Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis
|
|
|
- Magnus Barrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral Pathology, Department of Dentistry, Health, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark Flemming Isidor, Section for Prosthetic Dentistry, Department of Dentistry, Health, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark Eva Karring, Department of Dentistry, Health, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark Corresponding author: Martin Saaby Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral Pathology and Section for Prosthetic Dentistry Department of Dentistry Health, Aarhus University Vennelyst Boulevard 9 DK-8000 Aarhus C Denmark Tel: Fax: msaa@odontologi.au.dk Key words: dental implants, oral implants, pathology, peri-implantitis, periodontitis, risk factors, smoking habits Abstract Objectives: To retrospectively assess the influence of potential risk factors, primarily smoking and a prior history of periodontitis, on the severity of peri-implantitis in patients referred for treatment of peri-implantitis. Materials and methods: Among 98 patients referred for treatment of peri-implantitis, 34 patients fulfilled the inclusion criteria: one or several implants with peri-implant marginal bone loss 2 mm concomitant with bleeding and/or pus on probing. Information about health status, smoking habits, reason for tooth loss, and performed implant treatment were obtained from the patient charts and interviews. Moreover, a detailed extra- and intraoral examination was performed, including intraoral radiographs of all implants. Risk factors were evaluated by a two-way ANOVA at patient level. Results: Smoking and a prior history of periodontitis were significant risk factors for increased severity of peri-implantitis. Furthermore, the presence of both smoking and a prior history of periodontitis did not further increase the severity of peri-implantitis, as compared to either of these two factors alone. Poor marginal fit of the suprastructure and extensive gingival imitations on implant-supported fixed full prostheses may also be potential risk factors. Conclusions: The study indicated that smoking and a prior history of periodontitis were important risk factors for increased severity of peri-implantitis, while concomitant presence of these two risk factors did not further increase the severity of peri-implantitis, as compared to either of these two risk factors alone. Therefore, early diagnosis and adequate treatment of peri-implantitis are important in patients with a prior history of periodontitis and in smokers to minimize the risk of advanced peri-implantitis in conjunction with focus on known risk factors, including meticulous infection control before implant treatment and a systematic maintenance care program. Date: Accepted 16 September 2014 To cite this article: Saaby M, Karring E, Schou S, Isidor F. Factors influencing severity of peri-implantitis. Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 27, 2016, 7 12 doi: /clr The prognosis of implant treatment has been addressed in several studies. Although it has been concluded within several systematic reviews that implant treatment in most cases is characterized by high survival of the implants as well as the suprastructures (Berglundh et al. 2002; Jung et al. 2012; Pjetursson et al. 2012), there is increasing focus on the occurrence of mechanical/technical and biological complications. Various risk factors of peri-implantitis have been described, including a prior history of periodontitis and smoking, as described in several published systematic reviews (Schou et al. 2006; Heitz- Mayfield 2008; Schou 2008; Heitz-Mayfield & Huynh-Ba 2009; Renvert & Persson 2009; Mombelli et al. 2012; Clementini et al. 2014). Previous research has mainly focused on the influence of a prior history of periodontitis and smoking on peri-implant bone loss and implant failure rather than on the occurrence and severity of peri-implantitis. Peri-implantitis was defined at the 1st European Workshop on Periodontology in 1993 as inflammatory reactions with loss of supporting bone in the tissues surrounding a functioning implant (Albrektsson & Isidor 1994). The definition did not include specific clinical and radiological criteria of inflammation and bone loss, thus compromising detailed analyses of the influence of various risk factors of peri-implantitis. Recent consensus conference statement (Sanz & Chapple 2012) and systematic review (Heitz- Mayfield & Huynh-Ba 2009) indicate inadequately reporting of occurrence of peri-implantitis, variations in radiographic reference points for measuring peri-implant marginal 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd 7
2 bone loss, and varying definitions of implant success. Consequently, the present knowledge about potential risk factors influencing the peri-implantitis severity is inadequately described. Therefore, the aim of the present retrospective study was to evaluate the influence of a prior history of periodontitis and smoking, among other potential risk factors such as poor marginal fit of the suprastructure indicated by obvious radiographical or clinical detectable discrepancies between the margin of suprastructure/abutment/implant and also extensive gingival imitations on the severity of peri-implantitis in patients referred for treatment of peri-implantitis. Table 1. Summary of patient interviews No. % Gender Female Male Reason for tooth loss Periodontitis Caries 6 18 Trauma 5 14 Congenitally missing teeth 6 18 Smoking Smokers and former smokers Non-smokers Systemic disease Diabetes 2 6 Cardiovascular disease 9 26 Osteoporosis 1 3 Autoimmune disease 3 9 No systemic disease Implant loss before referral Implant loss 5 15 No implant loss Material and methods Inclusion criteria and patient characteristics The patients were included from a total of 98 patients consecutively referred from November 1, 2008 to February 1, 2014 to the Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral Pathology and the Section for Prosthetic Dentistry, Department of Dentistry, Health, Aarhus University, Denmark, for treatment of peri-implantitis. The following inclusion criteria were applied: Presence of peri-implantitis defined as 2 mm peri-implant marginal bone loss (see later) concomitant with bleeding and/or pus on probing around one or more implants at the time of examination (Sanz & Chapple 2012). A total of 34 patients (18 women, 16 men) with a mean age of 38 years (range: years) at the time of examination fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Consequently, a total of 64 patients were excluded due to bone loss <2 mm and/or lack of bleeding/pus on probing (21 due to bone loss <2 mm, 29 due to lack of bleeding/pus on probing, and 14 due to bone loss <2 mm combined with lack of bleeding/pus on probing). Information about patient characteristics and the performed implant treatment were obtained by structured patient interviews and review of patient charts (Table 1). Briefly, 16 (47%) of the patients were smokers, and 17 (50%) lost their teeth due to periodontitis, while the remaining 17 (50%) had missing teeth due to other reasons (Caries, trauma, and congenitally missing teeth). Systemic disease, predominantly well regulated, was reported in 15 (44%) of the patients, mainly cardiovascular disease (9/ 26%). All patients with implant loss before referral had a prior history of periodontitis. The performed implant treatment is summarized in Table 2. A total of 118 titanium Table 2. Summary of performed implant treatment No. % Type of implant Nobel Biocare Branemark Astra Straumann 6 5 Ankylos 4 3 Nobel Biocare Replace Frialit 6 5 Other Total Implant site, maxilla Central incisor Lateral incisor 10 8 Canine Premolar Molar 10 8 Total Implant site, mandible Central incisor 7 6 Lateral incisor 4 3 Canine 3 3 Premolar Molar Total No. of implants per patient* Patients with 1 3 implants Patients with 4 6 implants Patients with 7 implants 3 9 Type of suprastructure Single-tooth replacement Fixed partial prosthesis Fixed full prosthesis 8 14 Overdenture 4 7 *Mean number of implants per patient was 3.5 (range: 1 12). implants were examined. Most of the patients were treated by dentists or oral and maxillofacial surgeons in private practice, while a minority was treated by dental students as part of their undergraduate dental curriculum at the Department of Dentistry, Health, Aarhus University, Denmark, under supervision by dentists and oral and maxillofacial surgeons, all with special knowledge within the field of oral implantology (Bonde et al. 2010, 2013). Most implants were placed in the maxilla (70/59%), and few patients were treated with more than six implants. The mean number of implants per patient was 3.5 (range: 1 12). In most patients, no bone regenerative procedure was performed. However, detailed information about the exact region of bone regeneration could not be obtained systematically from the patient charts. Most suprastructures were fixed, and the few overdentures were retained by either ball or bar attachments. The average time of function of the suprastructure was 6.1 years (range: 1 19 years). The patients have been included in various maintenance programs. Clinical and radiographic examination A detailed extra- and intraoral examination was performed. The assessment of all implants included (i) Plaque (yes, no), (ii) Deepest clinical probing depth measured to the nearest mm (six sites per implant), (iii) 8 Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 27, 2016 / John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd
3 Bleeding and/or pus on probing (yes, no), (iv) Fistula (yes, no), (v) Keratinized peri-implant mucosa (yes, no), (vi) Recession of the periimplant mucosa (yes, no), (vii) Mobility of the implant (yes, no), (viii) Mechanical/technical complications (yes, no), and (ix) Poor marginal fit of suprastructure (yes, no). Moreover, diseases of the oral mucosa (yes, no) and clinical signs of xerostomia were assessed (yes, no). All clinical examinations were performed with fixed prostheses attached to the implants. Intraoral radiographic images of all implants were taken with the parallel technique (Larheim & Eggen 1982) at the time of the clinical examination using a phosphor plate system (Digora â fmx, Soredex Orion Cooperation, Helsinki, Finland). The distance from a reference point to the most coronal bone in contact with the implant was measured mesially and distally parallel with the long axis of the implant on the radiographs taken at the time of the clinical examination using Image J Software (Research Services Branch, National Institute of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). The reference point was defined as the implant abutment connection for all 2-piece implants, while the border between the machined and rough implant surface was used for 1-piece implants. The peri-implant marginal bone loss was calculated after correction of magnification based on the known distance between implant threads. All measurements were performed by one examiner (MS). Data analyses Descriptive statistics were initially carried out. After initial testing of possible associations between the peri-implant marginal bone loss and various independent variables, a two-way analysis of variance with the periimplant marginal bone loss as the dependent variable and smoking habits and reason for tooth loss as the independent variables was finally performed followed by an all pairwise multiple comparison procedure (Holm-Sidak method). Data were initially transformed using the logarithm function to obtain normality. The applicability of the two-way analysis of variance was tested using the Shapiro Wilk normality test and the equal variance test. The statistical unit was the patient. For patients with more than one implant, a mean for each parameter was calculated from the registrations of all implants. The level of significance was Data management including calculation of descriptive statistics was conducted in Excel (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA), while SigmaPlot 11 (Systat Software, San Jose, CA, USA) was used for the statistical analyses. Results The main clinical findings including descriptive statistics are summarized in Table 3. All implant-supported fixed full prostheses were characterized by extensive gingival imitations compromising adequate oral hygiene procedures (Fig. 1). All implant-supported single-tooth replacements and fixed partial prostheses except one mandibular fixed partial prosthesis were without gingival imitations and with no or limited plaque accumulation. A total of 68% of the implants were characterized by bleeding and/or pus on probing. In addition, probing depth of >5 mm was registered around 58% of the implants. Few fistulas were observed, all within the maxillary incisor and canine region. Most implants were surrounded by keratinized mucosa (83%), and recession was frequently seen (28%), predominantly in relation to implants in the mandibular incisor region (Fig. 2). Finally, poor marginal fit of the suprastructure was frequently observed (12%). Assessment of the peri-implant marginal bone level was possible at all implants. The mean periimplant marginal bone loss is presented in Table 4 in relation to smoking habits and a prior history of periodontitis. The two-way analysis of variance showed a significant interaction between smoking Table 3. Summary of clinical examination No. % Plaque Yes No Bleeding and/or pus Yes on probing No Most profound clinical 0 3 mm probing depth* 3 5 mm >5 mm Fistula Yes 7 6 No Keratinized peri-implant Yes mucosa No Recession of peri-implant Yes mucosa No Implant mobility Yes 6 5 No Poor marginal fit of Yes suprastructure No Mechanical/technical Yes 1 1 complication No Xerostomia Yes 2 6 No Disease of oral mucosa Yes 4 12 No *Detailed registration of probing depth was not possible in some cases due to the design of the suprastructure. habits and reason for tooth loss in relation to peri-implant marginal bone loss (P = 0.043). The additional all pairwise multiple comparison procedures revealed when smoking habits were considered that peri-implant marginal bone loss was significantly more advanced in smokers than in non-smokers in the group of patients who lost their teeth due to other reasons than periodontitis (P = 0.007). In contrast, no significant association between smoking habits and peri-implant marginal bone loss was found among patients who had lost their teeth due to periodontitis (P = 0.903). Furthermore, when reason for tooth loss was considered no significant effect of tooth loss due to periodontitis was seen on the peri-implant marginal bone loss in the group of patients who smoked (P = 0.306), whereas tooth loss due to periodontitis was almost significantly associated with the periimplant marginal bone loss in non-smoking patients (P = 0.060). Discussion The aim of the present retrospective study was to assess the influence of various risk factors on the severity of peri-implantitis in patients referred for treatment of peri-implantitis. In these patients, smoking and/or a prior history of periodontitis were associated with a significantly increased (20%) periimplant marginal bone loss as compared to non-smokers with tooth loss due to other reasons than periodontitis. Consequently, the present study indicated that smoking and a prior history of periodontitis were important risk factors for increased severity of peri-implantitis, while concomitant presence of these two risk factors did not further increase the severity of peri-implantitis, as compared to either of them alone. The present retrospective study involved initially 98 patients referred for treatment of peri-implantitis. Assessment of the influence of various risk factors on peri-implantitis requires a strict definition of peri-implantitis. As described within the introduction, periimplantitis was initially defined as inflammatory reactions with concomitant loss of supporting bone in the tissues surrounding a functioning implant (Albrektsson & Isidor 1994). Presence of a peri-implant marginal bone loss 2 mm concomitant with bleeding and/or pus on probing involving one or more implants at the time of examination was used in the present study as the criteria of peri-implantitis, in accordance with recent recommendations (Sanz & Chapple 2012) John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd 9 Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 27, 2016 / 7 12
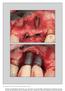
4 Fig. 1. A 60-year-old female smoker with tooth loss due to periodontitis. Implants were inserted 4 years before examination. To create an esthetic acceptable full fixed prosthesis, extensive gingival imitations were made which compromised oral hygiene procedures. Intraoral radiographic image of implants in the anterior maxilla. Extensive peri-implant marginal bone loss (lines) can be observed. Fig. 2. A 23-year-old male non-smoker with congenitally missing mandibular central incisors. Implants were placed 3 years before examination. Recession and absence of keratinized peri-implant mucosa can be seen. Intraoral radiographic image revealed moderate peri-implant marginal bone loss (lines). Table 4. Compared peri-implant marginal bone loss Category Mean peri-implant marginal bone loss in mm (range) Smoking Smokers 5.3 (2 11.5) habits Non-smokers 3.5 (2 7.5) Reason for Periodontitis 5.3 (2 9.8) tooth loss Other reasons than periodontitis 3.8 (2 11.5) Using these recently accepted inclusion criteria, a total of 34 patients were finally included. Consequently, 64 patients were excluded. The background of exclusion could be related to various factors. The used radiographic criteria addressed bone loss only mesially and distally. The bone loss buccally and lingually could only be assessed at a surgical intervention, which was not indicated in all cases. Therefore, presence of buccal bone loss could not be considered systematically. In addition, some patients were referred with peri-implant marginal bone loss without bleeding on probing at the time of examination or peri-implant. Previous studies on risk factors of peri-implantitis have mainly focused on survival of the suprastructures, survival of the implants, and peri-implant marginal bone loss (for review, see Schou et al. 2006; Heitz-Mayfield 2008; Schou 2008; Heitz-Mayfield & Huynh- Ba 2009; Renvert & Persson 2009; Mombelli et al. 2012; Clementini et al. 2014). Few recent studies have addressed the occurrence of peri-implantitis defined by bleeding/pus on probing concomitant with well-defined criteria for peri-implant marginal bone loss (Koldsland et al. 2011; Renvert et al. 2014). Despite the limited study population, statistical analyses could be carried out using a twoway analysis of variance after logarithmic transformation. The analyses were performed at patient level, because the implants cannot be considered as independent units due to the so-called cluster complication effect and the exposure of all implants within each patient by the same systemic risk factors (Jemt & H ager 2006). Therefore, assessment at implant level would from a statistical point of view not be appropriate (Sanz & Chapple 2012). The mean peri-implant marginal bone level at all implants, with and without peri-implantitis, was calculated and used to access the influence of smoking and tooth loss due to periodontitis on the severity of peri-implantitis. In other words, all patients with at least one implant affected by peri-implantitis were included, despite the presence of some implants without peri-implantitis in some patients. The performed statistical analyses within the present study indicated that smoking was a significant risk factor for increased severity of peri-implantitis, especially in patients with non-periodontitis-associated tooth loss. Previously published systematic reviews have concluded that smokers have an increased risk of (i) Loss of the implants, (ii) Periimplant marginal bone loss, and (iii) Occurrence of peri-implantitis (Klokkevold & Han 2007; Heitz-Mayfield 2008; Heitz-Mayfield & Huynh-Ba 2009; Mombelli et al. 2012; Clementini et al. 2014). It has been concluded within several systematic reviews that patients with tooth loss due to periodontitis are characterized by a significantly increased risk of (i) Loss of the suprastructures, (ii) Loss of the implants, (iii) Peri-implant marginal bone loss, and (iv) Occurrence of peri-implantitis (for review, see Schou et al. 2006; Heitz-Mayfield 2008; Schou 2008; Heitz-Mayfield & Huynh-Ba 2009; Renvert & Persson 2009; Mombelli et al. 2012). However, it has not previously been addressed in detail whether peri-implantitis is more severe in periodontitis patients as compared to non-periodontitis patients, although previous studies have addressed the peri-implant marginal bone loss. The results of present study indicate that within the group of non-smokers, patients with tooth loss due to periodontitis are characterized by increased severity of peri-implantitis as compared to patients with non-periodontitis-associated tooth loss. 10 Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 27, 2016 / John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd
5 It has recently been concluded in a systematic review that the combination of a prior history of periodontitis and smoking seems to further increase the risk of implant loss, peri-implant marginal bone loss, and peri-implantitis as compared to smokers and periodontitis patients, respectively (Heitz- Mayfield & Huynh-Ba 2009). Therefore, in accordance with the present study, two-way analyses are needed to assess to influence of smoking and tooth loss due to periodontitis as risk factors. The present study indicated that the concomitant presence of smoking and a prior history of periodontitis did not further increase the severity of peri-implantitis, as compared to either of these two risk factors alone. However, these results must be interpreted cautiously due to the relatively small study population. It was not possible in detail to evaluate the influence of several potential risk factors influencing the severity of peri-implantitis, including implant overload, plaque, systemic disease, medication, type of implant, implant region, type of suprastructure, poor marginal fit of suprastructure, presence of extensive gingival imitations, absence of keratinized periimplant mucosa, absence of a systematic maintenance program, disease of the oral mucosa, clinical signs of xerostomia, and lack of buccal bone (Fig. 3.), mainly due to the limited number of included patients. It has previously been described that limited accessibility to proper oral hygiene was associated with peri-implantitis (Serino & Str om 2009). In addition, excess cement has been associated with peri-implantitis (Korsch et al. 2013, 2014), while poor marginal fit of the suprastructure has not previously been described as a significant risk factor. In the present study, only one case of excess cement was identified (Fig. 4), while poor marginal fit was often observed. Fistulas were frequently observed without concomitant peri-implant marginal bone loss in patients with congenitally missing teeth and optimal oral hygiene, why these patients were excluded from the study. Further studies addressing these potential risk factors are needed before final conclusions can be made. Finally, only one case with extensive peri-implant marginal bone loss concomitant with implant fracture was observed (Fig. 5). Conclusions Fig. 3. A 58-year-old female smoker with tooth loss due to periodontitis. Implants were placed 8 years before examination. Extensive lack of buccal bone was observed. Intraoral radiographic image of the right implant revealed moderate peri-implant marginal bone loss (line). Fig. 4. A 35-year-old male non-smoker with loss of the left maxillary central incisor due to trauma. The implant was placed 8 years before examination. A peri-implant marginal bone defect was observed after removal of excess cement and granulation tissue. A large piece of excess cement was identified during the surgical procedure. (c) Intraoral radiographic image showed poor marginal fit of implant crown, excess cement (arrow), and extensive periimplant marginal bone loss (line). Fig. 5. A 56-year-old smoker with tooth loss due to periodontitis. The implant in the left mandibular second premolar region had extensive peri-implant marginal bone loss concomitant with implant fracture. The intraoral radiographic image confirmed fracture of implant (arrow) and extensive peri-implant marginal bone loss (line). (c) The present study indicated that a prior history of periodontitis and smoking were important risk factors for increased severity of peri-implantitis, while concomitant presence of these two risk factors did not further increase the severity of peri-implantitis, as compared to either of them alone. Therefore, early diagnosis and adequate treatment of peri-implantitis are important in patients with a prior history of periodontitis and in smokers to minimize the risk of advanced peri-implantitis in conjunction with focus on 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd 11 Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 27, 2016 / 7 12
6 known risk factors, including meticulous infection control before implant treatment and a systematic maintenance care program. Acknowledgements: The study was supported by grants from the Danish Dental Association and the Danish Society for Oral Implantology. We are deeply thankful to both organizations for their support. The authors declare no conflict of interests. References Albrektsson, T. & Isidor, F. (1994) Consensus report of session IV. In: Lang, N.P. & Karring, T., eds. Proceedings of the 1st European Workshop on Periodontology, London: Quintessence. Berglundh, T., Persson, L. & Klinge, B. (2002) A systematic review of the incidence of biological and technical complications in implant dentistry reported in prospective longitudinal studies of at least 5 years. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 29(Suppl. 3): Bonde, M.J., Stokholm, R., Isidor, F. & Schou, S. (2010) Outcome of implant-supported singletooth replacements performed by dental students. A 10-year clinical and radiographic retrospective study. European Journal of Oral Implantology 3: Bonde, M.J., Stokholm, R., Schou, S. & Isidor, F. (2013) Patient satisfaction and aesthetic outcome of implant-supported single-tooth replacements performed by dental students: a retrospective evaluation 8 to 12 years after treatment. European Journal of Oral Implantology 6: Clementini, M., Rossetti, P.H., Penarrocha, D., Micarelli, C., Bonachela, W.C. & Canullo, L. (2014) Systemic risk factors for peri-implant bone loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants 43: Heitz-Mayfield, L.J. (2008) Peri-implant diseases: diagnosis and risk indicators. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 35(Suppl. 8): Heitz-Mayfield, L.J. & Huynh-Ba, G. (2009) History of treated periodontitis and smoking as risks for implant therapy. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants 24(Suppl.): Jemt, T. & H ager, P. (2006) Early complete failures of fixed implant-supported prostheses in the edentulous maxilla: a 3-year analysis of 17 consecutive cluster failure patients. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research 8: Jung, R.E., Zembic, A., Pjetursson, B.E., Zwahlen, M. & Thoma, D.S. (2012) Systematic review of the survival rate and the incidence of biological, technical, and aesthetic complications of single crowns on implants reported in longitudinal studies with a mean follow-up of 5 years. Clinical Oral Implants Research 23(Suppl. 6): Klokkevold, P.R. & Han, T.J. (2007) How do smoking, diabetes, and periodontitis affect outcomes of implant treatment? International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants 22(Suppl.): Koldsland, O.C., Scheie, A.A. & Aass, A.M. (2011) The association between selected risk indicators and severity of peri-implantitis using mixed model analyses. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 38: Korsch, M., Obst, U. & Walther, W. (2014) Cementassociated peri-implantitis: a retrospective clinical observational study of fixed implant-supported restorations using a methacrylate cement. Clinical Oral Implants Research 25: Korsch, M., Robra, B.P. & Walther, W. (2013) Predictors of excess cement and tissue response to fixed implant-supported dentures after cementation. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research 17(Suppl 1): e Larheim, T.A. & Eggen, S. (1982) Measurements of alveolar bone height at tooth and implant abutments on intraoral radiographs. A comparison of reproducibility of Eggen technique utilized with and without a bite impression. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 9: Mombelli, A., M uller, N. & Cionca, N. (2012) The epidemiology of peri-implantitis. Clinical Oral Implants Research 23(Suppl. 6): Pjetursson, B.E., Thoma, D., Jung, R., Zwahlen, M. & Zembic, A. (2012) A systematic review of the survival and complication rates of implant-supported fixed dental prostheses (FDPs) after a mean observation period of at least 5 years. Clinical Oral Implants Research 23(Suppl. 6): Renvert, S., Aghazadeh, A., Hallstr om, H. & Persson, G.R. (2014) Factors related to peri-implantitis - a retrospective study. Clinical Oral Implants Research 25: Renvert, S. & Persson, G.R. (2009) Periodontitis as a potential risk factor for peri-implantitis. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 36(Suppl. 10): Sanz, M. & Chapple, I.L. (2012) Working Group 4 of the VIII European Workshop on Periodontology. Clinical research on peri-implant diseases: consensus report of Working Group 4. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 39(Suppl. 12): Schou, S. (2008) Implant treatment in periodontitissusceptible patients: a systematic review. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 35(Suppl 1): Schou, S., Holmstrup, P., Worthington, H.V. & Esposito, M. (2006) Outcome of implant therapy in patients with previous tooth loss due to periodontitis. Clinical Oral Implants Research 17(Suppl. 2): Serino, G. & Str om, C. (2009) Peri-implantitis in partially edentulous patients: association with inadequate plaque control. Clinical Oral Implants Research 20: Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 27, 2016 / John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Risk Factors in Implant Therapy
 Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Risk Factors in Implant Therapy David L. Cochran, DDS, MS, PhD, MMSci 1 /Søren Schou, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont 2 / Lisa J. A. Heitz-Mayfield,
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Risk Factors in Implant Therapy David L. Cochran, DDS, MS, PhD, MMSci 1 /Søren Schou, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont 2 / Lisa J. A. Heitz-Mayfield,
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Please visit the C.E. Pavilion to validate your course attendance Or If There s a Line Go cdapresents.com
 UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Abstract Purpose: Materials and methods Results:
 Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Straumann SmartOne. Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance. Step 2 Maintenance visit
 Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance Step 2 Maintenance visit Overview Assessment and treatment planning Step 1 Patient's expectations, history and examination Step 2 Treatment planning Step 3 Consultation
Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance Step 2 Maintenance visit Overview Assessment and treatment planning Step 1 Patient's expectations, history and examination Step 2 Treatment planning Step 3 Consultation
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
The Brånemark osseointegration method, using titanium dental implants (fixtures)
 Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This
 1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Porous titanium granules in the treatment of peri-implant osseous defects a 7-year follow-up study
 Andersen et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:50 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0106-2 International Journal of Implant Dentistry SHORT REPORT Open Access Porous titanium granules in the
Andersen et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:50 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0106-2 International Journal of Implant Dentistry SHORT REPORT Open Access Porous titanium granules in the
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Areview of recent studies concerning molar. Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report
 Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report George E. Romanos, Dr med dent 1 /Georg H. Nentwig, Prof Dr med dent 2 Many clinical studies have
Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report George E. Romanos, Dr med dent 1 /Georg H. Nentwig, Prof Dr med dent 2 Many clinical studies have
Fixed Partial Dentures /FPDs/, Implant Supported. in implant prosthodontics
 Fixed Partial Dentures /FPDs/, Implant Supported Prosthesis/ISP/ in implant prosthodontics Prof.dr.Tamas Divinyi Semmelweis University, Faculty of Dentistry Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Fixed Partial Dentures /FPDs/, Implant Supported Prosthesis/ISP/ in implant prosthodontics Prof.dr.Tamas Divinyi Semmelweis University, Faculty of Dentistry Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Peri-implant marginal bone loss: What is the current concensus? an academic controversy or a clinical challenge?
 Peri-implant marginal bone loss; What is the current concensus? Bjorn.Klinge@mah.se Peri-implant marginal bone loss: an academic controversy or a clinical challenge? Björn Klinge Eur J Oral Implantol 2012;5
Peri-implant marginal bone loss; What is the current concensus? Bjorn.Klinge@mah.se Peri-implant marginal bone loss: an academic controversy or a clinical challenge? Björn Klinge Eur J Oral Implantol 2012;5
Proposed score for occlusal-supporting ability
 Open Journal of Stomatology, 2013, 3, 230-234 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojst.2013.33040 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojst/) OJST Proposed score for occlusal-supporting ability
Open Journal of Stomatology, 2013, 3, 230-234 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojst.2013.33040 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojst/) OJST Proposed score for occlusal-supporting ability
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 827 Thirty-Two Year Success of Dental Implants in Periodontally Compromised Dentition Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 Glenn J. Wolfinger,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 827 Thirty-Two Year Success of Dental Implants in Periodontally Compromised Dentition Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 Glenn J. Wolfinger,
م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION
 Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate
 AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate The AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry provides an opportunity for AO members to demonstrate that they have attained a level of education and experience
AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate The AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry provides an opportunity for AO members to demonstrate that they have attained a level of education and experience
Diagnosis. overt Examination. Definitive Examination. History. atient interview. Personal History. Clinical Examination.
 Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Case Presentation. Overall Health. Oral Hygiene. Chief Complaint. I hate my upper denture. I can t taste food. I want an implant solution
 Case Presentation Medical History Age & Gender 62 years old female Peri-implant Osteitis Overall Health Good Hx of Smoking 5 cigarets per day (Peri-implantitis) Oral Hygiene Fair Systemic Disease Osteoarthritis
Case Presentation Medical History Age & Gender 62 years old female Peri-implant Osteitis Overall Health Good Hx of Smoking 5 cigarets per day (Peri-implantitis) Oral Hygiene Fair Systemic Disease Osteoarthritis
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter
 THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of
 Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study
 Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
A systematic review of survival of single implants as presented in longitudinal studies with a follow-up of at least 10 years
 REVIEW S155 Lars Hjalmarsson, Maryam Gheisarifar, Torsten Jemt A systematic review of survival of single implants as presented in longitudinal studies with a follow-up of at least 10 years Key words 10-year
REVIEW S155 Lars Hjalmarsson, Maryam Gheisarifar, Torsten Jemt A systematic review of survival of single implants as presented in longitudinal studies with a follow-up of at least 10 years Key words 10-year
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial
 Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
The Effects of Anti-infective Preventive Measures on the Occurrence of Biologic Implant Complications and Implant Loss: A Systematic Review
 The Effects of Anti-infective Preventive Measures on the Occurrence of Biologic Implant Complications and Implant Loss: A Systematic Review Giovanni E. Salvi, DMD, Prof Dr Med Dent 1 /Nicola U. Zitzmann,
The Effects of Anti-infective Preventive Measures on the Occurrence of Biologic Implant Complications and Implant Loss: A Systematic Review Giovanni E. Salvi, DMD, Prof Dr Med Dent 1 /Nicola U. Zitzmann,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 699 A Classification System for Peri-implant Diseases and Conditions Hector L. Sarmiento, DMD, MSc 1 Michael R. Norton, BDS, FDS, RCS(Ed)
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 699 A Classification System for Peri-implant Diseases and Conditions Hector L. Sarmiento, DMD, MSc 1 Michael R. Norton, BDS, FDS, RCS(Ed)
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
Multidisciplinary treatment planning for patients with severe periodontal disease
 Clinical Multidisciplinary treatment planning for patients with severe periodontal disease Josselin Lethuillier, 1 Sébastien Felenc, 2 Philippe Bousquet 3 Abstract Periodontally compromised patients usually
Clinical Multidisciplinary treatment planning for patients with severe periodontal disease Josselin Lethuillier, 1 Sébastien Felenc, 2 Philippe Bousquet 3 Abstract Periodontally compromised patients usually
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Mini implants for Stabilization of partial dentures
 Systematically to the goal Mini implants for Stabilization of partial dentures Winfried Walzer Prostheses are still considered by many to be aesthetically pleasing, cost-effective, but often associated
Systematically to the goal Mini implants for Stabilization of partial dentures Winfried Walzer Prostheses are still considered by many to be aesthetically pleasing, cost-effective, but often associated
An osseointegrated oral implant is characterized
 Mobility Assessment with the Periotest System in Relation to Histologic Findings of Oral Implants Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont* The relationship between mobility assessment with the Periotest system
Mobility Assessment with the Periotest System in Relation to Histologic Findings of Oral Implants Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont* The relationship between mobility assessment with the Periotest system
Mario Roccuzzo Luca Bonino Paola Dalmasso Marco Aglietta
 Mario Roccuzzo Luca Bonino Paola Dalmasso Marco Aglietta Long-term results of a three arms prospective cohort study on implants in periodontally compromised patients: 10-year data around sandblasted and
Mario Roccuzzo Luca Bonino Paola Dalmasso Marco Aglietta Long-term results of a three arms prospective cohort study on implants in periodontally compromised patients: 10-year data around sandblasted and
Alveolar Ridge Preservation:
 Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
The Endodontic / Implant Controversy
 The Endodontic / Implant Controversy Innovations in Endodontics Series Robert Handysides DDS Associate Professor and Chair Department of Endodontics Loma Linda University School of Dentistry Endodontic
The Endodontic / Implant Controversy Innovations in Endodontics Series Robert Handysides DDS Associate Professor and Chair Department of Endodontics Loma Linda University School of Dentistry Endodontic
Effect of thread size on the implant neck area: preliminary results at 1 year of function
 Young-Il Kang* Dong-Won Lee* Kwang-Ho Park Ik-Sang Moon Effect of thread size on the implant neck area: preliminary results at 1 year of function Authors affiliations: Young-Il Kang*, Dong-Won Lee*, Ik-Sang
Young-Il Kang* Dong-Won Lee* Kwang-Ho Park Ik-Sang Moon Effect of thread size on the implant neck area: preliminary results at 1 year of function Authors affiliations: Young-Il Kang*, Dong-Won Lee*, Ik-Sang
Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction with Hybrid Restorations
 Philip L. Fava II, DMD, MDSc Robert A. Levine, DDS, FCPP, FISPPS 9880 Bustleton Ave, Suite 211 Philadelphia, PA 19115 PADentalImplants.com 215-677-8686 Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction
Philip L. Fava II, DMD, MDSc Robert A. Levine, DDS, FCPP, FISPPS 9880 Bustleton Ave, Suite 211 Philadelphia, PA 19115 PADentalImplants.com 215-677-8686 Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction
Dental Services Referral Form- Orthodontic Clinic
 Dental Services Referral Form- Orthodontic Clinic Date / / Title: Surname Given name Date of birth: Street address Suburb Postcode Name of Residential Facility (if applicable) Room: Phone - Home: Mobile:
Dental Services Referral Form- Orthodontic Clinic Date / / Title: Surname Given name Date of birth: Street address Suburb Postcode Name of Residential Facility (if applicable) Room: Phone - Home: Mobile:
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, :54 AM
 Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, 2015 9:54 AM 1. The definition of Trauma From Occlusion: Primary TFO, Secondary TFO, and Combined TFO 2. Clinical and Radiographic signs
Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, 2015 9:54 AM 1. The definition of Trauma From Occlusion: Primary TFO, Secondary TFO, and Combined TFO 2. Clinical and Radiographic signs
GuidedService. The ultimate guide for precise implantations
 GuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations ABGuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations At A.B. Dental we've brought implantology into the future with a 3D digitally planned
GuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations ABGuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations At A.B. Dental we've brought implantology into the future with a 3D digitally planned
Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report
 CASE REPORT J Korean Dent Sci. 2013;6(1):27-33 http://dx.doi.org/10.5856/jkds.2013.6.1.27 ISSN 2005-4742 Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report Se Hoon Kahm
CASE REPORT J Korean Dent Sci. 2013;6(1):27-33 http://dx.doi.org/10.5856/jkds.2013.6.1.27 ISSN 2005-4742 Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report Se Hoon Kahm
4. What about age? There is no age limit. After puberty, anyone can get dental implants.
 Dental Implants 1. What are Osseointegrated implants? Osseointegrated implants are a new generation of dental implants in Rio de Janeiro, introduced in the 1960 s, they come in different shapes and sizes.
Dental Implants 1. What are Osseointegrated implants? Osseointegrated implants are a new generation of dental implants in Rio de Janeiro, introduced in the 1960 s, they come in different shapes and sizes.
Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402
 Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402 Subject Mucogingival Surgery and Soft Tissue Grafting Originating Department Clinical Professional Services Signature Authority Dental Director Type: New
Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402 Subject Mucogingival Surgery and Soft Tissue Grafting Originating Department Clinical Professional Services Signature Authority Dental Director Type: New
Risk of Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss in Subjects with a History of Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
 Risk of Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss in Subjects with a History of Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Syarida H. Safii, DDS [Correction added after online publication 1 June
Risk of Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss in Subjects with a History of Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Syarida H. Safii, DDS [Correction added after online publication 1 June
Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets
 Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
Primary prevention of periimplantitis: peri-implant mucositis S152
 J Clin Periodontol 2015; 42 (Suppl. 16): S152 S157 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12369 Primary prevention of periimplantitis: Managing peri-implant mucositis Jepsen S, Berglundh T, Genco R, Aass AM, Demirel K, Derks
J Clin Periodontol 2015; 42 (Suppl. 16): S152 S157 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12369 Primary prevention of periimplantitis: Managing peri-implant mucositis Jepsen S, Berglundh T, Genco R, Aass AM, Demirel K, Derks
G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM
 American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 2013 Dental Implant Conference December 5 7, 2013 Sheraton Chicago Hotel & Towers G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM Prosthetic Complications
American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 2013 Dental Implant Conference December 5 7, 2013 Sheraton Chicago Hotel & Towers G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM Prosthetic Complications
Telescopic Retainers: An Old or New Solution? A Second Chance to Have Normal Dental Function
 Telescopic Retainers: An Old or New Solution? A Second Chance to Have Normal Dental Function Joseph B. Breitman, DMD, FACP, 1,2 Scott Nakamura, DMD, 3 Arnold L. Freedman, DDS, 4 & Irving L. Yalisove, DDS
Telescopic Retainers: An Old or New Solution? A Second Chance to Have Normal Dental Function Joseph B. Breitman, DMD, FACP, 1,2 Scott Nakamura, DMD, 3 Arnold L. Freedman, DDS, 4 & Irving L. Yalisove, DDS
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
IMPLANTS. Guideline Number: DCG Effective Date: January 1, 2018
 IMPLANTS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG007.04 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1 COVERAGE RATIONALE...1
IMPLANTS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG007.04 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1 COVERAGE RATIONALE...1
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 729 Resective Treatment of Peri-implantitis: Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes After 2 Years Emmanuel Englezos, DDS, MSc 1 Jan Cosyn,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 729 Resective Treatment of Peri-implantitis: Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes After 2 Years Emmanuel Englezos, DDS, MSc 1 Jan Cosyn,
Consensus Report Biomechanics/risk management (Working Group 2)
 Mariano Sanz Ignace Naert Consensus Report Biomechanics/risk management (Working Group 2) Members of Working Group: Klaus Gotfredsen Flemming Isidor Franck Renouard Phoebus Madianos Carlos Madrid Pascal
Mariano Sanz Ignace Naert Consensus Report Biomechanics/risk management (Working Group 2) Members of Working Group: Klaus Gotfredsen Flemming Isidor Franck Renouard Phoebus Madianos Carlos Madrid Pascal
A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran
 Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
John P. Zarb, BA, DDS George A. Zarb, BChD, DDS, MS, MS, FRCD(C)
 C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E Implant Prosthodontic Management of Anterior Partial Edentulism: Long-Term Follow-Up of a Prospective Study John P. Zarb, BA, DDS George A. Zarb, BChD, DDS, MS, MS, FRCD(C)
C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E Implant Prosthodontic Management of Anterior Partial Edentulism: Long-Term Follow-Up of a Prospective Study John P. Zarb, BA, DDS George A. Zarb, BChD, DDS, MS, MS, FRCD(C)
As an increasing number of
 LITERATURE REVIEWS Understanding Peri-implantitis: A Strategic Review Preetinder Singh, MDS* The high survival rate of osseointegrated dental implants is well documented, but it is becoming increasingly
LITERATURE REVIEWS Understanding Peri-implantitis: A Strategic Review Preetinder Singh, MDS* The high survival rate of osseointegrated dental implants is well documented, but it is becoming increasingly
Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors
 Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors Faiza M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc. (1) Zainab M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc (2) ABSTRACT Background: Gingival recession
Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors Faiza M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc. (1) Zainab M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc (2) ABSTRACT Background: Gingival recession
Failures in implant therapy. Biological and mechanical complications. Their prevention management. Dr. Katalin Csurgay Dr.
 Failures in implant therapy. Biological and mechanical complications. Their prevention management. Dr. Katalin Csurgay Dr. Tatiana Shkolnik Complications could be: Doctor related Patient related Early
Failures in implant therapy. Biological and mechanical complications. Their prevention management. Dr. Katalin Csurgay Dr. Tatiana Shkolnik Complications could be: Doctor related Patient related Early
Removable Partial Dentures
 Removable Partial Dentures Replacement of missing teeth Fixed partial denture Removable partial denture Complete removable Transitional denture Partial removable Implant retained prosthodontics No prosthetic
Removable Partial Dentures Replacement of missing teeth Fixed partial denture Removable partial denture Complete removable Transitional denture Partial removable Implant retained prosthodontics No prosthetic
Principles of. By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah
 Principles of By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah 1. Utilize what's present: Whenever possible, select a design that fits the teeth and soft tissues, rather than choosing one that requires tissue alteration. When minimal
Principles of By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah 1. Utilize what's present: Whenever possible, select a design that fits the teeth and soft tissues, rather than choosing one that requires tissue alteration. When minimal
Many of the problems reported by conventional
 Maxillary Overdentures Retained by Splinted and Unsplinted Implants: A Retrospective Study Timo O. Närhi, DDS, PhD 1 /Miluska Hevinga, DDS 2 / Ralph A. C. A. Voorsmit, DDS, PhD 3 /Warner Kalk, DDS, PhD
Maxillary Overdentures Retained by Splinted and Unsplinted Implants: A Retrospective Study Timo O. Närhi, DDS, PhD 1 /Miluska Hevinga, DDS 2 / Ralph A. C. A. Voorsmit, DDS, PhD 3 /Warner Kalk, DDS, PhD
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
Endosseous dental implants initially showed very
 Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Clinical and Radiographic Assessment of Reasons for Replacement of Metal- Ceramic Fixed Dental Prostheses in Patients Referring to Dental School
 Journal section: Prosthetic Dentistry Publication Types: Research doi:0.437/jced.380 http://dx.doi.org/0.437/jced.380 Clinical and Radiographic Assessment of Reasons for Replacement of Metal- Ceramic Fixed
Journal section: Prosthetic Dentistry Publication Types: Research doi:0.437/jced.380 http://dx.doi.org/0.437/jced.380 Clinical and Radiographic Assessment of Reasons for Replacement of Metal- Ceramic Fixed
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. To systematically appraise the impact of mechanical/technical risk factors on
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. To systematically appraise the impact of mechanical/technical risk factors on
Uppers are from Mars, Lowers from Venus Clarifying Overdentures
 Uppers are from Mars, Lowers from Venus Clarifying Overdentures M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S. Thomas P. Hinman Dental Meeting Atlanta, GA March 23, 2017 About Your Speaker: M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S.
Uppers are from Mars, Lowers from Venus Clarifying Overdentures M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S. Thomas P. Hinman Dental Meeting Atlanta, GA March 23, 2017 About Your Speaker: M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S.
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Framework and Proposal of a New Classification and Case Definition. By: Kimberly Hawrylyshyn
 Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Framework and Proposal of a New Classification and Case Definition By: Kimberly Hawrylyshyn Background Periodontitis is a microbe induced inflammatory disease that
Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Framework and Proposal of a New Classification and Case Definition By: Kimberly Hawrylyshyn Background Periodontitis is a microbe induced inflammatory disease that
The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys
 The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys Takashi Miyata, DDS, DDSc 1 /Yukinao Kobayashi, DDS 2 /Hisao Araki, DDS, DDSc 3 / Takaichi Ohto,
The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys Takashi Miyata, DDS, DDSc 1 /Yukinao Kobayashi, DDS 2 /Hisao Araki, DDS, DDSc 3 / Takaichi Ohto,
It has been proposed that partially edentulous maxillectomy
 CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture Using Modified Impression Technique: A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver.VII (Oct. 2015), PP 102-107 www.iosrjournals.org Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver.VII (Oct. 2015), PP 102-107 www.iosrjournals.org Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture
Astra Tech Implant System. Scientific Summary
 Astra Tech Implant System Scientific Summary Why we do what we do? Our vision of a world where everyone eats, speaks and smiles with confidence permeates and inspires everything we do. We believe in an
Astra Tech Implant System Scientific Summary Why we do what we do? Our vision of a world where everyone eats, speaks and smiles with confidence permeates and inspires everything we do. We believe in an
There are three referral categories used in the dental referral system:
 Restorative Dentistry Referral Criteria Restorative Dentistry referral criteria are outlined to provide General Dental Practitioners (GDPs), Community Dental Service (CDS) Dentists, Primary Care Specialists,
Restorative Dentistry Referral Criteria Restorative Dentistry referral criteria are outlined to provide General Dental Practitioners (GDPs), Community Dental Service (CDS) Dentists, Primary Care Specialists,
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Case Report Immediate, Early, and Conventional Implant Placement in a Patient with History of Periodontitis
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 217895, 10 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/217895 Case Report Immediate, Early, and Conventional Implant Placement in a Patient with History of Periodontitis
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 217895, 10 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/217895 Case Report Immediate, Early, and Conventional Implant Placement in a Patient with History of Periodontitis
Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS
 Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS Considering both surgical Aim and prosthetic aspects in the planning of implant prosthetics Arrangements for implant therapy Preliminary examinations
Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS Considering both surgical Aim and prosthetic aspects in the planning of implant prosthetics Arrangements for implant therapy Preliminary examinations
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1
 PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1 Overview A 32 year-old patient presented with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Treatment included non-surgical therapy with adjunctive antibiotics and surgical treatment.
PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1 Overview A 32 year-old patient presented with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Treatment included non-surgical therapy with adjunctive antibiotics and surgical treatment.
Ankylos. Scientific Summary
 Ankylos Scientific Summary Implanting TissueCare For over 25 years, the Ankylos implant system stands for stable, long-term esthetics. The results from numerous publications and long-term clinical experience
Ankylos Scientific Summary Implanting TissueCare For over 25 years, the Ankylos implant system stands for stable, long-term esthetics. The results from numerous publications and long-term clinical experience
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Newport News Public Schools Summary Schedule of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan
 Newport News Public Schools Summary of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan Services In-Network Out-of-Network PPO Premier All Other Diagnostic & Preventive Oral Exams & Teeth Cleanings Fluoride Applications
Newport News Public Schools Summary of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan Services In-Network Out-of-Network PPO Premier All Other Diagnostic & Preventive Oral Exams & Teeth Cleanings Fluoride Applications
Foundation for Oral Rehabilitation (FOR) consensus text on The Rehabilitation of Missing Single Teeth
 CONSENSUS STATEMENTS S173 Foundation for Oral Rehabilitation (FOR) consensus text on The Rehabilitation of Missing Single Teeth Methodology used for establishing the consensus text The Foundation for Oral
CONSENSUS STATEMENTS S173 Foundation for Oral Rehabilitation (FOR) consensus text on The Rehabilitation of Missing Single Teeth Methodology used for establishing the consensus text The Foundation for Oral
Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research. DOI: /sjodr. ISSN (Print) Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website:
 DOI:10.21276/sjodr Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297 (Online)
DOI:10.21276/sjodr Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297 (Online)
Appendix 1 - Restorative Dentistry Referral Guidelines for referring practitioners
 Appendix 1 - Restorative Dentistry Referral Guidelines for referring practitioners These guidelines are intended to assist General Dental Practitioners (GDPs), Community Dental Service (CDS) Dentists and
Appendix 1 - Restorative Dentistry Referral Guidelines for referring practitioners These guidelines are intended to assist General Dental Practitioners (GDPs), Community Dental Service (CDS) Dentists and
Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I.
 Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I. Removable dentures Partial Complete (full) lenka.roubalikova@tiscali.cz 2 Prosthetic dentistry replacement of Damaged teeth reconstruction of the crown (inlays, crowns)
Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I. Removable dentures Partial Complete (full) lenka.roubalikova@tiscali.cz 2 Prosthetic dentistry replacement of Damaged teeth reconstruction of the crown (inlays, crowns)
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
MALO CLINIC PROTOCOL IMMEDIATE-FUNCTION CONCEPT UPPER AND LOWER JAW REHABILITATION: A CLINICAL REPORT
 MALO CLINIC PROTOCOL IMMEDIATE-FUNCTION CONCEPT UPPER AND LOWER JAW REHABILITATION: A CLINICAL REPORT PURPOSE Rehabilitation case with an implant-supported rehabilitation with immediate function implants.
MALO CLINIC PROTOCOL IMMEDIATE-FUNCTION CONCEPT UPPER AND LOWER JAW REHABILITATION: A CLINICAL REPORT PURPOSE Rehabilitation case with an implant-supported rehabilitation with immediate function implants.
