Effects of Citric Acid and EDTA on Periodontally Involved Root Surfaces: A SEM Study
|
|
|
- Myles Brown
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 /jp-journals Sunkara Shree Ramalinga Prasad et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Effects of Citric Acid and EDTA on Periodontally Involved Root Surfaces: A SEM Study Sunkara Shree Ramalinga Prasad, Chitturi Radharani, Siddhartha Varma, SV Kiran Kumar Soumya Sinha, Bijle Mohammed Nadeem Ahmed ABSTRACT Aim: Root debridement by scaling and root planing may not completely remove contaminated cementum particularly in more apical areas. The smear layer formed during root planing inhibits cell migration and attachment leading to impaired marginal periodontal healing. The present study was done to compare the morphological effects of root surface demineralization using citric acid and EDTA as root-conditioning agents. Materials and methods: Thirty fragments of human dental roots previously exposed to periodontal disease were scaled and randomly divided into the following groups of treatment: Group I: Hand instrumentation and conditioning with normal saline for 5 minutes as control; group II: Hand instrumentation and conditioning with citric acid (ph 1) for 5 minutes and group III: Hand instrumentation and conditioning with EDTA (ph-7.4) for 5 minutes. Scanning electron microscopy was used to check for the presence of residual smear layer and for measuring the number and area of exposed dentin tubules. Results: The mean efficacy of smear layer removal was compared between groups I and II, groups I and III and groups II and III, it was found to be statistically significant at 5%. When the mean diameter of the dentinal tubules and mean total surface area occupied by the dentinal tubule orifices was compared between groups II and III it was found to be statistically significant at 1% level of significance. Conclusion: Citric acid causes greater degree of morphological alterations than EDTA and is considered to be a better rootconditioning agent. However, the use of EDTA cannot be ruled out. Clinical significance: This study supports the hypothesis that demineralizing agents can be used as an adjunct to the periodontal treatment aiming at restoring the biocompatibility of roots and helps in choosing an appropriate agent for root conditioning. Keywords: Root planning, Smear layer, Root conditioning. How to cite this article: Prasad SSR, Radharani C, Varma S, Kumar SVK, Sinha S, Bijle MNA. Effects of Citric Acid and EDTA on Periodontally Involved Root Surfaces: A SEM study. J Contemp Dent Pract 2012;13(4): Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None declared 446 INTRODUCTION Periodontitis-affected cementum presents loss of collagen fiber insertion, may harbor bacterial cells and may be contaminated by endotoxins which may suppress fibroblast migration and proliferation on cementum. Root debridement by scaling and root planing may not completely remove contaminated cementum particularly in more apical areas and the smear layer formed during root planing inhibits cell migration and attachment leading to impaired marginal periodontal healing. 1 There is considerable interest in the use of chemical agents to assist in root preparation. Agents have been proposed to accomplish the following: Eliminate cytotoxic material from affected root surfaces Clean the exposed dentin surfaces Decalcify planed root surfaces exposing dentine or cementum matrix collagen and thus facilitate attachment between the root surface and the healing connective tissue. 7 In the present study, an attempt is made to compare the morphological effects of root surface demineralization using citric acid and EDTA as root-conditioning agents. Objective of the study: To test efficacy of smear layer removal. Appreciation of collagen fiber-like structures within intertubular dentin. Evaluate number of dentinal tubule orifices. Estimate diameter of individual dentinal tubules. Evaluate total surface area occupied by the dentinal tubules. MATERIALS AND METHODS Fifteen extracted single-rooted human teeth of 12 subjects with advanced periodontitis were collected from the JAYPEE
2 JCDP Effects of Citric Acid and EDTA on Periodontally Involved Root Surfaces: A SEM study Department of Oral Surgery, SDM College of Dental Sciences, Dharwad. Criteria for Selection of the Teeth No history of root planing, scaling and prophylaxis in the previous 6 months No history of acute pain or swelling necessitating their removal Proximal attachment loss of 5 mm or more Bleeding on gentle probing Abscence of caries on the proximal surface selected for the study No history of use of antibiotics during the previous 6 months No history of any systemic diseases. The extracted teeth were placed in sterile vials containing normal saline solutions which were processed without delay. Preparation of Teeth The teeth were cleaned of blood and saliva with a soft bristled brush and distilled water. A dissecting microscope was used to determine the level of connective tissue attachment and that was marked with a small dental bur. The reference groove was then accentuated by deepening the groove with a diamond disk in high speed hand piece under continuous water coolant. The proximal surfaces of each tooth were vigorously root planed with Gracey No.1 and 2 hand curette which was resharpened after each block in an attempt to remove all cementum and achieve a smooth, hard, glass-like surface. The instrumented surfaces were then re-examined to ensure removal of all calculus. Using a high speed handpiece with copious water coolant the crowns were resected at the cementoenamel junction (CEJ). To provide an experimental surface, each tooth was sectioned longitudinally as 2 parts, and the pulpal side was flattened with a straight bur followed by a small inverted cone to make a horizontal groove on the pulpal surface for identification purpose. Lastly, these specimen were harvested by a horizontal cut in the coronal 1/3rd of each tooth half, to yield dentin slabs about 4 4 mm in size. This yielded a total of 40 dentin slabs. Then each tooth section was then scrubbed with a soft brush and distilled water to remove grinding debris. Preparation of Acid Solutions A citric acid solution was prepared by slowly adding 65 gm of citric acid crystals into 100 ml of distilled water and stirred constantly. This gave a ph 1 solution, when checked with a ph meter. EDTA solution was prepared by slowly adding 24 gm of disodium salt of EDTA to 100 ml of distilled water and stirred constantly. This gave a ph of 7.4 when checked with a ph meter. Both the solutions were prepared immediately before the experimental treatment. Out of the 30 dentine slabs, 10 sections were randomly assigned to the following three treatment groups Group I: Hand instrumentation and conditioning with normal saline for 5 minutes as control Group II: Hand instrumentation and conditioning with citric acid (ph 1) for 5 minutes Group III: Hand instrumentation and conditioning with EDTA (ph - 7.4) for 5 minutes. List of Armamentarium Soft bristle brush Dissecting microscope Sterile vials Diamond-cutting disks and cone bur Gracey s No I and II hand curette Tweezer and cotton pellets ph meter Electron microscope. Chemical Treatment of Root Surfaces The acid solutions were applied for 5 minutes to the experimental root surfaces with cotton pellets moistened with the agent, and the cotton pellets were changed 2 times per minute. These solutions were applied with light pressure to allow the agent to wet the surface without burnishing the agent into the root surface. Additional tooth sections served as controls and treated with cotton pellets moistened with normal saline solution. After conditioning, specimens were rinsed for 2 minutes with distilled water. Preparation for SEM Study After treatment of the root surfaces, samples were fixed in 2.5% gluteraldehyde in phosphate buffer (ph 7.3) for 24 hours at 40 C, washed three times for 10 minutes each in phosphate buffer, post fixed in phosphate-buffered 1.5% osmium tetroxide for 2 hours and washed three more times in phosphate buffer. The specimens were then dehydrated in a graded series of aqueous ethanol solutions 50, 70, 85, 95 and 100% ethanol for 10 minutes each. After 2 more 10 minutes washing in absolute ethanol, the samples were dried overnight in a dessicator jar containing silica gel. They were mounted on SEM stubs with silver paint and sputter coated with gold. The mounted slabs were evaluated using a Jeol 100 CX SEM. The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice, July-August 2012;13(4):
3 Sunkara Shree Ramalinga Prasad et al SEM Examination The presence of smear layer, exposure of the collagen fiber like structures, the number of dentinal tubules, diameter of the tubules and the average total surface area occupied by the tubules were measured at a magnification of 3,000 with zero tilt angle. The efficacy of smear layer removal by using different solutions was estimated by the following scores: Score 0: No patches of smear layer present. Score 1: Small patches of smear layer present. Score 2: Definite patches of smear layer present. Score 3: Considerable amount of smear layer present. Score 4: Completely covered by smear layer. The appreciations of collagen fiber like structures within the intertubular area were estimated by using the following scores: Score 1: Poor (cannot be appreciated) Score 2: Moderate Score 3: Good Score 4: Excellent. The diameter of the dentinal tubule orifices, total surface area occupied by the dentinal tubule orifices were measured directly from the screen of the SEM with caliberated scales. A single investigator performed all morphometric measurements. Total of m 2 area was measured from each specimen. RESULTS The study consisted of 30 specimens, out of which, 10 specimens were randomly assigned to three treatment groups: Group I saline, group II citric acid and group III EDTA. After the treatment the specimens were immediately prepared for the SEM examination. A single investigator performed all the morphometric analysis. The mean values obtained for various parameters in the different groups were subjected to statistical analysis by applying Students t-test. Efficacy of Smear Layer Removal When the mean efficacy of smear layer removal was compared between groups I and II, groups I and III and groups II and III, it was found to be statistically significant at 5% level of significance (p < 0.05) as shown in Table 1 (Figs 1 and 2). Appreciation of Collagen Fiber-like Structures When the mean appreciation of collagen fiber-like structures was compared between groups I and II, groups I and III and groups II and III it was found to be satistically significant at 5% level of significance as shown in Table 2. Number of Dentinal Tubule Orifices When the mean number of dentinal tubule orifices was compared between groups II and III it was found to be statistically not significant as shown in Table 3. Table 1: Mean efficacy of smear layer removal: Comparison between different groups Variables Mean SD t-value p-value Significance Saline <0.05 S Citric acid Saline <0.05 S EDTA Citric acid <0.05 S EDTA Fig. 1: Group II: Hand instrumented and citric acid-treated surface. It had smooth to undulating surface texture. Round to oval dentinal tubules are evident and devoid of smear layer 448 Fig. 2: Group III: Hand instrumented and EDTA treated surface. It had smooth to undulating surface texture. Open dentinal tubules can be appreciated JAYPEE
4 JCDP Effects of Citric Acid and EDTA on Periodontally Involved Root Surfaces: A SEM study Table 3: Mean comparison of dentinal tubule orifices between different treatment groups Variable Material Mean SD t-value p-value Significance Tubule orifice Citric acid >0.01 NS EDTA NS: Nonsignificant Table 2: Mean appreciation of collagen-like structures: Comparison between different groups Variables Mean SD t-value p-value Significance Saline <0.05 S Citric acid Saline <0.05 S EDTA Citric acid <0.05 S EDTA S: Significant Diameter of the Dentinal Tubules When the mean diameter of the dentinal tubules was compared between groups II and III it was found to be statistically significant at 1% level of significance as shown in Table 4. Total Surface Area Occupied by the Dentinal Tubule Orifices When the mean total surface area occupied by the dentinal tubule orifices was compared between groups II and III it was found to be statistically significant at 1% level of significance as shown in Table 5. Extensive surface cracking was a frequent finding among all the different groups. DISCUSSION The surface appearance of the root-planed specimens in this study resemble those in previous investigations and thus may represent a smear layer. 2,3,7 Smear layer is formed irrespective of the treatment modality used, 3 i.e. ultrasonic, curette or diamond bur. In this study, both the acids (citric acid and EDTA) used were effective in removing the smear layer than the saline-treated group. Out of these, citric acid had better efficacy in smear removal than EDTA. The agents used in this study either diminished or completely removed the smear layer and exposed the dentinal tubule. This study is in agreement with the study done by Hanes PJ et al 4 who had observed some amount of surface debris on specimens treated with different acids. The method of application has varied among the clinicians, i.e. placement of the agent either passively or burnishing. In the present study, application with light pressure is preferred over burnishing technique as the later may itself form smear layer which may partially or completely obliterate the dentinal tubule openings. Furthermore, both the techniques were found to be equally effective in removing the smear layer in a study done by Rosa wen C et al. 5 The results of this study indicate that citric acid causes greater degree of collagen fiber exposure than EDTA. Counting of the dentinal tubule orifices in saline group was not possible as the root surface was covered by smear layer. Hence, comparison was made between the acids used. Comparing the mean number of dentinal tubule orifices exposed there was no statistically significant difference between both the acid groups. This indicated that both the acids were effective in exposing the dentinal tubules almost to the same extent. Intergroup comparison showed that citric acid had greater mean diameter (1.75 m) than EDTA (1.24 m). However, it appears that the mean diameter of the acidtreated groups is higher than the mean diameter of the control Table 4: Mean comparison of diameter of dentinal tubule orifices between different treatment groups Variable Material Mean SD t-value p-value Significance Tubule diameter Citric acid <0.01 S EDTA Table 5: Mean comparison of total surface area occupied by the dentinal tubule orifices between different treatment groups Variable Material Mean SD t-value p-value Significance Surface area Citric acid <0.01 S EDTA NS: Nonsignificant; S: Significant The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice, July-August 2012;13(4):
5 Sunkara Shree Ramalinga Prasad et al specimens (1.05 m) in a study done by Labahn R et al. 5 This widening of dentinal tubule orifices was due to the preferential demineralization of peritubular dentin. The results of this study were similar to the studies done by Hanes PJ and Labahn R. 4,6 However, this study is in contrast to studies done by Lafferty and Lasho where the dentinal tubules and the dentin between the tubules were affected to the same degree by either of the acid solutions. 7,8 Intergroup comparison showed citric acid had greater mean total surface area occupied by the dentinal tubules than EDTA. This was due to the greater diameter of the dentinal tubules obtained in citric acid groups. This finding was in agreement with the study done by Hanes PJ et al who compared between citric acid and EDTA. Baker et al 9 have clearly demonstrated the superiority of citric acid in comparison to EDTA when applied for 5 minutes on planed dentin root surfaces. Ruggeri et al 10 presented reliable findings using monoclonal antibodies and field emission in-lens scanning electron microscopy (FEISEM) showing that both citric acid and EDTA treatments are able to etch and expose collagen fibrils and proteoglycans without any degradation of dentin collagen matrix. Study done by Natalia et al 11 to compare four of the most frequently used chemical root conditioners according to their efficiency on smear layer removal and dentin tubule widening showed that citric acid was the most effective followed by tetracycline-hcl, phosphoric acid and EDTA. This information can be of value as an extraparameter for choosing one of them for root conditioning. The results of this study are limited to the physical finding of root surface changes and do not present in vivo differences that may result from the physiologic effect of these acids. Differences between our results and those of other studies may be related to the disease status of the dentine specimens utilized, the demineralizing agent or a combination of these variables. Additional studies of these variables with better standardization are needed for better understanding. CONCLUSION Since, Register and Burdick 12 compared root conditioning with citric acid (ph 1 for 2-3 min) and other chemical substances and found optimal cementogenesis and connective tissue new attachment, several investigators have devoted considerable time studying conditioning agents to improve periodontal regeneration. Unfortunately, numerous and often uncontrolled histological and clinical studies have created controversy and confusion about the positive or negative effects of those agents. 13 Both the acids are effective in removing the smear layer and exposing the collagen fibers. Citric acid is more effective in removing the smear layer and exposing the root collagen compared with EDTA. Citric acid causes greater degree of morphological alterations (mean diameter, mean total surface area occupied by dentinal tubules) than EDTA. Citric acid is considered to be a better root conditioning agent. However, the use of EDTA cannot be ruled out. CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE Studies have suggested that the presence of smear layer interposed between the root surface and the adjacent connective tissue may serve as a physical barrier to the development of a connective tissue attachment to the root surface. Our present study, supports the hypothesis that demineralizing agents can be used as an adjunct to the periodontal treatment aiming at restoring the biocompatibility of roots and helps in choosing an appropriate agent for root conditioning. REFERENCES 1. Aleo JJ, De Renzis FA, Farber PA. In vitro attachment of human gingival fibroblasts to root surfaces. J Periodontol 1975;46: Blomlof J, Blomlf LB, Lindskog SF. Smear layer removal and collagen exposure after nonsurgical root planing followed by etching with an EDTA gel preparation. J Periodontol 1996;67: Blomlof J, Blomlof LB, Lindskog SF. Smear layer formed by different root planing modalities and its removal by ethylenediaminetetra acetic acid gel preparation. Int Periodont Rest Dent 1997;17: Henes PJ, O Brien NJ, Garnick JJ. A morphologic comparison of radicular dentine following root planing and treatment with citric acid or tetracycline HCL. J Clin Periodontol 1991;18: Rosa wen C, Caffesse RG, Morrison EC, Nasjletti CE, Parikh UK. In vitro effects of citric acid application technique on dentine surfaces. J Periodontol 1992;63: Labahn R, Fahrenbach WH, Clark SM, Lie T. Root dentine morphology after different modes of citric acid and tetracycline HCL conditioning. J Periodontol 1992; Lafferty TA, Gher ME, Gray JL. Comparative SEM study on the effect of acid etching with tetracycline HCL or citric acid on instrumented periodontally involved root surfaces. J Periodontol 1993;64: Lasho DJ, O leary TJ, Kafrawy AH. A scanning electron microscope study of the effects of various agents on instrumented periodontally involved root surfaces. J Periodontol 1983;54: Baker DL, Stanley Pavlow SA, Wikesjö UME. Fibrin clot adhesion to dentin conditioned with protein constructs: An in vitro proof-of-principle study. J Clin Periodontol 2005;32: Ruggeri A, Prati C, Mazzoni A, Nucci C, Di Lenarda R, Mazzotti G, et al. Effects of citric acid and EDTA conditioning on exposed root dentin: An immunohistochemical analysis of collagen and proteoglycans. Arch Oral Biol 2007;52: JAYPEE
6 JCDP Effects of Citric Acid and EDTA on Periodontally Involved Root Surfaces: A SEM study 11. Nathalia GA, Maria LR, Fabiana H, Marcus GS, Adriana CP, et al. Comparison among four commonly used demineralizing agents for root conditioning. A scanning electron microscopy. J Appl Oral Sci 2011;19(5): Register AA, Burdick FA. Accelerated reattachment with cementogenesis to dentin demineralized in situ. I. Optimun range. J Periodontol 1975;46: Mariotti A. Efficacy of chemical root surface modifers in the treatment of periodontal disease. A systematic review. Ann Periodontol 2006;8: ABOUT THE AUTHORS Sunkara Shree Ramalinga Prasad Professor, Department of Periodontics, Drs Sudha and Nageswara Rao Siddhartha Institute of Dental Sciences, Krishna, Andhra Pradesh India Chitturi Radharani Professor, Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry, Gitam Dental College, Vizag, Andhra Pradesh, India Siddhartha Varma Senior Lecturer, Department of Periodontics, School of Dental Sciences, KIMSDV, Karad, Maharashtra, India SV Kiran Kumar Senior Lecturer, Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry MA Rangoonwala College of Dental Sciences and Research Centre Pune, Maharashtra, India Soumya Sinha Senior Lecturer, Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry MA Rangoonwala College of Dental Sciences and Research Centre Pune, Maharashtra, India Bijle Mohammed Nadeem Ahmed (Corresponding Author) Postgraduate Student, Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry, MA Rangoonwala College of Dental Sciences and Research Centre, Pune, Maharashtra, India, Phone: info@drnadeembijle.com/nbijle@yahoo.co.in The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice, July-August 2012;13(4):
The effect of root surface conditioning on smear layer removal in periodontal regeneration (a scanning electron microscopic study)
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The effect of root surface conditioning on smear layer removal in periodontal regeneration (a scanning electron microscopic study) To cite this article:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The effect of root surface conditioning on smear layer removal in periodontal regeneration (a scanning electron microscopic study) To cite this article:
Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study
 ISSN 0970-4388 Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study BOGRA P a, KASWAN S b ABSTRACT: In the present study, 25% EDTA, in gel form, was used to analyse its micromorphological effects on tooth surfaces with
ISSN 0970-4388 Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study BOGRA P a, KASWAN S b ABSTRACT: In the present study, 25% EDTA, in gel form, was used to analyse its micromorphological effects on tooth surfaces with
Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location
 Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Blood clot stabilization on root dentin conditioned by the combination of tetracycline and EDTA
 Original Article Braz J Oral Sci. April June 2014 - Volume 13, Number 2 Blood clot stabilization on root dentin conditioned by the combination of tetracycline and EDTA Gustavo Giacomelli Nascimento 1,
Original Article Braz J Oral Sci. April June 2014 - Volume 13, Number 2 Blood clot stabilization on root dentin conditioned by the combination of tetracycline and EDTA Gustavo Giacomelli Nascimento 1,
Initial Therapy. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS. Oral sulcular epithelium. Oral. epithelium. Junctional. epithelium. Connective tissue.
 Oral sulcular epithelium Junctional epithelium E Oral epithelium Initial Therapy Connective tissue Bone Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Non-surgical Therapy Scaling: Instrumentation of the crown and root
Oral sulcular epithelium Junctional epithelium E Oral epithelium Initial Therapy Connective tissue Bone Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Non-surgical Therapy Scaling: Instrumentation of the crown and root
Abstract. Seer Publishing
 The Attachment of V79 and Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts on Periodontally Involved Root Surfaces Following Treatment with EDTA, Citric Acid, or Tetracycline HCL: An SEM in vitro Study Abstract
The Attachment of V79 and Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts on Periodontally Involved Root Surfaces Following Treatment with EDTA, Citric Acid, or Tetracycline HCL: An SEM in vitro Study Abstract
Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth
 Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth B.Sc., D.D.S., Specialty Certificate in Oral Pathology, M.S. Department of
Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth B.Sc., D.D.S., Specialty Certificate in Oral Pathology, M.S. Department of
Objective: The purpose of this study was to investigate the ultramorphology of the root
 www.scielo.br/jaos Ultramorphology of the root surface subsequent to hand-ultrasonic simultaneous instrumentation during non-surgical periodontal treatments. An in vitro study Simone D. ASPRIELLO 1, Matteo
www.scielo.br/jaos Ultramorphology of the root surface subsequent to hand-ultrasonic simultaneous instrumentation during non-surgical periodontal treatments. An in vitro study Simone D. ASPRIELLO 1, Matteo
The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic
 1 1 INTRODUCTION The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic bacteria, aims at the regeneration of a periodontal attachment composed of new cementum, alveolar bone
1 1 INTRODUCTION The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic bacteria, aims at the regeneration of a periodontal attachment composed of new cementum, alveolar bone
Corresponding Author:Dr.Sneha Vaidya 3
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. VII (Nov. 2017), PP 75-81 www.iosrjournals.org Efficacy of Endoactivator Irrigation
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. VII (Nov. 2017), PP 75-81 www.iosrjournals.org Efficacy of Endoactivator Irrigation
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS Dentists need to understand that the decision to remove or not reimplant an avulsed incisor must be made very carefully. The loss of such a tooth in
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS Dentists need to understand that the decision to remove or not reimplant an avulsed incisor must be made very carefully. The loss of such a tooth in
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
A New Solution for the Removal of the Smear Layer
 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2003 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 29, NO. 3, MARCH 2003 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES A New Solution for the Removal of the Smear Layer Mahmoud
JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2003 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 29, NO. 3, MARCH 2003 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES A New Solution for the Removal of the Smear Layer Mahmoud
Comparison of removal of endodontic smear layer using NaOCl, EDTA, and different concentrations of maleic acid A SEM study
 Endodontology, Vol. 15, 2003 Comparison of removal of endodontic smear layer using NaOCl, EDTA, and different concentrations of maleic acid A SEM study *Prabhu SG **Rahim N ***Bhat KS ***Mathew J ABSTRACT
Endodontology, Vol. 15, 2003 Comparison of removal of endodontic smear layer using NaOCl, EDTA, and different concentrations of maleic acid A SEM study *Prabhu SG **Rahim N ***Bhat KS ***Mathew J ABSTRACT
STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT. Cynthia Fong, RDH, MS
 STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT 2014 Kentucky Dental Association Louisville, KY Friday, March 14, 2014 9:00 a.m. 12 Noon STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course provides
STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT 2014 Kentucky Dental Association Louisville, KY Friday, March 14, 2014 9:00 a.m. 12 Noon STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course provides
DENTIN It a hard vital tissue, surrounds the pulp & underlies the enamel on the crown & the cementum on the roots of the teeth.
 Lec. 7 Dr. Ali H.Murad DENTIN It a hard vital tissue, surrounds the pulp & underlies the enamel on the crown & the cementum on the roots of the teeth. Physical properties: 1-Dentin is pale yellow in color,
Lec. 7 Dr. Ali H.Murad DENTIN It a hard vital tissue, surrounds the pulp & underlies the enamel on the crown & the cementum on the roots of the teeth. Physical properties: 1-Dentin is pale yellow in color,
Original Article Effects of minocycline-hcl paste root conditioning on periodontal surgery: in vitro and in vivo studies
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):4080-4086 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0004763 Original Article Effects of minocycline-hcl paste root conditioning on periodontal surgery: in vitro and in vivo studies
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):4080-4086 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0004763 Original Article Effects of minocycline-hcl paste root conditioning on periodontal surgery: in vitro and in vivo studies
The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato, Carlo Baldi, Roberto Rotundo, Debora Franceschi,
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato, Carlo Baldi, Roberto Rotundo, Debora Franceschi,
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary Vol.:9 No.:2 2012
 MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
Root end preparation techniques Summary of papers
 Root end preparation techniques Summary of papers 34 Flath 1987 This paper presented 2 cases in which retrograde fillings were carried out using new sonic or ultrasonic instruments (endo files held in
Root end preparation techniques Summary of papers 34 Flath 1987 This paper presented 2 cases in which retrograde fillings were carried out using new sonic or ultrasonic instruments (endo files held in
Root Dentine Sensitivity
 Indian Medical Gazette JULY 2012 269 Original Study Root Dentine Sensitivity Jyoti Ajay Khade, Associate Professor, Dept. of Dentistry, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS) Adilabad, A.P.
Indian Medical Gazette JULY 2012 269 Original Study Root Dentine Sensitivity Jyoti Ajay Khade, Associate Professor, Dept. of Dentistry, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS) Adilabad, A.P.
Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical investigation
 American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com eissn: 2347-2766 Original Research Article Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical Ninad Moon 1, Prasant Pillai
American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com eissn: 2347-2766 Original Research Article Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical Ninad Moon 1, Prasant Pillai
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the. Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System
 Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation. Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman
 Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman Outline Classification of periodontal instruments General principles of instrumentation Principles of scaling
Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman Outline Classification of periodontal instruments General principles of instrumentation Principles of scaling
Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV.
 Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV. Class V. Cervical defects - Dental caries - Non carious lesions (erosion, abrasion, V shaped defects) Types of defects Caries Erosion Abrasion V shaped
Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV. Class V. Cervical defects - Dental caries - Non carious lesions (erosion, abrasion, V shaped defects) Types of defects Caries Erosion Abrasion V shaped
PERIODONTAL CHANGES IN FLUOROSED AND NONFLUOROSED TEETH BY SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY
 128 PERIODONTAL CHANGES IN FLUOROSED AND NONFLUOROSED TEETH BY SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY Vandana KL, a Pauline George, b Charles M Cobb c Karnataka, India. SUMMARY: To date, studies on the effect of
128 PERIODONTAL CHANGES IN FLUOROSED AND NONFLUOROSED TEETH BY SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY Vandana KL, a Pauline George, b Charles M Cobb c Karnataka, India. SUMMARY: To date, studies on the effect of
stabilisation and surface protection
 Guiding the way to caries stabilisation and surface protection Fissure sealing MI restorations Pulp capping Hypersensitivity Protection Caries stabilisation Fuji Triage from GC. Temporary restorations
Guiding the way to caries stabilisation and surface protection Fissure sealing MI restorations Pulp capping Hypersensitivity Protection Caries stabilisation Fuji Triage from GC. Temporary restorations
SUBCHAPTER 16H - DENTAL ASSISTANTS SECTION CLASSIFICATION AND TRAINING
 SUBCHAPTER 16H - DENTAL ASSISTANTS SECTION.0100 - CLASSIFICATION AND TRAINING 21 NCAC 16H.0101 CLASSIFICATION Based upon education, training, and experience, a dental assistant shall be categorized as
SUBCHAPTER 16H - DENTAL ASSISTANTS SECTION.0100 - CLASSIFICATION AND TRAINING 21 NCAC 16H.0101 CLASSIFICATION Based upon education, training, and experience, a dental assistant shall be categorized as
Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA in the Apical Sealing Ability of Lased And Unlased Root Canal Walls - A Pilot Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XIV (June 2016), PP 100-104 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XIV (June 2016), PP 100-104 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA
Tooth Retained Implant: No More an Oxymoron
 بنام خدا بنام خدا OPEN ACCESS Freely Available Online Original Hypothesis Tooth Retained Implant: No More an Oxymoron Divya Bhat a Abstract a Department of Periodontics, D.A.P.M.R.V. Dental College, Karnataka,
بنام خدا بنام خدا OPEN ACCESS Freely Available Online Original Hypothesis Tooth Retained Implant: No More an Oxymoron Divya Bhat a Abstract a Department of Periodontics, D.A.P.M.R.V. Dental College, Karnataka,
Evaluation of Blood Cell Attachment on Er:Yag Laser Applied Root Surface Using Scanning Electron Microscopy
 560 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper International Journal of Medical Sciences 2013; 10(5):560-566. doi: 10.7150/ijms.5233 Evaluation of Blood Cell Attachment on Er:Yag Laser Applied Root
560 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper International Journal of Medical Sciences 2013; 10(5):560-566. doi: 10.7150/ijms.5233 Evaluation of Blood Cell Attachment on Er:Yag Laser Applied Root
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
Dental Journal. (Majalah Kedokteran Gigi) 2016 March; 49(1): 5 9
 5 Research Report Dental Journal (Majalah Kedokteran Gigi) 2016 March; 49(1): 5 9 The difference of saline and sterile water for tetracycline hydrochloride solvents in cementum demineralization Shinta
5 Research Report Dental Journal (Majalah Kedokteran Gigi) 2016 March; 49(1): 5 9 The difference of saline and sterile water for tetracycline hydrochloride solvents in cementum demineralization Shinta
Department of Oral Surgery, Heinrich Heine University, D Düsseldorf, Germany.
 Lasers Surg Med. 2007 Jun;39(5):428-40 Immunohistochemical characterization of periodontal wound healing following nonsurgical treatment with fluorescence controlled Er:YAG laser radiation in dogs. Schwarz
Lasers Surg Med. 2007 Jun;39(5):428-40 Immunohistochemical characterization of periodontal wound healing following nonsurgical treatment with fluorescence controlled Er:YAG laser radiation in dogs. Schwarz
Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases. As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
 Melissa Rudzinski Preventive Dentistry Shaunda Clark November 2013 Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
Melissa Rudzinski Preventive Dentistry Shaunda Clark November 2013 Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
A SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY STUDY OF ROOT SURFACE SMEAR LAYER REMOVAL AFTER TOPICAL APPLICATION OF EDTA PLUS A DETERGENT
 www.fob.usp.br/revista or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci 2005; 13(3): 247-52 A SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY STUDY OF ROOT SURFACE SMEAR LAYER REMOVAL AFTER TOPICAL APPLICATION OF EDTA PLUS A DETERGENT
www.fob.usp.br/revista or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci 2005; 13(3): 247-52 A SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY STUDY OF ROOT SURFACE SMEAR LAYER REMOVAL AFTER TOPICAL APPLICATION OF EDTA PLUS A DETERGENT
21 NCAC 16G.0101 FUNCTIONS THAT MAY BE DELEGATED
 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 NCAC 1G.01is proposed for amendment as follows: 1 NCAC 1G.01 FUNCTIONS THAT MAY BE DELEGATED A dental hygienist may be delegated functions to be performed under the control and
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 NCAC 1G.01is proposed for amendment as follows: 1 NCAC 1G.01 FUNCTIONS THAT MAY BE DELEGATED A dental hygienist may be delegated functions to be performed under the control and
Fuji II LC. A Perfect Choice
 A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
For the Perfect Class V and All Cervical Area Gingival Margins when Placing Direct Composites, Create an Injection Molding Matrix
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report For the Perfect Class V and All Cervical Area Gingival Margins when Placing Direct Composites, Create an Injection Molding Paul C Belvedere* Adjunct Professor,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report For the Perfect Class V and All Cervical Area Gingival Margins when Placing Direct Composites, Create an Injection Molding Paul C Belvedere* Adjunct Professor,
Hereditary Gingival Fibromatosis with Distinctive Facies
 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1248 Sunkara Shree Ramalinga Prasad et al CASE REPORT Sunkara Shree Ramalinga Prasad, Chitturi Radharani, Soumya Sinha, SV Kiran Kumar ABSTRACT Hereditary gingival enlargement
10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1248 Sunkara Shree Ramalinga Prasad et al CASE REPORT Sunkara Shree Ramalinga Prasad, Chitturi Radharani, Soumya Sinha, SV Kiran Kumar ABSTRACT Hereditary gingival enlargement
Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession
 World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 117-121, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82175 Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession 1 1 1
World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 117-121, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82175 Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession 1 1 1
Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports
 0 Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports R.G. Caffesse, B.A. Smith/ B. Duff, E.C. Morrison, D. Merrill/ and W. Becker In the cases reported here, the response
0 Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports R.G. Caffesse, B.A. Smith/ B. Duff, E.C. Morrison, D. Merrill/ and W. Becker In the cases reported here, the response
DENTAL CARIES CARACTERISTICS, HANDPIECES, HAND INSTRUMENTS, (USED IN PHANTOM LAB) HYSTOPATHOLOGY. BURS. 3rd year, 1st semester
 DENTAL CARIES CARACTERISTICS, HYSTOPATHOLOGY. HANDPIECES, HAND INSTRUMENTS, BURS. (USED IN PHANTOM LAB) 3rd year, 1st semester DENTAL CARIES CARIES Dental caries is a multifactorial chronic, irreversible
DENTAL CARIES CARACTERISTICS, HYSTOPATHOLOGY. HANDPIECES, HAND INSTRUMENTS, BURS. (USED IN PHANTOM LAB) 3rd year, 1st semester DENTAL CARIES CARIES Dental caries is a multifactorial chronic, irreversible
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of
 Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Effect of Bioconditioning on Surface Characteristics of Periodontally-affected Roots of Diabetic Patients
 wjd WJD Effect of Bioconditioning on Surface Characteristics of Periodontally-affected 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1264 Roots of Diabetic Patients Original Research Effect of Bioconditioning on Surface Characteristics
wjd WJD Effect of Bioconditioning on Surface Characteristics of Periodontally-affected 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1264 Roots of Diabetic Patients Original Research Effect of Bioconditioning on Surface Characteristics
Preclinical Dentistry. I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects. Lenka Roubalíková
 Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková Understanding dental caries crown pulp chamber neck root canal root Dental
Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková Understanding dental caries crown pulp chamber neck root canal root Dental
The dentogingival junction to the
 Volume 79 Number 10 RedefiningtheBiologicWidthinSevere, Generalized, Chronic Periodontitis: Implications for Therapy M. John Novak,* Huda M. Albather, and John M. Close Background: Previous studies demonstrated
Volume 79 Number 10 RedefiningtheBiologicWidthinSevere, Generalized, Chronic Periodontitis: Implications for Therapy M. John Novak,* Huda M. Albather, and John M. Close Background: Previous studies demonstrated
Semiconductor Diode Lasers in Periodontics : An Innovative and Safe
 Semiconductor Diode Lasers in Periodontics : An Innovative and Safe Dr. Sushma S. Lagdive 1, Dr. Pramod P. Marawar 2, Dr. Amit M. Mani 3 1 Senior Lecturer, Dept. of Periodontics, Rural Dental College,
Semiconductor Diode Lasers in Periodontics : An Innovative and Safe Dr. Sushma S. Lagdive 1, Dr. Pramod P. Marawar 2, Dr. Amit M. Mani 3 1 Senior Lecturer, Dept. of Periodontics, Rural Dental College,
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Objectives: The debridement of diseased root surface is usually performed by mechanical
 www.scielo.br/jaos A comparative evaluation of the efficacy of manual, magnetostrictive and piezoelectric ultrasonic instruments an in vitro and SEM study 1 2 3 1- BDS, Post Graduate student, Department
www.scielo.br/jaos A comparative evaluation of the efficacy of manual, magnetostrictive and piezoelectric ultrasonic instruments an in vitro and SEM study 1 2 3 1- BDS, Post Graduate student, Department
PUBLISHED VERSION. This document has been archived with permission from the Australian Dental Association, received 18th January, 2007.
 PUBLISHED VERSION Saunders, J. G. C.; McIntyre, John Malcolm The ability of 1.23% acidulated phosphate fluoride gel to inhibit simulated endogenous erosion in tooth roots Australian Dental Journal, 2005;
PUBLISHED VERSION Saunders, J. G. C.; McIntyre, John Malcolm The ability of 1.23% acidulated phosphate fluoride gel to inhibit simulated endogenous erosion in tooth roots Australian Dental Journal, 2005;
DiaDent Group International DIA.DENT DiaRoot BioAggregate. Root Canal Repair Material
 DiaDent Group International 1.877.DIA.DENT www.diadent.com DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material PRECISION. PURITY. RESULTS ABOUT DIAROOT... DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material is
DiaDent Group International 1.877.DIA.DENT www.diadent.com DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material PRECISION. PURITY. RESULTS ABOUT DIAROOT... DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material is
Nanoionomer: Evaluation of microleakage
 Original Article Nanoionomer: Evaluation of microleakage Abstract Background: Glass ionomer cements are widely used in pediatric practice due to their advantage of fluoride release and chemical bond to
Original Article Nanoionomer: Evaluation of microleakage Abstract Background: Glass ionomer cements are widely used in pediatric practice due to their advantage of fluoride release and chemical bond to
Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin
 Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin Bright Chang D2 Dental Student UAB School of Dentistry Final report (revision) July 26, 2017 Mentors: Nathaniel Lawson,
Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin Bright Chang D2 Dental Student UAB School of Dentistry Final report (revision) July 26, 2017 Mentors: Nathaniel Lawson,
Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1035 CLINICAL ARTICLE Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1035 CLINICAL ARTICLE Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate
Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2006;51:(2):175-179 Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique GM Knight,* JM McIntyre,* Mulyani*
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2006;51:(2):175-179 Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique GM Knight,* JM McIntyre,* Mulyani*
Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control
 Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control REST 528A
Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control REST 528A
The Histology of Dentin
 The Histology of Dentin Pauline Hayes Garrett, D.D.S. Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore This material was taken from: Essentials of Oral
The Histology of Dentin Pauline Hayes Garrett, D.D.S. Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore This material was taken from: Essentials of Oral
Influence of Bioactive Materials on Whitened Human Enamel Surface in vitro study
 Influence of Bioactive Materials on Whitened Human Enamel Surface Influence of Bioactive Materials on Whitened Human Enamel Surface in vitro study Pinheiro HB, Cardoso PEC, Universidade de São Paulo, São
Influence of Bioactive Materials on Whitened Human Enamel Surface Influence of Bioactive Materials on Whitened Human Enamel Surface in vitro study Pinheiro HB, Cardoso PEC, Universidade de São Paulo, São
Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice
 Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
In vitro evaluation of the effect of natural orange juices on dentin morphology
 Restorative Dentistry Restorative Dentistry In vitro evaluation of the effect of natural orange juices on dentin morphology Daniela Leal Zandim (a) Fernanda Oliveira Bello Corrêa (a) Carlos Rossa Júnior
Restorative Dentistry Restorative Dentistry In vitro evaluation of the effect of natural orange juices on dentin morphology Daniela Leal Zandim (a) Fernanda Oliveira Bello Corrêa (a) Carlos Rossa Júnior
PROFOUND HEMOSTASIS AND FLUID CONTROL TISSUE MANAGEMENT
 TISSUE MANAGEMENT PROFOUND HEMOSTASIS AND FLUID CONTROL Unparalleled tissue management starts with rapid, profound hemostasis. To control bleeding and sulcular fluid, no one offers a more complete line
TISSUE MANAGEMENT PROFOUND HEMOSTASIS AND FLUID CONTROL Unparalleled tissue management starts with rapid, profound hemostasis. To control bleeding and sulcular fluid, no one offers a more complete line
Fig 1. An everyday clinical condition that requires a perio-restorative protocol.
 WHY A CORE BUILDUP? In today s restorative practice, we treat patients with substantial amounts of existing restorative dentistry. Old amalgam fillings, 20+ year old crowns and posterior composites that
WHY A CORE BUILDUP? In today s restorative practice, we treat patients with substantial amounts of existing restorative dentistry. Old amalgam fillings, 20+ year old crowns and posterior composites that
CHAPTER 7. ROOT TREATMENT, REATTACHMENT, AND REPAIR
 112 CHAPTER 7. ROOT TREATMENT, REATTACHMENT, AND REPAIR Section 1. Root Healing CHAPTER 7. ROOT TREATMENT, REATTACHMENT, AND REPAIR Section 1. Root Healing DEFINITIONS Repair: Healing of a wound by tissue
112 CHAPTER 7. ROOT TREATMENT, REATTACHMENT, AND REPAIR Section 1. Root Healing CHAPTER 7. ROOT TREATMENT, REATTACHMENT, AND REPAIR Section 1. Root Healing DEFINITIONS Repair: Healing of a wound by tissue
Root Surface Protection Simple. Effective. Important.
 GC Fuji VII / Fuji VII EP Root Surface Protection Simple. Effective. Important. Brush up your painting skills and help your patients Q&A Prof. Laurie Walsh University of Queensland lifestyle factors (frequency
GC Fuji VII / Fuji VII EP Root Surface Protection Simple. Effective. Important. Brush up your painting skills and help your patients Q&A Prof. Laurie Walsh University of Queensland lifestyle factors (frequency
1 Principal and HOD, Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic, C.K.S Theja institute of dental
 ORIGINAL ART TICLE AODMR A Comparative Evaluation of Smear Layer removal between GaAlAs Diode Laser and : an In-Vitro Scanning Electron Microscopic Study a Short Study Datta Prasad S 1, Anusha S 2, Sunil
ORIGINAL ART TICLE AODMR A Comparative Evaluation of Smear Layer removal between GaAlAs Diode Laser and : an In-Vitro Scanning Electron Microscopic Study a Short Study Datta Prasad S 1, Anusha S 2, Sunil
Cutting instruments. Instruments
 Instruments أﻧﺲ اﻟﻌﺒﯿﺪي. د The removal and shaping of tooth structure are essential aspects of restorative dentistry. Initially this was a difficult process accomplished entirely by the use of - Hand instruments.
Instruments أﻧﺲ اﻟﻌﺒﯿﺪي. د The removal and shaping of tooth structure are essential aspects of restorative dentistry. Initially this was a difficult process accomplished entirely by the use of - Hand instruments.
Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93.
 Julia Collins Den 1200 Journal #4 1. Demographics Patient is J.S. age 29, Heavy/II 2. Assessment Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93. Patient does
Julia Collins Den 1200 Journal #4 1. Demographics Patient is J.S. age 29, Heavy/II 2. Assessment Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93. Patient does
Patient demand for esthetic dentistry
 PROFILE Masters of Esthetic Dentistry Keys to Success in Creating Esthetic Class IV Restorations Robert C. Margeas, DDS Current occupation Private Practice Adjunct Professor, Department of Operative Dentistry,
PROFILE Masters of Esthetic Dentistry Keys to Success in Creating Esthetic Class IV Restorations Robert C. Margeas, DDS Current occupation Private Practice Adjunct Professor, Department of Operative Dentistry,
Townie Guest Editorial. Gingival Attachment Loss: Evaluation and Surgical Options. Daniel J. Melker, DDS. fig. 1
 Gingival Attachment Loss: Evaluation and Surgical Options Daniel J. Melker, DDS Attached connective tissue (a.k.a. attached tissue) in the simplest terms is the body s only barrier between the underlying
Gingival Attachment Loss: Evaluation and Surgical Options Daniel J. Melker, DDS Attached connective tissue (a.k.a. attached tissue) in the simplest terms is the body s only barrier between the underlying
Operative dentistry. Lec: 10. Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE):
 Operative dentistry Lec: 10 د.عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE): There are 2 types: 1) Unreinforced ZOE (ordinary type): supplied as powder (zinc oxide + some additives like zinc acetate, white
Operative dentistry Lec: 10 د.عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE): There are 2 types: 1) Unreinforced ZOE (ordinary type): supplied as powder (zinc oxide + some additives like zinc acetate, white
Pelagia Research Library. Comparison of microleakage in bonded amalgam restrorations using different adhesive materials: An invitro study
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2011, 1 (2):92-96 ISSN: 2248 9215 Comparison of microleakage in bonded amalgam restrorations using different
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2011, 1 (2):92-96 ISSN: 2248 9215 Comparison of microleakage in bonded amalgam restrorations using different
Diameter and Density of Dentinal Tubule in Human Primary Teeth
 Original Article Diameter and Density of Dentinal Tubule in Human Primary Teeth Jittikarn Sikanta 1, Sitthichai Wanachantararak 2 and Varisara Sirimaharaj 1 1 Department of Orthodontics and Pediatric Dentistry,
Original Article Diameter and Density of Dentinal Tubule in Human Primary Teeth Jittikarn Sikanta 1, Sitthichai Wanachantararak 2 and Varisara Sirimaharaj 1 1 Department of Orthodontics and Pediatric Dentistry,
Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children
 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1108 Nidhi ORIGINAL Gupta, Manohar ARTICLE Bhat Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children 1
10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1108 Nidhi ORIGINAL Gupta, Manohar ARTICLE Bhat Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children 1
A Step-by-Step Approach to
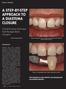 A Step-by-Step Approach to a Diastema Closure A Dual-Purpose Technique that Manages Black Triangles Marcos Vargas, DDS, MS Figure 1: Preoperative view of a patient who presented with a diastema between
A Step-by-Step Approach to a Diastema Closure A Dual-Purpose Technique that Manages Black Triangles Marcos Vargas, DDS, MS Figure 1: Preoperative view of a patient who presented with a diastema between
Scanning Electron Microscope Assessment of Several Resharpening Techniques on the Cutting Edges of Gracey Curettes
 Scanning Electron Microscope Assessment of Several Resharpening Techniques on the Cutting Edges of Gracey Curettes Abstract Aim: Treatment of periodontal diseases is based on efficient scaling and root
Scanning Electron Microscope Assessment of Several Resharpening Techniques on the Cutting Edges of Gracey Curettes Abstract Aim: Treatment of periodontal diseases is based on efficient scaling and root
CITRIC ACID ROOT BIOMODIFICATION IN RECESSION COVERAGE WITH LATERAL PEDICLE FLAP TECHNIQUE- A CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 05 CITRIC ACID ROOT BIOMODIFICATION IN RECESSION COVERAGE WITH LATERAL PEDICLE FLAP TECHNIQUE- A CASE REPORT Mamta Singh
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 05 CITRIC ACID ROOT BIOMODIFICATION IN RECESSION COVERAGE WITH LATERAL PEDICLE FLAP TECHNIQUE- A CASE REPORT Mamta Singh
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association
 All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Calibra. Cements. The Simple Choice for Easy Cleanup
 Calibra Cements The Simple Choice for Easy Cleanup www.calibracement.com The Calibra family of definitive cements was designed to make it easier than ever to achieve consistent, successful results in your
Calibra Cements The Simple Choice for Easy Cleanup www.calibracement.com The Calibra family of definitive cements was designed to make it easier than ever to achieve consistent, successful results in your
Root surface conditioning with nicotine or cotinine reduces viability and density of fibroblasts in vitro
 Clin Oral Invest (2005) 9: 180 186 DOI 10.1007/s00784-004-0294-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Aurora Esmeralda Traverso Martinez. Karina Gonzales Silverio. Jose Carlos Fogo. Keith Lough Kirkwood. Carlos Rossa Jr Root
Clin Oral Invest (2005) 9: 180 186 DOI 10.1007/s00784-004-0294-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Aurora Esmeralda Traverso Martinez. Karina Gonzales Silverio. Jose Carlos Fogo. Keith Lough Kirkwood. Carlos Rossa Jr Root
College Of Dental Sciences And Research, Ghaziabad, India
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 1 Ver. X (January. 2017), PP 113-118 www.iosrjournals.org Clinical Evaluation of two Different
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 1 Ver. X (January. 2017), PP 113-118 www.iosrjournals.org Clinical Evaluation of two Different
Dental material for filling the root canals "AUREOSEAL M.T.A."
 Dental material for filling the root canals "AUREOSEAL M.T.A." Highly biocompatible root canal cement without eugenol. 1. Composition: Powder: Mineral-trioxide-agregat (М.Т.А.) based on Portland cement,
Dental material for filling the root canals "AUREOSEAL M.T.A." Highly biocompatible root canal cement without eugenol. 1. Composition: Powder: Mineral-trioxide-agregat (М.Т.А.) based on Portland cement,
The Effect of Irrigation with Doxycycline or Citric Acid on Leakage and Osseous Wound Healing
 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2002 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 29, NO. 1, JANUARY 2003 The Effect of Irrigation with Doxycycline or Citric Acid on Leakage and
JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2002 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 29, NO. 1, JANUARY 2003 The Effect of Irrigation with Doxycycline or Citric Acid on Leakage and
Comparison of shear bond strength of aesthetic restorative materials
 Comparison of shear bond strength of aesthetic restorative materials Suryakumari B. P. Nujella, Manisha T. Choudary 1, Satyanarayana P. Reddy 2, Kiran kumar M. 3, Gopal T. 4 Abstract Aim: The present study
Comparison of shear bond strength of aesthetic restorative materials Suryakumari B. P. Nujella, Manisha T. Choudary 1, Satyanarayana P. Reddy 2, Kiran kumar M. 3, Gopal T. 4 Abstract Aim: The present study
Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative. Filtek. Supreme Plus Universal Restorative
 Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative TM. Multishade
Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative TM. Multishade
Pediatric endodontics. Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR
 Pediatric endodontics Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR WHY TO PRESERVE PRIMARY TEETH? The preservation of the primary dentition until their normal anticipated exfoliation can be justified
Pediatric endodontics Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR WHY TO PRESERVE PRIMARY TEETH? The preservation of the primary dentition until their normal anticipated exfoliation can be justified
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect Of Strong Organic Acids On Dentinal Tubules Of Teeth- A Scanning Electron Microscopic Study
 IJCMR 445 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect Of Strong Organic Acids On Dentinal Tubules Of Teeth- A Scanning Electron Microscopic Study Daksh Sharma 1, Shreedhar Balasundari 2, Kamboj Mala 3, Natarajan S 4 ABSTRACT
IJCMR 445 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect Of Strong Organic Acids On Dentinal Tubules Of Teeth- A Scanning Electron Microscopic Study Daksh Sharma 1, Shreedhar Balasundari 2, Kamboj Mala 3, Natarajan S 4 ABSTRACT
WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2
 C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary
 SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary Summary of In Vivo Use Of Bioresorbable Xenograft Bone Graft Materials In The Treatment Of One-Walled Intrabony Defects In A Canine Model
SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary Summary of In Vivo Use Of Bioresorbable Xenograft Bone Graft Materials In The Treatment Of One-Walled Intrabony Defects In A Canine Model
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth
 New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children
 Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objective Discuss the role and importance of cements in paediatric dentistry Calcium hydroxide This is a colourless crystal or white powder prepared
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objective Discuss the role and importance of cements in paediatric dentistry Calcium hydroxide This is a colourless crystal or white powder prepared
"Designing a fixed partial denture without a pontic"- Case report
 Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 "Designing a fixed partial denture without a pontic"- Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Khurshid Mattoo, Assistant Professor, Prosthodontics, College of Dental
Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 "Designing a fixed partial denture without a pontic"- Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Khurshid Mattoo, Assistant Professor, Prosthodontics, College of Dental
Give your teeth a hug: a simplified brushing technique for children Journal of Dentistry for Children No.291, September-October, 1984
 Data Sheet no.3 in support of the Collis Curve Toothbrush Give your teeth a hug: a simplified brushing technique for children Journal of Dentistry for Children No.291, September-October, 1984 David Collis
Data Sheet no.3 in support of the Collis Curve Toothbrush Give your teeth a hug: a simplified brushing technique for children Journal of Dentistry for Children No.291, September-October, 1984 David Collis
The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS
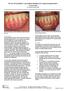 The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS LOCALIZED RECESSION ON TOOTH #25 DUE TO BONE RECESSION (PRE OP) Introduction Tissue grafting
The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS LOCALIZED RECESSION ON TOOTH #25 DUE TO BONE RECESSION (PRE OP) Introduction Tissue grafting
Take-Home Whitening. in vitro study. Benefits of ACP TAKE-HOME WHITENING
 Fluoride and Potassium Nitrate-Fluoride Whitening Agents: in vitro Caries Study Fluoride and Potassium Nitrate-Fluoride Whitening Agents: in vitro Caries Study in vitro study Hicks J and Flaitz C. Effects
Fluoride and Potassium Nitrate-Fluoride Whitening Agents: in vitro Caries Study Fluoride and Potassium Nitrate-Fluoride Whitening Agents: in vitro Caries Study in vitro study Hicks J and Flaitz C. Effects
Management of Inadequate Margins and Gingival Recession Presenting as Tooth Sensitivity
 Management of Inadequate Margins and Gingival Recession Presenting as Tooth Sensitivity Nicolas Elian, DDS Private Practice Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey David Geon U Kim, DDS, MS Faculty and Research Coordinator
Management of Inadequate Margins and Gingival Recession Presenting as Tooth Sensitivity Nicolas Elian, DDS Private Practice Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey David Geon U Kim, DDS, MS Faculty and Research Coordinator
Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
PERIODONTAL (GUM) DISEASE & IT S TREATMENT
 PERIODONTL (GUM) DISESE & IT S TRETMENT What do healthy gums look like? In a healthy mouth, gums are pink and do not bleed on tooth brushing. They are firm and cannot be easily separated from teeth. What
PERIODONTL (GUM) DISESE & IT S TRETMENT What do healthy gums look like? In a healthy mouth, gums are pink and do not bleed on tooth brushing. They are firm and cannot be easily separated from teeth. What
