Dynamic retentive force of a mandibular unilateral removable partial denture framework with a back-action clasp
|
|
|
- Homer Murphy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Med Dent Sci 2001; 48: Original Article Dynamic retentive force of a mandibular unilateral removable partial denture framework with a back-action clasp Innim Park, DDS*, Miho Eto, DDS*, Noriyuki Wakabayashi, DDS, PhD**, Masayuki Hideshima, DDS, PhD*** and Takashi Ohyama, DDS, PhD**** Removable Prosthodontics, Department of Masticatory Function Rehabilitation, Division of Oral Health Sciences, Graduate School, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo, Japan (Graduate Student*, Research Associate**, Assistant Professor***, Professor****) Part of this study was presented at the 104th meeting of the Japan Prosthodontic Society (Osaka, Japan, November 2000). Correspondence to: Dr. Innim Park Removable Prosthodontics, Department of Masticatory Function Rehabilitation, Division of Oral Health Sciences, Graduate School, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, , Yushima 1-chome, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo , Japan Fax: Int park.rpro@ tmd.ac.jp Received May 9; Accepted September 25, 2001 Purpose: The purpose of this study was to investigate the dynamic retentive force of a mandibular unilateral distal-extension partial denture framework with a back-action clasp that was designed in a buccally tilted cast on a dental surveyor. The retention mechanism of this framework was analyzed in comparison with other typical unilateral and bilateral frameworks for the mandibular Kennedy class II case. Materials and Methods: Experimental gold alloy frameworks of three designs were repositioned to the master cast, and lifted upward to the vertical direction to the occlusal plane. The load required to dislodge each framework was recorded. The retentive force of each framework was determined by the maximum load in a dislodgment cycle. The bending strength of a plain clasp pattern of the same length as the clasp arm used in each framework was also measured by cantilever beam test. Results: The mean retentive force of the unilateral framework with a back-action clasp of relatively low bending strength was significantly higher (P < 0.01) than that of the unilateral framework with two Akers clasps of relatively high bending strength, and 70 to 80% of the bilateral framework with two Akers clasps on the edentulous side and a double Akers clasp on the contralateral side. The unilateral framework with a back-action clasp showed the greatest early load resistance in the dislodgment cycle among the three designs. Conclusion: The reasonable retention mechanism was demonstrated by the unilateral framework with a back-action clasp. Key words: retentive force, removable partial denture, back-action clasp Introduction In a distal-extension removable partial denture (RPD) for a unilateral edentulous area, the retention and stability of the denture are usually gained by an indirect retainer placed in the contralateral side of the arch to the saddle. The indirect retainer in a form such as a double Akers clasp, connected by a major connector to the denture saddle, is expected to stabilize the saddle by the cross-arch bracing 1,2.
2 106 I. PARK et al. J Med Dent Sci Fig. 1. Schematic illustrations of the unilateral denture framework with a back-action clasp. A, an occlusal view; B, a linguo-distal view. Notice that the back-action clasp arm and the proximal plate placed on the distal surface of the right second premolar is separated by a minute slit. Fig. 2. A frontal view of the back-action clasp arm on the mandibular second premolar. A, perpendicular direction to the occlusal plane; B, the modified direction of placement by tilting the cast buccally on surveying; Bu, buccal arms; Li, lingual arms. The dotted line shows a survey line before tilting the cast, and the solid line represents a survey line after tilting the cast. Unilateral distal-extension RPDs have not been broadly used because of their potential problems of lack of retention 3 and stability that may cause vertical and horizontal hazardous denture displacement in function 4. The lack of stability may allow excessive stresses on residual ridge and abutment teeth, resulting in tissue absorption and eventual loss of the teeth 5. The major connectors and multiple retainers usually incorporated in the bilateral RPDs, however, can be obstructive to the patients. Patients wearing unilateral RPDs are likely to feel comfortable due to their simplicity during speech, swallowing, or mastication. In the partially edentulous case with missing unilateral first and second molars, we have proposed a unilateral distal-extension RPD design that features a back-action clasp as a direct retainer, and an embrasure hook engaged in anterior abutment of the edentulous side as an indirect retainer (Fig. 1). To overcome the difficulty in gaining retention and stability of the unilateral denture, the path of denture placement is intentionally determined by tilting the cast buccally on surveying, as shown in Fig. 2. Consequently, the lingual arm of the clasp and a part of the minor connector on the lingual surface of the abutments are located in the undercut area to the vertical direction to the occlusal plane. It is expected that vertical dislodgment of the denture is strongly resisted in function by those rigid parts of the framework. The purpose of this study was to investigate the dynamic retentive force of the mandibular unilateral partial denture framework with a back-action clasp, and analyze the retention mechanism of this framework in comparison with other typical unilateral and bilateral frameworks for a Kennedy class II partially edentulous case. Materials and Methods Experimental denture frameworks A mandibular dentate plaster model (E , Nissin Dental Products Inc., Kyoto, Japan), with a posterior edentulous area due to missing right first and second molars, was used as the master cast in the experiment. The abutment teeth of the plaster model; the right canine, and the bilateral first and second premolars, were replaced with gold alloy (PGA-2, Ishifuku Metal Industry Co., Tokyo, Japan) casting teeth to avoid surface wear and breakage during the testings. Schematic designs of three framework designs are illustrated in Fig. 3. Framework A employed a unilateral design with a single back-action clasp as a direct retainer on the second right premolar. The design concept of this framework was described in the introduction. The path of denture placement was determined on the dental surveyor by tilting the cast 10 degrees buccally to the perpendicular direction to the occlusal plane. Frameworks B and C were designed on teeth relative to the horizontal survey. Framework B featured two Akers clasps on the right first and second premolars. Framework C featured the cross-arch design with a lingual bar, two Akers clasps on the right premolars, and a double Akers clasp on the left premolars as an indirect retainer. Both the buccal and the lingual tips of the Akers clasps engaged 0.2 mm undercut area while that of the back-action clasp engaged an undercut of 0.25 mm. The back-action clasp arm was approximately 22 mm long, while the buccal and lingual arms of Akers clasps were 13 mm and 10 mm, respectively. Each clasp arm was formed by means of a preformed wax pattern (Bego, Bremen,
3 DYNAMIC RETENTIVE FORCE OF A MANDIBULAR 107 Germany), and cast in the same gold alloy as used for the abutment teeth. Three experimental frameworks were prepared each for the three framework designs. Each framework incorporated a metal plate at the saddle skeleton standing perpendicular to the occlusal plane for retention of tensile rod. Retentive force of the frameworks Each framework was repositioned to the master cast fixed on the experimental stage in the universal testing machine (AGS-H, Shimadzu Co., Kyoto, Japan). For the first series of experiments (grip test), the metal plate with retention holes in each framework was temporarily attached to a tensile rod connected to the testing machine by means of an autopolymerizing resin (Unifast Trad, GC, Tokyo, Japan). Schematic illustrations of the testing device are shown in Fig. 4. Each framework was then subjected to tensile loading and lifted upward perpendicularly to the occlusal plane at a cross-head loading speed of 5 mm per minute. For the second series of experiments (suspension test), each framework was hanged and lifted from the testing machine by means of a S-shaped metal hook, then subjected to tensile loading at the same loading speed as for the grip test. The load required to dislodge each framework as a function of vertical displacement was recorded. The retentive force of each framework was determined as the maximum load in a dislodgment cycle. The test was repeated five times for each experimental framework. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Scheffe s post-hoc test (Statview 4.5, Abacus Concepts Inc., USA) were performed to determine significant differences in the retentive forces among the framework designs (P < 0.01). The dislodgment tests were monitored by means of a digital video camera (DCR-TRV 900, Sony, Tokyo, Japan) for confirmation and analysis of the dislodgment pathways of the frameworks. Bending strength of the clasp beams The bending strength of a plain clasp pattern beam (Bego, Bremen, Germany) with the same length as each clasp arm used in the experimental frameworks was measured by cantilever beam test to provide reference data for the retention test. Each plain clasp beam was clamped at the neck of the clasp, and loaded at the clasp tip from the inner surface to the outer surface of the clasp perpendicularly to the beam direction until the beam deflected the length corresponding to the amount of undercut used in the Fig. 3. Experimental framework designs used in the study. Fig. 4. Schematic illustrations of the dislodgment test. A, grip test; B, suspension test; P, retention plate in the framework saddle; R, tensile rod connected to the universal testing machine; and S, S-shaped metal hook.
4 108 I. PARK et al. J Med Dent Sci experimental framework. The bending strength was then recorded three times for each clasp beam, and the average value was used as the bending strength of the clasp beam. Results Fig. 5 shows load-vertical displacement curves of representative frameworks each from three design groups in the grip test. The means and standard deviations of the retentive forces for the three design groups in the grip test are summarized in Fig. 6. The mean retentive force of framework C (25.6 N) was the highest, followed by frameworks A (20.0 N) and B (16.1 N). There were significant differences between any two experimental groups in the three groups (P < 0.01). In the load-vertical dislodgment curves (Fig 5), framework A demonstrated the greatest inclination (increase rate) in its early stage of dislodgment (39.0 N/mm), followed by frameworks C (33.2 N/mm) and B (20.8 N/mm). Fig. 7 shows load-vertical displacement curves of representative frameworks each from three design groups in the suspension test. For framework C, there were two peaks in the load-vertical displacement curve; the first peak obviously represented the dislodgment of the direct retainer, and the second peak coincided with the dislodgment of the indirect retainer on contralateral side of the arch. The maximum load resistance (retentive force) was recorded consistently at the first peak of the curve. The means and standard deviations of the retentive forces for the three design groups in the suspension test are summarized in Fig. 8. Framework C revealed the highest mean retentive force (10.0 N), followed by frameworks A (6.9 N) and B (4.6 N). There were significant differences between any two experimental groups in the three groups (P < 0.01). The retentive forces in the suspension test were approximately 30 40% of those in the suspension test. In the load-vertical displacement curves (Fig 7), framework A demonstrated the greatest inclination (increase rate) in its early stage of dislodgment (10.6 N/mm), followed by frameworks C (8.0 N/mm) and B (7.0 N/mm). Table 1 shows the means and standard deviations of the bending strengths of the plain clasp beams by the cantilever beam test. The mean bending strength of the back-action clasp beam with corresponding length to the clasp arm in framework A, was less than 1 N when the tip of the clasp deflected 0.25 mm (the amount of undercut). The buccal and lingual arms of clasp beams that corresponded to the clasps in the frameworks B and C, demonstrated bending strengths of between 2 N and 5 N. As the length of a clasp arm increased, the strength required to deflect the clasp clearly decreased. Fig. 5. Load-vertical displacement curves of representative frameworks each from the three designs (A, B, and C) in the grip test. Fig. 6. The means and standard deviations of the retentive forces for the three designs in the grip test.
5 DYNAMIC RETENTIVE FORCE OF A MANDIBULAR 109 Fig. 7. Load-vertical displacement curves of representative frameworks each from the three designs (A, B, and C) in the suspension test. Fig. 8. The means and standard deviations of the retentive forces for the three designs in the suspension test. Table 1. The mean bending strengths of the plain clasp arm beams by cantilever beam test *The amount of deflection (undercut); clasp arm in framework A, 0.25 mm; clasp arms in frameworks B and C, 0.2 mm. Discussion Although cobalt-chromium alloy has been the most popular partial denture alloy because of its low cost and rigidity, the gold alloy used in the experimental frameworks may be suitable for clasps because of its high flexibility, high yield strength, and relatively low modulus of elasticity 6. In addition to these clinical advantages, the excellent castability 7 and fatigue resistance 8 of the gold alloy were another reasons of using this alloy in the experimental frameworks. The grip tests were conducted so that the direction path of dislodgment was regulated by fixing the framework to the tensile rod. The experimental condition in the grip test might not reproduce the denture dislodgment or removal in a real clinical situation, but it was likely to express the total amount of bending strengths of the clasps incorporated in each framework. The retentive forces demonstrated in each framework design in the grip test were much higher than those supposed to be sufficient for ordinary clinical requirements 9. The experimental condition in the suspension tests, on the other hand, might be closer to clinical situations than that on the grip test, because it allows hor-
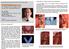
6 110 I. PARK et al. J Med Dent Sci izontal or rotational denture displacement during testing. The mean retentive forces in the suspension test (4 to 10 N) were approximately 30~40% of those in the grip test, but they were still considered enough for ordinary clinical requirements 9. Framework C revealed the highest mean retentive force among the three designs in both grip and suspension tests, probably because it had more buccal and lingual retentive clasp arms with relatively high bending strengths. Despite the fact that framework A contained only a single back-action clasp of relatively low bending strength while frameworks B and C included multiple buccal and lingual clasps of high bending strengths, the mean retentive force of framework A was significantly higher than that of framework B, and between 70 % and 80 % of that of framework C in both grip and suspension tests. The results may be attributed to a unique retention mechanism generated in framework A. Fig. 9(a) captured an experimental view of a framework A in its early dislodgment stage in the suspension test before the load reached the peak (retentive force), and Fig. 9(b) demonstrated another view of the same framework immediately after the peak load was recorded in the same experimental sequence as shown in Fig 9(a). The buccal arm of the back-action clasp was lifted off at first, then the total part of the framework was dislodged in the late stage of the sequence. It was clearly shown in the suspension test that framework A was dislodged from the master cast with a lingually rotational movement as schematically illustrated in Fig. 10. This rotational movement might occur due to the frictional resistance generated (a) (b) by the rigid lingual bracing arm of the back-action clasp and a part of the minor connector located in a sufficient undercut area perpendicular to the occlusal plane. The retention mechanism demonstrated in framework A was quite different from other frameworks that obtained the most of their retention from the bending strengths of retentive clasp arms. This retention mechanism shown in framework A may also reasonably explain the greatest inclination value (increase rate) in its early stage of the load-vertical displacement curve among the three framework designs. Mandibular premolars that are usually used as abutments for direct and indirect retainers of distalextension RPDs occasionally tilt lingually to the vertical direction to the occlusal plane, resulting in a relatively high survey line on the lingual surface of the abutment 10. The lingual reciprocal arm of a circumferential clasp is required to be engaged at the corresponding height to the buccal arm to avoid a tilting effect of the clasp to the abutment during placement and removal of the denture. By tilting the cast buccally on surveying, the survey line on the lingual surface of the abutment is lowered, while that on the buccal surface is raised. Consequently, the lingual arm of the clasp in a lowered position may promise a reasonable reciprocal effect of the buccal arm, and may also generate the strong retention and stability to the denture 11. The framework design featured in this study may be placed in an alternative category of the rotational path RPDs that have been described by King 12, Krol 13, and Jacobson 14. The rotational path RPDs incorporate a curved or arcuate path of placement, allowing one or more of the rigid components of the framework to gain access to and engage an undercut area. The framework in this study is designed to be inserted on the linguo-buccal rotational axis, while the conventional rotational path framework is inserted on the mesio-distal rotational axis. In both design methodologies, the rigid part of the frameworks play an important role to Fig. 9. (a) An experimental view from a motion picture of a framework A in its early dislodgment stage in the suspension test before the load (retentive force) reached the peak. (b) Another view of the same framework immediately after the peak load was recorded. Note that the framework with the retention plate lingually rotated. Fig. 10. The back-action clasp arm of framework A on the second premolar in a frontal view, before (a) and after (b) the peak load was recorded in the suspension test.
7 DYNAMIC RETENTIVE FORCE OF A MANDIBULAR 111 abridge some conventional retainers, and to enable gaining simplicity in the frameworks without compromising retention of the denture. Acknowledgments This study was financially supported by a Grant-in- Aid for Scientific Research ( and ) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture, Japan. References 1. Walter JD. Removable partial denture design. London: British Dental Association, 1990: Zarb GA, Bergman B, Clayton JA, MacKay HF (eds). Prosthodontic treatment for partially edentulous patients. St Louis: CV Mosby, 1978: Lammie GA, Laird WRE. Osborne & Lammie s partial dentures, 5th ed. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1986: Garver DG. A new clasping system for unilateral distalextension removable partial dentures. J Prosthet Dent 1978;39: Bates JF, Huggett R, Stafford GD. Removable denture construction, 3rd ed. London: Wright, 1991: Cunningham DM. Comparison of base metal alloys and type IV gold alloys for removable partial denture frameworks. Dent Clin North Am 1973;17: Pulskamp FE. A comparison of the casting accuracy of base metal and gold alloys. J Prosthet Dent 1979;41: Vallittu PK, Kokkonen M. Deflection fatigue of cobalt-chromium, titanium, and gold alloy cast denture clasp. J Prosthet Dent 1995;74: Frank RP, Nicholls JI. A study of the flexibility of wrought wire clasps. J Prosthet Dent 1981;45: Fuller JL, Denehy GE. The permanent mandibular premolars. In: Hall SA (ed). Concise dental anatomy and morphology, 7th ed. Chicago: Year book medical publishers, 1984: McGiveney GP, Castleberry DJ. McCracken s removable partial prosthodontics, 9th ed. St Louis: CV Mosby, 1995: King GE. Dual-path design for removable partial dentures. J Prosthet Dent 1978;39: Krol AJ, Finzen FC. Rotational path removable partial dentures, Part 1: Replacement of posterior teeth. Int J Prosthodont 1988;1: Jacobson TE, Krol AJ. Rotational path removable partial denture design. J Prosthet Dent 1982;48:
Original Article. Masako Yanagawa a, Kenji Fueki b and Takashi Ohyama c
 J Med Dent Sci 2004; 51: 115 119 Original Article Influence of length of food platform on masticatory performance in patients missing unilateral mandibular molars with distal extension removable partial
J Med Dent Sci 2004; 51: 115 119 Original Article Influence of length of food platform on masticatory performance in patients missing unilateral mandibular molars with distal extension removable partial
Removable partial dentures
 Removable partial dentures Feb, 4, 2015 McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics, Twelfth Edition Carr, Alan B 1 Prosthesis that replaces the missing teeth and associated supporting structures in a
Removable partial dentures Feb, 4, 2015 McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics, Twelfth Edition Carr, Alan B 1 Prosthesis that replaces the missing teeth and associated supporting structures in a
Surveying. 3rd year / College of Dentistry/University of Baghdad ( ) Page 1
 د. فائزة Lec.3 Prosthodontics Surveying The ideal requirements for successful removable partial denture are: 1. Be easily inserted and removed by the patient. 2. Resist dislodging forces. 3. It should
د. فائزة Lec.3 Prosthodontics Surveying The ideal requirements for successful removable partial denture are: 1. Be easily inserted and removed by the patient. 2. Resist dislodging forces. 3. It should
Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers
 Turk J Med Sci 31 (2001) 445-449 TÜB TAK Filiz KEYF Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers Received: November 30,
Turk J Med Sci 31 (2001) 445-449 TÜB TAK Filiz KEYF Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers Received: November 30,
Indirect retainers. 1 i
 8 1 i Indirect retainers Factors Influencing Effectiveness Indirect Retainers Auxiliary Functions Indirect Retainers Forms Indirect Retainers Auxiliary occlusal rest Canine extensions fiom occlusal rests
8 1 i Indirect retainers Factors Influencing Effectiveness Indirect Retainers Auxiliary Functions Indirect Retainers Forms Indirect Retainers Auxiliary occlusal rest Canine extensions fiom occlusal rests
DL 313 Removable Partial Dentures II
 DL 313 Removable Partial Dentures II Survey & Design Survey The procedure of studying the relative parallelism or lack of parallelism of the teeth and associated structures so as to select a path of placement
DL 313 Removable Partial Dentures II Survey & Design Survey The procedure of studying the relative parallelism or lack of parallelism of the teeth and associated structures so as to select a path of placement
DENT Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008
 University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2008-01 DENT 718 - Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008 Shotwell, Jeffrey Shotwell, J. (2008, April 23) Advanced Topics in Removable
University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2008-01 DENT 718 - Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008 Shotwell, Jeffrey Shotwell, J. (2008, April 23) Advanced Topics in Removable
SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015
 SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015 Dental Surveyor: It is a mechanical device used to determine the relative parallelism of the teeth surfaces and the undercuts areas in relation to
SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015 Dental Surveyor: It is a mechanical device used to determine the relative parallelism of the teeth surfaces and the undercuts areas in relation to
Clasp design. Many RPD design principles are based. prosthetics PRACTICE
 8 J. Clasp design C. Davenport, 1 R. M. Basker, 2 J. R. Heath, 3 J. P. Ralph, 4 P-O. Glantz, 5 and P. Hammond, 6 PRACTICE In this article statements related to the design of clasps are listed and discussed.
8 J. Clasp design C. Davenport, 1 R. M. Basker, 2 J. R. Heath, 3 J. P. Ralph, 4 P-O. Glantz, 5 and P. Hammond, 6 PRACTICE In this article statements related to the design of clasps are listed and discussed.
DENT Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008
 University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2008-01 DENT 718 - Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008 Shotwell, Jeffrey Shotwell, J. (2008, April 23) Advanced Topics in Removable
University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2008-01 DENT 718 - Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008 Shotwell, Jeffrey Shotwell, J. (2008, April 23) Advanced Topics in Removable
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama
 Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
It has been proposed that partially edentulous maxillectomy
 CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
Principles of. By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah
 Principles of By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah 1. Utilize what's present: Whenever possible, select a design that fits the teeth and soft tissues, rather than choosing one that requires tissue alteration. When minimal
Principles of By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah 1. Utilize what's present: Whenever possible, select a design that fits the teeth and soft tissues, rather than choosing one that requires tissue alteration. When minimal
Frame designed partial prosthesis for the rehabilitation of a maxillectomy patient
 VARIA Frame designed partial prosthesis for the rehabilitation of a maxillectomy patient Sorin Popºor, Lia Maria Coman Târgu Mureº, Romania Summary This article is a case report and it describes a technique
VARIA Frame designed partial prosthesis for the rehabilitation of a maxillectomy patient Sorin Popºor, Lia Maria Coman Târgu Mureº, Romania Summary This article is a case report and it describes a technique
Comparison of Different Methods of Abutment Splinting and Attachments on Teeth Kinetics (Part I)
 wjd Ahmed N Elsherbini, Wilhelm Niedermeier Original Article 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1464 Comparison of Different Methods of Abutment Splinting and Attachments on Teeth Kinetics (Part I) 1 Ahmed N Elsherbini,
wjd Ahmed N Elsherbini, Wilhelm Niedermeier Original Article 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1464 Comparison of Different Methods of Abutment Splinting and Attachments on Teeth Kinetics (Part I) 1 Ahmed N Elsherbini,
AESTHETIC DESIGNS IN REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURES
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5738 AESTHETIC DESIGNS IN REMOVABLE
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5738 AESTHETIC DESIGNS IN REMOVABLE
Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License.
 Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Copyright 2008, Jeffrey Shotwell The following information is intended to inform
Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Copyright 2008, Jeffrey Shotwell The following information is intended to inform
Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I.
 Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I. Removable dentures Partial Complete (full) lenka.roubalikova@tiscali.cz 2 Prosthetic dentistry replacement of Damaged teeth reconstruction of the crown (inlays, crowns)
Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I. Removable dentures Partial Complete (full) lenka.roubalikova@tiscali.cz 2 Prosthetic dentistry replacement of Damaged teeth reconstruction of the crown (inlays, crowns)
م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION
 Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
Removable Partial Dentures
 Removable Partial Dentures Replacement of missing teeth Fixed partial denture Removable partial denture Complete removable Transitional denture Partial removable Implant retained prosthodontics No prosthetic
Removable Partial Dentures Replacement of missing teeth Fixed partial denture Removable partial denture Complete removable Transitional denture Partial removable Implant retained prosthodontics No prosthetic
Component parts of Chrome Cobalt Removable Partial Denture
 Lec. 5 د.بسام الطريحي Component parts of Chrome Cobalt Removable Partial Denture Major connectors: Are either bars or plates, the difference between them is in the amount of tissue covers. Plates are broad
Lec. 5 د.بسام الطريحي Component parts of Chrome Cobalt Removable Partial Denture Major connectors: Are either bars or plates, the difference between them is in the amount of tissue covers. Plates are broad
Arrangement of the artificial teeth:
 Lecture Prosthodontic Dr. Osama Arrangement of the artificial teeth: It s the placement of the teeth on a denture with definite objective in mind or it s the setting of teeth on temporary bases. Rules
Lecture Prosthodontic Dr. Osama Arrangement of the artificial teeth: It s the placement of the teeth on a denture with definite objective in mind or it s the setting of teeth on temporary bases. Rules
Stress distribution within circumferential clasp arms
 Journal of Oral Rehabilitation, 1976, Volume 3, pages 387-394 Stress distribution within circumferential clasp arms H. MORRIS, J. W. FARAH, R. G. CRAIG and J. A. A. HOOD Veterans Administration Hospital,
Journal of Oral Rehabilitation, 1976, Volume 3, pages 387-394 Stress distribution within circumferential clasp arms H. MORRIS, J. W. FARAH, R. G. CRAIG and J. A. A. HOOD Veterans Administration Hospital,
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This
 1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
Dual Path: A Concept to Improve the Esthetic Replacement of Missing Anterior Teeth with a Removable Partial Denture
 Dual Path: A Concept to Improve the Esthetic Replacement of Missing Anterior Teeth with a Removable Partial Denture Adriana da Fonte Porto Carreiro, DDS, MSc, PhD, 1 Ana Lucia Machado, DDS, MSc, PhD, 2
Dual Path: A Concept to Improve the Esthetic Replacement of Missing Anterior Teeth with a Removable Partial Denture Adriana da Fonte Porto Carreiro, DDS, MSc, PhD, 1 Ana Lucia Machado, DDS, MSc, PhD, 2
Construction of Removable Partial Denture
 Construction of Removable Partial Denture Peter Hermann Department of Prosthodontics Semmelweis University Treatment options for edentulous spaces Fixed prosthodontics (crowns/bridges) Removable prosthodontics
Construction of Removable Partial Denture Peter Hermann Department of Prosthodontics Semmelweis University Treatment options for edentulous spaces Fixed prosthodontics (crowns/bridges) Removable prosthodontics
ACRYLIC REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE(RPD)
 ACRYLIC REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE(RPD) is a dental prosthesis which artificially supplies teeth and associated structure in a partially edentulous arch, made from acrylic resin and can be inserted and
ACRYLIC REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE(RPD) is a dental prosthesis which artificially supplies teeth and associated structure in a partially edentulous arch, made from acrylic resin and can be inserted and
CLASSIFICATION OF RPDs AND PARTIALLY EDENTULOUS ARCHES
 د.حكمت جميل Lec: 2 Prosthodontic CLASSIFICATION OF RPDs AND PARTIALLY EDENTULOUS ARCHES The classification of RPDs and partially edentulous arches simplifies communication and discussions. Requirements
د.حكمت جميل Lec: 2 Prosthodontic CLASSIFICATION OF RPDs AND PARTIALLY EDENTULOUS ARCHES The classification of RPDs and partially edentulous arches simplifies communication and discussions. Requirements
Arrangement of posterior artificial teeth Standardized parameters Curve of Wilson Curve of Spee
 . Arrangement of posterior artificial teeth Posterior teeth are set up in tight centric occlusion. The mandibular teeth are set in the wax occlusion rim over the residual ridge in their ideal buccolingual
. Arrangement of posterior artificial teeth Posterior teeth are set up in tight centric occlusion. The mandibular teeth are set in the wax occlusion rim over the residual ridge in their ideal buccolingual
SCD Case Study. Attachments in Prosthodontics
 SCD Case Study Attachments in Prosthodontics Precision attachments are retention units milled out of alloy. They have male and female parts that fit together with tolerances of 10 microns. It is important
SCD Case Study Attachments in Prosthodontics Precision attachments are retention units milled out of alloy. They have male and female parts that fit together with tolerances of 10 microns. It is important
Corresponding author: *Heba Wageh Abo-Zaed Elsaed. DOI: / Page
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. II (July. 2017), PP 114-119 www.iosrjournals.org Double-Arm Clasp with Anterior Placed
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. II (July. 2017), PP 114-119 www.iosrjournals.org Double-Arm Clasp with Anterior Placed
Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the application of attachment for obturator framework in unilateral maxillary defect
 Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 2007 Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the application of attachment for obturator framework in unilateral maxillary defect S. JIAN*, J. TING*, T. YING &W.DONG-MEI
Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 2007 Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the application of attachment for obturator framework in unilateral maxillary defect S. JIAN*, J. TING*, T. YING &W.DONG-MEI
Journal of American Science 2010;6(9) Emiel A. M. Hanna *1 and Salah A. F. Hegazy 2
 Modified Rotation Joint Connection Unite Versus Double Aker Clasp used for Bracing of Maxillary unilateral Free End Removable Partial Dentures (In Vitro Analysis of Stresses on Principle Abutments and
Modified Rotation Joint Connection Unite Versus Double Aker Clasp used for Bracing of Maxillary unilateral Free End Removable Partial Dentures (In Vitro Analysis of Stresses on Principle Abutments and
Comparison between Acetal Resin and Cobalt-Chromium. Removable Partial Denture Clasp Retention: An in vitro Study.
 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1076 Tarek ORIGINAL Mohamed RESEARCH et al Comparison between Acetal Resin and Cobalt-Chromium Removable Partial Denture Clasp Retention: An in vitro Study Tarek Mohamed, Osama
10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1076 Tarek ORIGINAL Mohamed RESEARCH et al Comparison between Acetal Resin and Cobalt-Chromium Removable Partial Denture Clasp Retention: An in vitro Study Tarek Mohamed, Osama
Concepts of occlusion Balanced occlusion. Monoplane occlusion. Lingualized occlusion. Figure (10-1)
 Any contact between teeth of opposing dental arches; usually, referring to contact between the occlusal surface. The static relationship between the incising or masticatory surfaces of the maxillary or
Any contact between teeth of opposing dental arches; usually, referring to contact between the occlusal surface. The static relationship between the incising or masticatory surfaces of the maxillary or
INDIRECT RETENTION REVISITED: RISKS, BENEFITS AND PARADIGM-SHIFT IN REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURES
 Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Integrity-Reliability-Failure, Porto/Portugal 24-28 July 2016 Editors J.F. Silva Gomes and S.A. Meguid Publ. INEGI/FEUP (2016) PAPER REF: 6413 INDIRECT
Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Integrity-Reliability-Failure, Porto/Portugal 24-28 July 2016 Editors J.F. Silva Gomes and S.A. Meguid Publ. INEGI/FEUP (2016) PAPER REF: 6413 INDIRECT
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
CHAPTER 9 DIRECT RETAINERS REQUIREMENTS OF A DIRECT RETAINER
 CHAPTER 9 DIRECT RETAINERS DEFINITIONS RETENTION is resistance to movement of a denture away from the teeth and/or tissues along the path of placement of the prosthesis. Most retention of RPDs is provided
CHAPTER 9 DIRECT RETAINERS DEFINITIONS RETENTION is resistance to movement of a denture away from the teeth and/or tissues along the path of placement of the prosthesis. Most retention of RPDs is provided
INDIAN DENTAL JOURNAL
 ATTACHMENT RETAINED CAST PARTIAL DENTURE USING RHEIN 83 OT-CAP Dr. Charu Gupta 1 Dr. Harshul Sharma 2 Dr. Merrily Nongsiej 3 Dr. AbhinavShekhar 4 1 Senior Resident, Department of Prosthodontics, King George
ATTACHMENT RETAINED CAST PARTIAL DENTURE USING RHEIN 83 OT-CAP Dr. Charu Gupta 1 Dr. Harshul Sharma 2 Dr. Merrily Nongsiej 3 Dr. AbhinavShekhar 4 1 Senior Resident, Department of Prosthodontics, King George
Jaw relation registration in RPD
 Jaw relation registration in RPD Why to Record the Jaw Relations? To establish and maintain a harmonious relationship with all oral structures and to provide a masticatory apparatus that is efficient and
Jaw relation registration in RPD Why to Record the Jaw Relations? To establish and maintain a harmonious relationship with all oral structures and to provide a masticatory apparatus that is efficient and
Selection and arrangement of teeth in rpd
 Selection and arrangement of teeth in rpd upon completion of the articulator mounting and a thorough assessment of the occlusal requirements, the practitioner should be able to perform the proper arrangement
Selection and arrangement of teeth in rpd upon completion of the articulator mounting and a thorough assessment of the occlusal requirements, the practitioner should be able to perform the proper arrangement
Occlusal rehabilitation of posterior fixed prostheses: A clinical report
 J Korean Acad Prosthodont : Volume 39, Number 3, 2001 Occlusal rehabilitation of posterior fixed prostheses: A clinical report In-Sung Yeo, DDS a, and Jae-Ho Yang, DDS, MSD, PhD b College of Dentistry,
J Korean Acad Prosthodont : Volume 39, Number 3, 2001 Occlusal rehabilitation of posterior fixed prostheses: A clinical report In-Sung Yeo, DDS a, and Jae-Ho Yang, DDS, MSD, PhD b College of Dentistry,
J Bagh College Dentistry Vol. 21(1), 2009 The effect of using different..
 The effect of using different impression techniques and materials on vertical tissue displacement in free end extension ridges. (Dental survey and clinical study) Rawia. N. AL- Dafaii, B.D.S., MSc. (1)
The effect of using different impression techniques and materials on vertical tissue displacement in free end extension ridges. (Dental survey and clinical study) Rawia. N. AL- Dafaii, B.D.S., MSc. (1)
Cleft lip and palate; oronasal istula; prosthetic treatment; O ring attachment
 Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 4 (2018) Issue 6 ISSN 2379-1039 Prosthetic treatment of a unilateral left cleft lip and palate with anoronasal istula: A case report Yesiboli Yeerken,
Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 4 (2018) Issue 6 ISSN 2379-1039 Prosthetic treatment of a unilateral left cleft lip and palate with anoronasal istula: A case report Yesiboli Yeerken,
The path of placement of a removable partial denture: a microscope based approach to survey and design
 http://jap.or.kr J Adv Prosthodont 2015;7:76-84 http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2015.7.1.76 The path of placement of a removable partial denture: a microscope based approach to survey and design John Sami
http://jap.or.kr J Adv Prosthodont 2015;7:76-84 http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2015.7.1.76 The path of placement of a removable partial denture: a microscope based approach to survey and design John Sami
Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois Phone: Fax:
 Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D. 2325 N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois 60614 Phone: 312-608-6881 Fax: 773-296-0601 Samanthawchou@gmail.com What is our role as the dentist? "We live in a culture in which people
Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D. 2325 N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois 60614 Phone: 312-608-6881 Fax: 773-296-0601 Samanthawchou@gmail.com What is our role as the dentist? "We live in a culture in which people
In 1977, Lew1 developed a passive
 CLINICAL AN OVERVIEW OF THE LEW ATTACHMENT: CLINICAL REPORTS Jack Piermatti, DMD Sheldon Winkler, DDS KEY WORDS Lew attachment Atrophic mandible Subperiosteal implant Root form implant Although the Lew
CLINICAL AN OVERVIEW OF THE LEW ATTACHMENT: CLINICAL REPORTS Jack Piermatti, DMD Sheldon Winkler, DDS KEY WORDS Lew attachment Atrophic mandible Subperiosteal implant Root form implant Although the Lew
Case report: Lingualized occlusion -A better way for enhancing function & esthetic
 Case report: Lingualized occlusion -A better way for enhancing function & esthetic 1Dr. Vishrut Shah, 2 Dr. Sunil Dhaded, 3 Dr. Chandrashekar Sajjan 1Post graduate student, Department of Prosthodontics,
Case report: Lingualized occlusion -A better way for enhancing function & esthetic 1Dr. Vishrut Shah, 2 Dr. Sunil Dhaded, 3 Dr. Chandrashekar Sajjan 1Post graduate student, Department of Prosthodontics,
The aim of this study was to evaluate the use of esthetic twin-flex clasp on remaining
 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 163:169 January, 2008 Twin-Flex clasp as an esthetic approach for remaining central incisor abutment in unilateral maxillectomy cases Salah AF Hegazy 1 and Emiel AM
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 163:169 January, 2008 Twin-Flex clasp as an esthetic approach for remaining central incisor abutment in unilateral maxillectomy cases Salah AF Hegazy 1 and Emiel AM
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note
 Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Chapter 12. Prosthodontics
 Chapter 12 Prosthodontics Golbarg Kolahi 1 Prosthesis [prahs-thee-sis] A replacement for a missing body part Golbarg Kolahi 2 Prosthesis In the dental field, it is a fixed or removable appliance replacing
Chapter 12 Prosthodontics Golbarg Kolahi 1 Prosthesis [prahs-thee-sis] A replacement for a missing body part Golbarg Kolahi 2 Prosthesis In the dental field, it is a fixed or removable appliance replacing
Reproducibility of Interocclusal Recording for Mandibular Removable Partial Denture in Bilateral Distal Extension Cases
 J Med Dent Sci 2003; 50: 53 61 Original Article Reproducibility of Interocclusal Recording for Mandibular Removable Partial Denture in Bilateral Distal Extension Cases Hiroshi Togano, Masayuki Hideshima
J Med Dent Sci 2003; 50: 53 61 Original Article Reproducibility of Interocclusal Recording for Mandibular Removable Partial Denture in Bilateral Distal Extension Cases Hiroshi Togano, Masayuki Hideshima
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences
 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences www.ijmrhs.com Volume 3 Issue 2 (April - Jun) Coden: IJMRHS Copyright @2014 ISSN: 2319-5886 Received: 1 st Jan 2014 Revised: 5 th Feb 2014 Accepted:
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences www.ijmrhs.com Volume 3 Issue 2 (April - Jun) Coden: IJMRHS Copyright @2014 ISSN: 2319-5886 Received: 1 st Jan 2014 Revised: 5 th Feb 2014 Accepted:
Distal extension base removable partial dentures exhibit composite type of support
 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (3), 379:393 September, 2008 stress analysis study of two treatment modalities rehabilitating distal extension cases with few remaining natural teeth Magdy Eid Mohammed
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (3), 379:393 September, 2008 stress analysis study of two treatment modalities rehabilitating distal extension cases with few remaining natural teeth Magdy Eid Mohammed
M.D.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION. (Revised Regulations) Branch VI PROSTHODONTICS. (For Candidates admitted from onwards)
 September 2008 [KT 389] Sub. Code: 2422. (Revised Regulations) Branch VI PROSTHODONTICS (For Candidates admitted from 2004-2005 onwards) Paper II REMOVABLE PROSTHODONTICS AND Time : Three hours Q.P. Code
September 2008 [KT 389] Sub. Code: 2422. (Revised Regulations) Branch VI PROSTHODONTICS (For Candidates admitted from 2004-2005 onwards) Paper II REMOVABLE PROSTHODONTICS AND Time : Three hours Q.P. Code
Clinical Management of Kennedy Class II Cases Using Osseointegrated Dental Implants
 Clinical Management of Kennedy Class II Cases Using Osseointegrated Dental Implants Thesis Submitted in the Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Doctor Degree in Removable Prosthodontics By
Clinical Management of Kennedy Class II Cases Using Osseointegrated Dental Implants Thesis Submitted in the Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Doctor Degree in Removable Prosthodontics By
Masticatory function after unilateral distal extension removable partial denture treatment: intra-individual comparison with opposite dentulous side
 J Med Dent Sci 2005; 52: 35 41 Original Article Masticatory function after unilateral distal extension removable partial denture treatment: intra-individual comparison with opposite dentulous side Wacharasak
J Med Dent Sci 2005; 52: 35 41 Original Article Masticatory function after unilateral distal extension removable partial denture treatment: intra-individual comparison with opposite dentulous side Wacharasak
Removable Partial Denture Design: A Study of a Selected Population in Saudi Arabia
 Removable Partial Denture Design: A Study of a Selected Population in Saudi Arabia Abstract Determination of the incidence of various classes of removable partial dentures (RPDs) including their designs
Removable Partial Denture Design: A Study of a Selected Population in Saudi Arabia Abstract Determination of the incidence of various classes of removable partial dentures (RPDs) including their designs
In vitro Assessment of Clasps of Cobalt-Chromium and Nickel-titanium Alloys in Removable Prosthesis
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Cobalt-Chromium 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1836 and Nickel-titanium Clasps In vitro Assessment of Clasps of Cobalt-Chromium and Nickel-titanium Alloys in Removable Prosthesis 1 Mohammed
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Cobalt-Chromium 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1836 and Nickel-titanium Clasps In vitro Assessment of Clasps of Cobalt-Chromium and Nickel-titanium Alloys in Removable Prosthesis 1 Mohammed
The Reinforced Removable Retainer
 The Reinforced Removable Retainer Abstract The aim of this paper is to present a new type of orthodontic removable retainer, which is of great help to the orthodontist as well as to the patient. The procedures
The Reinforced Removable Retainer Abstract The aim of this paper is to present a new type of orthodontic removable retainer, which is of great help to the orthodontist as well as to the patient. The procedures
Mandibular ridge changes after adaptation. An issue of shortened dental arch to be considered from changes of soft tissues after unattended tooth loss
 (Journal of Dental Outlook, Vol.110, Vol.6:1021~1027, Japan 2007. An issue of shortened dental arch to be considered from changes of soft tissues after unattended tooth loss Dr. Jiro Abe Abe Dental Clinic
(Journal of Dental Outlook, Vol.110, Vol.6:1021~1027, Japan 2007. An issue of shortened dental arch to be considered from changes of soft tissues after unattended tooth loss Dr. Jiro Abe Abe Dental Clinic
International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Science (IJDOS) ISSN:
 International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Science (IJDOS) ISSN: 2377-8075 A Novel Functional Impression Procedure for Distal-Extension Removable Partial Dentures Li QL *, Cao Y Case Report Department
International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Science (IJDOS) ISSN: 2377-8075 A Novel Functional Impression Procedure for Distal-Extension Removable Partial Dentures Li QL *, Cao Y Case Report Department
DIAGNOSTIC/PREVENTIVE SERVICES
 DIAGNOSTIC/PREVENTIVE SERVICES Diagnostic Services D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 100% 100% D0140 Limited oral evaluation problem focused 100% 100% D0150 Comprehensive oral evaluation 100% 100% D0160 Detailed
DIAGNOSTIC/PREVENTIVE SERVICES Diagnostic Services D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 100% 100% D0140 Limited oral evaluation problem focused 100% 100% D0150 Comprehensive oral evaluation 100% 100% D0160 Detailed
Paper submission. Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case
 Paper submission Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case A. Izumida Department of Comprehensive Dentistry, Tohoku
Paper submission Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case A. Izumida Department of Comprehensive Dentistry, Tohoku
In Vitro Comparative Study of Retention of Maxillary Kennedy Class I Removable Partial Denture Retained with Four Different Designs of Esthetic Clasps
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Abstract In Vitro Comparative Study of Retention of Maxillary Kennedy Class I Removable Partial Denture Retained with Four Different Designs of
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Abstract In Vitro Comparative Study of Retention of Maxillary Kennedy Class I Removable Partial Denture Retained with Four Different Designs of
Occlusal Rehabilitation in a Partially Edentulous Patient with Lost Vertical Dimension Using Dental Implants: A Clinical Report
 Occlusal Rehabilitation in a Partially Edentulous Patient with Lost Vertical Dimension Using Dental Implants: A Clinical Report Azam Sadat Madani, DDS, MS; Amir Moeintaghavi, DDS, MS; Maryam Rezaeei, DDS,MS
Occlusal Rehabilitation in a Partially Edentulous Patient with Lost Vertical Dimension Using Dental Implants: A Clinical Report Azam Sadat Madani, DDS, MS; Amir Moeintaghavi, DDS, MS; Maryam Rezaeei, DDS,MS
Fixed Partial Denture
 University of Minnesota School of Dentistry Fixed Partial Denture Self-guided Instructional Material for Dental Students Authors Ranier M. Adarve, DMD, MS, MHPE Lisa Fedor James, DDS, Cert. Pros. Fixed
University of Minnesota School of Dentistry Fixed Partial Denture Self-guided Instructional Material for Dental Students Authors Ranier M. Adarve, DMD, MS, MHPE Lisa Fedor James, DDS, Cert. Pros. Fixed
4/15/2015. Secondary Impressions: Anatomic and Physiologic Impressions. April, 8, Impressions for tooth-supported RPDs
 Secondary Impressions: Anatomic and Physiologic Impressions Impressions for tooth-supported RPDs April, 8, 2015 Impressions for tooth and tissue supported RPDs In tooth-supported removable partial denture
Secondary Impressions: Anatomic and Physiologic Impressions Impressions for tooth-supported RPDs April, 8, 2015 Impressions for tooth and tissue supported RPDs In tooth-supported removable partial denture
Infraocclusion Treated with Removable Prosthesis on Occlusal Surface of Severely Attritioned Teeth
 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1051 Akinori Tasaka et al CASE REPORT Infraocclusion Treated with Removable Prosthesis on Occlusal Surface of Severely Attritioned Teeth Akinori Tasaka, Takayuki Ueda, Kaoru Sakurai
10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1051 Akinori Tasaka et al CASE REPORT Infraocclusion Treated with Removable Prosthesis on Occlusal Surface of Severely Attritioned Teeth Akinori Tasaka, Takayuki Ueda, Kaoru Sakurai
2015 Member Speaker Forum. Chair: L. Scott Brooksby, DDS, BS. Friday, October 23, :30 AM 3:45 PM. Coral Ballroom. 3.
 2015 Member Speaker Forum Chair: L. Scott Brooksby, DDS, BS Friday, October 23, 2015 11:30 AM 3:45 PM Coral Ballroom 3.25 CE Credits 11:30 a.m. 3:45 p.m. Member Speaker Forum 11:30 11:40 a.m. Introduction
2015 Member Speaker Forum Chair: L. Scott Brooksby, DDS, BS Friday, October 23, 2015 11:30 AM 3:45 PM Coral Ballroom 3.25 CE Credits 11:30 a.m. 3:45 p.m. Member Speaker Forum 11:30 11:40 a.m. Introduction
Occlusion and removable prosthodontics
 12 Occlusion and removable prosthodontics R. Jagger Synopsis Occlusal considerations for removable prostheses are essentially the same as for fixed restorations. The approach to establishing occlusion
12 Occlusion and removable prosthodontics R. Jagger Synopsis Occlusal considerations for removable prostheses are essentially the same as for fixed restorations. The approach to establishing occlusion
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 1:10 January, Ahmad Fahmy 1, Ehab M. Abuelroos 2 and Mohammad M. Nada 3
 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 1:10 January, 2008 Effect of Using Attachment on Implant Supported Distal Extension Lower Partial Over-dentures Ahmad Fahmy 1, Ehab M. Abuelroos 2 and Mohammad M.
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 1:10 January, 2008 Effect of Using Attachment on Implant Supported Distal Extension Lower Partial Over-dentures Ahmad Fahmy 1, Ehab M. Abuelroos 2 and Mohammad M.
Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options
 Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options First Name Last Name Objectives Identify the need and opportunity to treat full arch patients with fixed detachable
Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options First Name Last Name Objectives Identify the need and opportunity to treat full arch patients with fixed detachable
The main challenge in using the natural dentition
 Use of Osseointegrated Implants for Orthodontic Anchorage DIANA WEBER, DDS, MS STEVEN HANDEL, DMD DANIEL DUNHAM, DDS The main challenge in using the natural dentition for anchorage of minor tooth movements,
Use of Osseointegrated Implants for Orthodontic Anchorage DIANA WEBER, DDS, MS STEVEN HANDEL, DMD DANIEL DUNHAM, DDS The main challenge in using the natural dentition for anchorage of minor tooth movements,
Implant and Tooth Supported Full-Mouth Rehabilitation with Hobo Twin-Stage Technique
 10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1099 Koshika Tandon et al CASE REPORT Implant and Tooth Supported Full-Mouth Rehabilitation with Hobo Twin-Stage Technique Koshika Tandon, Ajay Singh, Himanshu Gupta, Rajdeep
10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1099 Koshika Tandon et al CASE REPORT Implant and Tooth Supported Full-Mouth Rehabilitation with Hobo Twin-Stage Technique Koshika Tandon, Ajay Singh, Himanshu Gupta, Rajdeep
Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path
 Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path Shogo Minagi, DDS, PhD, a Toshiyuki Tanaka, DDS, b Takashi Sato, DDS, PhD, c and Tadashi Matsunaga, DDS, PhD d Department
Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path Shogo Minagi, DDS, PhD, a Toshiyuki Tanaka, DDS, b Takashi Sato, DDS, PhD, c and Tadashi Matsunaga, DDS, PhD d Department
THE LOAD EXERTED BY REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE CLASPS CONFORMING TO AVERAGE TOOTH CURVATURES, IN CLINICALLY ENCOUNTERED UNDERCUTS.
 THE LOAD EXERTED BY REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE CLASPS CONFORMING TO AVERAGE TOOTH CURVATURES, IN CLINICALLY ENCOUNTERED UNDERCUTS. Noland Naidoo Student number: 586244 A research report submitted to the
THE LOAD EXERTED BY REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE CLASPS CONFORMING TO AVERAGE TOOTH CURVATURES, IN CLINICALLY ENCOUNTERED UNDERCUTS. Noland Naidoo Student number: 586244 A research report submitted to the
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE GOVERNMENT EXAMINATION SYLLABUS
 MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE GOVERNMENT EXAMINATION SYLLABUS OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE ACADEMIC YEAR 2016/2017 1 1. Biomechanics of
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE GOVERNMENT EXAMINATION SYLLABUS OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE ACADEMIC YEAR 2016/2017 1 1. Biomechanics of
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment
 Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
Effect of Different Clasps on Asymmetric Distal Extension Base Supporting Structures. Egypt. Cairo, Egypt.
 Effect of Different Clasps on Asymmetric Distal Extension Base Supporting Structures Fatma ELzahraa Awad 1, Asma Gadallah 2, Hana a Gamal Youssef 3,Yasser Shawky 3 1 - Professor of Removable Prosthodontics,
Effect of Different Clasps on Asymmetric Distal Extension Base Supporting Structures Fatma ELzahraa Awad 1, Asma Gadallah 2, Hana a Gamal Youssef 3,Yasser Shawky 3 1 - Professor of Removable Prosthodontics,
ROTATIONAL PATH PARTIAL DENTURES: AN UNDERUTILIZED TREATMENT MODALITY IN AESTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE
 PARTIAL DENTURES ROTATIONAL PATH PARTIAL DENTURES: AN UNDERUTILIZED TREATMENT MODALITY IN AESTHETIC DENTAL Adam Perry Tow 1a* 1 Department of Restorative Dental Sciences, College of Dentistry, University
PARTIAL DENTURES ROTATIONAL PATH PARTIAL DENTURES: AN UNDERUTILIZED TREATMENT MODALITY IN AESTHETIC DENTAL Adam Perry Tow 1a* 1 Department of Restorative Dental Sciences, College of Dentistry, University
Evaluation of Acetal Resin and Cobalt Chromium Clasp Deformation and Fatigue Resistance in Removable Partial Denture Clasps - An In Vitro Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Acetal Resin and Cobalt Chromium Clasp Deformation and Fatigue Resistance in Removable Partial Denture Clasps - An In Vitro Study Mohamed A.Helal 1, Ibrahiem A. Abd-Elrahman
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Acetal Resin and Cobalt Chromium Clasp Deformation and Fatigue Resistance in Removable Partial Denture Clasps - An In Vitro Study Mohamed A.Helal 1, Ibrahiem A. Abd-Elrahman
Mandibular implant-supported hybrid prostheses
 Occlusal Contacts of Edentulous Patients with Mandibular Hybrid Dentures Opposing Maxillary Complete Dentures Tetsuya Suzuki, DDS, PhD*/Hiroshi Kumagai, DDS, PhD**/ Nobuyuki Yoshitomi, DDS, PhD***/Edwin
Occlusal Contacts of Edentulous Patients with Mandibular Hybrid Dentures Opposing Maxillary Complete Dentures Tetsuya Suzuki, DDS, PhD*/Hiroshi Kumagai, DDS, PhD**/ Nobuyuki Yoshitomi, DDS, PhD***/Edwin
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics.
 In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
In Vitro Study of Reduction of Stress Transferred onto Tissues around Implants Using a Resilient Material in Maxillary Implant Overdentures
 J Med Dent Sci 2007; 54: 17 23 Original Article In Vitro Study of Reduction of Stress Transferred onto Tissues around Implants Using a Resilient Material in Maxillary Implant Overdentures Manabu Kanazawa,
J Med Dent Sci 2007; 54: 17 23 Original Article In Vitro Study of Reduction of Stress Transferred onto Tissues around Implants Using a Resilient Material in Maxillary Implant Overdentures Manabu Kanazawa,
Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of a Partially Edentulous Hemiglossectomy Patient: A Clinical Report
 case report 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1067 Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of a Partially Edentulous Hemiglossectomy Patient: A Clinical Report 1 Ragini Sudhakar Sanaye, 2 Sabita M Ram, 3 Naisargi Shah, 4
case report 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1067 Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of a Partially Edentulous Hemiglossectomy Patient: A Clinical Report 1 Ragini Sudhakar Sanaye, 2 Sabita M Ram, 3 Naisargi Shah, 4
Dimensional Accuracy of Optical Bite Registration in Single and Multiple Unit Restorations
 Ó Operative Dentistry, 2013, 38-3, 309-315 Dimensional Accuracy of Bite Registration in Single and Multiple Unit Restorations Y Iwaki N Wakabayashi Y Igarashi Clinical Relevance Based on the dimensional
Ó Operative Dentistry, 2013, 38-3, 309-315 Dimensional Accuracy of Bite Registration in Single and Multiple Unit Restorations Y Iwaki N Wakabayashi Y Igarashi Clinical Relevance Based on the dimensional
Nagri D et al. Linear occlusion and Neutral Zone recording for severely resorbed ridges
 Doi:10.21276/ledent.2018.02.01.02 Case Report LINEAR OCCLUSION AND NEUTRAL ZONE RECORDING USING TISSUE CONDITIONER REPORT OF A SEVERELY RESORBED RIDGE Divya Nagri, 1Ashish Kakkar, 2Neeraj Mittal, 3Lovely
Doi:10.21276/ledent.2018.02.01.02 Case Report LINEAR OCCLUSION AND NEUTRAL ZONE RECORDING USING TISSUE CONDITIONER REPORT OF A SEVERELY RESORBED RIDGE Divya Nagri, 1Ashish Kakkar, 2Neeraj Mittal, 3Lovely
INDICATIONS. Fixed Appliances are indicated when precise tooth movements are required
 DEFINITION Fixed Appliances are devices or equipments that are attached to the teeth, cannot be removed by the patient and are capable of causing tooth movement. INDICATIONS Fixed Appliances are indicated
DEFINITION Fixed Appliances are devices or equipments that are attached to the teeth, cannot be removed by the patient and are capable of causing tooth movement. INDICATIONS Fixed Appliances are indicated
Symposium on Occlusal Articulation. Mandibular Movement Recordings and Articulator Adjustments Simplified. Harry C. Lundeen, D.D.S.
 Symposium on Occlusal Articulation Mandibular Movement Recordings and Articulator Adjustments Simplified Harry C. Lundeen, D.D.S. Judging from the volume of writing that has appeared in the dental literature
Symposium on Occlusal Articulation Mandibular Movement Recordings and Articulator Adjustments Simplified Harry C. Lundeen, D.D.S. Judging from the volume of writing that has appeared in the dental literature
Strain on the Framework of a Mandibular Free-End Saddle Partial Denture Under Load*
 1'01,. 1, PP. 263-274 (1967) Strain on the Framework of a Mandibular Free-End Saddle Partial Denture Under Load* R. G. CRAIG and F. A. PEYTON, School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Mirhigan.@lo4
1'01,. 1, PP. 263-274 (1967) Strain on the Framework of a Mandibular Free-End Saddle Partial Denture Under Load* R. G. CRAIG and F. A. PEYTON, School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Mirhigan.@lo4
Dental Removable Prosthodontics: Partial Dentures
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dental Removable Prosthodontics: Partial Dentures Unit code: F1MD 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is about the theory and skills
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Dental Removable Prosthodontics: Partial Dentures Unit code: F1MD 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is about the theory and skills
FR Attachment Instructions Removable Partial Dentures
 www.preat.com 800-232-7732 FR Attachment Instructions Removable Partial Dentures 1 2 Adjust the master cast on mounting platform of the surveyor to the chosen angle of insertion. Check to be sure the tooth
www.preat.com 800-232-7732 FR Attachment Instructions Removable Partial Dentures 1 2 Adjust the master cast on mounting platform of the surveyor to the chosen angle of insertion. Check to be sure the tooth
Charles Kim. Step 1 Kennedy classification
 Step 3 Survey cast Step 2 Anatomical landmarks Step 1 Kennedy classification Classification criteria -Class 1: bilateral edentulous areas posterior to the remaining teeth -Class 2: unilateral edentulous
Step 3 Survey cast Step 2 Anatomical landmarks Step 1 Kennedy classification Classification criteria -Class 1: bilateral edentulous areas posterior to the remaining teeth -Class 2: unilateral edentulous
Cast Partial Denture Improving Emergence and Masticatory Function - A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. VI (Sep. 2015), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Cast Partial Denture Improving Emergence
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. VI (Sep. 2015), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Cast Partial Denture Improving Emergence
CAUSE OF TECHNICAL FAILURES OF CONICAL CROWN-RETAINED DENTURE (CCRD): A CLINICAL REPORT
 J Korean Acad Prosthodont : Volume 41, Number 6, 2003 CAUSE OF TECHNICAL FAILURES OF CONICAL CROWN-RETAINED DENTURE (CCRD): A CLINICAL REPORT Yang-Jin Yi, D.D.S.,M.S.D.,Ph.D., Lee-Ra Cho, D.D.S.,M.S.D.,Ph.D.,
J Korean Acad Prosthodont : Volume 41, Number 6, 2003 CAUSE OF TECHNICAL FAILURES OF CONICAL CROWN-RETAINED DENTURE (CCRD): A CLINICAL REPORT Yang-Jin Yi, D.D.S.,M.S.D.,Ph.D., Lee-Ra Cho, D.D.S.,M.S.D.,Ph.D.,
Controlled Space Closure with a Statically Determinate Retraction System
 Original Article Controlled Space Closure with a Statically Determinate Retraction System Kwangchul Choy, DDS, MS, PhD a ; Eung-Kwon Pae, DDS, MSc, PhD b ; Kyung-Ho Kim, DDS, MS, PhD c ; Young Chel Park,
Original Article Controlled Space Closure with a Statically Determinate Retraction System Kwangchul Choy, DDS, MS, PhD a ; Eung-Kwon Pae, DDS, MSc, PhD b ; Kyung-Ho Kim, DDS, MS, PhD c ; Young Chel Park,
Removable Partial Denture Manual. Robert W. Loney, DMD, MS 2008
 Removable Partial Denture Manual Robert W. Loney, DMD, MS 2008 Removable Partial Denture Manual Robert W. Loney, DMD, MS 2008 Table of Contents - i Table of Contents Introduction to Removable Partial
Removable Partial Denture Manual Robert W. Loney, DMD, MS 2008 Removable Partial Denture Manual Robert W. Loney, DMD, MS 2008 Table of Contents - i Table of Contents Introduction to Removable Partial
IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE AND MATERIALS
 IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE AND MATERIALS DR ZURYATI AB GHANI BDS (WALES), Grad Dip Clin Dent (Adelaide), Doctor in Clinical Dentistry (prosthodontics( prosthodontics), Adelaide, FRACDS (Australia). 29.06.08
IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE AND MATERIALS DR ZURYATI AB GHANI BDS (WALES), Grad Dip Clin Dent (Adelaide), Doctor in Clinical Dentistry (prosthodontics( prosthodontics), Adelaide, FRACDS (Australia). 29.06.08
PROSTHETIC REHABILITATION OF MAXILLARY DEFECTS: A REVIEW
 Review Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 01,Issue 04 PROSTHETIC REHABILITATION OF MAXILLARY DEFECTS: A REVIEW Sanjeeva Rao Olepu 1, Mithilesh Kumar 2,Ramu Rajesh Babu 3,Tanvi
Review Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 01,Issue 04 PROSTHETIC REHABILITATION OF MAXILLARY DEFECTS: A REVIEW Sanjeeva Rao Olepu 1, Mithilesh Kumar 2,Ramu Rajesh Babu 3,Tanvi
