Alterations of papilla dimensions after orthodontic closure of the maxillary midline diastema: a retrospective longitudinal study
|
|
|
- Vanessa Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Periodontal Implant Sci Jun;46(3): pissn eissn Research Article after orthodontic closure of the maxillary midline diastema: a retrospective longitudinal study Jin-Seok Jeong, 1 Seung-Youp Lee, 2,3 Moontaek Chang 1,3,* 1 Department of Periodontology, Chonbuk National University School of Dentistry and Institute of Oral Bioscience, Jeonju, Korea 2 Department of Orthodontics, Chonbuk National University School of Dentistry and Institute of Oral Bioscience, Jeonju, Korea 3 Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University Biomedical Research Institute of Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea Received: Mar 6, 2016 Accepted: Apr 22, 2016 *Correspondence to Moontaek Chang Department of Periodontology, Chonbuk National University School of Dentistry, Geonjiro 20, Deokjin-gu, Jeonju 54907, Korea. chang@chonbuk.ac.kr Tel: Fax: Copyright 2016 Korean Academy of Periodontology This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/). ORCID Jin-Seok Jeong Seung-Youp Lee Moontaek Chang Conflict of Interest No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. ABSTRACT Purpose: The aim of this study was to evaluate alterations of papilla dimensions after orthodontic closure of the diastema between maxillary central incisors. Methods: Sixty patients who had a visible diastema between maxillary central incisors that had been closed by orthodontic approximation were selected for this study. Various papilla dimensions were assessed on clinical photographs and study models before the orthodontic treatment and at the follow-up examination after closure of the diastema. Influences of the variables assessed before orthodontic treatment on the alterations of papilla height (PH) and papilla base thickness (PBT) were evaluated by univariate regression analysis. To analyze potential influences of the 3-dimensional papilla dimensions before orthodontic treatment on the alterations of PH and PBT, a multiple regression model was formulated including the 3-dimensional papilla dimensions as predictor variables. Results: On average, PH decreased by 0.80 mm and PBT increased after orthodontic closure of the diastema (P<0.01). Univariate regression analysis revealed that the PH (P=0.002) and PBT (P=0.047) before orthodontic treatment influenced the alteration of PH. With respect to the alteration of PBT, the diastema width (P=0.045) and PBT (P=0.000) were found to be influential factors. PBT before the orthodontic treatment significantly influenced the alteration of PBT in the multiple regression model. Conclusions: PH decreased but PBT increased after orthodontic closure of the diastema. The papilla dimensions before orthodontic treatment influenced the alterations of PH and PBT after closure of the diastema. The PBT increased more when the diastema width before the orthodontic treatment was larger. Keywords: Dental esthetics; Gingiva; Orthodontic space closure 197
2 INTRODUCTION Lack of interdental papilla, which can arise from many causes, creates esthetic problems that concern clinicians and patients alike. The degree of interdental papilla fill is influenced by various embrasure dimensions such as the vertical distance between the contact point position and the bone crest, the horizontal interdental distance, and the facio-lingual thickness of the papilla base [1,2]. In the presence of the diastema between teeth, the interdental papilla may be absent, since no contact point exists. Hence, it has been suggested that a new contact point can be created between two adjacent teeth by orthodontic approximation with bodily movement [3,4]. Lowering the contact point position by stripping off the proximal surfaces of the adjacent teeth has also been favored to improve papilla fill after closure of the diastema [5]. Furthermore, it has been claimed that the papilla height level could move coronally by creeping of the proximal gingiva as well as by squeezing the gingival volume in the proximal embrasure space during orthodontic closure of the diastema [3,4,6]. With respect to the direction of orthodontic movements, it has been suggested that the palatal movement and intrusive movement of the teeth could increase the height of interdental papilla [7]. In fact, orthodontic approximation of maxillary incisors with an interproximal gap due to pathologic tooth movement was found to significantly enhance the level of the interdental papilla, as well as the interproximal bone level [8]. In contrast, the height of interdental papilla decreased after orthodontic closure of the diastema [7]. Hence, it is not clear whether the papilla height was increased or not by orthodontic approximation of teeth with diastemas. Facio-lingual thickness of the papilla has been suggested to play an important role in supporting the papilla height level [9]. In addition, the probability of a complete papilla fill was significantly affected by the facio-lingual dimension of the papilla base [2]. However, information regarding the alteration of the facio-lingual dimensions of the papilla base during orthodontic closure of the diastema is not available in the literature. The aim of this study was to evaluate alterations of papilla dimensions after orthodontic closure of the diastema between maxillary central incisors. MATERIALS AND METHODS Subject sample Subjects for this study were consecutively selected from the pool of patients who had been treated during the period between January 1994 and May 2014 at the Department of Orthodontics, Chonbuk National University Dental Hospital, Jeonju, South Korea. For inclusion in the study, the subject should have (i) a visible diastema between the maxillary central incisors that was closed by orthodontic approximation, (ii) no clinically visible gingival inflammation and periodontal bone loss at the maxillary central incisors, (iii) no medication history related to gingival enlargement, (iv) no apparent extrusion and/or severe buccal tipping of the maxillary central incisors, and (v) study models and clinical photographs taken before the initiation of orthodontic treatment and at the follow-up examinations after completion of orthodontic closure of the diastema. Maxillary central incisors were mainly subjected to orthodontic bodily movement so that the diastema between the teeth could be closed. To retain stability of the moved teeth and to prevent a relapse of tooth movement afterwards, the teeth were passively splinted with a 0.7 mm twist flex wire (Remanium wire, Dentaurum, Ispringen, Germany). 198
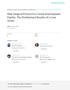
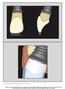
3 Figure 1. Clinical photographs of a 13-year-old female patient. (A) Before orthodontic closure of the diastema between maxillary central incisors; (B) At the follow-up examination after closure of the diastema. Approval of the original study protocol was obtained from the Ethics Committee at the Chonbuk National University Hospital (IRB #CUH ). The study was performed in accordance with the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki, which was revised in Photographic assessments Photographs focusing on the proximal embrasure between maxillary central incisors were taken before the orthodontic treatment and at the follow-up examination (Figure 1A and B). The following variables were assessed on the digitized images with the use of the measuring tool available in a software program (Photoshop CS6, Adobe, USA). The ratio between the clinical crown height in the photograph and that in the study model was calculated, and it was used for calibration of the linear measurements in the individual photograph [2,10] (Figure 2A). Clinical crown height (CCH): the distance between the most apical gingival margin and the incisal edge of the crown of the right maxillary central incisor measured to the nearest 0.1 mm. Papilla height (PH): the distance from the top of the papilla between maxillary central incisors to a line connecting the most apical level of the gingival margin of the two teeth, measured to the nearest 0.1 mm [11]. Further, the degree of papilla fill between central incisors was determined at the follow-up examinations using the scoring system of the Papilla Index [12]. Study model assessments The following variables were measured to the nearest 0.1 mm on diagnostic casts obtained before orthodontic treatment and at follow-up examinations with the use of calipers (Digimatic caliper, Mitutoyo Corporation, Kawasaki, Japan; Iwanson Spring Caliper, HuFriedy Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA) (Figure 2B and C). Figure 2. Photographic (A) and study model assessments (B and C). CCH, clinical crown height; PH, papilla height; REF, reference line; PBW, papilla base width; CCW, clinical crown width; DW, diastema width; PBT, papilla base thickness. 199
4 Clinical crown height (CCH): the distance between the most apical gingival margin and the incisal edge of the crown of the right maxillary central incisor measured to the nearest 0.1 mm. Clinical crown width (CCW): the widest mesio-distal dimension of the crown of the right maxillary central incisor measured to the nearest 0.1 mm. Papilla base thickness (PBT): measured as the distance between the facial and lingual midpoint of lines connecting the facial/lingual levels of the most apical gingival margins at the maxillary central incisors. Papilla base width (PBW): measured as the length of a line connecting the most apical level of gingival margins at the maxillary central incisors. Diastema width (DW): the length of the horizontal gap between maxillary central incisors measured by the number of Tofflemire matrix bands with a thickness of 38 μm (Water Pik Inc., Fort Collins, CO, USA) that could be inserted into the diastema. One calibrated examiner (JJ), who had been trained in calibration and was not involved in the treatment of the patients, performed all assessments included in the study. Error in the methods The validity of the assessments was examined by a comparison of CCH assessments in 15 patients, measured on photographs and on diagnostic casts. The mean difference between the two measurements was 0.02 mm (SD 0.12). In 87% of the paired assessments (13/15), the difference was less than 0.1 mm. Intra-examiner reproducibility of photographic and study model assessments was determined by repeated measurements in 15 randomly selected patients with a 2-week interval. Intraclass correlation coefficients calculated for consistency and absolute agreement of a single rater were well over 0.9 for all the tested variables. The mean difference was 0.01 mm (SD 0.10) for CCH, 0.05 mm (SD 0.06) for CCW, 0.02 mm (SD 0.03) for DW, and 0.04 mm (SD 0.13) for PBT measured on the study models, and 0.07 mm (SD 0.15) for PH measured on the photographs. Data analysis Hypotheses to be tested in this study were as follows: (1) Do PH and PBT increase or decrease after orthodontic closure of the diastema?, (2) Do relationships exist between various papilla dimensions before the orthodontic treatment and those at the follow-up examinations after closure of the diastema?, and (3) Do the PH, PBT, and PBW before orthodontic treatment influence the alterations of PH and PBT?. The primary outcome of the study was the alteration of PH and PBT after orthodontic closure of the diastema. Mean values, standard deviations, ranges, 95% confidence intervals, and the distributions of the variables were calculated for data description with the subject as a statistical unit. Correlations between the papilla dimensions before orthodontic treatment and those at the follow-up examinations were analyzed. Data analyses were performed with the use of a statistical software program (SPSS 22, IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Alterations of the PH and PBT after orthodontic closure of the diastema were analyzed with a paired t-test after testing normality of the data with the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The influence of age, sex, follow-up period, CCW/CCH ratio, PH, DW, and PBT before orthodontic treatment on the alterations of the PH and PBT after closure of the diastema was analyzed with univariate regression analysis. To analyze the potential influences of 3-dimensional papilla dimensions 200
5 Table 1. Description of the patient samples Variable Outcome assessment No. of patients 60 Mean age (range:yr) 19 (10-46) Sex ratio (male/female) 24/36 Mean follow-up (range:mon) 28 (6-209) Mean diastema width before orthodontic treatment (range:mm) 1.1 ( ) before orthodontic treatment on the alterations of PH and PBT, a multiple regression model was formulated including the PH, PBT, and PBW before the orthodontic treatment as predictor variables. A P-value <0.05 was considered to be statistically significant in all analyses. RESULTS Sixty patients (36 females/24 males) were consecutively selected for this study. The mean age was 19 years (range, years), and the average follow-up period was 28 months (range, months) (Table 1). PH decreased by 0.80 mm and PBT increased after orthodontic closure of the diastema (P<0.01). However, CCH assessed on the study models did not change (P=0.32) (Table 2). In terms of frequency, PH was decreased in 82% of the patients (49/60), and PBT was increased in 85% of the patients (47/55) after closure of the diastema. Five sites with an artifact in the study model were excluded from PBT assessment on the study models. On photographic assessment, all 60 proximal sites (100%) were judged as having a complete papilla fill (Papilla Index Score 3) at the follow-up examinations [12]. The correlation analysis between the papilla dimensions before orthodontic treatment and those at follow-up examinations revealed that the PH and PBT before the orthodontic treatment were significantly correlated (Pearson s r=0.534, P<0.001). In univariate regression analysis, the PH (P=0.002) and PBT (P=0.047), among independent variables that is, age, sex, follow-up period, CCW/CCH ratio, and the PH, PBT, DW dimensions before the orthodontic treatment significantly influenced the alteration of PH (Figure 3A and B). With respect to the alteration of PBT, the DW (P=0.045) and PBT (P<0.001) before the orthodontic treatment were found to be significant influential factors in the univariate regression analysis (Figure 3C and D). The multiple regression model that was formulated to explore the potential effects of the PH, PBT, and PBW before orthodontic treatment on the alteration of PH did not reach statistical significance (P=0.06). However, it was found that 27% of the variance in the alteration of PBT could be explained by the PH, PBT, and PBW before the orthodontic treatment. Among the Table 2. Alterations of the papilla height, clinical crown height, and papilla base thickness after orthodontic closure of the diastema Variable Before orthodontic At follow-up Difference 95 % confidence P-value treatment examination interval Photographic assessment Papilla height 5.52± ± ± / Study model assessment Clinical crown height 9.85± ± ± / Papilla base thickness 8.38± ± ± / Values are presented as mean±standard deviation. 201
6 Figure 3. Relationships between the papilla dimensions assessed before orthodontic treatment and the alterations of papilla height and papilla base thickness after orthodontic closure of the diastema. (A) Papilla height versus papilla height alteration; (B) Papilla base thickness versus papilla height alteration; (C) Diastema width versus papilla base thickness alteration; (D) Papilla base thickness versus papilla base thickness alteration. PH, papilla height; PBT, papilla base thickness; DW, diastema width. three independent variables, only the PBT (P<0.001) significantly influenced the outcome, while the PBW and PH did not significantly influence the outcome (Table 3). DISCUSSION After orthodontic closure of the maxillary midline diastema, PH decreased by 0.8 mm apically, but PBT increased by 0.5 mm in the facio-lingual direction. It has been claimed that orthodontic approximation of two adjacent teeth with diastema would increase PH coronally by squeezing the papilla volume in the proximal area [3,4,6]. However, the results of the clinical studies assessing the PH change after orthodontic closure of diastema were contradictory. In corroboration of the current study results, the heights of the interdental 202
7 Table 3. Multiple regression analysis with the alteration of papilla base thickness after orthodontic closure of the maxillary midline diastema as the dependent variable (mean change 0.5 mm) Independent Variables a) (Adjusted R 2 : 0.27) F-value: P-value of the model: Estimate SE of estimate P-value Intercept PBT PBW PH SE, standard error; PBT, papilla base thickness; PBW, papilla base width; PH, papilla height. a) Assessed before orthodontic treatment. papillae reduced following closure of the diastema in young patients between 13 and 16 years of age [7]. In contrast, it has been reported that orthodontic approximation of two adjacent teeth with diastema in adult periodontitis patients significantly enhanced the levels of the interdental papilla [8]. However, patients were reported to have a certain degree of extrusion and labial inclination due to pathologic tooth migration as a result of periodontal disease. There is a possibility of orthodontic palatal and intrusive movements that may affect the clinical crown height, and consequently the papilla level as well, since the papilla level was measured as the distance from the incisal margin of the two adjacent target teeth to the corresponding tips of interdental papillae [7]. However, the present study included only periodontally healthy young patients, and excluded patients who showed severe extrusion or labial tipping of the maxillary anterior teeth. Furthermore, to minimize the effect of possible intrusion during orthodontic treatment, PH was measured as the distance between the papilla tip level and the reference line connecting the mid-facial gingival margins of two maxillary central incisors [11] (Figure 2A). In fact, CCH, which could be influenced by the palatal and intrusive movements, did not change during the orthodontic treatment (P=0.32) (Table 2). With respect to the measurements of PH, the proportion of the papilla level in relation to CCH was used to indirectly assess the PH changes after orthodontic closure of the diastema in the clinical photographs [7], and the distance between the incisal edge and the papilla tip was measured directly in the patients with an electronic caliper [8]. In the current study, since the exact location of the papilla tip was not visible in most study models, indirect photographic assessment was utilized to assess alterations of PH. It has been shown that carefully taken photographs and study models could provide accurate measurements in comparison to the direct clinical measures of keratinized gingiva [10]. To minimize potential errors in the assessments, the CCH in each photograph was calibrated to that measured on the study model taken on the same date. The mean difference in the CCH between the two measurements was 0.02 mm (SD 0.12). Hence, the results of this study could be considered reliable, with this level of accuracy of the methods. Incomplete papilla fill, resulting in a black triangle in the proximal embrasure between the teeth, is a concern from an esthetic perspective, particularly in the visible anterior teeth region. Hence, the degree of papilla fill is a critical assessment in the judgment of the esthetic outcome [13]. Even though PH was statistically significantly decreased after orthodontic closure of the diastema in the present study (0.8 mm; P<0.001), all 60 patients were judged to have a complete papilla fill between maxillary central incisors after closure of the diastema. Hence, a complete papilla fill seemed to have been achieved by the creation of a new proximal contact between the maxillary central incisors, and possibly with a relatively short distance between the contact point and the bone crest in the proximal area [2]. The 0.8 mm difference in PH after 203
8 orthodontic closure of the diastema may not be as critical for laypeople as it is for dentists in appreciation of the papilla appearance. The laypersons did not perceive a significant difference in attractiveness even when evaluating the maximum 2 mm deviation in the papilla level [14]. In addition to PH, which is considered to be an important factor from an esthetic perspective, facio-lingual thickness of the papilla base (PBT) was evaluated in the current study. The PBT dimension was emphasized in relation to the papilla height and fill [2,15,16]. These findings were based on the observation of a positive relationship between tissue thickness and height of periodontal tissue [17] as well as peri-implant mucosa [9,18]. In the current study, PBT increased by 0.5 mm after orthodontic closure of the diastema (P<0.001), and 82% of the 55 sites showed an increase in the PBT dimension. Besides, the PBT change after orthodontic closure of the diastema was greater when the diastema width before the orthodontic treatment was greater. Based on the results, the squeezing force generated during orthodontic closure of the diastema seemed to push the papilla in the mesio-distal direction and not in the apico-coronal direction. Hence, PBT increased, but PH decreased after orthodontic closure of the diastema. The alterations of PH and PBT after orthodontic closure of the diastema were negatively influenced by the PBT before the treatment. This means that the greater the PBT before orthodontic treatment, the more the PH and PBT decreased. In contrast, the lesser the PBT before orthodontic treatment, the more the PH and PBT increased. Hence, the final PH and PBT dimensions after closure of the diastema appeared to converge toward a certain dimension, that is, biologic width. Based on the above-mentioned findings from the present study, it seemed that the primary dimensions before orthodontic treatment, especially the PBT dimension, significantly affected the alteration of the PH and PBT after orthodontic closure of the diastema. The vertical dimension of the soft tissues at the proximal sites, that is, the papilla height between an implant and a tooth in the maxillary anterior region, was greater in individuals with a thick gingival/periodontal biotype in comparison to those with a thin biotype [18]. In line with this finding, it was reported that the shape of the teeth had a significant impact on the interdental papilla score in the patients with pathologic tooth migration [8]. In the present study, the CCW/CCH ratio did not influence the alterations of PH or PBT after orthodontic closure of the diastema, but, interestingly, the correlation analysis between the papilla dimensions before orthodontic treatment revealed that PH was significantly correlated with PBT (P<0.001, Pearson s r=0.534). However, all patients in the present study were periodontally healthy and were found to have a complete papilla fill after orthodontic closure of the diastema. In order to better understand the role of the dimensional factors constituting the papilla embrasure space in the alteration of PH and PBT after orthodontic closure of the diastema, we formulated a multivariate model including the 3-dimensional papilla dimensions, that is, PH, PBT, and PBW before the orthodontic treatment as predictors [19]. Among the 3-dimensional papilla dimensions, only the PBT before treatment influenced the alterations of PBT after orthodontic closure of the diastema. Hence, one has to evaluate the PBT dimension before the orthodontic treatment as a potential factor for esthetic appreciation since PBT was reported to affect the papilla height and fill in the literature. 204
9 The limitations of this study were that the amount of the diastema closed by orthodontic approximation was limited (mean 1.1 mm, range, mm), since the patients were selected from an esthetic point of view, and hard tissue assessment was not made in relation to its role in supporting the overlying soft tissues [8]. The present study mainly focused on the evaluation of various papilla dimensions before orthodontic treatment in relation to the alterations of PH and PBT after orthodontic closure of the diastema. However, there may be additional factors, for example, tooth positions in relation to extrusion and buccal tipping, or directions and degree of orthodontic approximation force, which should be evaluated as potential factors influencing the alterations of PH and PBT after orthodontic closure of the diastema. In conclusion, PH decreased but PBT increased after orthodontic closure of the diastema. The papilla dimensions before orthodontic treatment influenced the alterations of PH and PBT after closure of the diastema. The PBT increased more when the diastema width before the orthodontic treatment was greater. REFERENCES 1. Chang LC. The association between embrasure morphology and central papilla recession. J Clin Periodontol 2007;34: Chang M, Wennström JL. Soft tissue topography and dimensions lateral to single implant-supported restorations. a cross-sectional study. Clin Oral Implants Res 2013;24: Kokich VG. Esthetics: the orthodontic-periodontic restorative connection. Semin Orthod 1996;2: Prato GP, Rotundo R, Cortellini P, Tinti C, Azzi R. Interdental papilla management: a review and classification of the therapeutic approaches. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2004;24: PUBMED 5. Sharma AA, Park JH. Esthetic considerations in interdental papilla: remediation and regeneration. J Esthet Restor Dent 2010;22: Sato S, Nomura N, Kawashima H, Ito K. Creation of a nonsurgical papilla in orthodontic treatment with severe periodontal disease: a case report. Quintessence Int 2007;38:e PUBMED 7. Kandasamy S, Goonewardene M, Tennant M. Changes in interdental papillae heights following alignment of anterior teeth. Aust Orthod J 2007;23: PUBMED 8. Kim YK, Kwon EY, Cho YJ, Lee JY, Kim SJ, Choi J. Changes in the vertical position of interdental papillae and interseptal bone following the approximation of anterior teeth. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2014;34: Cardaropoli G, Lekholm U, Wennström JL. Tissue alterations at implant-supported single-tooth replacements: a 1-year prospective clinical study. Clin Oral Implants Res 2006;17: Trentini CM, Moriarty JD, Phillips C, Tulloch JF. Evaluation of the use of orthodontic records to measure the width of keratinized tissue. J Periodontol 1995;66: Olsson M, Lindhe J, Marinello CP. On the relationship between crown form and clinical features of the gingiva in adolescents. J Clin Periodontol 1993;20: Jemt T. Regeneration of gingival papillae after single-implant treatment. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 1997;17: PUBMED 205
10 13. Fürhauser R, Florescu D, Benesch T, Haas R, Mailath G, Watzek G. Evaluation of soft tissue around singletooth implant crowns: the pink esthetic score. Clin Oral Implants Res 2005;16: Kokich VO, Kokich VG, Kiyak HA. Perceptions of dental professionals and laypersons to altered dental esthetics: asymmetric and symmetric situations. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2006;130: Gastaldo JF, Cury PR, Sendyk WR. Effect of the vertical and horizontal distances between adjacent implants and between a tooth and an implant on the incidence of interproximal papilla. J Periodontol 2004;75: Chow YC, Wang HL. Factors and techniques influencing peri-implant papillae. Implant Dent 2010;19: Wennström JL. Mucogingival considerations in orthodontic treatment. Semin Orthod 1996;2: Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K, Umezu K, Kois JC. Dimensions of peri-implant mucosa: an evaluation of maxillary anterior single implants in humans. J Periodontol 2003;74: Teughels W, Merheb J, Quirynen M. Critical horizontal dimensions of interproximal and buccal bone around implants for optimal aesthetic outcomes: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 2009;20 Suppl 4:
Analysis of the embrasure dimensions between maxillary central incisors in relation to the topography of the interdental papilla
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:273-278 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2011.41.6.273 Analysis of the embrasure dimensions between maxillary central incisors in relation to the topography
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:273-278 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2011.41.6.273 Analysis of the embrasure dimensions between maxillary central incisors in relation to the topography
Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 373e378 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 373e378 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
An analysis on the factors responsible for relative position of interproximal papilla in healthy subjects
 Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:160-167 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.4.160 An analysis on the factors responsible for relative position of interproximal
Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:160-167 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.4.160 An analysis on the factors responsible for relative position of interproximal
The Association between Embrasure Morphology and Central Papilla Recession: A Noninvasive Assessment Method. Li-Ching Chang, DDS, MS
 Original Article 445 The Association between Embrasure Morphology and Central Papilla Recession: A Noninvasive Assessment Method Li-Ching Chang, DDS, MS Background: The distance from bone crest to contact
Original Article 445 The Association between Embrasure Morphology and Central Papilla Recession: A Noninvasive Assessment Method Li-Ching Chang, DDS, MS Background: The distance from bone crest to contact
Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
 International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 125146, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/125146 Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 125146, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/125146 Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
Gender Based Comparison of Gingival Zenith Esthetics Humagain M, Rokaya D, Srii R, Dixit S, Kafle D
 Gender Based Comparison of Gingival Zenith Esthetics Humagain M, Rokaya D, Srii R, Dixit S, Kafle D ABSTRACT Background Department of Dentistry Kathmandu University School of Medical Sciences, Dhulikhel,
Gender Based Comparison of Gingival Zenith Esthetics Humagain M, Rokaya D, Srii R, Dixit S, Kafle D ABSTRACT Background Department of Dentistry Kathmandu University School of Medical Sciences, Dhulikhel,
Diastema closure with direct composite: architectural gingival contouring
 pissn 1225-0864 / eissn 2093-8179 http://dx.doi.org/10.5395/jkacd.2011.36.6.515 Case Report Diastema closure with direct composite: architectural gingival contouring Yeon-Hwa Kim, Yong-Bum Cho* Department
pissn 1225-0864 / eissn 2093-8179 http://dx.doi.org/10.5395/jkacd.2011.36.6.515 Case Report Diastema closure with direct composite: architectural gingival contouring Yeon-Hwa Kim, Yong-Bum Cho* Department
Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations
 C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Biology of periodontal and periimplant. The ideal soft tissue profile around teeth and implants
 The ideal soft tissue profile around teeth and implants Biology of periodontal and periimplant tissues Individualized abutment Péter Windisch Prof. Dr. Med. Dent. Head Of The Department Of Periodontology
The ideal soft tissue profile around teeth and implants Biology of periodontal and periimplant tissues Individualized abutment Péter Windisch Prof. Dr. Med. Dent. Head Of The Department Of Periodontology
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques
 I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2014;1(2):49-53 April-June All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and
I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2014;1(2):49-53 April-June All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association
 All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Intrusion of Incisors to Facilitate Restoration: The Impact on the Periodontium
 Note: This is a sample Eoster. Your EPoster does not need to use the same format style. For example your title slide does not need to have the title of your EPoster in a box surrounded with a pink border.
Note: This is a sample Eoster. Your EPoster does not need to use the same format style. For example your title slide does not need to have the title of your EPoster in a box surrounded with a pink border.
IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
This PDF is available for free download from a site hosted by Medknow Publications
 Review Article Esthetic considerations for the interdental papilla: Eliminating black triangles around restorations: A literature review Iyer Satishkumar Krishnan, Mohit G. Kheur Department of Prosthodontics,
Review Article Esthetic considerations for the interdental papilla: Eliminating black triangles around restorations: A literature review Iyer Satishkumar Krishnan, Mohit G. Kheur Department of Prosthodontics,
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques
 Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques Mohammad Assaf Assistant Professor, Faculty of Dentistry, Al-Quds University, Jerusalem, Palestine. ABSTRACT Correspondence
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques Mohammad Assaf Assistant Professor, Faculty of Dentistry, Al-Quds University, Jerusalem, Palestine. ABSTRACT Correspondence
SMILE AESTHETICS APPRECIATED BY LAYPERSONS
 Cite this article: Ionescu-Lungu AV, Iacob M, Zetu IN. Smile Aesthetics Appreciated by Laypersons. Stoma Edu J. 2015;2(1):17-24 SMILE APPRECIATED BY LAYPERSONS Andreea-Virginia Ionescu-Lungu a, Mihnea
Cite this article: Ionescu-Lungu AV, Iacob M, Zetu IN. Smile Aesthetics Appreciated by Laypersons. Stoma Edu J. 2015;2(1):17-24 SMILE APPRECIATED BY LAYPERSONS Andreea-Virginia Ionescu-Lungu a, Mihnea
Enameloplasty and Esthetic Finishing in Orthodontics Identification and Treatment of Microesthetic Features in Orthodontics Part 1jerd_
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Enameloplasty and Esthetic Finishing in Orthodontics Identification and Treatment of Microesthetic Features in Orthodontics Part 1jerd_446 296..302 DAVID M. SARVER, DMD, MS*, ABSTRACT
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Enameloplasty and Esthetic Finishing in Orthodontics Identification and Treatment of Microesthetic Features in Orthodontics Part 1jerd_446 296..302 DAVID M. SARVER, DMD, MS*, ABSTRACT
Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
 Galore International Journal of Health Sciences and Research Vol.3; Issue: 1; Jan.-March 2018 Website: www.gijhsr.com Review Article P-ISSN: 2456-9321 Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
Galore International Journal of Health Sciences and Research Vol.3; Issue: 1; Jan.-March 2018 Website: www.gijhsr.com Review Article P-ISSN: 2456-9321 Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars
 Received: 14 June. 2015 Accepted: 7 Dec. 2015 Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars Abstract Asghar Ebadifar DDS, MSc 1, Mohammad Hossien Shafazand
Received: 14 June. 2015 Accepted: 7 Dec. 2015 Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars Abstract Asghar Ebadifar DDS, MSc 1, Mohammad Hossien Shafazand
Analysis of crown size and morphology, and gingival shape in the maxillary anterior dentition in Korean young adults
 https://jap.or.kr J Adv Prosthodont 2017;9:315-20 https://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2017.9.4.315 Analysis of crown size and morphology, and gingival shape in the maxillary anterior dentition in Korean young
https://jap.or.kr J Adv Prosthodont 2017;9:315-20 https://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2017.9.4.315 Analysis of crown size and morphology, and gingival shape in the maxillary anterior dentition in Korean young
Alarge number of sound clinical
 Volume 83 Number 5 Long-Term 8-Year Outcomes of Coronally Advanced Flap forrootcoverage Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato,* Debora Franceschi,* Roberto Rotundo,* Francesco Cairo,* Pierpaolo Cortellini, and Michele
Volume 83 Number 5 Long-Term 8-Year Outcomes of Coronally Advanced Flap forrootcoverage Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato,* Debora Franceschi,* Roberto Rotundo,* Francesco Cairo,* Pierpaolo Cortellini, and Michele
Black triangle dilemma and its management in esthetic dentistry
 Dental Research Journal Review Article Black triangle dilemma and its management in esthetic dentistry Vijendra P. Singh 1, Ashita S. Uppoor 2, Dilip G. Nayak 2, Dipen Shah 3 1 Departments of Periodontology,
Dental Research Journal Review Article Black triangle dilemma and its management in esthetic dentistry Vijendra P. Singh 1, Ashita S. Uppoor 2, Dilip G. Nayak 2, Dipen Shah 3 1 Departments of Periodontology,
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants. Agenda. Agenda. Smile line revitalization with implants Priest Prosthodontics, LLC 1
 Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
SMALL TISSUE WITH BIG ISSUE ABSTRACT
 SMALL TISSUE WITH BIG ISSUE Dr. Arshiya Goswamy., Dr. H.S. Grover.,Dr. Shalini Kapoor *Department of Periodontology, SGT Dental College & Research Institute, Gurgaon, Delhi-NCR (Received on Date: 7 th
SMALL TISSUE WITH BIG ISSUE Dr. Arshiya Goswamy., Dr. H.S. Grover.,Dr. Shalini Kapoor *Department of Periodontology, SGT Dental College & Research Institute, Gurgaon, Delhi-NCR (Received on Date: 7 th
Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors
 Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors Faiza M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc. (1) Zainab M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc (2) ABSTRACT Background: Gingival recession
Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors Faiza M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc. (1) Zainab M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc (2) ABSTRACT Background: Gingival recession
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
A Step-by-Step Approach to
 A Step-by-Step Approach to a Diastema Closure A Dual-Purpose Technique that Manages Black Triangles Marcos Vargas, DDS, MS Figure 1: Preoperative view of a patient who presented with a diastema between
A Step-by-Step Approach to a Diastema Closure A Dual-Purpose Technique that Manages Black Triangles Marcos Vargas, DDS, MS Figure 1: Preoperative view of a patient who presented with a diastema between
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 385 Papilla Proportions in the Maxillary Anterior Dentition Stephen J. Chu, DMD, MSD, CDT* Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS ** Jocelyn H.-P. Tan,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 385 Papilla Proportions in the Maxillary Anterior Dentition Stephen J. Chu, DMD, MSD, CDT* Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS ** Jocelyn H.-P. Tan,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 69 Analysis of the Shapes of Maxillary Central Incisors in a Caucasian Population Luca Gobbato, DDS*/Teppei Tsukiyama, DDS*/Paul A. Levi,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 69 Analysis of the Shapes of Maxillary Central Incisors in a Caucasian Population Luca Gobbato, DDS*/Teppei Tsukiyama, DDS*/Paul A. Levi,
Keratinized Gingiva Width Alteration during Orthodontic Alignment and Leveling Phase; a Preliminary Investigation
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 7 Number 2 Keratinized Gingiva Width Alteration during Orthodontic Alignment and Leveling Phase; a Preliminary A Dannan, M Darwish, M Sawan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 7 Number 2 Keratinized Gingiva Width Alteration during Orthodontic Alignment and Leveling Phase; a Preliminary A Dannan, M Darwish, M Sawan Citation
Comparing esthetic smile perceptions among laypersons with and without orthodontic treatment experience and dentists
 Original Article THE KOREAN JOURNAL of ORTHODONTICS pissn 2234-7518 eissn 2005-372X Comparing esthetic smile perceptions among laypersons with and without orthodontic treatment experience and dentists
Original Article THE KOREAN JOURNAL of ORTHODONTICS pissn 2234-7518 eissn 2005-372X Comparing esthetic smile perceptions among laypersons with and without orthodontic treatment experience and dentists
Orthodontic space opening during adolescence is
 ONLINE ONLY Postorthodontic root approximation after opening space for maxillary lateral incisor implants Taylor M. Olsen a and Vincent G. Kokich, Sr b Seattle, Wash Introduction: Orthodontic space opening
ONLINE ONLY Postorthodontic root approximation after opening space for maxillary lateral incisor implants Taylor M. Olsen a and Vincent G. Kokich, Sr b Seattle, Wash Introduction: Orthodontic space opening
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Attachment G. Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080. ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA for Permanent Dentition YES NO
 First Review IL HFS Dental Program Models Second Review Ortho cad Attachment G Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080 Ceph Film X-Rays Photos Narrative Patient Name: DOB: ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA
First Review IL HFS Dental Program Models Second Review Ortho cad Attachment G Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080 Ceph Film X-Rays Photos Narrative Patient Name: DOB: ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA
Comparative Evaluation of Smile Arc in Population of Central India
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 3 Ver. VI (Mar. 2015), PP 46-51 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Evaluation of Smile Arc in
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 3 Ver. VI (Mar. 2015), PP 46-51 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Evaluation of Smile Arc in
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
RESEARCH REVIEW. Gingival recession: a proposal for a new classification ISSN :
 RESEARCH REVIEW Gingival recession: a proposal for a new classification Shantipriya Reddy, Sanjay Kaul, Prasad M.G.S., Jaya Agnihotri, Amudha D., Soumya Kambali ABSTRACT An accurate diagnosis is often
RESEARCH REVIEW Gingival recession: a proposal for a new classification Shantipriya Reddy, Sanjay Kaul, Prasad M.G.S., Jaya Agnihotri, Amudha D., Soumya Kambali ABSTRACT An accurate diagnosis is often
The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org ( this information is current as of July 11, 2011):
 Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
Esthetic Assessment of the Effect of Gingival Exposure in the Smile of Patients with Unilateral and Bilateral Maxillary Incisor Agenesis
 Esthetic Assessment of the Effect of Gingival Exposure in the Smile of Patients with Unilateral and Bilateral Maxillary Incisor Agenesis Teresa Pinho, DDS, PhD, 1 Carlos Bellot-Arcís, DDS, PhD, 2 José
Esthetic Assessment of the Effect of Gingival Exposure in the Smile of Patients with Unilateral and Bilateral Maxillary Incisor Agenesis Teresa Pinho, DDS, PhD, 1 Carlos Bellot-Arcís, DDS, PhD, 2 José
Papillary regeneration: anatomical aspects and treatment approaches
 ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Oct-Dec;9(4):448-56 Literature Review Article Papillary regeneration: anatomical aspects and treatment approaches Jaína Dias de
ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Oct-Dec;9(4):448-56 Literature Review Article Papillary regeneration: anatomical aspects and treatment approaches Jaína Dias de
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Variables Affecting the Gingival Embrasure Space in Aesthetically Important Regions: Differences between Central and Lateral Papillae
 The Open Dentistry Journal,,, - Open Access Variables Affecting the Gingival Embrasure Space in Aesthetically Important Regions: Differences between Central and Lateral Papillae Marco Montevecchi, Vittorio
The Open Dentistry Journal,,, - Open Access Variables Affecting the Gingival Embrasure Space in Aesthetically Important Regions: Differences between Central and Lateral Papillae Marco Montevecchi, Vittorio
Coronal height after expansion using a Damon system
 DOI: 10.1051/odfen/2017020 J Dentofacial Anom Orthod 2017;20:403 The authors Coronal height after expansion using a Damon system B. Ducroz 1, D. Brézulier 2, V. Bertaud-Gounot 3, O. Sorel 4 1 Qualified
DOI: 10.1051/odfen/2017020 J Dentofacial Anom Orthod 2017;20:403 The authors Coronal height after expansion using a Damon system B. Ducroz 1, D. Brézulier 2, V. Bertaud-Gounot 3, O. Sorel 4 1 Qualified
A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran
 Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported
 PROSTHODONTICS Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported crown Luca Gobbato, DDS 1 /Gianluca Paniz, DDS 2 /Fabio Mazzocco, DDS 3 / Andrea Chierico,
PROSTHODONTICS Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported crown Luca Gobbato, DDS 1 /Gianluca Paniz, DDS 2 /Fabio Mazzocco, DDS 3 / Andrea Chierico,
KJLO. A Sequential Approach for an Asymmetric Extraction Case in. Lingual Orthodontics. Case Report INTRODUCTION DIAGNOSIS
 KJLO Korean Journal of Lingual Orthodontics Case Report A Sequential Approach for an Asymmetric Extraction Case in Lingual Orthodontics Ji-Sung Jang 1, Kee-Joon Lee 2 1 Dream Orthodontic Clinic, Gimhae,
KJLO Korean Journal of Lingual Orthodontics Case Report A Sequential Approach for an Asymmetric Extraction Case in Lingual Orthodontics Ji-Sung Jang 1, Kee-Joon Lee 2 1 Dream Orthodontic Clinic, Gimhae,
Perception of maxillary dental midline shift in asymmetric faces
 Perception of maxillary dental midline shift in asymmetric faces Bruno Pereira Silva, DMD, PhD Clinical Professor of Prosthodontics School of Dentistry, University of Seville Emilio Jiménez-Castellanos,
Perception of maxillary dental midline shift in asymmetric faces Bruno Pereira Silva, DMD, PhD Clinical Professor of Prosthodontics School of Dentistry, University of Seville Emilio Jiménez-Castellanos,
Alveolar bone development before the placement
 CLINICIAN S CORNER A novel approach for implant site development through root tipping Flavio Uribe, a Thomas Taylor, b David Shafer, c and Ravindra Nanda d Farmington, Conn Implant site development through
CLINICIAN S CORNER A novel approach for implant site development through root tipping Flavio Uribe, a Thomas Taylor, b David Shafer, c and Ravindra Nanda d Farmington, Conn Implant site development through
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial
 Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Smile Design. Daniel H Ward DDS 1080 Polaris Pkwy Ste 130 Columbus OH
 Smile Design Daniel H Ward DDS 1080 Polaris Pkwy Ste 130 Columbus OH 43240 614-430-8990 dward@columbus.rr.com Incisal Placement Incisal plane parallel to the interpupillary line Vertical midline in the
Smile Design Daniel H Ward DDS 1080 Polaris Pkwy Ste 130 Columbus OH 43240 614-430-8990 dward@columbus.rr.com Incisal Placement Incisal plane parallel to the interpupillary line Vertical midline in the
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Analysis of the Shapes of Maxillary Central Incisors in a Caucasian Population Luca Gobbato, DDS*/Teppei Tsukiyama, DDS*/Paul A. Levi
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Analysis of the Shapes of Maxillary Central Incisors in a Caucasian Population Luca Gobbato, DDS*/Teppei Tsukiyama, DDS*/Paul A. Levi
Clinical Management of Tooth Size Discrepanciesjerd_
 Clinical Management of Tooth Size Discrepanciesjerd_520 155..159 Guest Experts DN GRUER, DDS, PhD* GVIN C. HEYMNN, DDS, MS ssociate Editor EDWRD J. SWIFT, JR., DMD, MS Esthetic anterior dental appearance
Clinical Management of Tooth Size Discrepanciesjerd_520 155..159 Guest Experts DN GRUER, DDS, PhD* GVIN C. HEYMNN, DDS, MS ssociate Editor EDWRD J. SWIFT, JR., DMD, MS Esthetic anterior dental appearance
Influence of certain tooth characteristics on the esthetic evaluation of a smile
 Influence of certain tooth characteristics on the esthetic evaluation of a smile Andréa Fonseca Jardim da Motta 1, José Nelson Mucha 2, Margareth Maria Gomes de Souza 3 Objective: To assess the influence
Influence of certain tooth characteristics on the esthetic evaluation of a smile Andréa Fonseca Jardim da Motta 1, José Nelson Mucha 2, Margareth Maria Gomes de Souza 3 Objective: To assess the influence
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Lifelong Craniofacial Growth and the Implications for Osseointegrated Implants
 Lifelong Craniofacial Growth and the Implications for Osseointegrated Implants Fereidoun Daftary, DDS, MSD 1 /Ramin Mahallati, DDS 1 / Oded Bahat, BDS, MSD, FACD 1 /Richard M. Sullivan, DDS 2 Purpose:
Lifelong Craniofacial Growth and the Implications for Osseointegrated Implants Fereidoun Daftary, DDS, MSD 1 /Ramin Mahallati, DDS 1 / Oded Bahat, BDS, MSD, FACD 1 /Richard M. Sullivan, DDS 2 Purpose:
New Surgical Protocol to Create Interimplant Papilla: The Preliminary Results of a Case Series
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/295813926 New Surgical Protocol to Create Interimplant Papilla: The Preliminary Results of
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/295813926 New Surgical Protocol to Create Interimplant Papilla: The Preliminary Results of
Course Objectives. HDA 2018 Dental Implant Complications. What are some common failures / problems we all encounter?
 HDA 2018 Dental Implant Complications 1 Course Objectives - Understand protocols for diagnosing and treatment planning to minimize complications - Recognize and manage intraoperative complications during
HDA 2018 Dental Implant Complications 1 Course Objectives - Understand protocols for diagnosing and treatment planning to minimize complications - Recognize and manage intraoperative complications during
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato, Carlo Baldi, Roberto Rotundo, Debora Franceschi,
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato, Carlo Baldi, Roberto Rotundo, Debora Franceschi,
Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique
 e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
 ISSN 1560-1587 81 7.18 11.51 9.21 72.84 4.94 22.22 4 Exploring the distance between upper central incisor edge and incisive papilla in Taiwanese population Sheau-Jiuan Huang 1, Tsau-Mau Chou 1, Huey-Er
ISSN 1560-1587 81 7.18 11.51 9.21 72.84 4.94 22.22 4 Exploring the distance between upper central incisor edge and incisive papilla in Taiwanese population Sheau-Jiuan Huang 1, Tsau-Mau Chou 1, Huey-Er
Root Proximity Characteristics and Type of Alveolar Bone Loss: A Case-control Study
 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 011 13/3: 73-79 Root Proximity Characteristics and Type of Alveolar Bone Loss: A Case-control Study 1 1 1 Maria-Anna Loukideli, Alexandra Tsami, Eudoxie
Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 011 13/3: 73-79 Root Proximity Characteristics and Type of Alveolar Bone Loss: A Case-control Study 1 1 1 Maria-Anna Loukideli, Alexandra Tsami, Eudoxie
Restorative Dentistry and Papilla Reconstruction in Reduced Periodontium
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT Restorative Dentistry and Papilla Reconstruction in Reduced Periodontium Robert Azzi, Daniel Etienne, Bernard Schweitz Restoring the loss of periodontal soft and hard tissues
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT Restorative Dentistry and Papilla Reconstruction in Reduced Periodontium Robert Azzi, Daniel Etienne, Bernard Schweitz Restoring the loss of periodontal soft and hard tissues
A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY
 THE EFFECTIVENESS OF SURESMILE TECHNOLOGY TO ACHIEVE PREDICTED TREATMENT OUTCOME A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY CHRISTOPHER JOHN VAUBEL IN PARTIAL
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF SURESMILE TECHNOLOGY TO ACHIEVE PREDICTED TREATMENT OUTCOME A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY CHRISTOPHER JOHN VAUBEL IN PARTIAL
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12 Accepted on:22/05/12
 SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(1): 9 18 Original Article doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0500 Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago Hiroki Imai 1), Tetsuhide Makiguchi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(1): 9 18 Original Article doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0500 Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago Hiroki Imai 1), Tetsuhide Makiguchi
Esthetic crown restorations require precise control of
 CLINICAL Technique REVIEW Crown Restorations A Review of the Positive Influence of Crown Contours on Soft-Tissue Esthetics Richard P. Kinsel, DDS; Bryan I. Pope, DMD, MSD; and Daniele Capoferri Abstract:
CLINICAL Technique REVIEW Crown Restorations A Review of the Positive Influence of Crown Contours on Soft-Tissue Esthetics Richard P. Kinsel, DDS; Bryan I. Pope, DMD, MSD; and Daniele Capoferri Abstract:
Changes of the Transverse Dental Arch Dimension, Overjet and Overbite after Rapid Maxillary Expansion (RME)
 Dental Journal Changes of the Transverse Dental Arch Dimension, Overjet and Overbite after Rapid Maxillary Expansion (RME) Department of Advanced General Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University.
Dental Journal Changes of the Transverse Dental Arch Dimension, Overjet and Overbite after Rapid Maxillary Expansion (RME) Department of Advanced General Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University.
Diastema closure using direct bonding restorations combined with orthodontic treatment: a case report
 Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Diastema closure using direct bonding restorations combined with orthodontic treatment: a case report Soon-Kong Hwang, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-
Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Diastema closure using direct bonding restorations combined with orthodontic treatment: a case report Soon-Kong Hwang, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-
A Clinical Study on the Dental and Tongue Plaque Removal Effect by Use of 360 o Round Toothbrush with Soft Bristle
 Original Article Int J Clin Prev Dent 2018;14(2):106-111 ㆍ https://doi.org/10.15236/ijcpd.2018.14.2.106 ISSN (Print) 1738-8546 ㆍ ISSN (Online) 2287-6197 A Clinical Study on the Dental and Tongue Plaque
Original Article Int J Clin Prev Dent 2018;14(2):106-111 ㆍ https://doi.org/10.15236/ijcpd.2018.14.2.106 ISSN (Print) 1738-8546 ㆍ ISSN (Online) 2287-6197 A Clinical Study on the Dental and Tongue Plaque
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques
 Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic case report.
 European International Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 6 No. 5 July 2017 Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic
European International Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 6 No. 5 July 2017 Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic
Alveolar Bone Remodeling and Development after Immediate Orthodontic Root Movement
 Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & Therapy Alveolar Bone Remodeling and Development after Immediate Orthodontic Root Abstract Introduction: Adult orthodontics is rapidly expanding primarily due
Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & Therapy Alveolar Bone Remodeling and Development after Immediate Orthodontic Root Abstract Introduction: Adult orthodontics is rapidly expanding primarily due
Nonsurgical Recovery of Interdental Title Supportive Periodontal Therapy. Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5
 Nonsurgical Recovery of Interdental Title Supportive Periodontal Therapy. Yanagishita, Y; Yoshino, K; Author(s) Matsukubo, T Taniguc Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/2851
Nonsurgical Recovery of Interdental Title Supportive Periodontal Therapy. Yanagishita, Y; Yoshino, K; Author(s) Matsukubo, T Taniguc Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/2851
Note: The short arm of the BLPG tip is of the same length and measurement as the long arm of the T-bar and the Inline tip.
 Crown Lengthening CROWN LENGTHENING (CL) GAUGE: The Crown Lengthening Gauge has the Biologic Periogauge (BLPG) tip on one end and the Papilla tip on the opposite end. The BLPG tip is used to achieve the
Crown Lengthening CROWN LENGTHENING (CL) GAUGE: The Crown Lengthening Gauge has the Biologic Periogauge (BLPG) tip on one end and the Papilla tip on the opposite end. The BLPG tip is used to achieve the
Soft Tissue Measurement Method Using Radiopaque Material on Cone-beam Computed Tomography: An Ex Vivo Validation Study
 Original Article Soft Tissue Measurement Method Using Radiopaque Material on Cone-beam Computed Tomography: An Ex Vivo Validation Study Hae-Seok Lee 1, Jeong-Ho Yun 2, Dong-Won Lee 1* 1 Department of Periodontology,
Original Article Soft Tissue Measurement Method Using Radiopaque Material on Cone-beam Computed Tomography: An Ex Vivo Validation Study Hae-Seok Lee 1, Jeong-Ho Yun 2, Dong-Won Lee 1* 1 Department of Periodontology,
RETENTION AND RELAPSE
 RETENTION AND RELAPSE DEFINITION Maintaining newly moved teeth long enough to aid in stabilizing their correction MOYERS loss of any correction achieved by any orthodontic treatment RELAPSE CAUSES OF RELAPSE
RETENTION AND RELAPSE DEFINITION Maintaining newly moved teeth long enough to aid in stabilizing their correction MOYERS loss of any correction achieved by any orthodontic treatment RELAPSE CAUSES OF RELAPSE
Scar formation and revision after the removal of orthodontic miniscrews
 Brief Report THE KOREAN JOURNAL of ORTHODONTICS pissn 2234-7518 eissn 2005-372X Scar formation and revision after the removal of orthodontic miniscrews Yoon Jeong Choi a Dong-Won Lee b Kyung-Ho Kim a Chooryung
Brief Report THE KOREAN JOURNAL of ORTHODONTICS pissn 2234-7518 eissn 2005-372X Scar formation and revision after the removal of orthodontic miniscrews Yoon Jeong Choi a Dong-Won Lee b Kyung-Ho Kim a Chooryung
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Patients esthetic demands and
 Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
THE PREVALENCE OF GINGIVAL RECESSIONS IN A GROUP OF STUDENTS IN CLUJ-NAPOCA Daniela Condor 1, H. Colo[i 2, Alexandra Roman 3
 Periodontology THE PREVALENCE OF GINGIVAL RECESSIONS IN A GROUP OF STUDENTS IN CLUJ-NAPOCA Daniela Condor 1, H. Colo[i 2, Alexandra Roman 3 1 Assistant Professor, the Department of Periodontology, the
Periodontology THE PREVALENCE OF GINGIVAL RECESSIONS IN A GROUP OF STUDENTS IN CLUJ-NAPOCA Daniela Condor 1, H. Colo[i 2, Alexandra Roman 3 1 Assistant Professor, the Department of Periodontology, the
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery
 CASE SERIES 1 OPEN ACCESS Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery Sangeeta ABSTRACT Introduction:
CASE SERIES 1 OPEN ACCESS Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery Sangeeta ABSTRACT Introduction:
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 335 Considerations of Implant Abutment and Crown Contour: Critical Contour and Subcritical Contour Huan Su, DDS* Oscar González-Martín,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 335 Considerations of Implant Abutment and Crown Contour: Critical Contour and Subcritical Contour Huan Su, DDS* Oscar González-Martín,
Several extraction socket classifications have been
 Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
치간유두보존을위한전략적연속발치술과즉시임플란트식립 : 증례보고
 CSE REPORT https://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2017.55.3.286 최근배 1 이정진 2 안승근 2 서재민 2 * 1 한빛치과의원, 2 전북대학교치의학전문대학원치과보철학교실및구강생체과학연구소 Strategic serial extractions and immediate implantation for interdental papilla
CSE REPORT https://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2017.55.3.286 최근배 1 이정진 2 안승근 2 서재민 2 * 1 한빛치과의원, 2 전북대학교치의학전문대학원치과보철학교실및구강생체과학연구소 Strategic serial extractions and immediate implantation for interdental papilla
