Morphology and adhesion on blood components in root surfaces treated by a piezoelectric ultrasonic: an in vitro study
|
|
|
- Caitlin Hodge
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ORIGINAL Morphology and adhesion on blood components in root surfaces treated by a piezoelectric ultrasonic: an in vitro study Análise da morfologia e da adesão de elementos sanguíneos em superfícies radiculares instrumentadas com ultrassom piezoelétrico: estudo in vitro Jackeline do Nascimento TSURUMAKI 1 Bráulio Henrique Marques SOUTO 1 Guilherme José Pimentel Lopes de OLIVEIRA 1 José Eduardo Cézar SAMPAIO 1 Rosemary Adriana Chiérici MARCANTONIO 1 ABSTRACT Objective The aim of this study was to evaluate the morphology and adhesion of blood components on root surfaces instrumented with piezoelectric ultrasonic Piezon Master Surgery. Methods 10 teeth were used in this study. The teeth had their proximal divided into four areas that received different treatments: Group 1: untreated control Group 2: scaling with manual instrument; Group 3: scaling with ultrasound; Group 4: Scaling with manual instruments and ultrasound. We obtained 20 samples, 10 of which were used to analyze the morphology and the other 10 were used for analysis of adhesion of blood components. The specimens were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy. Photomicrographs were analyzed by the scores of adhesion of blood components and the index of root morphology. The results were statistically by the Kruskall-Wallis and Mann-Whitney with a significance level of 95%. Results The morphological analysis showed that the Group 1 had a surface unchanged in relation to other groups (Group 1 X Group 2 = ; Group 1 X Group 3 = ; Group 1 X Group 4 = ) and Group 2 presented a smoother surface compared to Group 1 and groups instrumented with ultrasound (Group 2 X Group 3 = ; Group 2 X Group 4 = ) there were no statistical differences between the Groups 3 and 4. analysis of adhesion of blood components showed that the Groups 2, 3 and 4 had no statistically significant differences between themselves, but more biocompatible surfaces promoted the surface untreated control (Group 1 X Group 2 = 0.02; Group 1 X Group 3 = 0.04; Group 1 X Group 4 = 0.005). Conclusion The instrumentation with piezoelectric ultrasonic promoted an irregular root surface, but did not negatively affect the adhesion of blood components. Indexing terms: Dental scaling. Regeneration. Ultrasonic. RESUMO Objetivo Avaliar a morfologia e a adesão de células sanguíneas em superfícies radiculares instrumentadas com o ultrassom piezoelétrico Piezon Master Surgery. Métodos Foram utilizados nesse estudo 10 dentes que tiveram suas proximais divididas em 4 áreas que receberam diferentes tratamentos: Grupo 1: controle sem tratamento; Grupo 2: raspagem com instrumento manual; Grupo 3: raspagem com ultrassom; Grupo 4: associação instrumento manual e ultrassom. Foram obtidas 20 amostras, sendo que 10 foram utilizadas para análise da morfologia e as outras 10 foram utilizadas para a análise de adesão de elementos sanguíneos. Os espécimes foram analisados em microscópio eletrônico de varredura. As fotomicrografias foram analisadas através dos scores de adesão de elementos sanguíneos e pelo índice de morfologia radicular e os resultados foram analisados estatisticamente através dos testes de Kruskall-Wallis e de Mann-Whitney com nível de significância de 95%. Resultados A Análise morfológica demonstrou que o Grupo 1 apresentou uma superfície inalterada em relação aos outros grupos (Grupo 1 X Grupo 2 = ; Grupo 1 X Grupo 3 = ; Grupo 1 X Grupo 4 = ), e o Grupo 2 apresentou uma superfície mais lisa em relação ao Grupo 1 e aos grupos instrumentados com ultrassom (Grupo 2 X Grupo 3 = ; Grupo 2 X Grupo 4 = ). Não houve diferenças estatísticas entre os Grupos 3 e Grupo 4. A análise de adesão de elementos sanguíneos demonstrou que o Grupo 2, Grupo 3 e Grupo 4 não apresentaram diferenças estatisticamente significantes entre si, porém promoveram superfícies mais biocompatíveis que a superfície controle sem tratamento (Grupo 1 X Grupo 2 = 0.02; Grupo 1 X Grupo 3 = 0.04;Grupo 1 X Grupo 4 = 0.005). Conclusão A instrumentação com ultrassom promoveu uma superfície radicular irregular, porém não afetou negativamente a adesão de elementos sanguíneos. Termos de indexação: Raspagem dentária. Regeneração. Ultrassom. 1 Universidade Estadual Paulista Júlio de Mesquita Filho, Faculdade de Odontologia, Departamento de Diagnóstico e Cirurgia. Rua Humaitá, 1680, Centro, , Araraquara, SP, Brasil. Correspondência para / Correspondence to: RAC MARCANTONIO. <adriana@foar.unesp.br 169
2 JN TSURUMAK et al. INTRODUCTION METHODS Periodontitis is a set of chronic destructive inflammatory diseases of the supporting structures of the tooth, which is mainly caused by periodontal pathogens with their endotoxins and other antigens found in biofilm, which induces an inflammatory response in the host 1-2. The main objective of periodontal treatment is biofilm removal with consequent reduction in the inflammatory process, causing the stagnation of disease progression 3-4. Scaling and root planing (SRP) with manual curettes is considered the gold standard treatment of periodontitis, due the efficacy of removing the calculus and biofilm attached to the root surface, and the clinical outcomes promoted by this tool in the treatment of periodontitis 2,5. However, some studies have reported limitations of SRP when treating regions with difficult access,such asfurcations, deep pockets and high dependence on the manual skill and experience of the clinician in obtaining good outcomes 2,4,6. Additionally, SRP promotes irregularities on the root surface and a high degree of tooth wear 4-5. Therefore, other tools have been proposed for the treatment of periodontal diseases with the aim of facilitating access to the root surfaces, such as ultrasonic scalers 7-8, lasers 9, air-polishing devices 10, and sonic scalers 3. Ultrasonic scalers have increasingly been applied in periodontics because they have several advantages such being easy to use, efficient during scaling procedures, availability of a variety of tips for access to different anatomical regions 3,11, causing reduced operator fatigue, and reducing treatment time 4,8. The Piezon Master Surgery ultrasonic scaler (Piezon Master - Electro Medical Systems) was introduced on the market with an indication for endodontic and surgical procedures, and thevibratory movements provided by this instrument are described as delicate, allowing its use in procedures such as augmentation of the maxillary sinus floor 12. This device has specific tips for periodontal treatment, but no research has evaluated the characteristics of root surfaces instrumented with this ultrasonic scaler. The aim of this study was to evaluate, by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), the morphology and adhesion of blood components to root surfaces instrumented with a piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler (Piezon Master - Electro Medical Systems). Ten single-rooted or multirootedteeth, extracted due to several factors were used in this study. The teeth were obtained from the Tooth Bank of the Araraquara Dental School (FoAr-UNESP), and this project was accepted by the Ethics Committee on Studies Involving Human Beings (CEP-12/09), respecting the ethical principles contained in the Declaration of Helsinki (2000). Sample preparation and treatment The proximal surfaces of the roots were delimited with grooves made with the aid of a multilaminar carbide bur (7664FKG Sorensen, Barueri, Brazil). The coronal groove was placed at the cemento-enamel junction, and the apical groove 4 mm apically to the coronal groove. The anterior and posterior grooves were placed on the boundary region of the dihedral angle between the proximal surfaces, with the buccal and lingual / palatal surfaces, respectively. The enclosed area was divided into four regions with similar area (2x2mm). The regions were treated with different protocols as follows (Figure 1): Group 1 (G1): the control group without treatment; Group 2 (G2): the samples were treated by SRP, which was performed in 50 traction movements in the cervicalocclusal direction,using a manual curette (Gracey curette, no. 5-6; Hu-Friedy, Chicago, IL, USA); Group 3 (G3): the samples were treated using the piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler (Piezon Master Surgery; Electro Medical Systems, Nyon, Geneva, Switzerland), with tip RS3, which was used in standard mode with 30 khz power and a water rate of 30 ml/min for 30 s; Group 4 (G4): the samples were treated by SRP associated with the ultrasonic scaler used with the same parameters as those used in Groups 2 and 3. All the treatments were performed by only one trained operator. Figure 1. Model of the sample used in the study. 170
3 Analysis of roots treated with uktrasound After this,using a diamond bur (KG Sorensen, Barueri, SP, Brazil) under slow rotation, the teeth were cross-sectioned in the following manner: The roots were crosscut at the first groove, thereby separating them from the crown; the second cut was performed in the buccolingual direction in middle third of the root and finally the third cut were made at the second groove located 4 mm apically of the first groove. Next, a markup was made in the region of Group 1 in order to facilitate orientation of the samples during the SEM analysis. Thus, one sample was obtained for the mesial surface and one sample for the distal surface, measuring about 1mm in thickness, totaling 2 samples per tooth and therefore 20 samples. Ten of these samples were used for the morphology analysis, and the other 10 samples were used for the analysis of blood component adhesion. SEM analysis of blood component adhesion and morphology After the treatment of the samples, 10 ml of blood was obtained from the peripheral blood vessels of an adult non-smoker without systemic impairment, via puncture with a syringe and disposable needle. This was performed at the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences in Araraquara, after the patient had signed the Term of Free and Informed Consent document. In all of the experimental groups, a drop of blood (1 ml) was deposited on the samples with the aid of a syringe and needle and kept in a humidifying chamber for 20 min. The samples were then immediately washed three times for 5 min with a phosphate buffer solution (PBS, ph 7.0) by means of a shaker. Immediately afterwards, the samples were identified and fixed in formaldehyde in a phosphate buffer solution (1%) for 15 min. After three 5-min washes with phosphate buffer solution, the samples were incubated for 10 min in 0.02 M of glycine in phosphate buffer solution and washed again. They were then fixed in glutaraldehyde in phosphate buffer solution (2.5%) for 30 minutes and washed again. Subsequently, the samples were dehydrated in a graded series of ethanol (25%, 50%, 75%, and 95%) for 10 min in each solution, and washed three times for 10 min in absolute ethanol. For the morphological analysis of the root surfaces, the samples were subjected to dehydration in a graded series of ethanol (25%, 50%, 75%, 95%, and 100%) for 1 h in each solution. After this procedure, the samples were placed on acrylic slides and hexamethyldisilazane (HMDS) was applied. First, 0.8 ml of HMDS ml of absolute alcohol, measured by means of an automatic pipette (Boeco, Hamburg, Germany) was placed in each well, and the samples remained in the HMDS/alcohol mixture for 30 min. The solution was then removed and the wells were filled with 1 ml of pure HMDS, in which the specimens remained for 10 min. All the samples subjected to these processing procedures were dried in ambient air for 20 min. After subsequent drying with a carbon dioxide critical point apparatus, the specimens were fixed on metal stubs and placed in a vacuum desiccator for 48 h. After this period, the samples were sputter-coated using a Balt-Tec SCD- 050 device for 120 s. The samples were analyzed by 20 kv SEM (Jeol-JSM, Tokyo, Japan) and photomicrographs were obtained at 1,000 and 2,000X magnifications. Next, the photos were analyzed by an experienced, calibrated examiner, who was blind to the identity of the samples, and made the description of blood component adhesion on the root surfaces according to the index of blood component adhesion 6 : 0) the absence of a fibrin network and blood cells; 1) a scarce fibrin network and/or blood cells; 2) a moderate fibrin network and a moderate number of blood cells; 3) a dense fibrin network and trapped blood cells. The same examiner evaluated the root morphology according to an index of root surface morphology: 0) an intact cementum; 1) a smooth root surface; 2) an irregular root surface with the presence of intact dentin and cementum; 3) an irregular root surface without the presence of intact dentin and cementum. Statistical analysis The Bioestat 5.0 (Belém, Brazil) software program was used for statistical analysis. To evaluate the significant differences between the groups with regard to blood component adhesion and root surface morphology, the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test was used. With the occurrence of significant differences between the groups, the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test was used to identify the groups that exhibited significant differences.all the tests used in this study were applied using a significance level of 95%. RESULTS Root surface morphology Group 1 (without treatment) - the majority of the samples of this groups presented an intact layer of cementum (80%), representative of score 0(Figure 2A). The other samples presented a smooth pattern, 171
4 JN TSURUMAK et al. with the presence of smear layer and cementum (20%), representative of score 2. Group 2 (SRP)-All the samples of this group (100%) presented a smooth aspect, with the presence of smear layer and occluded dentinal tubules, and these features are representative of score 2 (Figure 2B). Group 3 (Ultrasonic Scaler)- An irregular root surface, with the presence of grooves promoted by the ultrasonic tip; presence of smear layer and occluded dentinal tubules were the main features observed after the ultrasonic scaler treatment (80%), representative of score 3 (Figure 3 C). In 20 % of the samples, a smooth surface was observed, with the presence of smear layer, and occluded dentinal tubules, representative of score 2. Group 4 (SRP + Ultrasonic Scaler)- The pattern observed in this group was similar to that observed in Group 3, in which the majority of the samples presented score 3 of the index of root surface morphology, which is characterized by an irregular root surface, with the presence of grooves, smear layer, and occluded dentinal tubules (80%)(Figure 2D). The other samples (20%) presented a smooth surface, with the presence of smear layer, and occluded dentinal tubules, representative of score 2. Figure 2. Morphological analysis- A: Group 1 (Control). Root surface with intact cementum (score 1); B: Group 2 (SRP). Smooth and regular root surface, with occluded dentinal tubules, and presence of smear layer (score 2); C: Group 3 (Ultrasonic scaler). Irregular root surface with presence of grooves, occluded dentinal tubules, and smear layer (score 3); D: Group 4 (Ultrasonic scaler+srp). Irregular root surface with presence of grooves, occluded dentinal tubules, and smear layer (score 3) (bar:10µm; original magnification: X 1000). The Kruskal-Wallis test showed significant differences among the groups (p ). The Mann- Whitney U test showed that the control group presented a layer of intact cementummore frequently than the others groups (G1XG2=0.0025; G1XG3=0.0003; G1XG4=0.0003), and the SRP group presented a smoother surface than the groups treated with the ultrasonic scaler (G2XG3=0.0025; G2XG4=0.0025). There were no statistical differences between groups treated with the piezoelectric ultrasonic scaleralone, or in association with the manual curettes. Blood component adhesion Group 1 (without treatment): the majority of the samples of this group presented score 0 for blood component adhesion (60%), which is characterized by an absence of blood component adhesion on the root surfaces (Figure 3A). The other samples presented a scarce (20%) or a moderate (20%) adhesion of blood cells interwoven in a thin fibrin network, which is represented by scores 1 and 2, respectively. Group 2 (SRP): in this group the majority of the samples (40%) presented score 3 for blood component adhesion, which represented a dense fibrin network with large entanglement and trapped blood (Figure 3B), followed by score 2 (30%), which represented a moderate number of adherent blood cells within a thin fibrin network;and 20 % of the samples presented score 0, due to the absence of blood component adhesion. Score 1 was observed in 10 % of the samples, in which scarce adhesion of blood components occurred. Group 3 (Ultrasonic Scaler): 50 % of the samples of this group presented score 3, due to the extensive adhesion of blood components trapped in a dense fibrin network (Figure 3C). In 40 % of the samples score 0 was shown, due to lack of blood component adhesion. In 10% of the samples score 1 was observed, due to the scarce adhesion of blood cells trapped in a thin fibrin network. Group 4 (SRP+ Ultrasonic Scaler): the majority of the samples of this group presented score 2 (40%), due to moderate adhesion of blood cells trapped in a thin fibrin network (Figure 3 D). The other samples of this group were equally distributed between scores 3 and 1 (30% each), which represented extensive and scarce adhesion of blood components on the root surfaces, respectively. The Kruskal-Wallis test showed that there were significant differences among the groups (p=0.006). The Mann-Whitney U test showed that the SRP, Ultrasonic scaler, and the SRP+Ultrasonicscaler groups presented no statistical differences among them, however, these groups showed a higher blood component adhesion than the control group without treatment (G1XG2=0.02;G1XG3= 0.04;G1XG4=0.005). 172
5 Analysis of roots treated with uktrasound Figure 3. Blood Component Adhesion Analysis- A: Group 1 (Control). Absence of blood components adhered to the root surfaces (score 0); B: Group 2 (SRP). Root surface with the presence of dense fibrin network with a huge number of adhered cells (score 3); C: Group 3 (Ultrasonic scaler). Root surface with huge number of adhered blood cells intertwined in a dense fibrin network (score 3); D: Group 4 (Ultrasonic scaler+srp). Root surface with a huge number of blood cells trapped in a dense fibrin network (score 3) (bar: 10µm; original magnification: X 1000). DISCUSSION. Knowledge of the root surface characteristics after periodontal treatment is of fundamental importance, because it provides information about the ability of this surface to facilitate biofilm adhesion, or whether it is compatible with the regenerative processes. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate, by SEM analysis, the morphology and blood component adhesion on root surfaces treated with the piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler (Piezon Master Surgery) which was recently proposed as a tool for periodontal treatment. Morphological analysis of the root surfaces showed that 80% of the samples of the control group presented a intact cementum, and this pattern was expected because the surfaces did not undergo any periodontal treatment during the study. In this group, 20% of the samples presented a smooth pattern, with the presence of cementum and smear layer, and it is likely that these areas had undergone some form of periodontal treatment prior to extraction. The SRP group presented 100% of the samples with smooth surface, with the presence of smear layer, and occluded dentinal tubules, and this pattern was similar to that found in other studies 4,6. The groups treated using the piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler alone or associated with the manual curettes (Group 3 and Group 4), presented 80% of the samples with an irregular surface, presence of grooves, smear layer, and occluded dentinal tubules and this morphological features is predominant after the treatment with ultrasonic scalers 4. The irregularities promoted by the ultrasonic scaler are caused by the vibrational motion of the tip and the cavitation activity of the jet of water ; and due to the higher roughness and irregularities 15, a higher degree of biofilm adherence may occur on the root surface. This research showed that the groups treated with the piezoelectric ultrasonicscaler alone or associated with SRP using manual curettes presented the same level of blood component adhesion as SRP with manual curettes alone. The results of this study are in agreement with the researches of Kishida et al. 16 and Crespi et al. 17, who evaluated the adhesion of fibroblasts on root surfaces after the ultrasonic instrumentation, which confirms the good biocompatibility of the root surfaces after ultrasonic instrumentation. As in this study, other treatments have not demonstrated superiority to SRP with manual curettes as regards the adhesion of blood components, such as treatment with lasers 6, and substances used for the biomodification of root surfaces 18. These results reaffirm the efficiency of SRP with manual curettes as the gold standard treatment of periodontal disease. The untreated control group did not show a good adhesion of blood components, with a significantly lower biocompatibility when compared with the treated groups. The reason for this lower biocompatibility is that the root surfaces used in this study were obtained from patients with periodontal disease. Endotoxins present on the root surface have been associated with the poor outcomes in fibroblast adhesion, and it is likely that this factor also hindered the adhesion of blood components in this study 19. A factor to be considered is the presence of irregularities and grooves observed on root surfaces after the use of piezoelectric ultrasonic scalers. These irregularities are associated with a higher adhesion of biofilm, which can hinder the regeneration of periodontal tissues 20. However, this effect can be observed only supragengivally, because the rough surface would be exposed to the oral environment and facilitate biofilm retention, and this effect is not observed in the middle subgingival environment 21. There fore supragingival root planing and polishing would be indicated on the surfaces treated with the piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler 22. It should be pointed out that this topic was not the objective of this study, asthere were no calculus adhering on the root surfaces, which demonstrates the effectiveness of all protocols used in this study for the periodontal treatment. This may explain the good result of blood component adhesion, and the good clinical outcomes found in this study, when SRP was performed with manual curettes associated with the ultrasonic scalers 2,
6 JN TSURUMAK et al. The use of the piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler alone or in association with the manual curettes is an alternative approach to SRP with manual curettes alone. It may be advantageous to apply the piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler in areas of difficult access to instrumentation, such as in deep pockets and in furcation defects. The piezoelectric ultrasonic scalers have been shown to promote less root wear and are also good alternatives as tools for instrumentation during the maintenance phase of periodontal treatment 7,23-24, however, further in vitro and in vivo studies are necessary to confirm these properties, also with the use of the piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler Piezon Master Surgery. CONCLUSION Based on the results obtained with the methodology applied, it can be concluded that the root surfaces instrumented with the piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler presented a higher degree of irregularities than the surface profile of roots treated with manual curettes. Furthermore, the root surfaces treated by SRP with manual curettes and with the piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler alone or in association with manual curettes had significantly higher adhesion of blood components than the untreated control. Collaborators JN TSURUMAKI and BHM SOUTO implemented the methodology and participated in the writing of the article. GJPL OLIVEIRA interpreted the data and participated in writing the article. JEC SAMPAIO analyzed the data and participated in writing the article. RAC MARCANTONIO supervised the research and participated in study design, data interpretation and writing of the article. REFERENCES 1. Khosravi M, Bahrami ZS, Atabaki MSJ, Shokrgozar MA, Shokri F. Comparative effectiveness of hand and ultrasonic instrumentations in root surface planing in vitro. J Clin Periodontol. 2004;31(3): doi: /j x. 2. Christgau M, Männer T, Beuer S, Hiller KA, Schmalz G. Periodontal healing after non-surgical therapy with a new ultrasonic device: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Clin Periodotol. 2007;34(2): doi: /j X x. 3. Schenk G, Flemming TF, Lob S, Ruckdeschel G, Hickel R. Lack of antimicrobial effect on periodontopathic bacteria by ultrasonic and sonic scalers in vitro. J Clin Periodontol. 2000;27(2): doi: /j x x. 4. Casarin RCV, Ribeiro FV, Sallum AW, Sallum EA, Nociti-Jr FH, Casati MZ. Root surface defect produced by hand instruments and ultrasonic scaler with different power setting: an in Vitro Study. Braz Dent J. 2009;20(1): doi: /S Kawashima H, Sato S, Kishida M, Ito K. Comparison of root surface instrumentation using two piezoeletric ultrasonic scaers and a hand scaler in vivo. J Periodont Res. 2007;42(1):90-5. doi: /j x. 6. Theodoro LH, Sampaio JEC, Haypek P, Bachmann L, Zezell DM, Garcia VG. Effect of Er:YAG and Diode lasers on the adhesion of blood components and on the morphology of irradiated root surfaces. J Periodont Res. 2006;41(5): doi: /j x. 7. Busslinger A, Lampe K, Beuchat M, Lehmann B. A comparative in vitro study of a magnetostrictive and a piezoelectric ultrasonic scaling instrument. J Clin Periodontol. 2001;28(7): doi: /j x x. 8. Flemming TF, Petersilka GJ, Mehl A, Hickel R, Klaiber B. The effect of working parameters on root substance removal using a piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler in vitro. J Clin Periodontol. 1998;25(2): doi: /j X.1998.tb02422.x 9. Herrero A, García-Kass AI, Gómez C, Sanz M, García-Nuñez JA. Effect of two kinds of Er:YAG laser systems on root surface in comparison to ultrasonic scaling: an in vitro study. Photomed Laser Surg. 2010;28(4): doi: doi: / pho Petersilka GJ, Schenk U, Flemming TF. Powder emission rates of four air polishing devices. J Clin Periodontol. 2002;29(8): doi: /j X x. 11. Lea SC, Felver B, Landini G, Walmsley AD. Ultrasonic scaler oscillations and tooth-surface defects. J Dent Res. 2009;88(3): Barone A, Santini S, Marconcini S, Giacomelli L, Gherlone E, Covani U. Osteotomy and membrane elevation during the maxillary sinus augmentation procedure. A comparative study: piezoelectric device vs. conventional rotative instruments. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008;19(5): doi: /j x. 174
7 Analysis of roots treated with uktrasound 13. Khambay B, Walmsley A. Acoustic microstreaming: detection and measurement around ultrasonic scalers. J Periodontol. 1999;70(6): doi: /jop Schmidlin PR, Beuchat M, Busslinger A, Lehmann B, Lutz F. Tooth substance loss resulting from mechanical, sonic and ultrasonic root instrumentation assessed by liquid scintillation. J Clin Periodontol. 2001;28(11): doi: /j X x. 15. Santos FA, Pochapski MT, Leal PC, Gimenes-Sakima PP, Marcantonio Jr E. Comparative study on the effect of ultrasonic instruments on the root surface in vivo. Clin Oral Investig. 2008;12(2): Kishida M, Sato S, Ito K. Effects of a new ultrasonic scaler on fibroblast attachment to root surfaces: a scanning electron microscopy analysis. J Periodontal Res. 2004;39(2): doi: /j x. 17. Crespi R, Romanos GE, Cassinelli C, Gherlone E. Effects of the Er:YAG and ultrasonic treatment on fibroblast attachment to root surfaces : an in vitro study. J Periodontol. 2006; 77(7): doi: /jop Leite FR, Moreira CS, Theodoro LH, Sampaio JE. Blood cell attachment to root surfaces treated with EDTA gel. Braz Oral Res. 2005;19(2): doi: /S Babay N, Mokeem S. The effect of two different demineralization methods with saturated tetracycline hydrochloride on the attachment and growth of gingival fibroblasts. A scanning electron microscopic study. Odontostomatol Trop. 2005;28(109): Tsuzuki CO, Martins FL, Giorgetti APO, Freitas PM, Duarte PM. In vitro adhesion of Streptococcus sanguinis to dentin root surface after treatment with Er:YAG laser, ultrasonic system, or manual curette. Photomed Laser Surg. 2009;27(5): doi: /pho Folwaczny M, George G, Thiele L, Mehl A, Hickel R. Root surface roughness following Er:YAG laser irradiation at different radiation energies and working tip angulations. J Clin Periodontol. 2002;29(7): doi: /j X x. 22. Kocher T, Rosin M, Langenbeck N, Bernhardt O. Subgingival polishing with a Teflon-coated sonic scaler insert in comparison to conventional instruments as assessed on extracted teeth. (II) Subgingival roughness. J Clin Periodontol. 2001;28(8): doi: /j X x. 23. Dragoo MR. A clinical evaluation of hand and ultrasonic instruments on subgingival debridement. 1. With unmodified and modified ultrasonic inserts. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1992;12(4): Ritz L, Hefti AF, Rateitschak KH. An in vitro investigation on the loss of root substance in scaling with various instruments. J Clin Periodontol. 1991;18(9): Received on: 2/8/2010 Final version resubmitted on: 19/9/2010 Approved on: 20/10/
Root Surface Defect Produced by Hand Instruments and Ultrasonic Scaler with Different Power Settings: an In Vitro Study
 58 Braz Dent J (2009) 20(1): 58-63 R.C.V. Casarin et al. ISSN 0103-6440 Root Surface Defect Produced by Hand Instruments and Ultrasonic Scaler with Different Power Settings: an In Vitro Study Renato Corrêa
58 Braz Dent J (2009) 20(1): 58-63 R.C.V. Casarin et al. ISSN 0103-6440 Root Surface Defect Produced by Hand Instruments and Ultrasonic Scaler with Different Power Settings: an In Vitro Study Renato Corrêa
Objectives: The debridement of diseased root surface is usually performed by mechanical
 www.scielo.br/jaos A comparative evaluation of the efficacy of manual, magnetostrictive and piezoelectric ultrasonic instruments an in vitro and SEM study 1 2 3 1- BDS, Post Graduate student, Department
www.scielo.br/jaos A comparative evaluation of the efficacy of manual, magnetostrictive and piezoelectric ultrasonic instruments an in vitro and SEM study 1 2 3 1- BDS, Post Graduate student, Department
A SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY STUDY OF ROOT SURFACE SMEAR LAYER REMOVAL AFTER TOPICAL APPLICATION OF EDTA PLUS A DETERGENT
 www.fob.usp.br/revista or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci 2005; 13(3): 247-52 A SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY STUDY OF ROOT SURFACE SMEAR LAYER REMOVAL AFTER TOPICAL APPLICATION OF EDTA PLUS A DETERGENT
www.fob.usp.br/revista or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci 2005; 13(3): 247-52 A SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY STUDY OF ROOT SURFACE SMEAR LAYER REMOVAL AFTER TOPICAL APPLICATION OF EDTA PLUS A DETERGENT
Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation. Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman
 Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman Outline Classification of periodontal instruments General principles of instrumentation Principles of scaling
Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman Outline Classification of periodontal instruments General principles of instrumentation Principles of scaling
Medical sciences (2018) 1 16
 Medical sciences (2018) 1 16 Profilometric and histological evaluation of the root surface after instrumentation in vitro with a fluorescence-controlled er: yag laser, hand instruments and an ultrasonic
Medical sciences (2018) 1 16 Profilometric and histological evaluation of the root surface after instrumentation in vitro with a fluorescence-controlled er: yag laser, hand instruments and an ultrasonic
Clinpro Glycine Prophy Powder
 Clinpro Glycine Prophy Powder 3M 2016. All Rights Reserved VIDEO 3M 2016. All Rights Reserved 2 Presentation Overview Air Polishing Procedure With Clinpro Glyciene Prophy Powder Use and Efficiency for
Clinpro Glycine Prophy Powder 3M 2016. All Rights Reserved VIDEO 3M 2016. All Rights Reserved 2 Presentation Overview Air Polishing Procedure With Clinpro Glyciene Prophy Powder Use and Efficiency for
In vitro evaluation of the effect of natural orange juices on dentin morphology
 Restorative Dentistry Restorative Dentistry In vitro evaluation of the effect of natural orange juices on dentin morphology Daniela Leal Zandim (a) Fernanda Oliveira Bello Corrêa (a) Carlos Rossa Júnior
Restorative Dentistry Restorative Dentistry In vitro evaluation of the effect of natural orange juices on dentin morphology Daniela Leal Zandim (a) Fernanda Oliveira Bello Corrêa (a) Carlos Rossa Júnior
COMPARATIVE IN VITRO STUDY OF ROOT ROUGHNESS AFTER INSTRUMENTATION WITH ULTRASONIC AND DIAMOND TIP SONIC SCALER
 www.fob.usp.br/revista or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci. 2006;14(2):124-9 COMPARATIVE IN VITRO STUDY OF ROOT ROUGHNESS AFTER INSTRUMENTATION WITH ULTRASONIC AND DIAMOND TIP SONIC SCALER ESTUDO COMPARATIVO
www.fob.usp.br/revista or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci. 2006;14(2):124-9 COMPARATIVE IN VITRO STUDY OF ROOT ROUGHNESS AFTER INSTRUMENTATION WITH ULTRASONIC AND DIAMOND TIP SONIC SCALER ESTUDO COMPARATIVO
The effect of root surface conditioning on smear layer removal in periodontal regeneration (a scanning electron microscopic study)
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The effect of root surface conditioning on smear layer removal in periodontal regeneration (a scanning electron microscopic study) To cite this article:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The effect of root surface conditioning on smear layer removal in periodontal regeneration (a scanning electron microscopic study) To cite this article:
Objectives: What s Your Therapeutic Goal?
 Objectives: List differences Magnetorestrictive scalers vs Piezoelectric Understand role of ultrasonic scaling and biofilm management Compare ultrasonic scaling versus hand instrumentation List advantages
Objectives: List differences Magnetorestrictive scalers vs Piezoelectric Understand role of ultrasonic scaling and biofilm management Compare ultrasonic scaling versus hand instrumentation List advantages
Blood clot stabilization on root dentin conditioned by the combination of tetracycline and EDTA
 Original Article Braz J Oral Sci. April June 2014 - Volume 13, Number 2 Blood clot stabilization on root dentin conditioned by the combination of tetracycline and EDTA Gustavo Giacomelli Nascimento 1,
Original Article Braz J Oral Sci. April June 2014 - Volume 13, Number 2 Blood clot stabilization on root dentin conditioned by the combination of tetracycline and EDTA Gustavo Giacomelli Nascimento 1,
Ultrasonics in Dentistry. Damien Walmsley UIA 2011
 Ultrasonics in Dentistry Damien Walmsley UIA 2011 Objectives Background of dental ultrasonics How they work How they are used in dentistry Future directions Frequency of Ultrasound Ultrasonic scalers 25
Ultrasonics in Dentistry Damien Walmsley UIA 2011 Objectives Background of dental ultrasonics How they work How they are used in dentistry Future directions Frequency of Ultrasound Ultrasonic scalers 25
Objective: The purpose of this study was to investigate the ultramorphology of the root
 www.scielo.br/jaos Ultramorphology of the root surface subsequent to hand-ultrasonic simultaneous instrumentation during non-surgical periodontal treatments. An in vitro study Simone D. ASPRIELLO 1, Matteo
www.scielo.br/jaos Ultramorphology of the root surface subsequent to hand-ultrasonic simultaneous instrumentation during non-surgical periodontal treatments. An in vitro study Simone D. ASPRIELLO 1, Matteo
Amajor goal of periodontal therapy
 J Periodontol July 2007 Effects of Er:YAG Laser Compared to Ultrasonic Scaler in Periodontal Treatment: A 2-Year Follow-Up Split-Mouth Clinical Study Roberto Crespi,* Paolo Capparè,* Isabel Toscanelli,*
J Periodontol July 2007 Effects of Er:YAG Laser Compared to Ultrasonic Scaler in Periodontal Treatment: A 2-Year Follow-Up Split-Mouth Clinical Study Roberto Crespi,* Paolo Capparè,* Isabel Toscanelli,*
Scanning Electron Microscope Assessment of Several Resharpening Techniques on the Cutting Edges of Gracey Curettes
 Scanning Electron Microscope Assessment of Several Resharpening Techniques on the Cutting Edges of Gracey Curettes Abstract Aim: Treatment of periodontal diseases is based on efficient scaling and root
Scanning Electron Microscope Assessment of Several Resharpening Techniques on the Cutting Edges of Gracey Curettes Abstract Aim: Treatment of periodontal diseases is based on efficient scaling and root
STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT. Cynthia Fong, RDH, MS
 STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT 2014 Kentucky Dental Association Louisville, KY Friday, March 14, 2014 9:00 a.m. 12 Noon STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course provides
STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT 2014 Kentucky Dental Association Louisville, KY Friday, March 14, 2014 9:00 a.m. 12 Noon STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course provides
Department of Oral Surgery, Heinrich Heine University, D Düsseldorf, Germany.
 Lasers Surg Med. 2007 Jun;39(5):428-40 Immunohistochemical characterization of periodontal wound healing following nonsurgical treatment with fluorescence controlled Er:YAG laser radiation in dogs. Schwarz
Lasers Surg Med. 2007 Jun;39(5):428-40 Immunohistochemical characterization of periodontal wound healing following nonsurgical treatment with fluorescence controlled Er:YAG laser radiation in dogs. Schwarz
Evaluation of Blood Cell Attachment on Er:Yag Laser Applied Root Surface Using Scanning Electron Microscopy
 560 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper International Journal of Medical Sciences 2013; 10(5):560-566. doi: 10.7150/ijms.5233 Evaluation of Blood Cell Attachment on Er:Yag Laser Applied Root
560 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper International Journal of Medical Sciences 2013; 10(5):560-566. doi: 10.7150/ijms.5233 Evaluation of Blood Cell Attachment on Er:Yag Laser Applied Root
CLINICAL APPLICATION GUIDE DIAGNOSTIC INSTRUMENTS & PERIODONTAL SCALERS/ CURETTES
 CLINICAL APPLICATION GUIDE DIAGNOSTIC INSTRUMENTS & PERIODONTAL SCALERS/ CURETTES DIAGNOSTIC INSTRUMENTATION EXPLORERS Explorers are used to examine tooth surfaces for calculus, decalcified and carious
CLINICAL APPLICATION GUIDE DIAGNOSTIC INSTRUMENTS & PERIODONTAL SCALERS/ CURETTES DIAGNOSTIC INSTRUMENTATION EXPLORERS Explorers are used to examine tooth surfaces for calculus, decalcified and carious
Corresponding Author:Dr.Sneha Vaidya 3
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. VII (Nov. 2017), PP 75-81 www.iosrjournals.org Efficacy of Endoactivator Irrigation
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. VII (Nov. 2017), PP 75-81 www.iosrjournals.org Efficacy of Endoactivator Irrigation
POWER SCALING PIEZON SOLUTIONS
 POWER SCALING PIEZON SOLUTIONS ADVANCED POWER SCALING THE PIEZON DIFFERENCE QUIETER TREATMENT GENTLE TIP MOVEMENT MORE POWER SETTINGS TREATMENT VERSATILITY FEEDBACK CONTROL Ultrasonic scaling is an integral
POWER SCALING PIEZON SOLUTIONS ADVANCED POWER SCALING THE PIEZON DIFFERENCE QUIETER TREATMENT GENTLE TIP MOVEMENT MORE POWER SETTINGS TREATMENT VERSATILITY FEEDBACK CONTROL Ultrasonic scaling is an integral
Cause related therapy: Professional mechanical plaque control Zsuzsanna Papp Prof. István Gera
 Cause related therapy: Professional mechanical plaque control Zsuzsanna Papp Prof. István Gera Periodontal Clinic, Semmelweis University, Budapest 2017.02.14. Complex periodontal therapy Systemic phase
Cause related therapy: Professional mechanical plaque control Zsuzsanna Papp Prof. István Gera Periodontal Clinic, Semmelweis University, Budapest 2017.02.14. Complex periodontal therapy Systemic phase
Confidence for you comfort for your patient
 Clinpro Glycine Prophy Powder For supra- and subgingival cleaning Clinpro Glycine Prophy Powder with TCP For added sensitivity relief Confidence for you comfort for your patient f TCP functionalized Tri-Calcium
Clinpro Glycine Prophy Powder For supra- and subgingival cleaning Clinpro Glycine Prophy Powder with TCP For added sensitivity relief Confidence for you comfort for your patient f TCP functionalized Tri-Calcium
Evaluation of Dentin Root Canal Permeability After Instrumentation and Er:YAG Laser Application
 Lasers in Surgery and Medicine 26:277 281 (2000) Evaluation of Dentin Root Canal Permeability After Instrumentation and Er:YAG Laser Application Jesus D. Pecora, DDS, PhD, 1 * Aldo Brugnera-Júnior, DDS,
Lasers in Surgery and Medicine 26:277 281 (2000) Evaluation of Dentin Root Canal Permeability After Instrumentation and Er:YAG Laser Application Jesus D. Pecora, DDS, PhD, 1 * Aldo Brugnera-Júnior, DDS,
A SIMPLIFIED INSTRUMENTATION APPROACH TO ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT Hands On Workshop
 A SIMPLIFIED INSTRUMENTATION APPROACH TO ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT Hands On Workshop 2014 Kentucky Dental Association Louisville, KY Friday, March 14, 2014 2:00 p.m. 5:00 p.m. A Simplified Instrumentation
A SIMPLIFIED INSTRUMENTATION APPROACH TO ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT Hands On Workshop 2014 Kentucky Dental Association Louisville, KY Friday, March 14, 2014 2:00 p.m. 5:00 p.m. A Simplified Instrumentation
Virtuosity is in your hands. Endodontic and Microsurgical Ultrasonic Instruments
 Virtuosity is in your hands Endodontic and Microsurgical Ultrasonic Instruments The advantages of ProUltra tips Patented contra-angled feature enhances access to all teeth Abrasive coating increases efficiency
Virtuosity is in your hands Endodontic and Microsurgical Ultrasonic Instruments The advantages of ProUltra tips Patented contra-angled feature enhances access to all teeth Abrasive coating increases efficiency
TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment. Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD
 TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE 2 The available evidence consistently shows that therapies intended to arrest and control periodontitis depend primarily
TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE 2 The available evidence consistently shows that therapies intended to arrest and control periodontitis depend primarily
Clinical Application Guide SCALERS and CURETTES
 Clinical Application Guide SCALERS and CURETTES Gracey Curettes Anterior SG1/2 Posterior SG Posterior SG11/12 Gracey Curette The Gracey curettes combine a unique offset blade with 9 different shank designs
Clinical Application Guide SCALERS and CURETTES Gracey Curettes Anterior SG1/2 Posterior SG Posterior SG11/12 Gracey Curette The Gracey curettes combine a unique offset blade with 9 different shank designs
The effect of wear on ultrasonic scaler tip displacement amplitude
 J Clin Periodontol 2006; 33: 37 41 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2005.00861.x The effect of wear on ultrasonic scaler tip displacement amplitude Simon C. Lea, Gabriel Landini and A. Damien Walmsley School of
J Clin Periodontol 2006; 33: 37 41 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2005.00861.x The effect of wear on ultrasonic scaler tip displacement amplitude Simon C. Lea, Gabriel Landini and A. Damien Walmsley School of
Win the Battle Against Biofilm: Leverage the Power of Ultrasonics
 1301 Smile Way York, PA 17404 800.989.8825 Department of Clinical Education www.professional.dentsply.com Win the Battle Against Biofilm: Leverage the Power of Ultrasonics COURSE DESCRIPTION This course
1301 Smile Way York, PA 17404 800.989.8825 Department of Clinical Education www.professional.dentsply.com Win the Battle Against Biofilm: Leverage the Power of Ultrasonics COURSE DESCRIPTION This course
Evaluation of Different Resharpening Techniques on the Working Edges of Periodontal Scalers: A Scanning Electron Microscopic Study
 Evaluation of Different Resharpening Techniques on the Working Edges of Periodontal Scalers: A Scanning Electron Microscopic Study Hani EL Nahass and Gihane Gharib Madkour Department of Oral Medicine,
Evaluation of Different Resharpening Techniques on the Working Edges of Periodontal Scalers: A Scanning Electron Microscopic Study Hani EL Nahass and Gihane Gharib Madkour Department of Oral Medicine,
Maxdent s.r.o.,ondračka Martin,tel:
 Maxdent s.r.o., Ondračka Martin, tel: 608 243 383, email: ondracka@max-dent.cz Maxdent s.r.o.,ondračka Martin,tel: 608 243 383,email:ondracka@max-dent.cz Multi-purpose ultrasonics Ultrasonics is an excellent
Maxdent s.r.o., Ondračka Martin, tel: 608 243 383, email: ondracka@max-dent.cz Maxdent s.r.o.,ondračka Martin,tel: 608 243 383,email:ondracka@max-dent.cz Multi-purpose ultrasonics Ultrasonics is an excellent
Periodontal Debridement with Sonic and Ultrasonic Scalers
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Periodontal Debridement with Sonic and Ultrasonic Scalers Gregor J. Petersilka, Thomas F. Flemmig Biofilm and calculus removal are very important components of periodontal
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Periodontal Debridement with Sonic and Ultrasonic Scalers Gregor J. Petersilka, Thomas F. Flemmig Biofilm and calculus removal are very important components of periodontal
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Patients often seek professional help for acute tooth
 A P P L I E D R E S E A R C H Influence of Natural Fruit Juices in Removing the Smear Layer from Root Surfaces An In Vitro Study Fernanda Oliveira Bello Corrêa, DDS, MS José Eduardo Cezar Sampaio, DDS,
A P P L I E D R E S E A R C H Influence of Natural Fruit Juices in Removing the Smear Layer from Root Surfaces An In Vitro Study Fernanda Oliveira Bello Corrêa, DDS, MS José Eduardo Cezar Sampaio, DDS,
Effect of air-polishing with glycine and bicarbonate powders on a. nanocomposite used in dental restoration: an in vitro study
 Effect of air-polishing with glycine and bicarbonate powders on a nanocomposite used in dental restoration: an in vitro study Luca Giacomelli 1,*, M.S., PhD, Marco Salerno 2, M.S., PhD, Giacomo Derchi
Effect of air-polishing with glycine and bicarbonate powders on a nanocomposite used in dental restoration: an in vitro study Luca Giacomelli 1,*, M.S., PhD, Marco Salerno 2, M.S., PhD, Giacomo Derchi
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 63 (2015 ) Ultrasonics in dentistry. A. D.
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 63 (2015 ) 201 207 43 rd Annual Symposium of the Ultrasonic Industry Association, UIA Symposium 2014 Ultrasonics in dentistry A.
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 63 (2015 ) 201 207 43 rd Annual Symposium of the Ultrasonic Industry Association, UIA Symposium 2014 Ultrasonics in dentistry A.
Root end preparation techniques Summary of papers
 Root end preparation techniques Summary of papers 34 Flath 1987 This paper presented 2 cases in which retrograde fillings were carried out using new sonic or ultrasonic instruments (endo files held in
Root end preparation techniques Summary of papers 34 Flath 1987 This paper presented 2 cases in which retrograde fillings were carried out using new sonic or ultrasonic instruments (endo files held in
Effect of Er:YAG and Diode lasers on the adhesion of blood components and on the morphology of irradiated root surfaces
 J Periodont Res 2006; 41; 381 390 All rights reserved Effect of Er:YAG and Diode lasers on the adhesion of blood components and on the morphology of irradiated root surfaces Theodoro LH, Sampaio JEC, Haypek
J Periodont Res 2006; 41; 381 390 All rights reserved Effect of Er:YAG and Diode lasers on the adhesion of blood components and on the morphology of irradiated root surfaces Theodoro LH, Sampaio JEC, Haypek
KaVo SONICflex Tips KaVo SONICflex tips
 KaVo SONICflex Tips KaVo SONICflex tips KaVo SONICflex tips overview SONICflex handpiece overview MASTER SERIES EXPERT SERIES Fast and comfortable change of tips - only one turn 3 VARIETY DEVELOPED TO
KaVo SONICflex Tips KaVo SONICflex tips KaVo SONICflex tips overview SONICflex handpiece overview MASTER SERIES EXPERT SERIES Fast and comfortable change of tips - only one turn 3 VARIETY DEVELOPED TO
Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters
 Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters REVIEWED PAPER Most patients visiting dental surgeries suffer from various types of periodontopathies. Since
Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters REVIEWED PAPER Most patients visiting dental surgeries suffer from various types of periodontopathies. Since
KaVo SONICflex tips overview. SONICflex Tip book. Comprehensive user reports on the KaVo tips may be found at
 KaVo SONICflex tips overview SONICflex Tip book. Comprehensive user reports on the KaVo tips may be found at www.kavo.com/spitzen KaVo SONICflex tips overview NEW Variety developed to a fine point. retro
KaVo SONICflex tips overview SONICflex Tip book. Comprehensive user reports on the KaVo tips may be found at www.kavo.com/spitzen KaVo SONICflex tips overview NEW Variety developed to a fine point. retro
Studies suggest that subgingival
 Volume 81 Number 5 Clinical and Microbiologic Follow-Up Evaluations After Non-Surgical Periodontal Treatment With Erbium:YAG Laser and Scaling and Root Planing Beatriz Maria Valério Lopes,* Leticia Helena
Volume 81 Number 5 Clinical and Microbiologic Follow-Up Evaluations After Non-Surgical Periodontal Treatment With Erbium:YAG Laser and Scaling and Root Planing Beatriz Maria Valério Lopes,* Leticia Helena
SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM
 SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Precision by design PS Instrument [>magnified 8 x ] PIEZON method PIEZON Method} SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Piezon ultrasound instruments for a complete range of treatments } Endodontics
SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Precision by design PS Instrument [>magnified 8 x ] PIEZON method PIEZON Method} SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Piezon ultrasound instruments for a complete range of treatments } Endodontics
SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM
 SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Precision by design PIEZON method PIEZON Method} SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Piezon ultrasound instruments for a complete range of treatments } Endodontics } Scaling } Perio } Cavity preparation
SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Precision by design PIEZON method PIEZON Method} SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Piezon ultrasound instruments for a complete range of treatments } Endodontics } Scaling } Perio } Cavity preparation
A New Perio Treatment
 A New Perio Treatment by John A. Hendy, DDS, Grants Pass, OR; Gregory T. Miller, PhD, Ashland, OR; George Quainoo PhD, Ashland, OR; and Diedre Krupp, Ashland, OR, Department of Chemistry & Physical Science,
A New Perio Treatment by John A. Hendy, DDS, Grants Pass, OR; Gregory T. Miller, PhD, Ashland, OR; George Quainoo PhD, Ashland, OR; and Diedre Krupp, Ashland, OR, Department of Chemistry & Physical Science,
Initial Therapy. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS. Oral sulcular epithelium. Oral. epithelium. Junctional. epithelium. Connective tissue.
 Oral sulcular epithelium Junctional epithelium E Oral epithelium Initial Therapy Connective tissue Bone Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Non-surgical Therapy Scaling: Instrumentation of the crown and root
Oral sulcular epithelium Junctional epithelium E Oral epithelium Initial Therapy Connective tissue Bone Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Non-surgical Therapy Scaling: Instrumentation of the crown and root
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
POWER AIR-FLOW HANDY 3.0 DEVICES
 POWER AIR-FLOW HANDY 3.0 DEVICES THE BETTER WAY FOR BIOFILM MANAGEMENT Introducing AIR-FLOW THERAPY AIR-FLOW Therapy is completely different than other air polishing systems. This advanced technology offers
POWER AIR-FLOW HANDY 3.0 DEVICES THE BETTER WAY FOR BIOFILM MANAGEMENT Introducing AIR-FLOW THERAPY AIR-FLOW Therapy is completely different than other air polishing systems. This advanced technology offers
An In Vitro Study of the Treatment of Implant Surfaces With Different Instruments
 An In Vitro Study of the Treatment of Implant Surfaces With Different Instruments Reiner Mengel, Dr med dent, DDS*/Christian-Eiben Buns, Dr med dent, DDS*/ Claudia Mengel, Dr med dent, DDS*/ Lavin Flores-de-Jacoby,
An In Vitro Study of the Treatment of Implant Surfaces With Different Instruments Reiner Mengel, Dr med dent, DDS*/Christian-Eiben Buns, Dr med dent, DDS*/ Claudia Mengel, Dr med dent, DDS*/ Lavin Flores-de-Jacoby,
PERIODONTAL THERAPY Ultra sonic scaling
 PERIODONTAL THERAPY Ultra sonic scaling Dr.Erry Mochamad Arief USM School of Dentistry 1 july 2007 ultrasonic scaling yr 2 2007 dr erry 1 PERIODONTAL THERAPY Phase I therapy Started after diagnosis and
PERIODONTAL THERAPY Ultra sonic scaling Dr.Erry Mochamad Arief USM School of Dentistry 1 july 2007 ultrasonic scaling yr 2 2007 dr erry 1 PERIODONTAL THERAPY Phase I therapy Started after diagnosis and
Root surface conditioning with nicotine or cotinine reduces viability and density of fibroblasts in vitro
 Clin Oral Invest (2005) 9: 180 186 DOI 10.1007/s00784-004-0294-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Aurora Esmeralda Traverso Martinez. Karina Gonzales Silverio. Jose Carlos Fogo. Keith Lough Kirkwood. Carlos Rossa Jr Root
Clin Oral Invest (2005) 9: 180 186 DOI 10.1007/s00784-004-0294-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Aurora Esmeralda Traverso Martinez. Karina Gonzales Silverio. Jose Carlos Fogo. Keith Lough Kirkwood. Carlos Rossa Jr Root
THE MULTI-FUNCTION ULTRASONIC TIPS FOR ALL APPLICATIONS TIP BOOK. Expect Perfection. PR-D265E Ver A. Powerful Partners
 TH MULTI-FUNCTION ULTRASONIC TIS FOR ALL ALICATIONS TI BOOK xpect erfection R-D265 Ver.1 05.04.10.A owerful artners Offers A Wide Choice of VARIOS Ultrasonic Scaler Tips For Clinical Applications. rosthetics
TH MULTI-FUNCTION ULTRASONIC TIS FOR ALL ALICATIONS TI BOOK xpect erfection R-D265 Ver.1 05.04.10.A owerful artners Offers A Wide Choice of VARIOS Ultrasonic Scaler Tips For Clinical Applications. rosthetics
Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study
 ISSN 0970-4388 Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study BOGRA P a, KASWAN S b ABSTRACT: In the present study, 25% EDTA, in gel form, was used to analyse its micromorphological effects on tooth surfaces with
ISSN 0970-4388 Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study BOGRA P a, KASWAN S b ABSTRACT: In the present study, 25% EDTA, in gel form, was used to analyse its micromorphological effects on tooth surfaces with
Scaler Periodontal Curette Explorer Root Planing Check Scaler Sharpening Product Periodontal Probe Resin Color Probe Medicine Applicator
 Scaler Periodontal Curette Explorer Root Planing Check Scaler Sharpening Product Periodontal Probe Resin Color Probe Medicine Applicator 14 20 24 24 25 29 31 32 13 Scaler -Single End- -Pair- *Efficiently
Scaler Periodontal Curette Explorer Root Planing Check Scaler Sharpening Product Periodontal Probe Resin Color Probe Medicine Applicator 14 20 24 24 25 29 31 32 13 Scaler -Single End- -Pair- *Efficiently
From Risk to Results: Periodontal Instrumentation for the Advanced Practitioner
 From Risk to Results: Periodontal Instrumentation for the Advanced Practitioner COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is based on current scientific literature providing the clinician with evidence based tools
From Risk to Results: Periodontal Instrumentation for the Advanced Practitioner COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is based on current scientific literature providing the clinician with evidence based tools
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Open Access Root Surface Bio-modification with Erbium Lasers- A Myth or a Reality??
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Dentistry Journal, 2015, 9, 79-86 79 Open Access Root Surface Bio-modification with Erbium Lasers- A Myth or a Reality?? Vamsi Lavu, Subramoniam
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Dentistry Journal, 2015, 9, 79-86 79 Open Access Root Surface Bio-modification with Erbium Lasers- A Myth or a Reality?? Vamsi Lavu, Subramoniam
Biological Effects of a Root Conditioning Treatment on Periodontally Affected Teeth An In Vitro Analysis
 Brazilian Dental Journal (2016) 27(2): 160-168 http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0103-6440201600427 Biological Effects of a Root Conditioning Treatment on Periodontally Affected Teeth An In Vitro Analysis Aline
Brazilian Dental Journal (2016) 27(2): 160-168 http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0103-6440201600427 Biological Effects of a Root Conditioning Treatment on Periodontally Affected Teeth An In Vitro Analysis Aline
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the. Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System
 Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Maintain Your Edge. Instrumental in the preservation of the environment and each other
 Maintain Your Edge Instrumental in the preservation of the environment and each other Thank you. To Toronto Academy of Dentistry To D-Sharp and rdhu Today we will 1. 2. 3. 4. Discuss the benefits of sharpening
Maintain Your Edge Instrumental in the preservation of the environment and each other Thank you. To Toronto Academy of Dentistry To D-Sharp and rdhu Today we will 1. 2. 3. 4. Discuss the benefits of sharpening
What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers
 http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2017/v72no8a8 < 387 What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers SADJ September 2017, Vol 72 no 8 p387- p391 Compiled and
http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2017/v72no8a8 < 387 What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers SADJ September 2017, Vol 72 no 8 p387- p391 Compiled and
PERIODONTAL CHANGES IN FLUOROSED AND NONFLUOROSED TEETH BY SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY
 128 PERIODONTAL CHANGES IN FLUOROSED AND NONFLUOROSED TEETH BY SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY Vandana KL, a Pauline George, b Charles M Cobb c Karnataka, India. SUMMARY: To date, studies on the effect of
128 PERIODONTAL CHANGES IN FLUOROSED AND NONFLUOROSED TEETH BY SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY Vandana KL, a Pauline George, b Charles M Cobb c Karnataka, India. SUMMARY: To date, studies on the effect of
Manual and Electronic Detection of Subgingival Calculus: Reliability and Accuracy
 DOI 10.7603/s40782-014-0008-7 Manual and Electronic Detection of Subgingival Calculus: Reliability and Accuracy Masud M., Zahari H. I. M., Sameon A. S. N., Mohamed N. A. H. Faculty of Dentistry, University
DOI 10.7603/s40782-014-0008-7 Manual and Electronic Detection of Subgingival Calculus: Reliability and Accuracy Masud M., Zahari H. I. M., Sameon A. S. N., Mohamed N. A. H. Faculty of Dentistry, University
Scanning Electronic Microscopy Analysis of the Apical Surface After of Root-End Resection With Different Methods
 SCANNING VOL. 37, 126 130 (2015) Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Scanning Electronic Microscopy Analysis of the Apical Surface After of Root-End Resection With Different Methods RICARDO AFFONSO BERNARDES, 1,2
SCANNING VOL. 37, 126 130 (2015) Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Scanning Electronic Microscopy Analysis of the Apical Surface After of Root-End Resection With Different Methods RICARDO AFFONSO BERNARDES, 1,2
Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location
 Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Û mectron Air-Polishing
 new! Û perio function Û mectron Air-Polishing 2 Û combi The new multi-talented prophylaxis unit offers several treatment options. The powerful, well controlled ultrasound allows gentle scaling. Over 40
new! Û perio function Û mectron Air-Polishing 2 Û combi The new multi-talented prophylaxis unit offers several treatment options. The powerful, well controlled ultrasound allows gentle scaling. Over 40
AHEAD. Are You. of the Ultrasonic Curve? 110 NOVEMBER 2017 // dentaltown.com. continuing education. AGD Code: 490
 continuing education Are You STAYING AHEAD of the Ultrasonic Curve? Approved PACE Program Provider FAGD/MAGD Credit Approval does not imply acceptance by a state or provincial board of dentistry or AGD
continuing education Are You STAYING AHEAD of the Ultrasonic Curve? Approved PACE Program Provider FAGD/MAGD Credit Approval does not imply acceptance by a state or provincial board of dentistry or AGD
Preclinical Dentistry. I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects. Lenka Roubalíková
 Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková Understanding dental caries crown pulp chamber neck root canal root Dental
Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková Understanding dental caries crown pulp chamber neck root canal root Dental
Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin
 Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin Bright Chang D2 Dental Student UAB School of Dentistry Final report (revision) July 26, 2017 Mentors: Nathaniel Lawson,
Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin Bright Chang D2 Dental Student UAB School of Dentistry Final report (revision) July 26, 2017 Mentors: Nathaniel Lawson,
1007/10/A/1 DENT-GPLFM-BRO
 and GRIPLITE & GRIPLITE S 6 and The Miltex GripLite family of hand instruments is designed with the dental hygienist in mind. After consulting with leaders in the field of hand ergonomics as well as with
and GRIPLITE & GRIPLITE S 6 and The Miltex GripLite family of hand instruments is designed with the dental hygienist in mind. After consulting with leaders in the field of hand ergonomics as well as with
Dr.Adel F.Ibraheem Partial Veneer Crown(Three quarter crown) Three quarter (¾ )crown: Uses: Indications ---- For posterior teeth ;
 Lecture.9 Dr.Adel F.Ibraheem Partial Veneer Crown(Three quarter crown) *It is a cast metal crown restoration that cover only a part of the clinical crown, most commonly used type of partial veneer crown
Lecture.9 Dr.Adel F.Ibraheem Partial Veneer Crown(Three quarter crown) *It is a cast metal crown restoration that cover only a part of the clinical crown, most commonly used type of partial veneer crown
Faculty of Dental Medicine, University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Tirgu Mures, Romania 2
 ORIGINAL PAPER Efficacy of periodontal debridement using an Erbium YAG laser: A scanning electron microscopic study Alexandra Stoica 1, Soos Reka 2, Tudor Hănțoiu 1 1 Faculty of Dental Medicine, University
ORIGINAL PAPER Efficacy of periodontal debridement using an Erbium YAG laser: A scanning electron microscopic study Alexandra Stoica 1, Soos Reka 2, Tudor Hănțoiu 1 1 Faculty of Dental Medicine, University
1. Rotosonic burs have 6 sides with non-cutting edge and will not injure soft and hard tissue.
 Rotosonic Scaler bur Rotosonic scaler bur are manufactured in two shape. One is perio type and the other is flame type. Perio type is made of stainless steel but flame type is made of carbide. Characteristics
Rotosonic Scaler bur Rotosonic scaler bur are manufactured in two shape. One is perio type and the other is flame type. Perio type is made of stainless steel but flame type is made of carbide. Characteristics
The use of the LiteTouch Er:YAG laser in peri-implantitis treatment
 The use of the LiteTouch Er:YAG laser in peri-implantitis treatment Authors_Prof. Tzi Kang Peng, Taiwan & Prof. Georgi Tomov, Bulgaria _Introduction With oral implantology experience its Renaissance, the
The use of the LiteTouch Er:YAG laser in peri-implantitis treatment Authors_Prof. Tzi Kang Peng, Taiwan & Prof. Georgi Tomov, Bulgaria _Introduction With oral implantology experience its Renaissance, the
Socket Graft Plus. Case Presentation. Ideal Bone Graft for All Socket Grafting Situations. Case #1
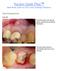 Socket Graft Plus Ideal Bone Graft for All Socket Grafting Situations Case Presentation Case #1 Tooth #3 presents with a buccal parulis, ensuring a buccal alveolar fenestration. The tooth will be remove
Socket Graft Plus Ideal Bone Graft for All Socket Grafting Situations Case Presentation Case #1 Tooth #3 presents with a buccal parulis, ensuring a buccal alveolar fenestration. The tooth will be remove
Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice
 Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic
 1 1 INTRODUCTION The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic bacteria, aims at the regeneration of a periodontal attachment composed of new cementum, alveolar bone
1 1 INTRODUCTION The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic bacteria, aims at the regeneration of a periodontal attachment composed of new cementum, alveolar bone
Full Arch Hygiene Protocol
 Full Arch Hygiene Protocol Patients should be evaluated and categorized into 3 different Recall Frequency Groups (RFG s). An evaluation of homecare should be made during the prosthetic phase of treatment
Full Arch Hygiene Protocol Patients should be evaluated and categorized into 3 different Recall Frequency Groups (RFG s). An evaluation of homecare should be made during the prosthetic phase of treatment
TIP BOOK THE MULTI-FUNCTION ULTRASONIC TIPS FOR ALL APPLICATIONS. Powerful Partners
 TIP BOOK TH MULTI-FUNCTION ULTRASONIC TIPS FOR ALL APPLICATIONS R00000 002 11.12.0.A Powerful Partners NSK Offers A Wide Choice of VARIOS Ultrasonic Scaler Tips For Clinical Applications. Prosthetics Pages
TIP BOOK TH MULTI-FUNCTION ULTRASONIC TIPS FOR ALL APPLICATIONS R00000 002 11.12.0.A Powerful Partners NSK Offers A Wide Choice of VARIOS Ultrasonic Scaler Tips For Clinical Applications. Prosthetics Pages
BioFilm Eraser. Advantages
 BioFilm Eraser Perio-Mate is used in the treatment of periodontal pockets and peri-implantitis. Avoiding injury to the soft tissues and root surfaces inside delicate periodontal pockets during cleaning
BioFilm Eraser Perio-Mate is used in the treatment of periodontal pockets and peri-implantitis. Avoiding injury to the soft tissues and root surfaces inside delicate periodontal pockets during cleaning
of the treated areas by means of a No. 3 explorer. The smoothness of the tooth-amalgam interface was then examined on each specimen by
 Removal of Amalgam Overhangs A Profilometric and Scanning Electron Microscopic Evaluation by Jose D. Freitas Vale, d.d.s., m.s.* Raul G. Caffesse, d.d.s., m.s. dr. ODONT.fl Subgingival restorations with
Removal of Amalgam Overhangs A Profilometric and Scanning Electron Microscopic Evaluation by Jose D. Freitas Vale, d.d.s., m.s.* Raul G. Caffesse, d.d.s., m.s. dr. ODONT.fl Subgingival restorations with
Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV.
 Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV. Class V. Cervical defects - Dental caries - Non carious lesions (erosion, abrasion, V shaped defects) Types of defects Caries Erosion Abrasion V shaped
Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV. Class V. Cervical defects - Dental caries - Non carious lesions (erosion, abrasion, V shaped defects) Types of defects Caries Erosion Abrasion V shaped
DENTAL EXTRACTIONS MADE EASIER. Brook A. Niemiec, DVM
 DENTAL EXTRACTIONS MADE EASIER Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Diplomate, European Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry San Diego Vet Dental
DENTAL EXTRACTIONS MADE EASIER Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Diplomate, European Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry San Diego Vet Dental
Periodontal Regeneration
 Periodontal Regeneration Regeneration The most ideal treatment Attempts to recreate the tissues destroyed by periodontitis Cement, bone and ligament Reduces the risk for recession and sensitivity (could
Periodontal Regeneration Regeneration The most ideal treatment Attempts to recreate the tissues destroyed by periodontitis Cement, bone and ligament Reduces the risk for recession and sensitivity (could
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
PREVENTIVE DENTISTRY. Straumann Next Generation Dentistry Prevent. Restore. Enhance.
 PREVENTIVE DENTISTRY Prevent. Restore. Enhance. 2 Next Generation Dentistry: Take a holistic approach with innovative solutions that enable preventive dentistry. If given the option, we all prefer prevention
PREVENTIVE DENTISTRY Prevent. Restore. Enhance. 2 Next Generation Dentistry: Take a holistic approach with innovative solutions that enable preventive dentistry. If given the option, we all prefer prevention
Hands-on Posterior Tooth Preparation. Practical Skills Courses, SWL, 25/11/2016
 Hands-on Posterior Tooth Preparation Practical Skills Courses, SWL, 25/11/2016 Hands-On Didactic Teaching A Tooth-Friendly-Approach - Hands-on Tooth Preparation Course - Dental Simulation to include: Posterior
Hands-on Posterior Tooth Preparation Practical Skills Courses, SWL, 25/11/2016 Hands-On Didactic Teaching A Tooth-Friendly-Approach - Hands-on Tooth Preparation Course - Dental Simulation to include: Posterior
Essentials of Periodontal Management in General Practice
 Essentials of Periodontal Management in General Practice Phil Ower MSc BDS MGDSRCS Specialist in Periodontics Briars Dental Centre, Newbury and www.periocourses.co.uk Introduction Effective management
Essentials of Periodontal Management in General Practice Phil Ower MSc BDS MGDSRCS Specialist in Periodontics Briars Dental Centre, Newbury and www.periocourses.co.uk Introduction Effective management
FS MTS. Micro Periodontal Tissue Scissors
 FEATHERLITE SCISSORS Our patented Flex Series Scissors are designed to have a 300% increase in its shearing angulation compared to conventional scissors. The result is that, no mater what is being cut,
FEATHERLITE SCISSORS Our patented Flex Series Scissors are designed to have a 300% increase in its shearing angulation compared to conventional scissors. The result is that, no mater what is being cut,
Field Guide to the Ultrasonic Revolution
 Helsē Ultrasonic Field Guide to the Ultrasonic Revolution 20 Endo Tasks... Simplified. Sparking an Ultrasonic Revolution At Helse Ultrasonic, our unwavering mission is to turn your ultrasonic unit into
Helsē Ultrasonic Field Guide to the Ultrasonic Revolution 20 Endo Tasks... Simplified. Sparking an Ultrasonic Revolution At Helse Ultrasonic, our unwavering mission is to turn your ultrasonic unit into
CHAPTER 7. ROOT TREATMENT, REATTACHMENT, AND REPAIR
 112 CHAPTER 7. ROOT TREATMENT, REATTACHMENT, AND REPAIR Section 1. Root Healing CHAPTER 7. ROOT TREATMENT, REATTACHMENT, AND REPAIR Section 1. Root Healing DEFINITIONS Repair: Healing of a wound by tissue
112 CHAPTER 7. ROOT TREATMENT, REATTACHMENT, AND REPAIR Section 1. Root Healing CHAPTER 7. ROOT TREATMENT, REATTACHMENT, AND REPAIR Section 1. Root Healing DEFINITIONS Repair: Healing of a wound by tissue
MECTRON ULTRASONIC INSERTS
 MECTRON ULTRASONIC INSERTS ULTRASONIC INSERTS MULTIPIEZO white A LARGE VARIETY OF APPLICATIONS Scaling, perio, endo, restorative mectron offers a wide range of applications. mectron s high-quality technique
MECTRON ULTRASONIC INSERTS ULTRASONIC INSERTS MULTIPIEZO white A LARGE VARIETY OF APPLICATIONS Scaling, perio, endo, restorative mectron offers a wide range of applications. mectron s high-quality technique
أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل CROWN AND BRIDGE جامعة تكريت كلية. Lec. (2) طب االسنان
 Lec. (2) CROWN AND BRIDGE أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل Patient selection and examination A thorough diagnosis must first be made of the patient's dental condition, considering both hard and soft tissues. this
Lec. (2) CROWN AND BRIDGE أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل Patient selection and examination A thorough diagnosis must first be made of the patient's dental condition, considering both hard and soft tissues. this
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
English. Perfectly in tune. Satelec Surgical Tips
 English Perfectly in tune Satelec Surgical Tips SATELEC, World Leader - Inventor of the piezoelectric technology applied to dentistry, - Constant R&D investments, in partnership with clinicians, universities
English Perfectly in tune Satelec Surgical Tips SATELEC, World Leader - Inventor of the piezoelectric technology applied to dentistry, - Constant R&D investments, in partnership with clinicians, universities
Periodontal conditions of teeth presenting pathologic migration Condições periodontais de dentes com migração dentária patológica
 Braz Oral Res 2004;18(4):301-5 Periodontics Periodontal conditions of teeth presenting pathologic migration Condições periodontais de dentes com migração dentária patológica Maurício Ribeiro Costa* Karina
Braz Oral Res 2004;18(4):301-5 Periodontics Periodontal conditions of teeth presenting pathologic migration Condições periodontais de dentes com migração dentária patológica Maurício Ribeiro Costa* Karina
SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM
 SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM PRECISION BY DESIGN PS Instrument [> magn nified 8 x] PIEZON METHOD PIEZON METHOD} SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM PIEZON ULTRASOUND INSTRUMENTS FOR A COMPLETE RANGE OF TREATMENTS } ENDODONTICS
SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM PRECISION BY DESIGN PS Instrument [> magn nified 8 x] PIEZON METHOD PIEZON METHOD} SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM PIEZON ULTRASOUND INSTRUMENTS FOR A COMPLETE RANGE OF TREATMENTS } ENDODONTICS
What You Should Know About Dental Implants: The Process of Care Applies
 Learn how the process of care model can apply to dental implants and empower decisions for providing quality care for clients. Starting with assessing the need for implants, the process covers documentation,
Learn how the process of care model can apply to dental implants and empower decisions for providing quality care for clients. Starting with assessing the need for implants, the process covers documentation,
