Systemic evaluation of various haemostatic agents following local application prior to direct pulp capping
|
|
|
- Ronald Blankenship
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Braz J Oral Sci. July-September Vol. 4 - Number 14 Systemic evaluation of various haemostatic agents following local application prior to direct pulp capping Franklin Garcia-Godoy 1 Peter E. Murray 2 1 DDS, MS, Professor and Associate Dean for Research, Nova Southeastern University, College of Dental Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida. 2 PhD, Assistant Professor, Director of Oral Biology, Nova Southeastern University, College of Dental Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida. Received for publication: March 11, 2005 Accepted: August 12, 2005 Abstracty Limited physiological information is available regarding the role of hemostatic agents to control the success of direct pulp capping treatment in order to help save vital pulps from pulpotomy, pulpectomy or extraction. The aim of this study was to test whether placement of various hemostatic agents would alter short-term pulp healing following direct pulp capping. Class V cavity preparations with pulp exposures were prepared in 31-nonhuman primate teeth, pulp hemorrhage was controlled by placement of epinephrine, Consepsis, sodium hypochlorite or combinations of these agents. Each exposure was then direct capped with composite resin and then observed immediately or after 13, and 28-days. Histological examination of pulp healing was conducted according to ISO standards for pulp inflammation, soft tissue organization, reactionary and reparative dentin bridge formation. Physiological measurement of heart rate and blood pressure were continuously recorded during the three operative procedures. Local pulp treatment with the various hemostatic agents did not alter systemic blood pressure or heart rate during local pulp application. All hemostatic treatments provided acceptable biocompatibility. Minor differences in pulp healing were observed, but there were no statistically significant differences between treatments (Pe 0.05). We conclude that hemostatic treatment had little effect on systemic pulp physiology or healing. Key Words: sodium hypochlorite, epinephrine, heart rate, blood pressure, healing Correspondence to: Franklin Garcia-Godoy Associate Dean for Research Nova Southeastern University, College of Dental Medicine Fort Lauderdale, FL Tel: (954) Fax: (954) godoy@nsu.nova.edu 791
2 Introduction Mechanical pulp exposure may occur during cavity preparation. However, it should be avoided because it reduces the prognosis of restorative treatment. The selection of a direct pulp capping agent to optimize pulp healing has proven controversial, although the consensus is shifting towards acceptance of composite resins, when calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2] was previously the only material of choice 1-3. Before pulp capping can take place, pulp lavage and hemorrhage control must be achieved. These procedures are most likely even more important to preserve pulp vitality than is the choice of a specific direct pulp capping agent, because of evidence that pulp healing is most compromised by hemorrhagic injury 4-5. The most common accepted clinical technique is simply to apply pressure to the exposure site with a sterile cotton pellet until hemorrhage subsides 6-7 sometimes the soaking of cotton pellets with sterile saline or other chemicals have been recommended While some alternatives such as electrosurgery 14, or laser irradiations 15 have proven to be of limited usefulness. hypochlorite [NaOCl] has a long history of removing diseased or infected tissues from wounds 16 and for removing diseased pulp tissue Since the 1950 s, NaOCl has demonstrated acceptable pulp biocompatibility when used as a local pulp hemostatic agent The solvent activity of a 5.25% concentration of NaOCl is limited to superficial pulp cells, leaving the subjacent pulp tissue unaffected Little is known about the biocompatible effects of other chemical agents such as epinephrine 25, 26 and commercial formulations of NaOCl agents. Consequently the aim of this study was to examine pulp healing and compare the biocompatibility of these chemicals when used as agents to control hemostasis following pulp exposure. Material and Methods Thirty one sound teeth were used from two-adult Rhesus macaca monkeys. The animals were procured and housed according to the University ethical and animal review guidelines and procedures. Prior to operative procedures, each animal was tranquillized and sedated. Teeth were scaled and polished with rubber cup and pumice paste to remove plaque and calculus. Saliva was controlled by high-speed evacuation and quadrants of teeth were isolated with sterile cotton rolls. Class V cavities were prepared with a #330 carbide bur at ultra-high speed under water spray coolant and the pulps intentionally exposed with the same bur; a new bur was used for every fourth tooth. Hemorrhage was controlled using a cotton pellet containing one of several agents; a commercial NaOCl-product,, or epinephrine (Table 1), each applied with light pressure for 30-seconds or until hemorrhage was clinically controlled. The cavities were gently rinsed with sterile water and the haemostatic agent reapplied if bleeding continued. Each pulp exposure was direct pulp capped by placing a thin layer of UltraBlend Plus only over the exposed pulp and light cured for 20-secs (Ultradent Inc., South Jordan, Utah). The enamel and dentin walls were etched with a 35% phosphoric acid for 15-secs, rinsed with sterile water for 10-secs and gently air dispersed; not dried. The bonding adhesive (PQ- 1 ) was evenly applied to the prepared cavity surfaces for 20-secs, without disturbing the pulp, and air thinned using a vacuum tip until the surface presented a glossy appearance. The adhesive was light-cured for 10-secs to avoid thermal damage to the underlying pulp tissue. Composite resin (Amelogen ) was placed to the axial floor and light cured for 20-secs. A second layer was placed, contoured and finished to the cavosurface margin, followed by etching, rinsing and sealing with (Perma-seal ) to ensure a complete seal of the restoration. The standardized methods and procedures used in this study are congruent with those described elsewhere The heart rate and blood pressure of the animals was continuously monitored and recorded during the three operative procedures: during cavity preparation, haemostatic, and the restorative phase. Table 1 -Tooth numbers, extraction interval, hemostatic agent formulations. Hemostatic agent Extracted [Days] Number of Teeth Hypochorite a 0 3 b 0 3 Hypochorite product c 13 3 Hypochorite product c + b 28 2 Epinephrine d + b 28 2 Hypochorite a 28 6 Hypochorite product c 28 6 Epinephrine d 28 6 a 5.25% NaOCl solution, b Chlorhexidine, Astra, Westborough, MA c Ultradent, South Jordan, Utah d 2% Xylocaine with epinephrine / 1:100,
3 Table 2 - Histological valuation criteria Inflammatory cell response The pulp contained few inflammatory cells, or an absence of inflammatory cells associated with the pulp beneath the cut tubules of the cavity floor. The pulp had localized inflammatory cell lesions predominated by polymorphonuclear leukocytes, or mononuclear lymphocytes. The pulp had polymorphonuclear leukocyte lesions involving more than one third of the coronal pulp. Severe The pulp tissue is largely necrotic, following chronic inflammatory cell injury. Soft tissue organization Normal Exposure cell loss Pulp cell loss No tissue injury, disruption, or loss of cell survival. A superficial loss of cell survival at the site of injury. An extensive loss of cell survival involving more than the superficial pulp. Reactionary dentin No secretion of reactionary dentine at the site of injury. A thin zone (d 10 µm) of dentine secretion by primary odontoblasts. A thick zone (e 10 µm) of dentine secretion by primary odontoblasts. Reparative dentin Bacterial staining Severe No secretion of reparative dentin by odontoblastoid cells at the site of injury. A thin zone (d 10 µm) of dentin secretion by odontoblastoid cells. A thick zone (e 10 µm) of dentin secretion by odontoblastoid cells to bridge the site of exposure. Absence of bacterial staining in any section. A positive bacterial staining reaction seen along the cavity walls. A positive bacterial staining reaction seen within the cut dentinal tubules of the cavity preparation. A positive bacterial staining reaction seen within the dental pulp. Serial sections of 7µm thickness stained with hematoxylin and eosin, were examined by light microscopy, and histological analysis was conducted according to International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Technical Report 7405 usage test guidelines 31. The inflammatory response of each pulp was categorized according to ISO guidelines and published criteria The categories of pulp inflammation and other histological assessment criteria are shown in Table 2. Bacterial contamination of each restoration was assessed using McKay s stain 32 to detect for the presence of Gram positive and Gram negative microorganisms. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) statistical procedures, and Chi-square (X 2 ) at a confidence level of 95% (STAT view software, SAS Inc.). These statistical analyses are reportedly among the most versatile and conservative of multiple comparison tests 33. Results Blood pressure, heart rate and pulp histology Table 3. Statistical correlations between haemostatic agents and variables Statistic Comparison between materials and: P value ANOVA Blood pressure ANOVA Heart rate X 2 Inflammation X 2 Soft tissue organization X 2 Reactionary dentin X 2 Reparative dentin bridge A comparison between the hemostatic agents demonstrated very little systemic differences between their effects on heart rate or blood pressure, suggesting that pulp hemorrhage control does not place a strain on the whole body systemic system, or do they present a serious threat to the individuals health during operative procedures, During the different stages of operative procedures there was little change in heart rate (P = ) or blood pressure (P = ) (Figures 1 and 2). Furthermore, there were few 793
4 Heart rate (Beats per minute) Braz J Oral Sci. 4(14): Phase of treatment Epinephrine Epinephrine/ / Hemostatic agent product Phase of treatment Cavity preparation Hemostasis Restorative Mean blood pressure (mm mercury) product Epinephrine Epinephrine/ Hemostatic agent / Cavity preparation Hemostasis Restorative Fig. 1 - Heart rate during operative procedures. Fig. 2 - Blood pressure during operative procedures. Inflammatory cell response Severe Soft tissue organization Pulp cell loss Exposure cell loss Normal Reactionary dentin Reparative dentin a. (0 days) b. (0 days) c. product (13 days) d. product (13 days) e. product + (13 days) f. Epinephrine + g. Epinephrine h. (0 days) Fig. 3 - Histological assessments of hemostatic treatments prior to pulp capping. differences in heart rate (P = 0.994) or blood pressure (P = ) between hemostatic treatments (Table 3, Figures 1 and 2). With some agents hemorrhage control was difficult to achieve, necessitating repeated re-applications, sometimes with alternative agents. Nevertheless, hemostatic control was always accomplished prior to pulp capping with the adhesive resin. Generally the histology showed that each hemostatic agent permits pulp healing against the composite resin, passing the ISO 7405 requirements for clinical testing. There were few differences between the agents (Table 2) in terms of inflammation (X 2, P = ), reactionary dentin (X 2, P = 0.988), reparative dentin (X 2, P = ) and tissue 794
5 organization (X 2, P = ). No bacterial microorganisms were observed in any of the teeth stained with McKay s stain. Immediate capping pulp histology Six capped pulps showed no inflammatory activity, reactionary or reparative dentin secretion or injury of cells, deeper than the superficial layer. However some extravasted red blood cells and operative debris were associated with pulp exposure. Histology of pulp capping after 13-days with NaOCl Three exposed pulps were treated with a NaOCl-product; only one-pulp showed some reactionary and reparative dentin formation associated with the composite resin capping material. The two remaining pulps had severe inflammation and one was proceeding to necrosis, no reactionary or reparative dentin was observed in these teeth. These pulps also showed the greatest mean loss in cells in comparison with other pulps (Figure 3). Histology of pulp capping after 28-days with NaOClproduct Twenty-two exposed pulps were treated with hemostatic agents and combinations of agents. Following the use of NaOCl-product, reactionary and reparative dentin was observed in all six-treated pulps, reparative dentin was observed subjacent to the capping material in four pulps, and in two pulps reparative dentin was observed in the deeper pulp. This level and positioning of reparative dentin secretion is not as complete as with other treatments after 28-days (Figure 3). The incidence of new dentin secretion (100%), contrasts with that observed in a third of teeth after 13-days (33%). Over the same time difference, the mean level of pulp inflammation reduced and tissue organization injury was not as severe (Figure 3). Histology of pulp capping after 28-days with NaOClproduct and Both of the 2 capped pulps showed normal tissue organization, no inflammation, and some reactionary and reparative dentin secretion at the exposure site (Figure 3). Histology of pulp capping after 28 days with epinephrine and Both of the 2 capped pulps showed low levels of pulp inflammation, near normal tissue organization, with some reactionary and reparative dentin secretion at the exposure site (Figure 3). Histology of pulp capping after 28-days with epinephrine The four capped pulps showed low levels of pulp inflammation, near normal tissue organization, with some reactionary and reparative dentin secretion at the exposure site (Figure 3). However, in contrast to the other treatments, reparative dentin secretion was generally not associated with the capping material (Figure 3). Histology of pulp capping after 28-days with NaOCl Six pulps were treated with NaOCl, two pulps showed each category of inflammation; none, slight and moderate. Therefore, the mean category of inflammation was slight (Figure 3). Tissue organization was largely normal, with a slight level of reactionary dentin and reparative dentin secretion at the site of exposure in most pulps (Figure 3). Discussion The histological observations from this study provide some biological insight into several issues that deal with direct pulp capping with adhesive systems. Each of the different hemorrhage control agents is acceptable to pass ISO biocompatibility usage screening requirements for clinical evaluation. However, because a few differences in pulp healing were observed between different hemostatic treatments, this suggests a role for the importance of the capping materials. A good reason for the lack of serious pulp inflammation and healing defects, was the lack of bacterial staining in any of these sections, this avoids the bacterial stimulus responsible for the most serious pulp inflammation and healing complications 10, These observations highlight the importance of sealing restorations along the enamel-resin margins to provide pulp protection and to attempt to improve the prognosis of operative treatment. Moreover, sealing of the restoration interface appears a more important factor than placement of any one particular direct capping agent; recently it has been demonstrated that reactionary and reparative dentin secretion is a natural healing response to pulp injury not a specific response to any specific Ca(OH) 2 agent, as originally assumed 37. The use of composite resin materials for direct pulp capping remains highly controversial, some investigators report serious pulp necrosis 38, while others report excellent healing 10, The lack of consensus is reflected in some reviews that have been indecisive over the most appropriate selection of pulp capping materials, failing to completely recommend composite resins, resinmodified glass ionomers or the traditional use of calcium hydroxide. There were few differences between the physiological and histological effects of the hemostatic treatments. However, NaOCl appeared to be the most effective agent in removing the cavity biofilm and to control hemorrhage, enabling the pulp capping materials to be placed most easily. However, it was not possible to measure the ease of use of NaOCl in comparison with the other treatments, because it is subjective and likely influenced by the level of operator experience. This ISO usage study showed that each tested 795
6 treatment regimen provides the necessary clinical requirements for placement of the composite resin material to accomplish direct pulp capping. This study has demonstrated that mechanically exposed pulps will heal naturally following proper haemostatic treatment and capping with composite resin, provided bacterial leakage can be prevented and maintained. However, this study can only be used as a guide to help address the short-term performance of these pulp-capping treatment regimens, unfortunately many questions remain to be answered over the longer term. The use of non-human primates as part of ISO preclinical testing 31 has shown that the cleansing of biofilm from all cavity surfaces, followed by sealing against exudates and leakage will mediate high levels of reparative dentin against direct adhesive capping, as observed in this study. Clearly, the dental pulp maintains its physiological vitality when bacteria and their toxic components are excluded from gaining access to the vital tissues of the dentin and pulp. The key to accomplishing improvements in the prognosis of direct pulp capped teeth requires further investigation of methods to control hemorrhage and preservation of pulp vitality. References 1. Hafez, AA, Kopel HM, Cox CF. Pulpotomy reconsidered: An application of an adhesive system to pulpotomized permanent primate pulps. Quintessence Int 2000; 21: Mjor IA. Pulp-dentin biology in restorative dentistry. Part 7: The exposed pulp. Quintessence Int 2002; 33: Murray PE, Smith AJ. Saving pulps a biological basis. Prim Dent Care 2002;9: Dummer PM, Hicks R, Huws D. Clinical signs and symptoms in pulp disease. Int Endod J 1980; 13: Matsuo T, Nakanishi T, Shimizu H, Ebisu S. A clinical study of direct pulp capping applied to carious-exposed pulps. J Endod 1996; 22: Hunter FA. Saving pulps. A Queer Process, Items of Interest 1883; 5: Seelig A. The formation of calcified tissue in dental pulps. N Y St Dent J 1956; 22: Hebling J, Giro E, Costa C. Biocompatibility of an adhesive system applied to exposed human dental pulp. J Endod 1999; 25: Horsted P, El Attar K, Langeland K. Capping of monkey pulps with Dycal and a Ca-eugenol cement. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1981; 52: Kitasako Y, Inokishi S, Fujitani M, Otsuki M, Tagami J. Shortterm reaction of exposed monkey pulp beneath adhesive resins. Oper Dent 1998; 23: Schröder U, Granath LE. Early reaction of inert human teeth to Ca(OH)2 following pulpotomy and its significance to the development of the hard tissue barrier. Odontol Revy 1971; 22: Schröder U. Effects of Ca(OH)2 containing pulp-capping agents on pulp cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation. J Dent Res 1985; 64: Fei AL, Udin RD, Johnson R. A clinical study of ferric sulfate as a pulpotomy agent in primary teeth. Ped Dent 1991; 13: Oztas N, Ulusu T, Oygur T, Cokpekin F. Comparison of elecrtosurgery and formocresol as pulpotomy techniques in dog primary teeth. J Clin Ped Dent 1994; 22: Wilkerson MK, Hill SD, Arcoria CJ. Effects of the argon laser on primary tooth pulpotomies in swine. J Clin Laser Med Surg 1996; 14: Dakin HD. On the use of certain antiseptic substances in the treatment of infected wound. Br Med J 1915; 2: Walker A. A definite and dependable therapy for pulpless teeth. J Am Dent Assoc 1936; 23: Masterton JB. Chemical debridement in the treatment of infected pulpless teeth and chronic periapical abscess. Dent Pract 1965; 15: Hirota K. A study on partial pulp removal (pulpotomy) using four different tissue solvents. J Jpn Stomatol Soc 1959; 26: Sudo C. A study on partial pulp removal (pulpotomy) using NaOCl (sodium hypochlorite). J Japanese Stomatological Soc 1959; 26: Cox CF, Hafez AA, Akimoto N, Otsuki M, Suzuki S, Tarim B. Biocompatibility of primer, adhesive and resin composite systems on non-exposed and exposed pulps of non-human primates. Am J Dent 1998;10: Cox CF, Hafez AA, Akimoto N, Otsuki M, Mills JC. Biological basis for clinical success: Pulp protection and the toothrestoration interface. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 1999; 11: Senia ES, Marshall FJ, Rosen S. The solvent action of sodium hypochlorite on pulp tissue of extracted teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1971; 31: Rosenfeld EF, James GA, Burch BS. Vital pulp tissue response to sodium hypochlorite. J Endod 1978; 4: Teixeira LS. Demarco FF. Coppola MC. Bonow ML. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of pulpotomies performed under intrapulpal injection of anaesthetic solution. Int Endod J 2001; 34: Thomas GP. Boyd JB. Soni NN. Palmer JE. Histologic study of pulp capping using chlorhexidine in dogs. NDA J 1995; 46: Cox CF. Evaluation and treatment of bacterial microleakage. Am J Dent 1994; 7: Cox CF, Subay RK, Ostro E, Suzuki S. Tunnel defects in dentin bridges: Their formation following direct pulp capping. Oper Dent 1996; 21 : Cox CF, Keall CL, Keall HJ, Ostro E, Bergenholtz G. Biocompatibility of surface-sealed dental materials against exposed pulps. J Prosthet Dent 1987; 57: Akimoto N, Momoi Y, Kohno A, Suzuki S, Otsuki M, Suzuki S, Cox CF. Biocompatibility of Clearfil Liner Bond 2 and Clearfil AP-X system on nonexposed and exposed primate teeth. Quintessence Int 1998; 29: ISO 7405 Preclinical evaluation of biocompatibility of medical devices used in dentistry; test methods for dental materials. Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization; McKay GS. Gram stain modified to improve colour contrast. J Clin Pathol 1970;23: Dawson-Saunders B, Trapp RG. Basic and clinical biostatistics. 2 nd ed. Norwalk, CT; Appleton and Lange; Kitasako Y, Inokishi S, Tagami J. Effect of direct resin pulp capping techniques on short-term response of mechanically exposed pulps. J Dent 1999; 27: Cox CF. Hafez AA. Biocomposition and reaction of pulp tissues to restorative treatments. Dent Clinics N Am 2001; 45: Murray PE, Hafez AA, Smith AJ, Cox CF. Hierarchy of pulp capping and repair activities responsible for dentin bridge formation. Am J Dent 2002; 15:
7 37. Yoshiba K, Yoshiba N, Iwaku M. Histological observations of hard tissue barrier formation in amputated dental pulp capped with tricalcium phosphate containing calcium hydroxide. Endod Dent Traumatol 1994; 10: Pameijer CH, Stanley HR. The disastrous effects of the Total Etch technique in vital pulp capping in primates. Am J Dent 1998;11(Spec Iss) S45-S Schuurs AH. Gruythuysen RJ. Wesselink PR. Pulp capping with adhesive resin-based composite Vs calcium hydroxide: a review. Endod Dent Traumatol 2000; 16: Pereira JC. Segala AD. Costa CA. Human pulpal response to direct pulp capping with an adhesive system. Am J Dent 2000; 13:
Remaining dentin thickness Shallow cavity depth Preparation 0.5 mm into dentin (ideal depth) Moderate cavity depth Remaining dentin over pulp of at le
 Deep carious lesions management Remaining dentin thickness Shallow cavity depth Preparation 0.5 mm into dentin (ideal depth) Moderate cavity depth Remaining dentin over pulp of at least 1-2 mm Deep cavity
Deep carious lesions management Remaining dentin thickness Shallow cavity depth Preparation 0.5 mm into dentin (ideal depth) Moderate cavity depth Remaining dentin over pulp of at least 1-2 mm Deep cavity
Pediatric endodontics. Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR
 Pediatric endodontics Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR WHY TO PRESERVE PRIMARY TEETH? The preservation of the primary dentition until their normal anticipated exfoliation can be justified
Pediatric endodontics Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR WHY TO PRESERVE PRIMARY TEETH? The preservation of the primary dentition until their normal anticipated exfoliation can be justified
Human pulp response after direct pulp capping with an adhesive system
 Human pulp response after direct pulp capping with an adhesive system Ali M. Abdul Kareem B.D.S, Ph.D. (1) ABSTRACT Background: The adhesive systems are experimentally used in direct pulp capping procedure.
Human pulp response after direct pulp capping with an adhesive system Ali M. Abdul Kareem B.D.S, Ph.D. (1) ABSTRACT Background: The adhesive systems are experimentally used in direct pulp capping procedure.
Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module A: Basic Concepts
 Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module A: Basic Concepts REST 528A Operative #3A
Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module A: Basic Concepts REST 528A Operative #3A
FINAL REPORT. Histopathology of Embrace and a 2-part light cured material on the pulp a subhuman primate study
 FINAL REPORT Histopathology of Embrace and a 2-part light cured material on the pulp a subhuman primate study Cornelis H. Pameijer DMD, DSc, PhD Professor Emeritus University of Connecticut DLC International
FINAL REPORT Histopathology of Embrace and a 2-part light cured material on the pulp a subhuman primate study Cornelis H. Pameijer DMD, DSc, PhD Professor Emeritus University of Connecticut DLC International
Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control
 Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control REST 528A
Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control REST 528A
PROFOUND HEMOSTASIS AND FLUID CONTROL TISSUE MANAGEMENT
 TISSUE MANAGEMENT PROFOUND HEMOSTASIS AND FLUID CONTROL Unparalleled tissue management starts with rapid, profound hemostasis. To control bleeding and sulcular fluid, no one offers a more complete line
TISSUE MANAGEMENT PROFOUND HEMOSTASIS AND FLUID CONTROL Unparalleled tissue management starts with rapid, profound hemostasis. To control bleeding and sulcular fluid, no one offers a more complete line
Short-Term Analysis of Human Dental Pulps After Direct Capping with Portland Cement
 The Open Dentistry Journal, 009,, -5 Open Access Short-Term Analysis of Human Dental Pulps After Direct Capping with Portland Cement Antonio Vinicius Holanda Barbosa,*, Gerhilde Callou Sampaio, Fábio Almeida
The Open Dentistry Journal, 009,, -5 Open Access Short-Term Analysis of Human Dental Pulps After Direct Capping with Portland Cement Antonio Vinicius Holanda Barbosa,*, Gerhilde Callou Sampaio, Fábio Almeida
CLINICAL AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF DIRECT PULP CAPPING PROCEDURES PERFORMED BY POSTGRADUATE STUDENTS
 CLINICAL AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF DIRECT PULP CAPPING PROCEDURES PERFORMED BY POSTGRADUATE STUDENTS Monica Monea Alexandru Sitaru Tudor Hantoiu Department of Odontology and Oral Pathology, Faculty
CLINICAL AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF DIRECT PULP CAPPING PROCEDURES PERFORMED BY POSTGRADUATE STUDENTS Monica Monea Alexandru Sitaru Tudor Hantoiu Department of Odontology and Oral Pathology, Faculty
Comparison of Calcium Hydroxide and Bioactive Glass after Direct Pulp Capping in Primary Teeth
 Original Article Comparison of Calcium Hydroxide and Bioactive Glass after Direct Pulp Capping in Primary Teeth R. Haghgoo 1, N. Jalayer Naderi 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatric Dentistry,
Original Article Comparison of Calcium Hydroxide and Bioactive Glass after Direct Pulp Capping in Primary Teeth R. Haghgoo 1, N. Jalayer Naderi 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatric Dentistry,
Histopathological response of infected cavities treated with Gluma and Scotchbond dentin bonding agents
 Histopathological response of infected cavities treated with Gluma and Scotchbond dentin bonding agents Charles F. Cox, BSc, MSc, David Felton, DDS, MS & Gunnar Bergenholtz, DDS, Dr Odont University of
Histopathological response of infected cavities treated with Gluma and Scotchbond dentin bonding agents Charles F. Cox, BSc, MSc, David Felton, DDS, MS & Gunnar Bergenholtz, DDS, Dr Odont University of
A Comparative Study between Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Calcium Hydroxide as Pulp Capping Agents in Dog s Teeth
 A Comparative Study between Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Calcium Hydroxide as Pulp Capping Agents in Dog s Teeth A. Eskandarizadeh*, M. Parirokh**, B. Eslami ***, S. Asgary****, M.J. Eghbal***** ABSTRACT
A Comparative Study between Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Calcium Hydroxide as Pulp Capping Agents in Dog s Teeth A. Eskandarizadeh*, M. Parirokh**, B. Eslami ***, S. Asgary****, M.J. Eghbal***** ABSTRACT
A Comparison of Two Liner Materials for Use in the Ferric Sulfate Pulpotomy
 A Comparison of Two Liner Materials for Use in the Ferric Sulfate Pulpotomy SADJ July 2008, Vol 63 no 6 p338 - p342 Dr. N Mohamed: BChD, BSc (Hons), MSc (Paediatric dentistry). Lecturer/ Snr Dentist, Department
A Comparison of Two Liner Materials for Use in the Ferric Sulfate Pulpotomy SADJ July 2008, Vol 63 no 6 p338 - p342 Dr. N Mohamed: BChD, BSc (Hons), MSc (Paediatric dentistry). Lecturer/ Snr Dentist, Department
Fuji II LC. A Perfect Choice
 A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
Study to evaluate the Efficacy of Resin-modified Glass Ionomer Cement Liner as a Direct Pulp Capping Material
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Study to evaluate the 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2382 Efficacy of Resin-modified GIC Liner Study to evaluate the Efficacy of Resin-modified Glass Ionomer Cement Liner as a Direct Pulp
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Study to evaluate the 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2382 Efficacy of Resin-modified GIC Liner Study to evaluate the Efficacy of Resin-modified Glass Ionomer Cement Liner as a Direct Pulp
Primary Tooth Vital Pulp Therapy By: Aman Bhojani
 Primary Tooth Vital Pulp Therapy By: Aman Bhojani Introduction The functions of primary teeth are: mastication and function, esthetics, speech development, and maintenance of arch space for permanent teeth.
Primary Tooth Vital Pulp Therapy By: Aman Bhojani Introduction The functions of primary teeth are: mastication and function, esthetics, speech development, and maintenance of arch space for permanent teeth.
Practical vital pulp treatment: MTA or calcium hydroxide?
 Practical vital pulp treatment: MTA or calcium hydroxide? Hal Duncan, Division of Restorative Dentistry and Periodontology, Dublin Dental University Hospital, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland NVvE Voorjaarscongres,
Practical vital pulp treatment: MTA or calcium hydroxide? Hal Duncan, Division of Restorative Dentistry and Periodontology, Dublin Dental University Hospital, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland NVvE Voorjaarscongres,
Effect of MTAD and Tea Tree Oil Irrigation before Pulp Capping on Healing of Exposed Dental Pulp.
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 6(7): 553-557, 2012 ISSN 1991-8178 Effect of MTAD and Tea Tree Oil Irrigation before Pulp Capping on Healing of Exposed Dental Pulp. 1 Sharaf N., 2 Aboul-Enein
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 6(7): 553-557, 2012 ISSN 1991-8178 Effect of MTAD and Tea Tree Oil Irrigation before Pulp Capping on Healing of Exposed Dental Pulp. 1 Sharaf N., 2 Aboul-Enein
stabilisation and surface protection
 Guiding the way to caries stabilisation and surface protection Fissure sealing MI restorations Pulp capping Hypersensitivity Protection Caries stabilisation Fuji Triage from GC. Temporary restorations
Guiding the way to caries stabilisation and surface protection Fissure sealing MI restorations Pulp capping Hypersensitivity Protection Caries stabilisation Fuji Triage from GC. Temporary restorations
Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module C: Clinical applications
 Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module C: Clinical applications REST 528A Operative
Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module C: Clinical applications REST 528A Operative
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary Vol.:9 No.:2 2012
 MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
DiaDent Group International DIA.DENT DiaRoot BioAggregate. Root Canal Repair Material
 DiaDent Group International 1.877.DIA.DENT www.diadent.com DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material PRECISION. PURITY. RESULTS ABOUT DIAROOT... DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material is
DiaDent Group International 1.877.DIA.DENT www.diadent.com DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material PRECISION. PURITY. RESULTS ABOUT DIAROOT... DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material is
MTA PULPOTOMY ASSOCIATED APEXOGENESIS OF HUMAN PERMANENT MOLAR WITH IRREVERSIBLE PULPITIS: A CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 05 MTA PULPOTOMY ASSOCIATED APEXOGENESIS OF HUMAN PERMANENT MOLAR WITH IRREVERSIBLE PULPITIS: A CASE REPORT Nabi Shahnaz
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 05 MTA PULPOTOMY ASSOCIATED APEXOGENESIS OF HUMAN PERMANENT MOLAR WITH IRREVERSIBLE PULPITIS: A CASE REPORT Nabi Shahnaz
Pelagia Research Library. Comparison of microleakage in bonded amalgam restrorations using different adhesive materials: An invitro study
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2011, 1 (2):92-96 ISSN: 2248 9215 Comparison of microleakage in bonded amalgam restrorations using different
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2011, 1 (2):92-96 ISSN: 2248 9215 Comparison of microleakage in bonded amalgam restrorations using different
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children
 Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objective Discuss the role and importance of cements in paediatric dentistry Calcium hydroxide This is a colourless crystal or white powder prepared
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objective Discuss the role and importance of cements in paediatric dentistry Calcium hydroxide This is a colourless crystal or white powder prepared
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS Dentists need to understand that the decision to remove or not reimplant an avulsed incisor must be made very carefully. The loss of such a tooth in
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS Dentists need to understand that the decision to remove or not reimplant an avulsed incisor must be made very carefully. The loss of such a tooth in
Metal-Free Restorations PROCEDURES FOR POSTERIOR DIRECT & SEMI-DIRECT COMPOSITE RESTORATIONS D I D I E R D I E T S C H I. For.
 PROCEDURES FOR POSTERIOR DIRECT & SEMI-DIRECT COMPOSITE RESTORATIONS Metal-Free Restorations D I D I E R D I E T S C H I The Geneva Smile Center D.M.D, PhD, Privat-Docent 2, Quai Gustave Ador 1207 Geneva
PROCEDURES FOR POSTERIOR DIRECT & SEMI-DIRECT COMPOSITE RESTORATIONS Metal-Free Restorations D I D I E R D I E T S C H I The Geneva Smile Center D.M.D, PhD, Privat-Docent 2, Quai Gustave Ador 1207 Geneva
Restorative Dentistry and it s related to Pulp health. Dr.Ahmed Al-Jobory
 Restorative Dentistry and it s related to Pulp health Dr.Ahmed Al-Jobory Pulp Is a viscous connective tissue of collagen fibers and ground substance supporting the vital cellular, vascular, and nerve structures
Restorative Dentistry and it s related to Pulp health Dr.Ahmed Al-Jobory Pulp Is a viscous connective tissue of collagen fibers and ground substance supporting the vital cellular, vascular, and nerve structures
Clinical studies on ferric sulphate as a pulpotomy medicament in primary teeth
 Clinical studies on ferric sulphate as a pulpotomy medicament in primary teeth L. PAPAGIANNOULIS ABSTRACT. Aim The purpose of this paper is to review three prospective and two retrospective studies that
Clinical studies on ferric sulphate as a pulpotomy medicament in primary teeth L. PAPAGIANNOULIS ABSTRACT. Aim The purpose of this paper is to review three prospective and two retrospective studies that
The Power of the Pulp
 The Power of the Pulp Part 1 Dr Kishan Sheth recently graduated from KCL as a runner-up for the prestigious Jose Souyave Prize and will embark on his vocational training in Central London. He has become
The Power of the Pulp Part 1 Dr Kishan Sheth recently graduated from KCL as a runner-up for the prestigious Jose Souyave Prize and will embark on his vocational training in Central London. He has become
Operative dentistry. Lec: 10. Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE):
 Operative dentistry Lec: 10 د.عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE): There are 2 types: 1) Unreinforced ZOE (ordinary type): supplied as powder (zinc oxide + some additives like zinc acetate, white
Operative dentistry Lec: 10 د.عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE): There are 2 types: 1) Unreinforced ZOE (ordinary type): supplied as powder (zinc oxide + some additives like zinc acetate, white
CARIES STABILIZATION AND TEMPORARY RESTORATION
 CARIES STABILIZATION AND TEMPORARY RESTORATION LEARNING OUTCOMES Justify the importance of caries stabilisation procedure in operative care. List and discuss the methods to stabilise caries ( include preventive
CARIES STABILIZATION AND TEMPORARY RESTORATION LEARNING OUTCOMES Justify the importance of caries stabilisation procedure in operative care. List and discuss the methods to stabilise caries ( include preventive
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (2), 177:185 May, Hana M. Jamjoom 1. Abstract INTRODUCTION
 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (2), 177:185 May, 2008 Clinical evaluation of directly pulp capped permanent teeth with glass ionomer materials Hana M. Jamjoom 1 1. Associate Professor Conservative Department,
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (2), 177:185 May, 2008 Clinical evaluation of directly pulp capped permanent teeth with glass ionomer materials Hana M. Jamjoom 1 1. Associate Professor Conservative Department,
One of the most difficult situations a dentist encounters
 Review Article Multifaceted Use of ProRoot TM MTA Root Canal Repair Material Don Schmitt DDS Jacob Lee DDS, FRCD(C) George Bogen DDS Dr. Schmitt is a second year pediatric dental resident at the University
Review Article Multifaceted Use of ProRoot TM MTA Root Canal Repair Material Don Schmitt DDS Jacob Lee DDS, FRCD(C) George Bogen DDS Dr. Schmitt is a second year pediatric dental resident at the University
Histological Considerations of
 Histological Considerations of Direct Pulp Capping Agents D. R. HEYS, C. F. COX, R. J. HEYS, and J. K. AVERY Laboratory of Oral Histology, School of Dentistry, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan
Histological Considerations of Direct Pulp Capping Agents D. R. HEYS, C. F. COX, R. J. HEYS, and J. K. AVERY Laboratory of Oral Histology, School of Dentistry, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan
HISTOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF INDIRECT PULP CAPPING PROCEDURES WITH CALCIUM HYDROXIDE AND MINERAL TRIOXIDE AGGREGATE
 HISTOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF INDIRECT PULP CAPPING PROCEDURES WITH CALCIUM HYDROXIDE AND MINERAL TRIOXIDE AGGREGATE Monica Monea, Associate Prof. Adriana Monea, Lecturer DMD, PhD Department of Odontology
HISTOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF INDIRECT PULP CAPPING PROCEDURES WITH CALCIUM HYDROXIDE AND MINERAL TRIOXIDE AGGREGATE Monica Monea, Associate Prof. Adriana Monea, Lecturer DMD, PhD Department of Odontology
DEFENSE MECHANISM OF DENTINE AND PULP AGAINST INJURY
 DEFENSE MECHANISM OF DENTINE AND PULP AGAINST INJURY DR.AHMED IBRAHIM AL-JOBORY B.D.S. M.SC. CONSERVATIVE DEPARTMENT/ BAGHDAD UNIVERSITY MEMBER OF IRAQI ENDODONTICS SOCIETY The reaction in dentine are
DEFENSE MECHANISM OF DENTINE AND PULP AGAINST INJURY DR.AHMED IBRAHIM AL-JOBORY B.D.S. M.SC. CONSERVATIVE DEPARTMENT/ BAGHDAD UNIVERSITY MEMBER OF IRAQI ENDODONTICS SOCIETY The reaction in dentine are
The traumatic injury of an immature permanent tooth can lead to the loss of pulp
 Regenerative Treatment of an Immature, Traumatized Tooth With Apical Periodontitis: Report of a Case Elisabetta Cotti, DDS, MS, Manuela Mereu, DDS, and Daniela Lusso, DDS Abstract This case report describes
Regenerative Treatment of an Immature, Traumatized Tooth With Apical Periodontitis: Report of a Case Elisabetta Cotti, DDS, MS, Manuela Mereu, DDS, and Daniela Lusso, DDS Abstract This case report describes
ENDODONTICS. Trycare
 ENDODONTICS www.trycare.co.uk/tehnodent Trycare 01274 88 55 44 dental@trycare.co.uk 1 Edetale Gel With Peroxide Using a file lubricant reduces stress on the instrument by softening the dentine. Simply
ENDODONTICS www.trycare.co.uk/tehnodent Trycare 01274 88 55 44 dental@trycare.co.uk 1 Edetale Gel With Peroxide Using a file lubricant reduces stress on the instrument by softening the dentine. Simply
A Posterior Composite Case Utilizing the Incremental and Stratified Layering Technique
 Operative Dentistry, 2006, 31-4, 512-516 Clinical Technique/Case Report A Posterior Composite Case Utilizing the Incremental and Stratified Layering Technique HH Chi Clinical Relevance This paper illustrates
Operative Dentistry, 2006, 31-4, 512-516 Clinical Technique/Case Report A Posterior Composite Case Utilizing the Incremental and Stratified Layering Technique HH Chi Clinical Relevance This paper illustrates
Success of electrofulguration pulpotomies covered by.z.in.c oxide and eugenol or calcium hydroxide: a clinical study
 Scientific Article Success of electrofulguration pulpotomies covered by.z.in.c oxide and eugenol or calcium hydroxide: a clinical study Scott A. Fishman, DDS Richard D. Udin, DDS David L. Good, DDS Fairborz
Scientific Article Success of electrofulguration pulpotomies covered by.z.in.c oxide and eugenol or calcium hydroxide: a clinical study Scott A. Fishman, DDS Richard D. Udin, DDS David L. Good, DDS Fairborz
Fig 1. An everyday clinical condition that requires a perio-restorative protocol.
 WHY A CORE BUILDUP? In today s restorative practice, we treat patients with substantial amounts of existing restorative dentistry. Old amalgam fillings, 20+ year old crowns and posterior composites that
WHY A CORE BUILDUP? In today s restorative practice, we treat patients with substantial amounts of existing restorative dentistry. Old amalgam fillings, 20+ year old crowns and posterior composites that
ÆLITE Composites. Bisco. Instructions for Use. Light- Cured. U.S. Patent: 6,709,271
 Bisco ÆLITE Composites 0459 Light- Cured Instructions for Use U.S. Patent: 6,709,271 IN-131R6 Rev. 4/16 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Road Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 847-534-6000 1-800-247-3368 Caution:
Bisco ÆLITE Composites 0459 Light- Cured Instructions for Use U.S. Patent: 6,709,271 IN-131R6 Rev. 4/16 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Road Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 847-534-6000 1-800-247-3368 Caution:
Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice
 Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
EQUIA. Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System
 EQUIA EQUIA Fil EQUIA Coat + Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System From the World Leader in Glass Ionomer Technology - A Complete Glass Ionomer Based Bulk Fill Rapid Restorative System Class
EQUIA EQUIA Fil EQUIA Coat + Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System From the World Leader in Glass Ionomer Technology - A Complete Glass Ionomer Based Bulk Fill Rapid Restorative System Class
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH
 FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
Emergency Management of Trauma
 Aims and Objectives Emergency Management of Trauma Susan Parekh/Paul Ashley Unit of Paediatric Dentistry Knowledge and understanding of the following: Epidemiology of traumatic injuries Classification
Aims and Objectives Emergency Management of Trauma Susan Parekh/Paul Ashley Unit of Paediatric Dentistry Knowledge and understanding of the following: Epidemiology of traumatic injuries Classification
with Pulp Capping: A Review of the Literature
 Operative Dentistry, 2009, 34-5, 615-625 Keys to Clinical Success with Pulp Capping: A Review of the Literature Invited Paper TJ Hilton Clinical Relevance Confusion and misconceptions surround direct and
Operative Dentistry, 2009, 34-5, 615-625 Keys to Clinical Success with Pulp Capping: A Review of the Literature Invited Paper TJ Hilton Clinical Relevance Confusion and misconceptions surround direct and
The healing touch of PRF-a case report
 Case Report: The healing touch of PRF-a case report Prof. (Dr.) Utpal Kumar Das¹, Prof. (Dr.) Aditya Mitra 2, Dr. Nabanita Bose 3 ¹HOD, Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics, Guru Nanak institute
Case Report: The healing touch of PRF-a case report Prof. (Dr.) Utpal Kumar Das¹, Prof. (Dr.) Aditya Mitra 2, Dr. Nabanita Bose 3 ¹HOD, Department of Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics, Guru Nanak institute
Enriched collagen solution as a pulp dressing in pulpotomized teeth in monkeys. Anna B. Fuks, CD S. Shoshan, PhD. Y. Michaeli, DMD. B.
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 19~4 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 6 Number 4 Enriched collagen solution as a pulp dressing in pulpotomized teeth in monkeys Anna B. Fuks, CD S. Shoshan,
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 19~4 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 6 Number 4 Enriched collagen solution as a pulp dressing in pulpotomized teeth in monkeys Anna B. Fuks, CD S. Shoshan,
Histological evaluation of electrosurgery and formocresol pulpotomy techniques in primary teeth in dogs
 Histological evaluation of electrosurgery and formocresol pulpotomy techniques in primary teeth in dogs Omar El-Meligy* / Medhat Abdalla** / Sahar El-Baraway*** / Magda El-Tekya**** / Jeffrey A Dean*****
Histological evaluation of electrosurgery and formocresol pulpotomy techniques in primary teeth in dogs Omar El-Meligy* / Medhat Abdalla** / Sahar El-Baraway*** / Magda El-Tekya**** / Jeffrey A Dean*****
East Java Propolis Inhibits cytokine Pro-inflammatory in Odontoblastlike cells Human Pulp
 East Java Propolis Inhibits cytokine Pro-inflammatory in Odontoblastlike cells Human Pulp Ira Widjiastuti Institute of Tropical Diseases Airlangga University Surabaya-Indonesia Introduction The maintainance
East Java Propolis Inhibits cytokine Pro-inflammatory in Odontoblastlike cells Human Pulp Ira Widjiastuti Institute of Tropical Diseases Airlangga University Surabaya-Indonesia Introduction The maintainance
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material
 Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
CONTENTS. Endodontic therapy Permanent open apex teeth Intracanal Medication. A. Introduction I. Problems II. III. IV. B. Research C.
 CONTENTS A. Introduction I. Problems II. III. IV. Endodontic therapy Permanent open apex teeth Intracanal Medication B. Research C. Conclusion INTRODUCTION A. Problems 1. In permanent teeth with open apex
CONTENTS A. Introduction I. Problems II. III. IV. Endodontic therapy Permanent open apex teeth Intracanal Medication B. Research C. Conclusion INTRODUCTION A. Problems 1. In permanent teeth with open apex
UNIVERSAL ADHESIVE SYSTEM. PEAK UNIVERSAL BOND Light-Cured Adhesive with Chlorhexidine
 UNIVERSAL ADHESIVE SYSTEM PEAK UNIVERSAL BOND Light-Cured Adhesive with Chlorhexidine 1 TOTAL-ETCH PEAK UNIVERSAL BOND SELF-ETCH UNIVERSAL BONDING The Peak Universal Adhesive System features a universal
UNIVERSAL ADHESIVE SYSTEM PEAK UNIVERSAL BOND Light-Cured Adhesive with Chlorhexidine 1 TOTAL-ETCH PEAK UNIVERSAL BOND SELF-ETCH UNIVERSAL BONDING The Peak Universal Adhesive System features a universal
how to technique How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. Disadvantages. 1 Issue Full coverage crown. >>
 Issue 37 2013 How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. 1 Full coverage crown. >> Advantages. A full crown can splint all sections of the tooth together. 1 Disadvantages. 1 Encircles crown and acts
Issue 37 2013 How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. 1 Full coverage crown. >> Advantages. A full crown can splint all sections of the tooth together. 1 Disadvantages. 1 Encircles crown and acts
Principle Investigators: Overview of Study Methods: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz
 Principle Investigators: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz Overview of Study Methods: Subjects in need of Class I and/or Class II restorations were enrolled in two clinical trials conducted in US dental
Principle Investigators: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz Overview of Study Methods: Subjects in need of Class I and/or Class II restorations were enrolled in two clinical trials conducted in US dental
Two Year Findings- Kalona Trial
 Medical Management of Caries Using Silver Nitrate and Fluoride Varnish Two Year Findings- Kalona Trial Michael Kanellis, DDS, MS & Arwa Owais, BDS, MS The University of Iowa College of Dentistry Background
Medical Management of Caries Using Silver Nitrate and Fluoride Varnish Two Year Findings- Kalona Trial Michael Kanellis, DDS, MS & Arwa Owais, BDS, MS The University of Iowa College of Dentistry Background
Inflammatory pulp conditions DR.AHMED IBRAHIM AL-JOBORY B.D.S. M.SC. CONSERVATIVE DEPARTMENT/ BAGHDAD UNIVERSITY
 Inflammatory pulp conditions DR.AHMED IBRAHIM AL-JOBORY B.D.S. M.SC. CONSERVATIVE DEPARTMENT/ BAGHDAD UNIVERSITY Inflammation is the single most important disease process affecting the dental pulp. Pulpitis
Inflammatory pulp conditions DR.AHMED IBRAHIM AL-JOBORY B.D.S. M.SC. CONSERVATIVE DEPARTMENT/ BAGHDAD UNIVERSITY Inflammation is the single most important disease process affecting the dental pulp. Pulpitis
An evaluation of pulpal therapy in primary incisors
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1988 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 10, Number 3 An evaluation of pulpal therapy in primary incisors James A. Coil, DMD, MS Stuart Josell, DMD, MS Steven
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1988 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 10, Number 3 An evaluation of pulpal therapy in primary incisors James A. Coil, DMD, MS Stuart Josell, DMD, MS Steven
RESTORATIVE MATERIALS
 Position Statement / Media Release RESTORATIVE MATERIALS Dental restorative materials are specially fabricated materials designed for use as dental restorations (fillings). Dental restorations are used
Position Statement / Media Release RESTORATIVE MATERIALS Dental restorative materials are specially fabricated materials designed for use as dental restorations (fillings). Dental restorations are used
Comparison of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Calcium Hydroxide as pulpotomy agents in Primary Molars
 Updat Dent. Coll.j 2013; 3(1):24-31 Original Article Comparison of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Calcium Hydroxide as pulpotomy agents in rimary Molars * Md. Farid Uddin a, Md. Shamsul Alam b, Ali Asgor
Updat Dent. Coll.j 2013; 3(1):24-31 Original Article Comparison of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Calcium Hydroxide as pulpotomy agents in rimary Molars * Md. Farid Uddin a, Md. Shamsul Alam b, Ali Asgor
International J. of Healthcare & Biomedical Research, Volume: 2, Issue: 1, October 2013, Pages 43-47
 Original article: Effect of cavity disinfection with chlorhexidine on microleakage of composite restorations using total etch and self etch single bottle adhesive systems: an in-vitro study 1Dr. Neha Agrawal
Original article: Effect of cavity disinfection with chlorhexidine on microleakage of composite restorations using total etch and self etch single bottle adhesive systems: an in-vitro study 1Dr. Neha Agrawal
BDA evidence summary. Dental liners and reducing post operative sensitivity
 BDA evidence summary Dental liners and reducing post operative sensitivity 2 The evidence summary is based on the original summary published in the BDJ (1) (June 2011). It evaluates the available evidence
BDA evidence summary Dental liners and reducing post operative sensitivity 2 The evidence summary is based on the original summary published in the BDJ (1) (June 2011). It evaluates the available evidence
General dentists in private practice place numerous
 PROACTIVE INTERVENTION DENTISTRY Incorporating Glass Ionomers into Everyday Dental Practice Todd Snyder, DDS, FAACD, FIADFE Introduction General dentists in private practice place numerous direct tooth
PROACTIVE INTERVENTION DENTISTRY Incorporating Glass Ionomers into Everyday Dental Practice Todd Snyder, DDS, FAACD, FIADFE Introduction General dentists in private practice place numerous direct tooth
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
Management of Permanent Tooth Dental Trauma in Children and Young Adolescents
 Management of Permanent Tooth Dental Trauma in Children and Young Adolescents Jessica Y. Lee DDS, MPH, PhD Chair and Distinguished Professor Department of Pediatric Dentistry University of North Carolina
Management of Permanent Tooth Dental Trauma in Children and Young Adolescents Jessica Y. Lee DDS, MPH, PhD Chair and Distinguished Professor Department of Pediatric Dentistry University of North Carolina
A comparative histological analysis of human pulp following direct pulp capping with Propolis, mineral trioxide aggregate and Dycal
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2010; 55: 59 64 doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2009.01179.x A comparative histological analysis of human pulp following direct pulp capping with Propolis, mineral
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2010; 55: 59 64 doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2009.01179.x A comparative histological analysis of human pulp following direct pulp capping with Propolis, mineral
FERRIC SULPHATE VERSUS FORMOCRESOL IN PULPOTOMIES OF PRIMARY MOLARS
 Original Article FERRIC SULPHATE VERSUS FORMOCRESOL IN PULPOTOMIES OF PRIMARY MOLARS INTRODUCTION Pulpotomy is a therapeutic procedure, used in reversible inflammation of pulp of primary teeth, when the
Original Article FERRIC SULPHATE VERSUS FORMOCRESOL IN PULPOTOMIES OF PRIMARY MOLARS INTRODUCTION Pulpotomy is a therapeutic procedure, used in reversible inflammation of pulp of primary teeth, when the
Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA in the Apical Sealing Ability of Lased And Unlased Root Canal Walls - A Pilot Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XIV (June 2016), PP 100-104 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XIV (June 2016), PP 100-104 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children
 Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objectives Discuss amalgam restorations Discuss resin restorations Describe the history and evolution of use of silicate cement Discuss the role
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objectives Discuss amalgam restorations Discuss resin restorations Describe the history and evolution of use of silicate cement Discuss the role
Get in front of the 8 ball with the new Fuji VIII GP. The first auto-cure, resin reinforced glass ionomer restorative
 Get in front of the 8 ball with the new Fuji VIII GP The first auto-cure, resin reinforced glass ionomer restorative 8 reasons to choose Fuji VIII GP Auto-cure, resin reinforced glass ionomer restorative
Get in front of the 8 ball with the new Fuji VIII GP The first auto-cure, resin reinforced glass ionomer restorative 8 reasons to choose Fuji VIII GP Auto-cure, resin reinforced glass ionomer restorative
JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL REGULATORS & HOMEOSTATIC AGENTS Vol. 30, no. 2 (S1), (2016)
 JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL REGULATORS & HOMEOSTATIC AGENTS Vol. 30, no. 2 (S1), 189-197 (2016) A HISTOLOGIC ASSESSMENT OF A HYBENX ORAL TISSUE DECONTAMINANT IN VITAL PULP THERAPY IN DOGS M. D. ROHRER 1, H.S.
JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL REGULATORS & HOMEOSTATIC AGENTS Vol. 30, no. 2 (S1), 189-197 (2016) A HISTOLOGIC ASSESSMENT OF A HYBENX ORAL TISSUE DECONTAMINANT IN VITAL PULP THERAPY IN DOGS M. D. ROHRER 1, H.S.
Contactless Dentistry. Cleans, Cuts, Prepares - Gently
 Contactless Dentistry Cleans, Cuts, Prepares - Gently Contactless Dentistry Unlike conventional rotary cutting instruments, the AquaCare handpiece is not in direct contact with the tooth structure, removing
Contactless Dentistry Cleans, Cuts, Prepares - Gently Contactless Dentistry Unlike conventional rotary cutting instruments, the AquaCare handpiece is not in direct contact with the tooth structure, removing
Evaluation of Dentin Root Canal Permeability After Instrumentation and Er:YAG Laser Application
 Lasers in Surgery and Medicine 26:277 281 (2000) Evaluation of Dentin Root Canal Permeability After Instrumentation and Er:YAG Laser Application Jesus D. Pecora, DDS, PhD, 1 * Aldo Brugnera-Júnior, DDS,
Lasers in Surgery and Medicine 26:277 281 (2000) Evaluation of Dentin Root Canal Permeability After Instrumentation and Er:YAG Laser Application Jesus D. Pecora, DDS, PhD, 1 * Aldo Brugnera-Júnior, DDS,
PRO-V IDS Kit. Bisco. Instructions for Use. Provisional Restorative System
 Bisco PRO-V IDS Kit Provisional Restorative System Instructions for Use U.S. Patent: 7,748,980; 8,106,110 IN-199R3 Rev. 5/16 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Rd. Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 847-534-6000
Bisco PRO-V IDS Kit Provisional Restorative System Instructions for Use U.S. Patent: 7,748,980; 8,106,110 IN-199R3 Rev. 5/16 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Rd. Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 847-534-6000
VITAL PULP THERAPY USING PLATELET-RICH FIBRIN IN AN IMMATURE PERMANENT TOOTH : CASE REPORTS
 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent 40(2) 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.2.120 VITAL PULP THERAPY USING PLATELET-RICH FIBRIN IN AN IMMATURE PERMANENT TOOTH : CASE REPORTS Ka-Young
ISSN (print) 1226-8496 J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent 40(2) 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.2.120 VITAL PULP THERAPY USING PLATELET-RICH FIBRIN IN AN IMMATURE PERMANENT TOOTH : CASE REPORTS Ka-Young
Adhese Universal. The universal adhesive. Direct Indirect Total-Etch Selective-Etch Self-Etch Wet & Dry. All in. one click
 Adhese Universal The universal adhesive Direct Indirect Total-Etch Selective-Etch Self-Etch Wet & Dry All in one click 1 Universal Adhesion with advanced delivery Adhese Universal is a singlecomponent,
Adhese Universal The universal adhesive Direct Indirect Total-Etch Selective-Etch Self-Etch Wet & Dry All in one click 1 Universal Adhesion with advanced delivery Adhese Universal is a singlecomponent,
Clinical Technique/Case Report
 Operative Dentistry, 2008, 33-3, 345-349 Clinical Technique/Case Report Modified Matrix Band Design for Ultra-conservative Posterior Restorations S Deliperi Clinical Relevance The combination of minimally
Operative Dentistry, 2008, 33-3, 345-349 Clinical Technique/Case Report Modified Matrix Band Design for Ultra-conservative Posterior Restorations S Deliperi Clinical Relevance The combination of minimally
Electronic Dental Records
 Electronic Dental Records Dr. Douglas K Benn, Professor of Maxillofacial Radiology & Director of Oral Diagnostic Systems, University of Florida and Health Conundrums LLC 8/2/2008 Dr Benn, University of
Electronic Dental Records Dr. Douglas K Benn, Professor of Maxillofacial Radiology & Director of Oral Diagnostic Systems, University of Florida and Health Conundrums LLC 8/2/2008 Dr Benn, University of
Fuji BULK. Robust. Rapid. Remarkable.
 Fuji BULK Robust. Rapid. Remarkable. Fuji BULK a truly remarkable GIC Fuji BULK is a robust, rapid-setting, multipurpose auto-cure glass ionomer cement (GIC) designed to meet the challenge of bulk placed
Fuji BULK Robust. Rapid. Remarkable. Fuji BULK a truly remarkable GIC Fuji BULK is a robust, rapid-setting, multipurpose auto-cure glass ionomer cement (GIC) designed to meet the challenge of bulk placed
Trauma to the Central Incisor: The Story So Far
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Review Article Trauma to the Central Incisor: The Story So Far Dania Siddik* Consultant Paediatric Dentist, Guy s & St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK *Corresponding
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Review Article Trauma to the Central Incisor: The Story So Far Dania Siddik* Consultant Paediatric Dentist, Guy s & St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK *Corresponding
Healing and Sealing Dental Caries: The Paradigm Has Shifted
 Healing and Sealing Dental Caries: The Paradigm Has Shifted Edmond R. Hewlett, D.D.S. This Afternoon s Topics Caries Management by Risk Assessment (CAMBRA) Remineralization with CPP/ACP Restoring carious
Healing and Sealing Dental Caries: The Paradigm Has Shifted Edmond R. Hewlett, D.D.S. This Afternoon s Topics Caries Management by Risk Assessment (CAMBRA) Remineralization with CPP/ACP Restoring carious
Fuji BULK. Rapid, Robust, Remarkable.
 Rapid, Robust, Remarkable. New it s truly remarkable is a robust, rapid-setting, multipurpose auto-cure glass ionomer cement (GIC) designed to meet the challenge of bulk placed restorations in more acidic
Rapid, Robust, Remarkable. New it s truly remarkable is a robust, rapid-setting, multipurpose auto-cure glass ionomer cement (GIC) designed to meet the challenge of bulk placed restorations in more acidic
10-year Clinical Evaluation. of a self-etching adhesive system,
 Operative Dentistry, 2007, 32-1, 3-10 10-year Clinical Evaluation of a Self-etching Adhesive System Clinical Research N Akimoto M Takamizu Y Momoi Clinical Relevance This 10-year clinical evaluation of
Operative Dentistry, 2007, 32-1, 3-10 10-year Clinical Evaluation of a Self-etching Adhesive System Clinical Research N Akimoto M Takamizu Y Momoi Clinical Relevance This 10-year clinical evaluation of
Pulp Vitality. in Pediatric Patients. Treating deep carious lesions in vital permanent teeth. 86 MAY 2017 // dentaltown.com. by Jarod Johnson, DDS
 Pulp Vitality in Pediatric Patients Treating deep carious lesions in vital permanent teeth by Jarod Johnson, DDS Jarod Johnson, DDS, earned a bachelor s degree in biomedical engineering from the University
Pulp Vitality in Pediatric Patients Treating deep carious lesions in vital permanent teeth by Jarod Johnson, DDS Jarod Johnson, DDS, earned a bachelor s degree in biomedical engineering from the University
BioCoat Featuring SmartCap Technology
 R R Breakthrough! BioCoat Featuring SmartCap Technology The only bioactive pit and fissure sealant that provides relentless protection through daily release of fluoride, calcium and phosphate ions. Bioactive
R R Breakthrough! BioCoat Featuring SmartCap Technology The only bioactive pit and fissure sealant that provides relentless protection through daily release of fluoride, calcium and phosphate ions. Bioactive
DPI Luting Cement. DPI Restorative Cement
 DPI Luting Cement DPI Luting Cement is Type I glass ionomer white luting cement. DPI glass ionomers are remarkably biocompatible and can be safely used in deep cavities provided the pulp is not exposed,
DPI Luting Cement DPI Luting Cement is Type I glass ionomer white luting cement. DPI glass ionomers are remarkably biocompatible and can be safely used in deep cavities provided the pulp is not exposed,
Dental material for filling the root canals "AUREOSEAL M.T.A."
 Dental material for filling the root canals "AUREOSEAL M.T.A." Highly biocompatible root canal cement without eugenol. 1. Composition: Powder: Mineral-trioxide-agregat (М.Т.А.) based on Portland cement,
Dental material for filling the root canals "AUREOSEAL M.T.A." Highly biocompatible root canal cement without eugenol. 1. Composition: Powder: Mineral-trioxide-agregat (М.Т.А.) based on Portland cement,
The Endodontics Introduction. By: Thulficar Al-Khafaji BDS, MSC, PhD
 The Endodontics Introduction By: Thulficar Al-Khafaji BDS, MSC, PhD Introduction Definition Endodontology form function health of the dental pulp and the periradicular tissues that surround the root(s)
The Endodontics Introduction By: Thulficar Al-Khafaji BDS, MSC, PhD Introduction Definition Endodontology form function health of the dental pulp and the periradicular tissues that surround the root(s)
A Step-by-Step Approach to
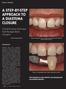 A Step-by-Step Approach to a Diastema Closure A Dual-Purpose Technique that Manages Black Triangles Marcos Vargas, DDS, MS Figure 1: Preoperative view of a patient who presented with a diastema between
A Step-by-Step Approach to a Diastema Closure A Dual-Purpose Technique that Manages Black Triangles Marcos Vargas, DDS, MS Figure 1: Preoperative view of a patient who presented with a diastema between
Glass Ionomers. Reputable, Durable, Long Lasting
 Glass Ionomers Reputable, Durable, Long Lasting Conventional Glass Ionomer Restoratives Glass Ionomeres Technology more up-to-date than ever before! Successfull well proven material Exhibit biocompatibility
Glass Ionomers Reputable, Durable, Long Lasting Conventional Glass Ionomer Restoratives Glass Ionomeres Technology more up-to-date than ever before! Successfull well proven material Exhibit biocompatibility
allinone... unbelievable? But true! Picture: Dr. Thano Kristallis
 allinone... unbelievable? But true! Picture: Dr. Thano Kristallis A well-made provisional is the basis of a successful restorative treatment 2 It is desirable that a provisional system is strong and durable,
allinone... unbelievable? But true! Picture: Dr. Thano Kristallis A well-made provisional is the basis of a successful restorative treatment 2 It is desirable that a provisional system is strong and durable,
How might Operative Dentistry be a Threat to the Pulp?
 How might Operative Dentistry be a Threat to the Pulp? Reshma Seeburrun, 4th year Dentistry 50 INTRODUCTION Operative dentistry is the art and science of diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of defects of
How might Operative Dentistry be a Threat to the Pulp? Reshma Seeburrun, 4th year Dentistry 50 INTRODUCTION Operative dentistry is the art and science of diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of defects of
Case Report Pulp Revascularization in Immature Permanent Tooth with Apical Periodontitis Using Mineral Trioxide Aggregate
 Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 564908, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/564908 Case Report Pulp Revascularization in Immature Permanent Tooth with Apical Periodontitis Using Mineral Trioxide
Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 564908, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/564908 Case Report Pulp Revascularization in Immature Permanent Tooth with Apical Periodontitis Using Mineral Trioxide
restorations. Al-Omari, Qasem D; Al-Omari, Wael M; Omar, Ridwaan Journal of the Irish Dental Association
 Factors associated with postoperative sensitivity of amalgam restorations. Item type Authors Citation Publisher Journal Rights Article Al-Omari, Qasem D; Al-Omari, Wael M; Omar, Ridwaan Factors associated
Factors associated with postoperative sensitivity of amalgam restorations. Item type Authors Citation Publisher Journal Rights Article Al-Omari, Qasem D; Al-Omari, Wael M; Omar, Ridwaan Factors associated
Posterior Adhesive Dentistry
 Posterior Adhesive Dentistry Stephen D. Poss DDS Michigan Dental The following pages contain a summary of information designed to assist you with the armamentarium, preparation, and cementation of anterior
Posterior Adhesive Dentistry Stephen D. Poss DDS Michigan Dental The following pages contain a summary of information designed to assist you with the armamentarium, preparation, and cementation of anterior
CLINICAL EVALUATION OF CHEMO-MECHANICAL CARIES REMOVAL USING CARIE-CARE SYSTEM AMONG SCHOOL CHILDREN
 Original Article NUJHS Vol. 4, No.3, September 2014, ISSN 2249-7110 CLINICAL EVALUATION OF CHEMO-MECHANICAL CARIES REMOVAL USING CARIE-CARE SYSTEM AMONG SCHOOL CHILDREN 1 2 3 4 Amitha M. Hegde, Preethi
Original Article NUJHS Vol. 4, No.3, September 2014, ISSN 2249-7110 CLINICAL EVALUATION OF CHEMO-MECHANICAL CARIES REMOVAL USING CARIE-CARE SYSTEM AMONG SCHOOL CHILDREN 1 2 3 4 Amitha M. Hegde, Preethi
