Use of cervicopectoral flap as an access for radical neck dissection and reconstruction of facial defects
|
|
|
- Jerome Owens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Use of cervicopectoral flap as an access for radical neck dissection and reconstruction of facial defects Balsam S. abdulhamed, B.D.S., F.I.C.M.S., H.D.L. (1) Bassem T. Merry, B.D.S. (2) ABSTRACT Background: The problem of reconstruction after surgical extirpation of head and neck cancer remain a corner stone that produce unique challenges to surgeon; surface defects are often contiguous with oral cavity requiring both lining and covering. Patients and methods: This study was conducted on 20 patients (13 :7 ), age rang (28-80years), whom suffered from malignant tumors in different sits in oro-facial region and salivary gland, to evaluate the C.P.F. as an access for cervical lymphadenectomy during treatment of head/neck malignant tumor and its use as immediate reconstruction for closing the defect resulted from tumor resection at the same procedure. Results and Conclusions: The C.P.F. was successfully covered the moderate and large size defect resulted from tumor ablation in the neck region with successful esthetic and function results. Keywords: Cervicopectoral flap, radical neck dissection, head and neck malignant tumor. (J Bagh Coll Dentistry 2012; 24(4):71-76). INTRODUCTION The problem of reconstruction after surgical extirpation of head and neck cancer produces unique challenges to surgeon; surface defects are often contiguous with oral cavity requiring both lining and covering. Neck dissection remain a corner stone with the surgical management of metastatic disease within the neck, many incisions have been described for neck dissection since Criles Land mark article in The facts that so many types of neck incision exist is strong testimony that there is hardly one incision that fits all contingencies. A modified single type for dissecting which had been described by Lakdasa (1) is a further step in the evolution of previously described single flap for neck dissection. The cervicopectoral flap (C.P.F.) is an axial rotation flap usually medially based, fed by the anterior thoracic perforators from the internal mammary artery, although a variant is a laterally based flap fed by the thoracoacromial perforators. It is considered a good method for covering large defects of the lower cheek below a line connecting the commissure of the mouth with the tragus of the ear.this study was conducted to evaluate the cervicopectoral flap as an access for cervical lymphadenectomy during treatment of oro-facial and salivary gland malignant tumor and its use in the immediate reconstructive procedure for closing the defect resulted from tumor resection at the same procedure. PATIENT AND METHODS The different types of carcinoma involved the facial skin, parotid gland and lymph node tumor completely excised through local resection with radical neck dissection (classical or extended) by Lakdasa incision through the neck extending to the sub-mammary area for designing of the cervicopectoral flap for construction of the primary defect. This study was carried out on 20 patients with primary malignant tumor of the cheek, parotid gland, lower jaw and variable sub-sites of the oral cavity with squamous cell carcinoma and sarcoma, regional lymph nodes metastasis were evaluated clinically, radiographically and histopathologically. Figure 2: Patient with S.C.C. (1)Maxillofacial Figure 3: Patient specialist. Al-Kadhmyea with S.C.C. Teaching Hospital. (2)Maxillofacial practitioner. Al-Kadhmyea Teaching Hospital. Figure 1: C.T. Scan reveals the tumor site. Treatment plan was adjusted according to these values and patient general Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Periodontology 71
2 The patients sample composed of (13 males: 7 females) with age range (28-80 years). All were examined and treated in the department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery in Gaze Al-Harrery, Al-Hussien (in Kerbala), Al-Sader (in Al Najaf) and Al-kadhmyea Teaching Hospitals in the period Every patient was checked for medical evaluation including systemic disease, also for the purpose of this study, personal information sheet were recorded in specially designed sheet. A Single cervicopectoral flap which had been used for the cases, had been modified that transverse limb run backward from sub-mental region at about (1-2 inches) below the mandible, as the area either involved by the lesion (primary tumor ulcerative fixed lymph nodes or both) or affected by radiotherapy. The transverse limb extends to the posterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. At the tip of the mastoid process or slightly above it, the incision curves gently downward keeping about 2 cm behind the anterior margin of trapezius muscle. This vertical limb extends downward to involve the deltopectoral flap medially based on the second and third branches of internal mammary artery. The dissection is done under the platisma muscle and pectoral fascia as shown in Figure 3 and 4. Figure 5: Cervicopectoral flap design RESULTS Twenty patients were collected in this prospective study, evaluated clinically, radiographically and underwent surgery with Figure 5: Dissection beneath the platisma and pectoral fascia reconstruction procedure. This data collected in , and the results were evaluated according to the following: Table 1: Age and Sex Distribution No Age Range % Age Range % Total Age Range % % 100% Table 2: TNM Classification T 4 X N b 2b 2a 1a 0 2a 1a 2a 2a 2a 1 2a 1a 2a 2a 2b 2b M % 5% 5% Mucoepidermoid carcinoma Rhabdomycosarcoma Figure 6: Hitopathological Diagnosis Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Periodontology 72
3 Table 3: Site of Tumor Primary site No. % Cheek 7 35% Parotid 3 15% Lower jaw 6 30% Unknown primary tumor 1 5% Skin of zygomatic region 1 5% Floor of mouth extended to cheek 2 10% 25% 75% Donor site closed by direct suturing (15 cases) Donor site closed by direct suturing with skin graft (5 cases) Figure 8: Morbidity of donor site Figure 8: Donor site closed by direct suturing 30% 70% No Pre-operative radiotherapy (14 cases) Pre-operative radiotherapy (6 cases) Figure 10: Donor site closed by skin graft DISCUSSION Successful reconstructive surgery is measured in terms of safe defect coverage with simultaneous restoration of form and function and avoidance of donor site deformity. To achieve the optimal result the surgeon must complete three important reconstructive phases: 1. Defect analysis with subsequent definition of reconstructive requirements. Figure 10: Viability of the flap in related to preoperative use of radiotherapy 2. Evaluation of potential sources of flap in regard to suitability for defect coverage or reconstruction. 3. Utilization of anatomic and technical data to reconstruct the defect successfully. The policy of the department is that the surgical treatment of the malignant tumor should be an aggressive procedure. Among the current therapeutic modalities of surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy and others, surgery with wide resection seems to offer the best chance of a cure. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Periodontology 73
4 Classical radical neck dissection remains the corner stone in the surgical management of metastatic tumor in the neck and many incisions have been described when Criles first introduced radical neck dissection. In attempting to reconstruct the types of defect presented in the study, three principles guide the surgeon, they are: 1. Restriction to sound oncologic principles of resection. 2. Preservation of function. 3. Attention to aesthetic to its best permitted limit. The cervicopectoral flap permits adherence to these principles. The C.P.F. has a robust nature due to its rich blood supply. The skin of the neck is supplied by the branches of five arteries, superiorly by the sternocleidomastoid branch of the occipital, cuteneous branch of facial, cuteneous branch of submental artery, inferiorly by the cutaneous branches of transverse cervical and by the suprascapular arteries. The skin of the anterior chest wall is supplied primarily by perforating branches of the internal mammary artery. Study of the design of the C.P.F. showed that all of above mentioned cervical vessels were in the ipsilateral side are divided in the elevation of the flap, so the excellent viability of the flap is insured by two sources, the rich anastomosis of cuteneous vessels across the midline in the cervical skin, and preservation of internal mammary branches especial the widely based pedicle of the flap. The flap then is essentially a mixed-axial and random-patterned flap. The distal part is considered as a musclocuteneous flap which contains platisma muscle with the skin covering it and nourishment of this part is randomly by collateral circulation of blood from other side of the neck. The proximal portion of the flap is considered as fasciocuteneous flap, as the deep fascia involved with the flap which is highly vascular by internal mammary perforator arteries. The C.P.F. is analogous to the family of the deltopectoral flap of Bakamjian (16). There is no controversy on the blood supply of the C.P.F. in all literature review. Although radiotherapy may be used as sole modality, it is frequently used in combination with surgery and/or chemotherapy. Radiotherapy was advocated in cases of large tumors in an attempt to shrink it prior to surgery, and sterilize of majority of viable malignant cells, so that the risk of tumor cells dissemination during surgery should be reduced. The effects of radiation divided to immediate, intermediate and late reaction (3): in our patient with tumors of the face and oral cavity, who received preoperative radiotherapy, followed (4 weeks later) by surgical intervention including malignant tumor excision with or without RND and reconstruction of primary defect by C.P.F. In those six cases the dissection and removal of the tumor was not very much affected and the healing of the C.P.F. used for the reconstruction, showed no necrosis, delay of healing, or even infection. The result does not coincident with that of Becker (4) and Wallis and Donald (2), who found that there was simple necrosis of the tip of the flap and left to be healed by secondary intention. Two cases (about 80 years) were presented with lump in the submandibular area with skin tethering of unknown primary tumor site, surgery was done and C.P.F. utilized for reconstruction of the primary defect, simple epidermolysis and dehiscence of the flap tip which was treated by local measurement and left for secondary intention. It is believed that the necrosis in the tip of the flap in these patients was due to general vascular condition of the patient. This finding is agreed with Math and Nahai (5) regarding aging process including the changes in vascular system. Smoking cigarette also affects the viability of the flap. It acts on blood supply by stimulation of sympathetic ganglia and adrenal medulla by nicotine, causes vasoconstriction of the blood vessels (6), decreasing oxygen carrying capacity (7), endothelial changes of the blood vessels wall (8), increase in the platelets adhesion (9),and affects blood vessels diameter and erythrocyte velocity (10). This effect presented in case no. 4, 53 years old male, presented with squamous cell carcinoma of lower jaw and buccal mucosa tethering to the skin, patient was heavy smoker (about 30 cigarette / day), when underwent surgery for excision of primary tumor enblock with RND and mobilized C.P.F. for external coverage, after 3 days the flap appeared congested and began to show marginal necrosis which was treated by local debridement and left to heal by secondary intention. This is in agreement with Becker (4) and Wallis and Donald (2). Also there are another four patients who smoked cigarette and have simple necrosis of the skin graft and marginal necrosis of the flap in others. Flap design determined initially by recipient sit requirements and secondary by donor site states. Reconstruction of soft tissue of facial defects should provides a good color match, texture and hair bearing characteristics, adequately restore Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Periodontology 74
5 facial contour, place scar in a favorable location and ideally accomplish these goals in single stage with minimal donor site morbidity. The cervicopectoral rotational-advancement flap is reliable to achieve these goals for the reconstruction of facial defects, as it composed from part of remnant of facial skin, cervical, neck and pectoral skin. The flap require rotation or advancement of lower facial preauricular loose skin, which becomes more abundant with aging, also the neck is another useful region outside the face, neck skin is plentiful, has good color and texture, and easy to move, this fact was also identified by Wallis and Donald (2) by the use of C.P.F. in reconstruction of facial defects. The forehead flap, time honored in external reconstruction of the face, has occasionally adapted for intra-oral, facial and cheek lining replacements (11-13), and advocated for use as soft tissue covering the primary mandibular bone graft (14). This most useful flap however has certain disadvantages which are not present in the C.P.F. The laterally based deltopectoral flap was introduced by Conley (15), for the resurfacing of the defect of the head and neck, but it was used as a skin flap only. Its advantages were that it furnished a large surface area and it may be elevated without a previous delay. Its disadvantages were that it must have a wide base at the shoulder, and it was too short to travel any region higher than the neck. The medially based deltopectoral flap which developed by Bakamjian (16), is used for reconstruction of defect in the head and neck region below the orbit, zygomatic region, and for ensuring of viability of the elevated flap, it needs delaying procedure of 10 days 2 weeks, then 3 weeks for pedicle transfer, so this flap for complete transfer to area which needs reconstruction requires about 2 months to complete the treatment, and the area of donor sites requires skin grafting to close it. Another disadvantage of deltopectoral flap is long hospitalization of the patient with multiple operations, and uncomfortable position of the patient during pedicle transfer, as specific position of the neck for holding the pedicle to avoid tension and/or kinking of the pedicle to prevent trauma to the nutrient vessels of the flap. The C.P.F. is easy to manipulated, gave good esthetic results in reconstruction of facial defects, required short time hospitalization and no need for multiple operations to transfer, mobilized of the skin from adjacent area to the face which is already exposed to outer environments as sun light and change in color that in face, and same characteristic of the hair growth like in face. Also the C.P.F. similar in thickness and no need for debulking like in deltopectoral flap which needs debulking in many instances in separate procedure to recounting with facial layer. The design of the flap in this study shares the neck incision of Lakdasa (1) for neck dissection, which it provides excellent view for cervical content and wide surgical field exposure. The view involves the entire cervical area extending from mandible superiorly to the clavicle inferiorly and from cervical midline medially to the trapezius muscle laterally. It is easy to reach and deal with the cervical contents without needs for excessive traction and unnecessary trauma that may caused accordingly. Also the advantages of using this design of neck incision for an access to the neck dissection for patient received radiotherapy before surgery, as the incision line does not very much affected by the radiotherapy. The horizontal limb of the incision done 2 cm below the mandible extended posteriorly reaching the mastoid tip, this gives good access to the submandibular area and extends 2 cm posterior to the anterior border of trapezius muscle vertically downward reaching the acroamioclavicular joint area, so horizontal incision provides excellent approach for mandibular resection if needed and also excision of intraoral tumor. The vertical limb will heal without contraction and webbing of the neck for location of incision line on the trapezius muscle and away from the underlying vital structures. After excision of the primary tumor enblock with radical neck dissection, the vertical limb is extended over the anterior chest wall to involve the third or fourth intercostals space terminating at 2 cm laterally to the sternum to preserve the blood supply of the flap for mobilization of C.P.F. This finding is in agreement with opinion of Wallis and Donald (2), who considered that the oncologic principles are not violated with this flap on excisional margins of primary tumor, not compromised for fear of creating too large surgical defect. They stated that the surgeon will have plentiful tissue with which to perform the reconstruction and the elevation of the flap in the neck is identical to that used in radical neck dissection operations and adequate access is gained to the whole of the neck dissection field. Also this finding is in agreement with Strauch et al. (17). As a conclusion: 1- The flap gave a good access for radical neck dissection enblock with excision of the primary tumor, and at the same time mobilized it for reconstruction of the resulted defect. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Periodontology 75
6 2- The flap has provided to be highly reliable and has significant benefits as a rapid, simple and effective method for reconstruction of moderate to large size defects. 3- The design of the flap provides adequate covering and protection to the underlying structures. 4- The flap gives good cosmetic results on color matching with facial skin, texture and hair bearing area, with minimal complications. 5- The flap can tolerate the preoperative radiotherapy and adjuvant therapy. 6- Donor site of the flap can be closed primarily by direct suturing, and in limited cases are may need grafting of the donor area. REFERENCES 1. Lakdasa D. A modified single flap for neck dissection in oral cancer. Head & Neck 1990; 12(1): Wallis A, Donald P. Lateral face construction with the medially based cervicopectoral flap. Arch otolaryngol Head Neck Surgery 1988; 114: Georgiate G, Riefkohl R, Levin L. Georgiate plastic, Maxillofacial and Reconstruction surgery. 3 rd ed. Baltimore: William and Wilkins; Becker DW. A cervicopectoral rotation flap for cheek coverage. J Plastic Reconstruction Surgery 1978; 61: Math S, Nahai F. Reconstructive Surgery: Principles, Anatomy, and Technique New York: Churchill Livingstone; Reus W, Robson MC, Zachary L. Acute effects of tobacco smoking on blood flow in cutaneous microcirculation. Br J Plast Surg 1984; 37: Astrup P, Kjeldsen K. Carbon monoxide, smoking and atherosclerosis. Med Clin North Am 1974; 58: Ress TD, Liverett DM, Guy CL. the effect of cigarette smoking on skin flap survival in the face lift patient. Plast Reconstr Surg 1984; 73: Tusr H, Daniller A, Straunch B. Neovascularization of skine flaps: route and timing. Plast Reconstr Surg 1980; 71: Fisher J, Wood MB. Late necrosis of a latissimus dorsi free flap. J Plastic Reconstruction Surgery 1984; 74: McGregor IA. The temporal flap in intra oral cancer: its use in repairing the post. excisional defect. British hornal of Plastic surgery 1963; 16: McGregor, I.A. The temporal flap in facial cancer. In ; 1964; Amsterdam: Expectra Medica. p McGregor IA, Reid WH. The user of temporal flap in the primary repair of full thickness defect in cheek. J Plastic Reconstructive Surgery 1966; 38: Milliard DR. Immediate reconstruction of lower jaw. J Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 1965; 35: Conley JJ. the prevention of carotid artery haemorrhage by the use of rotation tissue flaps. Ann Surgery 1953; 54: Bakamjian VY. At two stages methods for pharyngoesophageal reconstruction with a primary pectoral skin flap. J Plastic Reconstructive Surgery 1965; 36: Strauch B, Vasconez L, Hall-Findlay E. Grabb's encyclopedia of flaps Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Periodontology 76
Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting
 Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting Received: 4/3/2013 Accepted: 14/5/2013 Introduction Reliable and simultaneous reconstruction of head-and-neck defects has been
Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting Received: 4/3/2013 Accepted: 14/5/2013 Introduction Reliable and simultaneous reconstruction of head-and-neck defects has been
ALTHOUGH FIRST described
 The Cervicodeltopectoral Flap for Single-Stage Resurfacing of Anterolateral Defects of the Face and Neck Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCSC; Jesse E. Smith, MD SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Objective: To evaluate prospectively
The Cervicodeltopectoral Flap for Single-Stage Resurfacing of Anterolateral Defects of the Face and Neck Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCSC; Jesse E. Smith, MD SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Objective: To evaluate prospectively
Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 258 262 CASE REPORTS Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects Kenji Yano*, Ko Hosokawa, Tateki Kubo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 258 262 CASE REPORTS Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects Kenji Yano*, Ko Hosokawa, Tateki Kubo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
Interesting Case Series. Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
 Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
An island flap based on the anterior branch of the superficial temporal artery for perioral defects
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article An island flap based on the anterior branch of the superficial temporal artery for perioral defects V. Bhattacharya, Ganji Raveendra Reddy, Sheikh Adil Bashir,
Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article An island flap based on the anterior branch of the superficial temporal artery for perioral defects V. Bhattacharya, Ganji Raveendra Reddy, Sheikh Adil Bashir,
be very thin and variable. Facial nerve branches that exit the parotid gland are deep to the SMAS.
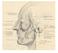 The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction
 THE PEDICLE!) SKIN FLAP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction of skin and soft tissue defects, differs from the
THE PEDICLE!) SKIN FLAP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction of skin and soft tissue defects, differs from the
cally, a distinct superior crease of the forehead marks this spot. The hairline and
 4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Traumatic Hemi Facial Soft Tissue Amputation. Immediate Surgical Flap Reconstruction
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 3 Number 1 Traumatic Hemi Facial Soft Tissue Amputation. Immediate Surgical Flap Reconstruction J Mohammad Citation J Mohammad. Traumatic Hemi Facial
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 3 Number 1 Traumatic Hemi Facial Soft Tissue Amputation. Immediate Surgical Flap Reconstruction J Mohammad Citation J Mohammad. Traumatic Hemi Facial
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
Anatomical study. Clinical study. R. Ogawa, H. Hyakusoku, M. Murakami, R. Aoki, K. Tanuma* and D. G. Pennington?
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2002) 55, 396-40 I 9 2002 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3877 PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical and clinical study of the dorsal intercostal
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2002) 55, 396-40 I 9 2002 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3877 PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical and clinical study of the dorsal intercostal
Surgery in Head and neck cancers.principles. Dr Diptendra K Sarkar MS,DNB,FRCS Consultant surgeon,ipgmer
 Surgery in Head and neck cancers.principles Dr Diptendra K Sarkar MS,DNB,FRCS Consultant surgeon,ipgmer Email:diptendrasarkar@yahoo.co.in HNC : common inclusives Challenges Anatomical preservation R0 Surgical
Surgery in Head and neck cancers.principles Dr Diptendra K Sarkar MS,DNB,FRCS Consultant surgeon,ipgmer Email:diptendrasarkar@yahoo.co.in HNC : common inclusives Challenges Anatomical preservation R0 Surgical
PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY
 PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
\C11 - f)~~8 THE PECTORALIS MAJOR MYOCUTANEOUS FLAP IN THE PRIMARY RECONSTRUCTION OF ORO-FACIAL DEFECTS
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 38 No. 2 June 1983 THE PECTORALIS MAJOR MYOCUTANEOUS FLAP IN THE PRIMARY RECONSTRUCTION OF ORO-FACIAL DEFECTS M. M. SUDHAKAR KRISHNAN A.CANAGANAYAGAM SUMMARY Pectoralis major myocutaneous
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 38 No. 2 June 1983 THE PECTORALIS MAJOR MYOCUTANEOUS FLAP IN THE PRIMARY RECONSTRUCTION OF ORO-FACIAL DEFECTS M. M. SUDHAKAR KRISHNAN A.CANAGANAYAGAM SUMMARY Pectoralis major myocutaneous
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman
 Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Septic Bone and Joint Surgery
 Septic Bone and Joint Surgery Bearbeitet von Reinhard Schnettler 1. Auflage 2010. Buch. 328 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 13 149031 5 Format (B x L): 19,5 x 27 cm Weitere Fachgebiete > Medizin > Chirurgie >
Septic Bone and Joint Surgery Bearbeitet von Reinhard Schnettler 1. Auflage 2010. Buch. 328 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 13 149031 5 Format (B x L): 19,5 x 27 cm Weitere Fachgebiete > Medizin > Chirurgie >
Nasolabial Flap Reconstruction of Oral Cavity Defects: A Report of 18 Cases
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58:1104-1108, 2000 Nasolabial Flap Reconstruction of Oral Cavity Defects: A Report of 18 Cases Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCS (C),* and Mark Burye, DDS Purpose: This article describes
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58:1104-1108, 2000 Nasolabial Flap Reconstruction of Oral Cavity Defects: A Report of 18 Cases Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCS (C),* and Mark Burye, DDS Purpose: This article describes
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
The bi-pedicle post-auricular tube flap for reconstruction of partial ear defects
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 593 598 The bi-pedicle post-auricular tube flap for reconstruction of partial ear defects Mohammed G. Ellabban*, Maamoun I. Maamoun, Moustafa Elsharkawi
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 593 598 The bi-pedicle post-auricular tube flap for reconstruction of partial ear defects Mohammed G. Ellabban*, Maamoun I. Maamoun, Moustafa Elsharkawi
THE SUBMENTAL ISLAND FLAP IN HEAD AND NECK RECONSTRUCTION
 THE SUBMENTAL ISLAND FLAP IN HEAD AND NECK RECONSTRUCTION Emre Vural, MD, James Y. Suen, MD Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, 4301 West Markham,
THE SUBMENTAL ISLAND FLAP IN HEAD AND NECK RECONSTRUCTION Emre Vural, MD, James Y. Suen, MD Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, 4301 West Markham,
Merkel Cell Carcinoma Case # 2
 DISCHARGE SUMMARY Admitted: 10/11/2010 Discharged: 10/13/2010 Merkel Cell Carcinoma Case # 2 Chief Compliant: A 79 year old lady status post tumor on the scalp excision and left neck likely dissection
DISCHARGE SUMMARY Admitted: 10/11/2010 Discharged: 10/13/2010 Merkel Cell Carcinoma Case # 2 Chief Compliant: A 79 year old lady status post tumor on the scalp excision and left neck likely dissection
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Mc Gregor Flap for Lower Eyelid Defect
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. V (April. 2017), PP 69-74 www.iosrjournals.org Mc Gregor Flap for Lower Eyelid Defect
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. V (April. 2017), PP 69-74 www.iosrjournals.org Mc Gregor Flap for Lower Eyelid Defect
The gastrocnemius with soleus bi-muscle flap
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 77 82 The gastrocnemius with soleus bi-muscle flap Ikuo Hyodo a, *, Bin Nakayama b, Mitsuru Takahashi c, Kazuhiro Toriyama d, Yuzuru Kamei d, Shuhei
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 77 82 The gastrocnemius with soleus bi-muscle flap Ikuo Hyodo a, *, Bin Nakayama b, Mitsuru Takahashi c, Kazuhiro Toriyama d, Yuzuru Kamei d, Shuhei
Vertical mammaplasty has been developed
 BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
Interesting Case Series. Reconstruction of Dorsal Wrist Defects
 Interesting Case Series Reconstruction of Dorsal Wrist Defects Maelee Yang, BS, and Joseph Meyerson, MD The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus Correspondence: maelee.yang@osumc.edu Keywords:
Interesting Case Series Reconstruction of Dorsal Wrist Defects Maelee Yang, BS, and Joseph Meyerson, MD The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus Correspondence: maelee.yang@osumc.edu Keywords:
The lumbar artery perforator based island flap: anatomical study and case reports
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (1999), 52, 541 546 1999 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons The lumbar artery perforator based island flap: anatomical study and case reports H. Kato*, M. Hasegawa,
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (1999), 52, 541 546 1999 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons The lumbar artery perforator based island flap: anatomical study and case reports H. Kato*, M. Hasegawa,
The Versatile Naso-Labial Flaps in Facial Reconstruction
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 17, No. 4, December: 245-250, 2005 The Versatile Naso-Labial Flaps in Facial Reconstruction HAMDY H. EL-MARAKBY, M.D., F.R.C.S. The Departments of National
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 17, No. 4, December: 245-250, 2005 The Versatile Naso-Labial Flaps in Facial Reconstruction HAMDY H. EL-MARAKBY, M.D., F.R.C.S. The Departments of National
T. Rapis, S.N. Zanakis, I.F. Letsa, A.P. Karamanos CLINICAL CASE. Summary. Introduction
 Journal of BUON 8: 397-401, 2003 2003 Zerbinis Medical Publications. Printed in Greece CLINICAL CASE Basal cell carcinoma of the posterior neck, reconstructed with lower trapezius island musculocutaneous
Journal of BUON 8: 397-401, 2003 2003 Zerbinis Medical Publications. Printed in Greece CLINICAL CASE Basal cell carcinoma of the posterior neck, reconstructed with lower trapezius island musculocutaneous
PECTORALIS MAJOR MYOCUTAJNEUUS FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF DEFECTS FOLLOWING RESECTIONS IN HEAD AND NECK AREA
 PECTORALIS MAJOR MYOCUTAJNEUUS FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF DEFECTS FOLLOWING RESECTIONS IN HEAD AND NECK AREA Pages with reference to book, From 72 To 76 Mohammad Arshad Cheema ( Department of Surgery,
PECTORALIS MAJOR MYOCUTAJNEUUS FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF DEFECTS FOLLOWING RESECTIONS IN HEAD AND NECK AREA Pages with reference to book, From 72 To 76 Mohammad Arshad Cheema ( Department of Surgery,
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
The gluteal perforator-based flap in repair of pressure sores
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 342 347 CASE REPORTS The gluteal perforator-based flap in repair of pressure sores Çilingir Meltem*, Çelik Esra, Fındık Hasan, Duman Ali Department
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 342 347 CASE REPORTS The gluteal perforator-based flap in repair of pressure sores Çilingir Meltem*, Çelik Esra, Fındık Hasan, Duman Ali Department
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck. M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick. Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974.
 Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck reconstruction
 European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 167 171 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck
European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 167 171 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lecture 07. Lymphatic's of Head & Neck. By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC
 Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Head and neck cancer - patient information guide
 Head and neck cancer - patient information guide The development of reconstructive surgical techniques in the last 20 years has led to major advances in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
Head and neck cancer - patient information guide The development of reconstructive surgical techniques in the last 20 years has led to major advances in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
McGregor Flap Reconstruction of Extensive Lower Lip Defects Following Excision of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 12, NO 2 May 2011 27 McGregor Flap Reconstruction of Extensive Lower Lip Defects Following Excision of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mohamed A. Albadawy, MD and Bassem M.
Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 12, NO 2 May 2011 27 McGregor Flap Reconstruction of Extensive Lower Lip Defects Following Excision of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mohamed A. Albadawy, MD and Bassem M.
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES
 CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD
 Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD Axial Based upon a named artery. Survival length depends upon the artery not the width of the flap. Random Has random unnamed vessels supplying it. Survival length is directly proportional
Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD Axial Based upon a named artery. Survival length depends upon the artery not the width of the flap. Random Has random unnamed vessels supplying it. Survival length is directly proportional
Nasolabial flap reconstruction in oral cancer
 Singh et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:227 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Nasolabial flap reconstruction in oral cancer Seema Singh, Rajesh Kumar Singh and Manoj
Singh et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:227 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Nasolabial flap reconstruction in oral cancer Seema Singh, Rajesh Kumar Singh and Manoj
FOLLOWING INTRODUCTION OF
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Alternative 1-Step Nasal Reconstruction Technique Kazuo Kishi, MD, PhD; Nobuaki Imanishi, MD, PhD; Yusuke Shimizu, MD; Ruka Shimizu, MD, PhD; Keisuke Okabe, MD; Hideo Nakajima, MD, PhD
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Alternative 1-Step Nasal Reconstruction Technique Kazuo Kishi, MD, PhD; Nobuaki Imanishi, MD, PhD; Yusuke Shimizu, MD; Ruka Shimizu, MD, PhD; Keisuke Okabe, MD; Hideo Nakajima, MD, PhD
Comparison of conventional and L-extension deltopectoral flaps in head-and-neck reconstructions
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 179e183 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of conventional and deltopectoral flaps in head-and-neck
Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 179e183 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of conventional and deltopectoral flaps in head-and-neck
THE ANGULAR TRACT: AN ANATOMICAL
 British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981) 19, 116-120 0 The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-117X/81/00170116$02.00 THE ANGULAR TRACT: AN ANATOMICAL OF SURGICAL SIGNIFICANCE STRUCTURE HAITHEM A.
British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981) 19, 116-120 0 The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-117X/81/00170116$02.00 THE ANGULAR TRACT: AN ANATOMICAL OF SURGICAL SIGNIFICANCE STRUCTURE HAITHEM A.
The eyebrow is so aesthetically important that. Reconstructive
 Original Article Reconstructive Extended Hair-bearing Lateral Orbital Flap for Simultaneous Reconstruction of Eyebrow and Eyelid Shinji Matsuo, MD Ichiro Hashimoto, MD Takuya Seike, MD Yoshiro Abe, MD
Original Article Reconstructive Extended Hair-bearing Lateral Orbital Flap for Simultaneous Reconstruction of Eyebrow and Eyelid Shinji Matsuo, MD Ichiro Hashimoto, MD Takuya Seike, MD Yoshiro Abe, MD
Lab Activity 11: Group I
 Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2
 RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sathyanarayana B. C, Somashekar Srinivas. Reconstruction of Scalp Defects:
RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sathyanarayana B. C, Somashekar Srinivas. Reconstruction of Scalp Defects:
Refresher Course EAR TUMOR. Sasikarn Chamchod, MD Chulabhorn Hospital
 Refresher Course EAR TUMOR Sasikarn Chamchod, MD Chulabhorn Hospital Reference: Perez and Brady s Principles and Practice of radiation oncology sixth edition Outlines Anatomy Epidemiology Clinical presentations
Refresher Course EAR TUMOR Sasikarn Chamchod, MD Chulabhorn Hospital Reference: Perez and Brady s Principles and Practice of radiation oncology sixth edition Outlines Anatomy Epidemiology Clinical presentations
Cutaneous Melanoma: Epidemiology (USA) The Sentinel Node in Head and Neck Melanoma. Cutaneous Melanoma: Epidemiology (USA)
 The Sentinel Node in Head and Neck Melanoma Cutaneous Melanoma: Epidemiology (USA) 6 th leading cause of cancer among men and women 68,720 new cases of invasive melanoma in 2009 8,650 deaths from melanoma
The Sentinel Node in Head and Neck Melanoma Cutaneous Melanoma: Epidemiology (USA) 6 th leading cause of cancer among men and women 68,720 new cases of invasive melanoma in 2009 8,650 deaths from melanoma
Head & Neck Contouring
 Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV
 DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery. Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University
 Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
BUILDING A. Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation. 70 OCTOBER 2016 // dentaltown.com
 BUILDING A MANDI Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation by Dr. Fayette C. Williams Fayette C. Williams, DDS, MD, FACS, is clinical faculty at John Peter Smith Hospital in Fort Worth, Texas,
BUILDING A MANDI Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation by Dr. Fayette C. Williams Fayette C. Williams, DDS, MD, FACS, is clinical faculty at John Peter Smith Hospital in Fort Worth, Texas,
CASE REPORT Reconstruction and Characterization of Composite Mandibular Defects Requiring Double Skin Paddle Fibular Free Flaps
 CASE REPORT Reconstruction and Characterization of Composite Mandibular Defects Requiring Double Skin Paddle Fibular Free Flaps Austin M. Badeau, BA, a and Frederic W.-B. Deleyiannis, MD, MPhil, MPH b
CASE REPORT Reconstruction and Characterization of Composite Mandibular Defects Requiring Double Skin Paddle Fibular Free Flaps Austin M. Badeau, BA, a and Frederic W.-B. Deleyiannis, MD, MPhil, MPH b
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 704 708 CASE REPORT Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases Lütfi Eroğlu a, *, Osman Ata Uysal b a Faculty of Medicine, Department of Plastic and
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 704 708 CASE REPORT Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases Lütfi Eroğlu a, *, Osman Ata Uysal b a Faculty of Medicine, Department of Plastic and
Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap.
 Case Report Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF, Patient Specific Plate Contouring (PSPC) and the MatrixMANDIBLE Plating
Case Report Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF, Patient Specific Plate Contouring (PSPC) and the MatrixMANDIBLE Plating
Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts
 Aesth. Plast. Surg. 24:90 96, 2000 DOI: 10.1007/s002660010017 2000 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts Ozan Sozer, M.D., and Thomas M. Biggs, M.D. İstanbul, Turkey and
Aesth. Plast. Surg. 24:90 96, 2000 DOI: 10.1007/s002660010017 2000 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts Ozan Sozer, M.D., and Thomas M. Biggs, M.D. İstanbul, Turkey and
Mentosternal Contracture Treated With an Occipito-Scapular Flap in a 5-year-old Boy: A Case Report
 Mentosternal Contracture Treated With an Occipito-Scapular Flap in a 5-year-old Boy: A Case Report Armin Kraus, MD, Hans-Eberhard Schaller, MD, and Hans-Oliver Rennekampff, MD Department for Hand, Plastic,
Mentosternal Contracture Treated With an Occipito-Scapular Flap in a 5-year-old Boy: A Case Report Armin Kraus, MD, Hans-Eberhard Schaller, MD, and Hans-Oliver Rennekampff, MD Department for Hand, Plastic,
Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery
 Objectives Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery Identify important functional anatomy and aesthetic units of the face. Describe techniques used in facial reconstruction. Discuss postoperative
Objectives Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery Identify important functional anatomy and aesthetic units of the face. Describe techniques used in facial reconstruction. Discuss postoperative
Wound coverage of plantar metatarsal ulcers in leprosy using a toe web flap
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article Wound coverage of plantar metatarsal ulcers in leprosy using a toe web flap J. Joshua, V. Chakraborthy Premananda Memorial Leprosy Hospital, The Leprosy
Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article Wound coverage of plantar metatarsal ulcers in leprosy using a toe web flap J. Joshua, V. Chakraborthy Premananda Memorial Leprosy Hospital, The Leprosy
Case Scenario. 7/13/12 Anterior floor of mouth biopsy: Infiltrating squamous cell carcinoma, not completely excised.
 Case Scenario 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of alcohol.
Case Scenario 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of alcohol.
Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H. Citation Journal of Clinical Urology, 7(5),
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Gluteal-fold adipofascial perforato fistula reconstruction Fujioka, Masaki; Hayashida, Kenji; Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H Citation Journal of Clinical
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Gluteal-fold adipofascial perforato fistula reconstruction Fujioka, Masaki; Hayashida, Kenji; Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H Citation Journal of Clinical
ISPUB.COM. Cutting Burr Otoplasty. D Wynne, N Balaji INTRODUCTION ANATOMY CUTTING BURR TECHNIQUE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 7 Number 1 D Wynne, N Balaji Citation D Wynne, N Balaji.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 7 Number 1. Abstract Prominent
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 7 Number 1 D Wynne, N Balaji Citation D Wynne, N Balaji.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 7 Number 1. Abstract Prominent
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS
 MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
Repair of scalp defect using a superficial temporal fascia pedicle VY advancement scalp flap *
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 676 680 Repair of scalp defect using a superficial temporal fascia pedicle VY advancement scalp flap * Kiyoshi Onishi a, *, Yu Maruyama b, Akiteru Hayashi
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 676 680 Repair of scalp defect using a superficial temporal fascia pedicle VY advancement scalp flap * Kiyoshi Onishi a, *, Yu Maruyama b, Akiteru Hayashi
AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION
 CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
Reconstruction of the Chest Wall
 HOW TO DO IT Reconstruction of the Chest Wall Reed 0. Dingman, M.D., and Louis C. Argenta, M.D. ABSTRACT Reconstruction of the chest wall can now be accomplished reliably and expeditiously. Past experience
HOW TO DO IT Reconstruction of the Chest Wall Reed 0. Dingman, M.D., and Louis C. Argenta, M.D. ABSTRACT Reconstruction of the chest wall can now be accomplished reliably and expeditiously. Past experience
New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description)
 New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description) 14301 Adjacent tissue transfer or rearrangement, any area; defect 30.1 sq cm to 60.0 sq cm 14302 each additional 30.0 sq cm,
New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description) 14301 Adjacent tissue transfer or rearrangement, any area; defect 30.1 sq cm to 60.0 sq cm 14302 each additional 30.0 sq cm,
Case Scenario 1. 7/13/12 Anterior floor of mouth biopsy: Infiltrating squamous cell carcinoma, not completely excised.
 Case Scenario 1 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of
Case Scenario 1 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of
Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies. No Disclosures or Conflicts of Interest. Anatomy 10/4/2013
 Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies Daniel G. Deschler, MD Director: Division of Head and Neck Surgery Massachusetts Eye & Ear Infirmary Massachusetts General Hospital Professor Harvard Medical School
Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies Daniel G. Deschler, MD Director: Division of Head and Neck Surgery Massachusetts Eye & Ear Infirmary Massachusetts General Hospital Professor Harvard Medical School
Hemangioma of Tongue with Phlebolith: A Rare presentation
 Journal of Government Dental College and Hospital, October 2017, Vol.-04, Issue- 01, P. 20-25 Original article: Hemangioma of Tongue with Phlebolith: A Rare presentation 1 Dr. Jigna S Shah (MDS) 1, 2 Dr.
Journal of Government Dental College and Hospital, October 2017, Vol.-04, Issue- 01, P. 20-25 Original article: Hemangioma of Tongue with Phlebolith: A Rare presentation 1 Dr. Jigna S Shah (MDS) 1, 2 Dr.
Aesthetic surgery techniques after excision of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a case report
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 556 560 CASE REPORT Aesthetic surgery techniques after excision of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a case report G. Dagregorio a, *, V. Darsonval b a Department
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 556 560 CASE REPORT Aesthetic surgery techniques after excision of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a case report G. Dagregorio a, *, V. Darsonval b a Department
Reconstruction of axillary scar contractures retrospective study of 124 cases over 25 years
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 100 105 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00035-3 Reconstruction
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 100 105 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00035-3 Reconstruction
Reconstruction for Oral Neoplasms in Indian Setup: Redebating the Utility of Radial Artery Free Flaps
 World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Reconstruction for Oral Neoplasms in Indian Setup: Redebating the Utility of Radial Artery Free Flaps Authors: Ranjan G Aiyer*, Rahul
World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Reconstruction for Oral Neoplasms in Indian Setup: Redebating the Utility of Radial Artery Free Flaps Authors: Ranjan G Aiyer*, Rahul
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialties
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialties ISSN 2455-2860 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Ear lobe reconstruction Techniques revisited ANANTHARAJAN NATARAJAN Department of Plastic Reconstructive Surgery,
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialties ISSN 2455-2860 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Ear lobe reconstruction Techniques revisited ANANTHARAJAN NATARAJAN Department of Plastic Reconstructive Surgery,
Large full-thickness nasal tip defects after Mohs
 RECONSTRUCTIVE CONUNDRUM Repair of a Large, Exposed-Cartilage Nasal Tip Defect Using Nasalis-Based Subcutaneous Pedicle Flaps and Full-Thickness Skin Grafting DIEGO E. MARRA, MD, EDGAR F. FINCHER, MD,
RECONSTRUCTIVE CONUNDRUM Repair of a Large, Exposed-Cartilage Nasal Tip Defect Using Nasalis-Based Subcutaneous Pedicle Flaps and Full-Thickness Skin Grafting DIEGO E. MARRA, MD, EDGAR F. FINCHER, MD,
Interesting Case Series. Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Scalp
 Interesting Case Series Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Scalp Vasanth S. Kotamarti, BS, Adam M. Feintisch, MD, and Frank Ciminello, MD Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark Correspondence:
Interesting Case Series Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Scalp Vasanth S. Kotamarti, BS, Adam M. Feintisch, MD, and Frank Ciminello, MD Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark Correspondence:
Cancer of the Oral Cavity
 The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology Cancer of the Oral Cavity Ashok Shaha Principals of Management of Oral Cancer A)
The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology Cancer of the Oral Cavity Ashok Shaha Principals of Management of Oral Cancer A)
Clinical teaching/experi ence. Lectures/semina rs/conferences Self-directed. learning. Clinical teaching/experi ence
 Regional Medical Center (The MED) Plastic Surgery PGY-3 By the end of the Plastic Surgery at the MED, the PGY-3 residents are expected to expand and cultivate knowledge and skills developed during previous
Regional Medical Center (The MED) Plastic Surgery PGY-3 By the end of the Plastic Surgery at the MED, the PGY-3 residents are expected to expand and cultivate knowledge and skills developed during previous
NEW THREE-FLAP SCALP RECONSTRUCTION TECHNIQUE
 NEW THREE-FLAP SCALP RECONSTRUCTION TECHNIQUE By MIGUEL ORTICOCHEA, M.D. Professor of Plastic Surgery, Medical School, Javeriana University, Bogotd, Colombia Former Student, Pasteur Hospital, Montevideo,
NEW THREE-FLAP SCALP RECONSTRUCTION TECHNIQUE By MIGUEL ORTICOCHEA, M.D. Professor of Plastic Surgery, Medical School, Javeriana University, Bogotd, Colombia Former Student, Pasteur Hospital, Montevideo,
SYLLABUS OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY
 MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY AND SID SYLLABUS OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY (State examination) ACADEMIC YEAR 2015 2016 1. Asepsis
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY AND SID SYLLABUS OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY (State examination) ACADEMIC YEAR 2015 2016 1. Asepsis
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
Survey of Laryngeal Cancer at SBUH comparing 108 cases seen here from to the NCDB of 9,256 cases diagnosed nationwide in 2000
 Survey of Laryngeal Cancer at comparing 108 cases seen here from 1998 2002 to the of 9,256 cases diagnosed nationwide in 2000 Stony Brook University Hospital Cancer Program Annual Report 2002-2003 Gender
Survey of Laryngeal Cancer at comparing 108 cases seen here from 1998 2002 to the of 9,256 cases diagnosed nationwide in 2000 Stony Brook University Hospital Cancer Program Annual Report 2002-2003 Gender
MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY: AN OVERVIEW
 MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY: AN OVERVIEW SKIN CANCER: Skin cancer is far and away the most common malignant tumor found in humans. The most frequent types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous
MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY: AN OVERVIEW SKIN CANCER: Skin cancer is far and away the most common malignant tumor found in humans. The most frequent types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous
The Whipple Operation Illustrations
 The Whipple Operation Illustrations Fig. 1. Illustration of the sixstep pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple operation) as described in a number of recent text books by Dr. Evans. The operation is divided
The Whipple Operation Illustrations Fig. 1. Illustration of the sixstep pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple operation) as described in a number of recent text books by Dr. Evans. The operation is divided
Upper arch. 1Prosthodontics. Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi. Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth
 1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
