S John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Spain; 2 University of Milano, Milan, Italy
|
|
|
- Kathleen Barber
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Clin Periodontol 2014; 41 (Suppl. 15): S92 S97 doi: /jcpe Surgical techniques on periodontal plastic surgery and soft tissue regeneration: Consensus Report of Group 3 of the 10th European Workshop on Periodontology Mariano Sanz 1 and Massimo Simion 2 on behalf of Working Group 3 of the European Workshop on Periodontology * 1 University Complutense of Madrid, Madrid, Spain; 2 University of Milano, Milan, Italy Sanz M, Simion M. Surgical techniques on periodontal plastic surgery and soft tissue regeneration: consensus report of Group 3 of the 10th European Workshop on Periodontology. J Clin Periodontol 2014; 41 (Suppl. 15): S92 S97. doi: /jcpe Abstract Background: The scope was to review the three main clinical indications in periodontal plastic surgical procedures. Aims: To review the fundamental principles in periodontal plastic surgery, the main surgical designs in flap surgery applied to the treatment of recessions, periimplant soft tissue deficiencies and soft tissue ridge augmentation, as well as the surgical principles of using autologous connective tissue grafts and soft tissue substitutes. Fundamental Principles in Plastic Surgery: In the pre-operative phase, the key elements are the control of prognostic factors affecting the patient, namely oral hygiene, tobacco smoking cessation and systemic disease control. In the operative phase, the principles of flap design, mobilization, advancement, adaptation and stabilization. In the post-operative phase infection control, including effective oral hygiene measures, antiseptic treatment and other medications. Critical Elements in Flap Design and Surgical Execution: In single recession defects, the most widely used flap technique is the coronally advanced flap and in specific clinical situations the laterally positioned flap. In multiple recession defects, the number of defects and their location and depth guide the surgical design, being one design with and the other without vertical releasing incisions. When flaps are used in combination with grafts the tunnel flap is also used extensively. Critical Elements in the Use of Soft Tissue Replacement Grafts: The key elements are the donor site selection and harvesting technique, its tissue integration and volume stability. Clinical Recommendations: Given the current evidence, various clinical recommendations on the use of flaps and grafts are provided. Key words: connective tissue grafts; periimplant deficiencies; periodontal plastic surgery; recessions; soft tissue substitutes; surgical designs Accepted for publication 28 November 2013 S92
2 Consensus report of Working Group 3 S93 Conflict of interest and source of funding statement This workshop was financially supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Geistlich AG, Switzerland to the European Federation of Periodontology. Group participants filed detailed conflict of interest statement related to the topic of the workshop. Disclosures included: having received speakers fees, consulting fees, and/or research grants from Geistlich AG, the Osteology Foundation (an independent body financially supported by Geistlich AG), Straumann AG, the ITI foundation (an independent body financially supported by Straumann AG), Organogenesis, Zimmer, Datum and Nobelbiocare. *Group 3 participants: Frank Abbas, Sofia Aroca, Zvi Artzi, Rino Burkhardt, Pierpaolo Cortellini, Korkud Demirel, Virginie Monnet Corti, Alberto Ortiz-Vigon, Giulio Rasperini, Massimo de Sanctis, Ignacio Sanz-Sanchez, Alberto Sicilia, Moshe Goldstein, Kay Horsch, Markus Hu rzeler, Niklaus P. Lang, Istvan Urban, Selcuk Yilmaz, Ion Zabalegui, Otto Zuhr. According to the Proceedings of the World Workshop in Periodontics (1996): Periodontal (and periimplant) plastic surgery encompasses the surgical procedures performed to prevent or correct anatomical, developmental, traumatic or diseaseinduced defects of the masticatory mucosa (gingiva), lining mucosa (alveolar mucosa) or bone. Based on these proceedings, the scope of this Workshop Group 3, however, was restricted to the three main indications in current clinical practice: recession treatment at teeth and/or soft tissue deficiencies treatment at implant sites and soft tissue ridge augmentation associated with implants or fixed dental prosthesis. The objective of this consensus report was to review the fundamental principles in periodontal plastic surgery, the main surgical designs in flap surgery applied to the treatment of recessions, peri-implant soft tissue deficiencies and soft tissue ridge augmentation, as well as the surgical principles of using autologous connective tissue grafts and soft tissue substitutes. Fundamental Principles in Periodontal Plastic Surgery The basic principles in periodontal flap surgery have to be observed preoperatively, during the intervention and post-operatively (Burkhardt & Lang 2014). The key elements in the pre-operative phase are as follows The impact of oral hygiene and infection control The role of an infection-free oral cavity and hence, a plaque free dentition has been demonstrated to be the key prerequisites for optimal outcomes of periodontal surgical procedures. Consequently, individually optimal standards of biofilm control and professional cause-related therapy have to precede the surgical intervention. In light of the aetiological impact of traumatic tooth brushing on the formation of recessions appropriate preventive measures have to be implemented. The impact of adverse habits: tobacco smoking It has been recognized that heavy ( 20 cigarettes/day) smoking negatively affects surgical treatment outcomes. Moreover, a dose-dependent negative influence has been demonstrated in recession coverage. Hence, smoking cessation counselling prior to plastic surgical interventions is strongly recommended. It has to be realized, however, that successful smoking cessation may require several months to years to result in a positive impact. Therefore, smoking cessation should be implemented as early as possible. Moreover, it has to be realized that inadequate biofilm control and smoking have been shown to have synergistic negative effects. Impact of impaired health (systemic diseases) As for any surgical procedure, systemic conditions such as diabetes mellitus may have a severe negative effect on wound healing, whereby infection may jeopardize the outcome. Also, the degree of diabetic
3 S94 Sanz and Simion control as expressed by the level of HbA1C and the duration of experienced diabetes may have a dosedependent impact. Consequently, it is advisable to consult with the patient s diabetologist and to request a documentation of the HbA1C level prior to the surgical intervention. Furthermore, the issue of a very low infective burden in the oral cavity cannot be neglected. The key elements in the operative phase are as follows Flap design Flap design depends on the quantity and quality of masticatory mucosal tissues and their vascularity. In this respect, flap design represents a three-dimensional issue, and the wound bed and the flap tissue are interdependent. The better the vascularity (number of vessels and diameter) of the tissue sources, the better are the healing outcomes. Moreover, the less traumatic the intervention, the better healing outcomes are to be expected. Whenever possible, minimally invasive surgical approaches should be implemented, which encompasses a diligent, precise and least traumatic surgical management of the tissues to reach the interventional objectives. Furthermore, magnification, bright and focused illumination, appropriate instruments and materials are essential to achieve this goal. It is advisable to reduce the number of or avoid releasing incisions. Moreover, the maintenance of the thickness of the masticatory mucosa needed must be a primary objective. Flap mobilization and advancement Whenever an advancement of a flap is needed, additional measures for achieving flap mobility are indicated. Periosteal releasing incisions and further splitting the flap apically to the mucogingival line have to be performed. The apical extension of the incision, however, should avoid the incorporation of muscle tissue into the flap. In many instances, however, the periosteal releasing incision may sufficiently increase flap mobility. Flap adaptation and stabilization A thin blood clot adhering to the vascularized or non-vascularized wound bed is of utmost importance to achieve optimal healing outcomes. The stability of the clot and its adherence is crucial to withstand disruptive forces on hard non-shedding surfaces. A flap with minimum tension positioned onto the wound bed resulting in passivity of the flap is a prerequisite for clot stability. The latter has to be assured by applying adequate suturing technique. This, in turn, means that a flap once placed in its final position should not retract upon minimal, physiological movement of the lips or cheeks before suturing. Final flap stability by suturing is dependent also on the selection of the anchoring points. The key elements in the post-operative phase are as follows Post-operative instructions Post-operative, preferably written instructions should be given to the patient including an explanation concerning all medications, potential discomfort and possible complications as well as diet modifications required and where to call if adverse events occur or questions arise. Wound healing resistance to infection It has been repeatedly demonstrated that optimal outcomes of periodontal plastic surgical procedures depend on an effective post-surgical biofilm control during the entire healing period. In essence, to reach a status of homeostasis, a period of 4 8 weeks has to be considered during which regular checks should verify the patients ability to perform optimal biofilm control. Mechanical interference of the surgical areas should be avoided during early phases of healing, what necessitates the application of antiseptics during this period. Moreover, the application of periodontal dressings on the recipient sites in periodontal plastic surgery is contraindicated. Effective antiseptic treatment To satisfy the principle of complete chemical plaque control following surgery, only antiseptics with high substantivity are appropriate and hence, a 0.12% or 0.2% chlorhexidine digluconate is recommended. Chemical plaque control should be supplemental, not a substitution of a modified mechanical biofilm removal. This is especially important during the first post-surgical weeks, when mechanical impacts to the surgical sites should be avoided. Effective oral hygiene programmes Mechanical biofilm removal is to be started after periodontal plastic surgical interventions as early as possible, but should avoid trauma to the surgical sites. Hence, ultrasoft toothbrushes soaked in antiseptic solutions should be used after suture removal. These brushes may be replaced with a soft brush after an additional 2 weeks. Wound infections; role of sutures Suturing with low tension and using delicate sutures best maintain the clot and flap stabilization. Suturing may, however, impinge on the microcirculation of flaps and sutures may collect biofilms and promote tissue inflammation, what may jeopardize optimal wound healing. Sutures usually keep their function within the first 3 4 days post-surgery. Consequently, sutures should remain as short as needed to assure stability in the early healing phase. From a clinical point of view, diligent removal of the sutures between 1 and 2 weeks should be recommended depending on the type of intervention and expected healing. Medications In periodontal plastic surgery, the administration of peri- or post-surgical systemic antibiotics, are generally not indicated, although depending on the extent of the surgical procedure and mainly when treating deficiencies at infected implant sites the administration of systemic or local antibiotics may be indicated. Conventional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have been widely used to control post-operative pain. They are proven to be effective, tolerated by patients, easy to administer and have an acceptable potential for interaction with other systemic drugs. Critical Elements in Flap Design and Surgical Execution The selection of a flap as the surgical technique of choice to treat soft tissue recessions around teeth will depend on local anatomic character-
4 Consensus report of Working Group 3 S95 istics, on the patient s aesthetic requirements and the surgeon preferences. These essential anatomical characteristics are as follows: the tooth location, the number of recession defects (multiple or single), the interdental attachment level (Miller Class), the amount and thickness of keratinized tissue (KT) apical and/or lateral to the recession, the vestibular depth and the size, height and width of the recession defect (De Sanctis & Clementini 2014). In single recession defects, the most widely used flap technique is the coronally advanced flap (CAF), although in specific clinical situations the laterally positioned flap (LPF) can also be considered. The most widely utilized CAF design is a trapezoidal flap consisting of two vertical-oblique incisions connected with a coronal incision through the sulcus. The location and shape of the coronal incision depend on the depth of the recession and should be extended to the anatomical papilla. When the amount and thickness of KT apical to the recession is unfavourable, the LPF is recommended if there is an adequate amount KT lateral to the recession. Its design consists of two parallel vertical incisions and a connecting submarginal horizontal incision maintaining enough attached gingiva in the donor site to prevent secondary recession. In multiple recession defects, the number of defects and their location and depth affect the surgical design. There are two possible different approaches one with and the other without vertical releasing incisions. When the size of the multiple recessions is rather even or the deepest recession is in the centre of the surgical area, representing the centre of rotation, the application of a flap without vertical releasing incision(s) is recommended. The needed mobility of this flap is achieved by the horizontal extension of the incision, allowing the advancement of the flap to achieve full coverage of all the recessions. When the depth of the multiple recessions remains uneven or when the deepest recession is located at the edges of the surgical area, vertical(s) releasing incision(s) are needed. In these designs, the flap should be elevated using a combination of split and full thickness dissection with the purpose to allow the full thickness of the flap component, including the periosteum, over the avascular tooth surface. The root should be mechanically debrided to allow a de-contaminated smooth surface. The use of chemical conditioning has not demonstrated an additional clinical value. The use of enamel matrix derivatives as a biological agent has shown a significantly increased percentage of root coverage and increased attachment levels when compared with CAF alone in single recession defects. The use of other biological agents (e.g. platelet aggregates) has failed to demonstrate a significant clinical added value. To properly advance the flap its passivity should be assured by split thickness dissection beyond the mucogingival junction detaching the base of the flap from the periosteum. In some instances it is recommended to perform a further superficial dissection to separate the flap from the muscle. The flap should be located in a position coronal to the cemento enamel junction (CEJ), completely passive and tension free. Sutures must assure the stability of the flap in this position. In the treatment of multiple recession defects, the tunnel flap has also been described and it is used extensively. All the available evidence, however, on the efficacy of this surgical design lies within the combined application of a soft tissue replacement graft. This technique consists of an intra-sulcular incision, a full thickness flap elevation beyond the mucogingival junction and a further split thickness dissection of the periosteum. The flap elevation must be continued horizontally underneath the buccal papilla connecting the sulcular incisions from adjacent teeth. The buccal aspect of papilla is elevated but not disconnected from its lingual aspect. The graft should be incorporated and stabilized in this surgically created tunnel with the use of specific suturing techniques. Moreover, the flap can be advanced to fully cover the graft also using specific suturing techniques. There is no evidence on the efficacy of the advanced flap on the treatment of soft tissue deficiencies around implant-supported restorations, as the scarce evidence available is limited to the combined use of advanced flaps and soft tissue replacement grafts. Furthermore, the evidence from the treatment of recessions around teeth cannot be extrapolated to deficiencies around implant-supported restorations as the anatomical characteristics of the soft tissues around dental implants are different. Clinical recommendations The most effective use of coronally or laterally advanced flaps (complete root coverage) can be considered when the following circumstances are met: Tooth location, as most of evidence is derived from maxillary anterior teeth Normal tooth position in relation to the adjacent teeth Integrity of the adjacent bone height and periodontal attachment level Presence of adequate height and thickness of KT Absence of non-carious cervical lesions invading the CEJ or deep root deficiencies A healthy non-smoker patient with proven oral hygiene efficacy, both in terms of plaque control and absence of gingival trauma An operator with demonstrated surgical skills and expertise. Critical Elements in the Use of Soft Tissue Replacement Grafts Soft tissue replacement grafts have become a substantial element in plastic periodontal and implant surgical procedures for clinical indications such as treatment of recessions and peri-implant soft tissue deficiencies, as well as soft tissue ridge augmentation. The critical elements on the use of soft tissue replacement grafts are the donor site selection and harvesting technique, together with the graft tissue integration and its volume stability (Zuhr et al. 2014). Donor site selection and harvesting technique When using autologous grafts, there are different donor sites that can be selected, but mainly subepitelial con-
5 S96 Sanz and Simion nective tissue grafts (SCTGs) are harvested from the palatal mucosa. Moreover, there are varying harvesting techniques resulting in different graft characteristics, both in terms of size and histological composition. SCTGs from the posterior palate are usually denser but limited in size, whereas SCTGs from the anterior palate are of looser consistency, but can be more extensive. A sound knowledge of the anatomy of the palate is essential when harvesting SCTGs in order to prevent complications. Due to the individual variability in the course of the palatal neurovascular bundle, extra care should be taken especially if SCTGs are harvested from the molar area. The pre-operative location of the great palatal foramen and the clinical evaluation of the palatal soft tissue thickness are imperative in each individual case. Clinical experience recommends harvesting SCTGs from the posterior palate when better volume stability over time is desired, such as in soft tissue augmentation procedures. On the other hand, this type of graft seems to be more sensitive to the local blood supply for its re-vascularization. There are several harvesting techniques for SCTGs described in the literature, but the most frequently reported are the single incision technique at the anterior palate, the trap door approach at the posterior palate and the distal wedge technique when harvesting SCTGs from the tuberosity area. In addition, FGG can be harvested and de-epithelialized extra orally. Each procedure has advantages and disadvantages and the choice depends on existing anatomical limitations, the goal of the procedure, the expected morbidity and the surgeon s expertise. Tissue integration and volume stability The survival of SCTGs depends on plasmatic circulation and the graft subsequent re-vascularization. For this reason, it is desirable to facilitate the best possible blood supply both from the recipient bed and the overlying flap. Furthermore, it is important to assure the graft immobilization, the intimate contact between the graft, the recipient bed and the overlying flap and the tension free flap closure with the use of appropriate suturing techniques. The application of minimally invasive principles based on precise and least traumatic soft tissue handling has been demonstrated to improve treatment outcomes. Although SCTGs can survive even with small parts of the grafts being exposed to the oral cavity, care should be taken to completely cover SCTGs, especially if they are placed on avascular surfaces. There is no evidence that the use of autologous plasma rich in growth factors or platelet-rich plasma in conjunction with SCTG provides additional benefit. When SCTGs are interposed between the root surface and flap, the attachment between the graft and the previously exposed root surfaces predominantly occurs by a long junctional epithelium. There is no evidence that the use of chemical root conditioning agents provides any additional benefit in this healing event. Whether or not the combination of SCTG and enamel matrix derivate can influence the type of attachment on the root surface, it is presently unclear and needs further scientific verification. When SCTGs are placed over composite restorations, there is limited short-term data indicating successful clinical outcomes in the treatment of recessions. When SCTGs are placed on implant-supported restorations in the treatment of soft tissue deficiencies variable clinical outcomes have been reported. Subepitelial connective tissue grafts can be used successfully for soft tissue augmentation in partially edentulous ridges. In these indications the SCTGs are placed on vascular beds where uneventful and favourable wound healing processes can be expected. However, the volumetric aspects have hardly been evaluated in the literature. Soft tissue substitutes The limited amount of autologous donor tissue and the increased patient morbidity are substantial disadvantages of SCTGs. For this reason, the search for suitable soft tissue substitutes is currently in the centre of interest of scientists and manufacturers. Allogenic, xenogenic and alloplastic materials are currently commercially available, but only few have reported scientific documentation. These materials have different structures, composition and therefore, require specific surgical manipulation. When used for root coverage and soft tissue volume augmentations, it is generally accepted to fully cover these materials. Considerations for Future Research After reviewing the current literature the group identified the need of: Clinical trials to compare different flap designs. Well-established clinical and patient-reported outcome variables that reflect the efficacy of these surgical interventions. Long-term information (at least 5 years) on the stability of these surgical interventions. The use of 3D image-based technologies to improve the flap designs. Understanding the healing characteristics and long-term volume stability of SCTGs harvested with different techniques and from different areas of the palate. Understanding the biological effects of SCTGs in different clinical indications. Understanding the possible effect of combining SCTGs with bioactive substances. Understanding the healing of SCTGs placed on restored teeth and implant-supported restorations. Understanding the biological mechanisms and the clinical potential of currently available and new generation soft tissue substitutes using tissue engineering principles.
6 Consensus report of Working Group 3 S97 Appendix Frank Abbas (NL) Sofia Aroca (F) Zvi Artzi (ISR) Rino Burkhardt (CH) Pierpaolo Cortellini (I) Korkud Demirel (TR) Virginie Monnet- Corti (F) Alberto Ortiz- Vigon (E) Giulio Rasperini (I) Massimo de Sanctis (I) Ignacio Sanz- Sanchez (E) Alberto Sicilia (E) Moshe Goldstein (ISR) Kay Horsch (CH, Osteology) Markus H urzeler (D) Niklaus P. Lang (CH, HK) References Istvan Urban (H) Selcuk Yilmaz (TR) Ion Zabalegui (E) Otto Zuhr (D) Burkhardt, R. & Lang, N. P. (2014) Fundamental principles in periodontal plastic surgery and mucosal augmentation a narrative review. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 41(Supplementum). De Sanctis, M. & Clementini, M. (2014) Flap approaches in plastic periodontal and implant surgery: critical elements in design and execution. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 41(Supplementum). Zuhr, O., B aumer, D. & H urzeler, M. B. (2014) The addition of soft tissue replacement grafts in plastic periodontal and implant surgery: critical elements in design and execution. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 41(Supplementum). Address: Mariano Sanz University Complutense of Madrid, Madrid Spain marianosanz@odon.ucm.es Clinical Relevance Periodontal plastic surgery is extensively used in current Clinical Periodontology, mainly due to the importance of social interaction an aesthetics in our society. These interventions are not only practiced by specialists, but also by general practitioners with special interest in Periodontology and it is therefore, fundamental that there is a wide knowledge on the basic surgical principles behind these techniques, as well as the main surgical designs both for flap surgical approaches as well as for applying autogenous grafts or soft tissue substitutes. In this consensus report the key elements and essential factors of both flapping and grafting are clearly depicted and should serve for the basis of effective periodontal plastic surgery.
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato, Carlo Baldi, Roberto Rotundo, Debora Franceschi,
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato, Carlo Baldi, Roberto Rotundo, Debora Franceschi,
SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT A PREDICTABLE INDICATOR FOR ROOT COVERAGE
 SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT A PREDICTABLE INDICATOR FOR ROOT COVERAGE Munishwar Singh* * 201 Military Dental Centre, C/o 99 APO, India Keywords: Gingival recession, Root coverage procedure, Connective
SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT A PREDICTABLE INDICATOR FOR ROOT COVERAGE Munishwar Singh* * 201 Military Dental Centre, C/o 99 APO, India Keywords: Gingival recession, Root coverage procedure, Connective
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
MUCOGINGIVAL THERAPY PERIODONTAL PLASTIC SURGERY
 MUCOGINGIVAL THERAPY PERIODONTAL PLASTIC SURGERY DR.H.Gharati Periodontist & Dental Implant Specialist Assistant Professor, School Of Dentistry Friedman(1957): DEFINITION Mucogingival surgery, Surgical
MUCOGINGIVAL THERAPY PERIODONTAL PLASTIC SURGERY DR.H.Gharati Periodontist & Dental Implant Specialist Assistant Professor, School Of Dentistry Friedman(1957): DEFINITION Mucogingival surgery, Surgical
Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery
 CASE SERIES 1 OPEN ACCESS Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery Sangeeta ABSTRACT Introduction:
CASE SERIES 1 OPEN ACCESS Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery Sangeeta ABSTRACT Introduction:
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Alarge number of sound clinical
 Volume 83 Number 5 Long-Term 8-Year Outcomes of Coronally Advanced Flap forrootcoverage Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato,* Debora Franceschi,* Roberto Rotundo,* Francesco Cairo,* Pierpaolo Cortellini, and Michele
Volume 83 Number 5 Long-Term 8-Year Outcomes of Coronally Advanced Flap forrootcoverage Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato,* Debora Franceschi,* Roberto Rotundo,* Francesco Cairo,* Pierpaolo Cortellini, and Michele
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
Townie Guest Editorial. Gingival Attachment Loss: Evaluation and Surgical Options. Daniel J. Melker, DDS. fig. 1
 Gingival Attachment Loss: Evaluation and Surgical Options Daniel J. Melker, DDS Attached connective tissue (a.k.a. attached tissue) in the simplest terms is the body s only barrier between the underlying
Gingival Attachment Loss: Evaluation and Surgical Options Daniel J. Melker, DDS Attached connective tissue (a.k.a. attached tissue) in the simplest terms is the body s only barrier between the underlying
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
TWO-STEP SURGICAL PROCEDURE FOR ROOT COVERAGE (FREE GINGIVAL GRAFT AND CORONALLY POSITIONED FLAP) - A CASE REPORT
 TWO-STEP SURGICAL PROCEDURE FOR ROOT COVERAGE (FREE GINGIVAL GRAFT AND CORONALLY POSITIONED FLAP) - A CASE REPORT Dr Prashant Bhusari*, Dr Apoorva Saxena**, Dr Jaya Jain***,Dr Rashmi Rathore***, Dr Aditi
TWO-STEP SURGICAL PROCEDURE FOR ROOT COVERAGE (FREE GINGIVAL GRAFT AND CORONALLY POSITIONED FLAP) - A CASE REPORT Dr Prashant Bhusari*, Dr Apoorva Saxena**, Dr Jaya Jain***,Dr Rashmi Rathore***, Dr Aditi
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery. Dr.maryam khosravi
 Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12 Accepted on:22/05/12
 SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
botiss dental bone & tissue regeneration biomaterials mucoderm 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic
 dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402
 Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402 Subject Mucogingival Surgery and Soft Tissue Grafting Originating Department Clinical Professional Services Signature Authority Dental Director Type: New
Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402 Subject Mucogingival Surgery and Soft Tissue Grafting Originating Department Clinical Professional Services Signature Authority Dental Director Type: New
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Efficacy of Lateral Pedicle Graft in the Treatment of Isolated Gingival Recession Defects
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 3 Issue 1 January 2014 PP.46-50 Efficacy of Lateral Pedicle Graft in the Treatment of
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 3 Issue 1 January 2014 PP.46-50 Efficacy of Lateral Pedicle Graft in the Treatment of
Role of flap tension in primary wound closure of mucoperiosteal flaps: a prospective cohort study
 R. Burkhardt N. P. Lang Role of flap tension in primary wound closure of mucoperiosteal flaps: a prospective cohort study Authors affiliation: R. Burkhardt, N. P. Lang, The University of Hong Kong, Hong
R. Burkhardt N. P. Lang Role of flap tension in primary wound closure of mucoperiosteal flaps: a prospective cohort study Authors affiliation: R. Burkhardt, N. P. Lang, The University of Hong Kong, Hong
Clinical sessions in recession coverage at teeth and implants
 Clinical sessions in recession coverage at teeth and implants Main sponsors: Clinical sessions in recession coverage at teeth and implants It is an honour for us to present this joint SEPA-SIdP symposium,
Clinical sessions in recession coverage at teeth and implants Main sponsors: Clinical sessions in recession coverage at teeth and implants It is an honour for us to present this joint SEPA-SIdP symposium,
Management of miller class II gingival recession by laterally positioned pedicle flap revised technique
 Management of miller class II gingival by laterally positioned pedicle flap revised technique Received: 2/4/206 Accepted: 3/0/206 Dildar Abdullah Othman* Abstract Background and objective: Gingival is
Management of miller class II gingival by laterally positioned pedicle flap revised technique Received: 2/4/206 Accepted: 3/0/206 Dildar Abdullah Othman* Abstract Background and objective: Gingival is
Gum Graft? Patient Need a. Does My. 66 JANUARY 2017 // dentaltown.com. by Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky
 by Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky was born in Dallas and attended college at the University of Texas at Austin. He continued his education at Baylor College of Dentistry in Dallas, where he
by Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky was born in Dallas and attended college at the University of Texas at Austin. He continued his education at Baylor College of Dentistry in Dallas, where he
Many techniques have been proposed for root coverage:
 Case Series Localized Gingival Recessions Treated With the Original Envelope Technique: A Report of 50 Consecutive Patients Jaime A. Vergara* and Raul G. Caffesse Background: The surgical techniques used
Case Series Localized Gingival Recessions Treated With the Original Envelope Technique: A Report of 50 Consecutive Patients Jaime A. Vergara* and Raul G. Caffesse Background: The surgical techniques used
Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
 Galore International Journal of Health Sciences and Research Vol.3; Issue: 1; Jan.-March 2018 Website: www.gijhsr.com Review Article P-ISSN: 2456-9321 Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
Galore International Journal of Health Sciences and Research Vol.3; Issue: 1; Jan.-March 2018 Website: www.gijhsr.com Review Article P-ISSN: 2456-9321 Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
Clinical sessions in recession coverage at teeth and implants
 Clinical sessions in recession coverage at teeth and implants Main sponsors: Friday November 23. 14.00-19.30 WORKSHOP 1 TUNNEL TREATMENT OF MULTIPLE ADJACENT GINGIVAL RECESSIONS Clinical sessions in recession
Clinical sessions in recession coverage at teeth and implants Main sponsors: Friday November 23. 14.00-19.30 WORKSHOP 1 TUNNEL TREATMENT OF MULTIPLE ADJACENT GINGIVAL RECESSIONS Clinical sessions in recession
Pouch and tunnel technique: Minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery for root coverage
 www.edoriumjournals.com case Series OPEN ACCESS Pouch and tunnel technique: Minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery for root coverage Sangeeta Singh ABSTRACT Introduction: The indications for root
www.edoriumjournals.com case Series OPEN ACCESS Pouch and tunnel technique: Minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery for root coverage Sangeeta Singh ABSTRACT Introduction: The indications for root
Biology of soft tissue wound healing and regeneration Consensus Report of Group 1 of the 10th European Workshop on Periodontology
 J Clin Periodontol 2014; 41 (Suppl. 15): S1 S5 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12221 Biology of soft tissue wound healing and regeneration Consensus Report of Group 1 of the 10th European Workshop on Periodontology
J Clin Periodontol 2014; 41 (Suppl. 15): S1 S5 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12221 Biology of soft tissue wound healing and regeneration Consensus Report of Group 1 of the 10th European Workshop on Periodontology
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF GINGIVAL RECESSION WITH SOFT TISSUE GRAFT PROCEDURE
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2018243.2149 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2018 Jul-Sep;24(3) Literature review
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2018243.2149 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2018 Jul-Sep;24(3) Literature review
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits. Your combination for success
 Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Revisions for CDT 2016
 Revisions for CDT 2016 This document was developed from preliminary actions of the Code Maintenance Committee (CMC). This document has been compared to the CMC meeting notes and the ASCII file. This document
Revisions for CDT 2016 This document was developed from preliminary actions of the Code Maintenance Committee (CMC). This document has been compared to the CMC meeting notes and the ASCII file. This document
Regaining Your Gum Tissue. Soft-Tissue Regeneration With Geistlich Mucograft
 Regaining Your Gum Tissue Soft-Tissue Regeneration With Geistlich Mucograft Why is Healthy Gum Tissue So Important? Gum tissue can recede due to grinding of the teeth, thin insufficient gum tissue, as
Regaining Your Gum Tissue Soft-Tissue Regeneration With Geistlich Mucograft Why is Healthy Gum Tissue So Important? Gum tissue can recede due to grinding of the teeth, thin insufficient gum tissue, as
CLINICAL. Free gingival grafts to manage recession when and how? Matthew B M Thomas CLINICAL
 CLINICAL CLINICAL Free gingival grafts to manage recession when and how? Matthew B M Thomas Gingival recession results from displacement of the gingival margin below the cemento-enamel junction leading
CLINICAL CLINICAL Free gingival grafts to manage recession when and how? Matthew B M Thomas Gingival recession results from displacement of the gingival margin below the cemento-enamel junction leading
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Free Gingival Graft as a Single Step Procedure for Treatment of Mandibular Miller Class I and II Recession Defects
 12 Gingival graft in mandibular defect Original Article Free Gingival Graft as a Single Step Procedure for Treatment of Mandibular Miller Class I and II Recession Defects Lata Goyal1*, Narender Dev Gupta2,
12 Gingival graft in mandibular defect Original Article Free Gingival Graft as a Single Step Procedure for Treatment of Mandibular Miller Class I and II Recession Defects Lata Goyal1*, Narender Dev Gupta2,
Regaining your gum tissue. Soft tissue regeneration with Geistlich Mucograft
 Regaining your gum tissue Soft tissue regeneration with Geistlich Mucograft Why is healthy gum tissue so important? Gum tissue can recede due to grinding of the teeth, thin insufficient gum tissue, as
Regaining your gum tissue Soft tissue regeneration with Geistlich Mucograft Why is healthy gum tissue so important? Gum tissue can recede due to grinding of the teeth, thin insufficient gum tissue, as
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Minimally invasive techniques for periodontal regeneration
 2016; 2(12): 230-234 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2016; 2(12): 230-234 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 04-10-2016 Accepted: 05-11-2016 Dr. Rizwan M Sanadi Professor,
2016; 2(12): 230-234 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2016; 2(12): 230-234 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 04-10-2016 Accepted: 05-11-2016 Dr. Rizwan M Sanadi Professor,
Free Gingival Autograft: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Free Gingival Autograft: A Case Report Veena Ashok. P. MDS, Bhargav Neetha BDS Abstract: Gingival recession is defined as Displacement of soft tissue margin apical to the cemento-enamel junction
CASE REPORT Free Gingival Autograft: A Case Report Veena Ashok. P. MDS, Bhargav Neetha BDS Abstract: Gingival recession is defined as Displacement of soft tissue margin apical to the cemento-enamel junction
The Internatonal Journal of Periodontics & Restoraive Dentistry
 The Internatonal Journal of Periodontics & Restoraive Dentistry 3 Incisive Vessel Based Palatal Flap for the Reconstruction of Anterior Maxillary Soft Tissues [Au: Text has been edited heavily. Please
The Internatonal Journal of Periodontics & Restoraive Dentistry 3 Incisive Vessel Based Palatal Flap for the Reconstruction of Anterior Maxillary Soft Tissues [Au: Text has been edited heavily. Please
The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS
 The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS LOCALIZED RECESSION ON TOOTH #25 DUE TO BONE RECESSION (PRE OP) Introduction Tissue grafting
The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS LOCALIZED RECESSION ON TOOTH #25 DUE TO BONE RECESSION (PRE OP) Introduction Tissue grafting
Clinical Application of Modified Apically Repositioned Flap in Class III/IV Gingival Recession Cases
 J Harjeet Singh et al SE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1200 linical pplication of Modified pically Repositioned Flap in lass III/IV Gingival Recession ases 1 Harjeet Singh, 2 Manab Kosala, 3 Vivek apurao
J Harjeet Singh et al SE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1200 linical pplication of Modified pically Repositioned Flap in lass III/IV Gingival Recession ases 1 Harjeet Singh, 2 Manab Kosala, 3 Vivek apurao
Contemporary Periodontal Surgery
 Contemporary Periodontal Surgery Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. CPCC Dental Hygiene Program October 18, 2011 Surgical Management of Periodontitis Periodontal Plastic Surgery Soft tissue and esthetics Dental
Contemporary Periodontal Surgery Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. CPCC Dental Hygiene Program October 18, 2011 Surgical Management of Periodontitis Periodontal Plastic Surgery Soft tissue and esthetics Dental
Treatment of multiple gingival recessions using subepithelial connective tissue grafting with a single-incision technique
 317 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 2, 317-321, 2009 Case Report Treatment of multiple gingival recessions using subepithelial connective tissue grafting with a single-incision technique Jun-Beom
317 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 2, 317-321, 2009 Case Report Treatment of multiple gingival recessions using subepithelial connective tissue grafting with a single-incision technique Jun-Beom
soft tissue mucoderm botiss native stable 3-dimensional 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft Handling, Clinical Application and Cases
 dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials mucoderm 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft Handling, Clinical Application and Cases by PD Dr. med. dent. Adrian Kasaj soft tissue native stable 3-dimensional
dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials mucoderm 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft Handling, Clinical Application and Cases by PD Dr. med. dent. Adrian Kasaj soft tissue native stable 3-dimensional
Geistlich Fibro-Gide. The Alternative Soft-Tissue Graft
 Geistlich Fibro-Gide The Alternative Soft-Tissue Graft Geistlich Fibro-Gide shows comparable results to connective tissue grafts in terms of change in soft-tissue volume over time., This demonstrates that
Geistlich Fibro-Gide The Alternative Soft-Tissue Graft Geistlich Fibro-Gide shows comparable results to connective tissue grafts in terms of change in soft-tissue volume over time., This demonstrates that
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Derma S O F T T I S S U E A U G M E N TAT I O N. Acellular dermal matrix
 Derma A XENOGENIC GRAFT FOR S O F T T I S S U E A U G M E N TAT I O N Acellular dermal matrix A xenogenic graft for soft tissue augmentation CHARACTERISTICS Obtained from derma of porcine origin, using
Derma A XENOGENIC GRAFT FOR S O F T T I S S U E A U G M E N TAT I O N Acellular dermal matrix A xenogenic graft for soft tissue augmentation CHARACTERISTICS Obtained from derma of porcine origin, using
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the. Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System
 Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF WHAT WE DO? TEAM PERIODONTICS: WORKING TOGETHER TO IMPROVE PATIENT CARE YOU ARE THE PERIODONTISTS IN YOUR PRACTICE!
 Setter Periodontics 2075 SW 1 st Ave #2L Portland, OR 97201 503-222-9961 michael@setterperio.com WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF WHAT WE DO? Gum Gardeners Study Club 2.27.17 TEAM PERIODONTICS: WORKING TOGETHER
Setter Periodontics 2075 SW 1 st Ave #2L Portland, OR 97201 503-222-9961 michael@setterperio.com WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF WHAT WE DO? Gum Gardeners Study Club 2.27.17 TEAM PERIODONTICS: WORKING TOGETHER
Rescuing Tooth with Regenerative Technique: A Case Report. Women,, Suraram Mainroad, Ghmc Quthbullapur, Hyderabad , Telangana.
 ISSN- O: 2458-868X, ISSN P: 2458 8687 Index Copernicus Value: 49. 23 PubMed - National Library of Medicine - ID: 101731606 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.956 International Journal of Medical Science and Innovative
ISSN- O: 2458-868X, ISSN P: 2458 8687 Index Copernicus Value: 49. 23 PubMed - National Library of Medicine - ID: 101731606 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.956 International Journal of Medical Science and Innovative
Over the years, mucogingival surgery
 The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation and Root Coverage: A Case Series Saroff Stephen Andrew Saroff, DDS, MSD 1 Abstract Over the years, mucogingival surgery has developed
The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation and Root Coverage: A Case Series Saroff Stephen Andrew Saroff, DDS, MSD 1 Abstract Over the years, mucogingival surgery has developed
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Avita Rath, 1 Smrithi Varma, 2 and Renny Paul Case Presentation. 1. Background
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 9289634, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9289634 Case Report Two-Stage Mucogingival Surgery with Free Gingival Autograft and Biomend Membrane and
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 9289634, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9289634 Case Report Two-Stage Mucogingival Surgery with Free Gingival Autograft and Biomend Membrane and
FRENECTOMY WITH LATERALLY DISPLACED FLAP: A CASE REPORT
 FRENECTOMY WITH LATERALLY DISPLACED FLAP: A CASE REPORT Dr. Minu.P. Mathew, Dr.R.Saravanakumar, Dr.Pratebha.B, Dr.Jannani.M, ABSTRACT An aberrant Maxillary labial frenum is capable of creating diastema
FRENECTOMY WITH LATERALLY DISPLACED FLAP: A CASE REPORT Dr. Minu.P. Mathew, Dr.R.Saravanakumar, Dr.Pratebha.B, Dr.Jannani.M, ABSTRACT An aberrant Maxillary labial frenum is capable of creating diastema
Clinical applications of minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery
 www.edoriumjournals.com CASE SERIES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Clinical applications of minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery Sangeeta Singh, Saravanan SP, Devendra Srivastava, Raghvendra MH, A.
www.edoriumjournals.com CASE SERIES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Clinical applications of minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery Sangeeta Singh, Saravanan SP, Devendra Srivastava, Raghvendra MH, A.
GUIDED BONE & TISSUE REGENERATION 2-DAY LIVE COURSE DR. ISABELLA ROCCHIETTA & DR. DAVID NISAND
 GUIDED BONE & TISSUE REGENERATION DR. ISABELLA ROCCHIETTA & DR. DAVID NISAND 2-DAY LIVE COURSE Soft tissue management is the key to achieve aesthetic success. Periodontal and peri-implant soft tissue management
GUIDED BONE & TISSUE REGENERATION DR. ISABELLA ROCCHIETTA & DR. DAVID NISAND 2-DAY LIVE COURSE Soft tissue management is the key to achieve aesthetic success. Periodontal and peri-implant soft tissue management
HDS PROCEDURE CODE GUIDELINES
 D4000 - D4999 Local anesthesia is usually considered to be part of Periodontal procedures. General Guidelines 1. Periodontal services are only benefited when performed on natural teeth for treatment of
D4000 - D4999 Local anesthesia is usually considered to be part of Periodontal procedures. General Guidelines 1. Periodontal services are only benefited when performed on natural teeth for treatment of
Case Report Esthetic Root Coverage with Double Papillary Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 509319, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/509319 Case Report Esthetic Root Coverage with Double Papillary Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft: A Case Report
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 509319, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/509319 Case Report Esthetic Root Coverage with Double Papillary Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft: A Case Report
Biology of soft tissue wound healing and regeneration consensus report of Group 1 of the 10th European Workshop on Periodontology
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2014 Biology of soft tissue wound healing and regeneration consensus report
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2014 Biology of soft tissue wound healing and regeneration consensus report
Localized Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Using a Two-step Approach with Different Soft Tissue Grafts: A Clinical Report
 Localized Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Using a Two-step Approach with Different Soft Tissue Grafts: A Clinical Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present the use of different soft tissue
Localized Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Using a Two-step Approach with Different Soft Tissue Grafts: A Clinical Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present the use of different soft tissue
1984 Lubow et al Endodontic flap design: analysis and recommendations for current usage
 Surgical Endodontics Endodontic flap design 1984 Lubow et al Endodontic flap design: analysis and recommendations for current usage Most important factor in flap design is blood supply therefore widest
Surgical Endodontics Endodontic flap design 1984 Lubow et al Endodontic flap design: analysis and recommendations for current usage Most important factor in flap design is blood supply therefore widest
Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Framework and Proposal of a New Classification and Case Definition. By: Kimberly Hawrylyshyn
 Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Framework and Proposal of a New Classification and Case Definition By: Kimberly Hawrylyshyn Background Periodontitis is a microbe induced inflammatory disease that
Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Framework and Proposal of a New Classification and Case Definition By: Kimberly Hawrylyshyn Background Periodontitis is a microbe induced inflammatory disease that
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques
 I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2014;1(2):49-53 April-June All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and
I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2014;1(2):49-53 April-June All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and
Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession
 World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 117-121, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82175 Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession 1 1 1
World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 117-121, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82175 Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession 1 1 1
Vertical and/or horizontal alveolar
 CLINICAL Vascularized Connective Tissue Flap for Bone Graft Coverage Alan S. Herford, DDS, MD 1 * Todd C. Cooper, DDS 1 Carlo Maiorana, DDS, MD 2 Marco Cicciù, DDS, PhD 2 Alveolar defects are characterized
CLINICAL Vascularized Connective Tissue Flap for Bone Graft Coverage Alan S. Herford, DDS, MD 1 * Todd C. Cooper, DDS 1 Carlo Maiorana, DDS, MD 2 Marco Cicciù, DDS, PhD 2 Alveolar defects are characterized
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report The Vestibular Incision Subperiosteal Tunnel Access (VISTA) for Treatment of Maxillary Anterior Gingival
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report The Vestibular Incision Subperiosteal Tunnel Access (VISTA) for Treatment of Maxillary Anterior Gingival
A New Papilla Preservation Technique for Periodontal Regeneration of Severely Compromised Teeth. Jose A. Moreno Rodríguez and Raúl G.
 A New Papilla Preservation Technique for Periodontal Regeneration of Severely Compromised Teeth Jose A. Moreno Rodríguez and Raúl G. Caffesse Introduction: Periodontal regeneration of hopeless teeth represents
A New Papilla Preservation Technique for Periodontal Regeneration of Severely Compromised Teeth Jose A. Moreno Rodríguez and Raúl G. Caffesse Introduction: Periodontal regeneration of hopeless teeth represents
Educational Training Document
 Educational Training Document Table of Contents Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer Page: 2 Part 2: Line Item Grade Sheets Page: 3 Release: 11/2016 Page 1 of 6 Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer The
Educational Training Document Table of Contents Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer Page: 2 Part 2: Line Item Grade Sheets Page: 3 Release: 11/2016 Page 1 of 6 Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer The
RESEARCH REVIEW. Gingival recession: a proposal for a new classification ISSN :
 RESEARCH REVIEW Gingival recession: a proposal for a new classification Shantipriya Reddy, Sanjay Kaul, Prasad M.G.S., Jaya Agnihotri, Amudha D., Soumya Kambali ABSTRACT An accurate diagnosis is often
RESEARCH REVIEW Gingival recession: a proposal for a new classification Shantipriya Reddy, Sanjay Kaul, Prasad M.G.S., Jaya Agnihotri, Amudha D., Soumya Kambali ABSTRACT An accurate diagnosis is often
Soft-Tissue Success with the. Clinical Success. Proven Matrix. with the Proven. Geistlich Mucograft Geistlich Mucograft Seal
 Soft-Tissue Success with the Clinical Success Proven Matrix with the Proven Bone Geistlich Mucograft Substitute Seal The Softer Side of Geistlich Innovation Decades of collagen expertise leads naturally
Soft-Tissue Success with the Clinical Success Proven Matrix with the Proven Bone Geistlich Mucograft Substitute Seal The Softer Side of Geistlich Innovation Decades of collagen expertise leads naturally
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
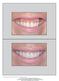 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 433 Lip Repositioning for Reduction of Excessive Gingival Display: A Clinical Report Ari Rosenblatt, DMD, DDS* Ziv Simon, DMD, MSc* Excessive
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 433 Lip Repositioning for Reduction of Excessive Gingival Display: A Clinical Report Ari Rosenblatt, DMD, DDS* Ziv Simon, DMD, MSc* Excessive
CITRIC ACID ROOT BIOMODIFICATION IN RECESSION COVERAGE WITH LATERAL PEDICLE FLAP TECHNIQUE- A CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 05 CITRIC ACID ROOT BIOMODIFICATION IN RECESSION COVERAGE WITH LATERAL PEDICLE FLAP TECHNIQUE- A CASE REPORT Mamta Singh
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 05 CITRIC ACID ROOT BIOMODIFICATION IN RECESSION COVERAGE WITH LATERAL PEDICLE FLAP TECHNIQUE- A CASE REPORT Mamta Singh
Maintenance. Periodontics & Restorative. Naoshi Sato. A Clinical Atlas
 Naoshi Sato Periodontics & Restorative Maintenance A Clinical Atlas London, Berlin, Chicago, Tokyo, Barcelona, Beijing, Istanbul, Milan, Moscow, New Delhi, Paris, Prague, São Paulo, Seoul and Warsaw Preface
Naoshi Sato Periodontics & Restorative Maintenance A Clinical Atlas London, Berlin, Chicago, Tokyo, Barcelona, Beijing, Istanbul, Milan, Moscow, New Delhi, Paris, Prague, São Paulo, Seoul and Warsaw Preface
TASKS. 2. Apply a disclosing agent to make the plaque visible.
 TASKS EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS Personal protective equipment Assortment of nylon, soft-bristled toothbrushes Assortment of dental Floss, waxed and nonwaxed Disclosing solution Face mirror 3. Demonstrate
TASKS EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS Personal protective equipment Assortment of nylon, soft-bristled toothbrushes Assortment of dental Floss, waxed and nonwaxed Disclosing solution Face mirror 3. Demonstrate
Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique
 e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
Where a licence is displayed above, please note the terms and conditions of the licence govern your use of this document.
 A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions - Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification G. Caton, Jack; Chapple, Iain; Armitage, Gary; Berglundh,
A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions - Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification G. Caton, Jack; Chapple, Iain; Armitage, Gary; Berglundh,
Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask
 Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure with serious potential complications and should only be performed by a trained veterinarian.
Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure with serious potential complications and should only be performed by a trained veterinarian.
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
A mucogingival technique for the treatment of multiple recession defects in the
 A mucogingival technique for the treatment of multiple recession defects in the mandibular anterior region: a case series with two-year follow-up. Nicola Bethaz, DDS* Federica Romano, DDS** Francesco Ferrarotti,
A mucogingival technique for the treatment of multiple recession defects in the mandibular anterior region: a case series with two-year follow-up. Nicola Bethaz, DDS* Federica Romano, DDS** Francesco Ferrarotti,
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Michael K. McGuire* and E. Todd Scheyer*
 Long-Term Results Comparing Xenogeneic Collagen Matrix and Autogenous Connective Tissue Grafts With Coronally Advanced Flaps for Treatment of Dehiscence-Type Recession Defects Michael K. McGuire* and E.
Long-Term Results Comparing Xenogeneic Collagen Matrix and Autogenous Connective Tissue Grafts With Coronally Advanced Flaps for Treatment of Dehiscence-Type Recession Defects Michael K. McGuire* and E.
Gingivectomy, excision gingival, each quadrant Gingivoplasty, each quadrant
 Dental in Nature Oral Surgery Effective CDT D3410 surgery - anterior D3421 surgery bicuspid (first root) D3425 surgery molar (first root) D3426 D3427 surgery (each additional root) Periradicular surgery
Dental in Nature Oral Surgery Effective CDT D3410 surgery - anterior D3421 surgery bicuspid (first root) D3425 surgery molar (first root) D3426 D3427 surgery (each additional root) Periradicular surgery
Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical investigation
 American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com eissn: 2347-2766 Original Research Article Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical Ninad Moon 1, Prasant Pillai
American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com eissn: 2347-2766 Original Research Article Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical Ninad Moon 1, Prasant Pillai
Peri-implant Augmentation
 Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 345 A Mucogingival Technique for the Treatment of Multiple Recession Defects in the Mandibular Anterior Region: A Case Series with a 2-Year
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 345 A Mucogingival Technique for the Treatment of Multiple Recession Defects in the Mandibular Anterior Region: A Case Series with a 2-Year
The addition of soft tissue replacement grafts in plastic periodontal and implant surgery: critical elements in design and execution
 J Clin Periodontol 2014; 41 (Suppl. 15): S123 S142 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12185 The addition of soft tissue replacement grafts in plastic periodontal and implant surgery: critical elements in design and execution
J Clin Periodontol 2014; 41 (Suppl. 15): S123 S142 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12185 The addition of soft tissue replacement grafts in plastic periodontal and implant surgery: critical elements in design and execution
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of
 Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Michael K. McGuire* and Martha Nunn
 Volume 74 Number 8 Evaluation of Human Recession Defects Treated with Coronally Advanced Flaps and Either Enamel Matrix Derivative or Connective Tissue. Part 1: Comparison of Clinical Parameters Michael
Volume 74 Number 8 Evaluation of Human Recession Defects Treated with Coronally Advanced Flaps and Either Enamel Matrix Derivative or Connective Tissue. Part 1: Comparison of Clinical Parameters Michael
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
SPECIALIST CURRICULUM 2019/2020
 Dental Regeneration SPECIALIST CURRICULUM 2019/2020 by the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE) PROF. DR. DR. RALF SMEETS - Head of Division Regenerative Orofacial Medicine, University Medical
Dental Regeneration SPECIALIST CURRICULUM 2019/2020 by the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE) PROF. DR. DR. RALF SMEETS - Head of Division Regenerative Orofacial Medicine, University Medical
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
