
 Hearing and Balance 1 Slide 3 Sound is produced by vibration of an object which produces alternating waves of pressure and rarefaction, for example this tuning fork. Slide 4 Two characteristics of sound
Hearing and Balance 1 Slide 3 Sound is produced by vibration of an object which produces alternating waves of pressure and rarefaction, for example this tuning fork. Slide 4 Two characteristics of sound
Hearing. By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa
 Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
PSY 214 Lecture # (11/9/2011) (Sound, Auditory & Speech Perception) Dr. Achtman PSY 214
 PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, Auditory System & Speech Perception Chapter 11, pages 270-289 Corrections: None Announcements: CD is available outside Dr Achtman s office if you would like to see demonstrations
PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, Auditory System & Speech Perception Chapter 11, pages 270-289 Corrections: None Announcements: CD is available outside Dr Achtman s office if you would like to see demonstrations
Spectrograms (revisited)
 Spectrograms (revisited) We begin the lecture by reviewing the units of spectrograms, which I had only glossed over when I covered spectrograms at the end of lecture 19. We then relate the blocks of a
Spectrograms (revisited) We begin the lecture by reviewing the units of spectrograms, which I had only glossed over when I covered spectrograms at the end of lecture 19. We then relate the blocks of a
Modeling of Mechanoelectrical Transduction of Hair Cells to Action Potentials in the Auditory Nerve
 Modeling of Mechanoelectrical Transduction of Hair Cells to Action Potentials in the Auditory Nerve Anthony Au, Yuchen Wang, Sibai Xie A Term Paper for BENG26 University of California, San Diego San Diego,
Modeling of Mechanoelectrical Transduction of Hair Cells to Action Potentials in the Auditory Nerve Anthony Au, Yuchen Wang, Sibai Xie A Term Paper for BENG26 University of California, San Diego San Diego,
Hearing. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 14. Hearing. Hearing
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
Consequences of Location-Dependent Organ of Corti Micro-Mechanics
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Consequences of Location-Dependent Organ of Corti Micro-Mechanics Yanju Liu 1, Sheryl M. Gracewski 1,2, Jong-Hoon Nam 1,2 * 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Rochester,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Consequences of Location-Dependent Organ of Corti Micro-Mechanics Yanju Liu 1, Sheryl M. Gracewski 1,2, Jong-Hoon Nam 1,2 * 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Rochester,
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221
 BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
An active cochlear model showing sharp tuning and high sensitivity
 Hearing Research, 9 (1983) 123-13 Elsevier Biomedical Press 123 An active cochlear model showing sharp tuning and high sensitivity Stephen T. Neely * and D.O. Kim Box 811, Washington Unitlersit}', St.
Hearing Research, 9 (1983) 123-13 Elsevier Biomedical Press 123 An active cochlear model showing sharp tuning and high sensitivity Stephen T. Neely * and D.O. Kim Box 811, Washington Unitlersit}', St.
HEARING. Structure and Function
 HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
Welcome to Cochlear Dead Regions and Implications for Fittings. Presenter: Audiologist, Speaker, Author. IHS Organizers: Housekeeping
 Welcome to Cochlear Dead Regions and Implications for Fittings Presenter: Ted Venema PhD Audiologist, Speaker, Author IHS rganizers: Fran Vincent Membership and Marketing Manager Ted Annis Senior Marketing
Welcome to Cochlear Dead Regions and Implications for Fittings Presenter: Ted Venema PhD Audiologist, Speaker, Author IHS rganizers: Fran Vincent Membership and Marketing Manager Ted Annis Senior Marketing
Chapter 1: Introduction to digital audio
 Chapter 1: Introduction to digital audio Applications: audio players (e.g. MP3), DVD-audio, digital audio broadcast, music synthesizer, digital amplifier and equalizer, 3D sound synthesis 1 Properties
Chapter 1: Introduction to digital audio Applications: audio players (e.g. MP3), DVD-audio, digital audio broadcast, music synthesizer, digital amplifier and equalizer, 3D sound synthesis 1 Properties
to vibrate the fluid. The ossicles amplify the pressure. The surface area of the oval window is
 Page 1 of 6 Question 1: How is the conduction of sound to the cochlea facilitated by the ossicles of the middle ear? Answer: Sound waves traveling through air move the tympanic membrane, which, in turn,
Page 1 of 6 Question 1: How is the conduction of sound to the cochlea facilitated by the ossicles of the middle ear? Answer: Sound waves traveling through air move the tympanic membrane, which, in turn,
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Chapter 3. Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics
 Chapter 3 Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics Sound Waves Compression/Rarefaction: speaker cone Sound travels 1130 feet per second Sound waves hit receiver Sound waves tend to spread out as they travel
Chapter 3 Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics Sound Waves Compression/Rarefaction: speaker cone Sound travels 1130 feet per second Sound waves hit receiver Sound waves tend to spread out as they travel
FIFTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION DECEMBER 15-18, 1997 ADELAIDE, SOUTH AUSTRALIA. Invited Paper LINEAR RESPONSE OF THE COCHLEA
 FIFTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION DECEMBER 15-18, 1997 ADELAIDE, SOUTH AUSTRALIA Invited Paper LINEAR RESPONSE OF THE COCHLEA David Alan Bies Visiting Research Fellow Department of Mechanical
FIFTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION DECEMBER 15-18, 1997 ADELAIDE, SOUTH AUSTRALIA Invited Paper LINEAR RESPONSE OF THE COCHLEA David Alan Bies Visiting Research Fellow Department of Mechanical
SPECIAL SENSES: THE AUDITORY SYSTEM
 SPECIAL SENSES: THE AUDITORY SYSTEM REVISION OF PHYSICS: WAVES A wave is an oscillation of power, sound waves have two main characteristics: amplitude, which is the maximum displacement or the power of
SPECIAL SENSES: THE AUDITORY SYSTEM REVISION OF PHYSICS: WAVES A wave is an oscillation of power, sound waves have two main characteristics: amplitude, which is the maximum displacement or the power of
Rods vs Cones 3/10/2014. Example 1: Light Sensitive Visual Receptors. Turning Light Waves Into Electrical Messages (Transduction)
 Example 1: Light Sensitive Visual Receptors The typical neuron is designed to receive neurotransmitter messages from other neurons. Sensory receptors, on the other hand, are specialized to receive sensory
Example 1: Light Sensitive Visual Receptors The typical neuron is designed to receive neurotransmitter messages from other neurons. Sensory receptors, on the other hand, are specialized to receive sensory
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
What you re in for. Who are cochlear implants for? The bottom line. Speech processing schemes for
 What you re in for Speech processing schemes for cochlear implants Stuart Rosen Professor of Speech and Hearing Science Speech, Hearing and Phonetic Sciences Division of Psychology & Language Sciences
What you re in for Speech processing schemes for cochlear implants Stuart Rosen Professor of Speech and Hearing Science Speech, Hearing and Phonetic Sciences Division of Psychology & Language Sciences
Auditory Periphery! external middle inner. stapes movement initiates a pressure wave in cochlear fluid
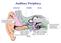 Auditory Periphery! external middle inner sound causes air pressure to increase at eardrum stapes movement initiates a pressure wave in cochlear fluid VIIIth nerve conveys neural signal to cochlear nucleus
Auditory Periphery! external middle inner sound causes air pressure to increase at eardrum stapes movement initiates a pressure wave in cochlear fluid VIIIth nerve conveys neural signal to cochlear nucleus
Chapter Fourteen. The Hearing Mechanism. 1. Introduction.
 Chapter Fourteen The Hearing Mechanism 1. Introduction. 2. Hearing. 3. The Ear. 4. The External Ear. 5. The Inner Ear. 6. Frequency Discrimination. 7. The Organ of Corti. 8. Tests and Exrecises. 9. References.
Chapter Fourteen The Hearing Mechanism 1. Introduction. 2. Hearing. 3. The Ear. 4. The External Ear. 5. The Inner Ear. 6. Frequency Discrimination. 7. The Organ of Corti. 8. Tests and Exrecises. 9. References.
Essential feature. Who are cochlear implants for? People with little or no hearing. substitute for faulty or missing inner hair
 Who are cochlear implants for? Essential feature People with little or no hearing and little conductive component to the loss who receive little or no benefit from a hearing aid. Implants seem to work
Who are cochlear implants for? Essential feature People with little or no hearing and little conductive component to the loss who receive little or no benefit from a hearing aid. Implants seem to work
EMANATIONS FROM RESIDUUM OSCILLATIONS IN HUMAN AUDITORY SYSTEM
 EMANATIONS FROM RESIDUUM OSCILLATIONS IN HUMAN AUDITORY SYSTEM V.S. Balaji, N.R.Raajan, S. Rakesh Kumar, Har Narayan Upadhyay School of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, SASTRA University Thanjavur,
EMANATIONS FROM RESIDUUM OSCILLATIONS IN HUMAN AUDITORY SYSTEM V.S. Balaji, N.R.Raajan, S. Rakesh Kumar, Har Narayan Upadhyay School of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, SASTRA University Thanjavur,
Auditory-based Automatic Speech Recognition
 Auditory-based Automatic Speech Recognition Werner Hemmert, Marcus Holmberg Infineon Technologies, Corporate Research Munich, Germany {Werner.Hemmert,Marcus.Holmberg}@infineon.com David Gelbart International
Auditory-based Automatic Speech Recognition Werner Hemmert, Marcus Holmberg Infineon Technologies, Corporate Research Munich, Germany {Werner.Hemmert,Marcus.Holmberg}@infineon.com David Gelbart International
AUDL GS08 and GAV1: 2013 Final exam page 1/13. You must complete all sections. Label all graphs. Show your work!
 AUDL GS08 and GAV1: 2013 Final exam page 1/13 You must complete all sections. Label all graphs. Show your work! Section A: Short questions concerning Signals & Systems A1. Give the sound pressure levels
AUDL GS08 and GAV1: 2013 Final exam page 1/13 You must complete all sections. Label all graphs. Show your work! Section A: Short questions concerning Signals & Systems A1. Give the sound pressure levels
Week 5. Fall 2016 Part 2: Structure and Function of Auditory System 1
 This outline summarizes major points covered in lecture. It is not intended to replace your own lecture notes. Week 5 How sound is heard: EAR Mechanical energy reaches the eardrum, moves to the middle
This outline summarizes major points covered in lecture. It is not intended to replace your own lecture notes. Week 5 How sound is heard: EAR Mechanical energy reaches the eardrum, moves to the middle
Chapter 13 Physics of the Ear and Hearing
 Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves
 The Auditory System PHYSIO: #3 DR.LOAI ZAGOUL 24/3/2014 Refer to the slides for some photos. Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves All waves have basic characteristics:
The Auditory System PHYSIO: #3 DR.LOAI ZAGOUL 24/3/2014 Refer to the slides for some photos. Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves All waves have basic characteristics:
Representation of sound in the auditory nerve
 Representation of sound in the auditory nerve Eric D. Young Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University Young, ED. Neural representation of spectral and temporal information in speech.
Representation of sound in the auditory nerve Eric D. Young Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University Young, ED. Neural representation of spectral and temporal information in speech.
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages
 PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
Academic and Research Staff Professor Dennis M. Freeman, Dr. Alexander Aranyosi, Dr. Stanley Hong
 Cochlear Mechanics Academic and Research Staff Professor Dennis M. Freeman, Dr. Alexander Aranyosi, Dr. Stanley Hong Graduate Students Chris Bergevin, Roozbeh Ghaffari, Wendy Gu, Kinuko Masaki, Scott Page
Cochlear Mechanics Academic and Research Staff Professor Dennis M. Freeman, Dr. Alexander Aranyosi, Dr. Stanley Hong Graduate Students Chris Bergevin, Roozbeh Ghaffari, Wendy Gu, Kinuko Masaki, Scott Page
Lecture 3: Perception
 ELEN E4896 MUSIC SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 3: Perception 1. Ear Physiology 2. Auditory Psychophysics 3. Pitch Perception 4. Music Perception Dan Ellis Dept. Electrical Engineering, Columbia University
ELEN E4896 MUSIC SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 3: Perception 1. Ear Physiology 2. Auditory Psychophysics 3. Pitch Perception 4. Music Perception Dan Ellis Dept. Electrical Engineering, Columbia University
Hearing. Juan P Bello
 Hearing Juan P Bello The human ear The human ear Outer Ear The human ear Middle Ear The human ear Inner Ear The cochlea (1) It separates sound into its various components If uncoiled it becomes a tapering
Hearing Juan P Bello The human ear The human ear Outer Ear The human ear Middle Ear The human ear Inner Ear The cochlea (1) It separates sound into its various components If uncoiled it becomes a tapering
Topic 4. Pitch & Frequency. (Some slides are adapted from Zhiyao Duan s course slides on Computer Audition and Its Applications in Music)
 Topic 4 Pitch & Frequency (Some slides are adapted from Zhiyao Duan s course slides on Computer Audition and Its Applications in Music) A musical interlude KOMBU This solo by Kaigal-ool of Huun-Huur-Tu
Topic 4 Pitch & Frequency (Some slides are adapted from Zhiyao Duan s course slides on Computer Audition and Its Applications in Music) A musical interlude KOMBU This solo by Kaigal-ool of Huun-Huur-Tu
Educational Module Tympanometry. Germany D Germering
 Educational Module anometry PATH medical Germany D-82110 Germering Our educational modules 1 are made for providing information on how the hearing organ works and which test procedures are used to test
Educational Module anometry PATH medical Germany D-82110 Germering Our educational modules 1 are made for providing information on how the hearing organ works and which test procedures are used to test
Compression in Hearing Aids
 Compression in Hearing Aids [Photo of Presenter] Presenter: Ted Venema PhD tvenema@shaw.ca From the desk of our Attorney The views expressed in presentations made at International Hearing Society (IHS)
Compression in Hearing Aids [Photo of Presenter] Presenter: Ted Venema PhD tvenema@shaw.ca From the desk of our Attorney The views expressed in presentations made at International Hearing Society (IHS)
external middle inner
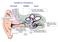 Auditory Periphery external middle inner 3. movement of stapes initiates a pressure wave in cochlear fluid. 1. sound causes air pressure to increase at eardrum 5. auditory nerve conveys neural signal to
Auditory Periphery external middle inner 3. movement of stapes initiates a pressure wave in cochlear fluid. 1. sound causes air pressure to increase at eardrum 5. auditory nerve conveys neural signal to
Topic 4. Pitch & Frequency
 Topic 4 Pitch & Frequency A musical interlude KOMBU This solo by Kaigal-ool of Huun-Huur-Tu (accompanying himself on doshpuluur) demonstrates perfectly the characteristic sound of the Xorekteer voice An
Topic 4 Pitch & Frequency A musical interlude KOMBU This solo by Kaigal-ool of Huun-Huur-Tu (accompanying himself on doshpuluur) demonstrates perfectly the characteristic sound of the Xorekteer voice An
Assessment of crossed auditory paths using Distortion-Product Otoacoustic Emissions
 AALBORG UNIVERSITY MASTER THESIS Assessment of crossed auditory paths using Distortion-Product Otoacoustic Emissions Author: Pablo CERVANTES FRUCTUOSO Supervisors: Dr. Rodrigo ORDOÑEZ Anders TORNVIG A
AALBORG UNIVERSITY MASTER THESIS Assessment of crossed auditory paths using Distortion-Product Otoacoustic Emissions Author: Pablo CERVANTES FRUCTUOSO Supervisors: Dr. Rodrigo ORDOÑEZ Anders TORNVIG A
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology II. Professor Dave Furness Keele University
 Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology II Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of this lecture Focus (2) on the biophysics of the cochlea, the dual roles
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology II Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of this lecture Focus (2) on the biophysics of the cochlea, the dual roles
Hearing I: Sound & The Ear
 Hearing I: Sound & The Ear Overview of Topics Chapter 5 in Chaudhuri Philosophical Aside: If a tree falls in the forest and no one is there to hear it... Qualities of sound energy and sound perception
Hearing I: Sound & The Ear Overview of Topics Chapter 5 in Chaudhuri Philosophical Aside: If a tree falls in the forest and no one is there to hear it... Qualities of sound energy and sound perception
Ear. Utricle & saccule in the vestibule Connected to each other and to the endolymphatic sac by a utriculosaccular duct
 Rahaf Jreisat *You don t have to go back to the slides. Ear Inner Ear Membranous Labyrinth It is a reflection of bony labyrinth but inside. Membranous labyrinth = set of membranous tubes containing sensory
Rahaf Jreisat *You don t have to go back to the slides. Ear Inner Ear Membranous Labyrinth It is a reflection of bony labyrinth but inside. Membranous labyrinth = set of membranous tubes containing sensory
L2: Speech production and perception Anatomy of the speech organs Models of speech production Anatomy of the ear Auditory psychophysics
 L2: Speech production and perception Anatomy of the speech organs Models of speech production Anatomy of the ear Auditory psychophysics Introduction to Speech Processing Ricardo Gutierrez-Osuna CSE@TAMU
L2: Speech production and perception Anatomy of the speech organs Models of speech production Anatomy of the ear Auditory psychophysics Introduction to Speech Processing Ricardo Gutierrez-Osuna CSE@TAMU
The Ear. The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear.
 The Ear The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The Ear There are three components of the outer ear: Pinna: the fleshy outer part of the ear which
The Ear The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The Ear There are three components of the outer ear: Pinna: the fleshy outer part of the ear which
Digital Speech and Audio Processing Spring
 Digital Speech and Audio Processing Spring 2008-1 Ear Anatomy 1. Outer ear: Funnels sounds / amplifies 2. Middle ear: acoustic impedance matching mechanical transformer 3. Inner ear: acoustic transformer
Digital Speech and Audio Processing Spring 2008-1 Ear Anatomy 1. Outer ear: Funnels sounds / amplifies 2. Middle ear: acoustic impedance matching mechanical transformer 3. Inner ear: acoustic transformer
Who are cochlear implants for?
 Who are cochlear implants for? People with little or no hearing and little conductive component to the loss who receive little or no benefit from a hearing aid. Implants seem to work best in adults who
Who are cochlear implants for? People with little or no hearing and little conductive component to the loss who receive little or no benefit from a hearing aid. Implants seem to work best in adults who
