Acquired Bilateral Dyspigmentation on Face and Neck: Clinically Appropriate Approaches
|
|
|
- Ashlee Lamb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINL RTICLE Dermatology J Korean Med Sci 206; 3: cquired ilateral Dyspigmentation on Face and Neck: Clinically ppropriate pproaches You Jin Lee, Ji Hye Park, Dong-Youn Lee, and Jong-Hee Lee,2 Department of Dermatology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea; 2 Department of Medical Device Management & Research, SIHST, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea Received: 8 June 206 ccepted: 4 September 206 ddress for Correspondence: Jong-Hee Lee, MD Department of Dermatology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 8, Irwon-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul 0635, Korea bell7@hanmail.net Facial dyspigmentation in sian women often poses diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. Recently, a distinctive bilateral hyperpigmentation of face and neck has occasionally been observed. This study was performed to investigate the clinico-pathological features of this dyspigmentation as well as proper treatment approaches. We retrospectively investigated the medical records including photographs, routine laboratory tests, histopathologic studies of both lesional and peri-lesional normal skin and patch test of thirty-one patients presented acquired bizarre hyperpigmentation on face and neck. The mean age of patients was 52.3 years and the mean duration of dyspigmentation was 24.2 months. In histologic evaluations of lesional skin, a significantly increased liquefactive degeneration of basal layer, pigmentary incontinence and lymphocytic infiltration were noted, whereas epidermal melanin or solar elastosis showed no statistical differences. mong 9 patients managed with a step-by-step approach, seven improved with using only topical antiinflammatory agents and moisturizer, and 2 patients gained clinical benefit after laser therapy without clinical aggravation. oth clinical and histopathologic findings of the cases suggest a distinctive acquired hyperpigmentary disorder related with subclinical inflammation. Proper step-by-step evaluation and management of underlying subclinical inflammation would provide clinical benefit. Keywords: Facial Dyspigmentation; Hyperpigmentation; Subclinical Inflammation; ntiinflammatory gents; Laser Therapy INTRODUCTION Facial dyspigmentation is a frustrating disorder to patients, particularly in sian countries (,2). Topical agents inhibiting synthesis or transfer of melanin, as well as enhancing exfoliation of preexisting melanin pigment have been used as the first-line treatment (3-7). Lasers and light-based devices working on pigment have been used with variable success (8). However, certain type of acquired facial hyperpigmentation shows different clinical features and unexpected responses to conventional treatment (9). Multiple laser treatments combined with topical whitening agent may not be effective, with clinical aggravation even after the multiple treatments (3). Recently, we have experienced patients with distinctive bilateral or symmetric hyperpigmentation often extending to neck, which failed to respond conventional treatment for hyperpigmentation. To provide clarification, clinical characteristics, histopathological features, and other diagnostic examination as well as responses to treatments were evaluated in this study. MTERILS ND METHODS Patients We conducted a retrospective review of 3 patients with similar clinical findings who were seen from January 202 to May 204. ll patients presented with unusual reticular hyperpigmentation on the face and neck. Patients professed no preceding erythema or itching before hyperpigmentation. Possible causes of associated conditions with abnormal skin hyperpigmentation, such as thyroid disease, hepatitis, and ddison s disease, were excluded in all patients. We analyzed gender, age, histopathologic findings along with other laboratory findings when available. We also assessed for possible triggering factors. Patch test Standard thin-layer rapid use epicutaneous (TRUE Test ; Smart- Practice, Phoenix, Z, US) were conducted on 20 patients at the first visit. The patch tests were applied on the back for 2 days and interpreted according to International Contact Dermatitis Research Group scoring scale (ICDRG) guideline at 48 and 96 hours as described previously (0). Skin biopsy 2-mm punch biopsy was performed on the very hyperpigmented lesion and peri-lesional normal skin, at least 3 cm apart from the lesion. Specimens were routinely processed by fixation in formaldehyde embedded in paraffin, sectioned and stained with haematoxylin-eosin and assessed with light microscopy. 206 The Korean cademy of Medical Sciences. This is an Open ccess article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons ttribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. pissn eissn
2 Lee YJ, et al. cquired ilateral Dyspigmentation on Face and Neck Immunohistochemical staining including HM-45, S-00, and Melan- were performed in both lesion and peri-lesional normal skin. Histopathologic findings were assessed by two skilled examiners and graded using a semi-quantitative score system: 0, none (normal);, minimal (equivocal); 2, mild; 3, moderate; 4, severe. Statistical analyses Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 20.0 (IM, rmonk, NY, US). The mean scores of each histopathologic finding in two groups were compared with using t-test. nd the χ 2 test was used to analyze the qualitative differences between lesion and peri-lesional normal skin. Statistical significance was established at P < Ethics statement This study was performed under institutional review board approval in Samsung Medical Center ( ). This was a retrospective chart review study, which waived informed consents regarding to this study. ll medical records including medical photographs, patch test results, punch biopsy results, and treatment outcomes were reviewed by the institutional review board. ll of the patients agreed publishing of the photographs of their face. RESULTS Patient demographics and clinical features total of 3 patients (3 males and 28 females) were enrolled in this analysis (Table ). ge at presentation ranged from 24 to 77 years (mean 52.3 years, median 5 years). ll patients presented with varying degrees of unusual brown to greyish mottled patches distributed over face and/or neck (Fig. ). In 28 patients with facial dyspigmentation, both the lateral face and peri-oral area were more commonly affected (22/28, 78.6%) than the lateral face alone (2/28, 7.%) or the peri-oral area alone (4/28, Table. Clinical characteristics of the 3 patients Case No. Sex/ge, yr Site of pigmentation Onset, mon PMHx Patch test Total IgE, U/mL F/63 Face (lateral, chin) 3 Hypercholesterol-emia Nickel F/44 Face (chin) 3 WNL Fragrance mix M/68 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 3 Pelvic pain syndrome ND F/57 Face (lateral) Neck 3 WNL Fragrance mix F/59 Face (chin) 3 Hormone replacement therapy ND ND ND (over 0 yr) 6 F/66 Face (lateral, chin) 4 WNL ND F/43 Face (lateral, chin) 4 WNL Negative F/42 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 4 WNL Thiomersal F/53 Face (lateral, chin) 6 reast cancer (3Y) Negative ND ND 0 M/5 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 6 WNL Fragrance mix, Carba mix, Quanternium Mercapto mix F/24 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 2 WNL Colophony F/77 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 2 Diabetes mellitus Negative F/55 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 2 WNL Fragrance mix, Potassium dichromate F/45 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 2 WNL Negative F/24 Face (lateral, chin) 2 WNL Potassium dichromate ND ND 6 F/65 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 2 WNL Negative F/59 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 2 WNL Negative F/36 Face (chin) 2 WNL ND ND ND 9 F/55 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 2 WNL Nickel sulphate, Potassium dichromate, Colophony F/50 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 8 WNL Thiomersal ND ND 2 F/6 Neck 24 WNL Fragrance mix F/45 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 24 WNL Nickel sulphate, Fragrance mix F/50 Neck 24 WNL Negative ND ND 24 F/49 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 24 WNL Nickel F/44 Face (chin) Neck 36 WNL Dodecyl gallate F/5 Face (lateral, chin) 36 Raynaud s syndrome Nickel F/33 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 60 WNL Cobalt F/5 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 96 WNL Nickel M/58 Neck 20 WNL ND ND ND 30 F/72 Face (lateral, chin) Neck 20 Hypertension, Diabetes mellitus ND F/72 Face (lateral) WNL Nickel ND ND Total IgE (U/mL) (normal range: U/mL), ECP (ng/ml). PMHx = premedical history, IgE = immunoglobulin E, ECP = eosinophil cationic protein, WNL = within normal limit, ND = not done. ECP, ng/ml
3 Lee YJ, et al. cquired ilateral Dyspigmentation on Face and Neck C Fig.. Clinical photographs. Pigmentation was prominent on lateral face, perioral and neck. () M/5 rownish mottled patch developed on face and neck 6 months ago. () F/55 Slate-greyish colored patch developed for 2 months on lateral face and neck. (C) F/33 Grey colored patch slowly developed over 5 years. 4.3%). Three patients showed neck dyspigmentation without facial lesion, and 8 patients showed both facial and neck dyspigmentation. The average duration of the lesions was 2 to 20 months (mean 24.2 months, median 2 months). The patients were otherwise healthy and had no relevant medical history. No one had additional pigmentary changes on the trunk or extremities. There was no family history of similar pigmentary alteration. Twentytwo patients had received multiple laser treatments including intense pulsed light and low fluence Q-switched Nd:YG laser before visiting our clinic. The treatments had all failed. Patch test and laboratory findings Patch test in 25 patients showed positive result in 7 (68.0%) and negative in 8 (32.0%) patients. The most common allergen was nickel sulfate (7 cases), followed by Fragrance mix (5 cases). Potassium dichromate was positive in 3 cases, and colophony in 2 cases, thiomerosal in 2 cases, and cobalt, dodecyl gallate, quanternium-5, and Carba mix in one case each (Table 2). ll laboratory findings were within normal limit, except for one patient
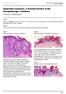
4 Lee YJ, et al. cquired ilateral Dyspigmentation on Face and Neck Table 2. Frequency of detected allergens in patch test Result of the patch test Detected No. Patients, %* Table 3. Comparison of histopathologic scores (mean ± SD) of biopsy specimens from patients Histopathologic findings Positive (n = 7) Nickel Fragrance mix Potassium dichromate Colophony Thiomersal Cobalt Dodecyl gallate Quanternium-5 Carba mix Negative (n = 8) mong 7 patients with positive patch test, four patients were positive more than one allergen; 2 allergen positive (n = 2), 3 allergen positive (n = ), 4 allergen positive (n = ). no. of detected allergen *% = ; llergen not in baseline series. Liquefactive degeneration of basal layer Pigmentary incontinence asal hyperpigmentation Dermal lymphohistiocytic inflammation Solar elastosis Lesion Peri-lesional normal skin 2.63 ±.00* 3.09 ±.02*.63 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± , none (normal);, minimal (equivocal); 2, mild; 3, moderate; 4, severe. Histopathologic findings of each group (Lesion vs. Peri-lesional normal skin) were compared using semi-quantitative score. Liquefactive degeneration, pigmentary incontinence, dermal lymphohistiocytic inflammations were significantly increased in lesion group in t-test. *P < 0.00 compared with peri-lesional normal skin; P < 0.05 compared with perilesional normal skin. total number of patient with patch test result. Lesion Peri-lesional normal skin Fig. 2. Histopathological evaluations of lesion and peri-lesional normal skin. Marked vacuolar degeneration of basal layer and melanin pigment deposition are found in lesional skin biopsy (, ). () Haematoxylin and eosin staining 200, () HM45 immunostaining 200. (case No. 22) with elevated immunoglobulin E (IgE). Histopathology The general histopathological features of lesional skin (22 cases) were compared with those of peri-lesional skin (7 cases). The major histopathological finding was basal layer degeneration and pigmentary incontinence, which was observed in all 22 lesional skin cases (Fig. 2). ll lesional biopsy specimens showed various degrees of liquefactive basal cell degeneration, pigmentary incontinence, increased basal pigmentation, solar elastosis, and perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltration in the upper dermis. No obvious spongiosis were observed. Only liquefactive change, pigmentary incontinence and dermal lymphohistiocytic inflammation was significantly increased in lehttp://jkms.org 2045
5 Lee YJ, et al. cquired ilateral Dyspigmentation on Face and Neck Fig. 3. Histologic evaluation of lesion () and perilesional normal skin (). Distinctive (over grade 2+) liquefactive degeneration of basal layer is observed in lesion () compared with peri-lesional normal skin (). (, ) Haematoxylin and eosin staining 200. Table 4. Comparison of the number of biopsy specimens showing definitive histopathological change (over grade 2) in Lesion vs. Peri-lesional normal skin Histopathology No. of biopsy specimens Liquefactive degeneration of basal layer Pigmentary incontinence Increased basal pigmentation Dermal lymphohistiocytic infiltration Solar elastosis Lesion, No. (%) Peri-lesional normal skin, No. (%) (90.9)* 20 (90.9)* (50.0) 8 (8.8) 2 (54.5) 7 4 (23.5) (5.9) 8 (47.) 7 (4.2) 0 (58.5) The frequency of liquefactive degeneration, pigmentary incontinence, dermal lymphohistiocytic infiltrate were significantly increased in Lesion group compare to Peri-lesional normal skin (χ2 test). *P < 0.00 compared with peri-lesional normal skin; P < 0.05 compared with perilesional normal skin. sional skin compared with peri-lesional normal skin (Table 3). Distinctive (over grade 2+) liquefactive basal layer change was obvious in lesions of 20 cases (20/22, 90.9%), while it was noted in only 4 cases of peri-lesional normal skin (4/7, 23.53%) (P < 0.00) (Fig. 3). Distinctive pigmentary incontinence also more frequently observed in the lesions (20/22, 90.9%) than in perilesional normal skin (/7, 5.9%) (P < 0.00). Lesional biopsy showed prominent dermal lymphohistiocytic infiltration in 8 specimens (8.8%) and solar elastosis in 2 cases (54.5%). However, there are no statistical differences compared with peri-lesional normal skin (Table 4). Follow-up and management The mean follow-up period was 2.2 months in total 3 patients (range, to 4.6 months). mong 3 patients, 9 patients who had been treated and followed-up over 6 months were analyzed for optimal treatment modalities and strategy. Seven patients had only applied topical anti-inflammatory agents (topical tacrolimus 0.% or pimecrolimus %) and used recommended moisturizers containing epidermal growth factor and ceramide as active ingredients. The moisturizers rec Fig. 4. Clinical photographs (patient No. 4). This female, 45-year-old patient developed hyperpigmentation on lateral face and chin about 2 months ago. Moderate degree (grade 3) of basal layer liquefaction was evident in the biopsy specimen. Topical agent without laser therapy was used. Considerable improvement in pigmentation was noticed in the comparison before treatment () and 6 months later (). ommended to patients during treatment do not have any fragrance or paraben. Two of the 7 patients showed considerable improvement after continuous uses of topical anti-inflammatory agents with moisturizers (mean application period 4.2 months) and the rest 5 patients were satisfied with the treatment results of topical application and agreed to continue topical treatments (Fig. 4). The mean follow-up period of these 5 patients was.7 months. Twelve patients were first treated with topical agents with anti-inflammatory agents and moisturizers. fter at least 3 months of topical treatments when hyperpigmentary lesion did not seem to extend, laser treatments were added for these patients. For the improvement of superficial pigmentation, fractional,927 nm laser (Fraxel Dual, Solta Medical, Heyward, C, US) was used first with the parameter of 5 to 0 mj, coverage 35 to 40% (level 3-4), 4-8 passes). Low fluence QS Nd:YG laser treatment (RevLite Cynosure Inc., Westford, M, US: 8 mm, 2.0 J/cm2, 0 Hz, 3 to 6 passes) was followed for the control of pigmentahttps://doi.org/0.3346/jkms
6 Lee YJ, et al. cquired ilateral Dyspigmentation on Face and Neck C D E F Fig. 5. Clinical photographs of patients 6 and 0. These patients were treated with topical tacrolimus 0.% for 6 months due to vacuolar degeneration of basal layer at initial work-up. Laser treatment was subsequently added. (, D) efore treatment in patient 6 and 0, respectively. (, E) Six months after topical tacrolimus 0.%, same respective order. (C, F) Eighteen months after treatment (topical tacrolimus 0.% 6 months followed by laser for 2 months), same respective order. tion in the dermis. Two to 4 times of fractional,927 nm laser treatments with or without 4-6 times of low fluence QS Nd:YG laser treatment was performed on patients. The mean followup period in these patients was 2.3 months. Topical agent has been used for 5.5 months on the average (range, 3 to 0 months) before beginning laser therapy. ll 2 patients showed clinical improvement and reported that they were very or extremely satisfied with the treatment (Fig. 5). DISCUSSION ll 3 patients presented with distinctive bilateral or symmetric bizarre hyperpigmentation of face and/or neck. Most of the patients were elderly with female preponderance, along with chro nic or refractory course of disease (mean duration; over 2 years). Pigmentation generally manifested as brown to slate-grey color with ill-defined margin. The lateral face (forehead and both cheeks) was uniquely involved and hyperpigmentation affected both sun-exposed and non-exposed area in neck. Perioral accentuation of pigmentation was another noticeable finding. ll enrolled patients were initially diagnosed as melasma at other clinics and most underwent multiple laser treatments before visiting our clinic. Melasma is usually pronounced in mid face, as a malar prominence or peri-ocular in middle aged women (6). lso it is associated with pregnancy, ultraviolet exposure, oral contraceptives and endocrine dysfunctions (), which were not found in our patients. Histopathologically, melasma shows increased epidermal melanin, rather than dermal melahttp://jkms.org 2047
7 Lee YJ, et al. cquired ilateral Dyspigmentation on Face and Neck nin (2). Distinctive liquefactive degeneration of basal laser is not a common finding in the lesion of melasma. These clinical and histopathological findings of our patients suggest a disease entity other than melasma. Lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP) or shy dermatosis (D: erythema dyschromicum perstans) should be taken into account for this clinical condition. LPP and D commonly presented as ill-defined oval, greyish brown pigmentation on the face and neck or trunk and limbs without an inflammatory phase. Clinical manifestation of our patients was different from LPP and D. No patients showed any truncal involvement. Lichenoid lympho-histiocytic infiltration or colloidal body in the epidermis was not prominent in the histopathological examination, which is the characteristic feature of two similar pigmentary disorders of LPP and D (3). The vacuolar change of basal layer without spongiosis accompanying dermal melanin deposition, implies the possibility of similar underlying pathomechanism as seen in pigmented contact dermatitis (PCD), also known as Riehl s melanosis (4). PCD is a rare variant of non-eczematous contact dermatitis, which is believed to be caused by repetitive contacts with very small amounts of allergens, such as washing powder, fragrance or cosmetics (5,6). The small amount of allergen induces spongiosis in epidermis, rather than the classical symptoms of contact dermatitis that include erythema, edema and vesicle formation. On the contrary, as subclinical damage persists, vacuolar change of basal layer results in pigmentary incontinence. Clinically, melanin pigment in upper dermis is so slowly absorbed that the hyperpigmentation appears to persist or worsen over time if consistent contact of possible allergens happens (7). Riehl s melanosis, first described by Riehl as war melanosis in 97, similarly affects the face, and is related with nutritional factors and sensitizing chemicals in cosmetics (8-20). Riehl s melanosis is considered synonymous with PCD, with the common allergen being fragrances and chemicals in cosmetics (9). Clinical and histological manifestation of our patients looked similar to that of PCD. Presently, 9 patients were presumed to involve personnel causative allergens including hair dyes (63.2%, 2/9 cases) and cosmetics (36.8%, 7/9 cases); however, no patient showed positive in the as is test with suspected product. Some patients (7 out of 25 patients) demonstrated positive result in T.R.U.E test, but their clinical relevance is doubtful due to lack of prolonged use of personnel cosmetics or fragrances based on their personal history. None of patients recalled any preceding erythema or itching which can be a possible sign of contact dermatitis. We did not perform photopatch test on these patients. For patients who presented with skin lesion especially on sun exposed area, photopatch test can be helpful for the exact diagnosis (2). However, patients in this analysis did not show definite photo-related skin lesion. Photos from Fig. demonstrated prominent pigmentary disturbance on perioral and lateral face rather than on the central area. The central neck area especially right under the chin is usually spared in photo-related disease unlike our patients who showed whole neck involvement of skin lesion. Laboratory tests, such as IgE or eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), which reflect allergic tendency, were not increased except one patient (22). The histological findings of our patients, which included basal layer disruption without spongiosis, suggest underlying subclinical inflammatory process as seen in PCD, which are not preceded by an obvious inflammatory injury. Therefore, the most plausible diagnosis would be PCD in our patients, although there was no definite relation of causative allergens with skin lesion found through all examination. Considering that most of our patients had tried repetitive laser treatments, it is possible that basal layer disruption is caused by unknown inflammatory causes as well as subclinical wounding incurred during laser treatments. The clinical course in which dyspigmentation worsens in many patients after the application of multiple laser treatments supports the possibility that repetitive laser treatments might play a role in disease progression. This hypothesis needs more study. The bizarre pigmentation in our patients was primarily due to dermal melanin deposition, mainly in dermal melanophages. Melanophages are primarily the result of cutaneous inflammatory process that affects the dermo-epidermal interface leading to deposition of pigment within dermis (23). Thus, the control of cutaneous inflammatory process should be prioritized in this condition, especially before laser treatment, which can cause superimposed subclinical inflammation, leading to secondary hyperpigmentation or pigmentary worsening. The triggering factors of inflammation are usually deducted by knowledge of a patient s history and location of inflammation. ut, for some diseases like PCD, which feature barely distinguishable inflammation, thorough history-taking and patch test should be done to identify any possible causative allergen. Histologic evaluation of pigmented lesion (skin biopsy) provides a diagnostic clue and valuable information of depth of pigment location and distribution as well as dermal nature which requires for optimal treatments. Punch biopsy of pigmentary lesion (2 to 3 mm) is sufficient with minimal risk of scarring. Concurrent evaluation of peri-lesional normal skin can provide better precise information in interpreting pathologic change of dyspigmentation (2). However, facial hyperpigmentation of women, especially middle aged sians, are frequently considered as melasma, whether it is or not. Sometimes, active laser therapy is tried based on this tentative diagnosis without suspicion of other disorders. However, this approach is unsatisfactory as there are many pigmentary disorders that clinically mimic melasma and the distinction between them invariably requires astute histopathological evaluation and subsequent clinical correlation (3). When it comes to the optimal treatment modalities in these
8 Lee YJ, et al. cquired ilateral Dyspigmentation on Face and Neck History taking of causative material - Cosmetic, hair dye - Other relevant chemicals Patch test with allergic lab Positive iopsy with normal control - To exclude alternative diagnosis - To determine target pigment depth - To confirm dermal nature pproach for managing facial dyspigmentation Positive finding below - Liquefactive basal degeneration - Moderate-severe inflammation - Severe solar change Consider laser therapy for pigment elimination voidance of causative material Consider oral medication to reduce allergic reaction - ntihistamine - Short term steroid Topical agent at least 3 months - Tacrolimus/Pimecrolimus - Tretinoin - Moisturizer Fig. 6. Step-by-step approach for refractory facial hyperpigmentation. In step, underlying allergic tendency is checked by with thorough history-taking and/or blood work. In step 2, the degree of inflammation and resiliency of dermis are determined. In step 3, the topical agent is used to reduce inflammation for at least several months. In step 4, possible adequate methods for removal of remnant pigments are considered. patients, laser therapy for hyperpigmentation should not be the first choice if there is a severe basal layer disruption and solar elastosis. Presence of liquefactive degeneration of basal layer and dense inflammatory cell infiltration in dermis suggests accumulative inflammatory damage (6), therefore topical agents of anti-inflammatory activity, not depigmenting or whitening agents should be used first. ccording to this well-defined stepby-step approach, among 2 patients who suffered with refractory, long-lasting dyspigmentation was considerably improved (Figs. 4 and 5). This approach is summarized in Fig. 6. Two of 7 patients who used only topical anti-inflammatory agents and moisturizers achieved excellent clinical improvement. The histopathologic findings and the prolonged course of the hyperpigmentation in our cases were both suggestive of a preceding causative subclinical inflammatory process. The underlying cause remains uncertain and multiple factors may have produced this clinical feature. When approaching to this longlasting or refractory facial dyspigmentation, clinicians should consider a step-by step approach. Step involves checking the underlying allergic tendency with thorough history taking and/ or blood lab. Step 2 involves determining the degree of inflammation and resiliency of dermis whether it could be properly restored after laser treatments. Step 3 is the application of a topical agent capable of reducing inflammation for at least months. Step 4 should consider possible adequate methods for removal of remnant pigments as the last step of treatment. We present 3 patients with peculiar clinical feature and longlasting course hyperpigmentation on the face and neck. The use of a systematic step-by-step approach with appropriate therapeutic modality can provide clinical benefit. DISCLOSURE The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose. UTHOR CONTRIUTION Study conception and design: Lee JH. Data collection and analysis: Park JH, Lee DY, Lee JH. Writing: Lee YJ. Revision: Lee YJ, Lee JH. Final approval: all authors. ORCID You Jin Lee Ji Hye Park Dong-Youn Lee Jong-Hee Lee REFERENCES. Pérez-ernal, Muñoz-Pérez M, Camacho F. Management of facial hyperpigmentation. m J Clin Dermatol 2000; : Rigopoulos D, Gregoriou S, Katsambas. Hyperpigmentation and melasma. J Cosmet Dermatol 2007; 6: Patel, Kubba R, Kubba. Clinicopathological correlation of acquired hyperpigmentary disorders. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 203; 79: Khanna N, Rasool S. Facial melanoses: Indian perspective. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 20; 77: de Souza, el-zhary R, Camilleri MJ, Wada D, ppert DL, Gibson LE. In search of prognostic indicators for lymphomatoid papulosis: a retrospective study of 23 patients. J m cad Dermatol 202; 66: Molinar VE, Taylor SC, Pandya G. What s new in objective assessment and treatment of facial hyperpigmentation? Dermatol Clin 204; 32: Grimes PE. Management of hyperpigmentation in darker racial ethnic groups. Semin Cutan Med Surg 2009; 28: Gernone, Frassanito M, Pellegrino, Vacca, Dammacco F. Multiple myeloma and mycosis fungoides in the same patient: clinical, immunologic, and molecular studies. nn Hematol 2002; 8: Kang HY. Melasma and aspects of pigmentary disorders in sians. nn Dermatol Venereol 202; 39 Suppl 4: S Lachapelle JM, Maibach HI; The International Contact Dermatitis Research Group. Patch Testing and Prick Testing. 2nd ed. erlin: Springer, Serrano G, Pujol C, Cuadra J, Gallo S, liaga. Riehl s melanosis: pigmented contact dermatitis caused by fragrances. J m cad Dermatol 989; 2: Grimes PE, Yamada N, hawan J. Light microscopic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural alterations in patients with melasma. m J Dermatopathol 2005; 27: Vega ME, Waxtein L, renas R, Hojyo T, Dominguez-Soto L. shy dermatosis and lichen planus pigmentosus: a clinicopathologic study of 3 cases. Int J Dermatol 992; 3: Park JY, Kim YC, Lee ES, Park KC, Kang HY. cquired bilateral melanosis
9 Lee YJ, et al. cquired ilateral Dyspigmentation on Face and Neck of the neck in perimenopausal women. r J Dermatol 202; 66: Jung JM, Han JS, Won CH, Chang SE, Lee MW, Choi JH, Moon KC. Pigmented contact dermatitis caused by hydroquinone: an unusual presentation and allergen. Korean J Dermatol 205; 53: Ebihara T, Nakayama H. Pigmented contact dermatitis. Clin Dermatol 997; 5: Calonje E, McKee PH. McKee s Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. Edinburgh: Elsevier/Saunders, Rorsman H. Riehl s melanosis. Int J Dermatol 982; 2: Shenoi SD, Rao R. Pigmented contact dermatitis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2007; 73: Li YH, Liu J, Chen JZ, Wu Y, Xu TH, Zhu X, Liu W, Wei HC, Gao XH, Chen HD. pilot study of intense pulsed light in the treatment of Riehl s melanosis. Dermatol Surg 20; 37: Chuah SY, Leow YH, Goon T, Theng CT, Chong WS. Photopatch testing in sians: a 5-year experience in Singapore. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 203; 29: Czarnobilska E, Obtułowicz K, Dyga W, Gołuch, Zwiewka M. Eosinophilia, ECP and Ecp/Eo ratio in allergic and non-allergic diseases. Przegl Lek 2005; 62: Lever WF, Elder DE. Lever s Histopathology of the Skin. 9th ed. Philadelphia, P: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,
Low-fluence Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (1064nm) laser for the treatment of facial melasma in local population
 Original Article Low-fluence Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (1064nm) laser for the treatment of facial melasma in local population Tahir Kamal, Usma Iftikhar* Department of Dermatology,
Original Article Low-fluence Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (1064nm) laser for the treatment of facial melasma in local population Tahir Kamal, Usma Iftikhar* Department of Dermatology,
SPECIAL TOPIC. Institut National de la Sante et de la Recherche Medicale (INSERM U895), Nice, France c
 November 2011 1260 Volume 10 Issue 1i Copyright 2011 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Journal of Drugs in Dermatology SPECIAL TOPIC A Pilot Study Using Reflectance Confocal Microscopy (RCM) in the Assessment of a Novel
November 2011 1260 Volume 10 Issue 1i Copyright 2011 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Journal of Drugs in Dermatology SPECIAL TOPIC A Pilot Study Using Reflectance Confocal Microscopy (RCM) in the Assessment of a Novel
Clinical Course of Segmental Vitiligo: A Retrospective Study of Eighty-Seven Patients
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 26, No. 1, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2014.26.1.61 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Course of Segmental Vitiligo: A Retrospective Study of Eighty-Seven Patients Ji-Hye Park, Mi-Young
Ann Dermatol Vol. 26, No. 1, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2014.26.1.61 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Course of Segmental Vitiligo: A Retrospective Study of Eighty-Seven Patients Ji-Hye Park, Mi-Young
Partial Unilateral Lentiginosis Treated with 532-nm and Subsequent Low-Fluence 1,064-nm Q-Switched Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Lasers
 OCT-2016 ISSUE Med Laser 2016;5(1):42-46 pissn 2287-8300 ㆍ eissn 2288-0224 Partial Unilateral Lentiginosis Treated with 532-nm and Subsequent Low-Fluence 1,064-nm Q-Switched Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum
OCT-2016 ISSUE Med Laser 2016;5(1):42-46 pissn 2287-8300 ㆍ eissn 2288-0224 Partial Unilateral Lentiginosis Treated with 532-nm and Subsequent Low-Fluence 1,064-nm Q-Switched Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum
ISPUB.COM. A Case of Actinic Lichen Planus. K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park Citation K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2009 Volume 8 Number. Abstract The
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park Citation K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2009 Volume 8 Number. Abstract The
A STUDY OF EFFICACY RESULT BETWEEN TOPICAL HERBAL RHUBARB LIQUID AND LIQUID BASE FOR THE TREATMENT OF MELASMA IN THAI PEOPLE
 A STUDY OF EFFICACY RESULT BETWEEN TOPICAL HERBAL RHUBARB LIQUID AND LIQUID BASE FOR THE TREATMENT OF MELASMA IN THAI PEOPLE Zhang Hui Dermatology science, School of Anti Aging and Regenerative Medicine,
A STUDY OF EFFICACY RESULT BETWEEN TOPICAL HERBAL RHUBARB LIQUID AND LIQUID BASE FOR THE TREATMENT OF MELASMA IN THAI PEOPLE Zhang Hui Dermatology science, School of Anti Aging and Regenerative Medicine,
Lichenoid Tissue Reaction in Malignant Melanoma A Potential Diagnostic Pitfall
 natomic Pathology / LICHENOID TISSUE RECTION IN MLIGNNT MELNOM Lichenoid Tissue Reaction in Malignant Melanoma Potential Diagnostic Pitfall CPT Scott R. Dalton, MC, US, 1,3 Capt Matt. aptista, USF, MC,
natomic Pathology / LICHENOID TISSUE RECTION IN MLIGNNT MELNOM Lichenoid Tissue Reaction in Malignant Melanoma Potential Diagnostic Pitfall CPT Scott R. Dalton, MC, US, 1,3 Capt Matt. aptista, USF, MC,
Comparative study of localised intradermal microinjection of tranexamic acid and oral tranexamic acid for the treatment of melasma
 International Journal of Research in Dermatology http://www.ijord.com Original Research rticle DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20183159 Comparative study of localised intradermal
International Journal of Research in Dermatology http://www.ijord.com Original Research rticle DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20183159 Comparative study of localised intradermal
Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), available at
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
JUST SEE ME! PIGMENTATION SOLUTIONS FOR HIGHER FITZPATRICKS
 1 2 3 JUST SEE ME! PIGMENTATION SOLUTIONS FOR HIGHER FITZPATRICKS Just See Me! Diversity AESTHETICS Training! 20+ years! Advanced Aesthetics Diversity Consultant and Trainer! Professional Speaker! Aesthetic
1 2 3 JUST SEE ME! PIGMENTATION SOLUTIONS FOR HIGHER FITZPATRICKS Just See Me! Diversity AESTHETICS Training! 20+ years! Advanced Aesthetics Diversity Consultant and Trainer! Professional Speaker! Aesthetic
A new classification system of nasal contractures
 Original Article J Cosmet Med 2017;1(2):106-111 https://doi.org/10.25056/jcm.2017.1.2.106 pissn 2508-8831, eissn 2586-0585 A new classification system of nasal contractures Geunuck Chang 1, Donghak Jung
Original Article J Cosmet Med 2017;1(2):106-111 https://doi.org/10.25056/jcm.2017.1.2.106 pissn 2508-8831, eissn 2586-0585 A new classification system of nasal contractures Geunuck Chang 1, Donghak Jung
Relation between the Peripherofacial Psoriasis and Scalp Psoriasis
 pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 28, No. 4, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2016.28.4.422 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relation between the Peripherofacial Psoriasis and Scalp Psoriasis Kyung Ho
pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 28, No. 4, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2016.28.4.422 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relation between the Peripherofacial Psoriasis and Scalp Psoriasis Kyung Ho
Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar
 Extragenital unilateral lichen sclerosus et atrophicus in a child: a case report Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar Department of Dermatolgy, Seth GSMC and KEM Hospital, Parel, Mumbai-400012, India Egyptian
Extragenital unilateral lichen sclerosus et atrophicus in a child: a case report Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar Department of Dermatolgy, Seth GSMC and KEM Hospital, Parel, Mumbai-400012, India Egyptian
Clinical Benefit of Combination Treatment with 1,550 nm Fractional Laser and a New Wavelength at 1,927 nm on Photorejuvenation in Asian Patients
 OA(Original Article) Med Laser 2014;3(1):11-16 pissn 2287-8300ㆍeISSN 2288-0224 Clinical Benefit of Combination Treatment with 1,550 nm Fractional Laser and a New Wavelength at 1,927 nm on Photorejuvenation
OA(Original Article) Med Laser 2014;3(1):11-16 pissn 2287-8300ㆍeISSN 2288-0224 Clinical Benefit of Combination Treatment with 1,550 nm Fractional Laser and a New Wavelength at 1,927 nm on Photorejuvenation
Chronology of lichen planus-like keratosis features by dermoscopy: a summary of 17 cases
 DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL www.derm101.com Chronology of lichen planus-like keratosis features by dermoscopy: a summary of 17 cases Soko Watanabe 1, Mizuki Sawada 1, Itaru Dekio 1, Sumiko Ishizaki
DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL www.derm101.com Chronology of lichen planus-like keratosis features by dermoscopy: a summary of 17 cases Soko Watanabe 1, Mizuki Sawada 1, Itaru Dekio 1, Sumiko Ishizaki
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide
 Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Short-term Effects of 308-nm Xenon-chloride Excimer Laser and Narrow-band Ultraviolet B in the Treatment of Vitiligo: A Comparative Study
 J Korean Med Sci 2005; 20: 273-8 ISSN 1011-8934 opyright The Korean cademy of Medical Sciences Short-term Effects of 308-nm Xenon-chloride Excimer Laser and Narrow-band Ultraviolet in the Treatment of
J Korean Med Sci 2005; 20: 273-8 ISSN 1011-8934 opyright The Korean cademy of Medical Sciences Short-term Effects of 308-nm Xenon-chloride Excimer Laser and Narrow-band Ultraviolet in the Treatment of
الاكزيماتيد= Eczematid
 1 / 7 2 / 7 Pityriasis Debate confusing of hypopigmentation characterized increasing surrounded differ hypomelanotic "progressive exists alba misnomer extensive a to observed term the applied term derived
1 / 7 2 / 7 Pityriasis Debate confusing of hypopigmentation characterized increasing surrounded differ hypomelanotic "progressive exists alba misnomer extensive a to observed term the applied term derived
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 10 Page October 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i10.125 Histomorphological Study of Lichen Planus
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i10.125 Histomorphological Study of Lichen Planus
Original article. Tanongkiet Tienthavorn, Poohglin Tresukosol and Poonnawis Sudtikoonaseth
 Original article Patch testing and Histopathology in Thai patients with hyperpigmentation due to Erythema dyschromicum perstans, Lichen planus pigmentosus, and Pigmented contact dermatitis Tanongkiet Tienthavorn,
Original article Patch testing and Histopathology in Thai patients with hyperpigmentation due to Erythema dyschromicum perstans, Lichen planus pigmentosus, and Pigmented contact dermatitis Tanongkiet Tienthavorn,
Invasive Pulsed-Type, Bipolar, Alternating Current Radiofrequency Treatment Using Microneedle Electrodes for Nasal Rosacea
 Med Laser 2017;6(1):32-36 https://doi.org/10.25289/ml.2017.6.1.32 pissn 2287-8300 ㆍ eissn 2288-0224 Invasive Pulsed-Type, Bipolar, Alternating Current Radiofrequency Treatment Using Microneedle Electrodes
Med Laser 2017;6(1):32-36 https://doi.org/10.25289/ml.2017.6.1.32 pissn 2287-8300 ㆍ eissn 2288-0224 Invasive Pulsed-Type, Bipolar, Alternating Current Radiofrequency Treatment Using Microneedle Electrodes
NONABLATIVE RESURFACING
 `AESTHETIC LASER SURGERY 0094-1298/00 $15.00 +.00 NONABLATIVE RESURFACING David J. Goldberg, MD TYPES OF LASERS AND THEIR DIFFERENCES Pulsed char-free CO2 laser skin resurfacing has provided a method of
`AESTHETIC LASER SURGERY 0094-1298/00 $15.00 +.00 NONABLATIVE RESURFACING David J. Goldberg, MD TYPES OF LASERS AND THEIR DIFFERENCES Pulsed char-free CO2 laser skin resurfacing has provided a method of
A New Diagnostic Approach for Idiopathic Circumscribed Acquired Hypermelanosis; A Clinicopathological Study
 American Journal of Dermatology and Venereology 214, 3(2): 35-42 DOI: 1.5923/j.ajdv.21432.3 A New Diagnostic Approach for Idiopathic Circumscribed Maytham M. Al-Hilo 1,2, Shakir J. Al-Saedy 1,2, Ali F.
American Journal of Dermatology and Venereology 214, 3(2): 35-42 DOI: 1.5923/j.ajdv.21432.3 A New Diagnostic Approach for Idiopathic Circumscribed Maytham M. Al-Hilo 1,2, Shakir J. Al-Saedy 1,2, Ali F.
NO MORE NEWS AN EVIDENCE BASED APPROACH ON LASERS IN SKIN OF COLOR PATIENTS DR. EDUARDO WEISS, M.D., FAAD
 NO MORE NEWS AN EVIDENCE BASED APPROACH ON LASERS IN SKIN OF COLOR PATIENTS DR. EDUARDO WEISS, M.D., FAAD KEY POINTS Hispanics/Latinos are the fastest growing segment of the skin of color population Use
NO MORE NEWS AN EVIDENCE BASED APPROACH ON LASERS IN SKIN OF COLOR PATIENTS DR. EDUARDO WEISS, M.D., FAAD KEY POINTS Hispanics/Latinos are the fastest growing segment of the skin of color population Use
Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides
 Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides M. El Darouti, S. Marzook, M. Bosseila, O. Abu Zeid, O. El- Safouri, A. Zayed, A. El-Ramly Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 2 (1):
Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides M. El Darouti, S. Marzook, M. Bosseila, O. Abu Zeid, O. El- Safouri, A. Zayed, A. El-Ramly Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 2 (1):
ISPUB.COM. Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations. D Sarma, S Repertinger
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
Lifa Disease: Frictional Dermal Melanosis over Bony Prominences (Clinicopathological Study) *
 Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications, 01,, 196-00 http://dx.doi.org/10.436/jcdsa.01.3036 Published Online September 01 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jcdsa) Lifa Disease: Frictional
Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications, 01,, 196-00 http://dx.doi.org/10.436/jcdsa.01.3036 Published Online September 01 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jcdsa) Lifa Disease: Frictional
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE
 Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
Eczema & Dermatitis Clinical features: Histopathological features: Classification:
 Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
Clinicopathologic characteristics of early-onset Becker s nevus in Korean children and adolescents
 Report Clinicopathologic characteristics of early-onset Becker s nevus in Korean children and adolescents Young J. Kim 1, *, MD, Mi R. Roh 2, *, MD, PhD, Ji H. Lee 2, MD, Jung I. Na 3, MD, PhD, Joo Y.
Report Clinicopathologic characteristics of early-onset Becker s nevus in Korean children and adolescents Young J. Kim 1, *, MD, Mi R. Roh 2, *, MD, PhD, Ji H. Lee 2, MD, Jung I. Na 3, MD, PhD, Joo Y.
Andrei Metelitsa, MD, FRCPC, FAAD Co-Director, Institute for Skin Advancement Clinical Associate Professor, Dermatology University of Calgary, Canada
 Andrei Metelitsa, MD, FRCPC, FAAD Co-Director, Institute for Skin Advancement Clinical Associate Professor, Dermatology University of Calgary, Canada Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved.
Andrei Metelitsa, MD, FRCPC, FAAD Co-Director, Institute for Skin Advancement Clinical Associate Professor, Dermatology University of Calgary, Canada Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved.
A case of rosacea fulminans in a pregnant woman
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2018) 26, 122-126 Views and Practice A case of rosacea fulminans in a pregnant woman JE Seol, SH Park, JU Kim, GJ Cho, SH Moon, H Kim Introduction Rosacea fulminans (RF)
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2018) 26, 122-126 Views and Practice A case of rosacea fulminans in a pregnant woman JE Seol, SH Park, JU Kim, GJ Cho, SH Moon, H Kim Introduction Rosacea fulminans (RF)
with particular emphasis on the vacuolar
 Tea JOURNAL OF TNvasTJoATrvg DERMAT0L00Y Copyright. 1959 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. vol. 52, No.2 Printed in U.S.A. TJLTRASTRUCTTJRAL PATHOLOGY OF ERYTHEMA DYSCHROMICUM PERSTANS* NICHOLAS A. SOTER,
Tea JOURNAL OF TNvasTJoATrvg DERMAT0L00Y Copyright. 1959 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. vol. 52, No.2 Printed in U.S.A. TJLTRASTRUCTTJRAL PATHOLOGY OF ERYTHEMA DYSCHROMICUM PERSTANS* NICHOLAS A. SOTER,
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation. Dermatopathology Specialists Needed. Changing Trends
 Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
An Efficacy Study of 3 Commercially Available Hydroquinone 4% Treatments for Melasma
 An Efficacy Study of 3 Commercially Available Hydroquinone 4% Treatments for Melasma Pearl E. Grimes, MD Melasma is a common disorder of hyperpigmentation typically characterized by relatively symmetric
An Efficacy Study of 3 Commercially Available Hydroquinone 4% Treatments for Melasma Pearl E. Grimes, MD Melasma is a common disorder of hyperpigmentation typically characterized by relatively symmetric
1,927-nm Fractional Thulium Fiber Laser for the Treatment of Nonfacial Photodamage: A Pilot Study
 1,927-nm Fractional Thulium Fiber Laser for the Treatment of Nonfacial Photodamage: A Pilot Study KRISTEL D. POLDER, MD, y APRIL HARRISON, PA-C, y LEIGH ELLEN EUBANKS, MD, y AND SUZANNE BRUCE, MD y BACKGROUND
1,927-nm Fractional Thulium Fiber Laser for the Treatment of Nonfacial Photodamage: A Pilot Study KRISTEL D. POLDER, MD, y APRIL HARRISON, PA-C, y LEIGH ELLEN EUBANKS, MD, y AND SUZANNE BRUCE, MD y BACKGROUND
Diffuse Pigmentation of Back and Arms: Macular Amyloidosis or Other?
 ORIGINAL REPORT Diffuse Pigmentation of Back and Arms: Macular Amyloidosis or Other? Seyed Zahra Ghodsi 1, Pari Rahimi 1, Amir Ehsani 1, Pedram Noormohammadpour 1, Masood Asgrai 2, and Fatemeh Gholamali
ORIGINAL REPORT Diffuse Pigmentation of Back and Arms: Macular Amyloidosis or Other? Seyed Zahra Ghodsi 1, Pari Rahimi 1, Amir Ehsani 1, Pedram Noormohammadpour 1, Masood Asgrai 2, and Fatemeh Gholamali
SPECIAL TOPIC. AboutSkin Dermatology & DermSurgery, Greenwood Village, CO b. The Aesthetic Clinique, Destin, FL c
 November 2016 611 Volume 15 Issue 11 Copyright 2016 ORIGINAL ARTICLES SPECIAL TOPIC Multi-Center Pilot Study to Evaluate the Safety Profile of High Energy Fractionated Radiofrequency With Insulated Microneedles
November 2016 611 Volume 15 Issue 11 Copyright 2016 ORIGINAL ARTICLES SPECIAL TOPIC Multi-Center Pilot Study to Evaluate the Safety Profile of High Energy Fractionated Radiofrequency With Insulated Microneedles
OCCUPATIONAL CONTACT DERMATITIS IN A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE EPIDEMIOLOGY, CLINICAL PROFILE AND PATCH TEST EVALUATION
 OCCUPATIONAL CONTACT DERMATITIS IN A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE EPIDEMIOLOGY, CLINICAL PROFILE AND PATCH TEST EVALUATION DONE BY : Dr.Ragini Rajan Final year Post Graduate MD(DVL) Govt.Stanley Medical College,
OCCUPATIONAL CONTACT DERMATITIS IN A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE EPIDEMIOLOGY, CLINICAL PROFILE AND PATCH TEST EVALUATION DONE BY : Dr.Ragini Rajan Final year Post Graduate MD(DVL) Govt.Stanley Medical College,
Photodamaged skin occurs as a result of its
 Plasma Skin Resurfacing for Regeneration of Neck, Chest, and Hands: Investigation of a Novel Device TINA S. ALSTER, MD, AND SAILESH KONDA, BS BACKGROUND Many noninvasive treatments to rejuvenate photodamaged
Plasma Skin Resurfacing for Regeneration of Neck, Chest, and Hands: Investigation of a Novel Device TINA S. ALSTER, MD, AND SAILESH KONDA, BS BACKGROUND Many noninvasive treatments to rejuvenate photodamaged
Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Invasive Pulsed-Type Bipolar Alternating Current Radiofrequency on Melasma and Rebound Hyperpigmentation
 Med Laser 2017;6(1):17-23 https://doi.org/10.25289/ml.2017.6.1.17 pissn 2287-8300 ㆍ eissn 2288-0224 Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Invasive Pulsed-Type Bipolar Alternating Current Radiofrequency on
Med Laser 2017;6(1):17-23 https://doi.org/10.25289/ml.2017.6.1.17 pissn 2287-8300 ㆍ eissn 2288-0224 Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Invasive Pulsed-Type Bipolar Alternating Current Radiofrequency on
The Efficacy and Safety of 4-n-butylresorcinol 0.1% Cream for the Treatment of Melasma: A Randomized Controlled Split-face Trial
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 22, No. 1, 2010 DOI: 10.5021/ad.2010.22.1.21 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Efficacy and Safety of 4-n-butylresorcinol 0.1% Cream for the Treatment of Melasma: A Randomized Controlled Split-face
Ann Dermatol Vol. 22, No. 1, 2010 DOI: 10.5021/ad.2010.22.1.21 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Efficacy and Safety of 4-n-butylresorcinol 0.1% Cream for the Treatment of Melasma: A Randomized Controlled Split-face
Multi-Application Platform. Summary of Peer-reviewed Articles for Various Clinical Indications April 2016
 Multi-Application Platform Summary of Peer-reviewed Articles for Various Clinical Indications April 2016 Various Clinical Indications Atrophic acne scars and acne Photo-aged skin, pigmentation & hyperpigmentation
Multi-Application Platform Summary of Peer-reviewed Articles for Various Clinical Indications April 2016 Various Clinical Indications Atrophic acne scars and acne Photo-aged skin, pigmentation & hyperpigmentation
Recent Trend in the Incidence of Premalignant and Malignant Skin Lesions in Korea between 1991 and 2006
 J Korean Med Sci 2010; 25: 924-9 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.6.924 Recent Trend in the Incidence of Premalignant and Malignant Skin Lesions in Korea between 1991 and 2006 We evaluated the
J Korean Med Sci 2010; 25: 924-9 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.6.924 Recent Trend in the Incidence of Premalignant and Malignant Skin Lesions in Korea between 1991 and 2006 We evaluated the
Progressive Macular Hypomelanosis in Korean Patients: A Clinicopathologic Study
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 2, No., 2009 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Progressive Macular Hypomelanosis in Korean Patients: A Clinicopathologic Study Seon Wook Hwang, M.D., Soon Kwon Hong, M.D., Sang Hyun Kim, M.D., Jeong Hoon
Ann Dermatol Vol. 2, No., 2009 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Progressive Macular Hypomelanosis in Korean Patients: A Clinicopathologic Study Seon Wook Hwang, M.D., Soon Kwon Hong, M.D., Sang Hyun Kim, M.D., Jeong Hoon
MELASMA Photoprotection and light devices
 MELASMA Photoprotection and light devices Pr. Thierry Passeron, MD, PhD Department of Dermatology & INSERM 05 team University Hospital of Nice, France Conflicts of interest Research grants and/or honoraria:
MELASMA Photoprotection and light devices Pr. Thierry Passeron, MD, PhD Department of Dermatology & INSERM 05 team University Hospital of Nice, France Conflicts of interest Research grants and/or honoraria:
Chapter 21: FotoFacial RF Pro Treatment of Specific Clinical Subtypes
 Chapter 21: FotoFacial RF Pro Treatment of Specific Clinical Subtypes 1. Erythema in Skin Types 1-3 (with or without Flushing, Laxity and Wrinkles) using the SR/SRA Head 116 The program usually takes 5-7
Chapter 21: FotoFacial RF Pro Treatment of Specific Clinical Subtypes 1. Erythema in Skin Types 1-3 (with or without Flushing, Laxity and Wrinkles) using the SR/SRA Head 116 The program usually takes 5-7
Papular Elastorrhexis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE Proceedings of UCLA Healthcare Papular Elastorrhexis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Aparche Yang, M.D., Jamie Zussman, M.D., Chandra Smart, M.D., Joseph Diehl, M.D., Dina
CLINICAL VIGNETTE Proceedings of UCLA Healthcare Papular Elastorrhexis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Aparche Yang, M.D., Jamie Zussman, M.D., Chandra Smart, M.D., Joseph Diehl, M.D., Dina
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Lichen planus along with Blaschko lines "Blaschkoian lichen planus"
 Original Article Lichen planus along with Blaschko lines "Blaschkoian lichen planus" Hossein Kavoussi, Mazaher Ramazani, Elias Salimi Dermatology Department, Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences,
Original Article Lichen planus along with Blaschko lines "Blaschkoian lichen planus" Hossein Kavoussi, Mazaher Ramazani, Elias Salimi Dermatology Department, Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences,
Treatment Seeking Behavior In Patients Suffering From Melasma Aneela Asghar, Tariq Rashid
 Original Article Treatment Seeking Behavior In Patients Suffering From Melasma Aneela Asghar, Tariq Rashid ABSTRACT Introduction: Melasma is a common hypermelanosis that typically involves sun exposed
Original Article Treatment Seeking Behavior In Patients Suffering From Melasma Aneela Asghar, Tariq Rashid ABSTRACT Introduction: Melasma is a common hypermelanosis that typically involves sun exposed
Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Wavelength-Converted 660-nm Q-Switched Ruby-Like Versatile YAG Treatment on Various Skin Pigmentation Disorders
 OA() Med Laser Epub 2014 July 14 pissn 2287-8300ㆍeISSN 2288-0224 Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Wavelength-Converted 660-nm Q-Switched Ruby-Like Versatile YAG Treatment on Various Skin Pigmentation
OA() Med Laser Epub 2014 July 14 pissn 2287-8300ㆍeISSN 2288-0224 Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Wavelength-Converted 660-nm Q-Switched Ruby-Like Versatile YAG Treatment on Various Skin Pigmentation
Clinical and Histopathological Spectrum of Mycosis Fungoides
 Awad Hasan Al-Tarawneh, MD, Jordan Board* Background: Early diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is essential but difficult and can be easily missed because it mimics many inflammatory skin diseases both clinically
Awad Hasan Al-Tarawneh, MD, Jordan Board* Background: Early diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is essential but difficult and can be easily missed because it mimics many inflammatory skin diseases both clinically
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Available online at Vol. 07, No. 02, pp , February, 2018 RESEARCH ARTICLE
 z Available online at http://www.ijcrls.com International Journal of Current Research in Life Sciences Vol. 07, No. 02, pp.1139-1143, February, 2018 ISSN: 2319-9490 RESEARCH ARTICLE THE TREATMENT OF DILATED
z Available online at http://www.ijcrls.com International Journal of Current Research in Life Sciences Vol. 07, No. 02, pp.1139-1143, February, 2018 ISSN: 2319-9490 RESEARCH ARTICLE THE TREATMENT OF DILATED
Treatment of periorbital wrinkles with 1,550 and 1,565 nm Er:Glass fractional photothermolysis lasers: A simultaneous split-face trial
 Treatment of periorbital wrinkles with 1,550 and 1,565 nm Er:Glass fractional photothermolysis lasers: A simultaneous split-face trial Jin Young Jung Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei
Treatment of periorbital wrinkles with 1,550 and 1,565 nm Er:Glass fractional photothermolysis lasers: A simultaneous split-face trial Jin Young Jung Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei
A Histopathologic Study of Connective Tissue Diseases of Skin
 Original Article Indian Journal of Pathology: Research and Practice 393 Volume 6 Number 2, April - June 2017 (Part 2) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21088/ijprp.2278.148x.6217.9 A Histopathologic Study of Connective
Original Article Indian Journal of Pathology: Research and Practice 393 Volume 6 Number 2, April - June 2017 (Part 2) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21088/ijprp.2278.148x.6217.9 A Histopathologic Study of Connective
Split-Face Study Using a 1,927-nm Thulium Fiber Fractional Laser to Treat Photoaging and Melasma in Asian Skin
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Split-Face Study Using a 1,927-nm Thulium Fiber Fractional Laser to Treat Photoaging and Melasma in Asian Skin HYUNG MIN LEE, MD,* 1 SIK HAW, MD, 1 JAE KYUNG KIM, MD,* SUNG EUN CHANG,
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Split-Face Study Using a 1,927-nm Thulium Fiber Fractional Laser to Treat Photoaging and Melasma in Asian Skin HYUNG MIN LEE, MD,* 1 SIK HAW, MD, 1 JAE KYUNG KIM, MD,* SUNG EUN CHANG,
Conventional ablative carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and
 Lower-Fluence, Higher-Density versus Higher-Fluence, Lower-Density Treatment with a 10,600-nm Carbon Dioxide Fractional Laser System: A Split-Face, Evaluator-Blinded Study JIN YOUNG JUNG, MD, JU HEE LEE,
Lower-Fluence, Higher-Density versus Higher-Fluence, Lower-Density Treatment with a 10,600-nm Carbon Dioxide Fractional Laser System: A Split-Face, Evaluator-Blinded Study JIN YOUNG JUNG, MD, JU HEE LEE,
Asian skin rejuvenation with PicoFractional laser
 Asian skin rejuvenation with PicoFractional laser Krystle Wang, MD Photoaging of the Skin Skin aging is a culmination of genetic and environmental factors and is largely influenced by the cumulative damage
Asian skin rejuvenation with PicoFractional laser Krystle Wang, MD Photoaging of the Skin Skin aging is a culmination of genetic and environmental factors and is largely influenced by the cumulative damage
A study of patch testing in subjects with hand eczema of different occupational groups
 International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Bhachech HT et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2016 Sep;3(9):2566-2570 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Research
International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Bhachech HT et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2016 Sep;3(9):2566-2570 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Research
The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural Decompression between FBSS or Not
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2014 January; Vol. 27, No. 1: 63-67 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.63 The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural
Original Article Korean J Pain 2014 January; Vol. 27, No. 1: 63-67 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.63 The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural
Hands-on: Lasers. NonAblative Rejuvenation
 Hands-on: Lasers NonAblative Rejuvenation Anthony M. Rossi, MD Assistant Attending Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Assistant Professor Weill Cornell Medical College DISCLOSURE OF RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Hands-on: Lasers NonAblative Rejuvenation Anthony M. Rossi, MD Assistant Attending Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Assistant Professor Weill Cornell Medical College DISCLOSURE OF RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
Vitiligo. Vasanop Vachiramon, MD. Assistant professor Division of Dermatology, Ramathibodi Hospital
 Vitiligo Vasanop Vachiramon, MD. Assistant professor Division of Dermatology, Ramathibodi Hospital Vitiligo Acquired pigmentary disorder Depigmented macules and patches Prevalence The worldwide prevalence
Vitiligo Vasanop Vachiramon, MD. Assistant professor Division of Dermatology, Ramathibodi Hospital Vitiligo Acquired pigmentary disorder Depigmented macules and patches Prevalence The worldwide prevalence
Efficacy and safety of ablative fractional carbon dioxide laser for acne scars
 Original Article Efficacy and safety of ablative fractional carbon dioxide laser for acne scars Tahir Jamil Ahmad*, Farhana Muzaffar**, Haroon Nabi *, Sarmad Malik*, Ayesha Noreen*, Rabiya Hayat *Department
Original Article Efficacy and safety of ablative fractional carbon dioxide laser for acne scars Tahir Jamil Ahmad*, Farhana Muzaffar**, Haroon Nabi *, Sarmad Malik*, Ayesha Noreen*, Rabiya Hayat *Department
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT
 Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Thai Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (TJPS)
 Thai Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (TJPS) 34 th International Annual Meeting in Pharmaceutical Sciences and 2 nd CU FPhS - RIKEN CDB Symposium (IAMPS34 and 2 nd CU FPhS - RIKEN CDB) The Effectiveness
Thai Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (TJPS) 34 th International Annual Meeting in Pharmaceutical Sciences and 2 nd CU FPhS - RIKEN CDB Symposium (IAMPS34 and 2 nd CU FPhS - RIKEN CDB) The Effectiveness
Melasma is acquired and
 Repeated Treatment Protocols for Melasma and Acquired Dermal Melanocytosis KOTARO YOSHIMURA, MD, KATSUJIRO SATO, MD, EMIKO AIBA-KOJIMA, MD, Daisuke Matsumoto, MD, Chiaki Machino, MD, Takashi Nagase, MD,
Repeated Treatment Protocols for Melasma and Acquired Dermal Melanocytosis KOTARO YOSHIMURA, MD, KATSUJIRO SATO, MD, EMIKO AIBA-KOJIMA, MD, Daisuke Matsumoto, MD, Chiaki Machino, MD, Takashi Nagase, MD,
Dermoscopic patterns in active and regressive lichen planus and lichen planus variants: a morphological study
 DERMTOLOGY PRCTICL & CONCEPTUL www.derm101.com Dermoscopic patterns in active and regressive lichen planus and lichen planus variants: a morphological study Şule Güngör 1, Ilteriş O. Topal 1, Emek K. Göncü
DERMTOLOGY PRCTICL & CONCEPTUL www.derm101.com Dermoscopic patterns in active and regressive lichen planus and lichen planus variants: a morphological study Şule Güngör 1, Ilteriş O. Topal 1, Emek K. Göncü
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma presented with annular erythematous patches over the face and cheek in a Chinese lady
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2009) 17, 151-155 Case Report Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma presented with annular erythematous patches over the face and cheek in a Chinese lady SKF Loo, LY
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2009) 17, 151-155 Case Report Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma presented with annular erythematous patches over the face and cheek in a Chinese lady SKF Loo, LY
Acne is one of the most common skin diseases. It usually occurs during adolescence, but can
 DOI: 10.5124/jkma.2010.53.7.623 pissn: 1975-8456 eissn: 2093-5951 http://jkma.org Pharmacotherapeutics Pharmacologic Treatment of Acne Dae Hun Suh, MD Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University
DOI: 10.5124/jkma.2010.53.7.623 pissn: 1975-8456 eissn: 2093-5951 http://jkma.org Pharmacotherapeutics Pharmacologic Treatment of Acne Dae Hun Suh, MD Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University
Diffuse Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma in a 69-Year-old Man with Extensive Extrathyroidal Extension: A Case Report
 SE REPORT Oncology & Hematology http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.3.480 J Korean Med Sci 2013; 28: 480-484 Diffuse Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid arcinoma in a 69-Year-old Man with Extensive
SE REPORT Oncology & Hematology http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.3.480 J Korean Med Sci 2013; 28: 480-484 Diffuse Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid arcinoma in a 69-Year-old Man with Extensive
Clinical Study Treatment of Mesh Skin Grafted Scars Using a Plasma Skin Regeneration System
 Plastic Surgery International Volume 00, Article ID 87448, 4 pages doi:0.55/00/87448 Clinical Study Treatment of Mesh Skin Grafted Scars Using a Plasma Skin Regeneration System Takamitsu Higashimori, Taro
Plastic Surgery International Volume 00, Article ID 87448, 4 pages doi:0.55/00/87448 Clinical Study Treatment of Mesh Skin Grafted Scars Using a Plasma Skin Regeneration System Takamitsu Higashimori, Taro
Successful Treatment of Refractory Melasma Using Invasive Micro-Pulsed Electric Signal Device
 CR(Case Report) Med Laser 2015;4(1):39-44 pissn 2287-8300ㆍeISSN 2288-0224 Successful Treatment of Refractory Melasma Using Invasive Micro-Pulsed Electric Signal Device Case Report Moon Choi 1 Seohee Choi
CR(Case Report) Med Laser 2015;4(1):39-44 pissn 2287-8300ㆍeISSN 2288-0224 Successful Treatment of Refractory Melasma Using Invasive Micro-Pulsed Electric Signal Device Case Report Moon Choi 1 Seohee Choi
Long-term exposure to UV radiation results
 Restorative esthetic Therapy Retrospective Evaluation of the Long-term ntiaging Effects of roadand Light Therapy Patrick itter Jr, MD; Jason Pozner, MD roadand Light (L), which utilizes visible and infrared
Restorative esthetic Therapy Retrospective Evaluation of the Long-term ntiaging Effects of roadand Light Therapy Patrick itter Jr, MD; Jason Pozner, MD roadand Light (L), which utilizes visible and infrared
A Comparison of the Efficacy of Ablative Fractional Laser-assisted Photodynamic Therapy according to the Density of Ablative Laser Channel
 A Comparison of the Efficacy of Ablative Fractional Laser-assisted Photodynamic Therapy according to the Density of Ablative Laser Channel in the Treatment of Actinic Keratosis Yeo-Rye Cho, Jeong-Hwan
A Comparison of the Efficacy of Ablative Fractional Laser-assisted Photodynamic Therapy according to the Density of Ablative Laser Channel in the Treatment of Actinic Keratosis Yeo-Rye Cho, Jeong-Hwan
Immunohistochemical study of lichen planus
 Immunohistochemical study of lichen planus SAI SHOUSHA AND JOHN SVIRBELY1 rom the Department of Histopathology, Royal ree Hospital, London NW3 2QG J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 569-574 SUARY The distribution
Immunohistochemical study of lichen planus SAI SHOUSHA AND JOHN SVIRBELY1 rom the Department of Histopathology, Royal ree Hospital, London NW3 2QG J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 569-574 SUARY The distribution
INTENSE PULSED LIGHT VERSUS ADVANCED FLUORESCENT TECHNOLOGY PULSED LIGHT FOR PHOTODAMAGED SKIN: A SPLIT-FACE PILOT COMPARISON
 22 COPYRIGHT 2007 INTENSE PULSED LIGHT VERSUS ADVANCED FLUORESCENT TECHNOLOGY PULSED LIGHT FOR PHOTODAMAGED SKIN: A SPLIT-FACE PILOT COMPARISON Martin Braun MD Vancouver Laser & Skin Care Centre Inc, Vancouver,
22 COPYRIGHT 2007 INTENSE PULSED LIGHT VERSUS ADVANCED FLUORESCENT TECHNOLOGY PULSED LIGHT FOR PHOTODAMAGED SKIN: A SPLIT-FACE PILOT COMPARISON Martin Braun MD Vancouver Laser & Skin Care Centre Inc, Vancouver,
Urticarial Dermatitis: Clinical Characteristics of Itch and Therapeutic Response to Cyclosporine
 Itch and Cyclosporine in Urticarial Dermatitis pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 29, No. 2, 2017 https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.2.143 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Urticarial Dermatitis: Clinical
Itch and Cyclosporine in Urticarial Dermatitis pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 29, No. 2, 2017 https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.2.143 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Urticarial Dermatitis: Clinical
A Novel Approach for Acne Treatment
 A Novel Approach for Acne Treatment E.V. Ross, M.D.; M.A. Blair, M.D.; B.S. Graham, M.D.; Naval Medical Center, San Diego, CA D.Y. Paithankar, Ph.D.; B.A. Saleh, M.Eng.; Candela Corporation, Wayland, MA
A Novel Approach for Acne Treatment E.V. Ross, M.D.; M.A. Blair, M.D.; B.S. Graham, M.D.; Naval Medical Center, San Diego, CA D.Y. Paithankar, Ph.D.; B.A. Saleh, M.Eng.; Candela Corporation, Wayland, MA
Treatment of Refractory Rosacea with a Dual Wavelength Long- Pulsed 755-nm Alexandrite and 1,064-nm Nd:YAG Laser
 Med Laser 2018;7(1):47-51 https://doi.org/10.25289/ml.2018.7.1.47 pissn 2287-8300 ㆍ eissn 2288-0224 Treatment of Refractory Rosacea with a Dual Wavelength Long- Pulsed 755-nm Alexandrite and 1,064-nm Nd:YAG
Med Laser 2018;7(1):47-51 https://doi.org/10.25289/ml.2018.7.1.47 pissn 2287-8300 ㆍ eissn 2288-0224 Treatment of Refractory Rosacea with a Dual Wavelength Long- Pulsed 755-nm Alexandrite and 1,064-nm Nd:YAG
Solar Lentigines: Evaluating Pulsed Dye Laser (PDL) as an Effective Treatment Option
 Original rticle Solar Lentigines: Evaluating Pulsed Dye Laser (PDL) as an Effective Treatment Option Hayedeh Ghaninejhadi, mirhooshang Ehsani, Ladan Edrisi, Fatemeh Gholamali, Zahra kbari, Pedram Noormohammadpour
Original rticle Solar Lentigines: Evaluating Pulsed Dye Laser (PDL) as an Effective Treatment Option Hayedeh Ghaninejhadi, mirhooshang Ehsani, Ladan Edrisi, Fatemeh Gholamali, Zahra kbari, Pedram Noormohammadpour
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A.
 BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A. Anvar Ali 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, Rehana Tippoo, P. Viswanathan,
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A. Anvar Ali 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, Rehana Tippoo, P. Viswanathan,
Epidemiological aspects and disease association of childhood vitiligo
 Original Article Epidemiological aspects and disease association of childhood S. Farajzadeh*, M. Aflatoonian*, S. Mohammadi*, B. Vares*, R. Amiri* * Department of Dermatology, Afzalipour hospital Kerman
Original Article Epidemiological aspects and disease association of childhood S. Farajzadeh*, M. Aflatoonian*, S. Mohammadi*, B. Vares*, R. Amiri* * Department of Dermatology, Afzalipour hospital Kerman
Histopathology of Melanoma
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 48, 409-416 (1975) Histopathology of Melanoma G. J. WALKER SMITH Department ofpathology, Yale University School ofmedicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, Connecticut
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 48, 409-416 (1975) Histopathology of Melanoma G. J. WALKER SMITH Department ofpathology, Yale University School ofmedicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, Connecticut
Comparative microanatomy of the normal skin with that of immunobullous condition
 Original article: Comparative microanatomy of the normal skin with that of immunobullous condition 1Dr BananiKundu, 2 DrAnirban Sadhu, 3 DrRudradev Meyur, 4 Dr SauravKundu, 5 Dr Alpana De, 6Dr SatabdiSarkar
Original article: Comparative microanatomy of the normal skin with that of immunobullous condition 1Dr BananiKundu, 2 DrAnirban Sadhu, 3 DrRudradev Meyur, 4 Dr SauravKundu, 5 Dr Alpana De, 6Dr SatabdiSarkar
Treatment of Melasma Using a Novel 1,927 nm Fractional Thulium Laser: A Retrospective Analysis of 68 Korean Patients
 Original Article Med Laser 2017;6(1):10-16 https://doi.org/10.25289/ml.2017.6.1.10 pissn 2287-8300 ㆍ eissn 2288-0224 Treatment of Melasma Using a Novel 1,927 nm Fractional Thulium Laser: A Retrospective
Original Article Med Laser 2017;6(1):10-16 https://doi.org/10.25289/ml.2017.6.1.10 pissn 2287-8300 ㆍ eissn 2288-0224 Treatment of Melasma Using a Novel 1,927 nm Fractional Thulium Laser: A Retrospective
Title: Dermographic, clinical and histopathological pro le of cutaneous lichen planus
 Original Research Paper Dermatology Title: Dermographic, clinical and histopathological pro le of cutaneous lichen planus Dr. Rikeeta S. Deshmukh Dr. Raju G. Chaudhary ABSTRACT KEYWORDS Introduction: Unique,
Original Research Paper Dermatology Title: Dermographic, clinical and histopathological pro le of cutaneous lichen planus Dr. Rikeeta S. Deshmukh Dr. Raju G. Chaudhary ABSTRACT KEYWORDS Introduction: Unique,
BRAND SPECIALISING IN THE TREATMENT OF DARK SPOTS
 2 Offers dermatologists, practitioners and beauty professionals a wide range of depigmentation products, providing treatments uniquely formulated according to the type of hyperpigmentation, skin type and
2 Offers dermatologists, practitioners and beauty professionals a wide range of depigmentation products, providing treatments uniquely formulated according to the type of hyperpigmentation, skin type and
Evaluation of the wound healing response post - deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRACEL
 12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post - deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRACEL Un-Cheol.Yeo, MD S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post - deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRACEL Un-Cheol.Yeo, MD S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
A CLINICAL STUDY OF MICRODERMABRASION WITH VITAMIN C SERUM FOR FACIAL MELANOSES AND REJUVENATION Sanjana A. S 1, S. Sacchidanand 2
 A CLINICAL STUDY OF MICRODERMABRASION WITH VITAMIN C SERUM FOR FACIAL MELANOSES AND REJUVENATION Sanjana A. S 1, S. Sacchidanand 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sanjana A. S, S. Sacchidanand. A Clinical Study
A CLINICAL STUDY OF MICRODERMABRASION WITH VITAMIN C SERUM FOR FACIAL MELANOSES AND REJUVENATION Sanjana A. S 1, S. Sacchidanand 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sanjana A. S, S. Sacchidanand. A Clinical Study
นพ.วาสนภ วช รมน หน วยโรคผ วหน ง คณะแพทยศาสตร โรงพยาบาลรามาธ บด
 Vitiligo Vitiligo Update Acquired pigmentary disorder Depigmented macules and patches นพ.วาสนภ วช รมน หน วยโรคผ วหน ง คณะแพทยศาสตร โรงพยาบาลรามาธ บด Prevalence The prevalence of vitiligo is often said
Vitiligo Vitiligo Update Acquired pigmentary disorder Depigmented macules and patches นพ.วาสนภ วช รมน หน วยโรคผ วหน ง คณะแพทยศาสตร โรงพยาบาลรามาธ บด Prevalence The prevalence of vitiligo is often said
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 05 Page May 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i5.82 Research Paper To Study the Therapeutic
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i5.82 Research Paper To Study the Therapeutic
Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point Using the Cricoid Cartilage as Landmark Through X-ray Review
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2011 September; Vol. 24, No. 3: 141-145 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.141 Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point
Original Article Korean J Pain 2011 September; Vol. 24, No. 3: 141-145 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.141 Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Advances in Lasers for Skin of Color
 Review Advances in Lasers for Skin of Color Heather Woolery-Lloyd, MD; Mohamed L. Elsaie, MD, MBA The popularity of cutaneous laser surgery has soared; however, the use of lasers in patients with skin
Review Advances in Lasers for Skin of Color Heather Woolery-Lloyd, MD; Mohamed L. Elsaie, MD, MBA The popularity of cutaneous laser surgery has soared; however, the use of lasers in patients with skin
Abrupt Intralesional Color Change on Dermoscopy as a New Indicator of Early Superficial Spreading Melanoma in a Japanese Woman
 Published online: June 24, 2015 1662 6567/15/0072 0123$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Published online: June 24, 2015 1662 6567/15/0072 0123$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Study the Effect of Illumination Time Parameter of Diode Laser on Wound Healing Process
 The 1 st Regional Conference of Eng. Sci. NUCEJ Spatial ISSUE vol.11, No.2, 2008 pp 536-543 Study the Effect of Illumination Time Parameter of Diode Laser on Wound Healing Process Assist. Prof. Dr. Munqith
The 1 st Regional Conference of Eng. Sci. NUCEJ Spatial ISSUE vol.11, No.2, 2008 pp 536-543 Study the Effect of Illumination Time Parameter of Diode Laser on Wound Healing Process Assist. Prof. Dr. Munqith
Mottled Hypopigmentation from Laser Toning in the Treatment of Melasma: A Catastrophic or Manageable Complication?
 Med Laser 2015;4(2):45-50 pissn 2287-8300 ㆍ eissn 2288-0224 Mottled Hypopigmentation from Laser Toning in the Treatment of Melasma: A Catastrophic or Manageable Complication? Young Woon Park 1 Un Cheol
Med Laser 2015;4(2):45-50 pissn 2287-8300 ㆍ eissn 2288-0224 Mottled Hypopigmentation from Laser Toning in the Treatment of Melasma: A Catastrophic or Manageable Complication? Young Woon Park 1 Un Cheol
