Surgical Anatomy of the Neck. M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick. Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974.
|
|
|
- Derrick Jennings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication of metastatic neoplasia originating in the head and neck region. Utilizing the steps of the radical neck dissections as an outline, we will present specific aspects of neck anatomy requisite to a complete and safe dissection. Lymphatics The purpose of the radical neck dissection is to remove the lymphatics and the drainage areas of primary cancers originating in the head and neck. Applying this principle of regional lymphatic excision (radical dissection), all cervical lymphatics and, in addition, certain adjacent muscles, nerves, and glands must be sacrificed to facilitate complete extirpation of the disease. A "partial" or upper neck dissection for carcinoma violates the lymph node bearing fields and negates the tenets of the en bloc dissection of cervical lymphatics. Rouviere has classified the cervical lymph nodes into ten principal groups. They may be further recognized conceptually as a superior horizontal chain arranged about the base of the head and jaw, leading to a vertical chain in the midportion of the neck and another horizontally oriented chain in the supraclavicular region. The groups of nodes in the superior horizontal chain are the submental, submandibular, preauricular (parotid), postauricular (mastoid), and occipital. These nodes receive afferents from the integument of the head and mucous membranes of the nasal and oral cavities and the adjacent nasopharynx, oropharynx, tonsil region, and the salivary glands. Their efferents drain into the vertically oriented deep jugular nodes. This jugular chain, in addition, receives major afferents to its important subdigastric nodes from the deep parotid region, the nasopharynx, and the tonsil. A posteriorly and more superficially oriented vertical group is in relation to the spinal accessory nerve and the external jugular vein. An anteriorly oriented chain drains the cervical viscera and the thyroid gland. The supraclavicular horizontal chain receives afferents from the vertical chains immediately superior, the upper thoracic wall, and the upper extremity. The primary lymphatic ducts deliver large volumes of lymph and chyle into the venous system, and if injured surgically should be securely ligated. On the right, three terminal lymphatic trunks empty into the junction of the right subclavian and the right internal jugular vein, either directly or indirectly. These trunks are the subclavian trunk from the supraclavicular nodes, the jugular trunk, and the bronchomediastinal trunk. It is unusual for these three trunks to coalesce to form a true right lymphatic duct. On the left, the chief collecting channel of the lymphatic system which drains all lymphatics from below the diaphragm, the left half of the thorax, the left side of the head and neck, and the left upper extremity is the thoracic duct. It may receive the jugular, subclavian, and bronchomediastinal trunks on the left side. Occasionally, however, one or more of these trunks may enter separately. 1
2 An en bloc resection of all the lymphatic bearing tissues will therefore require dissection from the inferior margin of the mandible to the clavicle and from the anterior aspect of the trapezius muscle to the muscles covering the cervical viscera. These tissues also lie between the deep investing cervical fascia and the prevertebral lamina of the deep cervical fascia. Of necessity, this en bloc resection includes the sternocleidomastoid muscle, the jugular vein, submaxillary gland, omohyoid muscle, spinal accessory nerve, the external jugular vein, and the tail of the parotid. Usually, the posterior belly of the digastric and the sternohyoid muscles are also included in the resection. If there is involvement in the submental region, the anterior belly of the digastric is taken. Incisions Cervical incisions should be designed to provide adequate exposure, avoid superimposition of intraoral, pharyngeal, or laryngeal incisions, and follow the natural transverse skin lines of the neck, thus favoring optimum healing and appearance. Particularly in cases which follow upon preoperative irradiation, these incisions should be adequately vascularized and so designed that the flaps are safe from necrosis or delayed healing over the carotid artery. The double transverse incision as described by MacFee is quite safe and meets these criteria admirably. Its upper limb extends at the level of the hyoid in a slight curve from the trapezius anteriorly to approximately midline. The lower incision is transverse 2.5 cm above the clavicle. An alternative incision has a vertical limb along the anterior trapezius and a single transverse limb extending anteriorly in the midportion of the neck. These incisions both avoid the oft used trifurcate incision of Crile and Martin which is so vulnerable to necrosis over the carotid artery. In order to gain access to the intraoral structures, the upper transverse limb of these incisions may be curved and extended to the midline of the lower lip, thus providing a well vascularized flap which can be rotated posteriorly. The cervical nodes all lie deep to the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia. Therefore, the skin flaps are elevated immediately beneath the thin platysma muscle and just above the investing layer. The primary superficial veins - external jugular, anterior jugular, and facial - lie just beneath the platysma and superficial to the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia. During elevation of the flaps, the sensory branches of the cervical plexus are divided as they emerge from the posterior aspect of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and penetrate the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia. These include the greater auricular nerve and branches C-2 through C-4. These cutaneous nerves will be divided again as they penetrate at the prevertebral lamina of the cervical fascia at the deep extent of the surgical field. Thus, a segment of them is included in the specimen. These nerves, particularly the greater auricular, are excellent for interposition donor grafts for nerve repairs such as the seventh. Root of the Neck Removal of the specimen always proceeds in centripetal fashion; in the manner the potential cancer-bearing lymphatics are not violated. The dissection usually beings in the supraclavicular area where the superficial or investing lamina of the deep cervical fascia over the sternocleidomastoid muscle is divided approximately 2 to 3 cm above the clavicle. This layer of fascia completely encompasses the neck and invests the sternocleidomastoid, 2
3 omohyoid, and trapezius muscles. It continues upward as the fascia of the parotid and submaxillary gland. The sternal and clavicular heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle are divided at this level parallel to the clavicle. The carotid sheath, a condensation of the cervical fascia, is entered 2 to 3 cm above the clavicle and the jugular vein is isolated, carefully ligated, and divided after absolute identification of the adjacent vagus nerve and protection of the common carotid artery. The vagus nerve may inadvertently be lifted up with the jugular vein and carelessly included in the ligating sutures. Injury at this level will include those fibers which make up the recurrent laryngeal nerve. The dissection then continues posterior in the supraclavicular triangle to the anterior border trapezius and down to the level of the prevertebral lamina. The main lymphatic trunks emptying into the junction of the subclavian and jugular veins are preserved; however, if injured they should be securely ligated. The external jugular vein, coursing to the subclavian vein, is ligated and divided and will be reflected upward with the specimen. The transverse cervical artery, a terminal branch of the thyrocervical trunk from the first portion of the subclavian artery, must be divided and included in the specimen along with the accompanying veins and lymph nodes about these vessels. The node-bearing fatty areolar tissue in the posteroinferior aspect of the supraclavicular triangle is included in the en bloc dissection. This posterior inferior limit of the dissection is the junction of the omohyoid and trapezius muscle. The prevertebral lamina of the deep cervical fascia is well-defined and the specimen is dissected upward based on this fascia. It is important to remember that the brachial plexus, phrenic nerve, subclavian vessels, scalene muscles, and dome of the pleura are all just beneath this lamina. The spinal accessory nerve, the only major nerve that lies above the superficial lamina of the deep cervical fascia, is divided at its entrance to the trapezius muscle and is reflected upward with the specimen along with its accompanying chain of lymph nodes. On occasion the spinal accessory nerve may be preserved if there is no gross metastatic disease in the neck. The vessels not remaining with the specimen are ligated with fine permanent ligatures and are not cauterized because sudden increase in venous pressure from straining or a Valsalva maneuver tends to dislodge the cauterized thrombus leading to bleeding beneath the flaps. As the dissection proceeds cephalad, the roots of the cervical plexus which emerge from the prevertebral lamina are identified. The phrenic nerve which is the only structure coursing from lateral to medial just beneath the prevertebral lamina is identified along the anterior aspect of the anterior scalene muscle. Its contribution from roots C-3 and C-5 must be accurately identified, and these cervical branches, which are quite substantial, are divided distal to their phrenic nerve contributions. The ansa hypoglossi, composed of the descendens hypoglossi from C-1 and the descendens cervicalis from C-2 and C-3. courses superficial to the carotid sheath to supply the sternohyoid, sternothyroid, and omohyoid muscles and must be divided to gain access to the deeper structures. The posterior aspect of the dissection is carried superiorly on the prevertebral fascia covering the splenius capitis and levator scapulae. Medially the jugular vein and its accompanying nodes are cleared from the carotid artery, vagus nerve, and posteriorly situated sympathetic trunk. The investing tissue over the carotid bulb is infiltrated with local anesthetic to preclude bradycardia and hypotension. Care must be taken lest undue traction be placed on the carotid artery during any of the dissection particularly in the elderly patient. An atheromatous plaque may fracture and loose microemboli of atheromatous material into the cerebral circulation. 3
4 The hypoglossal nerve is identified as looping over the external carotid artery beneath the posterior belly of the digastric muscle and the mylohyoid muscle to provide motor supply to the intrinsic and extrinsic tongue musculature, including the styloglossus and hyoglossus muscles. The superior thyroid and external maxillary arteries are divided, care being taken to preserve the external laryngeal nerve which is just deep to the superior thyroid artery. This nerve originates at the nodose ganglion of the vagus and provides sensory innervation to the mucosa of the larynx and to the cricothyroid muscle. The ranine plexus of veins is in close relationship to the hypoglossal nerve. These veins are ordinarily quite small and inconspicuous. After distal ligation of the internal jugular vein, these ranine veins become engorged and distended. They must be handled carefully and securely lest undue bleeding obscure the field of dissection and lead to inadvertent injury of underlying structures. The external maxillary artery is divided as it approaches the submandibular triangle just beneath the posterior belly of the digastric. The omohyoid muscle is also divided from its origin on the hyoid; thus both bellies of the omohyoid are divided and it is included in the specimen in its entirety. Superior Aspect of the Dissection The en bloc specimen must be separated from the upper neck and mandible unless additional tissue is to be resected in continuity, such as primary tumors of the tongue, jaw, floor of mouth, or pharynx. The platysma, which is innervated by the lowermost fibers of the facial nerve, is divided along the inferior aspect of the mandible. In the absence of adjacent metastatic disease, the mandibular ramus of the 7th nerve, which supplies motor innervation to the lateral aspect of the lower lip, is identified and preserved. This branch of the facial nerve usually crosses above the posterior facial vein and its course is deep to the platysma. It usually crosses the external maxillary artery and anterior facial vein at or above the inferior border of the mandible. However, on occasion it may be up to 1 cm below the inferior border in relationship to these vessels. Nerve fibers to the platysma are frequently mistaken for the ramus mandibularis but are at a lower level in the neck. The submandibular triangle is cleaned down to the anterior belly of the digastric muscle. If there is gross clinical disease in this region, the anterior belly of the digastric is divided at its mandibular insertion and reflected with the specimen. The floor of this dissection is the mylohyoid muscle. At the posterior border of the mylohyoid muscle, the external maxillary artery and vein are divided at the level of the lower border of the mandible. The mylohyoid muscle is retracted anteriorly and the lingual nerve, a terminal branch of the mandibular portion of the trigeminal, is identified high under the mandible while the submaxillary gland is retracted downward. Its two small branches to the submaxillary ganglion are divided, which permits removal of the submaxillary gland and the nodes within the submaxillary triangle. These tissues are cleaned down to the hyoglossus muscle and Wharton's duct is ligated and divided. The hypoglossal nerve posterior and inferior to the submaxillary gland is carefully preserved, unless the major portion of the tongue is to be removed to include a primary carcinoma. Posteriorly the inferior pole of the parotid is divided in line with the lower mandible. The adjacent nodes are reflected downward to be included in the specimen. The posterior 4
5 facial vein within the parotid is identified and ligated at this time. The main trunk of the facial nerve is above this level and is not usually encountered. The sternocleidomastoid muscle is divided at its origin from the mastoid process and reflected downward. The posterior belly of the digastric and the stylohyoid, originating from the styloid process, are divided and reflected downward. This gives good access to the jugular vein near its exit from the base of the skull and also makes it possible to clear adequately the high jugular nodes and the subdigastric nodes which are frequently the site of metastatic disease. Prior to division of the jugular vein high in the neck, the spinal accessory nerve is again divided and the vagus and hypoglossal nerves, which also exist the jugular foramen and hypoglossal canals respectively, are carefully identified and preserved. At this point the dissection is complete. It must be stressed that the specific type of en bloc procedure depends upon the type, location, and histology of the primary tumor. The basic principle, however, is extirpation of the gross regional lymphatic drainage system of a tumor at the time of operation. 5
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli.
 Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
The Neck. BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat
 The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lecture 07. Lymphatic's of Head & Neck. By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC
 Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES
 CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy. Raleigh E. Lingeman
 Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy Raleigh E. Lingeman Surgeons doing head and neck surgery must first master the surgical anatomy and technique of doing neck dissection. Neck dissection is either the classic
Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy Raleigh E. Lingeman Surgeons doing head and neck surgery must first master the surgical anatomy and technique of doing neck dissection. Neck dissection is either the classic
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
Tympanic Bulla Temporal Bone. Digastric Muscle. Masseter Muscle
 Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Oral vestibule : is slit like space between.
 Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Neck of Condylar. Process. Anterior Border of Ramus. Mandibular. Foramen. Posterior Border of Ramus Incisive Fossa.
 Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
THYROID & PARATHYROID. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy
 THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
HEAD & NECK ANATOMY - MCQ HEAD & NECK ANATOMY
 . ' HEAD & NECK ANATOMY I. Deep investing layer of cervical fascia splits to enclose: A. Sternocleidomastoid B. Trapezius C. Parotid gland D. Omohyoid 2. Regarding the prevertebral fascia, the following
. ' HEAD & NECK ANATOMY I. Deep investing layer of cervical fascia splits to enclose: A. Sternocleidomastoid B. Trapezius C. Parotid gland D. Omohyoid 2. Regarding the prevertebral fascia, the following
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
 Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY
 PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
Head & Neck Contouring
 Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
Chapter 28: The neck. Fascia of the neck
 Chapter 28: The neck Fascia of the neck The superficial fascia is a fatty areolar layer between the skin and the more obvious deep fascia. It contains the platysma muscles and the external jugular veins
Chapter 28: The neck Fascia of the neck The superficial fascia is a fatty areolar layer between the skin and the more obvious deep fascia. It contains the platysma muscles and the external jugular veins
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Thyroid gland. importance. relations and connections. external laryngeal nerves. malformations.
 Thyroid gland 1. Recognize and understand the coverings of the thyroid gland and their clinical importance. 2. Recognize and understand the main parts of the thyroid gland and their locations, relations
Thyroid gland 1. Recognize and understand the coverings of the thyroid gland and their clinical importance. 2. Recognize and understand the main parts of the thyroid gland and their locations, relations
Lecture 01. The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands. By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018
 Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (FIG. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (FIG. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (FIG. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI
 Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
SURGERY. This article is one of a. of the Head and Neck
 SURGERY of the Head and Neck Mary Sutton, CST, CFA This article is one of a series that will discuss head and neck surgeries from an otolaryngology perspective. Most of these surgeries involve cancer,
SURGERY of the Head and Neck Mary Sutton, CST, CFA This article is one of a series that will discuss head and neck surgeries from an otolaryngology perspective. Most of these surgeries involve cancer,
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Anatomical Complications in General Surgery. John E. Skandalakis, Stephen W. Gray, Joseph S. Rowe. Chapter 1: The Neck
 Anatomical Complications in General Surgery John E. Skandalakis, Stephen W. Gray, Joseph S. Rowe Chapter 1: The Neck The human neck is so designed that the swelling of a normal structure or the presence
Anatomical Complications in General Surgery John E. Skandalakis, Stephen W. Gray, Joseph S. Rowe Chapter 1: The Neck The human neck is so designed that the swelling of a normal structure or the presence
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH
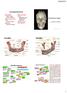
 ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
CHAPTER 9. The Neck THE "CERVICAL CAVITY" TRACHEA ESOPHAGUS THYROID GLAND PARATHYROID GLANDS
 281 CHAPTER 9 The Neck CERVICAL VERTEBRAE POSTERIOR TRIANGLE OF NECK Trapezius and Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS REGARDING TRAPEZIUS Sternocleidomastoid CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS
281 CHAPTER 9 The Neck CERVICAL VERTEBRAE POSTERIOR TRIANGLE OF NECK Trapezius and Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS REGARDING TRAPEZIUS Sternocleidomastoid CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS
Gateway to the upper limb. An area of transition between the neck and the arm.
 Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Alexander C Vlantis. Total Laryngectomy 57
 07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
General Anatomic Layout
 General Anatomic Layout 2 Core Messages At the start of the dissection exercise, we must take a panoramic look for orientation. We then establish the limits of the area of operation and the main landmarks.
General Anatomic Layout 2 Core Messages At the start of the dissection exercise, we must take a panoramic look for orientation. We then establish the limits of the area of operation and the main landmarks.
Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream
 1! Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream 2! Flow increase - like thumb over garden hose Pressure drop - narrower space forces pressure drop due to speed
1! Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream 2! Flow increase - like thumb over garden hose Pressure drop - narrower space forces pressure drop due to speed
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments
 Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
THE ANGULAR TRACT: AN ANATOMICAL
 British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981) 19, 116-120 0 The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-117X/81/00170116$02.00 THE ANGULAR TRACT: AN ANATOMICAL OF SURGICAL SIGNIFICANCE STRUCTURE HAITHEM A.
British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981) 19, 116-120 0 The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-117X/81/00170116$02.00 THE ANGULAR TRACT: AN ANATOMICAL OF SURGICAL SIGNIFICANCE STRUCTURE HAITHEM A.
Anatomy 2. Parotid bed (V.imp): meaning that gland is sleeping on structures and they are:
 Anatomy 2 Parotid Gland: "refer to previous sheet for extra details." Its pyramidal in shape, apex is toward pharynx. Its Medial surface is divided into Anterio-medial and posterio-medial and its posterio-medial
Anatomy 2 Parotid Gland: "refer to previous sheet for extra details." Its pyramidal in shape, apex is toward pharynx. Its Medial surface is divided into Anterio-medial and posterio-medial and its posterio-medial
APRIL
 APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory fibers to the skin of the clavicular area
 YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY WRITTEN EXAM 2 -- October 10, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-42. 1. Each of the following statements is CORRECT EXCEPT: A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory
YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY WRITTEN EXAM 2 -- October 10, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-42. 1. Each of the following statements is CORRECT EXCEPT: A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory
Learning Outcomes. The Carotid 20/02/2013. Scalp, Face, Parotid. Layers of the Scalp. The Parotid Gland. The Scalp. The Carotid The Facial Artery
 Learning Outcomes The Scalp Layers of the Scalp Bleeding from the Scalp The Carotid The Facial Artery Major Muscles of the Face and Jaw(s) Muscles of Mastication Muscles of Facial Expression The Parotid
Learning Outcomes The Scalp Layers of the Scalp Bleeding from the Scalp The Carotid The Facial Artery Major Muscles of the Face and Jaw(s) Muscles of Mastication Muscles of Facial Expression The Parotid
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity. Dr. Faghih
 Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of
![function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of](/thumbs/74/71276096.jpg) Nerves I. Cranial nerves A. Olfactory (CN I) 1. Olfactory bulb 2. Olfactory tract B. Optic n. (CNII) function - carries visual sensory information from the neural retina to the diencephalon & midbrain
Nerves I. Cranial nerves A. Olfactory (CN I) 1. Olfactory bulb 2. Olfactory tract B. Optic n. (CNII) function - carries visual sensory information from the neural retina to the diencephalon & midbrain
Anatomy of thoracic wall
 Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP STEP 3 SEPARATE PAROTID GLAND FROM SCM STEP 2 IDENTIFICATON OF GREAT AURICULAR NERVE
 STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP Create a modified Blair Figure 1 or facelift incision. Figure 2 Raise a superficial cervico-fascial flap between the Superficial Musculo Aponeurotic System (SMAS)
STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP Create a modified Blair Figure 1 or facelift incision. Figure 2 Raise a superficial cervico-fascial flap between the Superficial Musculo Aponeurotic System (SMAS)
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh
 3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions.
 Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
A Review on Neck Dissection
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. III (June. 2017), PP 86-101 www.iosrjournals.org A Review on Neck Dissection Dr.Shalini
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. III (June. 2017), PP 86-101 www.iosrjournals.org A Review on Neck Dissection Dr.Shalini
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature Introduction The skeletal muscle of the body can be subdivided into: Axial musculature Muscles that position
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature Introduction The skeletal muscle of the body can be subdivided into: Axial musculature Muscles that position
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy
 Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM
 REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve. The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions
 Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Neck dissection with cervical sensory preservation in thyroid cancer
 Review Article Neck dissection with cervical sensory preservation in thyroid cancer Shuai Xue, Peisong Wang, Guang Chen Thyroid surgery department, the 1 st hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130021,
Review Article Neck dissection with cervical sensory preservation in thyroid cancer Shuai Xue, Peisong Wang, Guang Chen Thyroid surgery department, the 1 st hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130021,
Resection of malignant tumors invading the thoracic inlet
 Resection of Superior Sulcus Tumors: Anterior Approach Marc de Perrot, MD, MSc Resection of malignant tumors invading the thoracic inlet represents a technical challenge because of the complex anatomy
Resection of Superior Sulcus Tumors: Anterior Approach Marc de Perrot, MD, MSc Resection of malignant tumors invading the thoracic inlet represents a technical challenge because of the complex anatomy
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
Cranial Nerves IX-X (Glossopharyngeal & Vagus Nerves)
 Cranial Nerves IX-X (Glossopharyngeal & Vagus Nerves) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Cranial Nerves IX-X (Glossopharyngeal & Vagus Nerves) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Larynx. Rudimentary. Behind the posterior surface : -stylopharyngeus - salpingopharyngeus -platopharyngeus
 Larynx The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages and is responsible for voice production. It extends from C3-C6: *Posterior: the pharynx *Lateral: the
Larynx The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages and is responsible for voice production. It extends from C3-C6: *Posterior: the pharynx *Lateral: the
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 [ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
[ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
THE NECK PART I BONES AND JOINTS OF THE NECK MUSCLES OF THE NECK SCM CAROTID TRIANGLE ENDOCRINE LAYER OF THE CERVICAL VISCERA
 THE NECK PART I BONES AND JOINTS OF THE NECK MUSCLES OF THE NECK SCM CAROTID TRIANGLE ENDOCRINE LAYER OF THE CERVICAL VISCERA THE NECK THE NECK The neck has four major compartments, which are enclosed
THE NECK PART I BONES AND JOINTS OF THE NECK MUSCLES OF THE NECK SCM CAROTID TRIANGLE ENDOCRINE LAYER OF THE CERVICAL VISCERA THE NECK THE NECK The neck has four major compartments, which are enclosed
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
1. Thyroxine (inactive form) also called T4 (90% of the secretion). 2. Triiodothyronine (active form) also called T3 (10% of the secretion).
 A Introduction The nomenclature of the thyroid gland comes from its close relation to the thyroid cartilage (the thyroid cartilage was named like this because thyroid means shield and it is shielding the
A Introduction The nomenclature of the thyroid gland comes from its close relation to the thyroid cartilage (the thyroid cartilage was named like this because thyroid means shield and it is shielding the
THE DESCENDING THORACIC AORTA
 Intercostal Arteries and Veins Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and two small anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces
Intercostal Arteries and Veins Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and two small anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces
Nose & Mouth OUTLINE. Nose. - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls. - Paranasal Sinuses. - Neurovascular Structures. Mouth. - Oral Cavity & Its Contents
 Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
CHAPTER 7. The Neck RETROMANDIBULAR REGION
 205 CHAPTER 7 The Neck BODY WALL OF THE NECK Skeletal Components Cervical Vertebrae The Hyoid Bone and the Styloid Process of the Skull Thyroid Cartilage Cricoid Cartilage Muscular Components Cervical
205 CHAPTER 7 The Neck BODY WALL OF THE NECK Skeletal Components Cervical Vertebrae The Hyoid Bone and the Styloid Process of the Skull Thyroid Cartilage Cricoid Cartilage Muscular Components Cervical
THE SURGEON S LIBRARY
 THE SURGEON S LIBRARY THE HISTORY AND SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE VAGUS NERVE Lee J. Skandalakis, M.D., Chicago, Illinois, Stephen W. Gray, PH.D., and John E. Skandalakis, M.D., PH.D., F.A.C.S., Atlanta, Georgia
THE SURGEON S LIBRARY THE HISTORY AND SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE VAGUS NERVE Lee J. Skandalakis, M.D., Chicago, Illinois, Stephen W. Gray, PH.D., and John E. Skandalakis, M.D., PH.D., F.A.C.S., Atlanta, Georgia
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
Anatomy and Physiology II. Spine
 Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
cardiac plexus is continuous with the coronary and no named branches pain from the heart and lungs
 Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD
 Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD SUNY-LICH Medical Center Department of Surgery Case Presentation xx year old male presents with sudden onset left lower neck swelling x 1 week Denies pain,
Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD SUNY-LICH Medical Center Department of Surgery Case Presentation xx year old male presents with sudden onset left lower neck swelling x 1 week Denies pain,
3. The Jaw and Related Structures
 Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
