Procjena stabilnosti implantata nakon podizanja dna sinusa i primjene različitih nadomjesnih materijala
|
|
|
- Brooke Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 25 ACTA STOMATOLOGICA CROATICA Acta stomatol Croat. 2014;48(1): IZVORNI ZNANSTVENI RAD ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC PAPER Damir Jelušić 1, Ivan Puhar 2, Darije Plančak 2 Procjena stabilnosti implantata nakon podizanja dna sinusa i primjene različitih nadomjesnih materijala Assessment of Implant Stability Following Sinus Lift Procedures with Different Grafting Materials 1 Dentalna poliklinika Dr. Jelušić, Opatija, Hrvatska Dental Polyclinic Dr Jelušić, Opatija, Croatia 2 Zavod za parodontologiju Stomatološkog fakulteta Sveučilišta u Zagrebu, Hrvatska Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, Zagreb, Croatia Sažetak Svrha: Željela se istražiti stabilnost implantata nakon podizanja dna sinusa i primjene dvaju nadomjesnih materijala te dobivene rezultate usporediti s implantatima postavljenima u neaugmentirani lateralni dio gornje čeljusti. Materijali i metode: Istraživanje je provedeno na 44 zdrava pacijenta s indikacijom za podizanje dna sinusa (ispitivana skupina). Nakon podizanja dna sinusa i primjene čistog beta trikalcijeva fosfata postavljeno je 46 implantata, a 39 je ugrađeno nakon augmentacije sa 60-postotnim hidroksiapatitom i 40-postotnim beta trikalcijevim fosfatom. U kontrolnoj skupini bilo je 48 zdravih pacijenata kojima je 85 implantata postavljeno u neaugmentirani lateralni dio gornje čeljusti. Svim ispitanicima ugrađeni su implantati Astra Tech OsseoSpeed. Njihova stabilnost određivala se metodom analize rezonantne frekvencije. Na temelju triju mjerenja izračunat je kvocijent stabilnosti implantata (ISQ). Rezultati: Nije pronađena statistički značajna razlika u ISQ-vrijednosti između implantata koji su postavljeni augmentacijskim postupkom i onih bez njega (p=0,789). Statistički značajna razlika nije uočena ni kada su ISQ-vrijednosti implantata postavljenih nakon pojedinog nadomjesnog materijala uspoređene s ISQ-vrijednostima odgovarajućih implantata u neaugmentiranoj kosti (p=0,697 i p=0,402). Zaključak: Ovo istraživanje pokazalo je da je stabilnost implantata usporediva između implantata koji su postavljeni u lateralni dio gornje čeljusti, neovisno o podizanju dna sinusa i nadomjesnom materijalu. Implantati ugrađeni u augmentirani lateralni dio gornje čeljusti mogu se predvidivo protetski opskrbiti kao i implantati postavljeni u neaugmentiranu gornju čeljust. Zaprimljen: 30. prosinca Prihvaćen: 1. ožujak Adresa za dopisivanje Dr. sc. Ivan Puhar Sveučilište u Zagrebu Stomatološki fakultet Zavod za parodontologiju Gundulićeva 5, Zagreb, Hrvatska tel: puhar@sfzg.hr Ključne riječi zubni implantati; podizanje dna sinusa; analiza rezonantne frekvencije; beta trikalcij-fosfat; hidroksiapatit Uvod U dentalnoj implantologiji lateralni dio gornje čeljusti često je povezan s različitim izazovima. Kako bi se taj dio čeljusti adekvatno opskrbio dentalnim implantatima, potrebna je dovoljna količina kosti u području grebena. No određena anatomska ograničenja koja se mogu susresti uključuju pojačanu pneumatizaciju maksilarnog sinusa, tanku kost s lateralne ili okluzalne strane, plitko nepce i blizinu sinusa u odnosu na alveolarni greben (1). Kod pacijenata s nedovoljnim volumenom kosti u lateralnom dijelu gornje čeljusti indicirano je podizanje dna sinusa kako bi se omogućilo postavljanje implantata. Otkako je tu tehniku sredinom 1970-ih izvorno opisao Tatum, podizanje dna maksilarnog sinusa detaljno se istraživalo s obzirom na različite nadomjesne materijale i usporedbu između srodnih tehnika (2 4). Najčešće korišteni terapijski modaliteti uključuju dvofaznu lateralnu antrostomiju, jednofaznu lateralnu antrostomiju i osteotomsku tehniku s krestalnim pristupom. Dvofazna lateralna antrostomija indicirana je kada je visina rezidualne Introduction The posterior maxilla is often associated with different challenges to the implant dentist. In order to adequately restore posterior maxilla with dental implants, a sufficient bone volume in the maxillary ridge is required. However, certain anatomic limitations can be encountered and these include increased pneumatization of the maxillary sinus, thin lateral and occlusal bone, flat palatal vault, and proximity of the sinus to crestal bone (1). In patients with insufficient bone volume of the posterior maxilla, elevation of the sinus floor is indicated to allow for implant restorations. Since it was originally described by Tatum in the mid 1970s, maxillary sinus floor elevation has been extensively investigated with respect to different grafting materials, and comparison between similar approaches (2-4). The most widely used treatment modalities include the two-step lateral antrostomy, the one-step lateral antrostomy, and the osteotome technique with crestal approach. The two-step lateral antrostomy is indicated when the residual
2 26 Jelušić i sur. Stabilnost implantata nakon podizanja dna sinusa This parallel study included 44 healthy subjects with an existing indication for unilateral or bilateral sinus lift procedure (test group), and 48 healthy patients who were treated with 85 implants but without bone augmentation in maxilkosti manja od 4 milimetra. Jednofazna lateralna antrostomija primjenjuje se za rezidualnu visinu kosti od 4 do 6 milimetara, a manje invazivna osteotomska tehnika preporučuje se kada je visina rezidualne kosti veća od 6 milimetara (5, 6). Premda se vlastita kost smatra najboljim nadomjesnim materijalom za augmentaciju sinusa, predlažu su i različite alternative kako bi se postupak pojednostavnio demineralizirana suho smrznuta kost, hidroksiapatit (HA), beta-trikalcijev fosfat (ß-TCP), anorganska deproteinizirana goveđa kost te kombinacija navedenih i ostalih materijala (7, 8). U preglednom radu je Del Fabbro sa suradnicima određivao stopu preživljavanja implantata postavljenih u augmentirani maksilarni sinus te djelovanje nadomjesnih materijala. Stopa preživljavanja implantata iznosila je 87,70 posto s autogenim materijalima, 94,88 posto kad se koristio autogenom kosti i različitim koštanim nadomjescima te 95,98 posto sa samo koštanim nadomjesnim materijalima. Na taj je način dokazano da su koštani nadomjesni materijali učinkoviti kao i autogena kost kada se primjenjuju sami ili u kombinaciji s autogenom kosti (9). Stabilnost implantata i uspješna oseointegracija preduvjeti su za njihovo preživljavanje. Stoga je kontinuirano praćenje na ponovljiv i objektivan način krucijalno za određivanje stabilnosti implantata. Danas za to postoje različite neinvazivne metode: rendgenske slike, obrnuti tork, otpor narezujućeg torka, modalna analiza i analiza rezonantne frekvencije (RFA). Usporedbom različitih metoda mjerenja pronađena je značajna povezanost narezujućeg ili insercijskog torka i RFA-metode (10, 11). Huang i suradnici proučavali su prirodnu frekvenciju kako bi procijenili sučelje implantata i kosti. Prirodna frekvencija je fizikalna karakteristika strukture koja je usko povezana s njezinim rubnim uvjetima. Zaključili su da se rubni uvjeti implantata mogu pratiti utvrđivanjem njegove prirodne frekvencije (12). U drugom su istraživanju isti autori istaknuli da je RFA-metoda pouzdana i točna kad je riječ o ranoj procjeni procesa oseointegracije. Ova mjerenja mogu poslužiti kao indikator i primarne i sekundarne stabilnosti implantata (13). Proučavanje RFA kod jednofaznih implantata tijekom razdoblja oseointegracije pokazalo je najmanju stabilnost tri do šest tjedana nakon postavljanja navedenih implantata bez protetske opskrbe. Vrijednosti dobivene s pomoću RFA mogu stoga biti korisne za određivanje različitih faza cijeljenja i stabilnosti dentalnih implantata. Ovi rezultati potvrđuju potrebu za kliničkom napravom kojom bi se ocjenjivala stabilnost implantata prije protetske opskrbe (14). Svrha ovog istraživanja bila je ocijeniti stabilnost implantata nakon podizanja dna sinusa i primjene dvaju nadomjesnih materijala, te dobivene rezultate usporediti s implantatima postavljenima u neaugmentirani lateralni dio gornje čeljusti. bone height is less than 4 mm. The one-step lateral antrostomy is used for the residual bone height of 4 to 6 mm, and the less invasive osteotome technique is recommended when more than 6 mm of residual bone height is present (5,6). Although the patient s own bone is considered the best grafting material for sinus augmentation, various alternatives have been proposed to simplify the grafting procedure including demineralized freeze-dried bone, hydroxyapatite (HA), beta-tricalcium phosphate (ß-TCP), anorganic deproteinized bovine bone and combination of these and others (7,8). In a systematic review, Del Fabbro et al. determined the survival rate of implants placed in the grafted maxillary sinus, and the effects of grafting materials. Implant survival rate was 87.70% with autogenous grafts, 94.88% when combining autogenous bone with different bone substitutes and 95.98% with bone substitutes alone. Therefore, bonesubstitute grafts were shown to be as effective as autogenous bone when used alone or in combination with autogenous bone (9). Implant stability and successful osseointegration are prerequisites for implant survival. Thus, continuous monitoring in a reproducible and objective manner is crucial in determining the implant stability. Various non-invasive methods are available today for this purpose: radiographs, reverse torque, cutting torque resistance, modal analysis, and resonance frequency analysis (RFA). When different measurements were compared, a significant correlation was found between cutting torque or insertion torque and RFA (10, 11). Huang et al. evaluated natural frequency to assess implant-bone interface. Natural frequency is a physical characteristic of a structure, which is closely related to its boundary conditions. They concluded that the boundary status of an implant can be monitored by detecting its natural frequency (12). In another study, the same researchers found RFA as a reliable and accurate method for early assessment of osseointegration process. These measurements cannot only be used as an indicator for primary stability, but can also be useful regarding the secondary implant stability (13). Study on RFA of one-stage dental implant stability during the osseointegration period revealed the weakest stability at 3-6 weeks in onestage non-loaded implants. Values obtained with RFA can be therefore valuable in determining different healing phases and the stability of dental implants. Those results support the need for a clinical device to evaluate implant stability prior to loading (14). The objective of this research was to evaluate implant stability following sinus lift with two grafting materials, and to compare it with the implants placed in a pristine posterior maxilla. Materijali i metode U ovom paralelnom istraživanju sudjelovala su 44 zdrava pacijenta s indikacijom za unilateralno ili bilateralno podizanje dna sinusa (ispitivana skupina) te 48 zdravih pacijenata kojima je 85 implantata postavljeno u neaugmentirani Materials and methods
3 Jelušić et al. Implant Stability Following Sinus Lift Procedures 27 lateralni dio gornje čeljusti (kontrolna skupina). Randomizacija je provedena samo za ispitivanu skupinu u kojoj je 46 implantata postavljeno nakon podizanja dna sinusa i primjene čistoga ß-TCP-a, a 39 implantata ugrađeno je nakon augmentacije s HA/ß-TCP-om. Kriteriji za uključivanje u ispitivanu skupinu bili su: dob iznad 18 godina, prekinut ili skraćen zubni luk u lateralnom dijelu gornje čeljusti, rezidualni koštani greben <5 mm i dobra oralna higijena. Kriteriji isključivanja bili su: sistemske kontraindikacije za augmentacijske postupke (trudnoća, narušeno opće zdravlje, nekontrolirana šećerna bolest, liječenje kortikosteroidima i bisfosfonatima, uznapredovala osteoporoza), zračenje maksilofacijalne regije, pušenje > 10 cigareta na dan, loša oralna higijena te infekcije ili tumori u području gornje čeljusti. Pacijenti su jedan sat prije operacije uzeli oralne antibiotike (1 g amoksicilina ili 600 mg klindamicina u slučaju alergije na penicilin). Nakon ispiranja 0,20-postotnim klorheksidinom i lokalne anestezije, učinjena je krestalna incizija s vertikalnim rasteretnim incizijama kako bi se formirao režanj pune debljine i prikazala bukalna kost maksilarnog sinusa. Koštani zid oprezno je fenestriran uz oblino hlađenje fiziološkom otopinom. Predoperativna visina kosti varirala je od 0,6 do 5,7 milimetara. Nakon odvajanja Schneiderove membrane od dna sinusa, ovisno o randomizaciji, postavljen je čisti ß-TCP koštani nadomjesni materijal (Bioresorb, Sybron Implant Solutions, Orange, SAD) ili 60 % HA s 40 % ß-TCP-a (Maxresorb, Botiss, Berlin, Njemačka) koji su prethodno rehidrirani s 1 do 5 ml sterilne fiziološke otopine. Bukalni prozor prekriven je rehidriranom kolagenom membranom (Jason membrane, Botiss, Berlin, Njemačka). Režanj pune debljine adaptiran je i rana je zašivena. S pomoću konične kompjutorizirane tomografije (CBCT) učinjena je kontrolna snimka kako bi se isključila dislokacija koštanog nadomjesnog materijala. Sljedećih pet dana pacijenti su uzimali 2 x 1000 mg amoksicilina ili 3 x 300 mg klindamicina u slučaju alergije na penicilin. Šavovi su uklonjeni sedam do deset dana nakon operacije. Nakon šestomjesečne faze cijeljenja ponovno je učinjena CBCT snimka kako bi se odredili položaj, duljina i promjer planiranog implantata. Svim ispitanicima postavljani su implantati Astra Tech OsseoSpeed (Astra Tech AB, Mölndal, Švedska) prema istom postupku bušenja, uzimajući u obzir kvalitetu kosti i upute proizvođača. U objema skupinama bilježio se insercijski tork u rasponu od lošeg do izvrsnog. Implantati su opterećeni prema standardnom protokolu četiri mjeseca nakon ugradnje. Imedijatno opterećenje nije se primijenilo, niti je između skupina bilo razlika u postupku opterećenja. Dok je trajalo istraživanje nije bilo gubitka implantata. Tijekom zahvata sanirano je sedam perforacija membrane sinusa, što nije utjecalo na daljnji protokol. Za određivanje stabilnosti implantata u objema skupinama korištena je metoda RFA (Osstell ISQ, Osstell, Gothenburg, Švedska). Nakon mapiranja rezonantnih frekvencija, ovom metodom dobivena je mjerna ljestvica ISQ-vrijednosti od 1 do 100 (kvocijent stabilnosti implantata). Srednja ISQvrijednost svakog implantata izračunata je na temelju triju mjerenja iz različitih smjerova. Kako bi se precizno usporedile srednje ISQ-vrijednosti, svaki implantat u ispitivanoj skula (control group). The study was only randomized in a test group where 46 implants were placed following sinus lift with pure-phase ß-TCP, while 39 implants were placed following augmentation with HA/ß-TCP material. The inclusion criteria for test groups were: age> 18 years, interrupted or shortened dental arch in the lateral part of the upper jaw, the amount of residual bone ridge <5mm and a good oral hygiene. The exclusion criteria were: systemic contraindications for augmentation procedures (pregnancy, poor general condition, untreated diabetes, glucocorticoids and bisphosphonates medication, and advanced osteoporosis), radiation of maxillofacial region, smoking > 10 cigarettes per day, poor oral hygiene, and infections or tumors of the maxillary area. One hour prior to surgery patients took oral antibiotics (1g amoxicillin or 600mg clindamycin if allergic to penicillin). After rinsing with 0.20% chlorhexidine and administration of local anesthesia, a crestal incision with vertical releasing incisions were performed to raise a full thickness flap and to expose a buccal bone wall of the maxillary sinus. Bone wall was carefully fenestrated with copious saline cooling. Preoperative residual bone height varied from 0.6 to 5.7 mm. After lifting the Schneiderian membrane from the sinus floor, depending on the randomization, a pure-phase ß-TCP bone grafting material (Bioresorb, Sybron Implant Solutions, Orange, USA) or a 60% HA with 40% ß-TCP material (Maxresorb, Botiss, Berlin, Germany) was applied after previous rehydration with 1-5 ml of sterile saline. Buccal window was covered with rehydrated collagen membrane (Jason membrane, Botiss, Berlin, Germany). A full thickness flap was adapted and the wound was sutured. Control conebeam computed tomography (CBCT) scan was recorded to exclude dislocation of the bone grafting material. Following 5 days after the surgery, patients took 2x1000mg amoxicillin or 3x300mg clindamycin if allergic to penicillin. Sutures were removed 7-10 days after the surgery. After the healing phase of 6 months, a CBCT scan was repeated to determine the position, length and width of the planned implant. In both groups, Astra Tech OsseoSpeed implants (Astra Tech AB, Mölndal, Sweden) were placed using the same drilling protocol, with regard to bone quality and in accordance with the manufacturer s recommendations. Insertion torque was recorded in a scale from poor to excellent in both groups. Standard loading protocol, without immediate loading or differences among groups, included loading 4 months after implant placement. No implant loss was observed during the study period. Seven sinus membrane perforations occurred, but they were immediately treated and did not influence the further protocol. RFA method (Osstell ISQ, Osstell, Gothenburg, Sweden) was used for determining implant stability in both groups. After mapping of resonance frequencies, this method provided a measurement scale of ISQ values (implant stability quotient). For each implant, a mean ISQ value was calculated on the basis of 3 ISQ measurements recorded from different directions. To precisely compare mean ISQ values, each implant in the test group was paired with the implant of the same length and diameter in the control group. RFA examinations were performed in both groups 4
4 28 Jelušić i sur. Stabilnost implantata nakon podizanja dna sinusa pini uparen je s implantatom iste duljine i promjera u kontrolnoj skupini. Isti iskusni doktor dentalne medicine obavio je RFA-mjerenja u objema skupinama četiri mjeseca nakon postavljanja implantata. Pacijenti u ispitivanoj skupini odabrani su nasumično kako bi se izbjegle pogreške pri odabiru i osigurala normalnost distribucije promatranih varijabli. Istraživanje je odobrilo Etičko povjerenstvo Stomatološkog fakulteta te je provedeno u skladu s etičkim načelima Helsinške deklaracije. Svi sudionici informirani su o prirodi istraživanja i potpisali su pristanak prije početka kliničkog ispitivanja. Podaci su analizirani u statističkom paketu SPSS v.21.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, SAD). Normalnost distribucije ocijenjena je Kolmogorov-Smirnovljevim testom. Wilcoxonov test rangiranih znakova korišten je za procjenu ISQ-vrijednosti implantata postavljenih augmentacijskim postupkom ili bez njega. Statistička značajnost postavljena je na p<0,05. Rezultati U obje je skupine većina od 85 uparenih implantata bila promjera 4,0 milimetra (76,5 %) i duljine 11 milimetara (48,2 %) (tablice 1. i 2.). Wilcoxonov test rangiranih znakova pokazao je da nema statistički značajne razlike u ISQ-vrijednostima implantata postavljenih augmentacijskim postupkom ili bez njega (p=0,789) (tablica 3.). Statistički značajna razlika nije uočena ni kada su ISQ-vrijednosti implantata postavljenih nakon augmentacije s pojedinim nadomjesnim materijalom uspoređene s ISQ-vrijednostima odgovarajućih implantata u neaugmentiranoj kosti. ISQ-vrijednosti implantata postavljenih nakon augmentacije ß-TCP-om bile su manje od kontrolnih vrijednosti, ali bez statističke značajnosti (p=0,697) (tablica 4.). Implantati postavljeni nakon augmentacije HA/ß-TCP-om imali su veće ISQ-vrijednosti, ali statistička značajnost nije uočena (p=0,402) (tablica 5.). months after implant placement by one and the same experienced dental examiner. The patients within the test group were randomly chosen to avoid selection bias and to ensure normal distribution of the sampled variables. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the School of Dental Medicine, and it was conducted in accordance with the ethical principles of the Helsinki Declaration. All participants were informed about the nature of the study and gave their written consent prior to clinical protocol. Data were analyzed with statistical software package SPSS v.21.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Normal distribution of the values was evaluated using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Wilcoxon signed ranks test was used to evaluate ISQ values of implants placed with and without augmentation procedure. The statistical significance was set at p<0.05. Results Out of 85 implants paired in both groups, most of them were 4.0 mm in diameter (76.5%) and 11 mm in length (48.2%) (Tables 1 and 2). Wilcoxon signed ranks test revealed no statistical difference in ISQ values of implants placed with and without augmentation procedure (p=0.789) (Table 3). Statistically significant difference was not found when ISQ values of implants placed following particular grafting material were compared with ISQ values of corresponding implants in a pristine bone. ISQ values of implants placed following ß-TCP were lower than in controls, but without significance (p=0.697) (Table 4). Implants placed following HA/ß-TCP showed higher ISQ values, but statistical significance was not observed (p=0.402) (Table 5). Tablica 1. Raspodjela promjera implantata u objema skupinama Table 1 Distribution of implant diameter in both groups Promjer Diameter mm ß-TCP HA/ß-TCP Neaugmentirana kost Pristine bone Tablica 2. Raspodjela duljine implantata u objema skupinama Table 2 Distribution of implant length in both groups Duljina Length mm ß-TCP HA/ß-TCP Neaugmentirana kost Pristine bone
5 Jelušić et al. Implant Stability Following Sinus Lift Procedures 29 Tablica 3. Usporedba ISQ-vrijednosti implantata u augmentiranoj i neaugmentiranoj gornjoj čeljusti Table 3 Comparison of ISQ values of implants placed in augmented and pristine maxilla N Srednja vrijednost Minimum Maksimum SD Mean Minimum Maximum ISQ augmentirana kost ISQ augmented bone ISQ neaugmentirana kost ISQ pristine bone Wilcoxonov test, SD = standardna devijacija, p = statistička značajnost Wilcoxon signed ranks test, SD = standard deviation, p = statistical significance P Tablica 4. ISQ-vrijednosti implantata u sinusu koji je augmentiran ß-TCP-om Table 4 ISQ values of implants placed in sinus augmented with ß-TCP N Srednja vrijednost Minimum Maksimum SD Mean Minimum Maximum ISQ ß-TCP ISQ neaugmentirana kost ISQ pristine bone Wilcoxonov test, SD = standardna devijacija, p = statistička značajnost Wilcoxon signed ranks test, SD = standard deviation, p = statistical significance P Tablica 5. ISQ-vrijednosti implantata u sinusu koji je augmentiran HA/ß-TCP-om Table 5 ISQ values of implants placed in sinus augmented with HA/ß-TCP N Srednja vrijednost Minimum Maksimum SD Mean Minimum Maximum ISQ HA/ß-TCP ISQ neaugmentirana kost ISQ pristine bone Wilcoxonov test, SD = standardna devijacija, p = statistička značajnost Wilcoxon signed ranks test, SD = standard deviation, p = statistical significance P Rasprava RFA-mjerenja pokazala su da nema razlike u stabilnosti implantata s obzirom na augmentacijski postupak i korišteni nadomjesni materijal. Srednje vrijednosti stabilnosti implantata postavljenih u lateralni dio gornje čeljusti augmentacijskim postupkom ili bez njega iznosile su 78,9±6,3 i 78,7±6,1. Prema znanstvenoj literaturi, ISQ-vrijednosti iznad 70 upućuju na visoku stabilnost i uspješnu oseointegraciju postavljenih implantata. Adekvatna stabilnost implantata osnovni je preduvjet za njihovo imedijatno i rano opterećenje (15, 16). Različiti klinički čimbenici koji mogu utjecati na vrijednosti rezonantne frekvencije proučavani su istraživanju Degidija i suradnika. Statistički značajna pozitivna korelacija uočena je između ISQ-vrijednosti i promjera i duljine implantata (17). Zato smo analizirali samo implantate jednakog promjera i duljine između ispitivane i kontrolne skupine kako bi se dobile usporedive ISQ-vrijednosti. Implantati koji su najčešće postavljani bili su promjera 4,0 milimetra i duljine 11 milimetara. Ersanli i suradnici istaknuli su da je ISQ-vrijednosti potrebno kalibrirati s obzirom na pojedini implantološki sustav jer je teško definirati općenite standardizirane raspone ISQvrijednosti uspješno integriranih implantata različitih sustava (14). Stoga se mjerenja dobivena u ovom istraživanju mogu primijeniti samo na implantate Astra Tech OsseoSpeed. Statistička analiza pokazala je da nema razlike u ukupnim ISQvrijednostima implantata postavljenih u lateralni dio gornje čeljusti augmentacijskim postupkom ili bez njega (p=0,789). Discussion RFA revealed no difference in implant stability with regard to grafting procedure or grafting material used. The mean values of stability of implants that were inserted in the posterior maxilla with or without augmentation procedure were 78.9±6.3 and 78.7±6.1, respectively. According to the scientific literature, ISQ values above 70 indicate high implant stability and successful osseointegration of inserted implant. Adequate implant stability value is the main prerequisite for immediate and early loading protocol (15, 16). Various clinical factors that could influence resonance frequency values were assessed in a study by Degidi et al. A statistically significant positive correlation was observed between ISQ values and implant diameter and length (17). For that reason, we only analyzed implants of the same diameter and length between test and control sites to obtain comparable ISQ values. Implants mostly used in the present study were 4.0 mm in diameter and 11 mm in length. Ersanli et al. emphasized that ISQ level should also be calibrated for each implant system separately, since it is difficult to define a general standardized range of ISQ values for successful implant integration for various implant systems (14). Stability measurements obtained with the present study, consequently, can only be applied to Astra Tech OsseoSpeed implants. Statistical analysis of measurements revealed no difference in overall ISQ values of implants that were inserted in posterior maxilla with or without augmentation procedure (p=0.789). Similar results were found with Astra Tech TiOblast implants that were inserted in grafted
6 30 Jelušić i sur. Stabilnost implantata nakon podizanja dna sinusa Rezultati se mogu usporediti s implantatima Astra Tech Ti- Oblast koji su postavljani u augmentiranu i neaugmentiranu gornju čeljust, pri čemu se pokazala slična stabilnost u ranoj fazi oseointegracije (18). Pregledom literature, kad je riječ o materijalima korištenima za podizanje dna sinusa, utvrđeno je da je inicijalna oseointegracija neovisna o primijenjenom biomaterijalu za augmentaciju (19). U našem istraživanju korištena su dva različita nadomjesna materijala (ß-TCP i HA/ß-TCP) koja su se prije toga pokazala pouzdanima u podizanje dna sinusa. Suba i suradnici uspoređivali su histomorfometrijom učinak ß-TCP-a i autogenoga koštanog materijala. Šest mjeseci nakon postavljanja materijala pokazalo se da je augmentirana kost u području sinusa čvrsta i prikladna za postavljanje implantata bez obzira na to je li korišten aloplastični ili autogeni materijal (20). Slično su uočili i Zijderveld i suradnici na temelju kliničkog i histološkog praćenja ß-TCP-a i autogene kosti uzete s brade (21). Osim toga, HA i ß-TCP zasebno su se uspoređivali tijekom augmentacijskih postupaka u području sinusa. Pokazalo se da je stvaranje nove kosti izraženije u HA-skupini s manje područja rezidualnih čestica materijala. Iako su oba materijala pokazala uspješnu osteokonduktivnost i biokompatibilnost za postupke podizanje dna sinusa, čini se da je HA učinkovitiji u osteokondukciji u odnosu na ß-TCP (22). Unatoč ovim razlikama, na naše ISQ-vrijednosti nije utjecao pojedini nadomjesni materijal s obzirom na to da nisu uočene značajne razlike u odnosu na ISQ-vrijednosti odgovarajućih implantata u neaugmentiranim područjima. Razlike uočene u vrijeme postavljanja implantata mogu se vjerojatno očekivati i tijekom dugoročnog praćenja. Degidi i suradnici proučavali su razvoj ISQ-vrijednosti nakon šest i dvanaest mjeseci od postavljanja implantata u augmentirano i neaugmentirano područje sinusa. Na temelju ovih mjerenja utvrđeno je da mjesta tretirana podizanjem dna sinusa mogu pružiti dobru dugoročnu stabilnost (23). U sličnoj 12-mjesečnoj kliničkoj studiji nisu nađene statistički značajne razlike u ISQ-vrijednostima implantata postavljenih u augmentirana i neugmentirana područja sinusa, ni nakon operacije ni nakon šest i dvanaest mjeseci (24). Naši rezultati također upućuju na to da se implantati postavljeni u augmentirani sinus, neovisno o nadomjesnom materijalu, mogu protetski opskrbiti kao i implantati postavljeni u nativnu, neaugmentiranu gornju čeljust. U prethodnim istraživanjima zaključeno je da na prognozu implantata postavljenih u augmentirane sinuse i fiksnih nadomjestaka na istim implantatima ne utječu čimbenici kao što su nadomjesni materijal, vrsta nadomjestka, rezidualna visina kosti i vrijeme postavljanja implantata (25). Stoga se RFA-mjerenja mogu preporučiti, posebice ako se razmatra imedijatno ili rano opterećenje implantata. Rezultati ovog istraživanja jasno su pokazali da je stabilnost promatranih implantata usporediva između implantata postavljenih u lateralni dio gornje čeljusti, neovisno o podizanju dna sinusa ili augmentacijskom postupku. Možeand non-grafted maxillary bone, and demonstrated similar stability during the early phase of osseointegration (18). A literature review on biomaterials in sinus augmentation procedures evidenced that initial osseointegration of dental implants seems to be independent of the biomaterial used in grafting procedure (19). In the present study, we used two different grafting materials (ß-TCP and HA/ß- TCP) that were previously shown to be reliable substitutes for sinus augmentation. Suba et al. compared the effects of ß-TCP and of autogenous bone graft using histomorphometry. The results showed that, 6 months after insertion of the grafts, the augmented sinus floor bone was strong and suitable for dental implant placement, regardless of whether alloplastic or autogenous graft had been applied (20). Similar findings were observed by Zijderveld et al. on the basis of the clinical and histologic formation ability of ß-TCP and autogenous chin bone (21). Also, HA and ß-TCP were separately compared when used for sinus augmentation procedures. It was demonstrated that a new bone formation was more pronounced in the HA group with less residual graft particle areas. Although both materials showed successful osteoconductivity and biocompatibility for the sinus floor elevation, HA appeared to be more efficient in osteoconduction when compared with ß-TCP (22). Despite these differences, our ISQ values were shown not to be influenced by a particular grafting material, because no significance was observed in comparison to ISQ values of corresponding implants in non-augmented sites. No difference that we observed at the time of implant placement can probably be expected in a long-term followup. Degidi et al. evaluated the evolution of ISQ values at 6 and 12 months from the implant insertion in sinus grafted and non-grafted sites. Using this method, it was found that sites treated with sinus lift can offer good long-term stability (23). In a similar 12-month clinical study, no statistically significant difference was found in ISQ values of implants placed in sinus-grafted and non-grafted sites after the surgery as well as at 6 and 12 months (24). Our results also indicate that implants inserted in a grafted sinus, regardless of the substitute material, can be predictably loaded as the implants inserted in a pristine, non-grafted maxilla. Previous studies concluded that the prognosis of implants inserted in augmented sinuses and fixed restoration supported by this implants seemed not to be influenced by factors such as graft material, type of restoration, residual bone height and time of implant placement (25). RFA measurements are therefore highly recommended, especially if a clinician is considering immediate or early implant loading. Zaključak Conclusion The results observed in this study clearly demonstrated that the examined implant stability is comparable among implants placed in the posterior maxilla regardless of sinus lift or grafting procedure. In conclusion, the implants placed
7 Jelušić et al. Implant Stability Following Sinus Lift Procedures 31 mo zaključiti da se implantati postavljeni u augmentirani sinus mogu predvidljivo protetski opskrbiti kao i implantati postavljeni u nativnu, neaugmentiranu gornju čeljust. RFA može poslužiti kao vrijedna klinička metoda za određivanje njihove stabilnosti. Zahvala Istraživanje je rađeno u sklopu projekta (Sistemni aspekti u etiologiji parodontnih bolesti, voditelj Darije Plančak) Ministarstva znanosti, obrazovanja i sporta Republike Hrvatske. Izjava Autori negiraju bilo kakav sukob interesa. in the grafted maxilla following sinus lift can be predictably loaded as the implants placed in a non-grafted, pristine maxilla. RFA can serve as a valuable clinical method for determining implant stability of the dental implant. Acknowledgements This paper was supported by the Ministry of Science, Education and Sport of the Republic of Croatia Grant No (chief investigator Darije Plančak, project Systemic aspects in the etiology of periodontal diseases ). Transparency declaration The authors deny any conflicts of interest. Abstract Objective: The objective of this research was to evaluate implant stability following sinus lift with two grafting materials, and to compare it with the results obtained for the implants placed in a pristine posterior maxilla. Materials and methods: The study included 44 healthy patients with an existing indication for sinus lift procedure (test group). 46 implants were placed following sinus lift with a pure-phase beta-tricalcium phosphate, while 39 implants were placed following augmentation with 60% hydroxyapatite with 40% beta-tricalcium phosphate material. The control group consisted of 48 healthy patients who were treated with 85 implants but without bone augmentation in posterior maxilla. Astra Tech OsseoSpeed implants were placed in all subjects. Resonance frequency analysis was used in both groups for determining implant stability 4 months after insertion. A mean implant stability quotient (ISQ) was calculated on the basis of 3 measurements. Results: No statistical difference was observed in ISQ values of implants placed with and without augmentation procedure (p=0,789). Statistically significant difference was not found when ISQ values of implants placed following particular grafting material were compared with ISQ values of corresponding implants in a pristine bone (p=0.697 and p=0.402). Conclusions: This study demonstrated that the implant stability is comparable among implants placed in the posterior maxilla regardless of sinus lift and grafting procedure. Implants placed in the grafted posterior maxilla can be predictably loaded as the implants placed in a non-grafted, pristine maxilla. Received: December 30, 2013 Accepted: March 1, 2014 Address for correspondence Ivan Puhar, DMD, PhD University of Zagreb School of Dental Medicine Department of Periodontology Gundulićeva 5 HR Zagreb, Croatia Tel: puhar@sfzg.hr Key words Dental Implants; Sinus Floor Augmentation; Resonance frequency analysis; Beta-tricalcium phosphate; Hydroxyapatites References 1. Woo I, Le BT. Maxillary sinus floor elevation: review of anatomy and two techniques. Implant Dent. 2004;13(1): Tatum H Jr. Maxillary and sinus implant reconstructions. Dent Clin North Am Apr;30(2): Stern A, Green J. Sinus lift procedures: an overview of current techniques. Dent Clin North Am Jan;56(1): Garofalo GS. Autogenous, allogenetic and xenogenetic grafts for maxillary sinus elevation: literature review, current status and prospects. Minerva Stomatol Jul- Aug;56(7-8): Zitzmann NU, Schärer P. Sinus elevation procedures in the resorbed posterior maxilla. Comparison of the crestal and lateral approaches. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral RadiolEndod Jan;85(1): Summers RB. A new concept in maxillary implant surgery: the osteotome technique. Compendium Feb;15(2): Browaeys H, Bouvry P, De Bruyn H. A literature review on biomaterials in sinus augmentation procedures. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2007;9(3): Handschel J, Simonowska M, Naujoks C, Depprich RA, Ommerborn MA, Meyer U, et al. A histomorphometric meta-analysis of sinus elevation with various grafting materials. Head Face Med Jun11;5: Del Fabbro M, Testori T, Francetti L, Weinstein R. Systematic review of survival rates for implants placed in the grafted maxillary sinus. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent Dec;24(6): Atsumi M, Park SH, Wang HL. Methods used to assess implant stability: current status. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants Sep- Oct;22(5): Cehreli MC, Karasoy D, Akca K, Eckert SE. Meta-analysis of methods used to assess implant stability. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants Nov-Dec;24(6): Huang HM, Pan LC, Lee SY, Chiu CL, Fan KH, Ho KN. Assessing the implant/bone interface by using natural frequency analysis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral RadiolEndod Sep;90(3): Huang HM, Chiu CL, Yeh CY, Lin CT, Lin LH, Lee SY. Early detection of implant healing process using resonance frequency analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res Aug;14(4): Ersanli S, Karabuda C, Beck F, Leblebicioglu B. Resonance frequency analysis of one-stage dental implant stability during the osseointegration period. J Periodontol Jul;76(7): Kokovic V, Jung R, Feloutzis A, Todorovic VS, Jurisic M, Hämmerle CH. Immediate vs. early loading of SLA implants in the posterior mandible: 5-year results of randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res Feb;25(2):e Bornstein MM, Hart CN, Halbritter SA, Morton D, Buser D. Early loading of nonsubmerged titanium implants with a chemically modified sand-blasted and acid-etched surface: 6-month results of a prospective case series study in the posterior mandible focusing on peri-implant crestal bone changes and implant stability quotient (ISQ) values. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res Dec;11(4): Degidi M, Daprile G, Piattelli A, Carinci F. Evaluation of factors influencing resonance frequency analysis values, at insertion surgery, of implants placed in sinus-augmented and nongrafted sites. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res Sep;9(3): Rasmusson L, Thor A, Sennerby L. Stability evaluation of implants integrated in grafted and nongrafted maxillary bone: a clinical study from implant placement to abutment connection. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res Mar;14(1): Browaeys H, Bouvry P, De Bruyn H. A literature review on biomaterials in sinus augmentation procedures.clin Implant Dent Relat Res Sep;9(3):
8 32 Jelušić i sur. Stabilnost implantata nakon podizanja dna sinusa 20. Suba Z, Takács D, Matusovits D, Barabás J, Fazekas A, Szabó G. Maxillary sinus floor grafting with beta-tricalcium phosphate in humans: density and microarchitecture of the newly formed bone. Clin Oral Implants Res Feb;17(1): Zijderveld SA, Zerbo IR, van den Bergh JP, Schulten EA, ten Bruggenkate CM. Maxillary sinus floor augmentation using a beta-tricalcium phosphate (Cerasorb) alone compared to autogenous bone grafts. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants May- Jun;20(3): Kurkcu M, Benlidayi ME, Cam B, Sertdemir Y. Anorganic bovinederived hydroxyapatite vs β-tricalcium phosphate in sinus augmentation: a comparative histomorphometric study. J Oral Implantol Sep;38 Spec No: Degidi M, Daprile G, Piattelli A. RFA values of implants placed in sinus grafted and nongrafted sites after 6 and 12 months. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res Sep;11(3): Di Lallo S, Ricci L, Orecchioni S, Piattelli A, Iezzi G, Perrotti V. Resonance Frequency Analysis Assessment of Implants Placed with a Simultaneous or a Delayed Approach in Grafted and Nongrafted Sinus Sites: A 12-Month Clinical Study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res Sep 11. [Epub ahead of print] 25. Tuna T, Yorgidis M, Strub JR. Prognosis of implants and fixed restorations after lateral sinus elevation: a literature review. J Oral Rehabil Mar;39(3):
Scientific & Clinical Evidence Jason membrane
 Scientific & Clinical Evidence Jason membrane Pericardium GBR/GTR Membrane Facts - CE since 2009 - so far no serious clinical complication or objection - approx. 250.000 successful clinical treatments
Scientific & Clinical Evidence Jason membrane Pericardium GBR/GTR Membrane Facts - CE since 2009 - so far no serious clinical complication or objection - approx. 250.000 successful clinical treatments
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
TOPICS. T O P I C S Day 1. Implant Locations. Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla. Anatomy and risk factors Option 1: Short implants
 T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
Mjerenje stabilnosti implantata nakon podizanja dna sinusa: kliničko pilot istraživanje
 228 ACTA STOMATOLOGICA CROATICA Acta stomatol Croat. 2015;49(3):228-233. DOI: 10.15644/asc49/3/5 PRETHODNO PRIOPĆENJE PRELIMINARY COMMUNICATION Muhamed Ajanović, Alma Kamber-Ćesir, Adis Hamzić, Selma Tosum
228 ACTA STOMATOLOGICA CROATICA Acta stomatol Croat. 2015;49(3):228-233. DOI: 10.15644/asc49/3/5 PRETHODNO PRIOPĆENJE PRELIMINARY COMMUNICATION Muhamed Ajanović, Alma Kamber-Ćesir, Adis Hamzić, Selma Tosum
Annals of Dental Research
 P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3.
 DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
Osstell ISQ. The objective way to measure implant stability.
 Osstell ISQ. The objective way to measure implant stability. www.osstell.com Three reasons why you need Osstell ISQ. Dr Tiziano Testori, Private Practice, Como, Italy: I use the Osstell meter as a quality-assurance
Osstell ISQ. The objective way to measure implant stability. www.osstell.com Three reasons why you need Osstell ISQ. Dr Tiziano Testori, Private Practice, Como, Italy: I use the Osstell meter as a quality-assurance
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years
 Original Article Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years AR. Rokn 1,2, AAR. Rasouli Ghahroudi 3,4, S. Hemati 5, A. Soolari 6 1 Associate
Original Article Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years AR. Rokn 1,2, AAR. Rasouli Ghahroudi 3,4, S. Hemati 5, A. Soolari 6 1 Associate
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re. Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T
 Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs
 Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS. Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel GTO I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E
 GTO THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel R E G E N E R A T I O N S C I E N C E I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E A unique biotechnology
GTO THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel R E G E N E R A T I O N S C I E N C E I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E A unique biotechnology
10 Years of XiVE Implantology Unlimited
 10 Years of XiVE Implantology Unlimited Implantology Unlimited is obligate for XiVE and every limit gives always a push to surrender new challenges: Primary stability in low bone quality? No problem with
10 Years of XiVE Implantology Unlimited Implantology Unlimited is obligate for XiVE and every limit gives always a push to surrender new challenges: Primary stability in low bone quality? No problem with
More than bone regeneration. A total solution.
 More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery
 An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery Huda Moutaz Asmael, B.D.S. (1) Thair Abdul Lateef, B.D.S., H.D.D., F.I.B.M.S. (2) ABSTRACT
An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery Huda Moutaz Asmael, B.D.S. (1) Thair Abdul Lateef, B.D.S., H.D.D., F.I.B.M.S. (2) ABSTRACT
In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla,
 Staged Sinus Floor Elevation Using the Crestal Core Elevation (CCE) Procedure: A Review of the Technique Michael, DDS Abstract In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla, trephined cores measuring
Staged Sinus Floor Elevation Using the Crestal Core Elevation (CCE) Procedure: A Review of the Technique Michael, DDS Abstract In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla, trephined cores measuring
Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material- A case Report
 A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
Long-term results of new deproteinized bovine bone material in a maxillary sinus graft procedure
 Long-term results of new deproteinized bovine bone material in a maxillary sinus graft procedure pissn 2093-2278 eissn 2093-2286 Seung-Yun Shin 1, You-Jeong Hwang 2, Jung-Hoon Kim 3,4, Yang-Jo Seol 3,
Long-term results of new deproteinized bovine bone material in a maxillary sinus graft procedure pissn 2093-2278 eissn 2093-2286 Seung-Yun Shin 1, You-Jeong Hwang 2, Jung-Hoon Kim 3,4, Yang-Jo Seol 3,
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation
 Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation Abstract Objective The aim of this article was to investigate postoperative swelling of the maxillary
Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation Abstract Objective The aim of this article was to investigate postoperative swelling of the maxillary
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Comparison of Lateral Window and Osteotome Techniques in Sinus Augmentation: Histological and Histomorphometric Evaluation
 Original Article Comparison of Lateral Window and Osteotome Techniques in Sinus Augmentation: Histological and Histomorphometric Evaluation N. Esfahanizadeh 1, A. R. Rokn 2, M. Paknejad 3, P. Motahari
Original Article Comparison of Lateral Window and Osteotome Techniques in Sinus Augmentation: Histological and Histomorphometric Evaluation N. Esfahanizadeh 1, A. R. Rokn 2, M. Paknejad 3, P. Motahari
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft
 The Atrophic crest Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft Dr. Paolo Borelli DDS, Italy Dr. Massimiliano Favetti DDS, Italy
The Atrophic crest Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft Dr. Paolo Borelli DDS, Italy Dr. Massimiliano Favetti DDS, Italy
A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation. Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics
 A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics Boyne, 1980 Maxillary Sinus Augmentations Maxillary sinus augmentation,
A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics Boyne, 1980 Maxillary Sinus Augmentations Maxillary sinus augmentation,
Clinical cases by Dr. Fernando Rojas-Vizcaya. botiss. dental bone & tissue regeneration. biomaterials. strictly biologic
 Clinical cases by Dr. Fernando Rojas-Vizcaya dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials strictly biologic botiss BTR system: BONE biologic potential bovine block & granules: pure bone mineral
Clinical cases by Dr. Fernando Rojas-Vizcaya dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials strictly biologic botiss BTR system: BONE biologic potential bovine block & granules: pure bone mineral
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PLACEMENT OF DENTAL IMPANT IN POSTERIOR MAXILLARY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRAFT: A CASE REPORT
 CSE REPORT PLCEMENT OF DENTL IMPNT IN POSTERIOR MXILLRY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRFT: CSE REPORT S.P.S Sooch 1, Puja 2, Seema ggarwal 3 (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 (p) ISSN Print:
CSE REPORT PLCEMENT OF DENTL IMPNT IN POSTERIOR MXILLRY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRFT: CSE REPORT S.P.S Sooch 1, Puja 2, Seema ggarwal 3 (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 (p) ISSN Print:
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants
 Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants Ofer Mardinger, DMD, BMedSc, a Gavriel Chaushu, DMD, MSc, b Sheli Sigalov, DMD, c Ran Herzberg, DMD, d Binyamin Shlomi,
Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants Ofer Mardinger, DMD, BMedSc, a Gavriel Chaushu, DMD, MSc, b Sheli Sigalov, DMD, c Ran Herzberg, DMD, d Binyamin Shlomi,
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Bone augmentation with biomaterials
 Patient information dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials Bone augmentation with biomaterials established safe natural X100 Implantation stability is crucial for success Atrophy of the
Patient information dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials Bone augmentation with biomaterials established safe natural X100 Implantation stability is crucial for success Atrophy of the
BioVin Collagen Membrane
 BioVin Collagen Membrane Resorbable cross-linked collagen membrane BioVin Bovine Bone Bovine Bone Substitute OToss Synthetic Bone Synthetic Resorbable Biphasic Calcium Phosphate OToss Synthetic Bone Inject
BioVin Collagen Membrane Resorbable cross-linked collagen membrane BioVin Bovine Bone Bovine Bone Substitute OToss Synthetic Bone Synthetic Resorbable Biphasic Calcium Phosphate OToss Synthetic Bone Inject
2: Canullo L, Tallarico M, Penarrocha D, Meloni SM, Penarrocha M. Abstracts. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2016;9 Suppl 1:9-54. PubMed PMID:
 1: Tallarico M, Xhanari E, Pisano M, De Riu G, Tullio A, Meloni SM. Single post-extractive ultra-wide 7 mm-diameter implants versus implants placed in molar healed sites after socket preservation for molar
1: Tallarico M, Xhanari E, Pisano M, De Riu G, Tullio A, Meloni SM. Single post-extractive ultra-wide 7 mm-diameter implants versus implants placed in molar healed sites after socket preservation for molar
Use of ß-tricalcium phosphate for alveolar preservation; a report on a series of cases.
 Use of ß-tricalcium phosphate for alveolar preservation; a report on a series of cases. Authors: Medina Ramírez Jorge Michel*, Gabriela Vilar Pineda**, René García Contreras***. Corresponding author: Gabriela
Use of ß-tricalcium phosphate for alveolar preservation; a report on a series of cases. Authors: Medina Ramírez Jorge Michel*, Gabriela Vilar Pineda**, René García Contreras***. Corresponding author: Gabriela
Secondary Objectives of Implant Therapy
 T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla
 IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
Cerasorb M DENTAL. O:\Zulassung\Cerasorb Dental Kanada 2013\Texte\Cerasorb M Dental final IFU docx
 Cerasorb M DENTAL Resorbable, pure-phase beta-tricalcium phosphate matrix with interconnecting porosity for bone regeneration for use in dental and maxillofacial surgery DESCRIPTION: Cerasorb M DENTAL
Cerasorb M DENTAL Resorbable, pure-phase beta-tricalcium phosphate matrix with interconnecting porosity for bone regeneration for use in dental and maxillofacial surgery DESCRIPTION: Cerasorb M DENTAL
Posterior mandible and vertical augmentation
 CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
Sinus Floor Augmentation with ß-Tricalcium Phosphate (R.T.R. Septodont)
 Sinus Floor Augmentation with ß-Tricalcium Phosphate (R.T.R. Septodont) Mario Ernesto García-Briseño DDS and Professor in Periodontics - Autonomous University of Guadalajara (UAG), Mexico Resorption of
Sinus Floor Augmentation with ß-Tricalcium Phosphate (R.T.R. Septodont) Mario Ernesto García-Briseño DDS and Professor in Periodontics - Autonomous University of Guadalajara (UAG), Mexico Resorption of
Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane
 10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1077 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane BC Deepthi, Shilpa Shetty, CL Satish Babu, P Rohit, DM Mallikarjuna,
10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1077 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane BC Deepthi, Shilpa Shetty, CL Satish Babu, P Rohit, DM Mallikarjuna,
Immediate loading in heavy smokers
 case report Immediate loading in heavy smokers Dr Dr Branislav Fatori & Dr Inge Schmitz, Germany Today, numerous implant systems and many modifications thereof are available on the market, and it may be
case report Immediate loading in heavy smokers Dr Dr Branislav Fatori & Dr Inge Schmitz, Germany Today, numerous implant systems and many modifications thereof are available on the market, and it may be
Zurich Open Repository and Archive. Sinus floor elevation using an osteotome technique without grafting materials or membranes
 University of Zurich Zurich Open Repository and Archive Winterthurerstr. 190 CH-8057 Zurich http://www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2008 Sinus floor elevation using an osteotome technique without grafting materials
University of Zurich Zurich Open Repository and Archive Winterthurerstr. 190 CH-8057 Zurich http://www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2008 Sinus floor elevation using an osteotome technique without grafting materials
More than pure esthetics. The natural and strong solution.
 More than pure esthetics. The natural and strong solution. Expand your patient pool with an innovative solution. With the Straumann PURE Ceramic Implant, clinicians have an additional option to convince
More than pure esthetics. The natural and strong solution. Expand your patient pool with an innovative solution. With the Straumann PURE Ceramic Implant, clinicians have an additional option to convince
T he lateral window approach
 496 PUTTY ALLOPLASTIC BONE SUBSTITUTE FOR INCREASED PRIMARY IMPLANT STABILITY KHER ET AL Implants Placed Simultaneously With Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Using a Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute
496 PUTTY ALLOPLASTIC BONE SUBSTITUTE FOR INCREASED PRIMARY IMPLANT STABILITY KHER ET AL Implants Placed Simultaneously With Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Using a Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute
Innovative Range of Regenerative Solutions
 TM Innovative Range of Regenerative Solutions MIS Implant Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved. Optimal volumes and quality of hard and soft tissue are required to satisfy the goals of oral rehabilitation
TM Innovative Range of Regenerative Solutions MIS Implant Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved. Optimal volumes and quality of hard and soft tissue are required to satisfy the goals of oral rehabilitation
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift
 Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Journal of Craniomaxillofacial Research. Vol. 3, No. 4 Autumn 2016
 Journal of Craniomaxillofacial Research Vol. 3, No. 4 Autumn 2016 Primary stability of implants inserted following sinus lift and bone graft in the posterior of the maxilla Mehdi Sezavar 1, Mohammad Reza
Journal of Craniomaxillofacial Research Vol. 3, No. 4 Autumn 2016 Primary stability of implants inserted following sinus lift and bone graft in the posterior of the maxilla Mehdi Sezavar 1, Mohammad Reza
complications (Zitzmann and Schaerer,
 Inadequate height and width of alveolar process is considered as the most common limiting factor for implant placement in maxillary alveolar process. Subsequent to tooth extraction, the decrease of occlusal
Inadequate height and width of alveolar process is considered as the most common limiting factor for implant placement in maxillary alveolar process. Subsequent to tooth extraction, the decrease of occlusal
A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS
 A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS INDICATIONS: 1/ SOCKET AND RIDGE PRESERVATION 2/ FILLING OF EXTRACTION SOCKETS Biomaterials offers portfolio of regenerative materials for implantology, aimed at
A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS INDICATIONS: 1/ SOCKET AND RIDGE PRESERVATION 2/ FILLING OF EXTRACTION SOCKETS Biomaterials offers portfolio of regenerative materials for implantology, aimed at
A New Technique for Minimally Invasive Maxillary Lateral Sinus Augmentation: a Case Report
 A New Technique for Minimally Invasive Maxillary Lateral Sinus Augmentation: a Case Report Xiu Lian HU 1, Xian ZHOU 1, Jian Hui LI 1, Ye LIN 1 Numerous techniques are described for lateral sinus augmentation,
A New Technique for Minimally Invasive Maxillary Lateral Sinus Augmentation: a Case Report Xiu Lian HU 1, Xian ZHOU 1, Jian Hui LI 1, Ye LIN 1 Numerous techniques are described for lateral sinus augmentation,
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus.
 Interventions for replacing missing teeth: augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus. Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Rees J, Karasoulos D, Felice P, Alissa R, Worthington HV, Coulthard P. Cochrane Database
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus. Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Rees J, Karasoulos D, Felice P, Alissa R, Worthington HV, Coulthard P. Cochrane Database
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
ß-tricalcium phosphate used with onlay graft for horizontal bone augmentation yielded preferable result: a case report
 ß-tricalcium phosphate used with onlay graft for horizontal bone augmentation yielded preferable result: a case report Yaqian Chen, Qingqing Wu, Yi Man State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, West China
ß-tricalcium phosphate used with onlay graft for horizontal bone augmentation yielded preferable result: a case report Yaqian Chen, Qingqing Wu, Yi Man State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, West China
INTRODUCTION. General Information. Important Warning
 S u r g i c a l M a n u a l F o r M a g i x D e n t a l I m p l a n t INTRODUCTION General Information Read this manual carefully before starting treatment. This manual should be used as a reference guide
S u r g i c a l M a n u a l F o r M a g i x D e n t a l I m p l a n t INTRODUCTION General Information Read this manual carefully before starting treatment. This manual should be used as a reference guide
Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
Alveolar Ridge Preservation:
 Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Bone Regeneration in a Bilateral Sinus Lift
 2 A comparative pilot case study between irradiated human cancellous bone and a synthetic analogue Bone Regeneration in a Bilateral Sinus Lift Anthony McGee, BDS, Staines, and Dr J. A. Hunt, Liverpool/England
2 A comparative pilot case study between irradiated human cancellous bone and a synthetic analogue Bone Regeneration in a Bilateral Sinus Lift Anthony McGee, BDS, Staines, and Dr J. A. Hunt, Liverpool/England
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Case reports by Dr. Roland Török IMPLANT INSTITUTE TÖRÖK. botiss. dental bone & tissue regeneration. biomaterials.
 Case reports by Dr. Roland Török dental bone & tissue regeneration Dr. Med. STOM. roland török IMPLANT INSTITUTE TÖRÖK botiss biomaterials strictly biologic botiss BTR system: BONE bovine block & granules:
Case reports by Dr. Roland Török dental bone & tissue regeneration Dr. Med. STOM. roland török IMPLANT INSTITUTE TÖRÖK botiss biomaterials strictly biologic botiss BTR system: BONE bovine block & granules:
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94
 ( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
T he cortical bone of the maxillary
 KIM ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 26, NUMBER 3 2017 351 Sinus Membrane Elevation by the Crestal Approach Using a Novel Drilling System Young-Kyun Kim, DDS, PhD,* Ji-Young Lee, DDS, Jin-Woo Park, DDS,
KIM ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 26, NUMBER 3 2017 351 Sinus Membrane Elevation by the Crestal Approach Using a Novel Drilling System Young-Kyun Kim, DDS, PhD,* Ji-Young Lee, DDS, Jin-Woo Park, DDS,
Sinus elevation with short implant
 Sinus elevation with short implant Authors: Prof. Dr Mauro Marincola, Prof. Dr Dr Rolf Ewers, Prof. Giorgio Lombardo (University of Verona) & Prof. Miguel Simancas Pallares (University of Cartagena), Austria/Italy/Colombia
Sinus elevation with short implant Authors: Prof. Dr Mauro Marincola, Prof. Dr Dr Rolf Ewers, Prof. Giorgio Lombardo (University of Verona) & Prof. Miguel Simancas Pallares (University of Cartagena), Austria/Italy/Colombia
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Product Catalog. Dental Bone & Tissue Regeneration
 Product Catalog Dental Bone & Tissue Regeneration Bone graft regeneration Guided bone substitutes regeneration Osteogenesis Controlled resorption rate Angiogenesis Long term volume stability Remodeling
Product Catalog Dental Bone & Tissue Regeneration Bone graft regeneration Guided bone substitutes regeneration Osteogenesis Controlled resorption rate Angiogenesis Long term volume stability Remodeling
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
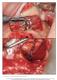 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
Simeonov, A. et al.: Determination of influence and differences in... Sport Science 10 (2017) Suppl 1:
 DETERMINATION OF INFLUENCE AND DIFFERENCES IN SPECIFIC PROFESSIONAL SAMPLE OF EXAMINEES Aleksandar Simeonov¹, Zoran Radić¹ and Ratko Pavlović² ¹Faculty of Physical Education, Sport and Health, University
DETERMINATION OF INFLUENCE AND DIFFERENCES IN SPECIFIC PROFESSIONAL SAMPLE OF EXAMINEES Aleksandar Simeonov¹, Zoran Radić¹ and Ratko Pavlović² ¹Faculty of Physical Education, Sport and Health, University
The Essential Choice. With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability
 The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study
 26 News No.26 January 2011 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study Make it Simple 2 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone
26 News No.26 January 2011 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study Make it Simple 2 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone
Procedure Manual and Catalog
 Procedure Manual and Catalog TM Why SynthoGraft? SynthoGraft offers a unique structure which provides stability, while its micro-porosity allows for rapid vascularization and subsequent resorption. Although
Procedure Manual and Catalog TM Why SynthoGraft? SynthoGraft offers a unique structure which provides stability, while its micro-porosity allows for rapid vascularization and subsequent resorption. Although
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits. Your combination for success
 Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION
 original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
The Essential Choice. With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability
 The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Crestal Window Sinus Lift, minimally invasive, predictable, and systematic approach to sinus grafting.
 Crestal Window Sinus Lift, minimally invasive, predictable, and systematic approach to sinus grafting. Samuel Lee, DDS*, Grace Kang-Lee, DDS, Kwang-Bum Park, DDS, MS, PhD, Thomas Han, DDS, MS Abstract
Crestal Window Sinus Lift, minimally invasive, predictable, and systematic approach to sinus grafting. Samuel Lee, DDS*, Grace Kang-Lee, DDS, Kwang-Bum Park, DDS, MS, PhD, Thomas Han, DDS, MS Abstract
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System
 Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
FOR INTERNAL REFERNCE ONLY
 TX to EV Transition Possibilities and Challenges TX to EV Transition Why? ASTRA TECH Implant System BioManagement Complex OsseoSpeed - more bone, more rapidly MicroThread - biomechanical bone stimulation
TX to EV Transition Possibilities and Challenges TX to EV Transition Why? ASTRA TECH Implant System BioManagement Complex OsseoSpeed - more bone, more rapidly MicroThread - biomechanical bone stimulation
Clinical Perspectives
 Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Implant survival, bone remodeling and implant stability of Neoss implants: a systematic review of the literature
 Letters on Implant Dentistry 2017; 1: 1520 SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Sahlin Implant survival, bone remodeling and implant stability of Neoss implants: a systematic review of the literature Herman Sahlin 1 1 Neoss
Letters on Implant Dentistry 2017; 1: 1520 SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Sahlin Implant survival, bone remodeling and implant stability of Neoss implants: a systematic review of the literature Herman Sahlin 1 1 Neoss
Immediate Implant Placement Along With Guided Bone Regeneration In Mandibular Anterior Region A Case Report.
 IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE
 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Specialized Modules: List of individual modules Specialized Module 1 Basic principles of implantology
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Specialized Modules: List of individual modules Specialized Module 1 Basic principles of implantology
Horizontal bone augmentation by means of guided bone regeneration
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 13 40 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Horizontal bone augmentation by means
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 13 40 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Horizontal bone augmentation by means
Four-years experience with dynamic implants with internal port for minimally invasive sinus elevation
 ORAL SURGERY Oded Nahlieli Four-years experience with dynamic implants with internal port for minimally invasive sinus elevation Oded Nahlieli, DMD 1 /Ami Zagury, DMD 2 /Eli Michaeli, DMD 3 /Noam Bruck,
ORAL SURGERY Oded Nahlieli Four-years experience with dynamic implants with internal port for minimally invasive sinus elevation Oded Nahlieli, DMD 1 /Ami Zagury, DMD 2 /Eli Michaeli, DMD 3 /Noam Bruck,
Benefits of CBCT in Implant Planning
 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up
 Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
