Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 1:10 January, Ahmad Fahmy 1, Ehab M. Abuelroos 2 and Mohammad M. Nada 3
|
|
|
- Loraine Greer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
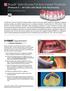
1 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 1:10 January, 2008 Effect of Using Attachment on Implant Supported Distal Extension Lower Partial Over-dentures Ahmad Fahmy 1, Ehab M. Abuelroos 2 and Mohammad M. Nada 3 1. Assistant Lecturer, Prosthodntic Department, Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine, Cairo University 2. Lecturer, Prosthodntic Department, Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine, Cairo University. 3. Professor, Prosthodntic Department, Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine, Cairo University. Abstract This study was performed to evaluate the effect of using attachment on implant supported distal extension lower partial overdenture. Ten lower kennedy class II partially edentulous patients were selected to receive implant at second molar area, then patients were divided into 2 groups according to the implant superstructures either (dome shaped-or-ball and cap attachment). Patients of both groups receive removable partial denture of the same design. Patients were followed up for one year both clinically and radiogarphically. The results showed no statically difference between the treatment plans. It could be concluded that Tooth-implant supported partial denture with or without attachment may be reasonable and simple solution for Kennedy class II partial denture. Ball and socket attachment could be considered as more favorable solution than the dome shaped one regarding prosthetics function and patients satisfaction. INTRODUCTION The unilateral distal extension base removable partial denture has always been associated with a number of problems, specifically concerning support, retention and stability. Most of these problems could be attributed to the absence of the posterior abutment (Wilson et al., 1987). Since, the difference in displacement between the mucosa and the periodontal ligament of last standing abutment was estimated to be up to 25 times (Wills and Manderson, 1977; Picton and Wills, 1978; Monteith, 1984). Consequently, when functional pressure is applied to the distal extension base removable partial denture, the resultant forces are extremely damaging to the abutment teeth and must be controlled if clinical treatment is to be successful (Phoenix et al., 2003). Aydinlik et al., 1983, pointed out that those patients with distal extension ridges may be treated by, a removable partial denture, a cantilever type of fixed partial denture, an implant denture. The authors clarified that the most conventional treatment is by a removable partial denture however, due to the lack of a distal abutment tooth, the denture may move to an undesirable extent during function. Rasmussen, 1987 clarified that osseointegrated implant-borne removable prostheses has been tried with reasonable success in partially edentulous cases with severely resorped ridges and patients with periodontally compromised remaining teeth. The incorporation of implants may enhance its longevity as they provide
2 (2) Ahmed Fahmy, et al. C.D.J. Vol. 24. No. (I) adjunct to the existing dentition by distributing forces and loads to the implant and reducing the stresses placed on the remaining teeth through the prostheses. In the same way, Keltjens et al., (1993) found that placement of osseointegrated implants beneath distal extension denture base of the cast framework could result in stable and durable occlusion and improved functional comfort. Starr, (2001) Clarified that using a posterior implant in cases of free end saddle cases to provide retention through using ball attachment; this treatment option offers greater function, esthetics, comfort and minimal maintenance up to 7 years. Moreover, Masahiro et al., (2003) suggested that the use of the ball / 0-ring attachment could be advantageous for implant supported overdentures with regard to optimizing stress and minimizing partial denture movement. Gerlad et al. (2006) mentioned that both ball attachments and resilient telescopic crowns used on isolated implants in the edentulous mandible are viable treatment options. Implant success and peri-implant condition did not differ between ball attachments and telescopic crowns used as retention modalities for implant overdentures, but the frequency of technical complications was significantly higher with ball attachments than with resilient telescopic crowns. Materials and methods Twenty partially edentulous patients indicated for implant installation were selected from Out patient clinic, Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine, Cairo University. All patients had Kennedy class II lower partially edentulous ridges with canine or first premolar being the last standing tooth on the distal extension sides. Opposing occlusion in upper jaws was dentulous or partially edentulous where it was restored with fixed prosthesis. Selected patients were divided into two equal groups according to method of treatment plane, as follows, Group (1) Each patient in Group (1) received partial overdenture supported in free end side by an implant at second molar area with dome shaped superstructure. While; Group (2) Each patient in Group (2) received partial overdenture supported in free end side by an implant at second molar area with ball and cap attachment as a super structure. Upper and lower diagnostic cast for each patient was mounted on a semi-adjustable articulator by the aid of centric occluding relation record. Occlusion was evaluated and corrected in the patient s mouth. Surgical Procedures For Implant Installation: Trial setting up of artificial teeth in edentulous areas of mounted upper and lower casts was carried out. Acrylic surgical template was fabricated on edentulous area of lower cast. Internally hexed screwed shaped (4mm diameter- 10.5mm) titanium implants were used. Standard surgical procedures were followed for implant installation at second molar area parallel to long axis of the anterior abutment. Four months after fixture installation, the patients were recalled, and a periapical radiographs were made to confirm the absence of any radiolucency around the implant and ensure osseointegration both radiographically and clincally. A healing collar of suitable length was selected according to the thickness of the mucosa covering the implant to be projected 2mm above the mucosal surface. In group (1), dome shaped healing collar was used as a super structures. While In group (2), ball attachment was used as super structures Fig.(1,2). Fig. (1)
3 Effect of Using Attachment on Implant (3) Fig. (2) Removable Partial Denture Framework Construction: Alginate impressions in stock tray were made for all patients in both groups and poured into stone cast. Primary surveying was done to detect amount of undercut and guiding planes. Custom made perforated acrylic resin tray was constructed. Mouth preparation was done for guiding plane and occlusal rests seats site according to data gained from primary surveying. Final impression was made and poured into type 4 improved dental stone to obtain master cast. Secondary surveying was done for master casts before duplication. Partial denture design: The design for all finished partial denture was the same. The only difference was in type of distal support and retention. In group (1): The prostheses were supported only by (dome shaped) healing collar superstructure over distal placing implant. Prosthesis consider as partial overdenture where implant provide support only in distal extension area. In group (2): Partial overdenture was supported and retained in distal free end site by using ball and cab attachment as implant superstructure. The design of finished partial denture for all patients was the same. a) Occlusal rests: Occlusal rests seats were prepared in the last standing natural teeth either in form of distal occlusal rest in lower first premolar or cingulum rest in lower canine. b) Direct retainer: Aker clasp was used In case of lower first or second premolar. In case of lower canine, wrought wire clasp was used. c) Major connection: Lingual bar major connector was used. d) Denture base: A hole was made around implant site in the metal frame work. Metal frame work was tried in inside patient mouth. Wax rim was made on the metal framework, centric occluding relation was registered. Setting up of artificial teeth was carried out using low cusp angles cross linked acrylic resin teeth. Waxed partial dentures were then tried inside patient s mouth, and then processed using heat cured acrylic resin, finished and polished Fig.(3). At time of delivery the adjustment of denture to accommodate super structure of implant by creating a hole in fitting surface of denture at area of super structures. Refitting of partial denture was made by self cure Acrylic resin. Direct pick-up for cap attachment from patient mouth was done. Patients were asked to return back 24 hours after denture insertion for soft tissue inspection and doing necessary adjustment. Fig. (3) Methods of evaluation: After denture insertion the following investigations were carried out for each patient to evaluate the supporting structures of the prosthesis both biologically and radiographically. I] Biological evaluation: Follows up records (the records presented the mean of the data for each abutment) were made at time of denture delivery, six, and twelve
4 (4) Ahmed Fahmy, et al. C.D.J. Vol. 24. No. (I) months after denture delivery. 1. Loss of attachment level: The mean value of loss of attachment was anterior measured at anter abutments and fixture abutments using the sensor probe (pressure sensitive probe). The distance from the tip of the probe to a marked sign on the natural abutment and to the top of the posterior abutment was measured. II] Radiographic evaluation: Direct digital radiography using Digora system to measure the following: 1- Changes in the marginal bone height distally in the anterior abutments, distally and mesially in the posterior fixture abutments. 2- Changes in the bone density of the fixture and natural abutments in both groups. For the bone changes, the mean values of the mesial or distal surfaces of all abutments along the whole study period were calculated. The Digora imaging plate, the Rinn (XCP) periapical film holders, individually constructed radiographic acrylic templates and long cone parallel technique were used for making standardized digital images for the anterior and posterior abutments by applying the long cone paralleling technique. perpendicular to a tangent drawn to the root apex. The second and third lines were equal and parallel to the first line and were 1-mm apart. Bone density along the three lines was recorded and the mean value of the readings was calculated Fig. (4). Statistical Analysis: Statistical analysis was carried out using SAS program (SAS, 1988). Student t test (Procedure TTEST of SAS) was run to test the effect of immediate and delayed treatment on means, and changes of different measurements within each time interval. Paired t test (Procedure Means of SAS) was used to test the significance of different measurements between each two intervals as well as during the whole follow-up period within each treatment (immediate and delayed). Simple correlation coefficient (Procedure Corr of SAS) was calculated between bone height and bone density within each interval as well as between changes in bone height and bone density within each interval (SAS, 1988). i. Marginal bone height measurements (Linear analysis): The linear measurement system supplied by the special soft-ware of the Digora was used to assess mesial and distal marginal bone height around the abutment teeth and implants at the time of denture insertion and at the end of different follow up periods. The distance from alveolar crest to junction between implant and abutment or to cementoenamel junction for natural abutment was measured. 2. Densitometric analysis for the anterior natural abutment: Three lines were drawn distal to the anterior abutment. The first line extended from the crest of the alveolar ridge to the apex of the tooth passing just distal to the lamina dura parallel to the root surface and RESULTS Fig. (4) The patients who participated in this study attended all follow up periods. Regarding patient s satisfaction, patients having ball and socket abutments in group (A) were more satisfied about retention than those in group (B) having dome shape abutments.
5 Effect of Using Attachment on Implant (5) Radiographic Evaluation: 1) Bone height (mm) at natural abutment The mean values of bone height changes in group (A) were 2.14 before denture wear and 2.18 and 2.22 six and twelve months respectively after denture wear. There was a statistically no significant increase in mean bone height after six months (P= 0.138) and after twelve months (P= 0.086) (Table 1). While in group (B) it was 2.36before denture wear and 2.8 and 2.83 six and twelve months respectively after denture wear. There was a statistically non significant increase in mean bone height after six months (P= 0.092) and after twelve months (P= 0.063) (Table 1). The percentage changes in mean bone height around the teeth showed a statistically no significant difference between the two groups after 6 months (P= 0.238) and after 12 months (P= 0.358) 2) Bone height (mm) at implant abutment The mean value of bone height changes in group (A) was 1.96 before denture wear and 2.2 and 2 six and twelve months respectively after denture wear. There was a statistically significant increase in mean bone height after six months (P= 0.028). After twelve months, there was a statistically none significant increase (P= 0.762) (Table 3). While in group (B) it was 2.15 before denture wear and 2.36 and 2.26 six and twelve month respectively after denture wear. There was a statistically non significant increase in mean bone height after six months (P= 0.206) and after twelve months (P= 0.276) (Table 2). The percentage changes in mean bone height around the implants showed a statistically non significant difference between the two groups after 6 months (P= 0.726) and after 12 months (P= 0.546) Table (1): Mean differences and comparison of the bone height along different time intervals in group A and B Tooth Group (A) P-value Group (B) P-value Table (2): Mean, difference and comparison of the bone height along different time intervals in group A and B Implant Group (A) P-value 0.028* Group (B) P-value *: Significant at P 0.05
6 (6) Ahmed Fahmy, et al. C.D.J. Vol. 24. No. (I) B) Bone Density Result: 1) Bone density at natural abutment The mean values of bone density changes in group (A) were before denture wear and and six and twelve months respectively after denture wear. There was a statistically non significant increase in mean bone density after six months (P= 0.898) as well as after twelve months (P= 0.612) (Table 5). While in group (B) it was before denture wear and and 118 six and twelve months respectively after denture wear. Again there was a statistically non significant increase in mean bone density after six months (P= 0.354) and after twelve months (P= 0.351) (Table 3). The percentage changes in mean bone density around the tooth showed a statistically non significant difference between the two groups after 6 months (P= 0.617) and after 12 months (P= 0.511) 2) Bone density at implant abutment:- The mean value of bone density change in group (A) was before denture wear and and six and twelve months respectively after denture wear. There was a statistically significant increase in mean bone density after six months (P=0.029) and after twelve months (P= 0.029) (Table 4). While in group (B) it was before denture wear and and six and twelve months respectively after denture wear. There was a statistically significant increase in mean bone density after six months (P= 0.042) and after twelve months (P= 0.037) (Table 4). The percentage changes in mean bone density around the implants showed non statistically significant difference between the two groups after 6 months (P= 0.836) and after 12 months (P= 0.248) Table (3) Changes in the bone density along different time intervals in group A and B Tooth Group (A) P-value Group (B) P-value Table (4): Mean, differences and comparison of the bone density along the different time intervals in group A and B Implant Group (A) P-value 0.029* 0.029* Group (B) P-value 0.042* 0.037*
7 Effect of Using Attachment on Implant (7) Attachment level (mm): 1) Attachment level values at natural abutments The mean values of attachment level in group (A) were 4.8 before denture wear and 5.1 and 5.4 six and twelve months respectively after denture wear. There was a statistically no significant increase in mean attachment level after six months (P= 0.064) and after twelve months (P= 0.055) (Table 5). While in group (B) it was 5.3 before denture wear and 5.5 and 5.8 six and twelve month respectively after denture wear. Again there was a statistically none significant increase in mean attachment level after six months (P= 0.167) and after twelve months (P= 0.085) (Table 5). The percentage changes in mean attachment level around the teeth showed a statistically none significant difference between the two groups after 6 months (P= 0.086) and after 12 months (P= 0.087) 2) Attachment level at implant abutment: The mean values of attachment level in group (A) were 7.1 before denture wear and 7.5 and 7.8 six and twelve months respectively after denture wear. There was a statistically none significant increase in mean attachment level after six months (P= 0.058) and after twelve months (P= 0.108) (Table 6). While in group (B) it was 7.3 before denture wear and 7.5 and 7.8 six and twelve month respectively after denture wear. The same result were again revealed as a statistically none significant increase in mean attachment level after six months (P= 0.062) and after twelve months (P= 0.051) (Table 6). The percentage changes in mean attachment level around the implants showed a statistically non significant difference between the two groups after 6 months (P= 0.178) and after 12 months (P= 0.460). Table (5) Changes in attachment level along the different time intervals in group A and B Tooth Group (A) Mean difference P-value Group (B) Mean difference P-value Table (6) Changes in the attachment level along the different time intervals in group A and B Implant Group (A) Mean difference P-value Group (B) Mean difference P-value
8 (8) Ahmed Fahmy, et al. C.D.J. Vol. 24. No. (I) DISCUSSION Most problems of the free end saddle cases can be solved by improving its support and /or retention and stability through the use of implant in the distal extension area. In this study implants were used to provide support and /or retention in partial implant overdenture so all factors that could affect ossointegration either systemically or locally were considered. Moreover, all factors that control the value of forces transmitted were considered as follow, length of the span of selected patients, abnormal or small ridges were excluded, moreover, the opposing arch in all selected cases was either dentulous or partially edentulous restored with fixed prostheses to standardize the effect of opposing occlusion and their effect on the force transmission (van Gouten et al., 1986, Desjardins, 1996 and Misch 1999). Simplified and hygienic designs was considered in this study, where every component of the partial denture should have definite function, Aker clasp design was used in case of first or second premolar and in case of canine wrought wire clasp was used, as the nature of support in free end saddle area changing from tooth-tissue support to tooth implant support. The long cone paralleling technique with Individual acrylic resin template of periapical radiograph was used to measure alveolar bone height as it is considered a standard technique for measuring, Cox & Zerb; (1986), Smith & Zarb; (1989). Generally speaking Kennedy class II has a main problem of support and retention which is pushing the patients usually for comparison between the two sides, the natural and artificial one. From the patient s point of view, all were satisfied with their partial dentures especially those with ball and cap attachment. This is due to that both the attachment and dome shaped-super structure provided posterior support, preventing tissuewards movement of the free end base, moreover, the attachment added another advantages for the patients who were satisfied as it not only helped in support but also added the retention for the partial denture. Both abutments either natural teeth or implant fixtures showed both biologic and radiographic changes in the two studied groups through out one year follow up period. These changes were accepted as it could be considered as a biologic response to the insertion of the partial denture in the patients mouth regarding micro-flora and the stresses transmitted to the investing structures (El-Ghamrawy 1977; Nada et al., 1987). Theoretically speaking, increase in alveolar bone height & density means that, the bone reacts favorably to the applied force. When the natural tooth was assisted by the implant to support an overdenture, the stress waves reached the tooth through the implant and bone, as well as, directly from the overdenture, hence the natural tooth was the primary recipient of the stress so bone resorption would occur, where periodontal ligament of the natural teeth absorbs most of the stresses relieving the implants from being subjected to overloading. This explained why in the current study bone resorption seemed to be more than bone formation regarding natural abutments and resulted in decrease bone height. The fact that, this decrease in bone height was non-significant might be attributed to optimum hygienic and simple design in removable partial denture used, allowing control and dissipating forces applied on natural teeth, less plaque accumulation and more facility for proper oral hygiene and hence less gingival inflammation. These results were previously reported by Abuelross (2003). Bone resorption recorded at the distal sides of natural abutments in both groups might be attributed to lateral forces that could produce distributing stresses unevenly over the entire root surface to the alveolar bone leading to pressure or tension. Pressure occurred more on distally relative to the length of the edentulous area, while tension occurred mesially. The increase in bone height relative to the implant abutment recorded in this work agrees with the findings reported by many investigators Taylor et al Such increase in the physiologic loading of the implant side enhances bone formation and bone density. This explains why the bone height was generally increased in implant abutments compared with the natural abutments in both groups in this present study. Patients with ball and cap attachments
9 Effect of Using Attachment on Implant (9) (Group A) had nylon sheath in cap attachment and those with dome shaped superstructure of implants with no lateral walls or sharp angels (Group B) which allowed dissipating all lateral forces only vertical forces were transmitted to the long access of tooth. Moreover, the use of non-rigid method of attachment to connect the implants and the teeth may help to relieve the stresses induced in the implants Elkerdawy (2005). Regarding the changes occurring in bone density around different abutments, it was found non-significant increase in bone density for both implants and anterior abutment in both groups was formed (Group A & B). This could be attributed to proper treatment plane regarding toothimplant support, simple and efficient design of partial denture as well as proper selection of implant super structure. Statistically, both groups showed no significant difference regarding the manner of the marginal bone height changes for both types of abutments in both sides and at different time periods. This denotes that the ball attachments and the copings transmitted force within the physiologic tolerance of the anchoring bone within a one year follow-up period. SUMMARY and CONCLUSION This study was performed to evaluate the effect of using attachment on implant supported distal extension lower partial overdenture. Ten lower kennedy class II partially edentulous patients were selected to receive implant at second molar area, then patients were divided into 2 groups according to the implant superstructures either(dome shaped-or-ball and cap attachment). Patients of both groups receive removable partial denture of the same design. Patients were followed up for one year both clinically & radiogarphically. The results showed statically difference between the treatment plans. It could be concluded that Tooth-implant supported partial denture with or without attachment may be reasonable and simple solution for Kennedy class II partial denture. Ball and socket attachment could be considered as more favorable solution than the dome shaped one regarding prosthetics function and patients satisfaction. References 1. AbuElroos, E.: Proposed solution for Kennedy class I partially edentulous cases using osseointegrated implant. Doctor thesis in prosthodontics, Cairo University, Aydinlik E., Dayangac B., and Celik E.: Effect of splinting on abutment tooth movement. J. Prosthet. Dent., 49 : 477, Cox, J.F. and Zerb, G.A.: The longitudinal clinical efficiency of osseointegrated dental implants. A 3-year report. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Imp Desjardins R.P.: Implants for the edentulous patient, Dent. Clin. Nor Amer., 40 : 195, El-Ghamrawy, E.: Ecologic oral changes caused by removable partial dentures. Egypt. Dent. J., 23: 23, Elkerdawy, M: Immediate versus delayed loading of overdenture implant abutments. Thesiss, Cairo university Gerald Krennmair, M.D., D.M.D, Ph D, Michael Weinlander, M.D., DMD, Martin Krainhofner, MD, DMD, Evapeihslinger, MD, DMD, PhD; Implant supported mandibular overdentures retained with ball or telescopic crown attachment, Int J prosthodont; 19 : Keltjens, H., Kayser, A., Hertel, R., Battistuzi, P.: Distalextension removable partial dentures supported by implants and residual teeth: considerations and case reports. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. 8: 208, Masahiro TO., Yasuyuki Mat and Kiyoshis Koy: In vitro study of mandibular implant overdenture retained with ball, magnet, or bar attachment: comparasion of load transfer and denture stability. Int J Prosthodont, 16 : , Misch, C.E.: Contemporary implant dentistry. 2 nd ed. Mosby co., St. Louis, Chicago, London, Toronto, Monteith B.D.: Management of loading forces on mandibular distal-extension prostheses. Part I: Evaluation of concepts for design. J. Prosthet. Dent. 52: 673, Nada, M., Gharraphy, S. and Badawy, H.S.: A two year longitudinal study on the effect of removable partial denture design on the health of remaining teeth. Egypt. Dent. J. 33: 85, 1987
10 (10) Ahmed Fahmy, et al. C.D.J. Vol. 24. No. (I) 12. Picton, D.C.A., and Wills, D.J.: Viscoelastic properties of the periodontal ligament and mucous membrane. J. Prosthet. Dent., 40: 263, Rasmussen, E.: Alternative prosthodontic technique for tissueintegrated prosthesis. J. Prosthet. Dent., 57: 198, Smith, D.E. and Zarb, G.A.: Criteria for success of osseointegrates endosseous implants. J. Prosthet. Dent., 62: 567, Starr N.L.: The distal extension case: an alternative restorative design for implant prosthetics. Int J periodontics restorative Dent. Feb; 21 (1): 61-7, Taylor T.D, Pflughoeft F.A, McGivney G.P.: Effect of two clasping assemblies on arch integrity as modified by base adaptation, J. Prosthet. Dent. 47: 120, Von Gonten, A.S. PaJik, J.F., Oberlander, B.A. and Rugh, J.: Nocturnal electromyographic evaluation of the masseter muscle activity in the complete edentulous patients. J. Prosthet. Dent., 56: 624, Wills, D.J and Mandersone.: Biomechanical aspects of the support of partial dentuers. J. Dent., 5: 310, Wilson HJ, Mansfield MA, Heath JR, Spence D. Dental technology and materials for students. 8 th edition, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford; 1987
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report
 Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report 1 2 1 1 Mittal R, Saxena D, Rao S, Kumar M Abstract: Statement of Problem: Complete denture rehabilitation
Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report 1 2 1 1 Mittal R, Saxena D, Rao S, Kumar M Abstract: Statement of Problem: Complete denture rehabilitation
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama
 Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This
 1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
INDIAN DENTAL JOURNAL
 ATTACHMENT RETAINED CAST PARTIAL DENTURE USING RHEIN 83 OT-CAP Dr. Charu Gupta 1 Dr. Harshul Sharma 2 Dr. Merrily Nongsiej 3 Dr. AbhinavShekhar 4 1 Senior Resident, Department of Prosthodontics, King George
ATTACHMENT RETAINED CAST PARTIAL DENTURE USING RHEIN 83 OT-CAP Dr. Charu Gupta 1 Dr. Harshul Sharma 2 Dr. Merrily Nongsiej 3 Dr. AbhinavShekhar 4 1 Senior Resident, Department of Prosthodontics, King George
Telescopic Retainers: An Old or New Solution? A Second Chance to Have Normal Dental Function
 Telescopic Retainers: An Old or New Solution? A Second Chance to Have Normal Dental Function Joseph B. Breitman, DMD, FACP, 1,2 Scott Nakamura, DMD, 3 Arnold L. Freedman, DDS, 4 & Irving L. Yalisove, DDS
Telescopic Retainers: An Old or New Solution? A Second Chance to Have Normal Dental Function Joseph B. Breitman, DMD, FACP, 1,2 Scott Nakamura, DMD, 3 Arnold L. Freedman, DDS, 4 & Irving L. Yalisove, DDS
Removable Partial Dentures
 Removable Partial Dentures Replacement of missing teeth Fixed partial denture Removable partial denture Complete removable Transitional denture Partial removable Implant retained prosthodontics No prosthetic
Removable Partial Dentures Replacement of missing teeth Fixed partial denture Removable partial denture Complete removable Transitional denture Partial removable Implant retained prosthodontics No prosthetic
Removable partial dentures
 Removable partial dentures Feb, 4, 2015 McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics, Twelfth Edition Carr, Alan B 1 Prosthesis that replaces the missing teeth and associated supporting structures in a
Removable partial dentures Feb, 4, 2015 McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics, Twelfth Edition Carr, Alan B 1 Prosthesis that replaces the missing teeth and associated supporting structures in a
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
Treatment Options for Restoring Edentulous Jaws using One- and Two-Piece Implants from Implant Direct Int l
 Treatment Options for Restoring Edentulous Jaws using One- and Two-Piece Implants from Implant Direct Int l Two-Piece ReActive Tri-Lobe Implants with Multi-Unit Abutments One-Piece ScrewIndirect Implants
Treatment Options for Restoring Edentulous Jaws using One- and Two-Piece Implants from Implant Direct Int l Two-Piece ReActive Tri-Lobe Implants with Multi-Unit Abutments One-Piece ScrewIndirect Implants
SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015
 SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015 Dental Surveyor: It is a mechanical device used to determine the relative parallelism of the teeth surfaces and the undercuts areas in relation to
SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015 Dental Surveyor: It is a mechanical device used to determine the relative parallelism of the teeth surfaces and the undercuts areas in relation to
Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I.
 Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I. Removable dentures Partial Complete (full) lenka.roubalikova@tiscali.cz 2 Prosthetic dentistry replacement of Damaged teeth reconstruction of the crown (inlays, crowns)
Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I. Removable dentures Partial Complete (full) lenka.roubalikova@tiscali.cz 2 Prosthetic dentistry replacement of Damaged teeth reconstruction of the crown (inlays, crowns)
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment
 Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
Construction of Removable Partial Denture
 Construction of Removable Partial Denture Peter Hermann Department of Prosthodontics Semmelweis University Treatment options for edentulous spaces Fixed prosthodontics (crowns/bridges) Removable prosthodontics
Construction of Removable Partial Denture Peter Hermann Department of Prosthodontics Semmelweis University Treatment options for edentulous spaces Fixed prosthodontics (crowns/bridges) Removable prosthodontics
Clinical Management of Kennedy Class II Cases Using Osseointegrated Dental Implants
 Clinical Management of Kennedy Class II Cases Using Osseointegrated Dental Implants Thesis Submitted in the Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Doctor Degree in Removable Prosthodontics By
Clinical Management of Kennedy Class II Cases Using Osseointegrated Dental Implants Thesis Submitted in the Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Doctor Degree in Removable Prosthodontics By
Surveying. 3rd year / College of Dentistry/University of Baghdad ( ) Page 1
 د. فائزة Lec.3 Prosthodontics Surveying The ideal requirements for successful removable partial denture are: 1. Be easily inserted and removed by the patient. 2. Resist dislodging forces. 3. It should
د. فائزة Lec.3 Prosthodontics Surveying The ideal requirements for successful removable partial denture are: 1. Be easily inserted and removed by the patient. 2. Resist dislodging forces. 3. It should
م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION
 Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
Fixed Partial Dentures /FPDs/, Implant Supported. in implant prosthodontics
 Fixed Partial Dentures /FPDs/, Implant Supported Prosthesis/ISP/ in implant prosthodontics Prof.dr.Tamas Divinyi Semmelweis University, Faculty of Dentistry Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Fixed Partial Dentures /FPDs/, Implant Supported Prosthesis/ISP/ in implant prosthodontics Prof.dr.Tamas Divinyi Semmelweis University, Faculty of Dentistry Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Overdenture: A Way of Preventive Prosthodontics
 CASE REPORT Overdenture: A Way of Preventive Prosthodontics Gorakhnath B Shinde 1 and Wadkar AP 2 Quick Response Code ABSTRACT: doi:... 1 Post Graduate Student 2 Professor and PG Guide Department of Prosthodontics
CASE REPORT Overdenture: A Way of Preventive Prosthodontics Gorakhnath B Shinde 1 and Wadkar AP 2 Quick Response Code ABSTRACT: doi:... 1 Post Graduate Student 2 Professor and PG Guide Department of Prosthodontics
Principles of. By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah
 Principles of By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah 1. Utilize what's present: Whenever possible, select a design that fits the teeth and soft tissues, rather than choosing one that requires tissue alteration. When minimal
Principles of By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah 1. Utilize what's present: Whenever possible, select a design that fits the teeth and soft tissues, rather than choosing one that requires tissue alteration. When minimal
BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note
 Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
SCD Case Study. Implant-supported overdentures
 SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture Using Modified Impression Technique: A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver.VII (Oct. 2015), PP 102-107 www.iosrjournals.org Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver.VII (Oct. 2015), PP 102-107 www.iosrjournals.org Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture
Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers
 Turk J Med Sci 31 (2001) 445-449 TÜB TAK Filiz KEYF Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers Received: November 30,
Turk J Med Sci 31 (2001) 445-449 TÜB TAK Filiz KEYF Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers Received: November 30,
It has been proposed that partially edentulous maxillectomy
 CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide
 Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide Drago, Carl DDS, MS ISBN-13: 9780813828831 Table of Contents Contributors. Foreword. Acknowledgments. Chapter 1. Introduction To Implant Dentistry. 1. Introduction.
Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide Drago, Carl DDS, MS ISBN-13: 9780813828831 Table of Contents Contributors. Foreword. Acknowledgments. Chapter 1. Introduction To Implant Dentistry. 1. Introduction.
TOOTH SUPPORTED MANDIBULAR OVERDENTURE: A FORGOTTEN CONCEPT
 TJPRC: International Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry & Research (TJPRC:IJPDR) Vol. 1, Issue 1, Jun 2017, 5-10 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. TOOTH SUPPORTED MANDIBULAR OVERDENTURE: A FORGOTTEN CONCEPT ANSUIA GUPTA 1,
TJPRC: International Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry & Research (TJPRC:IJPDR) Vol. 1, Issue 1, Jun 2017, 5-10 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. TOOTH SUPPORTED MANDIBULAR OVERDENTURE: A FORGOTTEN CONCEPT ANSUIA GUPTA 1,
Journal of American Science 2010;6(9) Emiel A. M. Hanna *1 and Salah A. F. Hegazy 2
 Modified Rotation Joint Connection Unite Versus Double Aker Clasp used for Bracing of Maxillary unilateral Free End Removable Partial Dentures (In Vitro Analysis of Stresses on Principle Abutments and
Modified Rotation Joint Connection Unite Versus Double Aker Clasp used for Bracing of Maxillary unilateral Free End Removable Partial Dentures (In Vitro Analysis of Stresses on Principle Abutments and
Diagnosis. overt Examination. Definitive Examination. History. atient interview. Personal History. Clinical Examination.
 Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Use of Implant Retained Overdenture in Atrophic Mandible - A Case Report
 Case report AODMR Use of Implant Retained Overdenture in Atrophic Mandible - A Case Report Sheren Fatima 1, Rajarshi Basu 2, Neelkamal Hallur 3, Aaisha Siddiqua 4, Syed Zakaullah 4, Sumaiyya 2, Chaitanya
Case report AODMR Use of Implant Retained Overdenture in Atrophic Mandible - A Case Report Sheren Fatima 1, Rajarshi Basu 2, Neelkamal Hallur 3, Aaisha Siddiqua 4, Syed Zakaullah 4, Sumaiyya 2, Chaitanya
Corresponding author: *Heba Wageh Abo-Zaed Elsaed. DOI: / Page
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. II (July. 2017), PP 114-119 www.iosrjournals.org Double-Arm Clasp with Anterior Placed
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. II (July. 2017), PP 114-119 www.iosrjournals.org Double-Arm Clasp with Anterior Placed
Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete Denture and Mandibular Teeth supported Overdenture
 Case Report imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Periodontics and Prosthodontics DOI: 10.21767/2471-3082.100041 Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete
Case Report imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Periodontics and Prosthodontics DOI: 10.21767/2471-3082.100041 Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete
In 1977, Lew1 developed a passive
 CLINICAL AN OVERVIEW OF THE LEW ATTACHMENT: CLINICAL REPORTS Jack Piermatti, DMD Sheldon Winkler, DDS KEY WORDS Lew attachment Atrophic mandible Subperiosteal implant Root form implant Although the Lew
CLINICAL AN OVERVIEW OF THE LEW ATTACHMENT: CLINICAL REPORTS Jack Piermatti, DMD Sheldon Winkler, DDS KEY WORDS Lew attachment Atrophic mandible Subperiosteal implant Root form implant Although the Lew
DENT Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008
 University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2008-01 DENT 718 - Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008 Shotwell, Jeffrey Shotwell, J. (2008, April 23) Advanced Topics in Removable
University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2008-01 DENT 718 - Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008 Shotwell, Jeffrey Shotwell, J. (2008, April 23) Advanced Topics in Removable
CAUSE OF TECHNICAL FAILURES OF CONICAL CROWN-RETAINED DENTURE (CCRD): A CLINICAL REPORT
 J Korean Acad Prosthodont : Volume 41, Number 6, 2003 CAUSE OF TECHNICAL FAILURES OF CONICAL CROWN-RETAINED DENTURE (CCRD): A CLINICAL REPORT Yang-Jin Yi, D.D.S.,M.S.D.,Ph.D., Lee-Ra Cho, D.D.S.,M.S.D.,Ph.D.,
J Korean Acad Prosthodont : Volume 41, Number 6, 2003 CAUSE OF TECHNICAL FAILURES OF CONICAL CROWN-RETAINED DENTURE (CCRD): A CLINICAL REPORT Yang-Jin Yi, D.D.S.,M.S.D.,Ph.D., Lee-Ra Cho, D.D.S.,M.S.D.,Ph.D.,
DENT Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008
 University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2008-01 DENT 718 - Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008 Shotwell, Jeffrey Shotwell, J. (2008, April 23) Advanced Topics in Removable
University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2008-01 DENT 718 - Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008 Shotwell, Jeffrey Shotwell, J. (2008, April 23) Advanced Topics in Removable
IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE AND MATERIALS
 IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE AND MATERIALS DR ZURYATI AB GHANI BDS (WALES), Grad Dip Clin Dent (Adelaide), Doctor in Clinical Dentistry (prosthodontics( prosthodontics), Adelaide, FRACDS (Australia). 29.06.08
IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE AND MATERIALS DR ZURYATI AB GHANI BDS (WALES), Grad Dip Clin Dent (Adelaide), Doctor in Clinical Dentistry (prosthodontics( prosthodontics), Adelaide, FRACDS (Australia). 29.06.08
Cast Partial Denture Improving Emergence and Masticatory Function - A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. VI (Sep. 2015), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Cast Partial Denture Improving Emergence
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. VI (Sep. 2015), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Cast Partial Denture Improving Emergence
Basic information on the. Straumann Pro Arch TL. Straumann Pro Arch TL
 Basic information on the Straumann Pro Arch TL Straumann Pro Arch TL Contents 1. Introduction 2 1.1 Discover more treatment options with the 4 mm Short Implant 2 2. Technical information 3 3. Step-by-step
Basic information on the Straumann Pro Arch TL Straumann Pro Arch TL Contents 1. Introduction 2 1.1 Discover more treatment options with the 4 mm Short Implant 2 2. Technical information 3 3. Step-by-step
Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident
 Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Case report: Lingualized occlusion -A better way for enhancing function & esthetic
 Case report: Lingualized occlusion -A better way for enhancing function & esthetic 1Dr. Vishrut Shah, 2 Dr. Sunil Dhaded, 3 Dr. Chandrashekar Sajjan 1Post graduate student, Department of Prosthodontics,
Case report: Lingualized occlusion -A better way for enhancing function & esthetic 1Dr. Vishrut Shah, 2 Dr. Sunil Dhaded, 3 Dr. Chandrashekar Sajjan 1Post graduate student, Department of Prosthodontics,
IMPRESSION PROCEDURES TRAINING MANUAL
 IMPRESSION PROCEDURES TRAINING MANUAL 01 01 A.B. DENTAL A.B. Dental is proud to present this impression taking procedure protocol. This manual explains, step by step, the procedure while using A.B. Dental
IMPRESSION PROCEDURES TRAINING MANUAL 01 01 A.B. DENTAL A.B. Dental is proud to present this impression taking procedure protocol. This manual explains, step by step, the procedure while using A.B. Dental
UDELL DENTAL LABORATORY Instructions for Use PREAT Precision Attachments
 Indications Instructions The Locator Root Attachment is designed for use with overdentures or partial dentures, retained in whole or in part by endodontically treated roots in the mandibular or maxilla.
Indications Instructions The Locator Root Attachment is designed for use with overdentures or partial dentures, retained in whole or in part by endodontically treated roots in the mandibular or maxilla.
Solid Zirconia Full-Arch Implant Prosthesis (Protocol C All-CAD with Multi-Unit Abutments) BruxZir. FIRST Appointment. The BruxZir
 (Protocol C All-CAD with Multi-Unit Abutments) Step-by-Step Restorative Protocol C The BruxZir Full-Arch Implant Prosthesis offers a fixed, all-zirconia implant solution for edentulous patients desiring
(Protocol C All-CAD with Multi-Unit Abutments) Step-by-Step Restorative Protocol C The BruxZir Full-Arch Implant Prosthesis offers a fixed, all-zirconia implant solution for edentulous patients desiring
Arrangement of the artificial teeth:
 Lecture Prosthodontic Dr. Osama Arrangement of the artificial teeth: It s the placement of the teeth on a denture with definite objective in mind or it s the setting of teeth on temporary bases. Rules
Lecture Prosthodontic Dr. Osama Arrangement of the artificial teeth: It s the placement of the teeth on a denture with definite objective in mind or it s the setting of teeth on temporary bases. Rules
Life Science Journal 2013;10(4) Retention Force Measurement of Telescopic Crowns with Different Clearance Fit
 Retention Force Measurement of Telescopic Crowns with Different Clearance Fit Hala Hassan 1, Fatma El Zahraa A. Sayed 2, Enas Mesallum 3 1 Private Practice, Cairo, Egypt 2 Prof., Faculty of Dentistry,
Retention Force Measurement of Telescopic Crowns with Different Clearance Fit Hala Hassan 1, Fatma El Zahraa A. Sayed 2, Enas Mesallum 3 1 Private Practice, Cairo, Egypt 2 Prof., Faculty of Dentistry,
Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois Phone: Fax:
 Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D. 2325 N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois 60614 Phone: 312-608-6881 Fax: 773-296-0601 Samanthawchou@gmail.com What is our role as the dentist? "We live in a culture in which people
Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D. 2325 N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois 60614 Phone: 312-608-6881 Fax: 773-296-0601 Samanthawchou@gmail.com What is our role as the dentist? "We live in a culture in which people
Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System)
 Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System) Mucosa-supported complete prostheses with poor fit greatly reduce people's quality of life. This is why the importance of implant-supported
Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System) Mucosa-supported complete prostheses with poor fit greatly reduce people's quality of life. This is why the importance of implant-supported
Legacy Prosthetic Catalog
 Legacy Prosthetic Catalog Straight Snap-On Straight Contoured Angled Contoured Ball Attachment Gold/Plastic Castable Locator Attachment Plastic Temporary Screw Receiving Plastic Non-Engaging Castable 15
Legacy Prosthetic Catalog Straight Snap-On Straight Contoured Angled Contoured Ball Attachment Gold/Plastic Castable Locator Attachment Plastic Temporary Screw Receiving Plastic Non-Engaging Castable 15
Indian Journal of Medical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences August 2016;3(8) ISSN: ISSN: DOI: /zenodo Impact Factor: 3.
 HYBRID VS CERAMOMETAL IMPLANT PROSTHESIS Dr.Rahul Patil* *Mds Prosthodontics, Senior Lecturer Sddc Dental College, Parbhani Keywords: Abstract A completely edentulous patient has few treatment options
HYBRID VS CERAMOMETAL IMPLANT PROSTHESIS Dr.Rahul Patil* *Mds Prosthodontics, Senior Lecturer Sddc Dental College, Parbhani Keywords: Abstract A completely edentulous patient has few treatment options
synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions
 synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions INTRODUCTION synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations 1 The synocta Meso abutments, available
synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions INTRODUCTION synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations 1 The synocta Meso abutments, available
Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of a Partially Edentulous Hemiglossectomy Patient: A Clinical Report
 case report 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1067 Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of a Partially Edentulous Hemiglossectomy Patient: A Clinical Report 1 Ragini Sudhakar Sanaye, 2 Sabita M Ram, 3 Naisargi Shah, 4
case report 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1067 Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of a Partially Edentulous Hemiglossectomy Patient: A Clinical Report 1 Ragini Sudhakar Sanaye, 2 Sabita M Ram, 3 Naisargi Shah, 4
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE GOVERNMENT EXAMINATION SYLLABUS
 MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE GOVERNMENT EXAMINATION SYLLABUS OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE ACADEMIC YEAR 2016/2017 1 1. Biomechanics of
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE GOVERNMENT EXAMINATION SYLLABUS OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE ACADEMIC YEAR 2016/2017 1 1. Biomechanics of
DL 313 Removable Partial Dentures II
 DL 313 Removable Partial Dentures II Survey & Design Survey The procedure of studying the relative parallelism or lack of parallelism of the teeth and associated structures so as to select a path of placement
DL 313 Removable Partial Dentures II Survey & Design Survey The procedure of studying the relative parallelism or lack of parallelism of the teeth and associated structures so as to select a path of placement
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
SimpleLine II Surgical / Prosthesis Manual
 SimpleLine II Surgical / Prosthesis Manual SimpleLine II SURGICAL MANUAL Surgical Drill Sequence 04 Fixture Installation 05 Fixture Connection 06 Surgical Kit Maintenance 08 Warnings 09 04 SimpleLine ll
SimpleLine II Surgical / Prosthesis Manual SimpleLine II SURGICAL MANUAL Surgical Drill Sequence 04 Fixture Installation 05 Fixture Connection 06 Surgical Kit Maintenance 08 Warnings 09 04 SimpleLine ll
SCD Case Study. Attachments in Prosthodontics
 SCD Case Study Attachments in Prosthodontics Precision attachments are retention units milled out of alloy. They have male and female parts that fit together with tolerances of 10 microns. It is important
SCD Case Study Attachments in Prosthodontics Precision attachments are retention units milled out of alloy. They have male and female parts that fit together with tolerances of 10 microns. It is important
 A New Procedure Reduces Laboratory Time to 6 Hours for the Elaboration of Immediate Loading Prostheses with a Titanium Frame Following Implant Placement Huard C, Bessadet M, Nicolas E, Veyrune JL * International
A New Procedure Reduces Laboratory Time to 6 Hours for the Elaboration of Immediate Loading Prostheses with a Titanium Frame Following Implant Placement Huard C, Bessadet M, Nicolas E, Veyrune JL * International
2015 Member Speaker Forum. Chair: L. Scott Brooksby, DDS, BS. Friday, October 23, :30 AM 3:45 PM. Coral Ballroom. 3.
 2015 Member Speaker Forum Chair: L. Scott Brooksby, DDS, BS Friday, October 23, 2015 11:30 AM 3:45 PM Coral Ballroom 3.25 CE Credits 11:30 a.m. 3:45 p.m. Member Speaker Forum 11:30 11:40 a.m. Introduction
2015 Member Speaker Forum Chair: L. Scott Brooksby, DDS, BS Friday, October 23, 2015 11:30 AM 3:45 PM Coral Ballroom 3.25 CE Credits 11:30 a.m. 3:45 p.m. Member Speaker Forum 11:30 11:40 a.m. Introduction
DIAGNOSTIC/PREVENTIVE SERVICES
 DIAGNOSTIC/PREVENTIVE SERVICES Diagnostic Services D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 100% 100% D0140 Limited oral evaluation problem focused 100% 100% D0150 Comprehensive oral evaluation 100% 100% D0160 Detailed
DIAGNOSTIC/PREVENTIVE SERVICES Diagnostic Services D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 100% 100% D0140 Limited oral evaluation problem focused 100% 100% D0150 Comprehensive oral evaluation 100% 100% D0160 Detailed
Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research. DOI: /sjodr. ISSN (Print) Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website:
 DOI:10.21276/sjodr Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297 (Online)
DOI:10.21276/sjodr Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297 (Online)
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 827 Thirty-Two Year Success of Dental Implants in Periodontally Compromised Dentition Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 Glenn J. Wolfinger,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 827 Thirty-Two Year Success of Dental Implants in Periodontally Compromised Dentition Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 Glenn J. Wolfinger,
Component parts of Chrome Cobalt Removable Partial Denture
 Lec. 5 د.بسام الطريحي Component parts of Chrome Cobalt Removable Partial Denture Major connectors: Are either bars or plates, the difference between them is in the amount of tissue covers. Plates are broad
Lec. 5 د.بسام الطريحي Component parts of Chrome Cobalt Removable Partial Denture Major connectors: Are either bars or plates, the difference between them is in the amount of tissue covers. Plates are broad
Simplified Method for fabrication of O- Ring Implant Supported Overdenture- Case Report
 CASE REPORT Simplified Method for fabrication of O- Ring Implant Supported Overdenture- Case Report Dr. Vikas Punia 1, Dr. Mohit Handa 2, Dr.Nikhil Verma 3, Dr.Virender Singh 4, Dr. Vivek Lath 5. M.D.S.,
CASE REPORT Simplified Method for fabrication of O- Ring Implant Supported Overdenture- Case Report Dr. Vikas Punia 1, Dr. Mohit Handa 2, Dr.Nikhil Verma 3, Dr.Virender Singh 4, Dr. Vivek Lath 5. M.D.S.,
Uppers are from Mars, Lowers from Venus Clarifying Overdentures
 Uppers are from Mars, Lowers from Venus Clarifying Overdentures M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S. Thomas P. Hinman Dental Meeting Atlanta, GA March 23, 2017 About Your Speaker: M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S.
Uppers are from Mars, Lowers from Venus Clarifying Overdentures M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S. Thomas P. Hinman Dental Meeting Atlanta, GA March 23, 2017 About Your Speaker: M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S.
Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid
 Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid Implant-Level Restoration Step-by-Step Restorative Protocol The Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid offers a fixed, all-ceramic implant solution for edentulous patients desiring
Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid Implant-Level Restoration Step-by-Step Restorative Protocol The Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid offers a fixed, all-ceramic implant solution for edentulous patients desiring
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Jaw relation registration in RPD
 Jaw relation registration in RPD Why to Record the Jaw Relations? To establish and maintain a harmonious relationship with all oral structures and to provide a masticatory apparatus that is efficient and
Jaw relation registration in RPD Why to Record the Jaw Relations? To establish and maintain a harmonious relationship with all oral structures and to provide a masticatory apparatus that is efficient and
ACRYLIC REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE(RPD)
 ACRYLIC REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE(RPD) is a dental prosthesis which artificially supplies teeth and associated structure in a partially edentulous arch, made from acrylic resin and can be inserted and
ACRYLIC REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE(RPD) is a dental prosthesis which artificially supplies teeth and associated structure in a partially edentulous arch, made from acrylic resin and can be inserted and
The restoration of partially and completely
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL IMPLANT FRACTURES. ACASE HISTORY Firas A. M. AL Quran, PhD, MSc Med; Bashar A. Rashan, MS; Ziad N. AL-Dwairi, PhD The widespread use of endosseous osseointegrated implants
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL IMPLANT FRACTURES. ACASE HISTORY Firas A. M. AL Quran, PhD, MSc Med; Bashar A. Rashan, MS; Ziad N. AL-Dwairi, PhD The widespread use of endosseous osseointegrated implants
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
Nagri D et al. Linear occlusion and Neutral Zone recording for severely resorbed ridges
 Doi:10.21276/ledent.2018.02.01.02 Case Report LINEAR OCCLUSION AND NEUTRAL ZONE RECORDING USING TISSUE CONDITIONER REPORT OF A SEVERELY RESORBED RIDGE Divya Nagri, 1Ashish Kakkar, 2Neeraj Mittal, 3Lovely
Doi:10.21276/ledent.2018.02.01.02 Case Report LINEAR OCCLUSION AND NEUTRAL ZONE RECORDING USING TISSUE CONDITIONER REPORT OF A SEVERELY RESORBED RIDGE Divya Nagri, 1Ashish Kakkar, 2Neeraj Mittal, 3Lovely
Hex-Lock Abutment System. Restorative Manual
 System Restorative Manual 32 Restorative options with s s are manufactured from titanium alloy and used as the support foundation for single- or multiple-unit cement-retained, partially edentulous fixed
System Restorative Manual 32 Restorative options with s s are manufactured from titanium alloy and used as the support foundation for single- or multiple-unit cement-retained, partially edentulous fixed
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations
 Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Science (IJDOS) ISSN:
 International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Science (IJDOS) ISSN: 2377-8075 A Novel Functional Impression Procedure for Distal-Extension Removable Partial Dentures Li QL *, Cao Y Case Report Department
International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Science (IJDOS) ISSN: 2377-8075 A Novel Functional Impression Procedure for Distal-Extension Removable Partial Dentures Li QL *, Cao Y Case Report Department
J Bagh College Dentistry Vol. 21(1), 2009 The effect of using different..
 The effect of using different impression techniques and materials on vertical tissue displacement in free end extension ridges. (Dental survey and clinical study) Rawia. N. AL- Dafaii, B.D.S., MSc. (1)
The effect of using different impression techniques and materials on vertical tissue displacement in free end extension ridges. (Dental survey and clinical study) Rawia. N. AL- Dafaii, B.D.S., MSc. (1)
..Bruxism is a potential risk factor for implants and superstructures. It increases the
 Cairo Dental Journal (25) Number (1), 17:24 Janurary, 2009 Prosthetic Rehabilitation Of Partially Edentulous Bruxing Patients Using Dental Implants Ashraf Abdmoem Amer 1 and Ehab M. Abuelroos 2 1. 2. Assistant
Cairo Dental Journal (25) Number (1), 17:24 Janurary, 2009 Prosthetic Rehabilitation Of Partially Edentulous Bruxing Patients Using Dental Implants Ashraf Abdmoem Amer 1 and Ehab M. Abuelroos 2 1. 2. Assistant
Case Report INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT. Sneha Gada 1, Deepak Nallaswamy 2, Ashish R. Jain 2 * ABSTRACT
 Case Report Full mouth rehabilitation of periodontally compromised partially edentulous arches with multiple missing teeth using telescopic crown and bridge - A case report Sneha Gada 1, Deepak Nallaswamy
Case Report Full mouth rehabilitation of periodontally compromised partially edentulous arches with multiple missing teeth using telescopic crown and bridge - A case report Sneha Gada 1, Deepak Nallaswamy
Chapter 12. Prosthodontics
 Chapter 12 Prosthodontics Golbarg Kolahi 1 Prosthesis [prahs-thee-sis] A replacement for a missing body part Golbarg Kolahi 2 Prosthesis In the dental field, it is a fixed or removable appliance replacing
Chapter 12 Prosthodontics Golbarg Kolahi 1 Prosthesis [prahs-thee-sis] A replacement for a missing body part Golbarg Kolahi 2 Prosthesis In the dental field, it is a fixed or removable appliance replacing
Components Of Implant Protective Occlusion A Review
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 7 Number 2 Components Of Implant Protective Occlusion A Review E Prashanti, K Sumanth, J Reddy Citation E Prashanti, K Sumanth, J Reddy. Components
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 7 Number 2 Components Of Implant Protective Occlusion A Review E Prashanti, K Sumanth, J Reddy Citation E Prashanti, K Sumanth, J Reddy. Components
Radiographic Stent for Simplified Placement of Implants in the Mandible
 10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1086 CASE REPORT Radiographic Stent for Simplified Placement of Implants in the Mandible ABSTRACT This article aims to present a modified yet simple technique for the placement
10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1086 CASE REPORT Radiographic Stent for Simplified Placement of Implants in the Mandible ABSTRACT This article aims to present a modified yet simple technique for the placement
Comparison of Different Methods of Abutment Splinting and Attachments on Teeth Kinetics (Part I)
 wjd Ahmed N Elsherbini, Wilhelm Niedermeier Original Article 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1464 Comparison of Different Methods of Abutment Splinting and Attachments on Teeth Kinetics (Part I) 1 Ahmed N Elsherbini,
wjd Ahmed N Elsherbini, Wilhelm Niedermeier Original Article 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1464 Comparison of Different Methods of Abutment Splinting and Attachments on Teeth Kinetics (Part I) 1 Ahmed N Elsherbini,
Abutment level impression Ⅰ. Combi abutment/dual abutment Multi units
 Pr osthetic par t Abutment level impression Ⅰ Combi abutment/dual abutment Multi units Prosthetic part Remove Cover screw Prosthetic part Remove Healing abutment Prosthetic part Select suitable Combi abutment,
Pr osthetic par t Abutment level impression Ⅰ Combi abutment/dual abutment Multi units Prosthetic part Remove Cover screw Prosthetic part Remove Healing abutment Prosthetic part Select suitable Combi abutment,
Recommended Professional Fee
 Fee Guide Development & Negotiation Committee 2018 Recommended Professional Fee and Laboratory Fee Guide Abbreviations T: Time Units / 1 Unit = 15 Minutes G: Gold L: Lab Disbursement E: Extra Expense B.R.:
Fee Guide Development & Negotiation Committee 2018 Recommended Professional Fee and Laboratory Fee Guide Abbreviations T: Time Units / 1 Unit = 15 Minutes G: Gold L: Lab Disbursement E: Extra Expense B.R.:
Indirect retainers. 1 i
 8 1 i Indirect retainers Factors Influencing Effectiveness Indirect Retainers Auxiliary Functions Indirect Retainers Forms Indirect Retainers Auxiliary occlusal rest Canine extensions fiom occlusal rests
8 1 i Indirect retainers Factors Influencing Effectiveness Indirect Retainers Auxiliary Functions Indirect Retainers Forms Indirect Retainers Auxiliary occlusal rest Canine extensions fiom occlusal rests
Distal extension base removable partial dentures exhibit composite type of support
 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (3), 379:393 September, 2008 stress analysis study of two treatment modalities rehabilitating distal extension cases with few remaining natural teeth Magdy Eid Mohammed
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (3), 379:393 September, 2008 stress analysis study of two treatment modalities rehabilitating distal extension cases with few remaining natural teeth Magdy Eid Mohammed
CASE REPORT. Prosthetic rehabilitation of edentulous mandible with two-implant retained fixed hybrid prosthesis: A case report.
 1828 CASE REPORT Prosthetic rehabilitation of edentulous mandible with two-implant retained fixed hybrid prosthesis: A case report Meisha Gul, Muhammad Rizwan Nazeer, Robia Ghafoor Abstract Removable complete
1828 CASE REPORT Prosthetic rehabilitation of edentulous mandible with two-implant retained fixed hybrid prosthesis: A case report Meisha Gul, Muhammad Rizwan Nazeer, Robia Ghafoor Abstract Removable complete
Advanced restorative techniques and the full mouth reconstruction: the use of gold copings in bridgework
 Clinical Advanced restorative techniques and the full mouth reconstruction: the use of gold copings in bridgework Paul Tipton 1 Introduction From the studies produced by Lindhe and Nyman, described earlier
Clinical Advanced restorative techniques and the full mouth reconstruction: the use of gold copings in bridgework Paul Tipton 1 Introduction From the studies produced by Lindhe and Nyman, described earlier
Implant osseointegration and successful restoration
 Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
OT EQUATOR CASTABLE Single Attachment for Overdentures
 OT EQUATOR CASTABLE Single Attachment for Overdentures pick-up impression OT EQUATOR PROFILE CASTABLE MALE ATTACHMENT individual tray RETENTIVE CAPS OT EQUATOR HOUSING VIOLET CAP RIGID RETENTION (2.7Kg)
OT EQUATOR CASTABLE Single Attachment for Overdentures pick-up impression OT EQUATOR PROFILE CASTABLE MALE ATTACHMENT individual tray RETENTIVE CAPS OT EQUATOR HOUSING VIOLET CAP RIGID RETENTION (2.7Kg)
The aim of this study was to evaluate the use of esthetic twin-flex clasp on remaining
 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 163:169 January, 2008 Twin-Flex clasp as an esthetic approach for remaining central incisor abutment in unilateral maxillectomy cases Salah AF Hegazy 1 and Emiel AM
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 163:169 January, 2008 Twin-Flex clasp as an esthetic approach for remaining central incisor abutment in unilateral maxillectomy cases Salah AF Hegazy 1 and Emiel AM
2018 MEDIHELP RATES - 54 PRACTICE Kindly see below Tariffs for Medihelp. Please note that not all tariff codes listed are covered by the respective
 2018 MEDIHELP RATES - 54 PRACTICE Kindly see below Tariffs for Medihelp. Please note that not all tariff codes listed are covered by the respective TARIFF CODE DESCRIPTION 2018 RATES 8101 Oral examination
2018 MEDIHELP RATES - 54 PRACTICE Kindly see below Tariffs for Medihelp. Please note that not all tariff codes listed are covered by the respective TARIFF CODE DESCRIPTION 2018 RATES 8101 Oral examination
Telescopic overdenture - A case report
 J. Int Oral Health 2011 Case Report All right reserved Telescopic overdenture - A case report Naveen YG* Patel Jayantilal R Sethuraman Rajesh Paranjay Prajapati *M.D.S, Senior Lecturer, M.D.S, Professor
J. Int Oral Health 2011 Case Report All right reserved Telescopic overdenture - A case report Naveen YG* Patel Jayantilal R Sethuraman Rajesh Paranjay Prajapati *M.D.S, Senior Lecturer, M.D.S, Professor
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
High Crown to Implant Ratio as Stress Factor in Short Implants Therapy
 10.1515/bjdm-2016-0015 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY High Crown to Implant Ratio as Stress Factor in Short Implants Therapy SUMMARY Background/Aim: The purpose
10.1515/bjdm-2016-0015 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY High Crown to Implant Ratio as Stress Factor in Short Implants Therapy SUMMARY Background/Aim: The purpose
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
Young-Jin Park, DDS,* and Sung-Am Cho, DDS, MS, PhD
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
