Detection of dentinal cracks using contrast-enhanced micro-computed tomography
|
|
|
- Kellie Welch
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J O U R N A L O F T H E M E C H A N I C A L B E H A V I O R O F B I O M E D I C A L M A T E R I A L S 3 ( ) available at journal homepage: Technical note Detection of dentinal cracks using contrast-enhanced micro-computed tomography Matthew D. Landrigan a, John C. Flatley a, Travis L. Turnbull a, Jamie J. Kruzic b, Jack L. Ferracane c, Thomas J. Hilton c, Ryan K. Roeder a, a Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, IN 46556, USA b School of Mechanical, Industrial, and Manufacturing Engineering, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331, USA c Division of Biomaterials and Biomechanics, Department of Restorative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR 97239, USA A R T I C L E I N F O A B S T R A C T Article history: Received 12 June 2009 Received in revised form 17 September 2009 Accepted 1 October 2009 Published online 13 October 2009 A new technique using contrast enhanced micro-computed tomography (micro-ct) was developed to improve the ability to detect dentinal cracks in teeth and assess associated risks to oral health. Extracted, whole human molars that exhibited visual evidence of external cracks following extraction and machined, partially fractured elephant dentin specimens were labeled by BaSO 4 precipitation and imaged by micro-ct. Contrastenhanced micro-ct was demonstrated in vitro to enable non-destructive, 3-D imaging of the presence, morphology and spatial location of dentinal cracks in whole human molars and machined specimens. BaSO 4 staining provided enhanced contrast for the detection of cracks that could not be detected prior to staining. Backscattered SEM micrographs showed that BaSO 4 was precipitated on the surfaces of dentinal cracks and within adjacent tubules. The new methods demonstrated in this study are expected to be useful for clinical and scientific studies investigating the etiology and treatment of dentinal cracks in teeth. c 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. 1. Introduction Cracked teeth are commonly observed in dental practice and are potentially symptomatic (Clark et al., 2003; Kahler, 2008; Snyder, 1976). Cracked teeth are the third most common cause of tooth loss after caries and periodontal disease (Braly and Maxwell, 1981; Hiatt, 1973). Treatment options are typically lengthy, expensive and include a risk of morbidity (Liu and Sidhu, 1995; Homewood, 1998; Geurtsen and García-Godoy, 1999; Kahler, 2008), yet there is little definitive evidence to support the diagnosis of cracks requiring intervention or the effectiveness of interventions (e.g., Bader et al., 1996). Therefore, treatments may be either over-prescribed or prescribed too late. Current methods for the diagnosis of cracks that may compromise teeth are all based on optical assessment, with or without the aid of surgical loupes, microscopes, dyes and/or transillumination (Clark et al., 2003; Kahler, 2008). Improvements in the detection and classification of cracks have been demonstrated using enhanced magnification Corresponding address: Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, University of Notre Dame, 148 Multidisciplinary Research Building, Notre Dame, IN 46556, USA. Tel.: ; fax: address: rroeder@nd.edu (R.K. Roeder) /$ - see front matter c 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi: /j.jmbbm
2 224 J O U R N A L O F T H E M E C H A N I C A L B E H A V I O R O F B I O M E D I C A L M A T E R I A L S 3 ( ) (Clark et al., 2003; Slaton et al., 2003) and transillumination (Wright et al., 2004). However, optical methods suffer from an inherent inability to assess the severity of cracks (e.g., crack depth), particularly sub-surface dentinal cracks. Moreover, dentinal cracks are generally not able to be detected in plain radiographs. Micro-CT is useful for non-invasive, three-dimensional (3-D) imaging of the internal structure of mineralized tissues, due to relative differences in x-ray attenuation. Cone beam volumetric micro-ct was recently demonstrated to provide more accurate assessment of proximal caries lesion depth compared to conventional radiographs (Kalathingal et al., 2007). Intra-oral systems limit the volume irradiated and thus achieve a low radiation dose to the patient; however, the spatial resolution is currently limited to 40 µm and the image contrast is low relative to conventional CT (Kalathingal et al., 2007). High-resolution micro-ct systems are commercially available for both in vivo imaging of small animals and in vitro imaging of tissue specimens. The spatial resolution is typically on the order of 10 µm and systems with 1 µm resolution are now available. However, the detection of small cracks ( 1 µm in width) in relatively large specimens (e.g., a molar) is limited by the resolution, maximum specimen size, and data collection time of the above instruments. X-ray tomography using high energy, monochromatic synchrotron radiation is able to image cracks in dentin (Kruzic et al., 2003), but is neither readily available nor amenable to imaging large numbers of tissue specimens that are relatively large in size. Non-destructive, 3-D imaging of the presence, spatial location and accumulation of microdamage in bone tissue was recently demonstrated for the first time using contrastenhanced micro-ct with a precipitated BaSO 4 stain (Leng et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2007). Although imaging of cracks and damage in bone had been previously demonstrated using high energy, monochromatic synchrotron radiation (Nalla et al., 2005), this approach enabled the use of commercially available bench top micro-ct instruments. BaSO 4 was precipitated within damaged tissue, cracks and vasculature, as verified by backscattered electron imaging and energy dispersive spectroscopy (Leng et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2007). Moreover, precipitated BaSO 4 enhanced the intensity of voxels in micro-ct due to the higher x-ray attenuation of BaSO 4 relative to bone tissue. The micro-ct scanner (10 µm resolution) was unable to detect microcracks or fatigue cracks without the use of the contrast agent. Therefore, contrastenhanced micro-ct is expected to find increased use in the study of mineralized tissue mechanics, complementing or replacing methods of damage/crack detection that are inherently destructive, two-dimensional and tedious. The objective of this study was to non-destructively and three-dimensionally image dentinal cracks using contrastenhanced micro-ct. Extracted, whole human molars that exhibited visual evidence of external cracks following extraction and machined, partially fractured elephant dentin specimens were labeled by BaSO 4 precipitation and imaged by micro-ct using methods adapted from previous studies investigating microdamage in bone tissue (Leng et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2007). 2. Materials and methods 2.1. Elephant dentin Two partially fractured, dehydrated compact-tension specimens of dentin from tusk shards of a single adult male elephant (Loxodonta africana) used in a previous study (Kruzic et al., 2003) provided well-characterized and highly controlled cracks for evaluating feasibility of the technique. Elephant dentin is similar to human dentin in containing tubules within an extracellular matrix of mineralized collagen fibers and avoids the specimen size limitations of human dentin. Compact-tension specimens were machined while hydrated to a thickness of 2.5 mm and width of 15 mm. Specimens were polished to a 1200 grit finish, followed by 1 and 0.05 µm alumina suspensions. An initial notch was introduced with a low speed diamond wafer saw such that the crack growth direction was oriented perpendicular to the long axis of the tubules and the crack plane was in the plane of the tubules. A final notch with root radius 15 µm was achieved by repeatedly sliding a razor blade over the initial notch. Fracture resistance (R-curve) testing was conducted in vacuo ( 10 4 Pa) in a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Specimens were rehydrated and stored in phosphate buffered saline upon receipt and during all interim periods before staining and micro-ct Whole human molars Ten extracted human molars from different donors were provided by the Practice-based Research in Oral Health (PROH) practitioner network through the Oregon Health and Science University. Teeth were screened after extraction for evidence of external cracks upon inspection with 3.5X surgical loupes. All teeth were maintained hydrated in a 0.05% solution of chloramine T during all interim periods before staining and micro-ct Histological staining and imaging Elephant dentin specimens and whole human molars were imaged before and after histological staining by micro- CT (µct-80, Scanco Medical AG, Bassersdorf, Switzerland) at 10 µm resolution, 70 kvp voltage, 113 µa current, and 400 ms integration time. Grayscale images were smoothed by Gaussian filtering. High intensity voxels representative of BaSO 4 were segmented to highlight cracks in 3-D reconstructions. An image subregion was used to remove the effect of non-specific BaSO 4 staining on specimen free surfaces which would have otherwise obscured the visualization of internal features in 3-D reconstructions. All specimens were stained by BaSO 4 precipitation, soaking in an equal parts mixture of 0.5 M barium chloride (Certified ACS crystal, Fisher Scientific, Fair Lawn, NJ) in de-ionized water, buffered saline, and acetone for 3 days, followed by an equal parts mixture of 0.5 M sodium sulfate (Anhydrous powder, Fisher Scientific, Fair Lawn, NJ) in deionized water, buffered saline, and acetone for 3 days, both under vacuum ( 50 mm Hg). The staining mechanism was a precipitation reaction where BaCl 2 (aq) + Na 2 SO 4 (aq) BaSO 4 (s) + 2NaCl(aq). Barium and sulfate ions diffused into
3 J O U R N A L O F T H E M E C H A N I C A L B E H A V I O R O F B I O M E D I C A L M A T E R I A L S 3 ( ) and concentrated within void space in the dentinal tissue e.g., tubules and cracks which acted as a micro-reactor and provided an abundance of heterogeneous nucleation sites on tissue surfaces (Leng et al., 2004, 2008). After staining and micro-ct, specimens were dehydrated in a graded series of alcohol solutions, dried overnight in an oven at 90 C, embedded in poly(methyl methacrylate), sectioned with a low-speed diamond wafer saw, polished with a series of diamond compounds to a 1 µm finish, and coated with Au Pd by sputter deposition for scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Specimens were imaged using backscattered electrons (Evo 50, LEO Electron Microscopy Ltd., Cambridge, UK) at an accelerating voltage of 20 kv and a working distance of 9 12 mm. Note that image contrast from backscattered electrons is primarily due to compositional differences in atomic number, with an increasing atomic number resulting in increased intensity. The elemental composition of the stain was verified by electron probe microanalysis using energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) (INCA x-sight model 7636, Oxford Instruments America, Concord, MA). 3. Results Contrast-enhanced micro-ct enabled non-destructive, 3-D imaging of the presence, morphology and spatial location of dentinal cracks in machined specimens (Fig. 1) and whole human molars (Fig. 2). In both types of specimens, BaSO 4 staining provided enhanced contrast for the detection of cracks that were not able to be detected prior to staining (Figs. 1(b), (c), and 2(b)). Note that the entire 3-D volume of grayscale image slices for the specimens shown in Figs. 1 and 2 are available as movie files (.avi) in Electronic Annex 1 and 2, respectively, of the online version of this article. Backscattered SEM micrographs showed that BaSO 4 was precipitated on the surfaces of dentinal cracks and within adjacent tubules (Fig. 1(e)). The highest levels of image intensity for both micro-ct and backscattered SEM were shown to correspond to the presence of elemental barium and sulfur measured using EDS. At higher magnification, SEM revealed the presence of BaSO 4 crystals and aggregates, typically submicron but up to 5 µm in size, on the surfaces of propagating cracks and within adjacent tubules. BaSO 4 was also precipitated on all free surfaces, including the root canal and pulp chamber (Fig. 2(a)). Therefore, a subregion was used to remove staining of the outer specimen surfaces and reveal internal features, including cracks, in segmented 3-D reconstructions (Figs. 1(a), and 2(a)). 4. Discussion The feasibility of non-destructive, 3-D imaging of dentinal cracks was demonstrated in vitro in machined, partially fractured specimens (Fig. 1) and whole human molars (Fig. 2) using contrast-enhanced micro-ct with a precipitated BaSO 4 stain. BaSO 4 precipitation on the surfaces of dentinal cracks and within adjacent tubules enhanced the intensity of voxels in micro-ct due to the higher x-ray attenuation of BaSO 4 a b c d e Fig. 1 A branched crack that propagated from a notch (left) in a compact tension specimen of elephant dentin was imaged by micro-ct before and after staining by BaSO 4 precipitation, and by backscattered SEM after staining by BaSO 4 precipitation. (a) A segmented, three-dimensional micro-ct reconstruction showed crack surfaces stained with BaSO 4. Cross-sectional grayscale micro-ct images at the same depth approximately midway through the specimen thickness (b) before and (c) after staining by BaSO 4 precipitation showed that the crack was unable to be detected at this location without the use of the contrast agent. The contrast-enhanced micro-ct image in (c) was compared to (d) a backscattered SEM micrograph for the same specimen at approximately the same cross-sectional depth and magnification. (e) A backscattered SEM micrograph of the crack tip in (d) at higher magnification showed BaSO 4 penetration into microtubules. Note that the presence of elemental Ba and S was verified by EDS (not shown).
4 226 J O U R N A L O F T H E M E C H A N I C A L B E H A V I O R O F B I O M E D I C A L M A T E R I A L S 3 ( ) a b Fig. 2 An extracted human molar which showed evidence of cracks upon visual inspection was imaged by micro-ct. (a) A segmented, three-dimensional micro-ct reconstruction revealed internal surfaces stained by BaSO 4 precipitation, including the root canal, pulp chamber and cracks, and other features exhibiting the highest x-ray attenuation, including the enamel and a composite filling. Note that the majority of the enamel crown of the tooth has been excluded from the image at the top. (b) Grayscale images of transverse cross-sections showed enhanced contrast for the detection of dentinal cracks after staining by BaSO 4 precipitation compared to the same image cross-section prior to staining. relative to dentin. The BaSO 4 contrast agent enabled the detection of dentinal cracks that were otherwise not able to be detected using a standard benchtop micro-ct instrument at 10 µm resolution (Figs. 1(b), (c), and 2(b)). The total crack length measured at the free surface in the elephant dentin compact-tension specimens was unchanged before and after staining, which suggests that the staining process did not introduce artifactual damage. Furthermore, the absence of BaSO 4 within cracks during subsequent electron microscopy also enabled discrimination of artifactual cracks that formed during specimen preparation, for example during dehydration, from cracks that formed in vivo or during in vitro mechanical loading. The new methods demonstrated in this study are expected to be very useful for in vitro scientific studies investigating the mechanical behavior of teeth, including the etiology and morphology of dentinal cracks. Insightful quantitative measurements of crack dimensions, volume, density, orientation, etc. can be subsequently obtained by applying common methods of image analysis to acquired micro-ct data. Such measurements would be extremely tedious, if not impossible, using conventional twodimensional (2-D) histological techniques. Moreover, even in a highly controlled fracture test, crack length and branching, for example, may exhibit significant 3-D spatial variation that would be otherwise undetected by observation of the specimen surface or any single 2-D cross-section (Fig. 1(a)). Finally, additional potential exists for use of this technique in vivo for clinical studies, perhaps with some modification to the staining method or contrast agent. Indeed, cone beam micro-ct with 40 µm resolution is under investigation for clinical use (Kalathingal et al., 2007). Some limitations should be noted for the new methods demonstrated in this study. BaSO 4 precipitation was nonspecific for cracks, including all void spaces such as vasculature and free surfaces. Furthermore, under the conditions of this study the BaSO 4 contrast agent was difficult to distinguish from the enamel, presumably due to comparable levels of x- ray attenuation. However, cracks in the enamel were readily detected by micro-ct both with and without the use of a contrast agent (Fig. 2(b)) due to the relatively low x-ray attenuation of the fluid space in the crack compared to the enamel. Therefore, the main limitation of the difficulty distinguishing BaSO 4 from enamel, as well as non-specific staining of exterior specimen surfaces with BaSO 4, was the need to remove the outermost voxels using contouring and a subregion analysis in order to visualize internal features in segmented, 3-D reconstructions. Last, the barium chloride and sodium sulfate staining solutions may or may not be acceptable within the oral cavity with some modification, warranting future work and potentially limiting this technique to in vitro studies. 5. Conclusions Contrast-enhanced micro-ct was demonstrated in vitro to enable non-destructive, 3-D imaging of the presence, morphology and spatial location of dentinal cracks in whole human molars and machined, partially fractured specimens. In both types of specimens, BaSO 4 staining provided enhanced contrast for the detection of cracks that were not able to be detected prior to staining. Backscattered SEM micrographs showed that BaSO 4 was precipitated on the surfaces of dentinal cracks and within adjacent tubules. The new methods demonstrated in this study are expected to be immediately useful for in vitro scientific studies investigating the etiology and treatment of dentinal cracks in teeth, and also possess potential for use in clinical studies with further development.
5 J O U R N A L O F T H E M E C H A N I C A L B E H A V I O R O F B I O M E D I C A L M A T E R I A L S 3 ( ) Acknowledgments This research was partially supported by the U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command (W81XWH ) through the Peer Reviewed Medical Research Program (PR054672). Appendix. Supplementary data Supplementary data associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi: /j.jmbbm R E F E R E N C E S Bader, J.D., Shugars, D.A., Roberson, T.M., Using crowns to prevent tooth fracture. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 24 (1), Braly, B.V., Maxwell, E.H., Potential for tooth fracture in restorative dentistry. J. Prosthet. Dent. 45 (4), Clark, D.J., Sheets, C.G., Parquette, J.M., Definitive diagnosis of early enamel and dentin cracks based on microscopic evaluation. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 15 (7), Geurtsen, W., García-Godoy, F., Bonded restorations for the prevention and treatment of the cracked tooth syndrome. Am. J. Dent. 13 (6), Hiatt, W.H., Incomplete crown-root fracture in pulpalperiodontal disease. J. Periodontol. 44 (6), Homewood, C.I., Cracked tooth syndrome Incidence, clinical findings and treatment. Aust. Dent. J. 43 (4), Kahler, W., The cracked tooth conundrum: Terminology, classification, diagnosis, and management. Am. J. Dent. 21, Kalathingal, S.M., Mol, A., Tyndall, D.A., Caplan, D.J., In vitro assessment of cone beam local computed tomography for proximal caries detection. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 104, Kruzic, J.J., Nalla, R.K., Kinney, J.H., Ritchie, R.O., Crack blunting, crack bridging and resistance-curve fracture mechanics in dentin: Effect of hydration. Biomaterials 24 (28), Leng, H., Wang, X., Niebur, G.L., Roeder, R.K., Synthesis of a barium sulfate nanoparticle contrast agent for microcomputed tomography of bone microstructure. Ceram. Trans. 159, Leng, H., Wang, X., Ross, R.D., Niebur, G.L., Roeder, R.K., Micro-computed tomography of fatigue microdamage in cortical bone using a barium sulfate contrast agent. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 1 (1), Liu, H.H., Sidhu, S.K., Cracked teeth treatment rationale and case management: Case reports. Quintessence Int. 26 (7), Nalla, R.K., Kruzic, J.J., Kinney, J.H., Ritchie, R.O., Mechanistic aspects of fracture and R-curve behavior in human cortical bone. Biomaterials 26 (2), Slaton, C.C., Loushine, R.J., Weller, R.N., Parker, M.H., Kimbrough, W.F., Pashley, D.H., Identification of resected root-end dentinal cracks: A comparative study of visual magnification. J. Endod. 29 (8), Snyder, D.E., The cracked-tooth syndrome and fractured posterior cusp. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 41 (6), Wang, X., Masse, D.B., Leng, H., Hess, K.P., Ross, R.D., Roeder, R.K., Niebur, G.L., Detection of trabecular bone microdamage by micro-computed tomography. J. Biomech. 40 (15), Wright, H.M., Loushine, R.J., Weller, R.N., Kimbrough, W.F., Waller, J., Pashley, D.H., Identification of resected root-end dentinal cracks: A comparative study of transillumination and dyes. J. Endod. 30 (10),
STRIATIONS RESULTING FROM FATIGUE CRACK GROWTH IN DENTIN
 STRIATIONS RESULTING FROM FATIGUE CRACK GROWTH IN DENTIN Devendra Bajaj 1, Narayana Sundaram 1, Dwayne Arola 1, 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Maryland, Baltimore County 1000 Hilltop
STRIATIONS RESULTING FROM FATIGUE CRACK GROWTH IN DENTIN Devendra Bajaj 1, Narayana Sundaram 1, Dwayne Arola 1, 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Maryland, Baltimore County 1000 Hilltop
Structure and mechanical properties of teeth. Advisors: M.A. Meyers & E. A. Olevsky Student :Yen-Shan Lin Date: 6/23/2008
 Structure and mechanical properties of teeth Advisors: M.A. Meyers & E. A. Olevsky Student :Yen-Shan Lin Date: 6/23/2008 Outline Basic structure and components of teeth Mechanical properties 1. tubule
Structure and mechanical properties of teeth Advisors: M.A. Meyers & E. A. Olevsky Student :Yen-Shan Lin Date: 6/23/2008 Outline Basic structure and components of teeth Mechanical properties 1. tubule
Biomechanics of Solids
 Biomechanics of Solids Devendra Bajaj Graduate Student, LAMP Department of Mechanical Engineering UMBC ENCH 484/693: Biomedical Engineering. (April 18, 2007) Historical Facts Leonardo da Vinci 1452-1519
Biomechanics of Solids Devendra Bajaj Graduate Student, LAMP Department of Mechanical Engineering UMBC ENCH 484/693: Biomedical Engineering. (April 18, 2007) Historical Facts Leonardo da Vinci 1452-1519
Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location
 Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
NANOINDENTATION STUDY OF NORMAL AND OSTEOPOROTIC BONES
 NANOINDENTATION STUDY OF NORMAL AND OSTEOPOROTIC BONES C.T. Lim, B.H.B. Omar and J.C.J. Goh 1 Division of Bioengineering & Department of Mechanical Engineering, 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National
NANOINDENTATION STUDY OF NORMAL AND OSTEOPOROTIC BONES C.T. Lim, B.H.B. Omar and J.C.J. Goh 1 Division of Bioengineering & Department of Mechanical Engineering, 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National
TITLE: Dental Loupes for Dental Procedures: A Review of the Clinical and Cost- Effectiveness
 TITLE: Dental Loupes for Dental Procedures: A Review of the Clinical and Cost- Effectiveness DATE: 08 October 2008 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: The use of magnification in dentistry is expanding rapidly.
TITLE: Dental Loupes for Dental Procedures: A Review of the Clinical and Cost- Effectiveness DATE: 08 October 2008 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: The use of magnification in dentistry is expanding rapidly.
PERSPECTIVES OF THE TOOTH RESTORATION TECHNOLOGY BASED ON THE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY DATA
 PERSPECTIVES OF THE TOOTH RESTORATION TECHNOLOGY BASED ON THE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY DATA Maxim Putrik *, Vladimir Ivanov, Igor Antsygin Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Education
PERSPECTIVES OF THE TOOTH RESTORATION TECHNOLOGY BASED ON THE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY DATA Maxim Putrik *, Vladimir Ivanov, Igor Antsygin Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Education
SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary
 SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary Summary of In Vivo Use Of Bioresorbable Xenograft Bone Graft Materials In The Treatment Of One-Walled Intrabony Defects In A Canine Model
SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary Summary of In Vivo Use Of Bioresorbable Xenograft Bone Graft Materials In The Treatment Of One-Walled Intrabony Defects In A Canine Model
Osteoporosis New Insights
 Osteoporosis New Insights by JOHN KINNEY Synchrotron radiation is giving us new insights into causes and treatments for osteoporosis. OSTEOPOROSIS IS A DISEASE characterized by fragile bones that results
Osteoporosis New Insights by JOHN KINNEY Synchrotron radiation is giving us new insights into causes and treatments for osteoporosis. OSTEOPOROSIS IS A DISEASE characterized by fragile bones that results
Stress ratio contributes to fatigue crack growth in dentin
 Stress ratio contributes to fatigue crack growth in dentin D. Arola, W. Zheng, N. Sundaram, J.A. Rouland Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Maryland Baltimore County, 1000 Hilltop Circle,
Stress ratio contributes to fatigue crack growth in dentin D. Arola, W. Zheng, N. Sundaram, J.A. Rouland Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Maryland Baltimore County, 1000 Hilltop Circle,
Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth
 Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth B.Sc., D.D.S., Specialty Certificate in Oral Pathology, M.S. Department of
Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth B.Sc., D.D.S., Specialty Certificate in Oral Pathology, M.S. Department of
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Human tooth root canal geometry assessment through micro-ct images
 Human tooth root canal geometry assessment through micro-ct images A. Garay 1, J.H. Legarreta 1, I. Macía 1, R. C. Aza 2 1 Vicomtech-ik4, Mikeletegi Pasealekua, 57 Teknologi Parkea 20009 Donostia, Spain
Human tooth root canal geometry assessment through micro-ct images A. Garay 1, J.H. Legarreta 1, I. Macía 1, R. C. Aza 2 1 Vicomtech-ik4, Mikeletegi Pasealekua, 57 Teknologi Parkea 20009 Donostia, Spain
Evidence of pulp disease in the inlayed teeth of the ancient Mayans: a micro-ct study
 Evidence of pulp disease in the inlayed teeth of the ancient Mayans: a micro-ct study M. A. Versiani 1, J. D. Pécora 1, M. D. Sousa-Neto 1 1 Department of Restorative Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, University
Evidence of pulp disease in the inlayed teeth of the ancient Mayans: a micro-ct study M. A. Versiani 1, J. D. Pécora 1, M. D. Sousa-Neto 1 1 Department of Restorative Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, University
Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials
 Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials A case study by Ann-Christin Meier, Dr. med. dent., Stapelfeld, Germany When large
Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials A case study by Ann-Christin Meier, Dr. med. dent., Stapelfeld, Germany When large
ON THE MICROHARDNESS AND YOUNG S MODULUS OF HUMAN TEETH
 ON THE MICROHARDNESS AND YOUNG S MODULUS OF HUMAN TEETH A.D.Zervaki 1, G.N. Haidemenopoulos 1 and A. Giannakopoulos 2 1. Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Thessaly, Volos, Greece 2. Department
ON THE MICROHARDNESS AND YOUNG S MODULUS OF HUMAN TEETH A.D.Zervaki 1, G.N. Haidemenopoulos 1 and A. Giannakopoulos 2 1. Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Thessaly, Volos, Greece 2. Department
Caries Inhibiting Effectiveness of the Origin SmartCrown An in-vitro Comparative Study
 Caries Inhibiting Effectiveness of the Origin SmartCrown An in-vitro Comparative Study B&D Dental Corporation Key Words Resin modified glass ionomer; Interproximal caries; Adjacent surfaces; Fluoride releasing;
Caries Inhibiting Effectiveness of the Origin SmartCrown An in-vitro Comparative Study B&D Dental Corporation Key Words Resin modified glass ionomer; Interproximal caries; Adjacent surfaces; Fluoride releasing;
Evaluation of Dentin Root Canal Permeability After Instrumentation and Er:YAG Laser Application
 Lasers in Surgery and Medicine 26:277 281 (2000) Evaluation of Dentin Root Canal Permeability After Instrumentation and Er:YAG Laser Application Jesus D. Pecora, DDS, PhD, 1 * Aldo Brugnera-Júnior, DDS,
Lasers in Surgery and Medicine 26:277 281 (2000) Evaluation of Dentin Root Canal Permeability After Instrumentation and Er:YAG Laser Application Jesus D. Pecora, DDS, PhD, 1 * Aldo Brugnera-Júnior, DDS,
Practice Impact Questionnaire
 Practice Impact Questionnaire Your practitioner identifier is: XXXXXXXX It is very important that ONLY YOU complete this questionnaire because your responses will be compared to responses that you provided
Practice Impact Questionnaire Your practitioner identifier is: XXXXXXXX It is very important that ONLY YOU complete this questionnaire because your responses will be compared to responses that you provided
how to technique How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. Disadvantages. 1 Issue Full coverage crown. >>
 Issue 37 2013 How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. 1 Full coverage crown. >> Advantages. A full crown can splint all sections of the tooth together. 1 Disadvantages. 1 Encircles crown and acts
Issue 37 2013 How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. 1 Full coverage crown. >> Advantages. A full crown can splint all sections of the tooth together. 1 Disadvantages. 1 Encircles crown and acts
Dimensional quality control of Ti-Ni dental file by optical coordinate metrology and computed tomography
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Dimensional quality control of Ti-Ni dental file by optical coordinate metrology and computed tomography Yagüe-Fabra, J.A.; Tosello, Guido; Ontiveros, S.;
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Dimensional quality control of Ti-Ni dental file by optical coordinate metrology and computed tomography Yagüe-Fabra, J.A.; Tosello, Guido; Ontiveros, S.;
PUBLISHED VERSION. This document has been archived with permission from the Australian Dental Association, received 18th January, 2007.
 PUBLISHED VERSION Saunders, J. G. C.; McIntyre, John Malcolm The ability of 1.23% acidulated phosphate fluoride gel to inhibit simulated endogenous erosion in tooth roots Australian Dental Journal, 2005;
PUBLISHED VERSION Saunders, J. G. C.; McIntyre, John Malcolm The ability of 1.23% acidulated phosphate fluoride gel to inhibit simulated endogenous erosion in tooth roots Australian Dental Journal, 2005;
DiaDent Group International DIA.DENT DiaRoot BioAggregate. Root Canal Repair Material
 DiaDent Group International 1.877.DIA.DENT www.diadent.com DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material PRECISION. PURITY. RESULTS ABOUT DIAROOT... DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material is
DiaDent Group International 1.877.DIA.DENT www.diadent.com DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material PRECISION. PURITY. RESULTS ABOUT DIAROOT... DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material is
Key words: Third molar, Impacted tooth, Tooth Eruption, Molar, Mandible, Unerupted Tooth.
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
Evaluation of a Digital Measurement Tool to Estimate Working Length in Endodontics
 Volume 2 Number 1 Winter Issue, 2001 Evaluation of a Digital Measurement Tool to Estimate Working Length in Endodontics Abstract The purpose of the study was to compare the segmental measurement tool from
Volume 2 Number 1 Winter Issue, 2001 Evaluation of a Digital Measurement Tool to Estimate Working Length in Endodontics Abstract The purpose of the study was to compare the segmental measurement tool from
Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig
 Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Current Concepts in Caries Management Diagnostic, Treatment and Ethical/Medico-Legal Considerations. Radiographic Caries Diagnosis
 Current Concepts in Caries Management Diagnostic, Treatment and Ethical/Medico-Legal Considerations Richard N. Bohay, DMD, MSc, MRCDC Associate Professor, Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry Schulich
Current Concepts in Caries Management Diagnostic, Treatment and Ethical/Medico-Legal Considerations Richard N. Bohay, DMD, MSc, MRCDC Associate Professor, Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry Schulich
2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J DENTAL TISSUE REPLACEMENT AND REGENERATION
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s/massachusetts General Hosp. VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J DENTAL TISSUE REPLACEMENT AND REGENERATION
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s/massachusetts General Hosp. VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J DENTAL TISSUE REPLACEMENT AND REGENERATION
Simulation of bone indentation
 Modelling in Medicine and Biology VII 113 Simulation of bone indentation S. Kasiri 1, G. Reilly 1,2 & D. Taylor 1 1 Trinity Centre for Bioengineering, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland 2 Institute of Technology
Modelling in Medicine and Biology VII 113 Simulation of bone indentation S. Kasiri 1, G. Reilly 1,2 & D. Taylor 1 1 Trinity Centre for Bioengineering, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland 2 Institute of Technology
Diameter and Density of Dentinal Tubule in Human Primary Teeth
 Original Article Diameter and Density of Dentinal Tubule in Human Primary Teeth Jittikarn Sikanta 1, Sitthichai Wanachantararak 2 and Varisara Sirimaharaj 1 1 Department of Orthodontics and Pediatric Dentistry,
Original Article Diameter and Density of Dentinal Tubule in Human Primary Teeth Jittikarn Sikanta 1, Sitthichai Wanachantararak 2 and Varisara Sirimaharaj 1 1 Department of Orthodontics and Pediatric Dentistry,
Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up
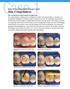 Case 1 This case study focuses on the restoration of an upper molar. Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up The existing, inadequate restoration led to the development
Case 1 This case study focuses on the restoration of an upper molar. Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up The existing, inadequate restoration led to the development
Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT
 Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT Author(s) 下尾, 嘉昭 Journal, (): - URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3605
Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT Author(s) 下尾, 嘉昭 Journal, (): - URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3605
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth
 New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
CHAPTER 3 - DEFINITION, SCOPE, AND INDICATIONS FOR ENDODONTIC THERAPY ARNALDO CASTELLUCCI
 Contents Volume I CHAPTER 1 - A BRIEF HISTORY OF ENDODONTICS CHAPTER 2 - EMBRYOLOGY Crown formation Root formation Single- and multiple-root formation The formation of lateral canals Exposed dentin and
Contents Volume I CHAPTER 1 - A BRIEF HISTORY OF ENDODONTICS CHAPTER 2 - EMBRYOLOGY Crown formation Root formation Single- and multiple-root formation The formation of lateral canals Exposed dentin and
GENERAL DENTISTRY & COMPREHENSIVE CARE
 GENERAL DENTISTRY & COMPREHENSIVE CARE Case Studies Volume 1 375 East Main Street East Islip, NY 11730 631-581-5121 www.drforlano.com Thank you for considering us for your general dental needs. All phases
GENERAL DENTISTRY & COMPREHENSIVE CARE Case Studies Volume 1 375 East Main Street East Islip, NY 11730 631-581-5121 www.drforlano.com Thank you for considering us for your general dental needs. All phases
High-resolution micro-ct scanning as an innovative tool for evaluating dental hard tissue development
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 15, NUMBER 4, 2014 High-resolution micro-ct scanning as an innovative tool for evaluating dental hard tissue development Guangyan Dong, 1 Qianqian Dong,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 15, NUMBER 4, 2014 High-resolution micro-ct scanning as an innovative tool for evaluating dental hard tissue development Guangyan Dong, 1 Qianqian Dong,
A Facile Method for Enhancing the Sensing Performance of Zinc Oxide. Nanofibers Gas Sensors
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI): A Facile Method for Enhancing the Sensing Performance of Zinc Oxide Nanofibers Gas Sensors Pei-Pei Wang a, Qi Qi a, Rui-Fei Xuan a,b, Jun Zhao a, Li-Jing Zhou
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI): A Facile Method for Enhancing the Sensing Performance of Zinc Oxide Nanofibers Gas Sensors Pei-Pei Wang a, Qi Qi a, Rui-Fei Xuan a,b, Jun Zhao a, Li-Jing Zhou
Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis)
 Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 505676, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/505676 Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 505676, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/505676 Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
Patient demand for esthetic dentistry
 PROFILE Masters of Esthetic Dentistry Keys to Success in Creating Esthetic Class IV Restorations Robert C. Margeas, DDS Current occupation Private Practice Adjunct Professor, Department of Operative Dentistry,
PROFILE Masters of Esthetic Dentistry Keys to Success in Creating Esthetic Class IV Restorations Robert C. Margeas, DDS Current occupation Private Practice Adjunct Professor, Department of Operative Dentistry,
Determining Collagen Distribution in Articular Cartilage by X-ray Micro-computed Tomography
 Determining Collagen Distribution in Articular Cartilage by X-ray Micro-computed Tomography Heikki J. Nieminen, Ph.D. 1, Mikko A. Finnilä, MHS 2, Sami Kauppinen 2, Tuomo Ylitalo 1,2, Edward Hæggström,
Determining Collagen Distribution in Articular Cartilage by X-ray Micro-computed Tomography Heikki J. Nieminen, Ph.D. 1, Mikko A. Finnilä, MHS 2, Sami Kauppinen 2, Tuomo Ylitalo 1,2, Edward Hæggström,
TECHNICAL GUIDE. For use with CEREC
 TECHNICAL GUIDE For use with CEREC THE FUTURE AND SOLUTION OF INNOVATIVE ZIRCONIA FEATURES TRANSLUCENCY SIMILAR TO NATURAL TOOTH ENAMEL BY SPEED SINTERING The collaboration of Kuraray Noritake Dental s
TECHNICAL GUIDE For use with CEREC THE FUTURE AND SOLUTION OF INNOVATIVE ZIRCONIA FEATURES TRANSLUCENCY SIMILAR TO NATURAL TOOTH ENAMEL BY SPEED SINTERING The collaboration of Kuraray Noritake Dental s
Principle Investigators: Overview of Study Methods: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz
 Principle Investigators: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz Overview of Study Methods: Subjects in need of Class I and/or Class II restorations were enrolled in two clinical trials conducted in US dental
Principle Investigators: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz Overview of Study Methods: Subjects in need of Class I and/or Class II restorations were enrolled in two clinical trials conducted in US dental
Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice
 Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin
 Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin Bright Chang D2 Dental Student UAB School of Dentistry Final report (revision) July 26, 2017 Mentors: Nathaniel Lawson,
Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin Bright Chang D2 Dental Student UAB School of Dentistry Final report (revision) July 26, 2017 Mentors: Nathaniel Lawson,
The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo
 The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo A Masters Thesis Submitted to the Department of Dentistry and the Graduate School of Yonsei University in partial fulfillment
The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo A Masters Thesis Submitted to the Department of Dentistry and the Graduate School of Yonsei University in partial fulfillment
Journal of Oral & Dental Health
 Research Article X-ray Microanalysis of ormal Primary Tooth Dentine and Primary Tooth Dentine in Teeth Diagnosed Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Type II oren JG 1 *, Sabel 1 and Cornell DH 2 Journal of Oral
Research Article X-ray Microanalysis of ormal Primary Tooth Dentine and Primary Tooth Dentine in Teeth Diagnosed Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Type II oren JG 1 *, Sabel 1 and Cornell DH 2 Journal of Oral
Fluorescent Properties of Porcelain-Restored Teeth and Their Discrimination
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 45, No. 4 (24) pp. 11 to 114 Special Issue on Frontiers of Smart Biomaterials #24 The Japan Institute of Metals Fluorescent Properties of Porcelain-Restored Teeth and Their
Materials Transactions, Vol. 45, No. 4 (24) pp. 11 to 114 Special Issue on Frontiers of Smart Biomaterials #24 The Japan Institute of Metals Fluorescent Properties of Porcelain-Restored Teeth and Their
In vitro evaluation of root canal preparation with plastic endodontic rotary finishing file - A SEM study
 Original Research In vitro evaluation of root canal preparation with plastic endodontic rotary finishing file - A SEM study ASHUTOSH * ASEEM P. TIKKU ** ANIL CHANDRA ** PROMILA VERMA *** RAKESH K. YADAV
Original Research In vitro evaluation of root canal preparation with plastic endodontic rotary finishing file - A SEM study ASHUTOSH * ASEEM P. TIKKU ** ANIL CHANDRA ** PROMILA VERMA *** RAKESH K. YADAV
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Acid-Resistant Mesoporous Metal Organic Framework Toward Oral Insulin Delivery: Protein Encapsulation, Protection & Release Yijing Chen, Peng Li, Justin A. Modica, Riki J.
Supplementary Information for Acid-Resistant Mesoporous Metal Organic Framework Toward Oral Insulin Delivery: Protein Encapsulation, Protection & Release Yijing Chen, Peng Li, Justin A. Modica, Riki J.
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alginate, tooth-shaped, for constructs, encapsulated pulp cells in, 589 590 Antibiotic paste, triple, change in root length and width
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alginate, tooth-shaped, for constructs, encapsulated pulp cells in, 589 590 Antibiotic paste, triple, change in root length and width
Frictional Behavior and Surface Failure of Human Enamel
 Frictional Behavior and Surface Failure of Human Enamel J. M. POWERS, R. G. CRAIG, and K. C. LUDEMA School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48104, USA, and College of Engineering,
Frictional Behavior and Surface Failure of Human Enamel J. M. POWERS, R. G. CRAIG, and K. C. LUDEMA School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48104, USA, and College of Engineering,
Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control
 Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control REST 528A
Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control REST 528A
Near-UV light detection
 C L I N I C A L Near-UV light detection Javier Tapia Guadix 1 Near-UV light induced fluorescence has already proven to be very useful as an alternative to classic caries-detector dyes. However its potential
C L I N I C A L Near-UV light detection Javier Tapia Guadix 1 Near-UV light induced fluorescence has already proven to be very useful as an alternative to classic caries-detector dyes. However its potential
Is there any clinical evidence?
 Current treatment objectives Anticariogenic capacity of restorative materials in paediatric dentistry: in vitro evidence vs. clinical efficiency Prof. Lisa Papagianoulis Restoration with minimal intervention
Current treatment objectives Anticariogenic capacity of restorative materials in paediatric dentistry: in vitro evidence vs. clinical efficiency Prof. Lisa Papagianoulis Restoration with minimal intervention
Evaluation of enamel pearls by cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT)
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 Evaluation of enamel pearls by cone-beam computed tomography
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 Evaluation of enamel pearls by cone-beam computed tomography
Micro-CT imaging of surgical screw tightening in human trabecular bone
 Micro-CT imaging of surgical screw tightening in human trabecular bone E. Perilli 1, M. Ryan 1, R. Ab-Lazid 1, J.J. Costi 1, K.J. Reynolds 1 1 Medical Device Research Institute, School of Computer Science,
Micro-CT imaging of surgical screw tightening in human trabecular bone E. Perilli 1, M. Ryan 1, R. Ab-Lazid 1, J.J. Costi 1, K.J. Reynolds 1 1 Medical Device Research Institute, School of Computer Science,
Restorative Dentistry and it s related to Pulp health. Dr.Ahmed Al-Jobory
 Restorative Dentistry and it s related to Pulp health Dr.Ahmed Al-Jobory Pulp Is a viscous connective tissue of collagen fibers and ground substance supporting the vital cellular, vascular, and nerve structures
Restorative Dentistry and it s related to Pulp health Dr.Ahmed Al-Jobory Pulp Is a viscous connective tissue of collagen fibers and ground substance supporting the vital cellular, vascular, and nerve structures
The purpose of this study was to investigate the kinetics of root fractures produced by root-end cavity preparation and the fracture resistance
 The purpose of this study was to investigate the kinetics of root fractures produced by root-end cavity preparation and the fracture resistance following root-end cavity preparation using Er:YAG laser
The purpose of this study was to investigate the kinetics of root fractures produced by root-end cavity preparation and the fracture resistance following root-end cavity preparation using Er:YAG laser
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations The outline form
 Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland School of Dentistry
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry-Biomaterials Structures, chemical properties, physical properties BASIC CONCEPTS ON HOW DENTAL MATERIALS WORK! Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry-Biomaterials Structures, chemical properties, physical properties BASIC CONCEPTS ON HOW DENTAL MATERIALS WORK! Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adults, common medical conditions in, 104 106 Aging population, diversity in education and socioeconomic status, 104 in United States, 103 106
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adults, common medical conditions in, 104 106 Aging population, diversity in education and socioeconomic status, 104 in United States, 103 106
Fuji II LC. A Perfect Choice
 A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
Gorduysus MO et al. Operating Microscope improves ability to locate and negotiate second canal
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH I.J.C.M.R Operating microscope improves ability to locate and negotiate second canal in mandibular ıncisors Mehmet Omer Gorduysus, Melahat Gorduysus, Zeliha Yilmaz * Department of Endodontics,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH I.J.C.M.R Operating microscope improves ability to locate and negotiate second canal in mandibular ıncisors Mehmet Omer Gorduysus, Melahat Gorduysus, Zeliha Yilmaz * Department of Endodontics,
CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals. Massimo Marenzana
 CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals Massimo Marenzana Introduction Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break. It can be defined as a systemic skeletal disease
CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals Massimo Marenzana Introduction Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break. It can be defined as a systemic skeletal disease
of the treated areas by means of a No. 3 explorer. The smoothness of the tooth-amalgam interface was then examined on each specimen by
 Removal of Amalgam Overhangs A Profilometric and Scanning Electron Microscopic Evaluation by Jose D. Freitas Vale, d.d.s., m.s.* Raul G. Caffesse, d.d.s., m.s. dr. ODONT.fl Subgingival restorations with
Removal of Amalgam Overhangs A Profilometric and Scanning Electron Microscopic Evaluation by Jose D. Freitas Vale, d.d.s., m.s.* Raul G. Caffesse, d.d.s., m.s. dr. ODONT.fl Subgingival restorations with
UTML Ultra Translucent Multi-Layered STML Super Translucent Multi-Layered ML Multi-Layered HTHigh-Translucent TECHNICAL GUIDE
 Ultra Translucent Multi-Layered STML Super Translucent Multi-Layered ML Multi-Layered HTHigh-Translucent TECHNICAL GUIDE High Esthetic Potential for Zirconia Dental Restorations * New series which features
Ultra Translucent Multi-Layered STML Super Translucent Multi-Layered ML Multi-Layered HTHigh-Translucent TECHNICAL GUIDE High Esthetic Potential for Zirconia Dental Restorations * New series which features
Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar Toshiko Inoue, Makoto Saito, Fumio Nishimura, Takashi Miyazaki ABSTRACT Abstract
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar Toshiko Inoue, Makoto Saito, Fumio Nishimura, Takashi Miyazaki ABSTRACT Abstract
Periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography for assessment of the periapical bone defect 1 week and 12 months after root-end resection
 (2009) 38, 531 536 2009 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography for assessment of the periapical bone defect 1 week
(2009) 38, 531 536 2009 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography for assessment of the periapical bone defect 1 week
stabilisation and surface protection
 Guiding the way to caries stabilisation and surface protection Fissure sealing MI restorations Pulp capping Hypersensitivity Protection Caries stabilisation Fuji Triage from GC. Temporary restorations
Guiding the way to caries stabilisation and surface protection Fissure sealing MI restorations Pulp capping Hypersensitivity Protection Caries stabilisation Fuji Triage from GC. Temporary restorations
Push-out of root canal filling using the material testing stage (MTS) inside a Micro-CT: preliminary observations
 Push-out of root canal filling using the material testing stage (MTS) inside a Micro-CT: preliminary observations G.B. Leoni, 1 M.Brito-Júnior, 1 E.A. Gomes, 2 J.Chaves, 1 Y.T.C. Silva-Sousa, 2 M.D.Sousa-Neto
Push-out of root canal filling using the material testing stage (MTS) inside a Micro-CT: preliminary observations G.B. Leoni, 1 M.Brito-Júnior, 1 E.A. Gomes, 2 J.Chaves, 1 Y.T.C. Silva-Sousa, 2 M.D.Sousa-Neto
Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision
 Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision Ridhima Suneja College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Three dimensional obturation of root space has always yielded
Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision Ridhima Suneja College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Three dimensional obturation of root space has always yielded
The Prevalence of Intrapulpal Cracks in 1st and 2nd Mandibular Molars Requiring Non-Surgical Root Canal Treatment
 Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2014 The Prevalence of Intrapulpal Cracks in 1st and 2nd Mandibular Molars Requiring Non-Surgical Root Canal
Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2014 The Prevalence of Intrapulpal Cracks in 1st and 2nd Mandibular Molars Requiring Non-Surgical Root Canal
Characterizing the Mechanical Properties of Bone with the Assistance of Digital Light Microscopy
 Characterizing the Mechanical Properties of Bone with the Assistance Abstract Micro-indentation analysis of cross-sectioned bone samples has the potential to unravel differences in bone quality and fracture
Characterizing the Mechanical Properties of Bone with the Assistance Abstract Micro-indentation analysis of cross-sectioned bone samples has the potential to unravel differences in bone quality and fracture
The Dental Microscope. Index. Acceptance of Microscope endodontic 17. Broken Instruments endodontic 26. Depth of Field managing 170
 257 Acceptance of Microscope endodontic 17 Index Broken Instruments endodontic 26 Depth of Field managing 170 Efficiency maximizing 243-245 Endodontics access debridement 40 access opening 28 anatomic
257 Acceptance of Microscope endodontic 17 Index Broken Instruments endodontic 26 Depth of Field managing 170 Efficiency maximizing 243-245 Endodontics access debridement 40 access opening 28 anatomic
Downloaded from Diagnosis and multidisciplinary management of a mandibular molar with crack tooth syndrome
 Medrech ISSN No. 2394-3971 DIAGNOSIS AND MULTIDISCIPLINARY MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR MOLAR WITH CRACK TOOTH SYNDROME Sathish Abraham, Rajan Mangrolia*, Aradhana Kamble, Salil Chaudhari Case Report Department
Medrech ISSN No. 2394-3971 DIAGNOSIS AND MULTIDISCIPLINARY MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR MOLAR WITH CRACK TOOTH SYNDROME Sathish Abraham, Rajan Mangrolia*, Aradhana Kamble, Salil Chaudhari Case Report Department
Custom-Made Products / Scientific Research Instruments
 Synchrotron Radiation Instruments Double Crystal Monochromator A double crystal monochromator is an instrument that extracts light of a specific wavelength using crystal diffraction. Light of various wavelengths
Synchrotron Radiation Instruments Double Crystal Monochromator A double crystal monochromator is an instrument that extracts light of a specific wavelength using crystal diffraction. Light of various wavelengths
Preclinical Dentistry. I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects. Lenka Roubalíková
 Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková Understanding dental caries crown pulp chamber neck root canal root Dental
Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková Understanding dental caries crown pulp chamber neck root canal root Dental
DICOM WG 22 Dentistry
 DICOM WG 22 Dentistry The Importance of Color in Dental Imaging FDA ICC Summit on Color in Medical Imaging Andrew Casertano, MS May 8-9, 2013 1 Hi, I m Andrew Casertano and I am a consultant for the ADA.
DICOM WG 22 Dentistry The Importance of Color in Dental Imaging FDA ICC Summit on Color in Medical Imaging Andrew Casertano, MS May 8-9, 2013 1 Hi, I m Andrew Casertano and I am a consultant for the ADA.
AFFINIS Sys360 putty maximum precision and easy to use
 AFFINIS Sys360 putty maximum precision and easy to use Dr. RALPH SCHÖNEMANN, November 2010 Dentists can now select from a wide range of very different impression materials supplied by a large number of
AFFINIS Sys360 putty maximum precision and easy to use Dr. RALPH SCHÖNEMANN, November 2010 Dentists can now select from a wide range of very different impression materials supplied by a large number of
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Current status of diagnostic imaging in dental university hospitals in Japan
 Oral Radiol (2004) 20:15 21 Japanese Society for Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology and Springer-Verlag Tokyo 2004 DOI 10.1007/s11282-004-0010-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Takehito Sasaki Minoru Fujita Tsuguhisa Katoh
Oral Radiol (2004) 20:15 21 Japanese Society for Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology and Springer-Verlag Tokyo 2004 DOI 10.1007/s11282-004-0010-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Takehito Sasaki Minoru Fujita Tsuguhisa Katoh
Polyoxometalate Macroion Induced Phase and Morphology
 Polyoxometalate Macroion Induced Phase and Morphology Instability of Lipid Membrane Benxin Jing a, Marie Hutin c, Erin Connor a, Leroy Cronin c,* and Yingxi Zhu a,b,* a Department of Chemical and Biomolecular
Polyoxometalate Macroion Induced Phase and Morphology Instability of Lipid Membrane Benxin Jing a, Marie Hutin c, Erin Connor a, Leroy Cronin c,* and Yingxi Zhu a,b,* a Department of Chemical and Biomolecular
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter. Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July Volume 2
 Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry. Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS
 KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS Pre-Clinical Endodontics Three (3) Credit Hours Third Year 2014-2015 Prepared
KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS Pre-Clinical Endodontics Three (3) Credit Hours Third Year 2014-2015 Prepared
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study
 ISSN 0970-4388 Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study BOGRA P a, KASWAN S b ABSTRACT: In the present study, 25% EDTA, in gel form, was used to analyse its micromorphological effects on tooth surfaces with
ISSN 0970-4388 Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study BOGRA P a, KASWAN S b ABSTRACT: In the present study, 25% EDTA, in gel form, was used to analyse its micromorphological effects on tooth surfaces with
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/12/e1601838/dc1 Supplementary Materials for General and programmable synthesis of hybrid liposome/metal nanoparticles Jin-Ho Lee, Yonghee Shin, Wooju Lee, Keumrai
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/12/e1601838/dc1 Supplementary Materials for General and programmable synthesis of hybrid liposome/metal nanoparticles Jin-Ho Lee, Yonghee Shin, Wooju Lee, Keumrai
Advance Dental Simulation Module on Crown Preparation
 Advance Dental Simulation Module on Crown Preparation Ranier M. Adarve, DMD, MS, MHPE Prosthodontist and Instructional Designer Introduction Welcome! This module is developed to guide dental students in
Advance Dental Simulation Module on Crown Preparation Ranier M. Adarve, DMD, MS, MHPE Prosthodontist and Instructional Designer Introduction Welcome! This module is developed to guide dental students in
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material
 Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA in the Apical Sealing Ability of Lased And Unlased Root Canal Walls - A Pilot Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XIV (June 2016), PP 100-104 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XIV (June 2016), PP 100-104 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA
Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF A SINGLE CANCELLOUS BONE TRABECULAE TAKEN FROM BOVINE FEMUR
 Advanced Materials Development and Performance (AMDP2011) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 6 (2012) 349-354 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S201019451200342X
Advanced Materials Development and Performance (AMDP2011) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 6 (2012) 349-354 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S201019451200342X
Acetate peel technique: a rapid way of preparing sequential surface replicas of dental hard tissues for microscopic examination
 Archives of Oral Biology (2005) 50, 837 842 www.intl.elsevierhealth.com/journals/arob Acetate peel technique: a rapid way of preparing sequential surface replicas of dental hard tissues for microscopic
Archives of Oral Biology (2005) 50, 837 842 www.intl.elsevierhealth.com/journals/arob Acetate peel technique: a rapid way of preparing sequential surface replicas of dental hard tissues for microscopic
The Histology of Dentin
 The Histology of Dentin Pauline Hayes Garrett, D.D.S. Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore This material was taken from: Essentials of Oral
The Histology of Dentin Pauline Hayes Garrett, D.D.S. Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore This material was taken from: Essentials of Oral
SPACE MAINTAINER. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of premature loss of primary teeth and use of space maintainers must
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of premature loss of primary teeth and use of space maintainers must
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary Vol.:9 No.:2 2012
 MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
Operative dentistry. Lec: 10. Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE):
 Operative dentistry Lec: 10 د.عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE): There are 2 types: 1) Unreinforced ZOE (ordinary type): supplied as powder (zinc oxide + some additives like zinc acetate, white
Operative dentistry Lec: 10 د.عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE): There are 2 types: 1) Unreinforced ZOE (ordinary type): supplied as powder (zinc oxide + some additives like zinc acetate, white
