The Association between Embrasure Morphology and Central Papilla Recession: A Noninvasive Assessment Method. Li-Ching Chang, DDS, MS
|
|
|
- Beverly Harris
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article 445 The Association between Embrasure Morphology and Central Papilla Recession: A Noninvasive Assessment Method Li-Ching Chang, DDS, MS Background: The distance from bone crest to contact point is only the most frequently studied of the many factors that influence whether interdental papilla are present. The purpose of this study was to discover the association between embrasure morphology and central papilla recession. Methods: The central papilla was visually assessed in 310 adults using paralleling periapical radiographs of the maxillary central incisors. The following vertical distances were measured: the recession distance, i.e., papilla tip (PT) to contact point (PT-CP), bone crest (BC) to contact point (BC-CP), proximal cementoenamel junction (pcej) to contact point (pcej-cp), papilla height (PH), and bone crest to proximal cementoenamel junction (BC-pCEJ). Interdental width was measured horizontally. Subjects were divided into 4 groups according to interdental width and pcej-cp distance: long-narrow, Results: short-narrow, long-wide, and short-wide. Statistical analysis revealed the following for all four study groups: a positive correlation between papilla recession distance and age, a positive correlation between bone crest-contact point distance and age, and a negative correlation between age and papilla height. Conclusion: Central papilla recession as a result of aging occurs most frequently in the long-wide group, that is, among people who have both a wide interdental width and a long distance between the proximal cementoenamel junction and the contact point. However, other factors also affect the likelihood of central papilla recession. Thus, there is a need for further study of the interaction among these causal factors. (Chang Gung Med J 2007;30:445-52) Key words: age factors, interdental papilla, radiography, dental morphology, embrasure Today s dentists face esthetic standards that require a soft-tissue contour with an intact papilla and a symmetrical gingival outline, especially in the interdental area of the maxillary central incisors (defined as the central papilla). (1) The interdental area comprises the contact area, the interproximal embrasure, and the interproximal dentogingival complex. (2) The interdental papilla is the gingival portion of the interdental area. However, the physiology of the papilla is more complex than that of other gingival regions. (3) The interdental gingiva of the incisor region usually is shaped as a pyramidal papilla, or it may appear as a slight gingival col, depending on the location of the contact area and the height of the gin- From the Department of Dentistry, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chiayi, Chang Gung University College of Medicine, Taoyuan, Taiwan. Received: Nov. 3, 2006; Accepted: Feb. 16, 2007 Correspondence to: Dr. Li-Ching Chang, Department of Dentistry, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital. 6, W. Sec., Jiapu Rd., Puzih City, Chiayi County 613, Taiwan (R.O.C.) Tel.: ext. 2277; Fax: ext. 2279; liching@ms39.hinet.net
2 Li-Ching Chang 446 giva. (4,5) The presence of space below the contact area can lead to esthetic impairment, phonic problems, and food impaction. (1,6,7) If papilla loss occurs due solely to soft-tissue damage, reconstructive techniques can completely restore it; but if severe periodontal disease and interproximal bone resorption cause the loss of interdental papilla, reconstruction is generally incomplete. (3,6) The morphologies of the interdental papilla and the osseous architecture housing the tooth can be categorized into two periodontal biotypes: the thin, scalloped periodontium, characterized by thin gingival tissue and long interdental papillae; and the thick, flat periodontium, characterized by a thick osseous structure, flat morphology, thick gingival tissue, and a short, wide papilla. (8-10) Individuals with the thin periodontal biotype may have more soft-tissue recession than those with the thick periodontal biotype. (11) Although the interdental gingival tissue possesses biologic tissue memory, rebound of gingival tissue is more likely in the thick periodontium than in the thin, scalloped periodontium, where recession is often permanent. (12,13) In 1992, Tarnow et al. reported that when the distance between the contact point and the bone crest was 5 mm or less, the papilla was usually present; when this distance was 7 mm or more, the papilla was usually absent. (7) In addition, other factors, such as age, angulation of the roots of adjacent teeth, the shape of the crown, the space between adjacent teeth, the volume of the embrasure space, and the course of the cementoenamel junction also help determine whether interdental papilla will be present. (1,3,6,7,14-17) The author was unable to find a published study that focused on the relationship between age and papilla recession in different embrasure morphologies. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to use a simple, noninvasive method to elucidate the relationship between embrasure morphology and age-related central papilla recession. METHODS Subjects Between July 2004 and January 2006, 380 adults with fully erupted permanent dentition were randomly selected from the patient population of the dental department of the Chang Gung memorial hospital, Chiayi branch. Inclusion criteria were healthy gingiva with a plaque-and-gingival index of 0-1 (18) and well-aligned natural-tooth maxillary central incisors. Exclusion criteria were systemic compromise (e.g., pregnancy or a history of taking medications known to increase the risk of gingival hyperplasia), central incisors with an artificial crown, proximal/cervical restorations or abrasion, a history of surgery in the anterior maxillary area, or open contact or crowding as observed visually without aid. Seventy subjects were excluded because of conditions such as an angular bone crest in the mesiodistal direction, open contact depicted on radiographs, or a distance from the bone crest to the contact area of more than 8 mm. There were 310 subjects included in the study. Data collection One periodontist performed visual examinations to detect a papilla between the central maxillary incisors. If no space was visible apical to the contact area, the papilla was recorded as present. If a space was visible apical to the contact area, it was filled with a temporary radiopaque restorative material (Caviton, GC Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). Periapical radiographs were obtained using a paralleling technique with a film holder (XCP, Rinn Corporation, Elgin, IL). (16,17) To verify the radiographic magnification, a 10- mm wire was bonded to the right central incisor on the labial surface of 20 subjects as an indicator of the magnification. The average magnification of the method was 1.06 times. The subjects sex and age were recorded. The following vertical distances were measured: 1. Papilla tip to contact point (PT-CP): the length of a vertical line from the apical margin of the space filled with the temporary hydraulic restorative to the apical point of the contact area. This distance is equal to the distance of papilla recession. 2. Proximal cementoenamel junction to contact point (pcej-cp): the length of a vertical line from the proximal CEJ line of the two central incisors to the apical point of the contact area. 3. Bone crest to contact point (BC-CP): the length of a vertical line from the bone crest to the apical point of the contact area. 4. Bone crest to papilla tip (BC-PT): the length of a vertical line from the crest of the bone to the papilla tip. This distance is also the papilla height.
3 447 Li-Ching Chang 5. Bone crest to proximal cementoenamel junction (BC-pCEJ): the length of a vertical line from the crest of the bone to the proximal CEJ line of the two central incisors. All vertical lines were measured along the long axis of an adjacent tooth. Interdental width (W), the width between the two central incisors at the proximal CEJ level, was measured horizontally. The vertical and horizontal distances were measured on periapical radiographs using an electric measuring ruler (Kinglife Corporation, R.O.C.). (Figures 1 and 2). In order to verify the reproducibility of measurements by the examiner, 5 periapical films were randomly selected, and the measurements for each were repeated 30 times. The standard deviations were all less than 0.16 mm. (19) Subjects were divided into four groups according to their W and pcej-cp measurements, as follows: short-narrow (SN group: W < 2 mm and pcej- CP < 4 mm); long-narrow (LN group: W < 2 mm and pcej-cp 4 mm); short-wide (SW group: W 2 mm and pcej-cp < 4 mm); and long-wide (LW group: W 2 mm and pcej-cp 4 mm). (Figures 3) Statistical analysis Commercially available statistical software (SPSS version 11.5, SPSS, Chicago, IL) was used to analyze the data. Data are presented as mean standard deviation. A Non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis Test was used to evaluate differences among the four study groups. Spearman rank correlation was used to measure associations between two variables, i.e., age and papilla recession. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis was used to define cutoff points for diagnostic tests, i.e., age > 29 and BC-CP distance > 5.1 mm. Logistic regression was applied when outcome variables were binary; i.e., logistic regression was applied to the odds of papilla recession. The level of statistical significance was set at p < Bone crest (BC) proximal cementoennamel junction (pcej) Papilla Tip (PT) Contact Point (CP) Interdental width Fig. 1 The horizontal lines indicate the following locations, from top to bottom: bone crest (BC), proximal cementoenamel junction (pcej), papilla tip (PT), and contact point (CP). The distance between PT and CP is PT-CP, the distance between pcej and CP is pcej-cp, the distance between BC and CP is BC-CP, the distance between BC and PT is papilla height, and the distance between BC and pcej is BC-pCEJ. Fig. 2 Interdental width (W) is the horizontal distance between central incisors at the level of the proximal cementoenamel junction.
4 Li-Ching Chang 448 A B C D Fig. 3 The different embrasure morphologies, including: long-narrow, short-narrow, long-wide, and short-wide groups. (A) Longnarrow: W < 2 mm and pcej-cp 4 mm. (B) Short-narrow: W < 2 mm and pcej-cp < 4 mm. (C) Long-wide: W 2 mm and pcej-cp 4 mm. (D) Short-wide: W 2 mm and pcej-cp < 4 mm. RESULTS The 310 study subjects comprised 180 males and 130 females. The mean age in years was The morphologic characteristics of the four groups are listed in Table 1. As Table 1 shows, many criteria-such as age, papilla recession distance, the vertical distance between bone crest and contact point, and papillary height-differed significantly among the four groups. Table 2 shows the associations between various distances and age. Age was positively related to the distance of the recession and negatively related to papillary height in all groups. This relation was much stronger in the long-wide group than in the other groups. The odds of papilla absence for the various groups are listed in Table 3. There was a lower risk of central papilla recession in the short-narrow group than in the other groups. This means that the likeli- Table 1. The Morphologic and Non-morphologic Variables of the Four Study Groups Long-narrow Short-narrow Long-wide Short-wide mean S.D. mean S.D. mean S.D. mean S.D. p value N Morphologic variables pcej-cp < 0.001* interdental width (W) < 0.001* pcej-cp/w ratio < 0.001* Non-morphologic variables Age (in years) < 0.001* PT-CP (papilla recession distance) < 0.001* BC-CP < 0.001* BC-PT (papilla height = PH) = 0.001* PH in PR (-) subgroup < 0.001* PH in PR (+) subgroup < 0.001* Abbreviations: *: Statistically significant; PR (-) : Without papilla recession; PR (+) : With papilla recession
5 449 Li-Ching Chang Table 2. The Correlation between Age and Bone Crest-contact Point Distance (BC-CP Distance), Papilla Height and Papilla Recession Distance Age Spearman rank p value correlation BC-CP Long-narrow < 0.001* Distance Short-narrow < 0.001* Long-wide * Short-wide < 0.001* Papilla height Long-narrow * Short-narrow * Long-wide < 0.001* Short-wide Papilla recession Long-narrow < 0.001* distance Short-narrow < 0.001* Long-narrow < 0.001* Short-wide < 0.001* *: Statistically significant Table 3. The Risk of Papilla Recession among the Four Study Groups Odds ratio 95% C.I. p value Non-adjustment by age and bone crest-contact point distance Short-narrow 1.00 Long-narrow Short-wide * Long-wide * Adjustment by age and bone crest-contact point distance Short-narrow 1.00 Long-narrow Short-wide Long-wide Age Age > < 0.001* BC-CP BC-CP > < 0.001* *: Statistically significant hood of papilla recession in the long-narrow group was 1.04 times the likelihood of papilla recession in the short-narrow group, but the odds in the long-narrow group were not statistically significant. The odds of papilla recession in the long-wide group and the short-wide group were 2.64 and 3.14, respectively (Table 3). Because a previous study by the author showed that age and BC-CP distance can affect the incidence of papilla presence, (16,17) further analysis was done after adjustment by age and BC-CP distance. There was no statistical significance in the odds for the four groups after adjustment by age and BC-CP distance (values of age > 29 and BC-CP distance > 5.1 mm were obtained from the ROC analysis used to define cutoff points for diagnostic tests in previous study) (20) (Table 3). DISCUSSION The recession of the interdental papilla, especially in the area of the central maxillary incisors, is of great concern to dentists and patients. Many factors account for the presence of the interdental papilla; the distance from bone crest to contact point is the most commonly studied of these, but there are many others. (1,3,6,7,14-17) There is an important need in esthetic dentistry to identify the risk factors for recession of the central papilla, including the association between embrasure morphology and central papilla presence. The author excluded subjects with a BC-CP distance greater than 8 mm, because all such subjects would have central papilla recession. Subsequently, the embrasure morphologies of the study subjects were classified into four groups according to pcej- CP distance and pcej width, respectively: long-narrow, short-narrow, long-wide, and short-wide. There were many more subjects in the SN group than any of the other groups. There was a positive relationship between age and BC-CP distance, owing to physical bone resorption. (17) The relationships between BC-CP distance and age were statistically significant in all four study groups (LN, SN, LW, SW). The relationships between papilla height and age were statistically significant for the LN, SN, and LW groups, but not for the SW group. Study results reveal that papilla height decreases with age. Vandana and Savitha observed that the gingivae of younger individuals were significantly thicker than
6 Li-Ching Chang 450 those of older individuals. This is because the papilla is constituted by a dense connective tissue covered by oral epithelium. Aging changes the oral epithelium by thinning it and diminishing keratinization. Traumatic oral hygiene or genetic factors may also contribute to the inverse relationship between age and papillary height. (6,21-23) The study also revealed a positive relationship between age and papilla recession distance. Papilla recession distance was equal to the difference between BC-CP distance and papilla height; thus, the strongest negative relation between age and papilla height was observed in the LW group. This finding may reflect greater bone volume loss at the same height of bone crest resorption in the wide groups (LW and SW) than in the narrow groups (LN and SN). Also, the LW group had narrower widths than the short-wide group, so the height of the black triangle (i.e., papilla recession distance) was greater in the LW group. (The area of the black triangle is approximately equal to PT width PT-CP height 0.5). In previous studies, papillary height was measured by sounding, with the patient under local anesthesia; however, this method is invasive and only allows for buccal measurement. (1,7,15) The author developed a noninvasive method of measurement that was accurate, simple to use, and easily accepted by subjects. (16,17) The method uses Caviton, a temporary radiopaque restorative material. Lee s study suggests another noninvasive method: using a radiopaque material (a 2:1 mixture of an endodontic sealer and barium sulfate) and periapical radiographs to measure the length of the interdental papilla in relation to the crestal bone. This method would enable more accurate prognoses for a regenerated papilla. (24) The results of this study revealed that the likelihood of central papilla recession can be ranked according to embrasure morphology as follows (in ascending order): SN, LN, LW, and SW. In a previous study, the author found that age and BC-CP distance had some effect on central papilla presence. (20) After adjusting for age and BC-CP distance, the groups can be ranked according to the odds of central papilla recession for each as follows (in ascending order): SN, LN, SW, and LW. Differences between the odds of papilla recession for the two analyses may arise from differences in mean age and mean BC-CP distance for the four study groups. Additionally, age and BC-CP distance may have a greater effect on central papilla presence than embrasure morphology. Consequently there was no statistical significance in all groups after adjustment. This study found the occurrence of a black triangle to be significantly related to age on account of to the increasing distance between bone crest and contact point and decreasing papilla height, especially in the long-wide group. Even so, other factors also helped determine whether the interdental papilla would be present or not. Further study of the interrelations among these factors is needed. REFERENCES 1. Choquet V, Hermans M, Adriaenssens P, Daelemans P, Tarnow DP, Malevz C. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of the papilla level adjacent to single-tooth dental implants: A retrospective study in the maxillary anterior region. J Periodontol 2001;72: Takei HH. The interdental space. Dent Clin North Am 1980;24: Zetu L, Wang HL. Management of inter-dental/interimplant papilla. J Clin Periodontol 2005;32: Cohen B. Morphological factors in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. Brit Dent J 1959;107: Cohen B. A study of the periodontal epithelium. Brit Dent J 1962;112: Prato GP, Rotundo R, Cortellini P, Tinti C, Azzi R. Interdental papilla management: A review and classification of the therapeutic approaches. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2004;24: Tarnow DP, Magner AW, Fletcher P. The effect of the distance from the contact point to the crest of bone on the presence or absence of the interproximal dental papilla. J Periodontol 1992;63: Oschsenbein C, Ross S. A reevaulation of osseous surgery. Dent Clin North Am 1969;13: Weisgold A. Contours of the full crown restoration. Alpha Omegan 1997;70: Becker W, Oschsenbein C, Tibbetts L, Becker BE. Alveolar bone anatomic profiles as measured from dry skulls: Clinical ramifications. J Clin Periodontol 1997;24: Olsson M, Lindhe J. Periodontal characteristics in individuals with varying form of the upper central incisors. J Clin Periodontol 1991;18: van der Velden U. Regeneration of the interdental soft tissue following denudation procedure. J Clin Periodontol 1982;9: Kan JKY, Rungcharassaeng K. Site development for anterior single implant esthetics: The dentulous site. Compendium 2001;22:
7 451 Li-Ching Chang 14. Kurth JR, Kokich VG. Open gingival embrasures after orthodontic treatment in adults: Prevalence and etiology. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2001;120: Gastaldo JF, Cury PR, Sendyk WR. Effect of the vertical and horizontal distances between adjacent implants and between adjacent implants and between a tooth and an implant on the incidence of interproximal papilla. J Periodontol 2004;75: Chang LC. The central papilla height in associated with age and gender - assessed with a new method. Chin J Periodontol 2006;11: Chang LC. The presence of a central papilla is associated with age but not gender. J Dent Sci 2006;1: Loe H, Silness J. Periodontal disease in pregnancy. I. Prevalence and severity. Acta Odontologica Scandinavica 1963;21: Wu YJ, Tu YK, Huang SM, Chan CP. The influence of the distance from the contact point to the crest of bone on the presence of the interproximal dental papilla. Chang Gung Med J 2003;26: Chang LC. Criteria for predicting the presence of the central papilla - using a noninvasive method. J Dent Sci 2007;2: Vandana KL, Savitha B. Thickness of gingivae in association with age, gender and dental arch location. J Clin Periodontol 2005;32: Wara-aswapati N, Pitiphat W, Chandrapho N, Rattanayatikul C, Karimbux N. Thickness of palatal masticatory mucosa associated with age. J Periodontol 2001;72: Litonjua LA, Andreana S, Bush PJ, Cohen RE. Toothbrushing and gingival recession. Int Dent J 2003;53: Lee DW, Kim CK, Park KH, Cho KS, Moon IS. Noninvasive method to measure the length of soft tissue from the top of the papilla to the crest bone. J Periodontol 2005;76:
8 452 (central papilla) (central papilla recession) - (bone crest-contact point distance) (papilla presence) x (Paralleling periapical radiography) x (Caviton) X ( bone crest-contact point distance, interdental width ) (narrowshort, narrow-long, wide-short and wide-long groups) ( 2007;30:445-52) Tel.: (05) ; Fax: (05) ; liching@ms39.hinet.net
Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 373e378 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 373e378 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
Factors influencing the length of the interproximal dental papilla between maxillary anterior teeth
 J Dent Sci 2009;4(3):103 109 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors influencing the length of the interproximal dental papilla between maxillary anterior teeth Min-Chieh Chen, 1,2 Chiu-Po Chan, 2,3 * Yu-Kang Tu, 4 Yu-Fang
J Dent Sci 2009;4(3):103 109 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors influencing the length of the interproximal dental papilla between maxillary anterior teeth Min-Chieh Chen, 1,2 Chiu-Po Chan, 2,3 * Yu-Kang Tu, 4 Yu-Fang
Diastema closure with direct composite: architectural gingival contouring
 pissn 1225-0864 / eissn 2093-8179 http://dx.doi.org/10.5395/jkacd.2011.36.6.515 Case Report Diastema closure with direct composite: architectural gingival contouring Yeon-Hwa Kim, Yong-Bum Cho* Department
pissn 1225-0864 / eissn 2093-8179 http://dx.doi.org/10.5395/jkacd.2011.36.6.515 Case Report Diastema closure with direct composite: architectural gingival contouring Yeon-Hwa Kim, Yong-Bum Cho* Department
Analysis of the embrasure dimensions between maxillary central incisors in relation to the topography of the interdental papilla
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:273-278 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2011.41.6.273 Analysis of the embrasure dimensions between maxillary central incisors in relation to the topography
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:273-278 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2011.41.6.273 Analysis of the embrasure dimensions between maxillary central incisors in relation to the topography
An analysis on the factors responsible for relative position of interproximal papilla in healthy subjects
 Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:160-167 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.4.160 An analysis on the factors responsible for relative position of interproximal
Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:160-167 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.4.160 An analysis on the factors responsible for relative position of interproximal
Restorative Dentistry and Papilla Reconstruction in Reduced Periodontium
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT Restorative Dentistry and Papilla Reconstruction in Reduced Periodontium Robert Azzi, Daniel Etienne, Bernard Schweitz Restoring the loss of periodontal soft and hard tissues
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT Restorative Dentistry and Papilla Reconstruction in Reduced Periodontium Robert Azzi, Daniel Etienne, Bernard Schweitz Restoring the loss of periodontal soft and hard tissues
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association
 All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
Alterations of papilla dimensions after orthodontic closure of the maxillary midline diastema: a retrospective longitudinal study
 J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016 Jun;46(3):197-206 pissn 2093-2278 eissn 2093-2286 Research Article after orthodontic closure of the maxillary midline diastema: a retrospective longitudinal study Jin-Seok
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016 Jun;46(3):197-206 pissn 2093-2278 eissn 2093-2286 Research Article after orthodontic closure of the maxillary midline diastema: a retrospective longitudinal study Jin-Seok
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org ( this information is current as of July 11, 2011):
 Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques
 I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2014;1(2):49-53 April-June All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and
I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2014;1(2):49-53 April-June All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 385 Papilla Proportions in the Maxillary Anterior Dentition Stephen J. Chu, DMD, MSD, CDT* Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS ** Jocelyn H.-P. Tan,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 385 Papilla Proportions in the Maxillary Anterior Dentition Stephen J. Chu, DMD, MSD, CDT* Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS ** Jocelyn H.-P. Tan,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
 International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 125146, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/125146 Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 125146, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/125146 Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
This PDF is available for free download from a site hosted by Medknow Publications
 Review Article Esthetic considerations for the interdental papilla: Eliminating black triangles around restorations: A literature review Iyer Satishkumar Krishnan, Mohit G. Kheur Department of Prosthodontics,
Review Article Esthetic considerations for the interdental papilla: Eliminating black triangles around restorations: A literature review Iyer Satishkumar Krishnan, Mohit G. Kheur Department of Prosthodontics,
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 69 Analysis of the Shapes of Maxillary Central Incisors in a Caucasian Population Luca Gobbato, DDS*/Teppei Tsukiyama, DDS*/Paul A. Levi,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 69 Analysis of the Shapes of Maxillary Central Incisors in a Caucasian Population Luca Gobbato, DDS*/Teppei Tsukiyama, DDS*/Paul A. Levi,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Black triangle dilemma and its management in esthetic dentistry
 Dental Research Journal Review Article Black triangle dilemma and its management in esthetic dentistry Vijendra P. Singh 1, Ashita S. Uppoor 2, Dilip G. Nayak 2, Dipen Shah 3 1 Departments of Periodontology,
Dental Research Journal Review Article Black triangle dilemma and its management in esthetic dentistry Vijendra P. Singh 1, Ashita S. Uppoor 2, Dilip G. Nayak 2, Dipen Shah 3 1 Departments of Periodontology,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Analysis of the Shapes of Maxillary Central Incisors in a Caucasian Population Luca Gobbato, DDS*/Teppei Tsukiyama, DDS*/Paul A. Levi
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Analysis of the Shapes of Maxillary Central Incisors in a Caucasian Population Luca Gobbato, DDS*/Teppei Tsukiyama, DDS*/Paul A. Levi
Variables Affecting the Gingival Embrasure Space in Aesthetically Important Regions: Differences between Central and Lateral Papillae
 The Open Dentistry Journal,,, - Open Access Variables Affecting the Gingival Embrasure Space in Aesthetically Important Regions: Differences between Central and Lateral Papillae Marco Montevecchi, Vittorio
The Open Dentistry Journal,,, - Open Access Variables Affecting the Gingival Embrasure Space in Aesthetically Important Regions: Differences between Central and Lateral Papillae Marco Montevecchi, Vittorio
Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations
 C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
SMALL TISSUE WITH BIG ISSUE ABSTRACT
 SMALL TISSUE WITH BIG ISSUE Dr. Arshiya Goswamy., Dr. H.S. Grover.,Dr. Shalini Kapoor *Department of Periodontology, SGT Dental College & Research Institute, Gurgaon, Delhi-NCR (Received on Date: 7 th
SMALL TISSUE WITH BIG ISSUE Dr. Arshiya Goswamy., Dr. H.S. Grover.,Dr. Shalini Kapoor *Department of Periodontology, SGT Dental College & Research Institute, Gurgaon, Delhi-NCR (Received on Date: 7 th
Esthetic crown restorations require precise control of
 CLINICAL Technique REVIEW Crown Restorations A Review of the Positive Influence of Crown Contours on Soft-Tissue Esthetics Richard P. Kinsel, DDS; Bryan I. Pope, DMD, MSD; and Daniele Capoferri Abstract:
CLINICAL Technique REVIEW Crown Restorations A Review of the Positive Influence of Crown Contours on Soft-Tissue Esthetics Richard P. Kinsel, DDS; Bryan I. Pope, DMD, MSD; and Daniele Capoferri Abstract:
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques
 Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques Mohammad Assaf Assistant Professor, Faculty of Dentistry, Al-Quds University, Jerusalem, Palestine. ABSTRACT Correspondence
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques Mohammad Assaf Assistant Professor, Faculty of Dentistry, Al-Quds University, Jerusalem, Palestine. ABSTRACT Correspondence
Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
 Galore International Journal of Health Sciences and Research Vol.3; Issue: 1; Jan.-March 2018 Website: www.gijhsr.com Review Article P-ISSN: 2456-9321 Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
Galore International Journal of Health Sciences and Research Vol.3; Issue: 1; Jan.-March 2018 Website: www.gijhsr.com Review Article P-ISSN: 2456-9321 Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
Biologic width: Understanding and its preservation Malathi K 1, Singh A 2
 Biologic width: Understanding and its preservation Malathi K 1, Singh A 2 Review Article 1 Dr K Malathi Professor & Head, Periodontics Government Dental college and Hospital Tamil Nadu, India 2 Dr Arjun
Biologic width: Understanding and its preservation Malathi K 1, Singh A 2 Review Article 1 Dr K Malathi Professor & Head, Periodontics Government Dental college and Hospital Tamil Nadu, India 2 Dr Arjun
Treatment of Altered Passive Eruption: Periodontal Plastic Surgery of the Dentogingival Junction
 CASE REPORT Publication Treatment of Altered Passive Eruption: Periodontal Plastic Surgery of the Dentogingival Junction Roberto Rossi, DDS, MScD Private Practice Genoa, Italy Remo Benedetti, MD, DDS Private
CASE REPORT Publication Treatment of Altered Passive Eruption: Periodontal Plastic Surgery of the Dentogingival Junction Roberto Rossi, DDS, MScD Private Practice Genoa, Italy Remo Benedetti, MD, DDS Private
Root Proximity Characteristics and Type of Alveolar Bone Loss: A Case-control Study
 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 011 13/3: 73-79 Root Proximity Characteristics and Type of Alveolar Bone Loss: A Case-control Study 1 1 1 Maria-Anna Loukideli, Alexandra Tsami, Eudoxie
Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 011 13/3: 73-79 Root Proximity Characteristics and Type of Alveolar Bone Loss: A Case-control Study 1 1 1 Maria-Anna Loukideli, Alexandra Tsami, Eudoxie
Papillary regeneration: anatomical aspects and treatment approaches
 ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Oct-Dec;9(4):448-56 Literature Review Article Papillary regeneration: anatomical aspects and treatment approaches Jaína Dias de
ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Oct-Dec;9(4):448-56 Literature Review Article Papillary regeneration: anatomical aspects and treatment approaches Jaína Dias de
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Black triangles causes and management: a review of literature. 1- Faculty of Dentistry, Aljouf University, Sakaka-Aljouf, Saudi Arabia.
 Black triangles causes and management: a review of literature Al-Zarea BK 1,Sghaireen MG 2, Alomari WM 3, Bheran H 4 and Taher I 5 1- Faculty of Dentistry, Aljouf University, Sakaka-Aljouf, Saudi Arabia.
Black triangles causes and management: a review of literature Al-Zarea BK 1,Sghaireen MG 2, Alomari WM 3, Bheran H 4 and Taher I 5 1- Faculty of Dentistry, Aljouf University, Sakaka-Aljouf, Saudi Arabia.
Gingival Biotype and Gingival Bioform: Determining Factors for Periodontal Disease Progression and Treatment Outcome
 Review Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/357 Gingival Biotype and Gingival Bioform: Determining Factors for Periodontal Disease Progression and Treatment Outcome
Review Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/357 Gingival Biotype and Gingival Bioform: Determining Factors for Periodontal Disease Progression and Treatment Outcome
Factors associated with the appearance of gingival papillae
 J Clin Periodontol 2010; 37: 719 727 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01594.x Factors associated with the appearance of gingival papillae Chow YC, Eber RM, Tsao Y-P, Shotwell JL, Wang H-L. Factors associated
J Clin Periodontol 2010; 37: 719 727 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01594.x Factors associated with the appearance of gingival papillae Chow YC, Eber RM, Tsao Y-P, Shotwell JL, Wang H-L. Factors associated
Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors
 Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors Faiza M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc. (1) Zainab M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc (2) ABSTRACT Background: Gingival recession
Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors Faiza M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc. (1) Zainab M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc (2) ABSTRACT Background: Gingival recession
Alveolar bone development before the placement
 CLINICIAN S CORNER A novel approach for implant site development through root tipping Flavio Uribe, a Thomas Taylor, b David Shafer, c and Ravindra Nanda d Farmington, Conn Implant site development through
CLINICIAN S CORNER A novel approach for implant site development through root tipping Flavio Uribe, a Thomas Taylor, b David Shafer, c and Ravindra Nanda d Farmington, Conn Implant site development through
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
14/09/15. Assessment of Periodontal Disease. Outline. Why is Periodontal assessment needed? The Basics of Periodontal assessment
 Assessment of Periodontal Disease Dr Wendy Turner Outline Why is Periodontal assessment needed? The Basics of Periodontal assessment Probing: Basic Periodontal Examination for adults and children. Detailed
Assessment of Periodontal Disease Dr Wendy Turner Outline Why is Periodontal assessment needed? The Basics of Periodontal assessment Probing: Basic Periodontal Examination for adults and children. Detailed
The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration
 IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12 Accepted on:22/05/12
 SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
A Step-by-Step Approach to
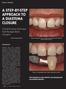 A Step-by-Step Approach to a Diastema Closure A Dual-Purpose Technique that Manages Black Triangles Marcos Vargas, DDS, MS Figure 1: Preoperative view of a patient who presented with a diastema between
A Step-by-Step Approach to a Diastema Closure A Dual-Purpose Technique that Manages Black Triangles Marcos Vargas, DDS, MS Figure 1: Preoperative view of a patient who presented with a diastema between
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
Intrusion of Incisors to Facilitate Restoration: The Impact on the Periodontium
 Note: This is a sample Eoster. Your EPoster does not need to use the same format style. For example your title slide does not need to have the title of your EPoster in a box surrounded with a pink border.
Note: This is a sample Eoster. Your EPoster does not need to use the same format style. For example your title slide does not need to have the title of your EPoster in a box surrounded with a pink border.
Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical investigation
 American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com eissn: 2347-2766 Original Research Article Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical Ninad Moon 1, Prasant Pillai
American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com eissn: 2347-2766 Original Research Article Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical Ninad Moon 1, Prasant Pillai
Patients esthetic demands and
 Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Implant Site Development Part I
 REVIEW ARTICLE Implant Site Development Part I 1 Umang Nayar, 2 Shankar Iyer IJCID Implant Site Development Part I 1 Consultant, Dental Surgeon and Periodontist at Max Health Care, New Delhi, Professor
REVIEW ARTICLE Implant Site Development Part I 1 Umang Nayar, 2 Shankar Iyer IJCID Implant Site Development Part I 1 Consultant, Dental Surgeon and Periodontist at Max Health Care, New Delhi, Professor
Dental Implants and Esthetics
 Continuing Education Brought to you by Dental Implants and Esthetics Course Author(s): Charles J. Goodacre, DDS, MSD; Chad J. Anderson, MS, DMD CE Credits: 1 hour Intended Audience: Dentists, Dental Hygienists,
Continuing Education Brought to you by Dental Implants and Esthetics Course Author(s): Charles J. Goodacre, DDS, MSD; Chad J. Anderson, MS, DMD CE Credits: 1 hour Intended Audience: Dentists, Dental Hygienists,
Study of etiology and prevalence of gingival recession in mandibular incisors in school children
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2016, 8 (3):273-278 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2016, 8 (3):273-278 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Gender Based Comparison of Gingival Zenith Esthetics Humagain M, Rokaya D, Srii R, Dixit S, Kafle D
 Gender Based Comparison of Gingival Zenith Esthetics Humagain M, Rokaya D, Srii R, Dixit S, Kafle D ABSTRACT Background Department of Dentistry Kathmandu University School of Medical Sciences, Dhulikhel,
Gender Based Comparison of Gingival Zenith Esthetics Humagain M, Rokaya D, Srii R, Dixit S, Kafle D ABSTRACT Background Department of Dentistry Kathmandu University School of Medical Sciences, Dhulikhel,
Uprighting Movement Relative to Defects Forced Eruption Alteration of the Gingival Embrasure Interactions with Implants
 Frank Celenza DDS Periodontist and Orthodontist Past President, Northeastern Society of Periodontists Associate Clinical Professor, New York University Member, ITI (International Team of Implantologists)
Frank Celenza DDS Periodontist and Orthodontist Past President, Northeastern Society of Periodontists Associate Clinical Professor, New York University Member, ITI (International Team of Implantologists)
Osseous surgery in periodontal treatment
 SCIENTIFIC SESSION Osseous surgery in periodontal treatment Essayist: Roberto Pontoriero Introduction In periodontally involved patients, periodontal therapy usually results in various degrees of soft-tissue
SCIENTIFIC SESSION Osseous surgery in periodontal treatment Essayist: Roberto Pontoriero Introduction In periodontally involved patients, periodontal therapy usually results in various degrees of soft-tissue
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
RAJ M. SAINI, DDS, MSD
 Restoring and Maintaining Periodontal Health with Orthodontic Treatment RAJ M. SAINI, DDS, MSD rajmsaini@yahoo.com Diplomate Of The American Board Of Orthodontics Clinical Professor Of Orthodontics New
Restoring and Maintaining Periodontal Health with Orthodontic Treatment RAJ M. SAINI, DDS, MSD rajmsaini@yahoo.com Diplomate Of The American Board Of Orthodontics Clinical Professor Of Orthodontics New
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 289 A Classification System for Crestal and Radicular Dentoalveolar Bone Phenotypes George A. Mandelaris, DDS, MS 1 Brian S. Vence, DDS
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 289 A Classification System for Crestal and Radicular Dentoalveolar Bone Phenotypes George A. Mandelaris, DDS, MS 1 Brian S. Vence, DDS
Orthodontic space opening during adolescence is
 ONLINE ONLY Postorthodontic root approximation after opening space for maxillary lateral incisor implants Taylor M. Olsen a and Vincent G. Kokich, Sr b Seattle, Wash Introduction: Orthodontic space opening
ONLINE ONLY Postorthodontic root approximation after opening space for maxillary lateral incisor implants Taylor M. Olsen a and Vincent G. Kokich, Sr b Seattle, Wash Introduction: Orthodontic space opening
Esthetic Implant Dentistry: Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
 SECTION 4 Implant Surgery 26 Esthetic Implant Dentistry: Diagnosis and Treatment Planning SAJ JIVRAJ, MAMALY RESHAD Introduction Achieving esthetics with implant restorations is significantly more challenging
SECTION 4 Implant Surgery 26 Esthetic Implant Dentistry: Diagnosis and Treatment Planning SAJ JIVRAJ, MAMALY RESHAD Introduction Achieving esthetics with implant restorations is significantly more challenging
Enameloplasty and Esthetic Finishing in Orthodontics Identification and Treatment of Microesthetic Features in Orthodontics Part 1jerd_
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Enameloplasty and Esthetic Finishing in Orthodontics Identification and Treatment of Microesthetic Features in Orthodontics Part 1jerd_446 296..302 DAVID M. SARVER, DMD, MS*, ABSTRACT
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Enameloplasty and Esthetic Finishing in Orthodontics Identification and Treatment of Microesthetic Features in Orthodontics Part 1jerd_446 296..302 DAVID M. SARVER, DMD, MS*, ABSTRACT
Nicholas Caplanis DMD MS 6/13/2012
 Considerations In The Esthetic Zone Nick Caplanis DMD MS Private Practice Periodontics and Implant Surgery Mission Viejo, California Nick@drcaplanis.com Assistant Professor Loma Linda University Anatomic
Considerations In The Esthetic Zone Nick Caplanis DMD MS Private Practice Periodontics and Implant Surgery Mission Viejo, California Nick@drcaplanis.com Assistant Professor Loma Linda University Anatomic
Attachment G. Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080. ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA for Permanent Dentition YES NO
 First Review IL HFS Dental Program Models Second Review Ortho cad Attachment G Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080 Ceph Film X-Rays Photos Narrative Patient Name: DOB: ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA
First Review IL HFS Dental Program Models Second Review Ortho cad Attachment G Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080 Ceph Film X-Rays Photos Narrative Patient Name: DOB: ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 313 Timing, Positioning, and Sequential Staging in Esthetic Implant Therapy: A Four-Dimensional Perspective Akiyoshi Funato, DDS* Maurice
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 313 Timing, Positioning, and Sequential Staging in Esthetic Implant Therapy: A Four-Dimensional Perspective Akiyoshi Funato, DDS* Maurice
WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF WHAT WE DO? TEAM PERIODONTICS: WORKING TOGETHER TO IMPROVE PATIENT CARE YOU ARE THE PERIODONTISTS IN YOUR PRACTICE!
 Setter Periodontics 2075 SW 1 st Ave #2L Portland, OR 97201 503-222-9961 michael@setterperio.com WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF WHAT WE DO? Gum Gardeners Study Club 2.27.17 TEAM PERIODONTICS: WORKING TOGETHER
Setter Periodontics 2075 SW 1 st Ave #2L Portland, OR 97201 503-222-9961 michael@setterperio.com WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF WHAT WE DO? Gum Gardeners Study Club 2.27.17 TEAM PERIODONTICS: WORKING TOGETHER
Smile Design. Daniel H Ward DDS 1080 Polaris Pkwy Ste 130 Columbus OH
 Smile Design Daniel H Ward DDS 1080 Polaris Pkwy Ste 130 Columbus OH 43240 614-430-8990 dward@columbus.rr.com Incisal Placement Incisal plane parallel to the interpupillary line Vertical midline in the
Smile Design Daniel H Ward DDS 1080 Polaris Pkwy Ste 130 Columbus OH 43240 614-430-8990 dward@columbus.rr.com Incisal Placement Incisal plane parallel to the interpupillary line Vertical midline in the
Thick vs. Thin Gingival Biotypes: A Key Determinant in Treatment Planning for Dental Implants
 r s Thick vs. Thin Gingival Biotypes: A Key Determinant in Treatment Planning for Dental Implants richard t. kao, dds, phd; mark c. fagan, ms, dds; and gregory j. conte, ms, dmd abstract During the treatment
r s Thick vs. Thin Gingival Biotypes: A Key Determinant in Treatment Planning for Dental Implants richard t. kao, dds, phd; mark c. fagan, ms, dds; and gregory j. conte, ms, dmd abstract During the treatment
Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants. Agenda. Agenda. Smile line revitalization with implants Priest Prosthodontics, LLC 1
 Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
ESTEHETIC SMILE A CONCERN DUE TO ALTERED PASSIVE ERUPTION - CASE REPORTS
 ESTEHETIC SMILE A CONCERN DUE TO ALTERED PASSIVE ERUPTION - CASE REPORTS Savitha A.N 1 * Sahar Razack 2 Rosh R.M 3 1. Professor, Department of Periodontics, The Oxford Dental College, 10 th Milestone,
ESTEHETIC SMILE A CONCERN DUE TO ALTERED PASSIVE ERUPTION - CASE REPORTS Savitha A.N 1 * Sahar Razack 2 Rosh R.M 3 1. Professor, Department of Periodontics, The Oxford Dental College, 10 th Milestone,
Alarge number of sound clinical
 Volume 83 Number 5 Long-Term 8-Year Outcomes of Coronally Advanced Flap forrootcoverage Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato,* Debora Franceschi,* Roberto Rotundo,* Francesco Cairo,* Pierpaolo Cortellini, and Michele
Volume 83 Number 5 Long-Term 8-Year Outcomes of Coronally Advanced Flap forrootcoverage Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato,* Debora Franceschi,* Roberto Rotundo,* Francesco Cairo,* Pierpaolo Cortellini, and Michele
The Prevalence of Maxillary Altered Passive Eruption in a Dental School Population.
 Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2010 The Prevalence of Maxillary Altered Passive Eruption in a Dental School Population. Francisco Carlos
Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2010 The Prevalence of Maxillary Altered Passive Eruption in a Dental School Population. Francisco Carlos
Case Report - Dr. Arthur Weiss
 High Esthetic Solutions with a Team Approach to Implant Dentistry The placement of hybrid abutments in the highly esthetic anterior zone Introduction Proper planning with a team approach ensures that highly
High Esthetic Solutions with a Team Approach to Implant Dentistry The placement of hybrid abutments in the highly esthetic anterior zone Introduction Proper planning with a team approach ensures that highly
MUCOGINGIVAL THERAPY PERIODONTAL PLASTIC SURGERY
 MUCOGINGIVAL THERAPY PERIODONTAL PLASTIC SURGERY DR.H.Gharati Periodontist & Dental Implant Specialist Assistant Professor, School Of Dentistry Friedman(1957): DEFINITION Mucogingival surgery, Surgical
MUCOGINGIVAL THERAPY PERIODONTAL PLASTIC SURGERY DR.H.Gharati Periodontist & Dental Implant Specialist Assistant Professor, School Of Dentistry Friedman(1957): DEFINITION Mucogingival surgery, Surgical
Relationships between different tooth shapes and patient s periodontal phenotype
 J Periodont Res 2013; 48: 657 662 All rights reserved Relationships between different tooth shapes and patient s periodontal phenotype 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd JOURNAL
J Periodont Res 2013; 48: 657 662 All rights reserved Relationships between different tooth shapes and patient s periodontal phenotype 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd JOURNAL
Course Objectives. HDA 2018 Dental Implant Complications. What are some common failures / problems we all encounter?
 HDA 2018 Dental Implant Complications 1 Course Objectives - Understand protocols for diagnosing and treatment planning to minimize complications - Recognize and manage intraoperative complications during
HDA 2018 Dental Implant Complications 1 Course Objectives - Understand protocols for diagnosing and treatment planning to minimize complications - Recognize and manage intraoperative complications during
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
The patient gave a history of hypertension and gastritis for which was taking Lacidipine 4mg, Omeprazole 20mg and Simvastatin 40mg.
 A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository
 University of Louisville ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository Electronic Theses and Dissertations 12-2006 Implant esthetics using a Nobel Replace Standard implant vs. Nobel
University of Louisville ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository Electronic Theses and Dissertations 12-2006 Implant esthetics using a Nobel Replace Standard implant vs. Nobel
The Effect of X Ray Vertical Angulation on Radiographic Assessment of Alveolar Bone Loss
 1 The Effect of X Ray Vertical Angulation on Radiographic Assessment of Alveolar Bone Loss ABSTRACT M. Mehdizadeh MD*, M. Amintavakoli MD**, M. Allahverdi MD*** Introduction: Radiographs provide unique
1 The Effect of X Ray Vertical Angulation on Radiographic Assessment of Alveolar Bone Loss ABSTRACT M. Mehdizadeh MD*, M. Amintavakoli MD**, M. Allahverdi MD*** Introduction: Radiographs provide unique
Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported
 PROSTHODONTICS Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported crown Luca Gobbato, DDS 1 /Gianluca Paniz, DDS 2 /Fabio Mazzocco, DDS 3 / Andrea Chierico,
PROSTHODONTICS Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported crown Luca Gobbato, DDS 1 /Gianluca Paniz, DDS 2 /Fabio Mazzocco, DDS 3 / Andrea Chierico,
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran
 Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations
 Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Several extraction socket classifications have been
 Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Esthetic Crown Lengthening
 Esthetic Crown Lengthening Esthetic Crown Lengthening ACCELERATED OSTEOGENIC ORTHODOTNICS (WILKODONTICS) It is a technique developed by Wilko brothers. has roots in orthopedics, back to the early 1900s
Esthetic Crown Lengthening Esthetic Crown Lengthening ACCELERATED OSTEOGENIC ORTHODOTNICS (WILKODONTICS) It is a technique developed by Wilko brothers. has roots in orthopedics, back to the early 1900s
Is Biologic Width of Anterior and Posterior Teeth Similar?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Biologic Width of Anterior and Posterior Teeth Similar? Amir Alireza Rasouli Ghahroudi 1, Afshin Khorsand 1, Siamak Yaghobee 1,2, and Farideh Haghighati 1 1 Department of Periodontology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Biologic Width of Anterior and Posterior Teeth Similar? Amir Alireza Rasouli Ghahroudi 1, Afshin Khorsand 1, Siamak Yaghobee 1,2, and Farideh Haghighati 1 1 Department of Periodontology,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
RESEARCH REVIEW. Gingival recession: a proposal for a new classification ISSN :
 RESEARCH REVIEW Gingival recession: a proposal for a new classification Shantipriya Reddy, Sanjay Kaul, Prasad M.G.S., Jaya Agnihotri, Amudha D., Soumya Kambali ABSTRACT An accurate diagnosis is often
RESEARCH REVIEW Gingival recession: a proposal for a new classification Shantipriya Reddy, Sanjay Kaul, Prasad M.G.S., Jaya Agnihotri, Amudha D., Soumya Kambali ABSTRACT An accurate diagnosis is often
New Surgical Protocol to Create Interimplant Papilla: The Preliminary Results of a Case Series
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/295813926 New Surgical Protocol to Create Interimplant Papilla: The Preliminary Results of
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/295813926 New Surgical Protocol to Create Interimplant Papilla: The Preliminary Results of
Nonsurgical Recovery of Interdental Title Supportive Periodontal Therapy. Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5
 Nonsurgical Recovery of Interdental Title Supportive Periodontal Therapy. Yanagishita, Y; Yoshino, K; Author(s) Matsukubo, T Taniguc Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/2851
Nonsurgical Recovery of Interdental Title Supportive Periodontal Therapy. Yanagishita, Y; Yoshino, K; Author(s) Matsukubo, T Taniguc Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/2851
The Endodontic / Implant Controversy
 The Endodontic / Implant Controversy Innovations in Endodontics Series Robert Handysides DDS Associate Professor and Chair Department of Endodontics Loma Linda University School of Dentistry Endodontic
The Endodontic / Implant Controversy Innovations in Endodontics Series Robert Handysides DDS Associate Professor and Chair Department of Endodontics Loma Linda University School of Dentistry Endodontic
Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage
 CASE REPORT Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage Mehmet Oguz Oztoprak, DDS, MSc, a Cigdem Demircan, DDS, b Tulin Arun, PhD, DDS, MSc c Transposition
CASE REPORT Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage Mehmet Oguz Oztoprak, DDS, MSc, a Cigdem Demircan, DDS, b Tulin Arun, PhD, DDS, MSc c Transposition
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry
 Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Periodontal response to early uncovering, autonomous eruption, and orthodontic alignment of palatally impacted maxillary canines
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Periodontal response to early uncovering, autonomous eruption, and orthodontic alignment of palatally impacted maxillary canines Andrew D. Schmidt a and Vincent G. Kokich b Rhinelander,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Periodontal response to early uncovering, autonomous eruption, and orthodontic alignment of palatally impacted maxillary canines Andrew D. Schmidt a and Vincent G. Kokich b Rhinelander,
(Images are at the end of article)
 Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Clinical Study Altered Passive Eruption and Familial Trait: A Preliminary Investigation
 International Dentistry, Article ID 874092, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/874092 Clinical Study Altered Passive Eruption and Familial Trait: A Preliminary Investigation Roberto Rossi, 1 Giorgio
International Dentistry, Article ID 874092, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/874092 Clinical Study Altered Passive Eruption and Familial Trait: A Preliminary Investigation Roberto Rossi, 1 Giorgio
Available online at International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp , December, 2015
 z Available online at http://www.journalcra.com International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp.24212-24216, December, 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH ISSN: 0975-833X REVIEW
z Available online at http://www.journalcra.com International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp.24212-24216, December, 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH ISSN: 0975-833X REVIEW
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System
 Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
