Continuing Education 2
|
|
|
- Asher Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Posterior Tooth Replacement with Dental Implants in Sites Augmented with rhbmp-2 at Time of Extraction A Case Series Barry P. Levin, DMD; and Peter Tawil, DDS Learning Objectives discuss the augmentation of molar extraction sockets with rhbmp-2/acs analyze the outcome of a case series of consecutively treated patients who received grafting of the alveolus at time of molar extraction explain the fate of implants placed under functional, occlusal load in sites augmented with any bone graft abstract This case series demonstrates seven molar-site implants placed in six consecutively treated patients. All sites were augmented with rhbmp-2 (1.50 mg/cc)/acs (recombinant human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2/Absorbable Collagen Sponge) at extraction to regenerate bone-facilitating implant placement. In four patients, osteotomies were initiated with trephines to evaluate qualitatively for native bone and for the absence of residual ACS. All sites facilitated implant placement after augmentation. All seven implants achieved primary stabilization and were functionally loaded. No implants were lost or developed complications. It can be concluded that augmenting molar extraction sockets with rhbmp-2/acs can allow standard implant placement in the posterior dentition that is capable of withstanding a functional load. 104 compendium February 2012
2 With the evolution of dental implant therapy, the treatment of extraction sockets has progressed from a simple matter of wound healing to what is often times a complex surgical procedure aimed at minimizing bone resorption. The consequences of physiologic wound healing from extractions often include both vertical and, more prominently, lateral reductions of the local alveolar process. The healing of extraction sockets is accompanied by marked ridge resorption within the first 3 to 4 months. 1 Schropp demonstrated approximately 50% horizontal bone loss 12 months after extractions. 2 Nevins et al demonstrated that when extraction of teeth with prominent roots are augmented with grafts, when compared to ungrafted sites the grafted sites facilitated favorable implant placement. Significantly fewer of the grafted sites required additional grafting procedures at the time of implant placement. 3 Although many ridge augmentation techniques exist, it is certainly more efficacious for both surgeons and patients to prevent bone modeling that results in physiologic resorption and necessitates more involved modalities. The term socket preservation usually refers to the placement of various bone replacement grafts that are often covered with a barrier membrane. The bone graft materials are used to maintain space and serve as an osteoconductive scaffold to support passive osteogenesis within the pores both between and within the graft particulate. Iasella et al demonstrated significantly greater 3-dimensional (3-D) ridge preservation for extraction sockets augmented with allograft bone and collagen membranes compared to ungrafted controls. 4 Araújo et al demonstrated in the canine model that the pores of tricalcium phosphate particulate can be invaded by erythrocytes, and that later these pores would become the locus of new bone formation. These same authors also noted that a degree of delayed healing and minimal bone formation occurred between the second and fourth weeks of recovery. These authors speculated that the β-tcp (beta-tricalcium phosphate) graft may have retarded bone formation. 5 In a review article, Darby et al concluded that ridge preservation is an effective procedure in limiting both horizontal and vertical ridge alterations in post-extraction sites, and that there is no technique superior to another. 6 The barrier membrane provides a soft-tissue exclusionary function, blocking the ingrowth of epithelial and fibroblastic cells and favoring the repopulation of osteoblast cells for bone replacement of the graft material. Investigators such Related content: as Carmagnola et al reported excellent clinical results when particulate xenograft coverage, without soft-tissue closure, was achieved when a collagen membrane was adapted over the bone For more information, read The Maxillary Sinus: Challenges and Treatments for Implant Placement at dentalaegis.com/go/cced57 graft and beneath the mucoperiosteal flap. 7 The majority of these procedures provide 3-D bone volume, facilitating prosthetically driven implant placement. The caveat of these treatments is that osseointegration occurs to support long-term tooth replacement that may involve permanent inclusion of graft material. At the inception of dental implantology, the phenomenon of osseointegration was investigated through histologic animal studies. Titanium implants were inserted into healed alveolar ridges, composed of native bone. Most long-term (over 10 to 15 years) studies followed these types of clinical situations. It would seem logical that ideal clinical situations would support the possibility of implant placement into sites composed of native bone, excluding bone graft materials occupying spaces of potential bony trabeculae. The challenge that still exists today, when teeth require extraction and site preparation is chosen to facilitate future implant placement, is to regenerate de novo bone and maintain osseous morphology favorable for restoratively driven implant placement. Recombinant technology has given surgeons the ability to stimulate wound healing and cellular differentiation, leading to tissue regeneration. The stimulatory properties of these peptides require vehicles for sustained delivery. Some of these growth factors are commercially available in combined packaging, with bone grafting particulate as the delivery vehicle. These materials possess some degree of osteoconductivity and occupy a physical space, preventing maximum osseous fill of the desired space. Some of these growth factors are not specific for osteoblastic differentiation. One of the few commercially available recombinant growth factors proven to be selectively osteoinductive is recombinant human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (rhbmp-2) (INFUSE Bone Graft, Medtronic, Inc. [FDA PMA submission number for INFUSE OMF indication is P ]). rhbmp2 is a differentiation factor that changes the phenotype of precursor cells (mesenchymal stem cells) into osteoblasts and chondroblasts. The standard dose of the protein is 1.50 mg per 1 cc of the solution. The lyophilized rhbmp-2 is combined with sterile water chairside. Once the solution is mixed, it is uniformly dispensed onto an absorbable collagen sponge (ACS). Following a minimal saturation time of 15 minutes, this collagen sponge can be cut into various size strips to be delivered to the site of desired regeneration. The release of the growth factor is sustained over an approximately 2-week time period. Because the ACS is not treated by crosslinking to delay degradation, it is resorbed quickly, leaving no remnants of graft material at the placement site. This facilitates a maximum potential for bone-fill of the grafted defect. The stimulatory regenerative and vascular invasion effects of rhbmp-2 also accelerates bone formation. This is significant because it can shorten the overall treatment time for patients. January 2012 compendium 105
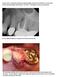
3 Fig 1. Fig 3. Fig 5. Fig 2. Fig 4. Fig 1. Extraction and debridement of tooth No. 30. Fig 2. Obturation of extraction socket with rhbmp-2/acs. Fig 3. Reentry demonstrating complete bone fill. Fig 4. Transmucosal healing of implant No. 30. Fig 5. Final, cement-retained crown No. 30. (restorative therapy by Louis Marion, DMD) Case 1 The patient was a 71-year-old man with significant caries and subsequent bone loss associated with tooth No. 30. The septal bone was lost, with the exception of the coronal aspect, resulting in a bridge of bone connecting the buccal and lingual cortices of the site (Figure 1). After reflection of the full-thickness buccal and lingual flaps, extraction, and manual and ultrasonic debridement of the socket to remove all visible soft-tissue remnants, the defect was obturated with the rhbmp-2/acs material (Figure 2). Fifteen weeks after the first procedure, the site was reopened to perform implant placement. Flap reflection revealed excellent and complete bone reformation (Figure 3). The implant osteotomy preparation was initialized with the harvest of an approximate 5-mm trephine core. The trephine had an internal diameter of 2 mm and an outer diameter of 2.7 mm. The completion of implant placement was performed according to the manufacturer s guidelines, resulting in the delivery of a 5-mm x 11-mm implant with primary stability. Because of excellent subjective stability, a transmucosal healing was chosen, with placement of a healing cap and a nonsubmerged closure (Figure 4). Qualitative histology demonstrated lamellar bone without evidence of the ACS carrier. Restorative therapy commenced approximately 4 months after implant placement. Delivery of the definitive prosthesis, consisting of a gold custom abutment and cement-retained crown, occurred at 5 months following implant placement surgery and 8.5 months after extraction and augmentation (Figure 5). Purpose The purpose of this article is to present a case series of consecutively treated patients (Table 1) who at the time of molar tooth extractions received grafting of the alveolus with the rhbmp-2/acs material alone. This retrospective analysis fully complies with the Helsinki Accords and Ethical Guideline for Clinical Research. All patients included in this case series signed written consent forms that explained the nature of the procedure undertaken, stating that they agreed to undergo the prescribed therapy. These patients were also informed that the material used for augmentation was a recently FDA-approved material that was indicated for grafting of extraction sockets. All grafted sites received dental implants within a 3- to 6-month time period following extraction. Surgical procedures were not altered in terms of underpreparation, bone condensing, or additional grafting at the time of implant placement, with the exception of the initiation of osteotomies with a small (2.7-mm outer and 2-mm inner diameter) trephine. The cores harvested were submitted for qualitative histologic evaluation to confirm the presence of vital bone. All implants subjectively achieved primary mechanical stability and were restored 3 to 8 months after placement. Case 2 The second patient was a 75-year-old woman who presented with a chronic infection associated with a fracture of the distobuccal root of tooth No. 3. Following flap reflection, complete buccal bone loss was associated with the root fracture. Tooth No. 3 was extracted, with all remaining bony walls of the extraction socket being preserved (Figure 6). Debridement was followed by obturation of the defect with the rhbmp-2/acs (Figure 7). A subepithelial, connective tissue pedicle graft was rotated to provide partial coverage of the grafting material. The graft was then closed with a monofilament polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) suture. Approximately 18 weeks following extraction and grafting, full-thickness flaps were reflected, revealing complete osseous regeneration of the original defect (Figure 8). The osteotomy was initiated with the same trephine bur to harvest a core of representative bone present at the site of implant insertion. Implant placement proceeded without alteration from the manufacturer s protocol by inserting a 4.8-mm x 8-mm fixture with primary, tactile, stability, and transmucosal healing properties. At about 8 months postplacement, the implant was restored with a custom abutment and cement-retained crown (Figure 9). 106 compendium February 2012
4 Case 3 The patient was a 66-year-old man who required removal of the three mandibular right molars due to rampant caries and attachment loss. Following flap reflection and extractions, the sockets were debrided with both ultrasonic and manual instrumentation (Figure 10). The sockets of the first and second molars were augmented with rhbmp-2/acs. The site of the third molar was obturated with a noncrosslinked, collagen plug for hemostatic purposes only. The restorative treatment plan encompassed tooth replacement in the first and second molar positions only, negating the need for the patient to incur the greater expense of augmenting the third molar site. Primary closure was achieved with a monofilament PTFE suture. Approximately 6 months after the extractions and augmentation procedure, the patient returned for implant placement surgery. Surgical reopening revealed excellent visual regeneration and ridge preservation (Figure 11). The site of the tooth No. 31 osteotomy was chosen for biopsy harvesting, because this is where the most severe bone loss existed at the time of extraction, and this site would be most representative of new bone formation, as opposed to possibly harvesting preexisting native bone. This trephine core qualitatively revealed what was diagnosed by the histopathologist as normal bone without any foreign body or inflammatory responses being evident (Figure 12). Serving as a historic control, Trombelli et al reported on histomorphometric measurements of various tissues present at different time intervals. These authors describe great variability in human trephine cores taken from extraction sites. In relation to the present case series, Trombelli et al described the presence of a provisional matrix and woven bone dominating what they described as late-phase healing taken at 12 to 24 weeks after extractions. Although tissue Fig 6. Fig 8. Related content: For more information, read Bone Grafting/Tissue Regeneration Materials at dentalaegis.com/go/cced58 Fig 7. Fig 9. Fig 6. Extraction socket of tooth No. 3 demonstrating loss of distobuccal cortex. Fig 7. Obturation of extraction socket with rhbmp-2/ ACS. Fig 8. Re-entry showing complete bone regeneration. Fig 9. Radiographic appearance of restored implant. modeling was described as fast, the authors found the remodeling of the newly formed bone to be what they called seemingly slow. The trephine core presented in this particular case demonstrated this type of healing, as described by Trombelli et al. 8 A high degree of woven bone as well as a cell and fiber-abundant provisional matrix was present. Two 4.8-mm x 10-mm implants were placed using standard protocol. These implants achieved primary stabilization and facilitated transmucosal healing. At just under 20 weeks, the two implants were restored with two individual cement-retained crowns (Figure 13). table 1 Case Series of Consecutively Treated Patients Patient Date extraction Placement Implant Implant Date Date Tooth # Diameter Length restored Pt. 1 (RF) 7/9/10 10/29/10 #30 5 mm 11 mm 3/3/11 Pt. 2 (EO) 7/28/09 12/4/09 #3 4.8 mm 8 mm 7/12/10 Pt. 3 (LS) 5/28/10 11/1/10 #30, # mm 10 mm 3/25/11 Pt. 4 (MH) 7/28/09 11/19/10 #3 4.8 mm 8 mm 2/24/10 Pt. 5 (BS) 3/9/10 9/13/10 # mm 10 mm 1/5/11 Pt. 6 (GS) 6/10/10 11/25/10 # mm 10 mm 3/10/11 February 2012 compendium 107
5 Findings All of the consecutively treated patients underwent extraction of molar teeth, simultaneous bone augmentation with rhbmp-2/acs, and implant placement approximately 4 to 6 months after the first procedure. It is important to point out several findings: First, all of the augmented sites facilitated restoratively driven implant placement that was not possible at the time of extraction because of bony insufficiency. Second, all implants subjectively achieved primary stability. No mobility or rotation of the implants occurred upon tightening of the healing abutments. Third, no additional bone augmentation was necessary at the time of implant placement in any of these cases. Implant placement resulted in circumferential bony coverage of the implant surfaces either to the collar of the implants, or to the rough smooth titanium border, depending on the implant type used in each individual situation. The most common adverse event or morbidity was mild to moderate postoperative edema that was noted intra- and extraorally. This reaction to oral grafting with rhbmp-2/acs has also been reported by Boyne et al. 9 These same investigators detected antibody production to rhbmp-2 in a small percentage (12%) of patients treated with a therapeutic dosage of 1.50 mg/ml. This was a transient finding that did not affect treatment outcomes or require further treatment. It is also worth mentioning that although the retrieved trephine cores revealed qualitative evidence of healthy bone, without evidence of persisting graft material or adverse cellular reactions, Fig 10. Fig 12. Fig 11. Fig 13. Fig 10. Extraction and debridement of tooth Nos. 30 through 32. Fig 11. Osteotomy preparation for two 4.8-mm wide implants into regenerated native bone. Fig 12. Histologic core (2.7 mm) of the No. 31 site demonstrating presence of native bone without any evidence of ACS. Note darkly staining artifact from removal from trephine drill. (hematoxylin and eosin; 10X magnification) Fig 13. Radiograph at time of restoration of two separate implants, with cement-retained crowns and healthy proximal bone levels. histomorphometry was not performed. The percentages of woven bone, lamellar bone, and soft tissue within the cores were not evaluated. The purpose of the histologic component of this report is to demonstrate the presence of viable native bone, without undesired inflammatory processes or residual graft materials, in the locations of implant insertions. Most importantly, from a clinical perspective, all consecutively placed implants in this case series achieved osseointegration and were functionally loaded in a standard period of time (3 to 8 months). Delayed loading due to poor subjective bone quality or suboptimal implant stability was not found with any of the implants in this case series. Discussion Ridge preservation is a frequently investigated subject. Numerous combinations of bone replacement grafts, barrier membranes, and the addition of various growth factors have been evaluated. The primary goal of these procedures is to preserve and/or regenerate alveolar bone associated with extraction sockets and prevent the anticipated, physiologic bone resorption that follows tooth loss. Araújo et al found that when canine extraction sockets are augmented with Bio-Oss Collagen (Osteohealth, com), some of the expected dimensional alterations could be offset. The collagen portion of the graft was readily eliminated, whereas the xenograft portion of the graft persisted, although bone formation occurred on the surface of the graft particles. 10 The presence of newly formed bone onto the nonresorbable graft surface demonstrates the passive process of osteoconduction. Graft particles are placed into the site and the repopulation of the bone-forming cells occurs over time and is dependent on the individual defect s and patient s ability to heal and regenerate lost or damaged tissue. This process lacks a stimulatory cellular component. According to Lane et al, 11 the tissue engineering model is composed of three elements. First, each site of regeneration requires that cells be capable of differentiating into the desired cell line needed to regenerate the desired lost tissue. Second, a signaling molecule is required to provide chemotactic, morphogenic, and differentiation messages to these cells. Third, the signaling molecule and migrating cells require a scaffold or matrix to provide the physical space necessary to carry the message to the site and facilitate cellular migration. The fate of implants placed under functional, occlusal load in sites augmented with any bone graft is a primary concern for clinicians and patients. The possibility of placing implants is the first step in a multistep process of tooth replacement. Initial stability, followed by secondary stability or osseointegration, is the specialty of the restorative dentist. Treatment is considered a failure if these implants do not function in a healthy state, under normal occlusal conditions. In an animal model, Jovanovic et al demonstrated that machined titanium implants can function for 12 months after 108 compendium February 2012
6 placement in sites of experimental defects augmented with rh- BMP-2/ACS 3 months prior to placement. Not only were these implants successfully loaded for 1 year, but the authors also noted that the bone-to-implant contact (BIC) for fixtures inserted into rh- BMP-2 grafted sites was comparable to implants placed into native bone. 12 In a pilot study conducted in humans, Cochran et al evaluated a subtherapeutic dose of rhbmp-2 (0.43 mg/cc) in extraction sockets or ridge augmentations. The 3-year results demonstrated safety and long-term efficacy of this growth factor for site development facilitating implant placement. 13 In a randomized controlled study, Fiorellini et al evaluated rhbmp-2/acs delivered at 1.50 mg/ cc, 0.75 mg/cc, ACS alone, and ungrafted controls in the treatment of maxillary extraction sockets with buccal wall defects. 14 Significant ridge height was preserved, and bone width was regenerated when the sites were augmented with rhbmp-2/acs. Ungrafted and ACSonly grafted sites demonstrated little bone regeneration. The sites grafted with the commercially available dosage of 1.50 mg/cc of rhbmp-2 outperformed the sockets grafted with the subtherapeutic dose of 0.75 mg/cc in terms of dimensional bone maintenance and regeneration. These investigators evaluated anterior sites for socket augmentation and preservation. The present case series follows consecutively treated molar sites. This may be of significance because most human studies evaluating rhbmp-2/acs for bone regeneration have focused on maxillary sinus grafts 14,15 or maxillary anterior extraction sites. When comparing the findings of the present case series with ungrafted extraction sockets, it can be concluded that regeneration of native bone not unlike normal bone remodeling occurred. Serving as another historic control, Evian et al studied histologic cores of ungrafted extraction sites at varying time intervals. These investigators noted two distinct regenerative phases. From 4 to 8 weeks, a progressive osteogenic phase was described. From 8 weeks on, the osteogenesis slows down and maturation of bony trabeculae increases in bone volume. Bone that was present in the 16-week study specimen was described as mature, with fewer cellular elements compared to earlier specimens. The bone found in this case series was qualitatively similar to the later specimens in the Evian study of ungrafted extraction sites. 16 Conclusion It can be concluded that augmentation of molar extraction sockets with rhbmp-2/acs results in the regeneration of de novo bone, capable of accepting timely implant placement, without altering manufacturer-specified osteotomy preparation, and functional loading in a standard time period. Because the implants were inserted and loaded prosthetically into native bone, without the presence of residual graft materials, these implants can be expected to achieve optimal long-term success, comparable to implants placed into unmanipulated, edentulous bone. ABOUT THE AUTHORS Barry P. Levin, DMD Clinical Associate Professor, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Peter Tawil, DDS Former Resident in Periodontics, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; Private Practice, Beirut, Lebanon References 1. Amler MH. The time sequence of tissue regeneration in human extraction wounds. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1969;27(3): Schropp L, Wenzel A, Kostopoulos L, Karring T. Bone healing and soft tissue contour changes following single-tooth extraction: a clinical and radiographic 12-month prospective study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2003;23(4): Nevins M, Camelo M, De Paoli S, et al. A study of the fate of the buccal wall of extraction sockets of teeth with prominent roots. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2006;26(1): Iasella JM, Greenwell H, Miller RL, et al. Ridge preservation with freeze-dried bone allograft and a collagen membrane compared to extraction alone for implant site development: a clinical and histologic study in humans. J Periodontol. 2003;74(7): Araújo MG, Liljenberg B, Lindhe J. beta-tricalcium phosphate in the early phase of socket healing: an experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(4): Darby I, Chen ST, Buser D. Ridge preservation techniques for implant therapy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24(suppl): Carmagnola D, Adriaens P, Berglundh T. Healing of human extraction sockets filled with Bio-Oss. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003;14(2): Trombelli L, Farina R, Marzola A, et al. Modeling and remodeling of human extraction sockets. J Clin Periodontol. 2008;35(7): Boyne PJ, Lilly LC, Marx RE, et al. De novo bone induction by recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhbmp-2) in maxillary sinus floor augmentation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;63(12): Araújo M, Linder E, Wennström J, Lindhe J. The influence of Bio-Oss Collagen on healing of an extraction socket: an experimental study in the dog. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2008;28(2): Lane JM, Yasko AW, Tomin E, et al. Bone marrow and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in osseous repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;361: Jovanovic SA, Hunt DR, Bernard GW, et al. Long-term functional loading of dental implants in rhbmp-2 induced bone. A histologic study in the canine ridge augmentation model. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003;14(6): Cochran DL, Jones AA, Lilly LC, et al. Evaluation of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in oral applications including the use of endosseous implants: 3-year results of a pilot study in humans. J Periodontol. 2000;71(8): Fiorellini JP, Howell TH, Cochran D, et al. Randomized study evaluating recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 for extraction socket augmentation. J Periodontol. 2005;76(4): Triplett RG, Nevins M, Marx RE, et al. Pivotal, randomized, parallel evaluation of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2/ absorbable collagen sponge and autogenous bone graft for maxillary sinus floor augmentation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;67(9): Evian CI, Rosenberg ES, Coslet JG, Corn H. The osteogenic activity of bone removed from healing extraction sockets in humans. J Periodontol. 1982;53(2): compendium February 2012
7 Quiz Posterior Tooth Replacement with Dental Implants in Sites Augmented with rhbmp-2 at Time of Extraction A Case Series Barry P. Levin, DMD; and Peter Tawil, DDS This article provides 2 hours of CE credit from AEGIS Publications, LLC. Record your answers on the enclosed answer form or submit them on a separate sheet of paper. You may also phone your answers in to or fax them to (215) or log on to and click on Continuing Education. Be sure to include your name, address, telephone number, and last 4 digits of your Social Security number. PLEASE COMPLETE ANSWER FORM ON Page 114, INCLUDING YOUR NAME AND PAYMENT INFORMATION. 1. Schropp demonstrated approximately what percentage of horizontal bone loss 12 months after extractions? A. 10% B. 25% C. 40% D. 50% 2. What term usually refers to the placement of various bone replacement grafts that are often covered with a barrier membrane? A. ridge augmentation B. socket preservation C. bone resorption D. recombinant technology 3. Darby et al concluded that ridge preservation is an effective procedure in limiting both horizontal and vertical ridge alterations in: A. post-extraction sites. B. barrier membrane. C. the mucoperiosteal flap. D. allograft bone. 4. recombinant technology has given surgeons the ability to stimulate wound healing and cellular differentiation, leading to: A. tooth restoration. B. de novo bone regeneration. C. tissue regeneration. D. bone grafting. 5. Lyophilized rhbmp-2 is combined with sterile water chairside. Once the solution is mixed, it is uniformly dispensed onto: A. an absorbable collagen sponge. B. beta-tricalcium phosphate. C. bone allograft. D. bovine bone material. 6. trombelli et al reported on histomorphometric measurements of various tissues present at different time intervals and described great variability in: A. pre-existing native bone. B. newly formed bone. C. human trephine cores taken from extraction sites. D. woven bone. 7. all of the augmented sites facilitated restoratively driven implant placement that was not possible at the time of extraction because of: A. bony insufficiency. B. significant caries. C. chronic infection. D. attachment loss. 8. in an animal model, Jovanovic et al demonstrated that machined titanium implants can function for how long after placement in sites of experimental defects augmented with rhbmp-2/acs? A. 12 months B. 18 months C. 2 years D. 5 years 9. When comparing the findings of the present case series with ungrafted extraction sockets, it can be concluded that: A. severe bone loss occurred. B. physiologic bone resorption occurred. C. regeneration of native bone occurred. D. regeneration of native bone did not occur. 10. Because the implants were inserted and loaded prosthetically into native bone, without the presence of residual graft materials, these implants can be expected to: A. fail to achieve primary stabilization. B. achieve optimal long-term success. C. develop complications. D. all of the above Course is valid from 2/1/2012 to 2/28/2015. Participants must attain a score of 70% on each quiz to receive credit. Participants receiving a failing grade on any exam will be notified and permitted to take one re-examination. Participants will receive an annual report documenting their accumulated credits, and are urged to contact their own state registry boards for special CE requirements. AEGIS Publications, LLC, is an ADA CERP Recognized Provider. ADA CERP is a service of the American Dental Association to assist dental professionals in identifying quality providers of continuing dental education. ADA CERP does not approve or endorse individual courses or instructors, nor does it imply acceptance of credit hours by boards of dentistry. Concerns or complaints about a CE provider may be directed to the provider or to ADA CERP at Program Approval for Continuing Education Approved PACE Program Provider FAGD/MAGD. Credit Approval does not imply acceptance by a state or provincial board of dentistry or AGD endorsement. (7/18/1990 to 12/31/2012) 112 compendium February 2012
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
Sinus Augmentation Studies Methods and Definition
 FDA approved indications for Infuse Bone Graft in the Maxillofacial Skeleton Alveolar Ridge Augmentation (Buccal Wall Defects) in the Maxilla Maxillary Sinus Floor augmentation Sinus Augmentation Studies
FDA approved indications for Infuse Bone Graft in the Maxillofacial Skeleton Alveolar Ridge Augmentation (Buccal Wall Defects) in the Maxilla Maxillary Sinus Floor augmentation Sinus Augmentation Studies
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Bone Grafting for Socket Preservation
 Bone Grafting for Socket Preservation Dr. Karl R. Koerner Normal extraction facial bone loss. Excessive force. Commonly the thickness of facial bone. Hussain, A. et al. Ridge preservation comparing a nonresorbable
Bone Grafting for Socket Preservation Dr. Karl R. Koerner Normal extraction facial bone loss. Excessive force. Commonly the thickness of facial bone. Hussain, A. et al. Ridge preservation comparing a nonresorbable
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
More than bone regeneration. A total solution.
 More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS
 A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS INDICATIONS: 1/ SOCKET AND RIDGE PRESERVATION 2/ FILLING OF EXTRACTION SOCKETS Biomaterials offers portfolio of regenerative materials for implantology, aimed at
A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS INDICATIONS: 1/ SOCKET AND RIDGE PRESERVATION 2/ FILLING OF EXTRACTION SOCKETS Biomaterials offers portfolio of regenerative materials for implantology, aimed at
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS. The unique collagenase-resistant membrane protects bone graft and supports treatment success even when exposed 4
 RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS 1 RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS RESISTANT TO EXPOSURE The unique collagenase-resistant membrane protects bone graft and supports treatment success even when exposed 4 RELIABLE BARRIER
RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS 1 RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS RESISTANT TO EXPOSURE The unique collagenase-resistant membrane protects bone graft and supports treatment success even when exposed 4 RELIABLE BARRIER
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Procedure Manual and Catalog
 Procedure Manual and Catalog TM Why SynthoGraft? SynthoGraft offers a unique structure which provides stability, while its micro-porosity allows for rapid vascularization and subsequent resorption. Although
Procedure Manual and Catalog TM Why SynthoGraft? SynthoGraft offers a unique structure which provides stability, while its micro-porosity allows for rapid vascularization and subsequent resorption. Although
The Original remains unique.
 The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Ridge Split Procedure
 Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Socket preservation using deproteinized horsederived
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2010;40:227-231 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.5.227 Socket preservation using deproteinized horsederived bone mineral Jang-Yeol Park, Ki-Tae Koo, Tae-Il Kim, Yang-Jo
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2010;40:227-231 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.5.227 Socket preservation using deproteinized horsederived bone mineral Jang-Yeol Park, Ki-Tae Koo, Tae-Il Kim, Yang-Jo
Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation. Sanju P. Jose
 Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation by Sanju P. Jose B.S., University of Maryland Baltimore County, 2008 D.D.S., University of Maryland School
Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation by Sanju P. Jose B.S., University of Maryland Baltimore County, 2008 D.D.S., University of Maryland School
Clinical cases by Dr. Fernando Rojas-Vizcaya. botiss. dental bone & tissue regeneration. biomaterials. strictly biologic
 Clinical cases by Dr. Fernando Rojas-Vizcaya dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials strictly biologic botiss BTR system: BONE biologic potential bovine block & granules: pure bone mineral
Clinical cases by Dr. Fernando Rojas-Vizcaya dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials strictly biologic botiss BTR system: BONE biologic potential bovine block & granules: pure bone mineral
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Maryland AGD AE and Socket Grafting 2015
 The Goodacre Study 5 year retrospective study looked at Crown & Bridge Caries Single crowns 1% FPD abutments 17% Periodontal Involvement Single crowns
The Goodacre Study 5 year retrospective study looked at Crown & Bridge Caries Single crowns 1% FPD abutments 17% Periodontal Involvement Single crowns
Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging
 Bone Grafting: Essential Indications and Techniques in Implant Dentistry Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging and sometimes unpredictable. Candidates for implant therapy must have
Bone Grafting: Essential Indications and Techniques in Implant Dentistry Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging and sometimes unpredictable. Candidates for implant therapy must have
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques
 Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
Socket Treatment. Procedure Guide
 Socket Treatment Procedure Guide www.implantdirect.com 888.649.6425 Extraction Healing and Ridge Resorption The Why Working with patients to educate them on the benefits of bone maintenance post extraction
Socket Treatment Procedure Guide www.implantdirect.com 888.649.6425 Extraction Healing and Ridge Resorption The Why Working with patients to educate them on the benefits of bone maintenance post extraction
Pre op Failed endodontic treatment with sinus involvement.
 Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration. Ph.D. Thesis. Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban
 Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
SOCKET WHETHER TO PRESERVE IT NOW OR TO CREATE LATER? - A CASE REPORT
 MAVEN CASE REPORT SOCKET WHETHER TO PRESERVE IT NOW OR TO CREATE LATER? - A CASE REPORT Dr. Parthasarathi Biswas 1, Dr. Debajyoti Mondal 1, Dr. B Praveena Devi 1, Dr. Indrasri Das 2, Dr. Somen Bagchi 3,
MAVEN CASE REPORT SOCKET WHETHER TO PRESERVE IT NOW OR TO CREATE LATER? - A CASE REPORT Dr. Parthasarathi Biswas 1, Dr. Debajyoti Mondal 1, Dr. B Praveena Devi 1, Dr. Indrasri Das 2, Dr. Somen Bagchi 3,
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
The Essential Choice. With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability
 The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
THINKING OUTSIDE THE PALATE
 THINKING OUTSIDE THE PALATE SIMPLIFIED RECESSION GRAFTING Course Objectives-In this course you will be able to: See how much less complicated this technique is compared to Pin-Hole and tunneling. Recognize
THINKING OUTSIDE THE PALATE SIMPLIFIED RECESSION GRAFTING Course Objectives-In this course you will be able to: See how much less complicated this technique is compared to Pin-Hole and tunneling. Recognize
Guided Tissue and Bone Regeneration
 Guided Tissue and Bone Regeneration One toolbox for your needs! Tefguide 9000 742 401 12x24 mm pc 1 Osgide 9000 701 520 15 x 20 mm pc 1 Osbone 9000 800 255 250-1000 μm 0.25 cc 5 Product Specifications
Guided Tissue and Bone Regeneration One toolbox for your needs! Tefguide 9000 742 401 12x24 mm pc 1 Osgide 9000 701 520 15 x 20 mm pc 1 Osbone 9000 800 255 250-1000 μm 0.25 cc 5 Product Specifications
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
REASONS TO USE R.T.R.
 3 REASONS TO USE R.T.R. AFTER EACH EXTRACTION Fully resorbable ß-TCP material RTR 3raisons 120x280.indd 1 16/06/15 10:52 1AVOID SPONTANEOUS RIDGE RESORPTION After tooth extraction, spontaneous healing
3 REASONS TO USE R.T.R. AFTER EACH EXTRACTION Fully resorbable ß-TCP material RTR 3raisons 120x280.indd 1 16/06/15 10:52 1AVOID SPONTANEOUS RIDGE RESORPTION After tooth extraction, spontaneous healing
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Horizontal bone augmentation by means of guided bone regeneration
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 13 40 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Horizontal bone augmentation by means
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 13 40 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Horizontal bone augmentation by means
Immediate Implant Placement in Deficient Bone Sites
 clinical Raj Chopra BSc, DDS Immediate Implant Placement in Deficient Bone Sites THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN PEER-REVIEWED. Introduction The presence of a low-lying sinus floor and inadequate bone volume often
clinical Raj Chopra BSc, DDS Immediate Implant Placement in Deficient Bone Sites THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN PEER-REVIEWED. Introduction The presence of a low-lying sinus floor and inadequate bone volume often
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES
 LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES The following is a complete list of those dental Services which will be considered for payment by Constitution Life Insurance Company after the expiration of any applicable
LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES The following is a complete list of those dental Services which will be considered for payment by Constitution Life Insurance Company after the expiration of any applicable
The Essential Choice. With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability
 The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft
 Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation
 Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation Historical Background Guided tissue regeneration is a well established concept in the repair of oral bone defects. The exclusion of soft tissue epithelial
Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation Historical Background Guided tissue regeneration is a well established concept in the repair of oral bone defects. The exclusion of soft tissue epithelial
Innovative Range of Regenerative Solutions
 TM Innovative Range of Regenerative Solutions MIS Implant Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved. Optimal volumes and quality of hard and soft tissue are required to satisfy the goals of oral rehabilitation
TM Innovative Range of Regenerative Solutions MIS Implant Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved. Optimal volumes and quality of hard and soft tissue are required to satisfy the goals of oral rehabilitation
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
The body wants to heal
 58 A promising new particulate graft material: a case study The body wants to heal DR PETER J.M. FAIRBAIRN, DETROIT MERCY, MI, USA, AND LONDON, ENGLAND, AND DR MINAS LEVENTIS, ATHENS, GREECE The notion
58 A promising new particulate graft material: a case study The body wants to heal DR PETER J.M. FAIRBAIRN, DETROIT MERCY, MI, USA, AND LONDON, ENGLAND, AND DR MINAS LEVENTIS, ATHENS, GREECE The notion
SOCKET PRESERVATION AND TECHNIQUES AN EVALUATION OF THE LITERATURE
 SOCKET PRESERVATION AND TECHNIQUES AN EVALUATION OF THE LITERATURE Raghav Khandelwal, DMD Highland General Hospital Assistant Program Director: Ben Shimel, DDS Program Director/Chair: Chan Park, DDS,MD
SOCKET PRESERVATION AND TECHNIQUES AN EVALUATION OF THE LITERATURE Raghav Khandelwal, DMD Highland General Hospital Assistant Program Director: Ben Shimel, DDS Program Director/Chair: Chan Park, DDS,MD
EDI Journal. Techniques to control or avoid cement around implant-retained restorations. European Journal for Dental Implantologists TOPIC
 ISSN 1862-2879 Issue 4/2013 Vol. 9 EDI Journal European Journal for Dental Implantologists TOPIC Techniques to control or avoid cement around implant-retained restorations»edi News: Coming up: 9th BDIZ
ISSN 1862-2879 Issue 4/2013 Vol. 9 EDI Journal European Journal for Dental Implantologists TOPIC Techniques to control or avoid cement around implant-retained restorations»edi News: Coming up: 9th BDIZ
Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs
 Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate
 AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate The AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry provides an opportunity for AO members to demonstrate that they have attained a level of education and experience
AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate The AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry provides an opportunity for AO members to demonstrate that they have attained a level of education and experience
Senior Dental Insurance Scheduled Allowance
 Senior Dental Insurance Scheduled Allowance LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES The following is a complete list of those dental services which will be considered for payment by The American Progressive Life
Senior Dental Insurance Scheduled Allowance LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES The following is a complete list of those dental services which will be considered for payment by The American Progressive Life
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
botiss dental bone & tissue regeneration biomaterials collacone max Innovative composite matrix socket preservation form-fitting resorbable composite
 dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials socket preservation Innovative composite matrix form-fitting resorbable composite 1 botiss regeneration system maxresorb flexbone* collacone.. max
dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials socket preservation Innovative composite matrix form-fitting resorbable composite 1 botiss regeneration system maxresorb flexbone* collacone.. max
botiss biomaterials bone & tissue regeneration collacone max Innovative composite matrix socket preservation form-fitting resorbable composite
 bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials socket preservation Innovative composite matrix form-fitting resorbable composite 1 Socket preservation safeguarding your sockets collacone.. max flexbone*
bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials socket preservation Innovative composite matrix form-fitting resorbable composite 1 Socket preservation safeguarding your sockets collacone.. max flexbone*
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes
 Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Vertical and horizontal alveolar ridge augmentation
 CLINICAL SIMULTANEOUS VERTICAL GUIDED BONE REGENERATION AND GUIDED TISSUE REGENERATION IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA USING RECOMBINANT HUMAN PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTOR: A CASE REPORT Istvan Urban, DMD,
CLINICAL SIMULTANEOUS VERTICAL GUIDED BONE REGENERATION AND GUIDED TISSUE REGENERATION IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA USING RECOMBINANT HUMAN PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTOR: A CASE REPORT Istvan Urban, DMD,
Alloplastic Grafts - Beta-tricalcium phosphate
 Alloplastic Grafts - Beta-tricalcium phosphate Presentation of clinical cases Mario Ernesto García-Briseño DDS and Professor in Periodontics - Autonomous University of Guadalajara (UAG), Mexico This case
Alloplastic Grafts - Beta-tricalcium phosphate Presentation of clinical cases Mario Ernesto García-Briseño DDS and Professor in Periodontics - Autonomous University of Guadalajara (UAG), Mexico This case
Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla
 IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
CONTINUING EDUCATION 2 : ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION
 CONTINUING EDUCATION 2 : ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION Alveolar Ridge Augmentation: Combining Bioresorbable Scaffolds with Osteoinductive Bone Grafts in Atrophic Sites. A Follow-Up to an Evolving Technique
CONTINUING EDUCATION 2 : ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION Alveolar Ridge Augmentation: Combining Bioresorbable Scaffolds with Osteoinductive Bone Grafts in Atrophic Sites. A Follow-Up to an Evolving Technique
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
Alveolar Ridge Preservation:
 Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Tooth out what's next?
 Tooth out what's next Content >> Treatment Options >> Clinical Cases >> Product Information >> Product related FAQs >> Why Ridge Preservation > Minimise invasion: Bone volume preservation > Minimise invasion:
Tooth out what's next Content >> Treatment Options >> Clinical Cases >> Product Information >> Product related FAQs >> Why Ridge Preservation > Minimise invasion: Bone volume preservation > Minimise invasion:
Techniques for the use of autogenous bone grafting to minimize morbidity and increase treatment outcome
 Front Cover Bone Symposium 2014 Dear Colleague, I want to personally invite you to attend the Pikos Institute sponsored Bone Symposium 2014. This one of a kind program will feature 12 of the world s master
Front Cover Bone Symposium 2014 Dear Colleague, I want to personally invite you to attend the Pikos Institute sponsored Bone Symposium 2014. This one of a kind program will feature 12 of the world s master
Bone augmentation with biomaterials
 Patient information dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials Bone augmentation with biomaterials established safe natural X100 Implantation stability is crucial for success Atrophy of the
Patient information dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials Bone augmentation with biomaterials established safe natural X100 Implantation stability is crucial for success Atrophy of the
Symbios Xenograft Granules Porcine Bone Graft Material
 Symbios Xenograft Granules Porcine Bone Graft Material 32671122-USX-1607_Symbios Highlight Brochure.indd 1 2016-09-27 12:12 Symbios Xenograft Granules Porcine bone graft material Symbios Xenograft Granules
Symbios Xenograft Granules Porcine Bone Graft Material 32671122-USX-1607_Symbios Highlight Brochure.indd 1 2016-09-27 12:12 Symbios Xenograft Granules Porcine bone graft material Symbios Xenograft Granules
Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident
 Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits. Your combination for success
 Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94
 ( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
Strong bone for beautiful teeth. Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide
 Strong bone for beautiful teeth Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Contents Smiling is the most beautiful way to show your teeth 3 What are the causes
Strong bone for beautiful teeth Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Contents Smiling is the most beautiful way to show your teeth 3 What are the causes
PRP Usage in Today's Implantology
 Volume 1, December 2004 www.implant.co.il PRP Usage in Today's Implantology by Dr. R. Shapira Introduction: Treating patients suffering from hematological disorders or using anticoagulant medications always
Volume 1, December 2004 www.implant.co.il PRP Usage in Today's Implantology by Dr. R. Shapira Introduction: Treating patients suffering from hematological disorders or using anticoagulant medications always
Scientific & Clinical Evidence Jason membrane
 Scientific & Clinical Evidence Jason membrane Pericardium GBR/GTR Membrane Facts - CE since 2009 - so far no serious clinical complication or objection - approx. 250.000 successful clinical treatments
Scientific & Clinical Evidence Jason membrane Pericardium GBR/GTR Membrane Facts - CE since 2009 - so far no serious clinical complication or objection - approx. 250.000 successful clinical treatments
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Clinical Perspectives
 Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS. Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel GTO I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E
 GTO THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel R E G E N E R A T I O N S C I E N C E I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E A unique biotechnology
GTO THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel R E G E N E R A T I O N S C I E N C E I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E A unique biotechnology
Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets
 Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
botiss dental bone & tissue regeneration biomaterials mucoderm 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic
 dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Gingivectomy, excision gingival, each quadrant Gingivoplasty, each quadrant
 Dental in Nature Oral Surgery Effective CDT D3410 surgery - anterior D3421 surgery bicuspid (first root) D3425 surgery molar (first root) D3426 D3427 surgery (each additional root) Periradicular surgery
Dental in Nature Oral Surgery Effective CDT D3410 surgery - anterior D3421 surgery bicuspid (first root) D3425 surgery molar (first root) D3426 D3427 surgery (each additional root) Periradicular surgery
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft
 Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior
 Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Whether a consequence of periodontal disease, caries or trauma to the root, losing an anterior tooth is psychologically
Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Whether a consequence of periodontal disease, caries or trauma to the root, losing an anterior tooth is psychologically
(Images are at the end of article)
 Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Immediate Implant Placement Along With Guided Bone Regeneration In Mandibular Anterior Region A Case Report.
 IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report
 Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
4766 Research Dr. San Antonio, TX insightdentalsystems.com
 OVERVIEW OF THE INSIGHT DENTAL IMPLANT DELIVERY SYSTEM The IDS system comes in a unit dose implant system where its advantage provides sterile instrumentation in one single-use kit. It is organized to
OVERVIEW OF THE INSIGHT DENTAL IMPLANT DELIVERY SYSTEM The IDS system comes in a unit dose implant system where its advantage provides sterile instrumentation in one single-use kit. It is organized to
BOSTON TEACHERS UNION PARAPROFESSIONAL HEALTH AND WELFARE FUND Schedule of Covered Dental Procedures for the Dental Plan - Effective January 1, 2009
 TYPE 1 D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 27.81 D0140 Limited oral evaluation - problem focused 43.15 D0145 Oral evaluation for a patient under three years of age and 22.20 counseling with primary caregiver
TYPE 1 D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 27.81 D0140 Limited oral evaluation - problem focused 43.15 D0145 Oral evaluation for a patient under three years of age and 22.20 counseling with primary caregiver
