Keywords Cholecystokinin. Enteroendocrine cells.
|
|
|
- Brandon Owen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diabetologia (215) 58: DOI 1.17/s SHORT COMMUNICATION Effect of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on the distribution and hormone expression of small-intestinal enteroendocrine cells in obese patients with type 2 diabetes Nicolai A. Rhee 1,2,3 & Camilla D. Wahlgren 1 & Jens Pedersen 2 & Brynjulf Mortensen 1 & Ebbe Langholz 4 & Erik P. Wandall 4 & Steffen U. Friis 4 & Peter Vilmann 4,5 & Sarah J. Paulsen 6 & Viggo B. Kristiansen 7 & Jacob Jelsing 6 & Louise S. Dalbøge 6 & Steen S. Poulsen 2 & Jens J. Holst 2 & Tina Vilsbøll 1 & Filip K. Knop 1,2 Received: 18 May 215 /Accepted: 19 June 215 /Published online: 18 July 215 # Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 215 Abstract Aims/hypothesis We studied the impact of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) on the density and hormonal gene expression of small-intestinal enteroendocrine cells in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Methods Twelve patients with diabetes and 11 age- and BMImatched controls underwent RYGB followed by enteroscopy ~1 months later. Mucosal biopsies taken during surgery and enteroscopy were immunohistochemically stained for glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), peptide YY (PYY), cholecystokinin (CCK), glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and prohormone convertase 2 (PC2) and the Electronic supplementary material The online version of this article (doi:1.17/s ) contains peer-reviewed but unedited supplementary material, which is available to authorised users. * Filip K. Knop filipknop@dadlnet.dk Center for Diabetes Research, Gentofte Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Kildegårdsvej 28, DK-29 Hellerup, Denmark NNF Center for Basic Metabolic Research and Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark Present address: Novo Nordisk Scandinavia AB, Copenhagen, Denmark Unit of Enteroscopy, Department of Medicine, Gentofte Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Hellerup, Denmark Present address: Gastro Unit D, Herlev Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Herlev, Denmark Gubra Aps, Hørsholm, Denmark Gastro Unit, Hvidovre Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Hvidovre, Denmark expression of GCG (encoding preproglucagon), PYY, CCK, GIP, GHRL (encoding ghrelin), SCT (encoding secretin), NTS (encoding neurotensin) and NR1H4 (encoding farnesoid X receptor) was evaluated. Results The density of cells immunoreactive for GLP-1, CCK and GIP increased in patients after RYGB and the density of those immunoreactive for GLP-1, PYY, CCK and PC2 increased in controls. In both groups, GHRL, SCT and GIP mrna was reduced after RYGB while PYY, CCK, NTS and NR1H4 gene expression was unaltered. GCG mrna was upregulated in both groups. Conclusions/interpretation Numerous alterations in the distribution of enteroendocrine cells and their expression of hormonal genes are seen after RYGB and include increased density of GLP-1-, PYY-, CCK-, GIP- and PC2-positive cells, reduced gene expression of GHRL, SCT and GIP and increased expression of GCG. Keywords Cholecystokinin. Enteroendocrine cells. Ghrelin. Glucagon-like peptide-1. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide. Immunohistochemistry. Obesity. Peptide YY. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Type 2 diabetes Abbreviations CCK Cholecystokinin GIP Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide GLP-1 Glucagon-like peptide-1 PC2 Prohormone convertase 2 PYY Peptide YY qpcr Quantitative PCR RYGB Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
2 Diabetologia (215) 58: Introduction Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is a widely used weightreducing surgical procedure [1] that also improves glucose regulation in individuals with impaired glucose homeostasis within days after the procedure [2]. These improvements are thought, at least in part, to be the result of RYGB-induced rerouting of nutrients, which in turn is thought to alter the secretion of several gut-derived hormones. Little is known about the effect of RYGB on the distribution of guthormone-producing cells, and the postoperative expression of their hormonal products remains unexplored in humans. In this study, we evaluated the changes in density and gene expression of several enteroendocrine cells after RYGB in obese participants with and without type 2 diabetes. Methods Participants Anthropometric data is shown in electronic supplementary material (ESM) Table 1. Twelve obese participants with type 2 diabetes and 11 age- and BMI-matched normoglycaemic participants referred to elective RYGB participated in the study. All gave informed consent and the study was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The participants with type 2 diabetes had been diagnosed with diabetes for 7.±1.6 (mean±sem) years and were all on oral glucose-lowering agents and/or insulin at the time of inclusion. Experimental procedures On experimental day 1, all participants underwent RYGB using standard laparoscopic RYGB technique as previously described [3]. During the RYGB procedure, a 1 cm segment was excised from the jejunal division site (proximal end) and designated area A. Some mucosal biopsies were placed in RNAlater (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) while others were placed in 4% formaldehyde,. On experimental day 2 ( 4 months after RYGB) after 8 h of fasting, an upper enteroscopy was performed in sedated participants using a colonoscope (PCF-Q18AL; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Nine mucosal biopsies were taken from each of three different anatomical locations (the alimentary limb, the common limb and the biliopancreatic limb), designated areas B, C and D, respectively. The biopsies were placed directly in RNAlater and 4% formaldehyde, respectively. Immunohistochemical staining, cell quantification and estimation of cell length The number of all immunopositive enteroendocrine cells was counted, providing an estimate of enteroendocrine cell density (i.e. number of cells per mucosal area). For a detailed description of immunohistochemical staining, cell quantification and estimation of cell length, see ESM Methods. RNA purification, cdna synthesis and quantitative PCR analysis For details of RNA purification, cdna synthesis and quantitative PCR (qpcr) analysis, see ESM Methods. For a summary of primers used in qpcr, see ESM Table 1. Statistical analyses Main effects of group, RYGB surgery and post-surgery biopsy site were investigated using a multifactorial ANOVA test performed in SAS version 9.1 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) with the mentioned factors included as independent variables. When significant main effects were observed in the ANOVA model, data were investigated further using post hoc Student s t tests. Statistical significance was accepted at p<.5. Immunohistochemical cell quantification data are presented as mean±sem and qpcr data are presented as log 1 -transformed mean±sem. Results The mean time (± SEM) between RYGB and enteroscopy was 1.4±.8 months. BMI on day 1 was 4.1±1.4 kg/m 2 and 39.±1.3 kg/m 2 in controls and type 2 diabetes patients, respectively (p=.465) and weight loss on day 2 was 29.4± 1.4 kg and 27.±3.7 kg, respectively (p=31). Changes in demographic and biochemical variables are displayed in ESM Table 2. Results from multi-factorial ANOVA are displayed in Table 1. Specific results are commented on below but generally there was an effect of RYGB and very few effects between groups and sites. Glucagon-like peptide-1 and the gene encoding preproglucagon We observed significantly higher expression levels of GCG (encoding preproglucagon) and density of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) immunoreactive cells after RYGB surgery. Post hoc t tests showed these effects to be present in both groups (Fig. 1a, b). Peptide YY The ANOVA model showed that although RYGB had no effect on the expression of PYY there was a significantly higher number of peptide YY (PYY)-positive cells after RYGB. A significant postoperative increase in the density of PYY-positive cells in the alimentary and biliopancreatic limbs was shown by t tests, but these differences were only observed in the control group (Fig. 1c, d). Cholecystokinin We saw no effects of surgery on CCK expression but there was a significantly higher cholecystokinin (CCK)-positive cell count after RYGB. Post hoc t tests showed that this effect was present in both groups (Fig. 1e, f).
3 2256 Diabetologia (215) 58: Table 1 Multi-factorial ANOVA Gene/protein Group (T2D vs CTRL) Effect of RYGB Site (B vs C vs D) GCG mrna GLP-1 Cell density.891 < PYY mrna PYY Cell density CCK mrna CCK Cell density.1297 < GIP mrna 158 < GIP Cell density GHRL mrna.1533 <.1.12 SCT mrna.6193 <.1.4 NTS mrna PC2 Cell density NR1H4 mrna Multi-factorial ANOVA with main effect of group (Group [T2D vs CTRL]), RYGB surgery (Effect of RYGB) and post-surgery biopsy site (Site [B vs C vs D]) on the expression (mrna) of GCG encoding GLP-1, PYY encoding PYY, CCK encoding CCK, GIP encoding GIP, GHRL encoding ghrelin, SCT encoding secretin, NTS encoding neurotensin and NR1H4 encoding the farnesoid X-receptor, and density of cells immunohistochemically positive for GLP-1, PYY, CCK, GIP and PC2. T2D, type 2 diabetes group; CTRL, control group; A, peri-operative area; B, alimentary limb (post-operative); C, common limb (post-operative); D, biliopancreatic limb (post-operative) Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide We observed significantly lower GIP mrna levels after RYGB, but the post-surgery density of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP)-positive cells was significantly higher. Post hoc t tests showed significant downregulation of GIP mrna in all post-surgery biopsy sites in both groups but upregulation of GIP-positive cells for sites B (both groups) and C (type 2 diabetes) post surgery (Fig. 1g, h). Ghrelin We observed significantly lower levels of GHRL mrna after RYGB. The t tests also showed significantly lower levels of GHRL mrna expression in post-surgery sites in both groups. Within post-surgery sites, we observed lower expression in the biliopancreatic limb vs the alimentary limb, but in the control group only (ESM Fig. 1). Farnesoid X receptor The ANOVA model revealed significantly higher levels of NR1H4 (encoding the farnesoid X receptor) expression in the type 2 diabetes group. Post hoc t tests showed significantly higher levels of NR1H4 expression in the type 2 diabetes group vs controls in the peri-operative sample and in the alimentary limb (ESM Fig. 1). Prohormone convertase 2 The ANOVA analyses showed significantly higher prohormone convertase 2 (PC2)-positive cell counts after RYGB as well as significant differences between post-surgery biopsy sites. Post hoc tests showed significantly higher cell counts in post-surgery sites in both groups. Within post-surgery sites, we observed lower cell counts in the common and biliopancreatic limb vs the alimentary limb, but only in the type 2 diabetes group (ESM Fig. 2). Secretin The ANOVA model showed significantly lower levels of SCT mrna after RYGB and post hoc t tests showed significant between site differences. (ESM Fig. 1). There was a significant downregulation in all areas after RYGB in both groups except for alimentary limb in the control group. Between groups there was a significant downregulation in the biliopancreatic limb vs the alimentary limb (control group) and a significant downregulation in the common vs alimentary limb (ESM Fig. 1b). Neurotensin We observed no significant effects on NTS mrna (ESM Fig. 1). Discussion Here we provide information on the distribution and transcriptional activity of a number of enteroendocrine cells in the mucosa of the small intestine before and after RYGB in both obese patients with type 2 diabetes and normoglycaemic controls. Main findings include increased density of CCK-, GIP-, GLP-1-, PYY- and PC2-positive cells, reduced gene expression of GHRL, SCT and GIP and increased expression of GCG. This study is the first to compare human mucosal biopsies taken from the small intestine during RYGB surgery with
4 Diabetologia (215) 58: Fig. 1 Gene expression levels of GCG, PYY, CCK and GIP and cell counts of GLP-1-, PYY-, CCKand GIP-positive cells. Log 1 - transformed gene expression levels in arbitrary units (AU) normalised to the housekeeping gene RSP18 are shown for GCG (a), PYY (c), CCK (e)andgip (g). Cell counts after immunohistochemical staining for GLP-1- (b), PYY- (d), CCK- (f) and GIP-positive cells (h) are also shown. White boxes, nondiabetic participants; grey boxes, patients with type 2 diabetes. Boxes represent the range of first, second and third quartiles; horizontal bars show median values and whiskers show minimum and maximum values. Letters shown on the x-axis represent the following regions: A, peri-operative area; B, alimentary limb (post-operative); C, common limb (post-operative); D, biliopancreatic limb (postoperative). *p<.5, **p<.1, ***p<.1 for A (perioperative) vs region B; p<.5, p<.1, p<.1 for Avs region C; p<.5, p<.1, p<.1 for A vs region D a GCG mrna (AU) c PYY mrna (AU) e CCK mrna (AU) * **,, GLP-1 + cells (n/mm 2 ) PYY + cells (n/mm 2 ) b d f CCK + cells (n/mm 2 ) ***, **, **, **, **, g GIP mrna (AU) ***, h GIP + cells (n/mm 2 ) ** **, endoscopically retrieved mucosal biopsies from the same individuals postoperatively. Of note, only areas B and D serve as proxy for area A after RYGB as they are very close (<8 cm) to the area that was designated A before RYGB. The use of enteroscopy allowed us to immediately preserve biopsies in suitable media, thereby stopping all biological breakdown and enzymatic processes and ensuring high-quality immunohistochemical analyses and minimal decay of mrna. The unaltered level of CCK mrna is in line with some previous findings [4] but is in contrast to the demonstration of increased CCK plasma levels after RYGB [5, 6]. However, these studies sampled plasma CCK levels in the postprandial state (or after OGTT) and in the present study biopsies were collected in the fasting state. GLP-1-immunoreactive cell density was increased, coupled with a corresponding increase in GCG expression. This increase in the density of GLP-1-producing cells in the common limb could be linked to an increased flow of nutrients and bile, since both bile [7], fatty acids, carbohydrates [8] and oligopeptides [9] are known secretagogues of GLP-1 and, thus, are potential stimulators of GCG expression. Similarly, our findings are consistent with the increased postprandial plasma levels of GLP-1 found after RYGB [1 13].
5 2258 Diabetologia (215) 58: PYY was the only hormone where the change in immunoreactivity was different between the two groups. The attenuated increase in the density of PYY-positive cells in the type 2 diabetes group could be a sign of a generally diminished L cell response in patients with type 2 diabetes, since PYYand GLP- 1 are to some extent co-localised in the L cell [14], although GLP-1 density was increased in the type 2 diabetes group as well. The somewhat disparate findings for PYY and GLP-1 may reflect the recent identification of (at least) two populations of L cells proximal cells with little PYYexpression and distal cells with more PYY expression [15, 16] but nevertheless identical rates of GLP-1 secretion. In conclusion, this study is the first to describe the anatomical and transcriptional changes in enteroendocrine cells of the mucosa seen after RYGB in humans. The observed changes may play a role in the improved glycaemic and metabolic status experienced by most participants undergoing RYGB. Thus, the significant alterations in enteroendocrine cell distribution and expression of specific genes described in this study may help to understand some of the mechanisms behind the well-documented changes in plasma gut hormone levels after RYGB. Acknowledgements We are grateful to our volunteers whose availability made this work possible. We especially thank L. S. Strange and H. Paulsen at the Panum Institute for performing the immunostaining as well as nurse D. G. Jørgensen from Hvidovre Hospital who assisted in contacting the volunteers. We would also like to thank Bariatric Group Hvidovre (S. Madsbad, D. Worm and D. L. Hansen) at Hvidovre Hospital for management of RYGB patients, the nurses at Gentofte Hospital for their work during enteroscopies and securing biopsy material and L. H. Jørgensen at Gubra Aps for assisting with the gene expression analyses. Funding This study was supported by unrestricted grants from the Novo Nordisk Foundation and the Danish National Advanced Technology Foundation. Duality of interest The authors declare that there is no duality of interest associated with this manuscript. Contribution statement NAR contributed to the study design, acquired, analysed and interpreted the data and drafted the manuscript. CDW, JP, BM, SJP, LSD and SSP analysed and interpreted data and revised the manuscript. EL, EPW, SUF and PV contributed to data acquisition and revised the manuscript. VBK contributed to the study design, acquired data and revised the manuscript. JJ interpreted data and revised the manuscript. JJH and TV contributed to study design, data interpretation and revised the manuscript. FKK conceived and designed the study, interpreted data and revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript. FKK is the guarantor of the present work. References 1. Chang S-H, Stoll CRT, Song J, Varela JE, Eagon CJ, Colditz GA (213) The effectiveness and risks of bariatric surgery: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis, JAMA Surg 149: Dirksen C, Jørgensen NB, Bojsen-Møller KN et al (212) Mechanisms of improved glycaemic control after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Diabetologia 7: Carlos do Rego Furtado L (21) Procedure and outcomes of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Br J Nurs 5: Rubino F, Gagner M, Gentileschi P et al (24) The early effect of the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on hormones involved in body weight regulation and glucose metabolism. Ann Surg 2: Dirksen C, Damgaard M, Bojsen-Møller KN et al (213) Fast pouch emptying, delayed small intestinal transit, and exaggerated gut hormone responses after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Neurogastroenterol Motil 4:346 e Jacobsen SH, Olesen SC, Dirksen C et al (212) Changes in gastrointestinal hormone responses, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell function within 2 weeks after gastric bypass in non-diabetic subjects. Obes Surg 7: Parker HE, Wallis K, le Roux CW, Wong KY, Reimann F, Gribble FM (212) Molecular mechanisms underlying bile acid-stimulated glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion. Br J Pharmacol 2: Herrmann C, Göke R, Richter G, Fehmann HC, Arnold R, Göke B (1995) Glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulin-releasing polypeptide plasma levels in response to nutrients. Digestion 2: Diakogiannaki E, Pais R, Tolhurst G et al (213) Oligopeptides stimulate glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in mice through proton-coupled uptake and the calcium-sensing receptor. Diabetologia 12: Korner J, Inabnet W, Febres G et al (29) Prospective study of gut hormone and metabolic changes after adjustable gastric banding and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Int J Obes (Lond) 7: Laferrère B, Heshka S, Wang K et al (27) Incretin levels and effect are markedly enhanced 1 month after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 7: Le Roux CW, Aylwin SJB, Batterham RL et al (26) Gut hormone profiles following bariatric surgery favor an anorectic state, facilitate weight loss, and improve metabolic parameters. Ann Surg 1: Peterli R, Steinert RE, Woelnerhanssen B et al (212) Metabolic and hormonal changes after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy: a randomized, prospective trial. Obes Surg 5: Böttcher G, Sjölund K, Ekblad E, Håkanson R, Schwartz TW, Sundler F (1984) Coexistence of peptide YY and glicentin immunoreactivity in endocrine cells of the gut. Regul Pept 4: Habib AM, Richards P, Cairns LS et al (212) Overlap of endocrine hormone expression in the mouse intestine revealed by transcriptional profiling and flow cytometry. Endocrinology 7: Svendsen B, Pedersen J, Albrechtsen NJW et al (215) An analysis of co-secretion and co-expression of gut hormones from male rat proximal and distal small intestine. Endocrinology 3:
Enteroendocrine K and L cells in healthy and type 2 diabetic individuals
 Diabetologia (21) 1:2 2 DOI 1.1/s12-1-- ARTICLE Enteroendocrine K and L cells in healthy and type 2 diabetic individuals Tina Jorsal 1 & Nicolai A. Rhee 1,2 & Jens Pedersen, & Camilla D. Wahlgren 1 & Brynjulf
Diabetologia (21) 1:2 2 DOI 1.1/s12-1-- ARTICLE Enteroendocrine K and L cells in healthy and type 2 diabetic individuals Tina Jorsal 1 & Nicolai A. Rhee 1,2 & Jens Pedersen, & Camilla D. Wahlgren 1 & Brynjulf
Gastric Emptying Time after Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 4, Issue 7-2018 Gastric Emptying Time
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 4, Issue 7-2018 Gastric Emptying Time
Appetite, Glycemia and Entero-Insular Hormone Responses Differ Between Oral, Gastric-Remnant and Duodenal Administration of a Mixed Meal Test After
 Appetite, Glycemia and Entero-Insular Hormone Responses Differ Between Oral, Gastric-Remnant and Duodenal Administration of a Mixed Meal Test After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass June 2018 How a surgical complication
Appetite, Glycemia and Entero-Insular Hormone Responses Differ Between Oral, Gastric-Remnant and Duodenal Administration of a Mixed Meal Test After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass June 2018 How a surgical complication
Gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y reconstruction as a lean model of bariatric surgery
 Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases ] (2018) 00 00 Original article Gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y reconstruction as a lean model of bariatric surgery Geoffrey P. Roberts, M.A. (Cantab), B.M., B.Ch.,
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases ] (2018) 00 00 Original article Gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y reconstruction as a lean model of bariatric surgery Geoffrey P. Roberts, M.A. (Cantab), B.M., B.Ch.,
Bariatric Surgery MM /11/2001. HMO; PPO; QUEST 05/01/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Outpatient; Inpatient
 Bariatric Surgery Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.003 09/11/2001 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 05/01/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Outpatient;
Bariatric Surgery Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.003 09/11/2001 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 05/01/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Outpatient;
Roux-and-Y Gastric Bypass and its Metabolic Effects
 Roux-and-Y Gastric Bypass and its Metabolic Effects Nicola Di Lorenzo President elect of SICOb Italian Society for Bariatric Surgery and Metabolic Diseases Dept. of General Surgery-Università di Roma Tor
Roux-and-Y Gastric Bypass and its Metabolic Effects Nicola Di Lorenzo President elect of SICOb Italian Society for Bariatric Surgery and Metabolic Diseases Dept. of General Surgery-Università di Roma Tor
Intestinal Hypertrophy and Increased Glucose Transporter Expression after Gastric Bypass. Senior Thesis. Presented to
 Intestinal Hypertrophy and Increased Glucose Transporter Expression after Gastric Bypass Senior Thesis Presented to The Faculty of the School of Arts and Sciences Brandeis University Undergraduate Program
Intestinal Hypertrophy and Increased Glucose Transporter Expression after Gastric Bypass Senior Thesis Presented to The Faculty of the School of Arts and Sciences Brandeis University Undergraduate Program
New Insights into Mechanism of Action
 Remission of Diabetes after Bariatric Surgery New Insights into Mechanism of Action Peng (Charles) Zhang, MD, PhD Shanghai Pudong Hospital Fudan University Pudong Medical Center March 20, 2015 Orlando,
Remission of Diabetes after Bariatric Surgery New Insights into Mechanism of Action Peng (Charles) Zhang, MD, PhD Shanghai Pudong Hospital Fudan University Pudong Medical Center March 20, 2015 Orlando,
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online November 16, 2009
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online November 16, 2009 Improved Glucose Tolerance After Gastric Bypass Postprandial diabetic glucose tolerance is normalized by gastric bypass feeding
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online November 16, 2009 Improved Glucose Tolerance After Gastric Bypass Postprandial diabetic glucose tolerance is normalized by gastric bypass feeding
Megan Lawless. Journal Club. January 20 th, 2011
 Megan Lawless Journal Club January 20 th, 2011 Gut-expressed gustducin and taste receptors regulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences September 2007 Abstract
Megan Lawless Journal Club January 20 th, 2011 Gut-expressed gustducin and taste receptors regulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences September 2007 Abstract
Hyperglucagonaemia analysed by glucagon sandwich ELISA: nonspecific interference or truly elevated levels?
 Diabetologia (2014) 57:1919 1926 DOI 10.1007/s00125-014-3283-z ARTICLE Hyperglucagonaemia analysed by glucagon sandwich ELISA: nonspecific interference or truly elevated levels? Nicolai J. Wewer Albrechtsen
Diabetologia (2014) 57:1919 1926 DOI 10.1007/s00125-014-3283-z ARTICLE Hyperglucagonaemia analysed by glucagon sandwich ELISA: nonspecific interference or truly elevated levels? Nicolai J. Wewer Albrechtsen
Postprandial Nutrient Handling and Gastrointestinal Hormone Secretion After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass vs Sleeve Gastrectomy
 Gastroenterology 2019;-:1 15 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 Q1
Gastroenterology 2019;-:1 15 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 Q1
CME Post Test. D. Treatment with insulin E. Age older than 55 years
 CME Post Test Translational Endocrinology & Metabolism: Metabolic Surgery Update Please select the best answer to each question on the online answer sheet. Go to http://www.endojournals.org/translational/
CME Post Test Translational Endocrinology & Metabolism: Metabolic Surgery Update Please select the best answer to each question on the online answer sheet. Go to http://www.endojournals.org/translational/
type 2 diabetes is a surgical disease
 M. Lannoo, MD, University Hospitals Leuven Walter Pories claimed in 1992 type 2 diabetes is a surgical disease Buchwald et al. conducted a large meta-analysis THE FIRST OBSERVATIONS W. Pories 500 patients
M. Lannoo, MD, University Hospitals Leuven Walter Pories claimed in 1992 type 2 diabetes is a surgical disease Buchwald et al. conducted a large meta-analysis THE FIRST OBSERVATIONS W. Pories 500 patients
Commonly Performed Bariatric Procedures in Singapore. Lin Jinlin Associate Consultant General, Upper GI and Bariatric Surgery Changi General Hospital
 Commonly Performed Bariatric Procedures in Singapore Lin Jinlin Associate Consultant General, Upper GI and Bariatric Surgery Changi General Hospital Scope 1. Introduction 2. Principles of bariatric surgery
Commonly Performed Bariatric Procedures in Singapore Lin Jinlin Associate Consultant General, Upper GI and Bariatric Surgery Changi General Hospital Scope 1. Introduction 2. Principles of bariatric surgery
An integrated glucose homeostasis model of glucose, insulin, C-peptide, GLP-1, GIP and glucagon in healthy subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes
 An integrated glucose homeostasis model of glucose, insulin, C-peptide, GLP-1, GIP and glucagon in healthy subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes Oskar Alskär, Jonatan Bagger, Rikke Røge, Kanji Komatsu,
An integrated glucose homeostasis model of glucose, insulin, C-peptide, GLP-1, GIP and glucagon in healthy subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes Oskar Alskär, Jonatan Bagger, Rikke Røge, Kanji Komatsu,
Bariatric Procedures and Mechanisms of Weight Loss. September 22 nd, 2018 Aryan Modasi MD MSc FRCSC
 Bariatric Procedures and Mechanisms of Weight Loss September 22 nd, 2018 Aryan Modasi MD MSc FRCSC Disclosures Nothing to Disclose Traditional View Restriction vs Malabsorption Traditional View Adjustable
Bariatric Procedures and Mechanisms of Weight Loss September 22 nd, 2018 Aryan Modasi MD MSc FRCSC Disclosures Nothing to Disclose Traditional View Restriction vs Malabsorption Traditional View Adjustable
Technique. Matthew Bettendorf, MD Essentia Health Duluth Clinic. Laparoscopic approach One 12mm port, Four 5mm ports
 Matthew Bettendorf, MD Essentia Health Duluth Clinic Technique Laparoscopic approach One 12mm port, Four 5mm ports Single staple line with no anastamosis 85% gastrectomy Goal to remove
Matthew Bettendorf, MD Essentia Health Duluth Clinic Technique Laparoscopic approach One 12mm port, Four 5mm ports Single staple line with no anastamosis 85% gastrectomy Goal to remove
Secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analyses of clinical studies
 Diabetologia (2013) 56:965 972 DOI 10.1007/s00125-013-2841-0 SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analyses of clinical
Diabetologia (2013) 56:965 972 DOI 10.1007/s00125-013-2841-0 SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analyses of clinical
BARIATRIC SURGERY AND TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
 BARIATRIC SURGERY AND TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS George Vl Valsamakis European Scope Fellow Obesity Visiting iti Associate Prof Warwick Medical School Diabetes is an increasing healthcare epidemic throughout
BARIATRIC SURGERY AND TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS George Vl Valsamakis European Scope Fellow Obesity Visiting iti Associate Prof Warwick Medical School Diabetes is an increasing healthcare epidemic throughout
Current Status of Bariatric Surgery in Asia
 Emerald hall A, 1:2-1:5, November 7, 213 Current Status of Bariatric Surgery in Asia Go Wakabayashi, MD, PhD, FACS Professor and Chairman Department of Surgery Iwate Medical University Numbers of bariatric
Emerald hall A, 1:2-1:5, November 7, 213 Current Status of Bariatric Surgery in Asia Go Wakabayashi, MD, PhD, FACS Professor and Chairman Department of Surgery Iwate Medical University Numbers of bariatric
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Diabetologia. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 February 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Diabetologia. 2013 February ; 56(2): 231 233. doi:10.1007/s00125-012-2788-6. Lipotoxicity impairs incretin signalling V. Poitout 1,2
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Diabetologia. 2013 February ; 56(2): 231 233. doi:10.1007/s00125-012-2788-6. Lipotoxicity impairs incretin signalling V. Poitout 1,2
Introduction ARTICLE. and 3.4%, respectively. In both the medium- and majorweight-reduction
 Diabetologia (2015) 58:1448 1453 DOI 10.1007/s00125-015-3591-y ARTICLE Incidence and remission of type 2 diabetes in relation to degree of obesity at baseline and 2 year weight change: the Swedish Obese
Diabetologia (2015) 58:1448 1453 DOI 10.1007/s00125-015-3591-y ARTICLE Incidence and remission of type 2 diabetes in relation to degree of obesity at baseline and 2 year weight change: the Swedish Obese
Effect of macronutrients and mixed meals on incretin hormone secretion and islet cell function
 Effect of macronutrients and mixed meals on incretin hormone secretion and islet cell function Background. Following meal ingestion, several hormones are released from the gastrointestinal tract. Some
Effect of macronutrients and mixed meals on incretin hormone secretion and islet cell function Background. Following meal ingestion, several hormones are released from the gastrointestinal tract. Some
Incretin Effect and Glucagon Responses to Oral and Intravenous Glucose in Patients With Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young Type 2 and Type 3
 2838 Diabetes Volume 63, August 2014 Signe H. Østoft, 1,2,3 Jonatan I. Bagger, 1,2,3 Torben Hansen, 3,4 Oluf Pedersen, 3 Jens J. Holst, 2,3 Filip K. Knop, 1,2,3 and Tina Vilsbøll 1 Incretin Effect and
2838 Diabetes Volume 63, August 2014 Signe H. Østoft, 1,2,3 Jonatan I. Bagger, 1,2,3 Torben Hansen, 3,4 Oluf Pedersen, 3 Jens J. Holst, 2,3 Filip K. Knop, 1,2,3 and Tina Vilsbøll 1 Incretin Effect and
Understanding the Effects of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) Surgery on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Chapter 19 Understanding the Effects of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) Surgery on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Raymond G. Lau, Michael Radin, Collin E. Brathwaite and Louis Ragolia Additional information
Chapter 19 Understanding the Effects of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) Surgery on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Raymond G. Lau, Michael Radin, Collin E. Brathwaite and Louis Ragolia Additional information
Type 2 diabetes and metabolic surgery:
 Type 2 diabetes and metabolic surgery: Shouldn't we call it again again bariatric? Josep Vidal Obesity Unit. Endocrinology and Nutrition Department Hospital Clínic, University of Barcelona (Spain) What
Type 2 diabetes and metabolic surgery: Shouldn't we call it again again bariatric? Josep Vidal Obesity Unit. Endocrinology and Nutrition Department Hospital Clínic, University of Barcelona (Spain) What
Gastrointestinal Hormones and Bariatric Surgery-induced Weight Loss
 Gastrointestinal Hormones and Bariatric Surgery-induced Weight Loss Viorica Ionut 1, Miguel Burch 2, Adrienne Youdim 3 and Richard N. Bergman 1 continues to be a major public health problem in the United
Gastrointestinal Hormones and Bariatric Surgery-induced Weight Loss Viorica Ionut 1, Miguel Burch 2, Adrienne Youdim 3 and Richard N. Bergman 1 continues to be a major public health problem in the United
What is Metabolic About Metabolic Surgery? The New ADA Recommendations
 What is Metabolic About Metabolic Surgery? The New ADA Recommendations Obesity Symposium September 16, 2017 Timothy Howland, MD Lourdes Endocrinology Bariatric from the Greek root bar- ("weight" as in
What is Metabolic About Metabolic Surgery? The New ADA Recommendations Obesity Symposium September 16, 2017 Timothy Howland, MD Lourdes Endocrinology Bariatric from the Greek root bar- ("weight" as in
SHORT COMMUNICATION. J. C. Reubi & A. Perren & R. Rehmann & B. Waser & E. Christ & M. Callery & A. B. Goldfine & M. E. Patti
 Diabetologia (2010) 53:2641 2645 DOI 10.1007/s00125-010-1901-y SHORT COMMUNICATION Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors are not overexpressed in pancreatic islets from patients with severe hyperinsulinaemic
Diabetologia (2010) 53:2641 2645 DOI 10.1007/s00125-010-1901-y SHORT COMMUNICATION Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors are not overexpressed in pancreatic islets from patients with severe hyperinsulinaemic
Comparison Between Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy and Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding for Morbid Obesity: a Meta-analysis
 OBES SURG (2013) 23:980 986 DOI 10.1007/s11695-013-0893-3 REVIEW Comparison Between Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy and Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding for Morbid Obesity: a Meta-analysis Sen Wang
OBES SURG (2013) 23:980 986 DOI 10.1007/s11695-013-0893-3 REVIEW Comparison Between Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy and Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding for Morbid Obesity: a Meta-analysis Sen Wang
Metabolic and Hormonal Changes After Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy: a Randomized, Prospective Trial
 OBES SURG (2012) 22:740 748 DOI 10.1007/s11695-012-0622-3 CLINICAL RESEARCH Metabolic and Hormonal Changes After Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy: a Randomized, Prospective
OBES SURG (2012) 22:740 748 DOI 10.1007/s11695-012-0622-3 CLINICAL RESEARCH Metabolic and Hormonal Changes After Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy: a Randomized, Prospective
OBESITY STUDIES RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS
 3104 Diabetes Volume 64, September 2015 Kim T. Nguyen, 1 Charles J. Billington, 2 Adrian Vella, 3 Qi Wang, 4 Leaque Ahmed, 5 John P. Bantle, 2 Marc Bessler, 5 John E. Connett, 4 William B. Inabnet, 6 Avis
3104 Diabetes Volume 64, September 2015 Kim T. Nguyen, 1 Charles J. Billington, 2 Adrian Vella, 3 Qi Wang, 4 Leaque Ahmed, 5 John P. Bantle, 2 Marc Bessler, 5 John E. Connett, 4 William B. Inabnet, 6 Avis
Serum lipase activity and concentration during intravenous infusions of GLP-1 and PYY 3-36 and after ad libitum meal ingestion in overweight men
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Physiological Reports ISSN 2051-817X Serum lipase activity and concentration during intravenous infusions of GLP-1 and PYY 3-36 and after ad libitum meal ingestion in overweight men Julie
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Physiological Reports ISSN 2051-817X Serum lipase activity and concentration during intravenous infusions of GLP-1 and PYY 3-36 and after ad libitum meal ingestion in overweight men Julie
Bariatric surgery: has anything changed in the last few years?
 Bariatric surgery: has anything changed in the last few years? Mauro Toppino University of Turin Digestive and Colorectal Surgery Minimal Invasive Surgery Center (Head:Prof. Mario Morino) XIV Annual Conference
Bariatric surgery: has anything changed in the last few years? Mauro Toppino University of Turin Digestive and Colorectal Surgery Minimal Invasive Surgery Center (Head:Prof. Mario Morino) XIV Annual Conference
A Bariatric Patient in my Waiting Room: Choosing the Right Patient for the Right Operation: Bariatric Surgery Indications
 A Bariatric Patient in my Waiting Room: Choosing the Right Patient for the Right Operation: Bariatric Surgery Indications Shahzeer Karmali MD FRCSC FACS Associate Professor Surgery University of Alberta
A Bariatric Patient in my Waiting Room: Choosing the Right Patient for the Right Operation: Bariatric Surgery Indications Shahzeer Karmali MD FRCSC FACS Associate Professor Surgery University of Alberta
Searching for the physiological role of glucosedependent insulinotropic polypeptide
 Searching for the physiological role of glucosedependent insulinotropic polypeptide Jens Juul Holst 1,2, *, Johanne Agerlin Windeløv 1,2, Geke Aline Boer 1,2, Jens Pedersen 1,2, Berit Svendsen 1,2, Mikkel
Searching for the physiological role of glucosedependent insulinotropic polypeptide Jens Juul Holst 1,2, *, Johanne Agerlin Windeløv 1,2, Geke Aline Boer 1,2, Jens Pedersen 1,2, Berit Svendsen 1,2, Mikkel
Treating Type 2 Diabetes with Bariatric Surgery. Goal of Treating T2DM. Remission of T2DM with Bariatric
 Treating Type 2 Diabetes with Bariatric Surgery Number (in Millions) of Persons with Diagnosed Diabetes, United States, 198 25 The number of Americans with diabetes increased from 5.6 to 15.8 million Guilherme
Treating Type 2 Diabetes with Bariatric Surgery Number (in Millions) of Persons with Diagnosed Diabetes, United States, 198 25 The number of Americans with diabetes increased from 5.6 to 15.8 million Guilherme
Bariatric Surgery MM /11/2001. HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 04/28/2017 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Outpatient; Inpatient
 Bariatric Surgery Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.003 09/11/2001 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 04/28/2017 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service:
Bariatric Surgery Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.003 09/11/2001 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 04/28/2017 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service:
A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets
 Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Preserved insulin secretory capacity and weight loss are the predominant predictors
 Page 1 of 23 Preserved insulin secretory capacity and weight loss are the predominant predictors of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes randomized to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass Kim T. Nguyen,
Page 1 of 23 Preserved insulin secretory capacity and weight loss are the predominant predictors of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes randomized to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass Kim T. Nguyen,
Pharmacotherapy IV: Liraglutide for Chronic Weight Management SARAH CAWSEY MD, FRCPC 2 ND ANNUAL OBESITY UPDATE SEPTEMBER 22, 2018
 Pharmacotherapy IV: Liraglutide for Chronic Weight Management SARAH CAWSEY MD, FRCPC 2 ND ANNUAL OBESITY UPDATE SEPTEMBER 22, 2018 Disclosures Faculty Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Medicine,
Pharmacotherapy IV: Liraglutide for Chronic Weight Management SARAH CAWSEY MD, FRCPC 2 ND ANNUAL OBESITY UPDATE SEPTEMBER 22, 2018 Disclosures Faculty Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Medicine,
Physiological and molecular responses to bariatric surgery: markers or mechanisms underlying T2DM resolution?
 Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. ISSN 0077-8923 ANNALS OF THE NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Issue: The Year in Diabetes and Obesity REVIEW ARTICLE Physiological and molecular responses to bariatric surgery: markers
Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. ISSN 0077-8923 ANNALS OF THE NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Issue: The Year in Diabetes and Obesity REVIEW ARTICLE Physiological and molecular responses to bariatric surgery: markers
Circadian rhythms of GIP and GLP1 in glucose-tolerant and in type 2 diabetic patients after biliopancreatic diversion
 Diabetologia (2009) 52:873 881 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1288-9 ARTICLE Circadian rhythms of GIP and GLP1 in glucose-tolerant and in type 2 diabetic patients after biliopancreatic diversion G. Mingrone &
Diabetologia (2009) 52:873 881 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1288-9 ARTICLE Circadian rhythms of GIP and GLP1 in glucose-tolerant and in type 2 diabetic patients after biliopancreatic diversion G. Mingrone &
4. Mechanisms Mediating Weight Loss and Diabetes Remission After Bariatric/ Metabolic Surgery
 4. Mechanisms Mediating Weight Loss and Diabetes Remission After Bariatric/ Metabolic Surgery David E. Cummings, MD Francesco Rubino, MD Rationale for Understanding the Mechanisms of Bariatric Surgery
4. Mechanisms Mediating Weight Loss and Diabetes Remission After Bariatric/ Metabolic Surgery David E. Cummings, MD Francesco Rubino, MD Rationale for Understanding the Mechanisms of Bariatric Surgery
The enteroinsular axis in the pathogenesis of prediabetes and diabetes in humans
 The enteroinsular axis in the pathogenesis of prediabetes and diabetes in humans Young Min Cho, MD, PhD Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism Seoul National University College of Medicine Plasma glucose
The enteroinsular axis in the pathogenesis of prediabetes and diabetes in humans Young Min Cho, MD, PhD Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism Seoul National University College of Medicine Plasma glucose
Weight Regulation after Bariatric Surgery
 Weight Regulation after Bariatric Surgery New Jersey Chapter of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists 11 th Annual Meeting October 6, 2018 Judith Korner, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Director,
Weight Regulation after Bariatric Surgery New Jersey Chapter of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists 11 th Annual Meeting October 6, 2018 Judith Korner, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Director,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Klebanoff MJ, Chhatwal J, Nudel JD, Corey KE, Kaplan LM, Hur C. Cost-effectiveness of bariatric surgery in adolescents with obesity. JAMA Surg. Published online October 26,
Supplementary Online Content Klebanoff MJ, Chhatwal J, Nudel JD, Corey KE, Kaplan LM, Hur C. Cost-effectiveness of bariatric surgery in adolescents with obesity. JAMA Surg. Published online October 26,
Discussion & Conclusion
 Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
OBESITY AND WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY FOR THE PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIAN
 OBESITY AND WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY FOR THE PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIAN Nicole Basa, M.D., F.A.C.S., F.A.S.M.B.S Assistant Professor of Surgery Texas A&M Medical School Bariatric Medical Director- Cedar Park Regional
OBESITY AND WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY FOR THE PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIAN Nicole Basa, M.D., F.A.C.S., F.A.S.M.B.S Assistant Professor of Surgery Texas A&M Medical School Bariatric Medical Director- Cedar Park Regional
Revision For Weight Regain
 Revision For Weight Regain When? Why? What? Ahmad Aly ANZMOSS Dietetics Workshop 2018 Reoperative Surgery What Is Reoperative? Reversal Correction Conversion } Revisional Surgery Revisional Surgery 4000
Revision For Weight Regain When? Why? What? Ahmad Aly ANZMOSS Dietetics Workshop 2018 Reoperative Surgery What Is Reoperative? Reversal Correction Conversion } Revisional Surgery Revisional Surgery 4000
Obesity and Weight Loss Surgery for the Primary Care Physician
 Saturday General Session Obesity and Weight Loss Surgery for the Primary Care Physician Nicole Basa, MD Bariatric and General Surgeon Cedar Park Surgeons, PA Cedar Park, Texas Educational Objectives By
Saturday General Session Obesity and Weight Loss Surgery for the Primary Care Physician Nicole Basa, MD Bariatric and General Surgeon Cedar Park Surgeons, PA Cedar Park, Texas Educational Objectives By
SELECTED ABSTRACTS AND POSTER PRESENTATIONS
 SELECTED ABSTRACTS AND POSTER PRESENTATIONS The following summaries are based on abstracts and posters presented at the American Diabetes Association s 65th Annual Scientific Sessions held in San Diego,
SELECTED ABSTRACTS AND POSTER PRESENTATIONS The following summaries are based on abstracts and posters presented at the American Diabetes Association s 65th Annual Scientific Sessions held in San Diego,
Reduction of insulinotropic properties of GLP-1 and GIP after glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance
 Diabetologia (5) 5:9 9 DOI.7/s5-5-5-y ARTICLE Reduction of insulinotropic properties of GLP- and GIP after glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance Marie Eriksen & David H. Jensen & Siri Tribler & Jens
Diabetologia (5) 5:9 9 DOI.7/s5-5-5-y ARTICLE Reduction of insulinotropic properties of GLP- and GIP after glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance Marie Eriksen & David H. Jensen & Siri Tribler & Jens
Oat beta glucan: Multiple roles in the gut. A.R. Mackie, B.H. Bajka, B. Kirkhus
 Oat beta glucan: Multiple roles in the gut A.R. Mackie, B.H. Bajka, B. Kirkhus Introduction Food is consumed Food resides in the stomach Chyme is gradually emptied into the duodenum Can oat beta glucan
Oat beta glucan: Multiple roles in the gut A.R. Mackie, B.H. Bajka, B. Kirkhus Introduction Food is consumed Food resides in the stomach Chyme is gradually emptied into the duodenum Can oat beta glucan
The intestinal endocrine cells produce hormones involved
 DIABETES-INSULIN-GLUCAGON-GASTROINTESTINAL An Analysis of Cosecretion and Coexpression of Gut Hormones From Male Rat Proximal and Distal Small Intestine Berit Svendsen, Jens Pedersen, Nicolai Jacob Wewer
DIABETES-INSULIN-GLUCAGON-GASTROINTESTINAL An Analysis of Cosecretion and Coexpression of Gut Hormones From Male Rat Proximal and Distal Small Intestine Berit Svendsen, Jens Pedersen, Nicolai Jacob Wewer
Abstract. KEY WORDS: obesity, type 2 diabetes, metabolic surgery, laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and bariatric surgery. Introduction.
 Original Article Early metabolic response after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in obese diabetes. Glycative Stress Research Online edition : ISSN 2188-3610 Print edition : ISSN 2188-3602 Received : August
Original Article Early metabolic response after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in obese diabetes. Glycative Stress Research Online edition : ISSN 2188-3610 Print edition : ISSN 2188-3602 Received : August
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Schauer PR, Kashyap SR, Wolski K, et al. Bariatric surgery
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Schauer PR, Kashyap SR, Wolski K, et al. Bariatric surgery
MULTI-CENTER, PROSPECTIVE, CONTROLLED TRIAL OF THE DUODENAL JEJUNAL BYPASS LINER FOR THE TREATMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES IN OBESE PATIENTS
 Bariatric endoscopy MULTI-CENTER, PROSPECTIVE, CONTROLLED TRIAL OF THE DUODENAL JEJUNAL BYPASS LINER FOR THE TREATMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES IN OBESE PATIENTS Marek Benes, Tomas Hucl, Pavel Drastich, Julius
Bariatric endoscopy MULTI-CENTER, PROSPECTIVE, CONTROLLED TRIAL OF THE DUODENAL JEJUNAL BYPASS LINER FOR THE TREATMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES IN OBESE PATIENTS Marek Benes, Tomas Hucl, Pavel Drastich, Julius
Other Ways to Achieve Metabolic Control
 Other Ways to Achieve Metabolic Control Nestor de la Cruz- Muñoz, MD, FACS Associate Professor of Clinical Surgery Chief, Division of Laparoendoscopic and Bariatric Surgery DeWitt Daughtry Family Department
Other Ways to Achieve Metabolic Control Nestor de la Cruz- Muñoz, MD, FACS Associate Professor of Clinical Surgery Chief, Division of Laparoendoscopic and Bariatric Surgery DeWitt Daughtry Family Department
Evidence for beneficial effects of compromised gastric inhibitory polypeptide action in obesity-related diabetes and possible therapeutic implications
 Diabetologia (2009) 52:1724 1731 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1422-8 REVIEW Evidence for beneficial effects of compromised gastric inhibitory polypeptide action in obesity-related diabetes and possible therapeutic
Diabetologia (2009) 52:1724 1731 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1422-8 REVIEW Evidence for beneficial effects of compromised gastric inhibitory polypeptide action in obesity-related diabetes and possible therapeutic
New insights in metabolic surgery
 New insights in metabolic surgery G.Hubens 11th Starters Package Who would have thought it? An operation proves to be the most effective therapy for adult onset diabetes W Pories 1995 222: 339-350 KEY
New insights in metabolic surgery G.Hubens 11th Starters Package Who would have thought it? An operation proves to be the most effective therapy for adult onset diabetes W Pories 1995 222: 339-350 KEY
SHORT COMMUNICATION. Diabetologia (2013) 56: DOI /s
 Diabetologia (2013) 56:1542 1546 DOI 10.1007/s00125-013-2914-0 SHORT COMMUNICATION The pro-inflammatory biomarker soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (supar) is associated with incident type
Diabetologia (2013) 56:1542 1546 DOI 10.1007/s00125-013-2914-0 SHORT COMMUNICATION The pro-inflammatory biomarker soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (supar) is associated with incident type
Benefits of Bariatric Surgery
 Benefits of Bariatric Surgery Dr Tan Bo Chuan Registrar, Department of Surgery GP Forum 27 May 2017 Improvements of Co-morbidities Type 2 diabetes mellitus Hypertension Hyperlipidemia Degenerative joint
Benefits of Bariatric Surgery Dr Tan Bo Chuan Registrar, Department of Surgery GP Forum 27 May 2017 Improvements of Co-morbidities Type 2 diabetes mellitus Hypertension Hyperlipidemia Degenerative joint
Dianne Kristine Joy Closa*, Armin Masbang, Dianne Shari Cabrera, Allan Dampil and Robert Mirasol
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DIABETES AND METABOLIC RESEARCH Research Article Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Glucose Control, Weight Reduction and Disease Remission among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus:
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DIABETES AND METABOLIC RESEARCH Research Article Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Glucose Control, Weight Reduction and Disease Remission among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus:
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4
 Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. Diabetes Volume 63, May Diabetes 2014;63: DOI: /db
 Diabetes Volume 63, May 2014 1725 Kirstine N. Bojsen-Møller, 1,2 Carsten Dirksen, 1,2 Nils B. Jørgensen, 1,2 Siv H. Jacobsen, 1,2 Annette K. Serup, 3 Peter H. Albers, 3,4 Dorte L. Hansen, 1 Dorte Worm,
Diabetes Volume 63, May 2014 1725 Kirstine N. Bojsen-Møller, 1,2 Carsten Dirksen, 1,2 Nils B. Jørgensen, 1,2 Siv H. Jacobsen, 1,2 Annette K. Serup, 3 Peter H. Albers, 3,4 Dorte L. Hansen, 1 Dorte Worm,
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Why would fatty foods aggravate the patient s RUQ pain? What effect does cholecystokinin (CCK) have on gastric emptying?
 CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
Bariatric surgery, such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
 B R I E F R E S E A R C H R E P O R T -Cell Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Contributes to Improved Glucose Tolerance After Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy Darline Garibay, Anne K. McGavigan, Seon A. Lee,
B R I E F R E S E A R C H R E P O R T -Cell Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Contributes to Improved Glucose Tolerance After Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy Darline Garibay, Anne K. McGavigan, Seon A. Lee,
Diabetes control and lessened cerebral cardiovascular risks after gastric bypass surgery in Asian Taiwanese with a body mass index <35 kg/m2
 Diabetes control and lessened cerebral cardiovascular risks after gastric bypass surgery in Asian Taiwanese with a body mass index
Diabetes control and lessened cerebral cardiovascular risks after gastric bypass surgery in Asian Taiwanese with a body mass index
Near normalisation of blood glucose improves the potentiating effect of GLP-1 on glucose-induced insulin secretion in patients with type 2 diabetes
 Diabetologia (28) 1:632 64 DOI 1.17/s1-8-943-x ARTICLE Near normalisation of blood glucose improves the potentiating effect of GLP-1 on glucose-induced insulin secretion in patients with type 2 diabetes
Diabetologia (28) 1:632 64 DOI 1.17/s1-8-943-x ARTICLE Near normalisation of blood glucose improves the potentiating effect of GLP-1 on glucose-induced insulin secretion in patients with type 2 diabetes
Oral glutamine increases circulating glucagon-like peptide 1, glucagon, and insulin concentrations in lean, obese, and type 2 diabetic subjects 1 4
 Oral glutamine increases circulating glucagon-like peptide 1, glucagon, and insulin concentrations in lean, obese, and type 2 diabetic subjects 1 4 Jerry R Greenfield, I Sadaf Farooqi, Julia M Keogh, Elana
Oral glutamine increases circulating glucagon-like peptide 1, glucagon, and insulin concentrations in lean, obese, and type 2 diabetic subjects 1 4 Jerry R Greenfield, I Sadaf Farooqi, Julia M Keogh, Elana
Interleukin-6 enhances insulin secretion by increasing L cell and cell glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion
 Supplementary online material to Interleukin-6 enhances insulin secretion by increasing L cell and cell glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion Helga Ellingsgaard 1, Irina Hauselmann 1, Beat Schuler 2, Abdella
Supplementary online material to Interleukin-6 enhances insulin secretion by increasing L cell and cell glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion Helga Ellingsgaard 1, Irina Hauselmann 1, Beat Schuler 2, Abdella
Digestion: Endocrinology of Appetite
 Digestion: Endocrinology of Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one on one relationship with a qualified health care professional
Digestion: Endocrinology of Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one on one relationship with a qualified health care professional
Sweetness and Glycaemic Regulation. (A focus on gut related and physiological aspects) John McLaughlin Manchester University
 Sweetness and Glycaemic Regulation (A focus on gut related and physiological aspects) John McLaughlin Manchester University Disclosures No personal conflicts of interest Funding from BBSRC, including Cargill
Sweetness and Glycaemic Regulation (A focus on gut related and physiological aspects) John McLaughlin Manchester University Disclosures No personal conflicts of interest Funding from BBSRC, including Cargill
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal pain, enteral therapy in acute pancreatitis and, 812 Abscess(es), pancreatic, nutritional support for, 814 815 Acute Physiology and
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal pain, enteral therapy in acute pancreatitis and, 812 Abscess(es), pancreatic, nutritional support for, 814 815 Acute Physiology and
Obesity Management Workshop for Health Professionals
 Obesity Management Workshop for Health Professionals 17 th November 2017 Dr Graeme Rich Gastroenterologist Director of Bariatrics Australia Is a procedure the magic bullet? Energy in >> Energy out Accepted
Obesity Management Workshop for Health Professionals 17 th November 2017 Dr Graeme Rich Gastroenterologist Director of Bariatrics Australia Is a procedure the magic bullet? Energy in >> Energy out Accepted
Genotype analysis by Southern blots of nine independent recombinated ES cell clones by
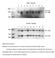 Supplemental Figure 1 Selected ES cell clones show a correctly recombined conditional Ngn3 allele Genotype analysis by Southern blots of nine independent recombinated ES cell clones by hybridization with
Supplemental Figure 1 Selected ES cell clones show a correctly recombined conditional Ngn3 allele Genotype analysis by Southern blots of nine independent recombinated ES cell clones by hybridization with
Evidence of Extrapancreatic Glucagon Secretion in Man
 Page 1 of 43 Evidence of Extrapancreatic Glucagon Secretion in Man Asger Lund 1,2, Jonatan I. Bagger 1,2, Nicolai J. Wewer Albrechtsen 2,7, Mikkel Christensen 1,2, Magnus Grøndahl 1, Bolette Hartmann 2,
Page 1 of 43 Evidence of Extrapancreatic Glucagon Secretion in Man Asger Lund 1,2, Jonatan I. Bagger 1,2, Nicolai J. Wewer Albrechtsen 2,7, Mikkel Christensen 1,2, Magnus Grøndahl 1, Bolette Hartmann 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Gastric Bypass vs Sleeve Gastrectomy for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastric Bypass vs Sleeve Gastrectomy for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus A Randomized Controlled Trial Wei-Jei Lee, MD, PhD; Keong Chong, MD; Kong-Han Ser, MD; Yi-Chih Lee, PhD; Shu-Chun Chen,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastric Bypass vs Sleeve Gastrectomy for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus A Randomized Controlled Trial Wei-Jei Lee, MD, PhD; Keong Chong, MD; Kong-Han Ser, MD; Yi-Chih Lee, PhD; Shu-Chun Chen,
Review Article Role of Gut-Related Peptides and Other Hormones in the Amelioration of Type 2 Diabetes after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Endocrinology Volume 2012, Article ID 504756, 13 pages doi:10.5402/2012/504756 Review Article Role of Gut-Related Peptides and Other Hormones in the Amelioration
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Endocrinology Volume 2012, Article ID 504756, 13 pages doi:10.5402/2012/504756 Review Article Role of Gut-Related Peptides and Other Hormones in the Amelioration
Blood glucose concentrations in healthy humans
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Glycemia on Plasma Incretins and the Incretin Effect During Oral Glucose Tolerance Test Marzieh Salehi, 1 Benedict Aulinger, 1 and David A. D Alessio 1,2 The incretin effect,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Glycemia on Plasma Incretins and the Incretin Effect During Oral Glucose Tolerance Test Marzieh Salehi, 1 Benedict Aulinger, 1 and David A. D Alessio 1,2 The incretin effect,
Energy Adaptations Persist 2 Years After Sleeve Gastrectomy and Gastric Bypass
 OBES SURG (2016) 26:459 463 DOI 10.1007/s11695-015-1972-4 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Energy Adaptations Persist 2 Years After Sleeve Gastrectomy and Gastric Bypass Charmaine S. Tam 1 & Georgia Rigas 2 & Leonie
OBES SURG (2016) 26:459 463 DOI 10.1007/s11695-015-1972-4 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Energy Adaptations Persist 2 Years After Sleeve Gastrectomy and Gastric Bypass Charmaine S. Tam 1 & Georgia Rigas 2 & Leonie
Policy Specific Section: April 14, 1970 June 28, 2013
 Medical Policy Bariatric Surgery Type: Medical Necessity and Investigational / Experimental Policy Specific Section: Surgery Original Policy Date: Effective Date: April 14, 1970 June 28, 2013 Definitions
Medical Policy Bariatric Surgery Type: Medical Necessity and Investigational / Experimental Policy Specific Section: Surgery Original Policy Date: Effective Date: April 14, 1970 June 28, 2013 Definitions
Metabolic surgery: gastric bypass for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
 Review Article Metabolic surgery: gastric bypass for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus Maria del Pilar Quevedo, Mariano Palermo, Edgardo Serra, Marianela A. Ackermann Division of Bariatric Surgery
Review Article Metabolic surgery: gastric bypass for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus Maria del Pilar Quevedo, Mariano Palermo, Edgardo Serra, Marianela A. Ackermann Division of Bariatric Surgery
My Journey in Endocrinology. Samuel Cataland M.D
 My Journey in Endocrinology Samuel Cataland M.D. 1968-2015 Drs Berson M.D. Yalow phd Insulin Radioimmunoassay Nobel Prize Physiology or Medicine 1977 Rosalyn Yalow: Radioimmunoassay Technology Andrew Schally
My Journey in Endocrinology Samuel Cataland M.D. 1968-2015 Drs Berson M.D. Yalow phd Insulin Radioimmunoassay Nobel Prize Physiology or Medicine 1977 Rosalyn Yalow: Radioimmunoassay Technology Andrew Schally
Sleeve Gastrectomy Debate: Everyone Needs a Sleeve!!! Dana Portenier, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Duke University Medical Center
 Sleeve Gastrectomy Debate: Everyone Needs a Sleeve!!! Dana Portenier, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Duke University Medical Center 1. Safety Two Year Excess Weight Loss Two Year Weight Loss and Mortality
Sleeve Gastrectomy Debate: Everyone Needs a Sleeve!!! Dana Portenier, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Duke University Medical Center 1. Safety Two Year Excess Weight Loss Two Year Weight Loss and Mortality
Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Augments Glucagon Responses to Hypoglycemia in Type 1 Diabetes
 72 Diabetes Volume 64, January 2015 Mikkel Christensen, 1,2 Salvatore Calanna, 1,3 Alexander H. Sparre-Ulrich, 1,4 Peter L. Kristensen, 5 Mette M. Rosenkilde, 4 Jens Faber, 6 Francesco Purrello, 3 Gerrit
72 Diabetes Volume 64, January 2015 Mikkel Christensen, 1,2 Salvatore Calanna, 1,3 Alexander H. Sparre-Ulrich, 1,4 Peter L. Kristensen, 5 Mette M. Rosenkilde, 4 Jens Faber, 6 Francesco Purrello, 3 Gerrit
Gut hormones KHATTAB
 Gut hormones PROF:ABD ALHAFIZ HASSAN KHATTAB Gut as an endocrine gland The talk will cover the following : Historical background. Why this subject is chosen. Gastro-intestinal hormones and their function.
Gut hormones PROF:ABD ALHAFIZ HASSAN KHATTAB Gut as an endocrine gland The talk will cover the following : Historical background. Why this subject is chosen. Gastro-intestinal hormones and their function.
Type 2 diabetes and metabolic surgery:
 Type 2 diabetes and metabolic surgery: Shouldn't we call it again Surgery for Type 2 DM again bariatric? Is it Metabolic or Bariatric surgery? Josep Vidal Obesity Unit. Endocrinology and Nutrition Department
Type 2 diabetes and metabolic surgery: Shouldn't we call it again Surgery for Type 2 DM again bariatric? Is it Metabolic or Bariatric surgery? Josep Vidal Obesity Unit. Endocrinology and Nutrition Department
Sitagliptin: first DPP-4 inhibitor to treat type 2 diabetes Steve Chaplin MSc, MRPharmS and Andrew Krentz MD, FRCP
 Sitagliptin: first DPP-4 inhibitor to treat type 2 diabetes Steve Chaplin MSc, MRPharmS and Andrew Krentz MD, FRCP KEY POINTS sitagliptin (Januvia) is a DPP-4 inhibitor that blocks the breakdown of the
Sitagliptin: first DPP-4 inhibitor to treat type 2 diabetes Steve Chaplin MSc, MRPharmS and Andrew Krentz MD, FRCP KEY POINTS sitagliptin (Januvia) is a DPP-4 inhibitor that blocks the breakdown of the
Defective amplification of the late phase insulin response to glucose by GIP in obese Type II diabetic patients
 Diabetologia (2002) 45:1111 1119 DOI 10.1007/s00125-002-0878-6 Defective amplification of the late phase insulin response to glucose by GIP in obese Type II diabetic patients T. Vilsbøll 1, 2, T. Krarup
Diabetologia (2002) 45:1111 1119 DOI 10.1007/s00125-002-0878-6 Defective amplification of the late phase insulin response to glucose by GIP in obese Type II diabetic patients T. Vilsbøll 1, 2, T. Krarup
(1) Upper Gastrointestinal Surgical Unit, The Alfred Hospital (2) Monash University Centre for Obesity Research and Education (CORE)
 Yazmin Johari (1,2), Geri Ooi (1,2), Paul Burton (1,2), Shourye Dwivedi (2), Cheryl Laurie (2), Kalai Shaw (1), Richard Chen (1,2), Wendy Brown (1,2), Peter Nottle (1) (1) Upper Gastrointestinal Surgical
Yazmin Johari (1,2), Geri Ooi (1,2), Paul Burton (1,2), Shourye Dwivedi (2), Cheryl Laurie (2), Kalai Shaw (1), Richard Chen (1,2), Wendy Brown (1,2), Peter Nottle (1) (1) Upper Gastrointestinal Surgical
Understanding the Biology of Weight and Weight Regain to Assist those Challenged with Obesity
 Understanding the Biology of Weight and Weight Regain to Assist those Challenged with Obesity Diana L Lawlor MN RN-NP Oct 2017 Our World Has Changed Our world has changed Energy In Vs Energy Out
Understanding the Biology of Weight and Weight Regain to Assist those Challenged with Obesity Diana L Lawlor MN RN-NP Oct 2017 Our World Has Changed Our world has changed Energy In Vs Energy Out
mellitus post Roux -en -Y gastric bypass in Asian patients
 Original Article Singapore Med J 2010; 51(12) 937 Early improvement in type 2 diabetes mellitus post Roux -en -Y gastric bypass in Asian patients Kiong K L, Ganesh R, Cheng A K S, Lekshiminarayanan R,
Original Article Singapore Med J 2010; 51(12) 937 Early improvement in type 2 diabetes mellitus post Roux -en -Y gastric bypass in Asian patients Kiong K L, Ganesh R, Cheng A K S, Lekshiminarayanan R,
Does metformin modify the effect on glycaemic control of aerobic exercise, resistance exercise or both?
 Diabetologia (2013) 56:2378 2382 DOI 10.1007/s00125-013-3026-6 SHORT COMMUNICATION Does metformin modify the effect on glycaemic control of aerobic exercise, resistance exercise or both? Normand G. Boulé
Diabetologia (2013) 56:2378 2382 DOI 10.1007/s00125-013-3026-6 SHORT COMMUNICATION Does metformin modify the effect on glycaemic control of aerobic exercise, resistance exercise or both? Normand G. Boulé
Gastrointestinal Hormones: Introduction and Index
 Gastrointestinal Hormones: Introduction and Index Digesting, absorbing and assimilating a meal requires precise coordination of a huge number of physiologic processes. Control over gastrointestinal function
Gastrointestinal Hormones: Introduction and Index Digesting, absorbing and assimilating a meal requires precise coordination of a huge number of physiologic processes. Control over gastrointestinal function
EAT TO LIVE: THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS. Felicia V. Nowak, M.D., Ph.D. Ohio University COM 22 January, 2008
 EAT TO LIVE: THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS Felicia V. Nowak, M.D., Ph.D. Ohio University COM 22 January, 2008 THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS Exocrine pancreas Endocrine pancreas THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS EXOCRINE
EAT TO LIVE: THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS Felicia V. Nowak, M.D., Ph.D. Ohio University COM 22 January, 2008 THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS Exocrine pancreas Endocrine pancreas THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS EXOCRINE
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
