Providing oral care to people with intellectual disability requires
|
|
|
- Moris Alexander
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Practical Oral Care for People With Intellectual Disability contents HealtH CHallenges In IntelleCtual disability and strategies for Care Mental challenges Behavior challenges Physical challenges Cerebral palsy Cardiovascular anomalies Seizures Visual impairments Hearing loss and deafness oral HealtH Problems In IntelleCtual disability and strategies for Care Periodontal disease Dental caries Malocclusion Missing permanent teeth, delayed eruption, and enamel hypoplasia Damaging oral habits Trauma and injury additional readings Providing oral care to people with intellectual disability requires adaptation of the skills you use every day. In fact, most people with mild or moderate intellectual disability can be treated successfully in the general practice setting. This booklet will help you make a difference in the lives of people who need professional oral care. Intellectual disability is a disorder of mental and adaptive functioning, meaning that people who are affected are challenged by the skills they use in everyday life. Intellectual disability is not a disease or a mental illness; it is a developmental disability that varies in severity and is usually Data indicate that people with associated with physical problems. intellectual disability While one person with intellectual have more untreated disability may have slight difficulty caries and a higher thinking and communicating, prevalence of gingivitis another may face major challenges and other periodontal with basic self-care and physical diseases than the mobility. general population. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES l NatioNal institutes of HealtH l National institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research
2 Health Challenges in Intellectual disability and strategies for Care Many people with intellectual disability also have other conditions such as cerebral palsy, seizure or psychiatric disorders, attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder, or problems with vision, communication, and eating. Though language and communication problems are common in anyone with intellectual disability, motor skills are typically more affected when a person has coexisting conditions. Before the appointment, obtain and review the patient s medical history. Consultation with physicians, family, and caregivers is essential to assembling an accurate medical history. Also, determine who can legally provide informed consent for treatment. MENTAL CHALLENgES. People with intellectual disability learn slowly and often with difficulty. Ordinary activities of daily living, such as brushing teeth and getting dressed, and understanding the behavior of others as well as their own, can all present challenges to a person with intellectual disability. Set the stage for a successful visit by involving the entire dental team from the receptionist s friendly greeting to the caring attitude of the dental assistant in the operatory. All should be aware of your patient s mental challenges. Reduce distractions in the operatory, such as unnecessary sights, sounds, or other stimuli, to compensate for the short attention spans commonly observed in people with intellectual disability. Talk with the parent or caregiver to determine your patient s intellectual and functional abilities, then explain each procedure at a level the patient can understand. Allow extra time to explain oral health issues or instructions and demonstrate the instruments you will use. Address your patient directly and with respect to establish a rapport. Even if the caregiver is in the room, direct all questions and comments to your patient. Use simple, concrete instructions and repeat them often to compensate for any short-term memory problems. Speak slowly and give only one direction at a time. Be consistent in all aspects of oral care, since long-term memory is usually unaffected. Use the same staff and dental operatory each time to help sustain familiarity. The more consistency you provide for your patients, the more likely they will cooperate. Listen actively, since communicating clearly is often difficult for people with intellectual disability. Show your patient whether you understand. Be sensitive to the methods he or she uses to communicate, including gestures and verbal or nonverbal requests. 2
3 intellectual disability BEHAVIOR CHALLENgES. While most people with intellectual disability do not pose significant behavior problems that complicate oral care, anxiety about dental treatment occurs frequently. People unfamiliar with a dental office and its equipment and instruments may exhibit fear. Some react to fear with uncooperative behavior, such as crying, wiggling, kicking, aggressive language, or anything that will help them avoid treatment. You can make oral health care a better experience by comforting your patients and acknowledging their anxiety. Talk to the caregiver or physician about techniques they have found to be effective in managing the patient s behavior. Schedule patients with intellectual disability early in the day if possible. Early appointments can help ensure that everyone is alert and attentive and that waiting time is reduced. Keep appointments short and postpone difficult procedures until after your patient is familiar with you and your staff. Allow extra time for your patients to get comfortable with you, your office, and the entire oral health care team. Invite patients and their families to visit your office before beginning treatment. Permit the parents or caregiver to come into the treatment setting to provide familiarity, help with communication, and offer a calming influence by holding your patient s hand during treatment. Some patients behavior may improve if they bring comfort items such as a stuffed animal or blanket. Reward cooperative behavior with compliments throughout the appointment. Consider nitrous oxide/oxygen sedation to reduce anxiety and fear and improve cooperation. Obtain informed consent from the legal guardian before administering any kind of sedation. Use immobilization techniques only when absolutely necessary to protect the patient and staff during dental treatment not as a convenience. There are no universal guidelines on immobilization that apply to all treatment settings. Before employing any kind of immobilization, it may help to consult available guidelines on federally funded care, your State department of mental health/ disabilities, and your State Dental Practice Act. Guidelines on behavior management published by the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry ( may also be useful. Obtain consent from your patient s legal guardian and choose the least restrictive technique that will allow you to provide care safely. Immobilization should not cause physical injury or undue discomfort. People with intellectual disability often engage in perseveration, a continuous, meaningless repetition of words, phrases, or movements. Your patient may mimic the sound of the suction, for example, or repeat an instruction over and again. Avoid demonstrating dental equipment if it triggers perseveration, and note this in the patient s record. allow extra time for your patient to get comfortable with you, your office, and the entire oral health care team. 3
4 PHySICAL CHALLENgES. Intellectual disabiliy does not always include a specific physical trait, although many people have distinguishing features such as orofacial abnormalities, scoliosis, unsteady gait, or hypotonia due to coexisting con ditions. Countering physical challenges requires attention to detail. Maintain clear paths for movement throughout the treatment setting. Keep instruments and equipment out of the patient s way. Place and maintain your patient in the center of the dental chair to minimize the risk of injury. Placing pillows on both sides of the patient can provide stability. If you need to transfer your patient from a wheelchair to the dental chair, ask the patient or caregiver about special preferences such as padding, pillows, or other things you can provide to ease the transition. The patient or caregiver can often explain how to make a smooth transfer. (See Wheelchair Transfer: A Health Care Provider s Guide, also part of this series.) Some patients cannot be moved into the dental chair but instead must be treated in their wheelchairs. Some wheelchairs recline or are specially molded to fit people s bodies. Lock the wheels, then slip a sliding board (also called a transfer board) behind the patient s back to provide support for the head and neck during care. CEREBRAL PALSy occurs in one-fourth of those who have intellectual disability and tends to affect motor skills more than cognitive skills. Un controlled body movements and reflexes associated with cerebral palsy can make it difficult to provide care. Place and maintain your patient in the center of the dental chair. Do not force arms and legs into unnatural positions, but allow your patient to settle into a position that is comfortable and will not interfere with dental treatment. Observe your patient s movements and look for patterns to help you anticipate direction and intensity. Trying to stop these movements may only intensify the involuntary response. Try instead to anticipate the movements, blending your movements with those of your patient or working around them. Softly cradle your patient s head during treatment. Be gentle and slow if you need to turn the patient s head. Help minimize the gag reflex by placing your patient s chin in a neutral or downward position. Stay alert and work efficiently in short appointments. Exert gentle but firm pressure on your patient s arm or leg if it begins to shake. Take frequent breaks or consider prescribing muscle relaxants when long procedures are needed. People with cerebral palsy may need sedation, general anesthesia, or hospitalization if extensive dental treatment is required. CARDIOVASCULAR ANOMALIES such as heart murmurs and damaged heart valves occur frequently in people with intellectual disability, especially those with Down syndrome or multiple disabilities. Consult the patient s physician to determine if antibiotic prophylaxis ( is necessary for dental treatment. 4
5 intellectual disability SEIzURES are common in this population but can usually be controlled with anti convulsant medications. The mouth is always at risk during a seizure: Patients may chip teeth or bite the tongue or cheeks. Persons with controlled seizure disorders can easily be treated in the general dental office. Face your patients when you speak and keep them apprised of each upcoming step, especially when water will be used. Rely on clear, descriptive language to explain procedures and demonstrate how equipment might feel and sound. Provide written instructions in large print (16 point or larger). Consult your patient s physician. Record information in the chart about the frequency of seizures and the medications used to control them. Determine before the appointment whether medications have been taken as directed. Know and avoid any factors that trigger your patient s seizures. Be prepared to manage a seizure. If one occurs during oral care, remove any instruments from the mouth and clear the area around the dental chair. Attaching dental floss to rubber dam clamps and mouth props when treatment begins can help you remove them quickly. Do not attempt to insert any objects between the teeth during a seizure. Stay with your patient, turn him or her to one side, and monitor the airway to reduce the risk of aspiration. VISUAL IMPAIRMENTS, most commonly strabismus (crossed or misaligned eyes) and refractive errors, can be managed with careful planning. Determine the level of assistance your patient requires to move safely through the dental office. Use your patients other senses to connect with them, establish trust, and make treatment a good experience. Tactile feedback, such as a warm handshake, can make your patients feel comfortable. HEARINg LOSS and DEAFNESS can also be accommodated with careful planning. Patients with a hearing problem may appear to be stubborn because of their seeming lack of response to a request. Patients may want to adjust their hearing aids or turn them off, since the sound of some instruments may cause auditory discomfort. If your patient reads lips, speak in a normal cadence and tone. If your patient uses a form of sign language, ask the interpreter to come to the appointment. Speak with this person in advance to discuss dental terms and your patient s needs. Visual feedback is helpful. Maintain eye contact with your patient. Before talking, eliminate background noise (turn off the radio and the suction). Sometimes people with a hearing loss simply need you to speak clearly in a slightly louder voice than normal. Remember to remove your facemask first or wear a clear face shield. Record in the patient s chart strategies that were successful in providing care. Note your patient s preferences and other unique details that will facilitate treatment, such as music, comfort items, and flavor choices. 5
6 oral Health Problems in Intellectual disability and strategies for Care a developmental disability in and of itself should not be perceived as a barrier to orthodontic treatment. In general, people with intellectual disability have poorer oral health and oral hygiene than those without this condition. Data indicate that people who have intellectual disability have more untreated caries and a higher prevalence of gingivitis and other periodontal diseases than the general population. PERIODONTAL DISEASE. Medications, malocclusion, multiple disabilities, and poor oral hygiene combine to increase the risk of periodontal disease in people with intellectual disability. Encourage independence in daily oral hygiene. Ask patients to show you how they brush, and follow up with specific recommendations on brushing methods or toothbrush adaptations. Involve your patients in hands-on demonstrations of brushing and flossing. Some patients cannot brush and floss independently due to impaired physical coordination or cognitive skills. Talk to their caregivers about daily oral hygiene. Do not assume that all caregivers know the basics; demonstrate proper brushing and flossing techniques. A power toothbrush or a floss holder can simplify oral care. Also, use your experiences with each patient to demonstrate sitting or standing positions for the caregiver. Emphasize that a consistent approach to oral hygiene is important caregivers should try to use the same location, timing, and positioning. Some patients benefit from the daily use of an antimicrobial agent such as chlorhexidine. Recommend an ap pro priate delivery method based on your patient s abilities. Rinsing, for example, may not work for a patient who has swallowing difficulties or one who cannot expectorate. Chlorhexidine applied using a spray bottle or toothbrush is equally efficacious. If use of particular medications has led to gingival hyperplasia, emphasize the importance of daily oral hygiene and frequent professional cleanings. DENTAL CARIES. People with intellectual disability develop caries at the same rate as the general population. The prevalence of untreated dental caries, however, is higher among people with intellectual disability, particularly those living in noninstitutional settings. Emphasize noncariogenic foods and beverages as snacks. Advise caregivers to avoid using sweets as incentives or rewards. Advise patients taking medicines that cause xerostomia to drink water often. Suggest sugar-free medicine if available and stress the importance of rinsing with water after dosing. Recommend preventive measures such as fluorides and sealants. MALOCCLUSION. The prevalence of malocclusion in people with intellectual disability is similar to that found in the general population, except for those with coexisting conditions such as cerebral palsy or Down syndrome. A developmental disability in and of itself should not be perceived as a barrier to orthodontic treatment. The ability of the patient or caregiver to maintain good daily oral hygiene is critical to the feasibility and success of treatment. tips for CaregIvers are available In the booklet Dental Care every Day: a Caregiver s guide, also Part of this series. 6
7 intellectual disability MISSINg PERMANENT TEETH, DELAyED ERUPTION, and ENAMEL HyPOPLASIA are more common in people with intellectual disability and coexisting conditions than in people with intellectual disability alone. Examine a child by his or her first birthday and regularly thereafter to help identify unusual tooth formation and patterns of eruption. Consider using a panoramic radiograph to determine whether teeth are congenitally missing. Patients often find this technique less threatening than individual films. Take appropriate steps to reduce sensitivity and risk of caries in your patients with enamel hypoplasia. DAMAgINg ORAL HABITS are a problem for some people with intellectual disability. Common habits include bruxism; mouth breathing; tongue thrusting; self-injurious behavior such as picking at the gingiva or biting the lips; and pica eating objects and substances such as gravel, cigarette butts, or pens. If a mouth guard can be tolerated, prescribe one for patients who have problems with self-injurious behavior or bruxism. TRAUMA and INJURy to the mouth from falls or accidents occur in people with intellectual disability. Suggest a tooth-saving kit for group homes. Emphasize to caregivers that traumas require immediate professional attention and explain the procedures to follow if a permanent tooth is knocked out. Also, instruct caregivers to locate any missing pieces of a fractured tooth, and explain that radiographs of the patient s chest may be necessary to determine whether any fragments have been aspirated. Physical abuse often presents as oral trauma. Abuse is reported more frequently in people with developmental disabilities than in the general population. If you suspect that a child is being abused or neglected, State laws require that you call your Child Protective Services agency. Assistance is also available from the Childhelp USA National Child Abuse Hotline at (800) or the Child Welfare Information Gateway ( Making a difference in the oral health of a person with intellectual disability may go slowly at first, but determination can bring positive results and invaluable rewards. By adopting the strategies discussed in this booklet, you can have a significant impact not only on your patients oral health, but on their quality of life as well. additional readings Batshaw ML, Shapiro B, Farber MLZ. Developmental Delay & Intellectual Disability. In Batshaw ML, Pellegrino L, Roizen NJ (eds.). Children With Disabilities (6th ed.). Baltimore, MD: Paul H. Brookes Publishing Co., Horwitz SM, Kerker BD, Owens PL, Zigler E. Dental health among individuals with mental retardation. In The Health Status and Needs of Individuals With Mental Retardation. New Haven, CT: Yale University School of Medicine, pp U.S. Public Health Service. Closing the Gap: A National Blueprint for Improving the Health of Individuals With Mental Retardation. Report of the Surgeon General s Conference on Health Disparities and Mental Retardation. Washington, DC, February Weddell JA, Sanders BJ, Jones JE. Dental problems of children with disabilities. In McDonald RE, Avery DR, Dean JA. Dentistry for the Child and Adolescent (8th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Mosby, pp For more information about intellectual disability, contact National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Information Resource Center P.O. Box 3006 Rockville, MD (800) NICHDIRC@mail.nih.gov 7
8 National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research Centers for Disease Control and Prevention This booklet is one in a series on providing oral care for people with mild or moderate developmental disabilities. The issues and care strategies listed are intended to provide general guidance on how to manage various oral health challenges common in people with intellectual disability. Other booklets in this series: Continuing Education: Practical Oral Care for People With Developmental Disabilities Practical Oral Care for People With Autism Practical Oral Care for People With Cerebral Palsy Practical Oral Care for People With Down Syndrome Wheelchair Transfer: A Health Care Provider s Guide Dental Care Every Day: A Caregiver s Guide Special Care Dentistry Association For additional copies of this booklet, contact National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research National Oral Health Information Clearinghouse 1 NOHIC Way Bethesda, MD (301) This publication is not copyrighted. Make as many photocopies as you need. NIH Publication No Reprinted August 2008 ACkNOWLEDgMENTS the National institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research thanks the oral health professionals and caregivers who contributed their time and expertise to reviewing and pretesting the Practical Oral Care series. Expert Review Panel Mae Chin, RDH, university of Washington, seattle, Wa sanford J. fenton, DDs, university of tennessee, Memphis, tn Ray lyons, DDs, New Mexico Department of Health, los lunas, NM Christine Miller, RDH, university of the Pacific, san francisco, Ca steven P. Perlman, DDs, special olympics special smiles, lynn, Ma David tesini, DMD, Natick, Ma
hearing loss. Additionally, most people with this disorder have mild or
 Practical Oral Care for People With Down Syndrome contents HealtH CHallenges In down syndrome and strategies for Care 2..................... Intellectual disability Behavior management 3.....................
Practical Oral Care for People With Down Syndrome contents HealtH CHallenges In down syndrome and strategies for Care 2..................... Intellectual disability Behavior management 3.....................
Developmental disabilities such as autism, cerebral palsy, Down syndrome,
 Continuing Education Practical Oral Care for People With Developmental Disabilities CONTENTS HEALTH CHALLENGES AND STRATEGIES FOR CARE 2..................... Mental capabilities Behavior problems Mobility
Continuing Education Practical Oral Care for People With Developmental Disabilities CONTENTS HEALTH CHALLENGES AND STRATEGIES FOR CARE 2..................... Mental capabilities Behavior problems Mobility
DENTAL CARE EVERY DAY
 DENTAL CARE EVERY DAY A Caregiver s Guide U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research Contents Getting Started... 2
DENTAL CARE EVERY DAY A Caregiver s Guide U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research Contents Getting Started... 2
ORAL HEALTH AND HYGIENE. Erica R. Thomas, MS DDA Health Initiative
 ORAL HEALTH AND HYGIENE Erica R. Thomas, MS DDA Health Initiative ORAL HEALTH CARE FOR PEOPLE WITH DISABILITIES Developmental disabilities affect the mind, the body and the skills people use in everyday
ORAL HEALTH AND HYGIENE Erica R. Thomas, MS DDA Health Initiative ORAL HEALTH CARE FOR PEOPLE WITH DISABILITIES Developmental disabilities affect the mind, the body and the skills people use in everyday
AADMD NATIONAL SRC NEWSLETTER
 AADMD SRC 10/31/2017 September/October Newsletter AADMD NATIONAL SRC NEWSLETTER UPDATES FROM SCHOOLS AROUND THE COUNTRY The University Of Minnesota School Of Dentistry completed many events this summer.
AADMD SRC 10/31/2017 September/October Newsletter AADMD NATIONAL SRC NEWSLETTER UPDATES FROM SCHOOLS AROUND THE COUNTRY The University Of Minnesota School Of Dentistry completed many events this summer.
PRINCIPLES OF CAREGIVING DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES MODULE
 PRINCIPLES OF CAREGIVING DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES MODULE CHAPTER 1: KNOWLEDGE OF DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES CONTENT: A. Developmental Disabilities B. Introduction to Human Development C. The Four Developmental
PRINCIPLES OF CAREGIVING DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES MODULE CHAPTER 1: KNOWLEDGE OF DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES CONTENT: A. Developmental Disabilities B. Introduction to Human Development C. The Four Developmental
Course #:
 Welcome to Lesson 7: Indicators of Problems of the Dental Health for Individuals with Disabilities webcast series. Please adjust your computer volume so that it is at a comfortable listening level for
Welcome to Lesson 7: Indicators of Problems of the Dental Health for Individuals with Disabilities webcast series. Please adjust your computer volume so that it is at a comfortable listening level for
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Dental Care for Individuals with Autism. Objectives. First Visits. Beverly King, M. Ed. First tooth or first birthday
 Slide 1 Dental Care for Individuals with Autism Beverly King, M. Ed. Slide 2 Objectives Learn ways to teach children proper oral hygiene. Discuss a variety of ways to support and facilitate good oral hygiene
Slide 1 Dental Care for Individuals with Autism Beverly King, M. Ed. Slide 2 Objectives Learn ways to teach children proper oral hygiene. Discuss a variety of ways to support and facilitate good oral hygiene
Improving Access for Patients with Developmental Disabilities. Candace Owen, RDH, MS, MPH April 26, 2017 National Oral Health Conference
 Improving Access for Patients with Developmental Disabilities Candace Owen, RDH, MS, MPH April 26, 2017 National Oral Health Conference Special Care Dentistry Provision of oral care services to people
Improving Access for Patients with Developmental Disabilities Candace Owen, RDH, MS, MPH April 26, 2017 National Oral Health Conference Special Care Dentistry Provision of oral care services to people
Fact Sheet. Dental health for people. with Down syndrome. Health. Dental health. Good dental health begins at home
 Health Fact Sheet Dental health for people with Down syndrome Dental health Dental care is important for everybody. For people with Down syndrome there can be some differences, but it s just as important.
Health Fact Sheet Dental health for people with Down syndrome Dental health Dental care is important for everybody. For people with Down syndrome there can be some differences, but it s just as important.
Three Good Reasons to See a Dentist Before Cancer Treatment
 Three Good Reasons to See a Dentist Before Cancer Treatment About Three Good Reasons To See a Dentist Before Cancer Treatment Thank you for your interest in Three Good Reasons To See a Dentist Before Cancer
Three Good Reasons to See a Dentist Before Cancer Treatment About Three Good Reasons To See a Dentist Before Cancer Treatment Thank you for your interest in Three Good Reasons To See a Dentist Before Cancer
Overview: The health care provider explores the health behaviors and preventive measures that enhance children s oral health.
 Lesson 5: Prevention Overview: The health care provider explores the health behaviors and preventive measures that enhance children s oral health. Goals: The health care provider will be able to describe:
Lesson 5: Prevention Overview: The health care provider explores the health behaviors and preventive measures that enhance children s oral health. Goals: The health care provider will be able to describe:
Dental Care in Scleroderma
 Dental Care in Scleroderma People living with scleroderma face unique challenges while trying to maintain their oral health. They are more likely to be affected by dental conditions such as small mouth,
Dental Care in Scleroderma People living with scleroderma face unique challenges while trying to maintain their oral health. They are more likely to be affected by dental conditions such as small mouth,
Visit DeltaDentalMN.org/SmilesAtSchool for additional program materials, including educational videos, activities and lesson plans.
 Smiles@School is a statewide initiative of Delta Dental of Minnesota Foundation to support children s oral health through education, prevention and dental sealant programs in schools. Education is the
Smiles@School is a statewide initiative of Delta Dental of Minnesota Foundation to support children s oral health through education, prevention and dental sealant programs in schools. Education is the
Dental care and dementia
 PBO 930022142 NPO 049-191 Dental care and dementia Good oral health is important for a person s sense of well-being and quality of life. Poor oral health can lead to pain and tooth loss, affecting self-esteem
PBO 930022142 NPO 049-191 Dental care and dementia Good oral health is important for a person s sense of well-being and quality of life. Poor oral health can lead to pain and tooth loss, affecting self-esteem
INSTRUCTOR S GUIDE. Oral Health. First Edition, 2006
 INSTRUCTOR S GUIDE Oral Health First Edition, 2006 California Childcare Health Program Administered by the University of California, San Francisco School of Nursing, Department of Family Health Care Nursing
INSTRUCTOR S GUIDE Oral Health First Edition, 2006 California Childcare Health Program Administered by the University of California, San Francisco School of Nursing, Department of Family Health Care Nursing
Ortho Hygiene. #2078, Tuscany Blvd. NW, Calgary, AB T3L 2V7 Phone: Fax:
 Ortho Hygiene You already know that maintaining good oral hygiene is important for everyone but when you re having orthodontic treatment, it s even more critical. Why? Because, while the appliances (such
Ortho Hygiene You already know that maintaining good oral hygiene is important for everyone but when you re having orthodontic treatment, it s even more critical. Why? Because, while the appliances (such
Feature Articles. Sponsored by:
 Feature Articles 2018 Sponsored by: Oral healthcare for seniors Today s seniors can expect to keep most, if not all, of their teeth as they age thanks to healthier lifestyles and advances in oral and medical
Feature Articles 2018 Sponsored by: Oral healthcare for seniors Today s seniors can expect to keep most, if not all, of their teeth as they age thanks to healthier lifestyles and advances in oral and medical
A Healthy Mouth for Your Baby
 A Healthy Mouth for Your Baby U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research Before your baby is born What you eat when
A Healthy Mouth for Your Baby U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research Before your baby is born What you eat when
Toddlers to Teens Dental Guide. A Quick Guide For Parents
 Toddlers to Teens Dental Guide A Quick Guide For Parents INTRODUCTION Your children mean more to you than anything in this world, but it can be hard to know the best way to care for them. Whether it s
Toddlers to Teens Dental Guide A Quick Guide For Parents INTRODUCTION Your children mean more to you than anything in this world, but it can be hard to know the best way to care for them. Whether it s
DW Dental History Survey. Data Collection Period n=100 April 25, 2017 September 22, 2017
 DW Dental History Survey Data Collection Period n=100 April 25, 2017 September 22, 2017 Q1. At what age did your loved one with Dandy-Walker first go to the dentist? Q1. Comments She has not gone yet
DW Dental History Survey Data Collection Period n=100 April 25, 2017 September 22, 2017 Q1. At what age did your loved one with Dandy-Walker first go to the dentist? Q1. Comments She has not gone yet
What are dental sealants?
 What are dental sealants? Sealants are thin, plastic coatings painted on the chewing surfaces of the back teeth. Sealants are put on in dentists offices, clinics, and sometimes in schools. Getting sealants
What are dental sealants? Sealants are thin, plastic coatings painted on the chewing surfaces of the back teeth. Sealants are put on in dentists offices, clinics, and sometimes in schools. Getting sealants
TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS... 1 ORAL HEALTH IS AN IMPORTANT PART OF TOTAL HEALTH... 2 DENTAL DECAY... 2
 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS... 1 ORAL HEALTH IS AN IMPORTANT PART OF TOTAL HEALTH... 2 DENTAL DECAY... 2 PRIMARY TEETH (BABY TEETH, DECIDUOUS TEETH)... 2 EARLY CHILDHOOD TOOTH DECAY... 2 CAREGIVER
TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS... 1 ORAL HEALTH IS AN IMPORTANT PART OF TOTAL HEALTH... 2 DENTAL DECAY... 2 PRIMARY TEETH (BABY TEETH, DECIDUOUS TEETH)... 2 EARLY CHILDHOOD TOOTH DECAY... 2 CAREGIVER
Good oral hygiene today
 Dental essentials Good oral hygiene today Healthy teeth and gums for life You know, there s nothing like the fresh, clean feeling in your mouth after you ve brushed and flossed your teeth to make you feel
Dental essentials Good oral hygiene today Healthy teeth and gums for life You know, there s nothing like the fresh, clean feeling in your mouth after you ve brushed and flossed your teeth to make you feel
The board certified pediatric dentists at Jenkins and LeBlanc are committed to helping you at every stage of tooth development.
 GROWING HEALTHY SMILES The board certified pediatric dentists at Jenkins and LeBlanc are committed to helping you at every stage of tooth development. WWW.KIDSMILEKC.COM TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION ONE Why
GROWING HEALTHY SMILES The board certified pediatric dentists at Jenkins and LeBlanc are committed to helping you at every stage of tooth development. WWW.KIDSMILEKC.COM TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION ONE Why
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PREVENTIVE PEDIATRIC ORAL HEALTH CARE
 Department of Health and Human Services MaineCare Services 242 State Street 11 State House Station Augusta, Maine 04333-0011 Tel.: (207) 287-2674; Fax: (207) 287-2675 TTY Users: Dial 711 (Maine Relay)
Department of Health and Human Services MaineCare Services 242 State Street 11 State House Station Augusta, Maine 04333-0011 Tel.: (207) 287-2674; Fax: (207) 287-2675 TTY Users: Dial 711 (Maine Relay)
Dental Implants. Are they an option for you? SAMPLE
 DENTAL PERIODONTAL TREATMENT Dental Implants Are they an option for you? Dental implants replace natural missing teeth Dental implants are posts surgically placed into the upper or lower jawbone. They
DENTAL PERIODONTAL TREATMENT Dental Implants Are they an option for you? Dental implants replace natural missing teeth Dental implants are posts surgically placed into the upper or lower jawbone. They
SAMPLE. Dental Implants Are they an option for you? ADA Healthy Smile Tips
 In this brochure: Types of dental implants Benefits of implants How implants are placed ADA Healthy Smile Tips Brush your teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste. Clean between your teeth daily. Eat
In this brochure: Types of dental implants Benefits of implants How implants are placed ADA Healthy Smile Tips Brush your teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste. Clean between your teeth daily. Eat
Oral Health Practices for Persons with Intellectual/ Developmental Disabilities
 Oral Health Practices for Persons with Intellectual/ Developmental Disabilities Theresa Brennan RDH, BS Health Education Tufts Dental Facilities Tufts Community Dental Program Speaker Introduction Theresa
Oral Health Practices for Persons with Intellectual/ Developmental Disabilities Theresa Brennan RDH, BS Health Education Tufts Dental Facilities Tufts Community Dental Program Speaker Introduction Theresa
A Healthy Mouth for Your Baby
 A Healthy Mouth for Your Baby U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health Healthy teeth are important even baby teeth. Children need healthy teeth to help them chew and to
A Healthy Mouth for Your Baby U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health Healthy teeth are important even baby teeth. Children need healthy teeth to help them chew and to
Dental Radiography Series
 Dental Radiography Series Guidelines for prescribing dental radiographs. Background Radiological s are used to discover and define the type and extent of disease in many clinical situations. However, public
Dental Radiography Series Guidelines for prescribing dental radiographs. Background Radiological s are used to discover and define the type and extent of disease in many clinical situations. However, public
Meeting someone with disabilities etiquette
 Meeting someone with disabilities etiquette Many people unsure how to go about meeting someone with a disability because they don t want to say or do the wrong thing. Here are a few tips to keep in mind
Meeting someone with disabilities etiquette Many people unsure how to go about meeting someone with a disability because they don t want to say or do the wrong thing. Here are a few tips to keep in mind
New Patient Information
 New Patient Information Bloomfield Children s Dentistry 6405 Telegraph Road Bloomfield Hills, MI 48301 In order to get to know your family better, and to provide you with the best service, we ask that
New Patient Information Bloomfield Children s Dentistry 6405 Telegraph Road Bloomfield Hills, MI 48301 In order to get to know your family better, and to provide you with the best service, we ask that
Knowledge and Oral Health Attitudes among Care Providers of Children with Intellectual Disabilities: A Cross-sectional Study
 Prajakta P Shanbhag et al research article 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1076 Knowledge and Oral Health Attitudes among Care Providers of Children with Intellectual Disabilities: A Cross-sectional Study 1
Prajakta P Shanbhag et al research article 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1076 Knowledge and Oral Health Attitudes among Care Providers of Children with Intellectual Disabilities: A Cross-sectional Study 1
HEALTHY SMILE, HAPPY LIFE
 Flyers HEALTHY SMILE, HAPPY LIFE Oral health is part of being well, and the foundation for a healthy and active lifestyle. When our mouths, gums or teeth aren t healthy, our bodies may be more susceptible
Flyers HEALTHY SMILE, HAPPY LIFE Oral health is part of being well, and the foundation for a healthy and active lifestyle. When our mouths, gums or teeth aren t healthy, our bodies may be more susceptible
When You Need a. General Dentist Vs. a Specialist
 When You Need a General Dentist Vs. a Specialist Most parents realize the importance of helping their kids get off to a healthy start when it comes to taking care of their teeth. They put in the time to
When You Need a General Dentist Vs. a Specialist Most parents realize the importance of helping their kids get off to a healthy start when it comes to taking care of their teeth. They put in the time to
DEMENTIA Dementia is NOT a normal part of aging Symptoms of dementia can be caused by different diseases Some symptoms of dementia may include:
 DEMENTIA Dementia is NOT a normal part of aging Symptoms of dementia can be caused by different diseases Some symptoms of dementia may include: 1. Memory loss The individual may repeat questions or statements,
DEMENTIA Dementia is NOT a normal part of aging Symptoms of dementia can be caused by different diseases Some symptoms of dementia may include: 1. Memory loss The individual may repeat questions or statements,
YMCA of Oakville. Accessibility Standard for Customer Service. Training Workbook
 YMCA of Oakville Accessibility Standard for Customer Service Training Workbook Contents The following workbook contains valuable information about the Accessibility Standard for Customer Service. Information
YMCA of Oakville Accessibility Standard for Customer Service Training Workbook Contents The following workbook contains valuable information about the Accessibility Standard for Customer Service. Information
PRE-SEDATION RECORD PHYSICIAN S ASSESSMENT
 PRE-SEDATION RECORD PHYSICIAN S ASSESSMENT Dear Doctor, Your patient is scheduled for dental treatment under intravenous sedation. Please complete this history and physical examination form and return
PRE-SEDATION RECORD PHYSICIAN S ASSESSMENT Dear Doctor, Your patient is scheduled for dental treatment under intravenous sedation. Please complete this history and physical examination form and return
Mouth Care without a Battle Worksheet. DVD 1: Module 1 Part 1 Mouth Care Basics (Basic Steps of Mouth Care)
 Mouth Care without a Battle Worksheet DVD 1: Module 1 Part 1 Mouth Care Basics (Basic Steps of Mouth Care) Always wear when providing mouth care and/or denture care. Mouth care is not merely, but a vital
Mouth Care without a Battle Worksheet DVD 1: Module 1 Part 1 Mouth Care Basics (Basic Steps of Mouth Care) Always wear when providing mouth care and/or denture care. Mouth care is not merely, but a vital
A Healthy Mouth for Your Baby
 A Healthy Mouth for Your Baby U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health A Healthy Mouth for Your Baby Healthy teeth are important even baby teeth. Children need healthy
A Healthy Mouth for Your Baby U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health A Healthy Mouth for Your Baby Healthy teeth are important even baby teeth. Children need healthy
When Do You Need a. General Dentist vs. a Specialist?
 When Do You Need a General Dentist vs. a Specialist? Most parents realize the importance of helping their kids get off to a healthy start when it comes to taking care of their teeth. They put in the time
When Do You Need a General Dentist vs. a Specialist? Most parents realize the importance of helping their kids get off to a healthy start when it comes to taking care of their teeth. They put in the time
DENTAL INSURANCE Name Employer Name Policy Holder Name Policy Holder Birthdate Policy Number Group Number Social Security Number
 ABOUT YOUR CHILD Nick Name ( ) Female ( ) Male Birthdate School Home Address DENTAL INSURANCE Employer Name Policy Holder Name Policy Holder Birthdate Policy Number Group Number Social Security Number
ABOUT YOUR CHILD Nick Name ( ) Female ( ) Male Birthdate School Home Address DENTAL INSURANCE Employer Name Policy Holder Name Policy Holder Birthdate Policy Number Group Number Social Security Number
Promoting Oral Health
 Promoting Oral Health Hope Saltmarsh, RDH, M.Ed. Doug Johnson, DMD October 2009 11/3/2009 12:14:04 PM 5864_ER_RED 1 Learning Objectives Identify Bright Futures recommendations for oral health. Describe
Promoting Oral Health Hope Saltmarsh, RDH, M.Ed. Doug Johnson, DMD October 2009 11/3/2009 12:14:04 PM 5864_ER_RED 1 Learning Objectives Identify Bright Futures recommendations for oral health. Describe
Lesson 8: Emergency Situations and Dental Procedures
 The following presentation was originally developed for individuals and families by Achieva (a Western PA service provider). Now offered as a webcast production, ODP is providing this valuable resource
The following presentation was originally developed for individuals and families by Achieva (a Western PA service provider). Now offered as a webcast production, ODP is providing this valuable resource
Appendix. CPT only copyright 2007 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. NTHSteps Dental Guidelines
 Appendix NTHSteps Dental Guidelines N N.1 American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Periodicity Guidelines.................. N-2 N.2 American Dental Association Guidelines for Prescribing Dental Radiographs.........
Appendix NTHSteps Dental Guidelines N N.1 American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Periodicity Guidelines.................. N-2 N.2 American Dental Association Guidelines for Prescribing Dental Radiographs.........
Dr Farayi Shakespeare Moyana /6/2017 Do my KIDS need dental braces?
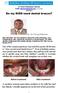 Do my KIDS need dental braces? By: Dr Farayi Moyana BDS; MPH (SMU, SA); B.Ed (Adult)(UZ); MBA(ZOU); PGdip (Orthodontics, Pret.); PGdip(Health Res ethics, Stellenbosch); PostGRAD cert (Dental Implants,
Do my KIDS need dental braces? By: Dr Farayi Moyana BDS; MPH (SMU, SA); B.Ed (Adult)(UZ); MBA(ZOU); PGdip (Orthodontics, Pret.); PGdip(Health Res ethics, Stellenbosch); PostGRAD cert (Dental Implants,
APPENDIX G: THSTEPS DENTAL GUIDELINES
 CHILDREN S SERVICES HANDBOOK APPENDIX G: THSTEPS DENTAL GUIDELINES G.1 American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Periodicity Guidelines (9 Pages)........ CH-382 G.2 American Dental Association Guidelines
CHILDREN S SERVICES HANDBOOK APPENDIX G: THSTEPS DENTAL GUIDELINES G.1 American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Periodicity Guidelines (9 Pages)........ CH-382 G.2 American Dental Association Guidelines
Tips for Effective Communications
 People who have Mobility Impairments Always ask the person how you can help before attempting any assistance. Every person and every disability is unique. Even though it may be important to evacuate the
People who have Mobility Impairments Always ask the person how you can help before attempting any assistance. Every person and every disability is unique. Even though it may be important to evacuate the
19/03/2018. Objectives
 Target group 10 to 14 years old Aims This presentation has been designed to provide those viewing it with information on how to maintain a good Oral Health Objectives At the end, the viewer will be able
Target group 10 to 14 years old Aims This presentation has been designed to provide those viewing it with information on how to maintain a good Oral Health Objectives At the end, the viewer will be able
Precious Moments. Giving comfort and support when someone you love is dying.
 Precious Moments Giving comfort and support when someone you love is dying www.stjoes.ca When someone you love is dying When someone you love is dying, you may want to know how you can provide comfort
Precious Moments Giving comfort and support when someone you love is dying www.stjoes.ca When someone you love is dying When someone you love is dying, you may want to know how you can provide comfort
Good Oral Health: The Path to Good Overall Health
 Good Oral Health: The Path to Good Overall Health Leading Age Spring Conference May 2, 2018 Carole Ferch, RDH Carol Van Aernam, RDH, BA Copyright 2018 IOWA CAREGIVERS All Rights Reserved Multi-stakeholder
Good Oral Health: The Path to Good Overall Health Leading Age Spring Conference May 2, 2018 Carole Ferch, RDH Carol Van Aernam, RDH, BA Copyright 2018 IOWA CAREGIVERS All Rights Reserved Multi-stakeholder
Infant and Toddler Oral Health
 Infant and Toddler Oral Health Photo CD Decompressor are needed to use this picture Greater New York Dental Meeting December 1, 2002 Steven Chussid D.D.S. Timing of First Visit Guidelines of the American
Infant and Toddler Oral Health Photo CD Decompressor are needed to use this picture Greater New York Dental Meeting December 1, 2002 Steven Chussid D.D.S. Timing of First Visit Guidelines of the American
Child Health & Disability Prevention (CHDP) Program Oral Health Educational Resources For Children and Teens (6-20 years)
 Child Health & Disability Prevention (CHDP) Program Oral Health Educational Resources For Children and (6-20 years) A healthy mouth is part of a healthy body. The Oral Health Educational Resources Guide
Child Health & Disability Prevention (CHDP) Program Oral Health Educational Resources For Children and (6-20 years) A healthy mouth is part of a healthy body. The Oral Health Educational Resources Guide
Tips When Meeting A Person Who Has A Disability
 Tips When Meeting A Person Who Has A Disability Many people find meeting someone with a disability to be an awkward experience because they are afraid they will say or do the wrong thing; perhaps you are
Tips When Meeting A Person Who Has A Disability Many people find meeting someone with a disability to be an awkward experience because they are afraid they will say or do the wrong thing; perhaps you are
International Journal of Advanced Dental Research DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CEREBRAL PALSY: A REVIEW
 International Journal of Advanced Dental Research e - ISSN - 2349-8005 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ijadr DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CEREBRAL PALSY: A REVIEW Richa Wadhawan 1*, Ruchi
International Journal of Advanced Dental Research e - ISSN - 2349-8005 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ijadr DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CEREBRAL PALSY: A REVIEW Richa Wadhawan 1*, Ruchi
Orofacial function of persons having. Spinal muscular atrophy
 Orofacial function of persons having Report from questionnaires 31 questionnaires Synonym SMA I (Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, SMA II, SMA III (Kugelberg-Welander disease). ICD-10 G12.0 Estimated occurance
Orofacial function of persons having Report from questionnaires 31 questionnaires Synonym SMA I (Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, SMA II, SMA III (Kugelberg-Welander disease). ICD-10 G12.0 Estimated occurance
Shelly K. Clark, DDS Dentistry For Children
 Shelly K. Clark, DDS Dentistry For Children Patient Last Name, First Name Middle Date of Birth Goes by: Whom may we thank for referring you to our office? Age: Male / Female Who is accompanying the child
Shelly K. Clark, DDS Dentistry For Children Patient Last Name, First Name Middle Date of Birth Goes by: Whom may we thank for referring you to our office? Age: Male / Female Who is accompanying the child
Names and ages of other children in family School Grade. Employer Phone
 Robert D. Elliott, DMD, MS Cary Pediatric Dentistry Julie R. Molina, DDS, MS 540 New Waverly Place Suite 300 Cary, NC 27518 Telephone: (919) 852-1322 FAX: (919) 852-1230 Demographic Information Patient
Robert D. Elliott, DMD, MS Cary Pediatric Dentistry Julie R. Molina, DDS, MS 540 New Waverly Place Suite 300 Cary, NC 27518 Telephone: (919) 852-1322 FAX: (919) 852-1230 Demographic Information Patient
Before Cancer Treatment
 Three Good Reasons to See a Dentist Before Cancer Treatment U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research About Three
Three Good Reasons to See a Dentist Before Cancer Treatment U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research About Three
A GUIDE TO CARING FOR YOUR CHILD S TEETH AND MOUTH
 A GUIDE TO CARING FOR YOUR CHILD S TEETH AND MOUTH A COLLABORATION BETWEEN Use this guide to learn about oral health and taking care of your child s teeth from birth to kindergarten and into their teen
A GUIDE TO CARING FOR YOUR CHILD S TEETH AND MOUTH A COLLABORATION BETWEEN Use this guide to learn about oral health and taking care of your child s teeth from birth to kindergarten and into their teen
Indications. Physical Properties of Nitrous Oxide. Nitrous Oxide/Oxygen Conscious Sedation in the Pediatric Patient. Steven Chussid, D.D.S.
 Nitrous Oxide/Oxygen Conscious Sedation in the Pediatric Patient Steven Chussid, D.D.S. Columbia University School of Dental and Oral Surgery Indications Reduce anxiety Increase pain threshold Suppress
Nitrous Oxide/Oxygen Conscious Sedation in the Pediatric Patient Steven Chussid, D.D.S. Columbia University School of Dental and Oral Surgery Indications Reduce anxiety Increase pain threshold Suppress
PATIENT INFORMATION DIABETES AND ORAL HEALTH
 PATIENT INFORMATION DIABETES AND ORAL HEALTH www.dentalcareireland.ie DIABETES AND ORAL HEALTH People with poor diabetes control can be more prone to oral health problems such as gum disease, dry mouth,
PATIENT INFORMATION DIABETES AND ORAL HEALTH www.dentalcareireland.ie DIABETES AND ORAL HEALTH People with poor diabetes control can be more prone to oral health problems such as gum disease, dry mouth,
Oral Health Care: The window to overall health. Head 2 Toe Conference May 9, 2013 Christy Cogil, RN, CFNP and Dr. Melissa Ravago, DMD
 Oral Health Care: The window to overall health Head 2 Toe Conference May 9, 2013 Christy Cogil, RN, CFNP and Dr. Melissa Ravago, DMD Oral Health in America Oral health is essential to the general health
Oral Health Care: The window to overall health Head 2 Toe Conference May 9, 2013 Christy Cogil, RN, CFNP and Dr. Melissa Ravago, DMD Oral Health in America Oral health is essential to the general health
Orofacial function of persons having. Report from questionnaires. Salla disease
 7-- Orofacial function of persons having Salla disease Report from questionnaires The survey comprises questionnaires. Synonyms: Sialic acid storage disorder, SIASD, Sialuria Finnish type. Estimated occurrence:
7-- Orofacial function of persons having Salla disease Report from questionnaires The survey comprises questionnaires. Synonyms: Sialic acid storage disorder, SIASD, Sialuria Finnish type. Estimated occurrence:
PERIODONTAL. Periodontal Disease. Don t wait until it hurts SAMPLE
 PERIODONTAL Periodontal Disease Don t wait until it hurts Periodontal disease is also known as gum disease Periodontal (perry-o-don-tal) Disease is an infection and inflammation that affects the tissues
PERIODONTAL Periodontal Disease Don t wait until it hurts Periodontal disease is also known as gum disease Periodontal (perry-o-don-tal) Disease is an infection and inflammation that affects the tissues
Confidence in every smile
 Confidence in every smile WE DESIGN CONFIDENCE IN EVERY SMILE American Aligners Technology is committed to helping practitioners achieve success by creating healthy, beautiful smile for their patients.
Confidence in every smile WE DESIGN CONFIDENCE IN EVERY SMILE American Aligners Technology is committed to helping practitioners achieve success by creating healthy, beautiful smile for their patients.
DENTAL TRAUMA IN DECIDUOUS TEETH
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of Dental Trauma in Deciduous Teeth must be made in conjunction with
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of Dental Trauma in Deciduous Teeth must be made in conjunction with
ALL-ON-4 DENTAL IMPLANTS AN ALTERNATIVE TO DENTURES. Pasha Hakimzadeh, DDS
 ALL-ON-4 DENTAL IMPLANTS AN ALTERNATIVE TO DENTURES Pasha Hakimzadeh, DDS MEDICAL INFORMATION DISCLAIMER: This book is not intended as a substitute for the medical advice of physicians. The reader should
ALL-ON-4 DENTAL IMPLANTS AN ALTERNATIVE TO DENTURES Pasha Hakimzadeh, DDS MEDICAL INFORMATION DISCLAIMER: This book is not intended as a substitute for the medical advice of physicians. The reader should
Lesson 9 Anxiety and Relaxation Techniques
 The following presentation was originally developed for individuals and families by Achieva (a Western PA service provider). Now offered as a webcast production, ODP is providing this valuable resource
The following presentation was originally developed for individuals and families by Achieva (a Western PA service provider). Now offered as a webcast production, ODP is providing this valuable resource
* Professor, Department of Pedodontics & Preventive Dentistry, St. Joseph Dental College, Eluru. India
 ALWAYS UNIQUE TOTALLY INTERESTING SOMETIMES MYSTERIOUS AUTISM * VIJAYA PRASAD K.E. * Professor, Department of Pedodontics & Preventive Dentistry, St. Joseph Dental College, Eluru. India ABSTRACT : Autism
ALWAYS UNIQUE TOTALLY INTERESTING SOMETIMES MYSTERIOUS AUTISM * VIJAYA PRASAD K.E. * Professor, Department of Pedodontics & Preventive Dentistry, St. Joseph Dental College, Eluru. India ABSTRACT : Autism
Difficulty judging body positioning in relation to objects in the environment
 ASPERGER SYNDROME & SENSORY ISSUES Accident Prone Is clumsy/accident prone; bumps into things and breaks things often Difficulty judging body positioning in relation to objects in the environment Seems
ASPERGER SYNDROME & SENSORY ISSUES Accident Prone Is clumsy/accident prone; bumps into things and breaks things often Difficulty judging body positioning in relation to objects in the environment Seems
Oral Health Improvement. Prevention in Practice Vicky Brand
 Oral Health Improvement Prevention in Practice Vicky Brand Quiz Question A B C The % of 5 yr olds in 05/06 in Greater Manchester who experienced tooth decay was just over Which of the following is more
Oral Health Improvement Prevention in Practice Vicky Brand Quiz Question A B C The % of 5 yr olds in 05/06 in Greater Manchester who experienced tooth decay was just over Which of the following is more
Oral health care is vital for seniors
 Oral health care is vital for seniors (NC) Statistics Canada estimates seniors represent the fastest growing segment of the Canadian population, a segment expected to reach 9.2 million by 2041. As more
Oral health care is vital for seniors (NC) Statistics Canada estimates seniors represent the fastest growing segment of the Canadian population, a segment expected to reach 9.2 million by 2041. As more
Accessibility Standard for Customer Service:
 Accessibility Standard for Customer Service: Employee Tips It has been said that it is not our differences that are the problem; it is our responses to differences. Manitoba s new accessibility standard
Accessibility Standard for Customer Service: Employee Tips It has been said that it is not our differences that are the problem; it is our responses to differences. Manitoba s new accessibility standard
Module 3: Oral Health Screening and Fluoride Varnish for Infants and Toddlers
 Module 3: Oral Health Screening and Fluoride Varnish for Infants and Toddlers Time: 2 hours Learning Objectives: List best practices for caries prevention specific to different age groups. Perform an oral
Module 3: Oral Health Screening and Fluoride Varnish for Infants and Toddlers Time: 2 hours Learning Objectives: List best practices for caries prevention specific to different age groups. Perform an oral
Early Childhood Oral Health for MCH Professionals. Julia Richman, DDS, MSD, MPH
 Early Childhood Oral Health for MCH Professionals Julia Richman, DDS, MSD, MPH Who are we? A. Medical care providers (ie MD, RN) B. Dental care providers C. Social services providers D. Other public health
Early Childhood Oral Health for MCH Professionals Julia Richman, DDS, MSD, MPH Who are we? A. Medical care providers (ie MD, RN) B. Dental care providers C. Social services providers D. Other public health
Dental Health. This document includes 12 tips that can be used as part of a monthly year-long dental health campaign or as individual messages.
 Dental Health This document includes 12 tips that can be used as part of a monthly year-long dental health campaign or as individual messages. What is gingivitis? Gingivitis is the beginning stage of gum
Dental Health This document includes 12 tips that can be used as part of a monthly year-long dental health campaign or as individual messages. What is gingivitis? Gingivitis is the beginning stage of gum
BODY SYSTEMS, DRUGS, AND OBSERVATIONS SCOPE OF UNIT: This unit includes guidelines for observing and reporting.
 LESSON PLAN: 10 COURSE TITLE: UNIT: III MEDICATION TECHNICIAN BODY SYSTEMS, DRUGS, AND OBSERVATIONS SCOPE OF UNIT: This unit includes guidelines for observing and reporting. INFORMATION TOPIC: III-10 OR
LESSON PLAN: 10 COURSE TITLE: UNIT: III MEDICATION TECHNICIAN BODY SYSTEMS, DRUGS, AND OBSERVATIONS SCOPE OF UNIT: This unit includes guidelines for observing and reporting. INFORMATION TOPIC: III-10 OR
Orofacial function of persons having. Report from questionnaires. Turner syndrome
 Orofacial function of persons having Turner syndrome Report from questionnaires The survey comprises questionnaires. Estimated occurrence: : girls born. Etiology: Girls with Turner syndrome are either
Orofacial function of persons having Turner syndrome Report from questionnaires The survey comprises questionnaires. Estimated occurrence: : girls born. Etiology: Girls with Turner syndrome are either
MOBILE PREMIER PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Maureen T. Baldy, D.M.D.
 MOBILE PREMIER PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Maureen T. Baldy, D.M.D. 3920 Airport Blvd, Mobile, AL 36608 251-342-3323 www.mobilekidsdentist.com Welcome! We would like to welcome you to our practice. Our goal is
MOBILE PREMIER PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Maureen T. Baldy, D.M.D. 3920 Airport Blvd, Mobile, AL 36608 251-342-3323 www.mobilekidsdentist.com Welcome! We would like to welcome you to our practice. Our goal is
NOE VALLEY SMILES FOR KIDS PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY
 NOE VALLEY SMILES FOR KIDS PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Date: Patient Information Child s Full Name Age Sex (M) (F) Nickname (if any) Birth Date Whom may we thank for referring you General Information Mother/ Father
NOE VALLEY SMILES FOR KIDS PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Date: Patient Information Child s Full Name Age Sex (M) (F) Nickname (if any) Birth Date Whom may we thank for referring you General Information Mother/ Father
FACT SHEET - KINDERGARTEN
 Fragile X Second edition 2013 Fragile X is the single most common inherited cause of intellectual impairment. There appears to be some discrepancy in the frequency of Fragile X as large scale population
Fragile X Second edition 2013 Fragile X is the single most common inherited cause of intellectual impairment. There appears to be some discrepancy in the frequency of Fragile X as large scale population
TMD: CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT AND PHYSICAL THERAPY OPTIONS
 TMD: CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT AND PHYSICAL THERAPY OPTIONS Massage: The temporalis on the side of the head is easy to locate. Press on it looking for painful nodules, massaging gently. Opening and closing
TMD: CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT AND PHYSICAL THERAPY OPTIONS Massage: The temporalis on the side of the head is easy to locate. Press on it looking for painful nodules, massaging gently. Opening and closing
Dental or Oral Surgery
 Patient Education Dental Clinic Dental or Oral Surgery Post-operative care instructions This handout provides care instructions for you to follow after your dental or oral surgery. It also provides the
Patient Education Dental Clinic Dental or Oral Surgery Post-operative care instructions This handout provides care instructions for you to follow after your dental or oral surgery. It also provides the
Preventing delirium while in the hospital
 Preventing delirium while in the hospital What is delirium? When an older person becomes ill and goes into the hospital, there is an increased risk of developing delirium and other problems. Delirium is
Preventing delirium while in the hospital What is delirium? When an older person becomes ill and goes into the hospital, there is an increased risk of developing delirium and other problems. Delirium is
Lecture Content and learning outcomes
 DIPLOMA IN PAEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Subject Lecture Content and learning outcomes Craniofacial growth and development The process of pre-natal development The process of post-natal craniofacial growth The
DIPLOMA IN PAEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Subject Lecture Content and learning outcomes Craniofacial growth and development The process of pre-natal development The process of post-natal craniofacial growth The
From the office of: Nahidh D. Andrews, DMD 3332 Portage Ave South Bend, IN (574) Are Your Teeth a Sensitive Subject?
 From the office of: Nahidh D. Andrews, DMD 3332 Portage Ave South Bend, IN 46628-3656 (574) 273-3900 Are Your Teeth a Sensitive Subject? A patient s guide to sensitive teeth and better oral care ARE YOUR
From the office of: Nahidh D. Andrews, DMD 3332 Portage Ave South Bend, IN 46628-3656 (574) 273-3900 Are Your Teeth a Sensitive Subject? A patient s guide to sensitive teeth and better oral care ARE YOUR
Autism One Conference May 25th, Pamela J. Johnson D.D.S, M.S.
 Treating The Patient With Autism In The Orthodontic Practice: Never Say Never Autism One Conference May 25th, 2012 Pamela J. Johnson D.D.S, M.S. Overview Oral Health And The Autistic Patient The Autistic
Treating The Patient With Autism In The Orthodontic Practice: Never Say Never Autism One Conference May 25th, 2012 Pamela J. Johnson D.D.S, M.S. Overview Oral Health And The Autistic Patient The Autistic
Patient s Full Name Age Sex: (M) (F) Whom may we thank for referring you?
 Date: / / Patient Information Patient s Full Name Age Sex: (M) (F) Nickname (if any) Birthdate: / / Whom may we thank for referring you? General Information Parent/Legal Guardian (full name) Birthdate:
Date: / / Patient Information Patient s Full Name Age Sex: (M) (F) Nickname (if any) Birthdate: / / Whom may we thank for referring you? General Information Parent/Legal Guardian (full name) Birthdate:
Teeth to Treasure. Grades: 4 to 6
 Teeth to Treasure Grades: 4 to 6 What is oral health? It s keeping your teeth, gums and mouth healthy! Why do you suppose this is important? Well, let s take a look at how we use and need our teeth. Appearance
Teeth to Treasure Grades: 4 to 6 What is oral health? It s keeping your teeth, gums and mouth healthy! Why do you suppose this is important? Well, let s take a look at how we use and need our teeth. Appearance
Orofacial function of persons having. Report from questionnaires. Rett syndrome
 7--8 Orofacial function of persons having Rett syndrome Report from questionnaires The survey comprises questionnaires. Estimated occurrence: : girls/women. Etiology: t entirely clarified. A mutation in
7--8 Orofacial function of persons having Rett syndrome Report from questionnaires The survey comprises questionnaires. Estimated occurrence: : girls/women. Etiology: t entirely clarified. A mutation in
Cognitive Impairment and Oral Health
 Geriatric Lectures Series: Cognitive Impairment and Oral Health Dr. Leo Marchini, DDS, MSD, PhD Department of Preventive and Community Dentistry University of Iowa College of Dentistry and Dental Clinics
Geriatric Lectures Series: Cognitive Impairment and Oral Health Dr. Leo Marchini, DDS, MSD, PhD Department of Preventive and Community Dentistry University of Iowa College of Dentistry and Dental Clinics
Dental Insights. Equipping Parents with Important Information About Children s Oral Health pril 2014
 Equipping Parents with Important Information About Children s Oral Health pril 2014 Introduction Despite tremendous advancements in dental care and treatment over the past 50 years, dental caries (tooth
Equipping Parents with Important Information About Children s Oral Health pril 2014 Introduction Despite tremendous advancements in dental care and treatment over the past 50 years, dental caries (tooth
When Do You Need a. General Dentist vs. a Specialist?
 When Do You Need a General Dentist vs. a Specialist? Most parents realize the importance of helping their kids get off to a healthy start when it There are two common routes that parents can take when
When Do You Need a General Dentist vs. a Specialist? Most parents realize the importance of helping their kids get off to a healthy start when it There are two common routes that parents can take when
Educator s Teaching Teeth Guidebook
 Educator s Teaching Teeth Guidebook This booklet is intended for Community Health Representatives (CHRs), Children s Oral Health Coordinators (COHCs), and other educators or health care workers who want
Educator s Teaching Teeth Guidebook This booklet is intended for Community Health Representatives (CHRs), Children s Oral Health Coordinators (COHCs), and other educators or health care workers who want
Care After Your Dental Treatment For Hospital Dentistry patients
 Patient Education Care After Your Dental Treatment For Hospital Dentistry patients Your surgeon today was Dr.. Please carefully follow the instructions in this handout. General Do not disturb the wound
Patient Education Care After Your Dental Treatment For Hospital Dentistry patients Your surgeon today was Dr.. Please carefully follow the instructions in this handout. General Do not disturb the wound
Periodontal. Disease. Don t wait until it hurts. ADA Healthy Smile Tips
 This brochure covers: the causes of gum disease the stages of gum disease how gum disease is diagnosed and treated how to keep your mouth healthy after treatment PERIODONTAL Periodontal ADA Healthy Smile
This brochure covers: the causes of gum disease the stages of gum disease how gum disease is diagnosed and treated how to keep your mouth healthy after treatment PERIODONTAL Periodontal ADA Healthy Smile
2/4/2010. Desensitization. Behaviour Therapy. Respondent conditioning Operant conditioning
 DESENSITIZATION to Health Related Procedures SUPPORTING INDIVIDUALS WITH DUAL DIAGNOSIS Julie Caissie Behaviour Consultant Desensitization Fear and anxiety often prevent an individual from participating
DESENSITIZATION to Health Related Procedures SUPPORTING INDIVIDUALS WITH DUAL DIAGNOSIS Julie Caissie Behaviour Consultant Desensitization Fear and anxiety often prevent an individual from participating
