Skin and soft tissue infections 3 M Al Madadha Sources :
|
|
|
- Magnus Bradford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Skin and soft tissue infections 3 M Al Madadha Sources : Harrisons infectious diseases 2 nd edition, Oxford Handbook of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology 2 nd edition
2 Hand foot and mouth disease Occurs in outbreaks, typically in schools (we had one a few months ago in nov) The typical disease: Children under 10 are mostly affected, more-so under 5 The causative agents are Coxsackie virus A16 (an enterovirus) Enterovirus 71 ( HAS BEEN ASSOCIATED WITH ENCEPHALITIS AND MYOCARDITIS)
3 Atypical disease: Higher age groups ( adults and teenagers) Caused by coxsackie A6 Can have severe presentation with fever, arthralgia and flu like symptoms with the rash as vesicles that affect (the nose, cheeks, extensor arms, elbows, thighs, buttocks, groin) Both typical and atypical disease are transmitted by fecooral route, or direct close contact to rash
4 Signs and symptoms of HFMD Symptoms and signs: URT symptoms before the skin lesions occur With fever, malaise and pharyngitis! The rash is typically on the soles and palms and buttocks The rash: ORAL : football shaped (eye shaped) painful vesicles, involves the buccal mucosa and tongue. (spares posterior pharynx as opposed to herpangina that spares anterior pharynx) SKIN: red papules that progress to gray vesicles on the soles and palms and buttocks
5
6 Rx Only symptomatic treatment ( treat fever, pain) Must maintain hydration Consider hospital admission in severe illness (enterovirus A71) which has high morbidity and mortality
7 Smallpox Smallpox is caused by variola virus, يan orthopoxvirus. There are two strains: variola major (mortality 20 50%) and variola minor The last reported case was in Somalia in 1977, and the virus was declared eradicated by the WHO in Virus stocks exist in two laboratories, and there are concerns about its potential use as a bioterrorism agent The incubation period is days and is followed by a prodromal period of 1 2 days. The centrifugal rash is initially maculopapular and progresses to vesicles, pustules, and scabs over 1 2 weeks. Death may occur with fulminant disease. Diagnosis may be confirmed by EM or PCR (to differentiate it from other poxviruses). There is no specific treatment (supportive)
8
9 Orf is caused by a DNA virus related to smallpox virus (parapoxvirus). Also called soremouth infection and infects the fingers of individuals who work around goats and sheep. Usually coming into contact with infected animals (petting, feedings, harnesses,bite), but can also transmit between people. There is no treatment, however, the papules may become infected by bacteria, or immune compromised Can be infected multiple times through out life (each time is less severe). Six stages: each about a week Small papule nodules ulcerate and crust
10
11 Molluscum contagiosum virus induces flaccid vesicles on the skin of healthy and immunocompromised individuals. Mcc 2-11 year olds, in adults as part of STD- transmission by direct contact Single or small clusters of vesicles (<30) raised papules, may look like vesicles, not erythematous!, with central umbilication On face and trunk, pubis and rarely mucosa Resolve on their own (cryotherapy or other dermatologic treatments can be done) may be present for YEARS If associated with HIV SEVERE
12
13 Infections Associated with Crusted Lesions
14 Impetigo Caused by S. aureus and/or GAS usual skin flora, with local trauma that allows colonizing bacteria to break through. Commonly affects children (2-5 years) in tropical/subtropical regions; also prevalent in temperate regions in summer months (so warm weather >). It is the most common bacterial skin infection in children 70% are non bullous and appear as crusted legions It is highly contagious (scratching, towels, clothing, autoinfection and spread in daycares)
15 Clinical features occurs on the face and extremities. Lesions start as small macule or papule small vesicles (with erythema) develop into flaccid bullae rupture, releasing a yellow discharge which forms thick crusts. Usually seen with regional LAP Can cause cellulitis ( deeper infection, see later) Or PSGN ( post strep GN) Treatment mupirocin is the best topical agent. Patients who have numerous lesions or who do not respond to topical treatment should receive oral antibiotics (flucloxacillin or cefalexin). If MRSA is suspected/isolated, then treatment with doxycycline, clindamycin, or co-trimoxazole.
16
17
18 Ecthyma Punched-out ulcers surrounded by raised deep red/violet margins invades into the dermis and leaves highly inflamed regions on the sides Caused by S. aureus or GAS. Other similar lesions (ecthyma gangrenosum) may occur with P. aeruginosa in neutropenic (reduced neutrophils in blood) patients. Empiric treatment is with flucloxacillin or cephalexin (unless cultures yield streptococci alone, in which case penicillin is appropriate). Antipseudomonal agents, e.g. piperacillin-tazobactam, should be given for P. aeruginosa infections.
19 ukeeassetsimgwatermark.gif_0_0_80_r_b_-5_-5_.jpg
20 Dermatophytes A group of fungi capable of invading the dead keratin of skin, hair, and nails (require keratin for their growth). They are spread by direct contact with patients or animals or soil Clinical classification is by age group: Children : -tinea capitis (scalp hair and the commonest in children), -tinea corporis (trunk and limbs) -tinea faciale (face)
21 cont. Adolescents: Adults: -tinea manuum and pedis (palms and soles athletes foot-, and the commonest overall worldwide) -tinea unguium (nail also known as onychomycosis) -tinea cruris (groin) AKA jock itch -tinea barbae (beard area and neck) -Tinea corporis Gladiatorum ( wrestlers)
22 Ringworm, corporis, circinata
23 ringworm_on_scalp.jpg?resize=646px:*&output-quality=100
24 Demarcation lines hint at A possible dermatophyte Infection, rather than acne vulgaris
25 Tinea corporis psoriasis
26
27 DIAGNOSIS The goal is to distinguish dermatophytoses from other causes of skin inflammation (such as psoriasis). Infections caused by bacteria, other fungi, and noninfectious disorders (psoriasis, contact dermatitis) may have similar features. KOH mounts of skin scrapings and infected hairs demonstrate hyphae. Some species fluoresce by a U.V. lamp. Culture is used when KOH preparations are negative.
28 TREATMENT AND PREVENTION Many local skin infections resolve spontaneously without chemotherapy. Topical use of tolnaftate, allylamines, or azoles is usually sufficient. Nail bed and more extensive skin infections require systemic therapy with griseofulvin or itraconazole and terbinafine + combined with topical therapy. Therapy must be continued over weeks to months, and relapses may occur. No specific preventive measures such as vaccines exist.
29 Cutaneous leishmaniasis
30 Vector and parasite Transmitted by sandflies Trypanosome (single flagellae) Has two forms: disease causing (resistant) form and infectious motile form On CBC shows reduced cell count (red, white or all), Dx by culture Deemed as a neglected tropical illness (causes mortality with small effort to battle it) Has many types (other than visceral), 1) old world in Asia, Africa and Europe long incubation time (MONTHS 2-24) Skin lesion(s) on the face or leg: papules become necrotic and then pigmented scars ( papule at site of bite small nodules painless ulcer crust (pigmented) leave ugly scars after healing (social issues)
31
32
33 Becoming an increasing problem in surrounding countries (syria and iraq) with poor sanitation and reduced living standards. L. major and L. tropics is most common Resolve over months, round depressed scars remain May resemble other skin lesions (nodular lymphangitis) caused by waterborne pathogens (such as Sporothrix schenckii, Nocardia brasiliensis, Mycobacterium marinum, Leishmania (Viannia). Nodular lymphangitis- granulamatous reaction to these pathogens on the path of lymphatics
34
35 Dx of CL: Remove crusts and take skin scrape for microbiology Biopsy (punch or needle aspirate) to retrieve organism and detect under microscope. Rx: Local heat to area for 2-3 hours a day Pentavalent antimonials (group of chemicals given for CL) Others include: (Liposomal amphotericin B, Oral miltefosine, Pentamidine ) Given for a minimum of 20 days!
36 Infections Associated with Bullae
37 Staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome (SSSS) Staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome (SSSS) in neonates is caused by a toxin (exfoliatin) from phage group II (bacteria is infected by this phage, acquires the gene to produce the toxin) S. aureus. SSSS must be distinguished from toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which occurs primarily in adults, is drug-induced, and is associated with a higher mortality rate. Punch biopsy with frozen section is useful in making this distinction since the cleavage plane is the stratum corneum in SSSS and the stratum germinatum in TEN
38 Due to HEMATOLOGIC (not local) spread of staphylococcal EXOTOXIN. That means there is a point of infection somewhere else in the body (Otitis media, Respiratory tract infection) Staph aureus that carry exfoliative toxins A and B (only about 5% of all S. aureus strains do carry these toxins) Breaks down desmoglein-1 resulting in Acantholysis (breakage of cell to cell adhesions)
39
40
41
42 SSSS Symptoms: Preceded by a prodromal illness ( URTI ) or Otitis Media, Pharyngitis, Conjunctivitis Then the actue phase hits: fever! + malaise (loss of fluids) and red painful skin with bullae formation Signs: Paper thin (peeling) skin Large flaccid BLISTERS, more in the flexor creases (see image above) Mucous membranes are SPARED! Positive Nikolsky s sign (detects acantholysis)
43 You make the bullae spread further by rubbing the side from affected skin to non affected skin
44 SSSS Dx and Rx Dx: blood cultures are often positive (remember hematologic spread of toxin bacteremia) Skin biopsy will show typical acantholysis In lab we can do exotoxin assay Rx: MUST ADMIT THE CHILD ( burn unit or ICU!) Systemic IV antibiotics are given (anti MRSA or anti S. aureus) + Systemic steroids ( only if patient doesn t look toxic/otherwise it is not used) In severe cases (IV Immunoglobulins and plasmapheresis) removal of plasma
45 As for TEN TEN, primarily seen in adults is potentially fatal. Intravenous γ-globulin is a promising treatment for TEN.
46 Necrotizing Fasciitis
47 Necrotizing fasciitis RAPIDLY progressing infection in the area between the fascia and deep subcutaneous tissue. Many risk factors increase the risk (see table next slide) Fibrous bands in this area prevents spread of infection These bands are present in the head but not in the extremities ( thus extremities are more susceptible) >50% in extermities 20% in perineum or buttocks ( esp in DM and alcoholics) 18% in trunk 9% head and neck
48 Necrotizing fasciitis (GAS) and gas gangrene (anaerobic clostridial infection) also induce bulla formation. In the USA, the estimated incidence of invasive GAS infection is 3.5 cases per persons necrotizing infections account for 6% of these.
49 Risk factors associated with necrotizing fasciitis Malnutrition Patient conditions Immunocompromised Poor blood supply Skin trauma in last 3 months Breaks in mucosa of GI or GU tracts (anaerobes) -Hypoalbuminemia -Alcoholism -Cirrhosis - >50 Year olds -Obesity -Cancer -Steroid therapy -Heart disease -PVD -DM -Burns -penetrating trauma -IV drugs -surgery -colon cancer -diverticulae -hemorrhoids or fissues -urethral tears -cirrhosis
50 Signs and Symptoms occur in order Pain/tenderness Unexplained fever (Early diagnosis may be difficult when pain or unexplained fever is the only presenting manifestation, remember infection is deep, might not present with pain yet ) Swelling Dark red induration BULLAE, filled with blueish or purple fluid Thrombosis of dermal blood vessels (The affected area becomes anaesthetic as a result of small vessel thrombosis and destruction of superficial nerves) Extension to deep fascia with rapid spread Most progressed symptoms : toxicity, shock and multi organ failures
51 Pain / redness
52 Dark red induration /swelling
53 Progressing to bullae /thrombosis
54
55 Microbiology causes: A) Polymicrobial ( Type I necrotizing fasciitis involves at least one anaerobic species ( Bacteroides or Peptostreptococcus spp.), as well as one or more facultative anaerobic species (e.g. non-gas, E. coli, Enterobacter, Klebsiella, Proteus spp.). usually a mix of aerobes and anaerobic bacteria ( clostridium perfringens) 1 - Break in Gastrointestinal or Genitourinary mucosa, typically on trunk and extremities 2- Fournier's Gangrene (in genitalia/perineal area) 3- mixed infection usually have comorbid states ( DM, PVD, immunecompromised)
56 Microbiology causes cont B) Type II necrotizing fasciitis is usually caused by GAS alone or in combination with other species (e.g. S. aureus). Group A, Beta hemolytic strep (GAS), S. pyogenes +- S. aureus Strains of MRSA that produce the PantonValentine leukocidin (PVL) toxin have been reported to cause necrotizing fasciitis. 1) usually following trauma in otherwise healthy individual or IV drug abusers (skin popping) 2) Fasciitis progresses to skin contusions due to seeding by transient bactermia 3) Gas production if mixed infections occurs 4) Severe toxicity and renal impairments shock 5) Myositis ( destruction of muscle tissue markedly increases CPK) 6) Mortality is high (upto 50%!)
57 Skin popping/drug abuse = basically SubQ injections in same area over and over
58 Necrotizing fasciitis caused by mixed aerobic-anaerobic bacteria begins with a breach in the integrity of a mucous membrane barrier, such as the mucosa of the gastrointestinal or genitourinary tract. The portal can be a malignancy, a diverticulum, a hemorrhoid, an anal fissure, or a urethral tear. Other predisposing factors include peripheral vascular disease, diabetes mellitus, surgery, and penetrating injury to the abdomen. Leakage into the perineal area results in a syndrome called Fournier s gangrene, characterized by massive swelling of the scrotum and penis with extension into the perineum or the abdominal wall and legs.
59 In the newborn, necrotizing fasciitis may complicate omphalitis and spread to involve the abdominal wall, flanks, and chest wall. Fournier s gangrene is a form of necrotizing fasciitis that affects the male genitals and is usually polymicrobial. Craniofacial necrotizing fasciitis is usually associated with trauma and caused by GAS. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis is usually associated with dental or pharyngeal infections and is polymicrobial.
60
61 Dx of necrotizing fasciitis Clinical findings are suggestive + surgical exploration/sample: a) Altered mental status b) Soft tissue infection signs (redness/swelling/pain) 70-80% of cases Bullae Pain is typically exaggerated out of exam Tenderness is outside the red erythematous borders (indicates further progress) c) are only seen in ¼ of cases d) Fever in less than 50% of the cases! e) Low BP in 21% f) crepitation (feeling of air pockets under skin upon examination) in 20%
62 Rx - empiric 3 drug combo/ 2 drug combo/ 1 drug ( each +MRSA coverage) 3 drug combo : 1- anaerobic coverage (and inhibits ribosomal production of toxins)= Clindamycin 2- G +ve coverage (Ampicillin-sulbactam) or ( Piperacillin-tazobactam) 3- G-ve coverage (Ciprofloxacin)
63 2 drug combo (Cefotaxime covers G+ and G- bacteria) + (anaerobic coverage by metronidazole or clindamycin) 1 drug combo ( Carbapenem 0 Imipenem, meropenem, ertapenem) The MRSA coverage to be added to any chosen empiric regimen includes = Vancomycin or Linezolid Hemorrhagic bullae may indicate presence of vibrio vulnificus, in which case doxycycline is used
64 Rx. Surgical debridement, and treatment in hospital Emergency surgical exploration and debridement confirm the diagnosis and are the mainstay of therapy. Reducing compartment pressure in extremities Prophylaxis for exposed house hold members (penicillin, rifampin, clindamycin or azirthromycin)
Omar Sami. M.Madadha. 1 P a g e
 4 Omar Sami M.Madadha 1 P a g e Studying microbiology might not seem so appealing to many of us; yet no one denies how important it is. However, microbiology is one of the, if not the most medical sharpening
4 Omar Sami M.Madadha 1 P a g e Studying microbiology might not seem so appealing to many of us; yet no one denies how important it is. However, microbiology is one of the, if not the most medical sharpening
General surgery department of SGMU Lecturer ass. Khilgiyaev R.H. Anaerobic infection. Gas gangrene
 Anaerobic infection Gas gangrene Anaerobic bacteria Anaerobic bacteria are the most numerous inhabitants of the normal gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium The
Anaerobic infection Gas gangrene Anaerobic bacteria Anaerobic bacteria are the most numerous inhabitants of the normal gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium The
-> Education -> Excellence
 Quality Conference 5/2557 Extravasations: Event -> Education -> Excellence รศ.นพ. รว ศ เร องตระก ล สาขาว ชาก มารศ ลยศาสตร ภาควชาศลยศาสตร Extravasations: Event 1. Thrombophlebitis - superficial vein 2.
Quality Conference 5/2557 Extravasations: Event -> Education -> Excellence รศ.นพ. รว ศ เร องตระก ล สาขาว ชาก มารศ ลยศาสตร ภาควชาศลยศาสตร Extravasations: Event 1. Thrombophlebitis - superficial vein 2.
In the absence of underlying edema or other skin abnormalities, erysipelas
 ERYSIPELAS Erysipelas is a distinct type of superficial cutaneous cellulitis with marked dermal lymphatic vessel involvement caused by group A β-hemolytic streptococcus (very uncommonly group C or G streptococcus)
ERYSIPELAS Erysipelas is a distinct type of superficial cutaneous cellulitis with marked dermal lymphatic vessel involvement caused by group A β-hemolytic streptococcus (very uncommonly group C or G streptococcus)
Morbidity & Mortality Conference Downstate Medical Center. Daniel Kaufman, MD
 Morbidity & Mortality Conference Downstate Medical Center University Case Presentation Hospital of Brooklyn Daniel Kaufman, MD Necrotizing Fasciitis and Soft- Tissue Infections Necrotizing Fasciitis Deep
Morbidity & Mortality Conference Downstate Medical Center University Case Presentation Hospital of Brooklyn Daniel Kaufman, MD Necrotizing Fasciitis and Soft- Tissue Infections Necrotizing Fasciitis Deep
COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS. Sports Medicine
 COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS Sports Medicine IMPETIGO IS A SUPERFICIAL BACTERIAL INFECTION CAUSED BY: STREPTOCOCCI OR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BOULOUS IMPETIGO IMPETIGO COMES IN TWO FORMS: BOULOUS OR NON- BOULOUS
COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS Sports Medicine IMPETIGO IS A SUPERFICIAL BACTERIAL INFECTION CAUSED BY: STREPTOCOCCI OR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BOULOUS IMPETIGO IMPETIGO COMES IN TWO FORMS: BOULOUS OR NON- BOULOUS
Skin and soft tissue infections Introduction/overview
 Skin and soft tissue infections Introduction/overview M Al Madadha Sources : Harrisons infectious diseases 2 nd edition, Oxford Handbook of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology 2 nd edition Anatomic relationships:
Skin and soft tissue infections Introduction/overview M Al Madadha Sources : Harrisons infectious diseases 2 nd edition, Oxford Handbook of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology 2 nd edition Anatomic relationships:
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest
 Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
Cellulitis and Soft Tissue Infections. Sally Williams MD
 Cellulitis and Soft Tissue Infections Sally Williams MD Cellulitis: A very common infection 25 cases per 1000 patient years More common in men, obese patients 60% occurs in the lower extremities 74% handled
Cellulitis and Soft Tissue Infections Sally Williams MD Cellulitis: A very common infection 25 cases per 1000 patient years More common in men, obese patients 60% occurs in the lower extremities 74% handled
(NATO STANAG 2122, CENTO STANAG 2122, SEATO STANAG 2122)
 (NATO STANAG 2122, CENTO STANAG 2122, SEATO STANAG 2122) Bacteria Bacteria are microscopic, single-celled forms of plant life, containing no chlorophyll. They live on the skin, on the surface of the stratum
(NATO STANAG 2122, CENTO STANAG 2122, SEATO STANAG 2122) Bacteria Bacteria are microscopic, single-celled forms of plant life, containing no chlorophyll. They live on the skin, on the surface of the stratum
Clinical Case. ! 2am: Call from Surgeon, Ballarat Hospital. ! Suspicion of Necrotizing Fasciitis: ! Need of HBOT?
 Clinical Case! 2am: Call from Surgeon, Ballarat Hospital! Suspicion of Necrotizing Fasciitis:! 59y, Police Officer, diabetic, overweight! 4pm: pain in right arm! 8pm: pain worsening " ED! HD instability
Clinical Case! 2am: Call from Surgeon, Ballarat Hospital! Suspicion of Necrotizing Fasciitis:! 59y, Police Officer, diabetic, overweight! 4pm: pain in right arm! 8pm: pain worsening " ED! HD instability
Abscess. A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body.
 Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE. Impetigo. This document should be read in conjunction with this DISCLAIMER
 Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Impetigo Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Impetigo Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
MERCY RETREAT Dermatology
 MERCY RETREAT 2016 Dermatology INFECTIONS IN DERMATOLOGY Why we do talk about infections today? These are some of the most commonly seen dermatologic diseases that present to primary care physician office
MERCY RETREAT 2016 Dermatology INFECTIONS IN DERMATOLOGY Why we do talk about infections today? These are some of the most commonly seen dermatologic diseases that present to primary care physician office
DEFINITION Impetigo vulgaris is a highly contagious, superficial bacterial infection of the skin.
 DEFINITION Impetigo vulgaris is a highly contagious, superficial bacterial infection of the skin. Nonbullous impetigo Formation of vesiculopustules that ruptures, leading to crusting with a characteristic
DEFINITION Impetigo vulgaris is a highly contagious, superficial bacterial infection of the skin. Nonbullous impetigo Formation of vesiculopustules that ruptures, leading to crusting with a characteristic
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7. Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods. Bacillus
 Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Skin & Soft Tissue Infections: Classic Case Presentations
 Skin & Soft Tissue Infections: Classic Case Presentations Mark Beilke, M.D. Professor of Medicine Chief of Infectious Diseases Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center Objectives Diagnose and treat water
Skin & Soft Tissue Infections: Classic Case Presentations Mark Beilke, M.D. Professor of Medicine Chief of Infectious Diseases Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center Objectives Diagnose and treat water
Mycology. BioV 400. Clinical classification. Clinical classification. Fungi as Infectious Agents. Thermal dimorphism. Handout 6
 BioV 400 Mycology Handout 6 Fungi as Infectious Agents True or primary fungal pathogens invades and grows in a healthy, noncompromise d host Most striking adaptation to survival and growth in the human
BioV 400 Mycology Handout 6 Fungi as Infectious Agents True or primary fungal pathogens invades and grows in a healthy, noncompromise d host Most striking adaptation to survival and growth in the human
Necrotizing Fasciitis. By Lisa Banks
 Necrotizing Fasciitis By Lisa Banks Foot infections are the most common softtissue infections in pts with diabetes Necrotizing fasciitis is the most important soft tissue infection in DM pts involving
Necrotizing Fasciitis By Lisa Banks Foot infections are the most common softtissue infections in pts with diabetes Necrotizing fasciitis is the most important soft tissue infection in DM pts involving
Common Superficial Fungal Infections
 How to recognise and treat Common Superficial Fungal Infections Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh) Types of superficial fungal infections Ringworm (Tinea) Candida (Thrush) Body Groin Feet Skin Nappy rash Vagina
How to recognise and treat Common Superficial Fungal Infections Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh) Types of superficial fungal infections Ringworm (Tinea) Candida (Thrush) Body Groin Feet Skin Nappy rash Vagina
MRSA: A TEAM APPROACH
 Eric Bosley, MD Laura Stadler, MD John MD J h Draus, D MRSA: A TEAM APPROACH PART I: OUTPATIENT ISSUES AND MANAGEMENT NOT REQUIRING I&D OR HOSPITALIZATION Eric L. Bosley, MD, FAAP Pediatric Associates,
Eric Bosley, MD Laura Stadler, MD John MD J h Draus, D MRSA: A TEAM APPROACH PART I: OUTPATIENT ISSUES AND MANAGEMENT NOT REQUIRING I&D OR HOSPITALIZATION Eric L. Bosley, MD, FAAP Pediatric Associates,
Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Soft Tissue Infections for the USMLE Step One Exam
 Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Soft Tissue Infections for the USMLE Step One Exam Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Email: Howard@12daysinmarch.com MSK Infections Bone and Joint Infections
Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Soft Tissue Infections for the USMLE Step One Exam Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Email: Howard@12daysinmarch.com MSK Infections Bone and Joint Infections
Skin Problems. Issues for a Child. Skin Problems. Paediatric Palliative Care For Home Based Carers. Common in children with HIV
 Skin Problems Paediatric Palliative Care For Home Based Carers Funded by British High Commission, Pretoria Small Grant Scheme Skin Problems Common in children with HIV Often conditions common in all children
Skin Problems Paediatric Palliative Care For Home Based Carers Funded by British High Commission, Pretoria Small Grant Scheme Skin Problems Common in children with HIV Often conditions common in all children
Common bacterial skin infections
 Common bacterial skin infections Cellulitis A localized area of soft tissue inflammation with skin infiltration with white cells, capillary dilatation and proliferation of bacteria. Staph aureus and Strep
Common bacterial skin infections Cellulitis A localized area of soft tissue inflammation with skin infiltration with white cells, capillary dilatation and proliferation of bacteria. Staph aureus and Strep
Prof Dr Najlaa Fawzi
 1 Prof Dr Najlaa Fawzi is an acute highly infectious disease, characterized by vesicular rash, mild fever and mild constitutional symptoms. is a local manifestation of reactivation of latent varicella
1 Prof Dr Najlaa Fawzi is an acute highly infectious disease, characterized by vesicular rash, mild fever and mild constitutional symptoms. is a local manifestation of reactivation of latent varicella
Common Childhood Rashes. The Itchy and the Scratchy presented by Trina Blythe MD, FAAP
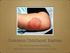 Common Childhood Rashes The Itchy and the Scratchy presented by Trina Blythe MD, FAAP Objectives Be able to identify some of the most common rashes of school age children Determine which rashes require
Common Childhood Rashes The Itchy and the Scratchy presented by Trina Blythe MD, FAAP Objectives Be able to identify some of the most common rashes of school age children Determine which rashes require
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY ORAL CAVITY. Oral Cavity Subsites 4/10/2013 LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL MUCOUS MEMBRANES PALATE TONGUE ORAL LYMPHOID TISSUES
 LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
29a Pathology - Integumentary System
 29a Pathology - Integumentary System 29a Pathology - Integumentary System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active
29a Pathology - Integumentary System 29a Pathology - Integumentary System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active
13/10. Microbiology Bacterial Skin Infections Dr Hani Masaadeh Areej al-arqan
 13/10 Microbiology Bacterial Skin Infections Dr Hani Masaadeh Areej al-arqan Salam soul, this is the first Microbiology lecture of this system given by Dr.hani masaadeh. I ll do my best to make it easy
13/10 Microbiology Bacterial Skin Infections Dr Hani Masaadeh Areej al-arqan Salam soul, this is the first Microbiology lecture of this system given by Dr.hani masaadeh. I ll do my best to make it easy
Outline Dermatomycoses Definition: diseases or fungal infections of the skin Transmission of Dermatomycoses Case Report 1 Presentation of Disease
 Outline Dermatomycoses Tinea corporis,tinea capitis,tinea pedis, Tinea cruris, Definition: diseases or fungal infections of the skin Dermatophyte infections are caused by Trichophyton, Microsporum, and
Outline Dermatomycoses Tinea corporis,tinea capitis,tinea pedis, Tinea cruris, Definition: diseases or fungal infections of the skin Dermatophyte infections are caused by Trichophyton, Microsporum, and
Objectives. Terminology. Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions. Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations of systemic disease
 Pediatric Visual Dermatological Diagnosis Fernando Vega, M.D. Objectives Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions Expand differential diagnosis Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations
Pediatric Visual Dermatological Diagnosis Fernando Vega, M.D. Objectives Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions Expand differential diagnosis Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations
Topic: Structure of the Skin. Structure of the Skin. (Ch19) Infectious Diseases: Skin. Functions of the skin. Composed of two main layers
 Topic: (Ch19) Infectious Diseases: Skin 1 Structure of the Skin Functions of the skin Prevents excessive water loss Important to temperature regulation Involved in sensory phenomena Barrier against microbial
Topic: (Ch19) Infectious Diseases: Skin 1 Structure of the Skin Functions of the skin Prevents excessive water loss Important to temperature regulation Involved in sensory phenomena Barrier against microbial
12/12/2018. Childhood Skin Infections. Objectives. Verruca vulgaris. Case #1. Case #2. Management 1. Evidence Updates
 Objectives Childhood Skin Infections Evidence Updates Brian Z. Rayala, MD Associate Professor Department of Family Medicine UNC School of Medicine At the end of lecture, learner will be able to:» Diagnose
Objectives Childhood Skin Infections Evidence Updates Brian Z. Rayala, MD Associate Professor Department of Family Medicine UNC School of Medicine At the end of lecture, learner will be able to:» Diagnose
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections. Masoud Mardani MD, MPH,FIDSA Prof of Infectious Dis Shahid Beheshti Medical University
 Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Masoud Mardani MD, MPH,FIDSA Prof of Infectious Dis Shahid Beheshti Medical University Usual Skin Flora Skin flora consists of those microbes able to adapt to the high salt
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Masoud Mardani MD, MPH,FIDSA Prof of Infectious Dis Shahid Beheshti Medical University Usual Skin Flora Skin flora consists of those microbes able to adapt to the high salt
Types of Skin Infections
 Anatomy of Skin Types of Skin Infections Bacterial Impetigo Folliculitis Acne Fungal /Parasitic Tinea Pedis Tinea Cruris Tinea Versicolor Tinea Corporis Toenail fungus Allergic/Irritation conditions Dermatitis
Anatomy of Skin Types of Skin Infections Bacterial Impetigo Folliculitis Acne Fungal /Parasitic Tinea Pedis Tinea Cruris Tinea Versicolor Tinea Corporis Toenail fungus Allergic/Irritation conditions Dermatitis
Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology. Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
 Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Fill In The Blank When you see on the skin, you think of a bacterial skin infection SEND SWABS VIRAL
Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Fill In The Blank When you see on the skin, you think of a bacterial skin infection SEND SWABS VIRAL
Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children
 May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition)
 Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
VARICELLA. Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division, Department of Child Health, Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 VARICELLA (Chicken pox) Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division, Department of Child Health, Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition : Varicella is a common contagious disease caused
VARICELLA (Chicken pox) Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division, Department of Child Health, Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition : Varicella is a common contagious disease caused
Core Content: Toxic Shock, Necrotizing Fasciitis, Erysipelas, Cellulitis, Tetanus Keith Conover, M.D., FACEP /11/2008 Tetanus 78-year old
 Core Content: Toxic Shock, Necrotizing Fasciitis, Erysipelas, Cellulitis, Tetanus Keith Conover, M.D., FACEP 1.01 11/11/2008 Tetanus 78-year old Russian man, speaks fair English, smoker, no past medical
Core Content: Toxic Shock, Necrotizing Fasciitis, Erysipelas, Cellulitis, Tetanus Keith Conover, M.D., FACEP 1.01 11/11/2008 Tetanus 78-year old Russian man, speaks fair English, smoker, no past medical
Communicable Disease Guidelines
 Note: This information is to assist in making decisions regarding the control of communicable diseases. It is not intended for the purposes of making diagnoses. Refer to disease specific information sheets
Note: This information is to assist in making decisions regarding the control of communicable diseases. It is not intended for the purposes of making diagnoses. Refer to disease specific information sheets
Red Stick ID Visual Diagnosis Questions August 22, 2014
 Red Stick ID Visual Diagnosis Questions August 22, 2014 James H. Brien, DO Case #1 The setting is a Pediatric Clinic in San Antonio, Texas on a Saturday in 1989. However, it could have been yesterday in
Red Stick ID Visual Diagnosis Questions August 22, 2014 James H. Brien, DO Case #1 The setting is a Pediatric Clinic in San Antonio, Texas on a Saturday in 1989. However, it could have been yesterday in
Communicable Disease Guidelines
 Communicable Disease Guidelines Note: This information is to assist in making decisions regarding the control of communicable diseases. It is NOT intended for the purposes of making diagnoses. Refer to
Communicable Disease Guidelines Note: This information is to assist in making decisions regarding the control of communicable diseases. It is NOT intended for the purposes of making diagnoses. Refer to
SEPTIC ARTHRITIS. Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA. University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014
 SEPTIC ARTHRITIS Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014 Objectives be able to define Septic Arthritis know what factors predispose
SEPTIC ARTHRITIS Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014 Objectives be able to define Septic Arthritis know what factors predispose
Cellulitis: a practical guide
 Cellulitis: a practical guide Dr John Day Consultant in Infectious Diseases & General Medicine Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust 77 yr old retired civil servant A&E presentation c/o rigors
Cellulitis: a practical guide Dr John Day Consultant in Infectious Diseases & General Medicine Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust 77 yr old retired civil servant A&E presentation c/o rigors
Sickness and Illness Policy
 Sickness and Illness Policy Children should not be at nursery if they are unwell. If your child becomes unable to stay at nursery, a member of staff will contact the parent or carer, asking them to come
Sickness and Illness Policy Children should not be at nursery if they are unwell. If your child becomes unable to stay at nursery, a member of staff will contact the parent or carer, asking them to come
Pathogens!! What are Pathogens? 12/7/14. Infectious Diseases are Caused by Pathogens
 Pathogens!! Copyright 2011. PEER.tamu.edu Infectious Diseases are Caused by Pathogens What are Pathogens? Pathogens are microbes (microscopic living organisms) or other agents that cause diseases. Ex:
Pathogens!! Copyright 2011. PEER.tamu.edu Infectious Diseases are Caused by Pathogens What are Pathogens? Pathogens are microbes (microscopic living organisms) or other agents that cause diseases. Ex:
Chapter 40. Alterations of the Integument in Children
 Chapter 40 Alterations of the Integument in Children Acne Vulgaris Most common skin disease Affects 85% of the population between ages 12 and 25 years Develops at sebaceous follicles located primarily
Chapter 40 Alterations of the Integument in Children Acne Vulgaris Most common skin disease Affects 85% of the population between ages 12 and 25 years Develops at sebaceous follicles located primarily
Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections
 Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections Objectives How do you to diagnose, classify and manage DFI? How do you diagnose
Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections Objectives How do you to diagnose, classify and manage DFI? How do you diagnose
Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014
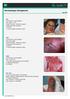 Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014 SJS YES MUCOSAL INVOLVEMENT MCC drugs >> HSV TARGET LESIONS, +NIKOLSKY, painful Prodromal flu-like symptoms
Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014 SJS YES MUCOSAL INVOLVEMENT MCC drugs >> HSV TARGET LESIONS, +NIKOLSKY, painful Prodromal flu-like symptoms
DERMATOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES. DR. Ian Hoyle MBBS DIP IMC RCS (Ed), DA (UK),FRACGP,FACRRM,DIP DERM(Wales) TASMANIAN SKIN AND BODY CENTRE
 DERMATOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES DR. Ian Hoyle MBBS DIP IMC RCS (Ed), DA (UK),FRACGP,FACRRM,DIP DERM(Wales) TASMANIAN SKIN AND BODY CENTRE Dermatological Emergencies INFECTIONS ERYTHRODERMA DRUG ERUPTIONS STEVENS-JOHNSON
DERMATOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES DR. Ian Hoyle MBBS DIP IMC RCS (Ed), DA (UK),FRACGP,FACRRM,DIP DERM(Wales) TASMANIAN SKIN AND BODY CENTRE Dermatological Emergencies INFECTIONS ERYTHRODERMA DRUG ERUPTIONS STEVENS-JOHNSON
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi Medical Microbiology
 1 Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Medical Microbiology Lecture-1- Fungi (Mycosis) They are a diverse group of saprophytic and parasitic eukaryotic organisms. Human fungal diseases (mycoses)
1 Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Medical Microbiology Lecture-1- Fungi (Mycosis) They are a diverse group of saprophytic and parasitic eukaryotic organisms. Human fungal diseases (mycoses)
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection
 Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
Patricia A. Treadwell, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics
 EXANTHEMS Patricia A. Treadwell, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Indiana University School of Medicine FACULTY DISCLOSURE I have the following financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial
EXANTHEMS Patricia A. Treadwell, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Indiana University School of Medicine FACULTY DISCLOSURE I have the following financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level
 Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
SKIN INFECTIONS. Caroline Charlier-Woerther February 2017
 SKIN INFECTIONS Caroline Charlier-Woerther February 2017 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Recognize the main types of infection Know the pathogens associated with them Know how to manage dermo-hypodermitis Know how
SKIN INFECTIONS Caroline Charlier-Woerther February 2017 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Recognize the main types of infection Know the pathogens associated with them Know how to manage dermo-hypodermitis Know how
Microbial Diseases of the Skin and Wounds
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University Packet #9 Chapter #19 Microbial Diseases of the Skin and Wounds Structure of the Skin Functions of the
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University Packet #9 Chapter #19 Microbial Diseases of the Skin and Wounds Structure of the Skin Functions of the
Rapid and progressive necrosis of the tissue underlying epidermis (cellulitis)
 Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Case 2. Case 3 - course. PE: uncomfortable, but NAD T 38.0 R 22 HR 120 BP130/60
 Case 2 42 y/o man c/o painful right arm and shoulder x 3 days. Hx of IDU ( skin popping heroin ). No other trauma or bite. PE: uncomfortable, but NAD T 38.0 R 22 HR 120 BP130/60 PMH: HCV, HBV, HIV negative,
Case 2 42 y/o man c/o painful right arm and shoulder x 3 days. Hx of IDU ( skin popping heroin ). No other trauma or bite. PE: uncomfortable, but NAD T 38.0 R 22 HR 120 BP130/60 PMH: HCV, HBV, HIV negative,
Dr Janakan Natkunarajah (Dr Jana)
 Dr Janakan Natkunarajah (Dr Jana) Diagnosis Furuncle (Boil) Deep follicular abscess Anti-staph antibiotics Systemic & topical Carbuncle Deep abscess formed in a group of follicles Incise and Drain Recurrent
Dr Janakan Natkunarajah (Dr Jana) Diagnosis Furuncle (Boil) Deep follicular abscess Anti-staph antibiotics Systemic & topical Carbuncle Deep abscess formed in a group of follicles Incise and Drain Recurrent
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
Suzan Schneeweiss MD, MEd, FRCPC
 Suzan Schneeweiss MD, MEd, FRCPC I have nothing to disclose 1. Discuss common pitfalls in the diagnosis and management of common paediatric rashes in the ED 2. Identify dermatologic conditions requiring
Suzan Schneeweiss MD, MEd, FRCPC I have nothing to disclose 1. Discuss common pitfalls in the diagnosis and management of common paediatric rashes in the ED 2. Identify dermatologic conditions requiring
EXANTHEMATOUS ILLNESS. IAP UG Teaching slides
 EXANTHEMATOUS ILLNESS 1 DEFINITIONS Exanthema eruption of the skin Exanthema eruption of mucosae Macule flat nonpalpable lesion Papule small palpable lesion Nodule large palpable lesion Vesicle small fluid
EXANTHEMATOUS ILLNESS 1 DEFINITIONS Exanthema eruption of the skin Exanthema eruption of mucosae Macule flat nonpalpable lesion Papule small palpable lesion Nodule large palpable lesion Vesicle small fluid
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
December 3, 2015 Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Antibiotic Guide
 Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Antibiotic Guide Surviving Sepsis: The choice of empirical antimicrobial therapy depends on complex issues related to the patient s history, including drug intolerances,
Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Antibiotic Guide Surviving Sepsis: The choice of empirical antimicrobial therapy depends on complex issues related to the patient s history, including drug intolerances,
The Integumentary System. Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases
 The Integumentary System Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases Definitions Disease- an abnormal condition of the body or the mind that causes dysfunction or discomfort. Disorder- a functional abnormality,
The Integumentary System Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases Definitions Disease- an abnormal condition of the body or the mind that causes dysfunction or discomfort. Disorder- a functional abnormality,
Chapter 19. Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria. Staphylococcus & Streptococcus
 Chapter 19 Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria Staphylococcus & Streptococcus Staphylococcus Normal members of every human's microbiota Can be opportunistic pathogens Facultative anaerobes Cells occur in
Chapter 19 Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria Staphylococcus & Streptococcus Staphylococcus Normal members of every human's microbiota Can be opportunistic pathogens Facultative anaerobes Cells occur in
Conflicts. Objectives. University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. Pediatrics Grand Rounds 24 August Pediatric Dermatology 101
 Pediatric Dermatology 101 John C. Browning, MD, FAAD, FAAP Conflicts Investigator: ViroXis Advisor: ViroXis Advisory Board: TopMD Speaker: Galderma Objectives Understand the meaning and importance of cutaneous
Pediatric Dermatology 101 John C. Browning, MD, FAAD, FAAP Conflicts Investigator: ViroXis Advisor: ViroXis Advisory Board: TopMD Speaker: Galderma Objectives Understand the meaning and importance of cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin lesions & Abrasions
 Skin lesions & Abrasions What Are Skin Lesions? A skin lesion is a part of the skin that has an abnormal growth or appearance compared to the skin around it Types of Skin Lesions Two types of skin lesions
Skin lesions & Abrasions What Are Skin Lesions? A skin lesion is a part of the skin that has an abnormal growth or appearance compared to the skin around it Types of Skin Lesions Two types of skin lesions
Sickness and Illness Policy
 Sickness and Illness Policy Children should not be at nursery if they are unwell. If your child becomes unable to stay at nursery, a member of staff will contact the parent or carer, asking them to come
Sickness and Illness Policy Children should not be at nursery if they are unwell. If your child becomes unable to stay at nursery, a member of staff will contact the parent or carer, asking them to come
COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES. Sharon Seguin MD FAAD
 COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD FAAD COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Rashes Infections And Infestations RASHES Dermatitis- Inflammation of the skin Eczema- Atopic Dermatitis Psoriasis Pityriasis
COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD FAAD COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Rashes Infections And Infestations RASHES Dermatitis- Inflammation of the skin Eczema- Atopic Dermatitis Psoriasis Pityriasis
Welcome to the Jungle! Dr Aileen Oon, 2017 Microbiology Registrar
 Welcome to the Jungle! Dr Aileen Oon, 2017 Microbiology Registrar AA 55M presented with sores on left olecranon and umbilical area Umbilical sores present for 3 weeks Left olecranon lesions for 1 week
Welcome to the Jungle! Dr Aileen Oon, 2017 Microbiology Registrar AA 55M presented with sores on left olecranon and umbilical area Umbilical sores present for 3 weeks Left olecranon lesions for 1 week
PSEUDO-CELLULITIS - ALL THAT S RED IS NOT INFECTION
 JAN 18 2018 ASP ECHO CLINIC CHARLES KRASNER, M.D. PSEUDO-CELLULITIS - ALL THAT S RED IS NOT INFECTION FIRST HOSPITALIZATION: 62 YEAR OLD MALE ADMITTED WITH DIAGNOSIS OF CELLULITIS Hx of AODM, Morbid Obesity,
JAN 18 2018 ASP ECHO CLINIC CHARLES KRASNER, M.D. PSEUDO-CELLULITIS - ALL THAT S RED IS NOT INFECTION FIRST HOSPITALIZATION: 62 YEAR OLD MALE ADMITTED WITH DIAGNOSIS OF CELLULITIS Hx of AODM, Morbid Obesity,
Concern for recurrence Stable virus especially in freeze dried form High infectivity in humans Vaccine supplies are limited No specific antiviral
 poxviruses Poxviruses Infect humans, birds, mammals, and insects. DsDNA brick shaped, enveloped multiply in the cytoplasm, 100x200x300 nm. lack normal capsid instead, layers of lipoprotiens and fibrils
poxviruses Poxviruses Infect humans, birds, mammals, and insects. DsDNA brick shaped, enveloped multiply in the cytoplasm, 100x200x300 nm. lack normal capsid instead, layers of lipoprotiens and fibrils
How is it transferred?
 STI s What is a STI? It is a contagious infection that is transferred from one person to another through sexual intercourse or other sexually- related behaviors. How is it transferred? The organisms live
STI s What is a STI? It is a contagious infection that is transferred from one person to another through sexual intercourse or other sexually- related behaviors. How is it transferred? The organisms live
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
To provide guidance on prevention and control of illness caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV).
 Effective Date: 04/18 Replaces: 0 4 / 1 3 / 1 7 Page 1 of 4 POLICY: To provide guidance on prevention and control of illness caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV). DEFINITIONS Two syndromes occur from
Effective Date: 04/18 Replaces: 0 4 / 1 3 / 1 7 Page 1 of 4 POLICY: To provide guidance on prevention and control of illness caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV). DEFINITIONS Two syndromes occur from
Objectives. Define classes of uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI) that drive empiric antimicrobial selection
 Objectives Define classes of uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI) that drive empiric antimicrobial selection Purulent SSTI Non-purulent SSTI Recognize conditions that suggest complications
Objectives Define classes of uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI) that drive empiric antimicrobial selection Purulent SSTI Non-purulent SSTI Recognize conditions that suggest complications
The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis
 Dermatology The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis The image to the left shows an image of skin cells and the proteins which
Dermatology The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis The image to the left shows an image of skin cells and the proteins which
Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings
 Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings List the four types of epithelial or connective membranes. The epithelial cutaneous includes your and is exposed to the. Its function is to. An example is..
Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings List the four types of epithelial or connective membranes. The epithelial cutaneous includes your and is exposed to the. Its function is to. An example is..
Abscess cellulitis pus
 Abscess cellulitis pus An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body.. If the condition is thought to be cellulitis rather than abscess,. 13-2-2018 Patients with skin
Abscess cellulitis pus An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body.. If the condition is thought to be cellulitis rather than abscess,. 13-2-2018 Patients with skin
Here is the first Microbiology lecture in this system given by our lovely Dr Hani Masaadeh.
 Here is the first Microbiology lecture in this system given by our lovely Dr Hani Masaadeh. This sheet is complete slides + Dr Comments, so you don t need to go back to the slides. Here is some dermatological
Here is the first Microbiology lecture in this system given by our lovely Dr Hani Masaadeh. This sheet is complete slides + Dr Comments, so you don t need to go back to the slides. Here is some dermatological
Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the
 Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the human body Many Microorganisms are part of normal flora
Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the human body Many Microorganisms are part of normal flora
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT
 HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
Controlling Communicable Diseases in the School Setting LCDR C. SCOTT LOVE, MD, MPH, FAAP DEPARTMENT HEAD, PEDIATRICS
 Controlling Communicable Diseases in the School Setting LCDR C. SCOTT LOVE, MD, MPH, FAAP DEPARTMENT HEAD, PEDIATRICS Disclosure There is no conflict of interest pertaining to this presentation, materials,
Controlling Communicable Diseases in the School Setting LCDR C. SCOTT LOVE, MD, MPH, FAAP DEPARTMENT HEAD, PEDIATRICS Disclosure There is no conflict of interest pertaining to this presentation, materials,
Herpes outbreak on knee and arm
 Aug 29, 2013. This is, like me, how you can have hsv-1 or 2 outbreaks below the belt (genitals, hips, butt, legs, knees, tailbone) concurrently with above the belt (mouth, tongue, lips, face, neck, back,
Aug 29, 2013. This is, like me, how you can have hsv-1 or 2 outbreaks below the belt (genitals, hips, butt, legs, knees, tailbone) concurrently with above the belt (mouth, tongue, lips, face, neck, back,
BRAINZ POLICY AND PROCEDURE ON COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
 BRAINZ POLICY AND PROCEDURE ON COMMUNICABLE DISEASES PURPOSE: To prevent the spread of communicable diseases to client and staff of Brainz Home care Agency from staff with contagious illnesses. POLICY:
BRAINZ POLICY AND PROCEDURE ON COMMUNICABLE DISEASES PURPOSE: To prevent the spread of communicable diseases to client and staff of Brainz Home care Agency from staff with contagious illnesses. POLICY:
Dermatophytes Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Dermatophytes Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Dermatophytoses are superficial infections of the skin and its appendages, commonly known as ringworm, athlete s foot, and jock itch. They are caused by species of
Dermatophytes Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Dermatophytoses are superficial infections of the skin and its appendages, commonly known as ringworm, athlete s foot, and jock itch. They are caused by species of
Issues in Dermatology. Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN
 Issues in Dermatology Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN Anatomy of the Skin Functions Protect Fluid balance Absorption Synthesis of Vitamin D Sensation/communication with external environment Thermoregulation
Issues in Dermatology Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN Anatomy of the Skin Functions Protect Fluid balance Absorption Synthesis of Vitamin D Sensation/communication with external environment Thermoregulation
Title Text. Rash/Skin-Related Illnesses B-8
 Title Text Rash/Skin-Related Illnesses B-8 Title Fifth Disease/Erythema Text Infectiosum/ Parvovirus B19 Note to Parents Recommended? Yes, mainly to advise susceptible women who are pregnant, or who might
Title Text Rash/Skin-Related Illnesses B-8 Title Fifth Disease/Erythema Text Infectiosum/ Parvovirus B19 Note to Parents Recommended? Yes, mainly to advise susceptible women who are pregnant, or who might
Severe β-lactam allergy. Alternative (use for mild-moderate β-lactam allergy) therapy
 Recommended Empirical Antibiotic Regimens for MICU Patients Notes: The antibiotic regimens shown are general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. Always assess for antibiotic allergies.
Recommended Empirical Antibiotic Regimens for MICU Patients Notes: The antibiotic regimens shown are general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. Always assess for antibiotic allergies.
Life-threatening infections. Frank Bowden October 5, 2018
 Life-threatening infections Frank Bowden October 5, 2018 David Sackett Evidence Based Medicine is the integration of best research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values. The Golden Rules
Life-threatening infections Frank Bowden October 5, 2018 David Sackett Evidence Based Medicine is the integration of best research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values. The Golden Rules
Section 10.5 Varicella
 Section 10.5 Varicella Chickenpox Introduction Transmission Signs and Symptoms Complications Diagnosis Treatment Infection Prevention and Control Precautions for Residents with Chickenpox Additional considerations
Section 10.5 Varicella Chickenpox Introduction Transmission Signs and Symptoms Complications Diagnosis Treatment Infection Prevention and Control Precautions for Residents with Chickenpox Additional considerations
What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system?
 Essential Questions: What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system? How are integumentary system disorders treated? How do you relate the integumentary
Essential Questions: What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system? How are integumentary system disorders treated? How do you relate the integumentary
Speaker and paid consultant for Galderma, Novartis and Jansen. No other potential conflicts to disclose. Review of Relevant Physiology
 Speaker and paid consultant for Galderma, Novartis and Jansen No other potential conflicts to disclose Review of Relevant Physiology Discussion of Common Problems Treatment Options Counselling Knowing
Speaker and paid consultant for Galderma, Novartis and Jansen No other potential conflicts to disclose Review of Relevant Physiology Discussion of Common Problems Treatment Options Counselling Knowing
Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens. Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM
 Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM Objectives Review Select Agent Viruses. Key features to recognize Smallpox virus Update on emerging Viruses of possible pandemic
Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM Objectives Review Select Agent Viruses. Key features to recognize Smallpox virus Update on emerging Viruses of possible pandemic
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Integumentary System Skin, hair, and nails. Skin: Epidermis: outer layer. Dermis: also called corium, or true skin. Subcutaneous fascia: innermost layer. Integumentary Glands Sudoriferous:
Integumentary System Integumentary System Skin, hair, and nails. Skin: Epidermis: outer layer. Dermis: also called corium, or true skin. Subcutaneous fascia: innermost layer. Integumentary Glands Sudoriferous:
Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Unit 1: Asepsis and Infection Control
 Unit 1: Asepsis and Infection Control Outlines - Type of microorganism causing infection. - Types of infection. - Nosocomial infection. - Chain of infection. - Body defenses against infection. - Factors
Unit 1: Asepsis and Infection Control Outlines - Type of microorganism causing infection. - Types of infection. - Nosocomial infection. - Chain of infection. - Body defenses against infection. - Factors
