Histology of Skin. dr. Alya Amila Fitrie, M.Kes dr. Radita Nur Anggraeni Department of Histology Medical Faculty University of North Sumatera 2008
|
|
|
- Antony Johns
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Histology of Skin dr. Alya Amila Fitrie, M.Kes dr. Radita Nur Anggraeni Department of Histology Medical Faculty University of North Sumatera
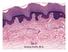
2 INTRODUCTION The heaviest single organ of the body, 16% of TBW. Presenting 1,2 2,3 m 2 of surface. Composed of : Epidermis : an epithelial layer of ectodermal origin Dermis : a layer of connective tissue of mesodermal origin. 2
3 Comparative thickness of the skin 3
4 EPIDERMIS Consist mainly of a stratified squamous keratinized epithelium keratinocytes. Three << abundant cell types : 1. Melanocytes : neural crest-derived cell 2. Langerhans cell : derived from bone marrow precursor 3. Merkel s cell : neural crest-derived cell 4
5 Five layers of keratin-producing cells (keratinocytes) : 1. Stratum basale (t (stratum t germinativum) 2. Stratum spinosum 3. Stratum granulosum 4. Stratum lucidum 5. Stratum corneum 5
6 Stratum basale (Stratum germinativum) Single layer of basophilic columnar or cuboidal cell resting on basement membrane at the dermal-epidermal junction. Desmosom (+), hemidesmosom (+) Stem cells intense mitotic activity & is responsible, in conjunction with the initial portion of the next layer, for constant t renewal of epidermal cells. Human epidermis is renewed about every days. 6
7 Stratum spinosum Consists of cuboidal or slighly flattened cell, a central nucleus, a cytoplasm s processes : bundles of keratin filaments, a spine-studded st appearance ance (tonofilaments). The filaments : Maintaining cohesion among cells Resisting the effect of abrasion Stratum t basale + stratum t spinosum = stratum Malpighi mitoses 7
8 Stratum spinosum (cont.) Stratum spinosum of the thick skin from sole of the foot. Pararosaniline-toluidine blue. Medium magnification 8
9 Stratum granulosum Consists of 3-5 layers of flattened polygonal l cells, cytoplasm filled with keratohyalin granules. The membrane-coated lamellar granules : containing i lamellar ll disks that are formed by lipid bilayers. This granules : fuse with cell membrane discharge their contents intercellular spaces of stratum granulosum form of sheets containing lipid 9
10 Stratum lusidum Translucent, thin layer of flattened eosinophilic epidermal cells. Organelles & nuclei (-) Cytoplasm : densely packed keratin filaments Desmosom (+) between adjacent cells 10
11 Stratum corneum Cornified envelope lipids Consists of layers of fflattened nonnucleated keratinized cells. Cytoplasm : a birerfringent filamentous scleroprotein, keratin. After keratinization, the cells consist of only fibrillar & amorphous proteins; & thickened plasma membrane horny cells or corneocyte 11
12 Melanocytes A specialized cell of the epidermis found beneath or between the cells of the stratum basale & in the hair follicles. Derived from neural crest cells. Hemidesmosomes(+), desmosome (-) 12
13 Melanogenesis php?pos=bl&im=images/melanocyte%20develop ment%20and%20pigmentation.jpg Tyrosinase is synthesized in the RER, accumulated in GoC vesikel : melanosom. Melanin synthesis in the melanosom II melanosom III melanin granules. Melanin granules migrates & transferred to the keratinocytes of the malpighian layer. 13
14 Melanocyte Melanin granules accumulate in the supranuclear region of the cytoplasm protecting from deleterious effects of solar radiation. 14
15 Langerhans Cells Star-shaped Location : stratum spinosum Bone marrow-derived Important in immunologic skin reaction 15
16 Merkel s Cells Generally in the thick skin of palms and soles. Resemble the epidermal epithelial l cells, with small dense granules in cytoplasm. Free nerve ending at the base. 16
17 Immunologic Activity in the Skin Its large size Lymphocytes >>> Antigen-presenting g cells (APC) Close contacts with antigenic molecules Epidermis has an important role in some types of immune response 17
18 DERMIS Dermis is connective tissue that Support epidermis i Binds epidermis to hypodermis The thickness : varies The surface : irregular dermal papillae >< epidermal ridges. Contains 2 layers : Papillary layer Reticular layer 18
19 Papillary Layer Composed of : Loose connective tissue Fibroblasts Other connective tissue cells : mast cells & macrophages Extravasated leukocytes Anchoring fibrils (+) : special collagen fibrils 19
20 Reticular Layer Composed of : Irregular dense connective tissue (type I collagen) More fb fibers, fewer cells. Contains a network of fibers of elastic system responsible for the elasticity of the skin. Thick section of skin stained for the fibers of the elastic fibers. Weigert s stain 20
21 DERMIS (cont ) Rich network of blood & lymph vessels. Arteriovenous shunt temperature regulation. In addition, dermis contains : epidermal derivatives : Hair follicle Sweat & sebaceous glands Nerves 21
22 Subcutaneous Tissue Consists of loose connective tissue. Contain fat cells that vary in number & size. Referred to superficial fascia, >> panniculus adiposus 22
23 Skin & Lymphatic Vessels The arterial vessels 2 plexuses : between papillary reticular layer between dermis subcutaneous tissue The venous 3 plexuses : Like arterial vessels + in the middle of the dermis. Lymphatic vessels : begin as closed sacs in the papillae of dermis form two plexuses. 23
24 Skin Sensorial Receptors Free nerve endings The expanded : Ruffini endings The encapsulated : Vater-Pacini Meissner Krause. 24
25 Meissner & Paccinian corpuscle 25
26 GLANDS OF THE SKIN Sweat glands Sebaceous glands Eccrine Apocrine Mammary gland 26
27 Sweat Gland Ecrine (merocrine) sweat gland Simple coiled tubular gland Throughout skin important in regulation of body temperature Secretory unit dark cells & clear cells Apocrine sweat gland Found only in axilla, areola nipple, anal region Modified apocrine sweat glands ceruminous glands of ear, glands of moll in eyelids Larger than eccrine, lumen of secretory tubulus is larger 27
28 Sweat Gland 28
29 Sebaceous Gland Secrete sebum oily substance Empty secretory product into the upper parts of the hair follicles Not found in palms of hand, soles of feet, sides of feet inferior of hairline Clinically the sebaceous glands are important in that they are liable to infections (e.g. with the development of acne) 29
30 Sebaceous Gland 30
31 HAIRS Elongated keratinized structure Develop from epidermis & invade the dermis & hypodermis Everywhere except palms, sole, glans penis, clitoris & labia minora Hairs grow discontinously have periods of growth (anagen) followed by period of rest (telogen) In scalp : growth period several years, rest period 3 months Hair in scalp, face & pubis strongly influenced by androgens, adrenal & thyroid hormones 31
32 Hair follicle 32
33 NAILS Highly keratinized epithelial cells arranged in plates of hard keratin Develop from nail matrix nail root Stratum corneum forms eponychium or cuticle nail plate Nail plate on nail bed 33
34 Histology of Nail E=eponychium, H= hyponychium, N=nail plate, DP=distal phalanx 34
35 References Junqueira, L.C. & Carneiro, J. Basic Histology, Text & Atlas, 11 th edition, Lange Medical Books McGraw-Hill Gartner, L.P. & Hiatt, J.L. Colour Textbook of Histology, Third Edition Kierszenbaum AL. Histology & Cell Biology, An Introduction to Pathology, 2 nd ed. Mosby Elsevier
36 Terima kasih. 36
Skin. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Integument. Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Melanoma. Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors
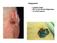 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Integument Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors Melanoma Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Derived from ectoderm Appendages hair follicles
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Integument Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors Melanoma Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Derived from ectoderm Appendages hair follicles
Cell Types in Epidermis
 Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Appendages hair follicles nails sweat glands sebaceous glands mammary glands Dermis Dense, irregular connective tissue Hypodermis Superficial fascia
Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Appendages hair follicles nails sweat glands sebaceous glands mammary glands Dermis Dense, irregular connective tissue Hypodermis Superficial fascia
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9
 Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
INTEGUMENTARY 1-Epidermis, 2-Dermis, Structure of thick and thin skin I- Epidermis . Stratum basale
 INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
Skin Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skin Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Integumentary system The skin is considered the largest organ of the body Basic Skin Histology The skin is composed of two
Skin Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Integumentary system The skin is considered the largest organ of the body Basic Skin Histology The skin is composed of two
Ex. 7: Integumentary
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Chapter 4 Opener Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Histology of Integumentary System
 Histology of Integumentary System CONTENT / Topics Integumentary System Skin, thick - Major Layers Epidermis Dermis Hair Skin, hairy and Hair Follicle Sebaceous Glands Sebaceous Gland Sweat Glands Merocrine
Histology of Integumentary System CONTENT / Topics Integumentary System Skin, thick - Major Layers Epidermis Dermis Hair Skin, hairy and Hair Follicle Sebaceous Glands Sebaceous Gland Sweat Glands Merocrine
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Chapter 5. Integumentary System 5-1
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
Chapter 5: Integumentary System
 Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Ch 5: Integumentary System
 Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS
 Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
2/5/2019. Organ System: Skin or Integumentary System. Hypodermis (or superficial fascia) Integumentary System - Learn and Understand
 Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Overview of the Integumentary System. Lab #7. Layers of the epidermis are known as strata. Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the Epidermis
 Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) i. Organ of the Integument. Connective Tissues. Epithelial Tissues
 Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System. Integumentary System. Page 1
 Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
Integumentary System and Body Membranes
 Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY
 CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
Epidermis. Integumentary system
 Epidermis the doctor mentioned at the begging of the lecture that the slides is from different sources and has information and details that is enough for us so we don t have to go back and read from the
Epidermis the doctor mentioned at the begging of the lecture that the slides is from different sources and has information and details that is enough for us so we don t have to go back and read from the
The Integumentary System: An Overview
 The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System. Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system
 Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function.
 Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Integumentary System. 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1
 Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur.
 Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
The Integementary System. The Skin & Its Parts
 The Integementary System The Skin & Its Parts General Structure 2. Accessory structures: hair, nails, exocrine glands 1. Cutaneous membrane: various layers Major Functions 1. Protection 2. Temperature
The Integementary System The Skin & Its Parts General Structure 2. Accessory structures: hair, nails, exocrine glands 1. Cutaneous membrane: various layers Major Functions 1. Protection 2. Temperature
****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
Chapter 4. The Integumentary System. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 The Integumentary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary
Chapter 4 The Integumentary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary
Consists of: 1. Skin (Epidermis, Dermis & hypodermis) 2. Accessory structures Hair Nails Glands. Integumentary System
 Dr. Nabil khouri Consists of: 1. Skin (Epidermis, Dermis & hypodermis) 2. Accessory structures Hair Nails Glands Integumentary System Functions of the Integumentary System Protection Chemical, physical,
Dr. Nabil khouri Consists of: 1. Skin (Epidermis, Dermis & hypodermis) 2. Accessory structures Hair Nails Glands Integumentary System Functions of the Integumentary System Protection Chemical, physical,
B. Incorrect! The ectoderm does not produce the dermis. C. Incorrect! The dermis is derived from the mesoderm.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Integumentary System
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System. Skin Cells. Layers of Skin. Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer beneath dermis not part of skin
 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Skin and adnexa Skin Adnexa (derivatives): hair nail sebaceous glands sweat glands mammary glands
 Integumentary system - skin and adnexa Skin and adnexa Skin Adnexa (derivatives): hair nail sebaceous glands sweat glands mammary glands Skin (cutis): structure epidermis stratified squamous keratinized
Integumentary system - skin and adnexa Skin and adnexa Skin Adnexa (derivatives): hair nail sebaceous glands sweat glands mammary glands Skin (cutis): structure epidermis stratified squamous keratinized
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Figure 6.1 Transparency Master 37
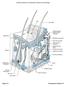 Pore Hair shaft Epidermis Dermal papillae (papillary layer of dermis) Meissner s corpuscle Dermis Free nerve ending Reticular layer of dermis Sebaceous (oil) gland Arrector pili muscle Sensory nerve fiber
Pore Hair shaft Epidermis Dermal papillae (papillary layer of dermis) Meissner s corpuscle Dermis Free nerve ending Reticular layer of dermis Sebaceous (oil) gland Arrector pili muscle Sensory nerve fiber
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis
 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis The Integument Means Covering Composed: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands The Integument Thickness 1.5 4 mm (or more) Weight 9 11
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis The Integument Means Covering Composed: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands The Integument Thickness 1.5 4 mm (or more) Weight 9 11
Ch 4. Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Chapter 6: Skin & the. 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing of Wounds
 Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1-6.2 September 10, 2012 Chapter 6: Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing
Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1-6.2 September 10, 2012 Chapter 6: Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing
Integumentary System. Integumentary System
 1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Chapter 5.1. Integumentary System
 Chapter 5.1 Integumentary System resistance to trauma and infection /// keratin /// acid mantle Functions of the Skin provide other barrier functions /// waterproofing - UV radiation - harmful chemicals
Chapter 5.1 Integumentary System resistance to trauma and infection /// keratin /// acid mantle Functions of the Skin provide other barrier functions /// waterproofing - UV radiation - harmful chemicals
The Integumentary System
 C h a p t e r 5 The Integumentary System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Introduction to the Integumentary System The integument is the largest system
C h a p t e r 5 The Integumentary System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Introduction to the Integumentary System The integument is the largest system
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument. Mikrogeo. com
 SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
Integumentary System
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Eleventh Edition. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
The Integumentary System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
Lesson Plan: Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
7/10/18. Introduction. Integumentary System. Physiology. Anatomy. Structure of the Skin. Epidermis
 Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
BI 121 LAB. WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System
 BI 121 LAB 2-1 WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System This week you will 1) Review the four major tissue types 2) Review the characteristics of epithelial tissues. 3) Learn the major characteristics
BI 121 LAB 2-1 WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System This week you will 1) Review the four major tissue types 2) Review the characteristics of epithelial tissues. 3) Learn the major characteristics
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 C H A P T E R 51 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY THE HUMAN INTEGUMENTARY BODY: AN SYSTEM ORIENTATION C H A P T E R 1 PART I THE HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION
C H A P T E R 51 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY THE HUMAN INTEGUMENTARY BODY: AN SYSTEM ORIENTATION C H A P T E R 1 PART I THE HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
The Integumentary System : Embryology & Genetic Bases. Purnomo Soeharso Department of Medical Biology FMUI
 The Integumentary System : Embryology & Genetic Bases Purnomo Soeharso Department of Medical Biology FMUI Tissue organization of the skin (integumentum) : - Epidermis stratified epithelium on the outer
The Integumentary System : Embryology & Genetic Bases Purnomo Soeharso Department of Medical Biology FMUI Tissue organization of the skin (integumentum) : - Epidermis stratified epithelium on the outer
Skin. Lecture #14. Ref:
 Skin Lecture #14 Ref: http://www.ccunix.ccu.edu.tw/~chenmsl/tea/skin_910721.htm Structure of Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutis 4. Hair follicle 5. Sebaceous gland 6. Sweat gland Skin Largest human
Skin Lecture #14 Ref: http://www.ccunix.ccu.edu.tw/~chenmsl/tea/skin_910721.htm Structure of Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutis 4. Hair follicle 5. Sebaceous gland 6. Sweat gland Skin Largest human
Chapter 05. APR Enhanced Lecture Slides
 Chapter 05 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 05 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
21 Skin and it s Accessories
 21 Skin and it s Accessories 21-001 Skin 1 2 Sweat glands Adipose tissue 3 Retinaculum cutis 21-01. Skin of the palm 1. General view. Human, H-E stain, x 3.3. Opening of sweat gland duct Stratum corneum
21 Skin and it s Accessories 21-001 Skin 1 2 Sweat glands Adipose tissue 3 Retinaculum cutis 21-01. Skin of the palm 1. General view. Human, H-E stain, x 3.3. Opening of sweat gland duct Stratum corneum
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
B. Connective tissue membranes lubricate & cushion 1. made of areolar tissue 2. synovial line fibrous joint capsules & secrete fluid
 I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
2.2 Integumentary System. Chapter 5
 2.2 Integumentary System Chapter 5 Skin Disorder Mini-Project The Integumentary System Written Response #12 In your notebook, complete the following items: 1. Drawing of a cross section of skin that includes
2.2 Integumentary System Chapter 5 Skin Disorder Mini-Project The Integumentary System Written Response #12 In your notebook, complete the following items: 1. Drawing of a cross section of skin that includes
DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY. Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations
 DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Epidermal Layers ECM Structure Dermis Structure Skin
DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Epidermal Layers ECM Structure Dermis Structure Skin
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Waterproofs Protein called keratin Protection 1 st line of defense against pathogens, chemicals & abrasions Insulation Regulates heat loss by controlling blood
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Waterproofs Protein called keratin Protection 1 st line of defense against pathogens, chemicals & abrasions Insulation Regulates heat loss by controlling blood
Levels of Organization
 Levels of Organization Oklahoma Laws Violators can be fined, arrested or jailed for making ugly faces at a dog. Females are forbidden from doing their own hair without being licensed by the state. Dogs
Levels of Organization Oklahoma Laws Violators can be fined, arrested or jailed for making ugly faces at a dog. Females are forbidden from doing their own hair without being licensed by the state. Dogs
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System 5.1-5.4 September 10, 2012 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System 5.1 Structure of the Skin 5.2 Accessory Structures of the Skin 5.3 Types of Skin 5.4 Functions of the Skin 5.5 Maintaining
The Integumentary System 5.1-5.4 September 10, 2012 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System 5.1 Structure of the Skin 5.2 Accessory Structures of the Skin 5.3 Types of Skin 5.4 Functions of the Skin 5.5 Maintaining
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
Unit 4 The Integumentary System
 Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Student Objectives. 7. Describe the structure of nails.
 Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: The Skin 1. Name the tissue types composing the epidermis and dermis. List
Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: The Skin 1. Name the tissue types composing the epidermis and dermis. List
ABCD rule. apocrine glands. arrector pili. ceruminous glands. contact dermatitis
 ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM (SKIN) Human Anatomy and Physiology S. McElwee CHS
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM (SKIN) Human Anatomy and Physiology S. McElwee CHS WHAT IS THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM? The integumentary system is 1 of 11 organ systems. It consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane),
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM (SKIN) Human Anatomy and Physiology S. McElwee CHS WHAT IS THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM? The integumentary system is 1 of 11 organ systems. It consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane),
Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh
 Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh 1) Which of the following is the least valuable when distinguishing between bone and hyaline cartilage?? A- lacunae B-canaliculi C-lamella D-cell nest E- harversian
Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh 1) Which of the following is the least valuable when distinguishing between bone and hyaline cartilage?? A- lacunae B-canaliculi C-lamella D-cell nest E- harversian
3. Dense connective tissue is found in skin, & surrounding blood vessels, nerves, and organs.
 Ch.4&5 Group Quiz True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. There are 4 basic types of tissue in the human body. 2. Cartilage is also known as osseous tissue. 3. Dense connective tissue
Ch.4&5 Group Quiz True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. There are 4 basic types of tissue in the human body. 2. Cartilage is also known as osseous tissue. 3. Dense connective tissue
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System. Introduction. Membranes
 Slide 1 Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System Slide 2 Introduction Skin often reveals our inner workings and general health In most manual therapies, the skin is primary interface with
Slide 1 Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System Slide 2 Introduction Skin often reveals our inner workings and general health In most manual therapies, the skin is primary interface with
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT
 ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
Epidermis. Stratum Basale
 Skin The skin covers the exterior of the body and constitutes a large organ with several functions. In humans, the skin accounts for about 7% of the total body weight and has a total surface area of about
Skin The skin covers the exterior of the body and constitutes a large organ with several functions. In humans, the skin accounts for about 7% of the total body weight and has a total surface area of about
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
II. Skin and Its Tissues. I. Introduction. Unit Two. Integument URLs.
 6 Integument URLs http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/integ.html http://www.aap.org/policy/s010116.html Chapter 6 Karen Webb Smith Unit Two I. Introduction A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more
6 Integument URLs http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/integ.html http://www.aap.org/policy/s010116.html Chapter 6 Karen Webb Smith Unit Two I. Introduction A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more
Histology review. Histology. Slides. Epithelial tissue. Another example - kidney. Simple cuboidal epithelium. What to look for
 Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
Integumentary System. Remember: Types of Membranes: Bio 250
 Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Consists of: - skin hair nails sebaceous (oil) glands sudoriferous (sweat) glands Functions: 1. Thermoregulation - through sweating and adjusting blood flow in the dermis 2. Protection
Integumentary System Consists of: - skin hair nails sebaceous (oil) glands sudoriferous (sweat) glands Functions: 1. Thermoregulation - through sweating and adjusting blood flow in the dermis 2. Protection
Integumentary System. Packet #12
 Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide
 Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
-Skin- -Integumentary-
 BIO 225: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 06 -Skin- -Integumentary- Dr. Lawrence G. Altman Illustrations courtesy of McGraw-Hill. 2 GENERAL FUNCTIONS Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis
BIO 225: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 06 -Skin- -Integumentary- Dr. Lawrence G. Altman Illustrations courtesy of McGraw-Hill. 2 GENERAL FUNCTIONS Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Define integumentary
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Define integumentary
Chapter 4. Skin and Body Membranes. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Body Membranes Functions of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form
Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Body Membranes Functions of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
