Diffusion Tensor Imaging for the Differentiation of Microangiopathy, Infarction and Perfusion-Diffusion Mismatch Lesions 1
|
|
|
- Patrick Flowers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diffusion Tensor Imaging for the Differentiation of Microangiopathy, Infarction and Perfusion-Diffusion Mismatch Lesions 1 Dong-Ho Ha, M.D., Sunseob Choi, M.D., Myong-Jin Kang, M.D., Jin Hwa Lee, M.D., Seong Kuk Yoon, M.D., Kyung Jin Nam, M.D. Purpose: This study was designed to evaluate the usefulness of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and the DTI indices for differentiating between microangiopathy lesions, acute infarction lesions and perfusion-diffusion mismatch areas. Materials and Methods: DTI was performed in 35 patients with the use of a 1.5 Tesla MRI system. The MRI parameters were as follows: a spin echo EPI sequence with a b- value = 1000 s/mm 2, 25 diffusion directions, a repetition time of 8400 msec, an echo time of 75 msec, a matrix size of , a FOV of 22 cm and a 4 mm slice thickness. From the diffusion tensor images, the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), fractional anisotropy (FA), volume ratio (VR), relative anisotropy (RA), anisotropy index (AI), exponential ADC (eadc) and magnitude diffusion coefficient (MDC) were measured for the contra-lateral normal area (28 cases), the microangiopathy lesions (10 cases), the infarction lesions (17 cases) and the perfusion-diffusion mismatch area (8 cases). Results: As compared to the normal area, the microangiopathy lesions showed increased ADC and MDC values and decreased FA, VR, RA, AI and eadc values. The infarction lesions showed increased VR, RA and eadc values, a normal FA, a decreased AI and decreased ADC and MDC values. The mismatch area showed a similar pattern as that for the microangiopathy lesions; however, the differences were not prominent, with an increase of the ADC and MDC values and a decrease of FA, VR, RA, AI and eadc values. Conclusion: The DTI indices could have a role in making the differential diagnosis of microangiopathy, acute infarction and perfusion-diffusion mismatch lesions. Index words : Brain Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging Cerebral Infarction Imaging processing, computed-assisted 1 Department of Radiology, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea Received July 8, 2009 ; Accepted August 4, 2009 Address reprint requests to : Sunseob Choi, M.D., Department of Radiology, Dong-A University Medical Center, 1,3-ga, Dongdaeshin-dong, Seo-gu, Busan , Korea. Tel Fax sschoi317@yahoo.co.kr 201
2 Dong-Ho Ha, et al : Diffusion Tensor Imaging for the Differentiation of Microangiopathy, Infarction and Perfusion-Diffusion Mismatch Lesions Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) is a unique method for observing the mobility of water in tissue, and it is used as a principal method for diagnosing acute infarction. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is used to investigate fiber connectivity and evaluating brain development by mapping water diffusion. DTI describes the magnitude, degree and orientation of diffusion anisotropy, and this modality is considered to be a robust method to characterize disease with high sensitivity. The theoretical background and clinical applications of the DTI and DTI indices, as well as the DTI method and tractography for examining the white matter (WM), have been well explained in previous reports (1-4). Microangiopathy is common finding when performing clinical MRI, but microangiopathy cannot be differentiated from acute infarction without performing DWI. A perfusion-diffusion mismatch area is unrecognizable without a perfusion study. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the use of DTI and to determine the differences and the usefulness of the various DTI indices for making the differential diagnosis of microangiopathy, acute infarction and the perfusion-diffusion mismatch areas. Materials and Methods DTI was performed in 35 patients with the use of a 1.5 Tesla MRI system with an 8-channel head coil (Signa Excite HD, GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI, USA). The MRI parameters were as follows: a spin echo EPI sequence with a b-value = 1000 s/mm 2, 25 diffusion directions, a repetition time of 8400 msec, an echo time of 75 msec, a matrix size of , a FOV of 22 cm and a 4 mm slice thickness. The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC, 10-3 mm 2 /sec), the fractional anisotropy (FA), volume ratio (VR), the relative anisotropy (RA), the anisotropy index (AI), the exponential ADC (eadc) and the magnitude diffusion coefficient (MDC) were measured by placement of region-of-interest (ROI) circles on the contra-lateral normal area (28 cases), the microangiopathy lesions (10 cases), the acute infarction lesions (17 cases) and the perfusion-diffusion mismatch area (8 cases) on the diffusion tensor images and using the vendor-supplied software (Functool 2; GE Medical Systems, Fremont, CA, USA) (Figs. 1, 2). T-tests were used to assess the significance of the differences of the values of the DTI indices. A p value < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. 202 Results The ADC values were 0.79 for the normal area, 1.16 for the microangiopathy lesions, 0.48 for the infarction lesions and 0.84 for the mismatch area. The FA values were 0.36 for the normal area, 0.21 for the microangiopathy lesions, 0.36 for the infarction lesions and 0.31 for the mismatch area. The VR values were 0.16 for the normal area, 0.05 for the microangiopathy lesions, 0.19 for the infarction lesions and 0.12 for the mismatch area. The RA values were 0.31 for the normal area, 0.18 for the microangiopathy lesions, 0.32 for the infarction lesions and 0.27 for the mismatch area. The AI values were 0.07 for the normal area, 0.04 for the microangiopathy lesions, 0.03 for the infarction lesions and 0.06 for the mismatch area. The eadc values were 0.46 for the normal area, 0.32 for the microangiopathy lesions, 0.64 for the infarction lesions and 0.44 for the mismatch areas. The MDC values were 0.83 for the normal area, 1.17 for the microangiopathy lesions, 0.50 for the infarction lesions and 0.87 for the mismatch area (Tables 1-4). As compared with the contra-lateral normal area, based on the use of the t-test, significant differences were determined for all the abnormalities for the ADC, FA, VR, RA, AI, eadc and MDC (p=0.000, p=0.001, p=0.004, p=0.002, p=0.035, p=0.000 and p=0.000, respectively). The differences between the microangiopathy lesions and the infarction lesions were significant for the ADC, FA, VR, RA, eadc and MDC (p=0.000, p=0.001, p=0.001, p=0.001, p=0.000 and p=0.000, respectively; only the AI was not significant, p=0.524). The differences between the microangiopathy lesions and the mismatch area were significant for the ADC, FA, VR, RA, eadc and MDC (p=0.000, p=0.020, p=0.039, p=0.020, p=0.000 and p=0.000, respectively; only the AI was not significant, p=0.300). The differences between the infarction lesions and the mismatch area were significant for the ADC, eadc and MDC (all p=0.000) and those for the FA, VR, RA and AI were not significant (p=0.337, p=0.132, p=0.308 and p=0.265, respectively). Discussion The DTI indices that are classified as isotropy indices include the ADC, Trace and eadc, and indices that are classified as anisotropy indices including FA, RA and VR (5). DTI is considered to have an important role for
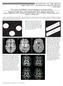
3 Fig. 1. The MR images of a 60-year-old woman, who suffered from hypertension and cognitive dysfunction, showed marked microangiopathy at the deep white matter. The diffusion tensor images were processed and they were used to measure the values of several indices at the contra-lateral normal area (left circle) and the area of microangiopathy (right circle). B 0 image (top line, left), Isotropic image (top line, middle), Apparent diffusion coefficient (top line, right), Fractional anisotropy (middle line, left), Volume ratios (middle line, middle), Relative anisotropy (middle line, right), Anisotropy index (bottom line, left), Exponential ADC (bottom line, middle). Magnitude diffusion coefficient (bottom line, left) 203
4 Dong-Ho Ha, et al : Diffusion Tensor Imaging for the Differentiation of Microangiopathy, Infarction and Perfusion-Diffusion Mismatch Lesions Fig. 2. A 67-year-old man who suffered from a right middle cerebral artery (MCA) infarction was evaluated at two hours after the attack. A perfusion-diffusion mismatch area was noted on the perfusion study (b) and the values of the DTI indices were measured at the infarction site (anterior circle) and the perfusion-diffusion mismatch area (posterior circle). Isotropic image (top line, left), Perfusion study (the time to peak image, top line, middle), Apparent diffusion coefficient (top line, right), Fractional anisotropy (middle line, left), Volume ratios (middle line, middle), Relative anisotropy (middle line, right), Anisotropy index (bottom line, left), Exponential ADC (bottom line, middle), Magnitude diffusion coefficient (bottom line, left) 204
5 diagnosing disease, predicting the prognosis and planning the treatment of ischemic brain injury (6). The combination of DTI and functional MRI (fmri) provides new insights into structure-function relationships (7); DTI allows visualization of the WM tracts and it is beneficial for the surgical planning of brain tumors (8). DWI and anisotropy have been introduced for evaluating patients after a stroke (9). The isotropic maps are appropriate to detect hyper-acute stroke and the anisotropic images are useful to differentiate hyperacute stroke from acute stroke (10). DTI makes it possible to distinguish the acute ischemic changes from the chronic ischemic changes. The ADC is increased for a chronic ischemic lesion (11) and vasogenic edema (10, 12, 13), and the ADC is decreased for acute ischemia (9) and cytotoxic edema (10, 13). The ADC values are useful to predict the viability of tissue and the outcome of stroke (14, 15). In previous studies, the measured ADC values in the thalamus and splenium were 0.72 and 0.62, respectively, and the measured ADC values in the ischemic WM and gray matter (GM) were 0.54 and 0.46, respectively (3, 16). The measured ADC value of the normal brain was 0.86, and the measured ADC values were 0.56, 0.73 and 0.87 for a WM infarction and 0.71, 0.78 and 1.21 for infarcted GM at 4.5 hours, 51 hours and 85 days, respectively (5). The ADC value of an acute infarct is reduced by 30-50% within 30 minutes of the onset (17), it initially decreases, it becomes normalized after seven to nine days and then it increases in the chronic phase (18). In our cases, the ADC was 0.79 in the normal brain and the ADC decreased by 39% to 0.48 for an acute infarction, and the ADC increased for microangiopathy to 1.15 and for a mismatch area to 0.84, which is a similar pattern of value changes as that for vasogenic edema or chronic infarction. In Wallerian degeneration, the ADC (0.96) was not different as compared to that of the normal brain (19). However, the ADC values were increased at the area of Wallerian degeneration of the corpus callosum, as seen on the serial diffusion tensor images (11). Secondary degeneration of Table 1. The Values of the DTI Indices in the Contra-Lateral Normal Area (Males:Females, 16:12; Mean Age: 61Years) Number ADC FA VR RA AI eadc MDC Mean SD ADC, apparent diffusion coefficient; FA, fractional anisotropy; VR; volume ratio; RA, relative anisotropy; AI, anisotropy index; eadc, exponential ADC; MDC, magnitude diffusion coefficient 205
6 Dong-Ho Ha, et al : Diffusion Tensor Imaging for the Differentiation of Microangiopathy, Infarction and Perfusion-Diffusion Mismatch Lesions the fiber tract proximal and distal to a primary lesion can be detected on ADC images (20). The diffusion tensor images reflect the pathological changes of the demyelinating process. The plaque centers of acute multiple sclerosis showed an increased ADC ( ) as compared with the rim, the normal-appearing WM and the chronic lesions (21). The eadc has been introduced to remove the contributions of the T2 signal intensity. The eadc is an index that has the advantages of DWI and ADC maps, and it can depict ischemic infarction with a pure diffusion effect. The eadc is increased for an acute infarct, it is normalized in 8-10 days and it is decreased for a chronic infarct; a hypointense signal reflects cellular lysis and the loss of cellular integrity (22). In our cases, the eadc was 0.46 for the normal brain, and the eadc increased for infarction lesions (0.64) and it decreased for the microangiopathy lesions (0.32) and the mismatch area (0.44). The early changes of diffusion anisotropy reflect the cellular changes in acute ischemia and they may provide a potential marker to predict the clinical outcome (5). Decreased anisotropy has been correlated with a motor deficit after stroke and diffusion anisotropy allows physicians to evaluate the prognosis of ischemic stroke (19). The diffusion anisotropy values are more Table 2. The Values of the DTI Indices for the Microangiopathy Lesions (Males:Females, 4:6,; Mean Age: 62 Years) Number ADC FA VR RA AI eadc MDC Mean SD ADC, apparent diffusion coefficient; FA, fractional anisotropy; VR; volume ratio; RA, relative anisotropy; AI, anisotropy index; eadc, exponential ADC; MDC, magnitude diffusion coefficient Table 3. The Values of the DTI Indices for Infarction Lesions (Males:Females, 12:5; Mean Age: 58 Years) Number ADC FA VR RA AI eadc MDC Mean SD ADC, apparent diffusion coefficient; FA, fractional anisotropy; VR; volume ratio; RA, relative anisotropy; AI, anisotropy index; eadc, exponential ADC; MDC, magnitude diffusion coefficient 206
7 Table 4. The Values of the DTI Indices for the Perfusion-Diffusion Mismatch Area (Males:Females, 4:4; Mean Age: 58 Years) Number ADC FA VR RA AI eadc MDC Mean SD ADC, apparent diffusion coefficient; FA, fractional anisotropy; VR; volume ratio; RA, relative anisotropy; AI, anisotropy index; eadc, exponential ADC; MDC, magnitude diffusion coefficient sensitive than the ADC to observe WM packing and myelination in newborns; further, FA is highly sensitive to micro-structural changes and it is considered a marker of the white matter s integrity (23). The FA decreases with age (24) and it decreases for patients with mild cognitive impairment prior to the development of dementia (25). Anisotropy is decreased in edema (12) and the FA is increased in the acute phase (26) and it is decreased in the chronic phase (11, 26). The FA of the thalamus and splenium have been measured as 0.37 and 0.84, respectively, and the FA of the ischemic WM and GM have been measured as 0.45 and 0.36, respectively (3). FA is hyperacutely elevated at the deep WM in less than seven hours (1.10) and it is reduced at 24 hours (0.85). Reduction of the FA suggests the commencement of tissue damage (16). In our cases, the FA value for infarction was same as that for the normal area (0.36), and the FA value was decreased for microangiopathy lesions (0.21) and the mismatch area (0.31). As determined in previous studies, the FA values for Wallerian degeneration decreased at the corpus callosum (11, 20) and the FA value was 0.39 (normal, 0.45) on the affected side and it was correlated with a motor deficit (19). The plaque centers for acute multiple sclerosis had decreased FA values ( ) as compared with the rim, the normal-appearing WM and the chronic lesions (21). The other DTI indices have not been well studied and the usefulness of the indices for clinical applications has not been evaluated. In our cases, all of the MDC and RA values showed a similar pattern with that of the ADC and FA, respectively. The VR and eadc also showed a similar pattern as that of the FA values, except for an increased VR (0.19, normal: 0.16) and eadc (0.64, normal: 0.46) for infarction lesions. The AI was decreased for all the abnormalities and it was most prominent for 207 infarction lesions (0.032, normal: 0.065). As compared with the contra-lateral normal area, the abnormal areas showed significant differences in all the DTI values and the differences between microangiopathy and the infarction lesions and between the microangiopathy lesions and the mismatch area were significant for all the DTI values except for the AI. The differences between the infarction lesions and the mismatch area were only significant for the ADC, eadc and MDC. In summary, the microangiopathy lesions showed increased ADC and MDC values, and decreased FA, VR, RA, AI and eadc values. The acute infarction lesions showed increased VR, RA and eadc values, normal FA values, a decreased AI value and decreased ADC and MDC values. The mismatch area showed a similar pattern as that of the microangiopathy lesions; however, any differences were not prominent, with a moderate increase of ADC and MDC values and a moderate decrease of the FA, VR, RA, AI and eadc values. In conclusion, we suggest that the DTI indices could have a role in making the differential diagnosis of microangiopathy, infarction and perfusion-diffusion mismatch lesions. References 1. Wang JJ, Chao TC, Wai YY, Hsu Y. Novel diffusion anisotropy indices: an evaluation. J Magn Reson Imaging 2006;24: Sundgren PC, Dong Q, Gomez-Hassan D, Mukherji SK, Maly P, Welsh R. Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain: review of clinical applications. Neuroradiology 2004;46: Sorensen AG, Wu O, Copen WA, Davis TL, Gonzalez RG, Koroshetz WJ, et al. Human acute cerebral ischemia: detection of changes in water diffusion anisotropy by using MR imaging. Radiology 1999;212: Jellison BJ, Field AS, Medow J, Lazar M, Salamat MS, Alexander AL. Diffusion tensor imaging of cerebral white matter: a pictorial
8 Dong-Ho Ha, et al : Diffusion Tensor Imaging for the Differentiation of Microangiopathy, Infarction and Perfusion-Diffusion Mismatch Lesions review of physics, fiber tract anatomy, and tumor imaging patterns. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2004;25: Yang Q, Tress BM, Barber PA, Desmond PM, Darby DG, Gerraty RP, et al. Serial study of apparent diffusion coefficient and anisotropy in patients with acute stroke. Stroke 1999; 30: Sotak CH. The role of diffusion tensor imaging in the evaluation of ischemic brain injury- a review. NMR Biomed 2002;15: Seghier ML, Lazeyras F, Zimine S, Maier SE, Hanquinet S, Delavelle, et al. Combination of event-related fmri and diffusion tensor imaging in an infant with perinatal stroke. Neuroimage 2004;21: Witwer BP, Moftakhar R, Hasan KM, Deshmukh P, Haughton V, Field A, et al. Diffusion-tensor imaging of white matter tracts in patients with cerebral neoplasm. J Neurosurg 2002;97: Van Gelderen P, de Vleeschouwer MH, DesPres D, Pekar J, Van Zijl PC, Moonen CT. Water diffusion and acute stroke. Magn Reson Med 1994;31: Harris AD, Pereira RS, Mitchell JR, Hill MD, Sevick RJ, Frayne R. A comparison of images generated from diffusion-weighted and diffusion-tensor imaging data in hyper-acute stroke. J Magn Reson Imaging 2004;20: Gupta RK, Saksena S, Hasan KM, Agarwal A, Haris M, Pandey CM, et al. Focal Wallerian degeneration of the corpus callosum in large middle cerebral artery stroke: serial diffusion tensor imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 2006;24: Alexander AL, Lee JE, Lazar M, Field AS. Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics 2007;4: Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, Breen J, Pao L, Wang A, et al. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med 1996;334: Yang Q, Tress BM, Barber PA, Desmond PM, Darby DG, Gerraty RP, et al. Serial study of apparent diffusion coefficient and anisotropy in patients with acute stroke. Stroke 1999;30: Schlaug G, Siewert B, Benfield A, Edelman RR, Warach S. Time course of the apparent diffusion coefficient(adc) abnormality in human stroke. Neurology 1997;49: Bhagat YA, Hussain MS, Stobbe RW, Butcher KS, Emery DJ, Shuaib A, et al. Elevations of diffusion anisotropy are associated with hyper-acute stroke: a serial imaging study. Magn Reson Imaging 2008;26: Zelaya F, Flood N, Chalk JB, Wang D, Doddrell DM, Strugnell W, et al. An evaluation of the time dependence of the anisotropy of the water diffusion tensor in acute human ischemia. Magn Reson Imaging 1999;17: Copen WA, Schwamm LH, Gonzalez RG, Wu O, Harmath CB, Schaefer PW, et al. Ischemic stroke: effects of etiology and patient age in the time course of the core apparent diffusion coefficient. Radiology 2001;221: Thomalla G, Glauche V, Koch MA, Beaulieu C, Weiller C, Rother J. Diffusion tensor imaging detects early wallerian degeneration of the pyramidal tract after ischemic stroke. NeuroImage 2004;22: Liang Z, Zeng J, Liu S, Ling X, Xu A, Yu J, et al. A prospective study of secondary degeneration following subcortical infarction using diffusion tensor imaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2007;78: Tievsky AL, Ptak T, Farkas J. Investigation of apparent diffusion coefficient and diffusion tensor anisotropy in acute and chronic multiple sclerosis lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1999;20: Engelter ST, Provenzale JM, Petrella JR, Alberts MJ, DeLong DM, MacFall JR. Use of exponential diffusion imaging to determine the age of ischemic infarcts. J Neuroimaging 2001;11: Neil JJ, Shiran SI, McKinstry RC, Schefft GL, Snyder AZ, Almli CR, et al. Normal brain in human newborns: apparent diffusion coefficient and diffusion anisotrophy measured by using diffusion tensor MR imaging. Radiology 1998;209: Pfefferbaum A, Sullivan EV, Hedehus M, Lim KO, Adalsteinsson E, Moseley M. Age-related decline in brain white matter anisotropy measured with spatially corrected echo-planar diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Med 2000;44: Medina D, detoledo-morrell L, Urresta F, Gabrieli JD, Moseley M, Fleischman D. et al. White matter changes in mild cognitive impairment and AD: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Neurology Aging 2006;27: Sorensen AG, Wu O, Copen WA, Davis TL, Gonzalez RG, Koroshetz WJ, et al. Human acute cerebral ischemia: detection of changes in water diffusion anisotropy by using MR imaging. Radiology 1999;212:
9 대한영상의학회지 2009;61: 뇌의미세혈관병증, 경색, 관류 - 확산불일치병변의감별을위한 Diffusion Tensor Imaging 1 1 동아대학교의과대학영상의학과 하동호 최순섭 강명진 이진화 윤성국 남경진 목적 : 뇌의미세혈관병증, 경색, 관류-확산불일치병변의감별에있어서여러가지확산텐서영상들의임상적용가능성을평가하는것이다. 대상과방법 : 1.5 테슬라자기공명영상장치를이용하여 35명의환자에서확산텐서영상을얻었다. 자기공명영상은 spin echo EPI sequence를확산계수 1000 s/mm 2, 확산경사방향 25, 반복시간 8400 msec, 에코시간 75 msec, 화소수 , 영상크기 22 cm, 절편두께 4 mm로하였다. 이들영상에서반대측정상부위 (28예), 미세혈관병증 (10예), 뇌경색 (17예), 관류-확산불일치병변부위 (8예) 에서 apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), fractional anisotropy (FA), volume ratio (VR), relative anisotropy (RA), anisotropy index (AI), exponential ADC (eadc), magnitude diffusion coefficient (MDC) 를측정하여비교하였다. 결과 : 정상부위보다미세혈관병증부위는 ADC와 MDC의증가를보였고, FA, VR, RA, AI, eadc의감소를보였다. 뇌경색부위는 VR, RA, eadc는증가하고, 정상 FA를보였으며, AI, ADC, MDC는감소하였다. 관류-확산불일치병변부위는미세혈관병증부위와비슷하게 ADC와 MDC는증가하고, FA, VR, RA, AI, eadc는감소하였으나, 차이는현저하지않았다. 결론 : 여러가지확산텐서영상들은뇌의미세혈관병증, 경색, 관류-확산불일치병변의감별진단에도움을줄수있다. 209
Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department
 298 / = Abstract = Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department Sung Pil Chung, M.D, Suk Woo Lee, M.D., Young Mo Yang, M.D., Young Rock Ha, M.D., Seung Whan Kim, M.D., and
298 / = Abstract = Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department Sung Pil Chung, M.D, Suk Woo Lee, M.D., Young Mo Yang, M.D., Young Rock Ha, M.D., Seung Whan Kim, M.D., and
Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
Dong Gyu Na, Vincent N. Thijs, Gregory W. Albers, Michael E. Moseley, and Michael P. Marks. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25: , September 2004
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1331 1336, September 2004 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Acute Ischemia: Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Signal Intensity Thresholds in Predicting Tissue at Risk
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1331 1336, September 2004 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Acute Ischemia: Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Signal Intensity Thresholds in Predicting Tissue at Risk
The Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Maps in Early Cerebral Ischemia
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1260 1267, August 2001 The Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Maps in Early Cerebral Ischemia Patricia M. Desmond, Amanda C. Lovell, Andrew A. Rawlinson, Mark W. Parsons,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1260 1267, August 2001 The Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Maps in Early Cerebral Ischemia Patricia M. Desmond, Amanda C. Lovell, Andrew A. Rawlinson, Mark W. Parsons,
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Naoaki Yamada, Satoshi Imakita, and Toshiharu Sakuma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
(anisotropic diffusion) (fractional anisotropy FA)
 2 3 3 1 020-8505 19-1 2 020-8505 19-1 3 020-0173 348-58 Alzheimer(AD) 3). AD PETSPECTstatistical parametric mapping (SPM) 4), 56) PETMRI (anisotropic diffusion) (fractional anisotropyfa) 710) PETMRI (rcbf)(rcmr0
2 3 3 1 020-8505 19-1 2 020-8505 19-1 3 020-0173 348-58 Alzheimer(AD) 3). AD PETSPECTstatistical parametric mapping (SPM) 4), 56) PETMRI (anisotropic diffusion) (fractional anisotropyfa) 710) PETMRI (rcbf)(rcmr0
The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke. Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV
 The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV Patient CR 62 yo F w/ 2 wk h/o altered mental status Presents to ED w/ confusion following a fall 1 day prior New onset left facial droop
The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV Patient CR 62 yo F w/ 2 wk h/o altered mental status Presents to ED w/ confusion following a fall 1 day prior New onset left facial droop
Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:692 698, May 2004 Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain Pierre Brugières, Philippe Thomas, Anne Maraval, Hassan Hosseini, Catherine Combes,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:692 698, May 2004 Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain Pierre Brugières, Philippe Thomas, Anne Maraval, Hassan Hosseini, Catherine Combes,
A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging
 Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography
 Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography Anitha Priya Krishnan 1, Isaac Asher 2, Dave Fuller 2, Delphine Davis 3, Paul Okunieff 2, Walter O Dell 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering
Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography Anitha Priya Krishnan 1, Isaac Asher 2, Dave Fuller 2, Delphine Davis 3, Paul Okunieff 2, Walter O Dell 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients
 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med Med J 2006; J 2006; 47(3) 47(3) : 198 : 1 Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients Parmar H, Golay
O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med Med J 2006; J 2006; 47(3) 47(3) : 198 : 1 Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients Parmar H, Golay
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection. Page inserted by evaluation version
 PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 August 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 August ; 143(2): 304 306. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2010.03.012. Application of diffusion tensor imaging
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 August ; 143(2): 304 306. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2010.03.012. Application of diffusion tensor imaging
Perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI) and diffusionweighted
 Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Thresholds Do Not Predict the Response to Acute Stroke Thrombolysis Poh-Sien Loh, FRACP; Ken S. Butcher, MD, PhD, FRCP(C), FRACP; Mark W. Parsons, PhD, FRACP; Lachlan MacGregor,
Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Thresholds Do Not Predict the Response to Acute Stroke Thrombolysis Poh-Sien Loh, FRACP; Ken S. Butcher, MD, PhD, FRCP(C), FRACP; Mark W. Parsons, PhD, FRACP; Lachlan MacGregor,
Characterization and Evolution of Diffusion MR Imaging Abnormalities in Stroke Patients Undergoing Intra-Arterial Thrombolysis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:951 957, June/July 2004 Characterization and Evolution of Diffusion MR Imaging Abnormalities in Stroke Patients Undergoing Intra-Arterial Thrombolysis Pamela W. Schaefer, Alvand
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:951 957, June/July 2004 Characterization and Evolution of Diffusion MR Imaging Abnormalities in Stroke Patients Undergoing Intra-Arterial Thrombolysis Pamela W. Schaefer, Alvand
Intraoperative Diffusion Imaging on a 0.5 Tesla Interventional Scanner
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 13:115 119 (2001) Original Research Intraoperative Diffusion Imaging on a 0.5 Tesla Interventional Scanner Yoshiaki Mamata, MD, PhD, Hatsuho Mamata, MD, Arya Nabavi,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 13:115 119 (2001) Original Research Intraoperative Diffusion Imaging on a 0.5 Tesla Interventional Scanner Yoshiaki Mamata, MD, PhD, Hatsuho Mamata, MD, Arya Nabavi,
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Research Article Corticospinal Tract Change during Motor Recovery in Patients with Medulla Infarct: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 524096, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/524096 Research Article Corticospinal Tract Change during Motor Recovery in Patients with Medulla Infarct: A Diffusion
BioMed Research International, Article ID 524096, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/524096 Research Article Corticospinal Tract Change during Motor Recovery in Patients with Medulla Infarct: A Diffusion
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive
 Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Identifies the Clinically Relevant Small-Penetrator Infarcts
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Identifies the Clinically Relevant Small-Penetrator Infarcts Jamary Oliveira-Filho, MD; Hakan Ay, MD; Pamela W. Schaefer, MD; Ferdinando
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Identifies the Clinically Relevant Small-Penetrator Infarcts Jamary Oliveira-Filho, MD; Hakan Ay, MD; Pamela W. Schaefer, MD; Ferdinando
Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1491 1499, September 1999 Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Andrew L. Tievsky, Thomas
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1491 1499, September 1999 Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Andrew L. Tievsky, Thomas
Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology
 Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology Dr. Alberto Bizzi Neuroradiology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta Milan, Italy Email: alberto_bizzi@fastwebnet.it Diffusion
Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology Dr. Alberto Bizzi Neuroradiology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta Milan, Italy Email: alberto_bizzi@fastwebnet.it Diffusion
Magnetic resonance imaging (MR!) provides
 0 Wallerian Degeneration of the Pyramidal Tract in Capsular Infarction Studied by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jesiis Pujol, MD, Josep L. Marti-Vilalta, MD, Carme Junqu6, PhD, Pere Vendrell, PhD, Juan Fernandez,
0 Wallerian Degeneration of the Pyramidal Tract in Capsular Infarction Studied by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jesiis Pujol, MD, Josep L. Marti-Vilalta, MD, Carme Junqu6, PhD, Pere Vendrell, PhD, Juan Fernandez,
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016)
 International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry
 WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) has become an important
 Serial Study of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Anisotropy in Patients With Acute Stroke Qing Yang, PhD; Brian M. Tress, MD, FRACR; P. Alan Barber, FRACP; Patricia M. Desmond, MSc, FRACR; David G. Darby,
Serial Study of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Anisotropy in Patients With Acute Stroke Qing Yang, PhD; Brian M. Tress, MD, FRACR; P. Alan Barber, FRACP; Patricia M. Desmond, MSc, FRACR; David G. Darby,
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Andrew Steven March 23, 2018 Ochsner Neuroscience Symposium None Disclosure 1 Objectives Review basic principles of BOLD fmri and DTI. Discuss indications and
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Andrew Steven March 23, 2018 Ochsner Neuroscience Symposium None Disclosure 1 Objectives Review basic principles of BOLD fmri and DTI. Discuss indications and
A nimal experiments and post-mortem examinations have
 PAPER A prospective study of secondary degeneration following subcortical infarction using diffusion tensor imaging Zhijian Liang, Jinsheng Zeng, Sirun Liu, Xueying Ling, Anding Xu, Jian Yu, Li Ling...
PAPER A prospective study of secondary degeneration following subcortical infarction using diffusion tensor imaging Zhijian Liang, Jinsheng Zeng, Sirun Liu, Xueying Ling, Anding Xu, Jian Yu, Li Ling...
Kurtosis is a descriptor of the peakedness of a variable relative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
Predicting Cerebral Ischemic Infarct Volume with Diffusion and Perfusion MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1785 1794, November/December 2002 Predicting Cerebral Ischemic Infarct Volume with Diffusion and Perfusion MR Imaging Pamela W. Schaefer, George J. Hunter, Julian He, Leena M.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1785 1794, November/December 2002 Predicting Cerebral Ischemic Infarct Volume with Diffusion and Perfusion MR Imaging Pamela W. Schaefer, George J. Hunter, Julian He, Leena M.
During human aging, the brain exhibits both macro- and
 Published November 5, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1862 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Q. Wang X. Xu M. Zhang Normal Aging in the Basal Ganglia Evaluated by Eigenvalues of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Published November 5, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1862 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Q. Wang X. Xu M. Zhang Normal Aging in the Basal Ganglia Evaluated by Eigenvalues of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Diffusion MRI explores new indications
 DECEMBER 2001 Diffusion MRI finds new indications Neuroimaging expands with functional MRI 3-tesla MRI bests 1.5-tesla in body and brain Diffusion MRI explores new indications Diffusion tensor imaging
DECEMBER 2001 Diffusion MRI finds new indications Neuroimaging expands with functional MRI 3-tesla MRI bests 1.5-tesla in body and brain Diffusion MRI explores new indications Diffusion tensor imaging
Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 20:555 562 (2004) Original Research Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 20:555 562 (2004) Original Research Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!!
 Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!! Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Agawane, M. R. Verma, D. P.
Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!! Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Agawane, M. R. Verma, D. P.
Diffusion Tensor Imaging 12/06/2013
 12/06/2013 Beate Diehl, MD PhD FRCP University College London National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure None Learning
12/06/2013 Beate Diehl, MD PhD FRCP University College London National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure None Learning
Diffusion Tensor Imaging Assessment of Brain White Matter Maturation During the First Postnatal Year
 DTI of White Matter in infants Neuroradiology Original Research James M. Provenzale 1 Luxia Liang 1,2 David DeLong 1 Leonard E. White 3 Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE Keywords: anisotropy,
DTI of White Matter in infants Neuroradiology Original Research James M. Provenzale 1 Luxia Liang 1,2 David DeLong 1 Leonard E. White 3 Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE Keywords: anisotropy,
CSM is the most common cause of spinal cord dysfunction
 Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic?
 Current Literature In Clinical Science Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic? Spatial Patterns of Water Diffusion Along White Matter Tracts in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.
Current Literature In Clinical Science Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic? Spatial Patterns of Water Diffusion Along White Matter Tracts in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain
 DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
Traumatic injuries of the cervical spine are potentially catastrophic.
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Shanmuganathan R.P. Gullapalli J. Zhuo S.E. Mirvis Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging in Cervical Spine Trauma BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our aim was to investigate the extent and severity of
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Shanmuganathan R.P. Gullapalli J. Zhuo S.E. Mirvis Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging in Cervical Spine Trauma BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our aim was to investigate the extent and severity of
Professional boxing is a controversial sport, and research
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
Clinical Experience with Diffusion-Weighted MR in Patients with Acute Stroke
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1061 1066, June 1998 Clinical Experience with Diffusion-Weighted MR in Patients with Acute Stroke Karl-Olof Lövblad, Hans-Joachim Laubach, Alison E. Baird, François Curtin, Gottfried
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1061 1066, June 1998 Clinical Experience with Diffusion-Weighted MR in Patients with Acute Stroke Karl-Olof Lövblad, Hans-Joachim Laubach, Alison E. Baird, François Curtin, Gottfried
Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging
 Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging Yoshiyuki Nomura, Hajime Sakuma, Kan Takeda, Tomoyasu Tagami, Yasuyuki Okuda,
Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging Yoshiyuki Nomura, Hajime Sakuma, Kan Takeda, Tomoyasu Tagami, Yasuyuki Okuda,
Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Prognostic Indicator in the Deep Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Prognostic Indicator in the Deep Intracerebral Hemorrhage 1 Department of Neurosurgery, Pundang CHA Hospital, Pochon CHA University, Seongnam, Korea 2 Department
Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Prognostic Indicator in the Deep Intracerebral Hemorrhage 1 Department of Neurosurgery, Pundang CHA Hospital, Pochon CHA University, Seongnam, Korea 2 Department
Predicting Final Infarct Size Using Acute and Subacute Multiparametric MRI Measurements in Patients With Ischemic Stroke
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 21:495 502 (2005) Original Research Predicting Final Infarct Size Using Acute and Subacute Multiparametric MRI Measurements in Patients With Ischemic Stroke Mei Lu,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 21:495 502 (2005) Original Research Predicting Final Infarct Size Using Acute and Subacute Multiparametric MRI Measurements in Patients With Ischemic Stroke Mei Lu,
Transient Ischemic Attack and Stroke Can Be Differentiated by Analyzing the Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Original rticle DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.280 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):280-288 Transient Ischemic ttack and Stroke Can e Differentiated by nalyzing the Diffusion Tensor
Original rticle DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.280 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):280-288 Transient Ischemic ttack and Stroke Can e Differentiated by nalyzing the Diffusion Tensor
Assessing Tissue Viability with MR Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:436 443, March 2003 Assessing Tissue Viability with MR Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging Pamela W. Schaefer, Yelda Ozsunar, Julian He, Leena M. Hamberg, George J. Hunter, A. Gregory
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:436 443, March 2003 Assessing Tissue Viability with MR Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging Pamela W. Schaefer, Yelda Ozsunar, Julian He, Leena M. Hamberg, George J. Hunter, A. Gregory
CT Perfusion Parameter Values in Regions of Diffusion Abnormalities
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1205 1210, August 2004 CT Perfusion Parameter Values in Regions of Diffusion Abnormalities Marcello Galvez, Gerald E. York, II, and James D. Eastwood BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Dynamic
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1205 1210, August 2004 CT Perfusion Parameter Values in Regions of Diffusion Abnormalities Marcello Galvez, Gerald E. York, II, and James D. Eastwood BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Dynamic
Neonatal Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy: Detection with Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :9 96, September Neonatal Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy: Detection with Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Kirsten P. N. Forbes, James G. Pipe, and Roger Bird BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :9 96, September Neonatal Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy: Detection with Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Kirsten P. N. Forbes, James G. Pipe, and Roger Bird BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Traumatic axonal injury is a frequent cause of impaired clinical
 Published July 10, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1213 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.R. Rutgers P. Fillard G. Paradot M. Tadié P. Lasjaunias D. Ducreux Diffusion Tensor Imaging Characteristics of the Corpus Callosum in Mild,
Published July 10, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1213 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.R. Rutgers P. Fillard G. Paradot M. Tadié P. Lasjaunias D. Ducreux Diffusion Tensor Imaging Characteristics of the Corpus Callosum in Mild,
POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES
 Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
High b-value q-space diffusion MRI in myelin-deficient rat spinal cords
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging 24 (2006) 161 166 High b-value q-space diffusion MRI in myelin-deficient rat spinal cords Inbal E. Biton a, Ian D. Duncan b, Yoram Cohen a, 4 a School of Chemistry, The Sackler
Magnetic Resonance Imaging 24 (2006) 161 166 High b-value q-space diffusion MRI in myelin-deficient rat spinal cords Inbal E. Biton a, Ian D. Duncan b, Yoram Cohen a, 4 a School of Chemistry, The Sackler
Diffusion tensor imaging detects Wallerian degeneration of the corticospinal tract early after cerebral infarction**
 NEUAL EGENEATION ESEACH Volume 7, Issue 12, April 2012 www.nrronline.org Cite this article as: Neural egen es. 2012;7(12):900-905. Diffusion tensor imaging detects Wallerian degeneration of the corticospinal
NEUAL EGENEATION ESEACH Volume 7, Issue 12, April 2012 www.nrronline.org Cite this article as: Neural egen es. 2012;7(12):900-905. Diffusion tensor imaging detects Wallerian degeneration of the corticospinal
Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to
 125 A B C Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to obtain entire dimension of the hippocampal body.
125 A B C Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to obtain entire dimension of the hippocampal body.
MRI of newly developing MS lesions provides a window
 Published May 10, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2975 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Eisele K. Szabo M. Griebe C. Roßmanith A. Förster M. Hennerici A. Gass Reduced Diffusion in a Subset of Acute MS Lesions: A Serial Multiparametric
Published May 10, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2975 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Eisele K. Szabo M. Griebe C. Roßmanith A. Förster M. Hennerici A. Gass Reduced Diffusion in a Subset of Acute MS Lesions: A Serial Multiparametric
MRI of newly developing MS lesions provides a window
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Eisele K. Szabo M. Griebe C. Roßmanith A. Förster M. Hennerici A. Gass Reduced Diffusion in a Subset of Acute MS Lesions: A Serial Multiparametric MRI Study BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Eisele K. Szabo M. Griebe C. Roßmanith A. Förster M. Hennerici A. Gass Reduced Diffusion in a Subset of Acute MS Lesions: A Serial Multiparametric MRI Study BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Diffusion- and Perfusion-Weighted MRI. The DWI/PWI Mismatch Region in Acute Stroke
 Diffusion- and Perfusion-Weighted MRI The DWI/PWI Mismatch Region in Acute Stroke Tobias Neumann-Haefelin, MD; Hans-Jörg Wittsack, PhD; Frank Wenserski, MD; Mario Siebler, MD; Rüdiger J. Seitz, MD; Ulrich
Diffusion- and Perfusion-Weighted MRI The DWI/PWI Mismatch Region in Acute Stroke Tobias Neumann-Haefelin, MD; Hans-Jörg Wittsack, PhD; Frank Wenserski, MD; Mario Siebler, MD; Rüdiger J. Seitz, MD; Ulrich
occlusions. Cerebral perfusion is driven fundamentally by regional cerebral
 Appendix Figures Figure A1. Hemodynamic changes that may occur in major anterior circulation occlusions. Cerebral perfusion is driven fundamentally by regional cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP). In response
Appendix Figures Figure A1. Hemodynamic changes that may occur in major anterior circulation occlusions. Cerebral perfusion is driven fundamentally by regional cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP). In response
Diffusion tensor imaging of normal prostate at 3 T: effect of number of diffusion-encoding directions on quantitation and image quality
 The British Journal of Radiology, 85 (2012), e279 e283 Diffusion tensor imaging of normal prostate at 3 T: effect of number of diffusion-encoding directions on quantitation and image quality C K KIM, MD,
The British Journal of Radiology, 85 (2012), e279 e283 Diffusion tensor imaging of normal prostate at 3 T: effect of number of diffusion-encoding directions on quantitation and image quality C K KIM, MD,
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry
 2003 KHBM DTI in Psychiatry Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry KHBM 2003. 11. 21. 서울대학교 의과대학 정신과학교실 권준수 Neuropsychiatric conditions DTI has been studied in Alzheimer s disease Schizophrenia Alcoholism
2003 KHBM DTI in Psychiatry Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry KHBM 2003. 11. 21. 서울대학교 의과대학 정신과학교실 권준수 Neuropsychiatric conditions DTI has been studied in Alzheimer s disease Schizophrenia Alcoholism
Journal of Ningxia Medical University. Diffusion Weighted Imaging DWI b 500 s / mm s / mm 2
 786 Journal of Ningxia Medical University 34 8 2012 8 1674-6309 2012 08-0786 - 04 MRI 1 2 2 2 2 1 1. 750002 2. 750004 MR Diffusion Weighted Imaging DWI 27 38 DWI2 b 500 s / mm 2 1000 s / mm 2 Apparent
786 Journal of Ningxia Medical University 34 8 2012 8 1674-6309 2012 08-0786 - 04 MRI 1 2 2 2 2 1 1. 750002 2. 750004 MR Diffusion Weighted Imaging DWI 27 38 DWI2 b 500 s / mm 2 1000 s / mm 2 Apparent
DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy
 DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy Poster No.: C-2328 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors:
DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy Poster No.: C-2328 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors:
Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction
 Original Article ISSN (o):2321 7251 Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction Kalidindi Ravi Kumar Varma 1, Chaparla Lakshmana Rao 2 1 - Associate Professor,Maharajah
Original Article ISSN (o):2321 7251 Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction Kalidindi Ravi Kumar Varma 1, Chaparla Lakshmana Rao 2 1 - Associate Professor,Maharajah
Evolution of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient, Diffusion-weighted, and T2-weighted Signal Intensity of Acute Stroke
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:637 644, April 2001 Evolution of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient, Diffusion-weighted, and T2-weighted Signal Intensity of Acute Stroke Maarten G. Lansberg, Vincent N. Thijs, Michael
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:637 644, April 2001 Evolution of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient, Diffusion-weighted, and T2-weighted Signal Intensity of Acute Stroke Maarten G. Lansberg, Vincent N. Thijs, Michael
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most common peripheral
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2012; 18:60 66 Turkish Society of Radiology 2012 MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging in carpal tunnel syndrome Neslihan Taşdelen, Bengi Gürses, Özgür Kılıçkesmez,
Diagn Interv Radiol 2012; 18:60 66 Turkish Society of Radiology 2012 MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging in carpal tunnel syndrome Neslihan Taşdelen, Bengi Gürses, Özgür Kılıçkesmez,
Assessment of Tissue Viability Using Diffusion- and Perfusion-Weighted MRI in Hyperacute Stroke
 Assessment of Tissue Viability Using Diffusion- and Perfusion-Weighted MRI in Hyperacute Stroke Won-Jin Moon, MD 1, 2 Dong Gyu Na, MD 1, 3 Jae Wook Ryoo, MD 1, 4 Hong Gee Roh, MD 1 Hong Sik Byun, MD 1
Assessment of Tissue Viability Using Diffusion- and Perfusion-Weighted MRI in Hyperacute Stroke Won-Jin Moon, MD 1, 2 Dong Gyu Na, MD 1, 3 Jae Wook Ryoo, MD 1, 4 Hong Gee Roh, MD 1 Hong Sik Byun, MD 1
MRI Physics: Basic to Advanced
 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Neuroimaging MRI Physics: Basic to Advanced Mike Moseley, PhD Department of Radiology Stanford University CA 94305-5488 USA http://www-radiology.stanford.edu moseley@stanford.edu
Annual Meeting of the American Society of Neuroimaging MRI Physics: Basic to Advanced Mike Moseley, PhD Department of Radiology Stanford University CA 94305-5488 USA http://www-radiology.stanford.edu moseley@stanford.edu
Overview. Fundamentals of functional MRI. Task related versus resting state functional imaging for sensorimotor mapping
 Functional MRI and the Sensorimotor System in MS Nancy Sicotte, MD, FAAN Professor and Vice Chair Director, Multiple Sclerosis Program Director, Neurology Residency Program Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Functional MRI and the Sensorimotor System in MS Nancy Sicotte, MD, FAAN Professor and Vice Chair Director, Multiple Sclerosis Program Director, Neurology Residency Program Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is a major consequence
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Assaf L. Ben-Sira S. Constantini L.C. Chang L. Beni-Adani Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Hydrocephalus: Initial Experience PURPOSE AND BACKGROUND: Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is an
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Assaf L. Ben-Sira S. Constantini L.C. Chang L. Beni-Adani Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Hydrocephalus: Initial Experience PURPOSE AND BACKGROUND: Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is an
Evidence for Cytotoxic Edema in the Pathogenesis of Cerebral Venous Infarction
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:450 455, March 200 Evidence for Cytotoxic Edema in the Pathogenesis of Cerebral Venous Infarction Kirsten P.N. Forbes, James G. Pipe, and Joseph E. Heiserman BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:450 455, March 200 Evidence for Cytotoxic Edema in the Pathogenesis of Cerebral Venous Infarction Kirsten P.N. Forbes, James G. Pipe, and Joseph E. Heiserman BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Hypoglycemic encephalopathy mimicking acute ischemic stroke in clinical presentation and magnetic resonance imaging: a case report
 Chuang et al. BMC Medical Imaging (2019) 19:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-019-0310-z CASE REPORT Hypoglycemic encephalopathy mimicking acute ischemic stroke in clinical presentation and magnetic resonance
Chuang et al. BMC Medical Imaging (2019) 19:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-019-0310-z CASE REPORT Hypoglycemic encephalopathy mimicking acute ischemic stroke in clinical presentation and magnetic resonance
Heejin Shim, Hyun Seok Choi, So-Lyung Jung, Kook-Jin Ahn, Bum-soo Kim
 Susceptibility Weighted MR Imaging at 3T in Patients with Occlusion of Middle Cerebral Artery : Comparison with Diffusion Weighted Imaging Score (ASPECTS) Heejin Shim, Hyun Seok Choi, So-Lyung Jung, Kook-Jin
Susceptibility Weighted MR Imaging at 3T in Patients with Occlusion of Middle Cerebral Artery : Comparison with Diffusion Weighted Imaging Score (ASPECTS) Heejin Shim, Hyun Seok Choi, So-Lyung Jung, Kook-Jin
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Patients With Major Cerebral Artery Occlusive Disease
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 43, 421 426, 2003 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Patients With Major Cerebral Artery Occlusive Disease Takashi INOUE, KuniakiOGASAWARA, HiromuKONNO, AkiraOGAWA, and Hiroyuki KABASAWA*
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 43, 421 426, 2003 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Patients With Major Cerebral Artery Occlusive Disease Takashi INOUE, KuniakiOGASAWARA, HiromuKONNO, AkiraOGAWA, and Hiroyuki KABASAWA*
Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Tractography of Median Nerve: Normative Diffusion Values
 Tractography of Median Nerve Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Neslihan Kabakci 1 Bengi Gürses 1 Zeynep Firat 1 Ali Bayram 1 Aziz Müfit Uluğ 2,3 Arzu Kovanlıkaya 1 İlhami Kovanlıkaya 1 Kabakci
Tractography of Median Nerve Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Neslihan Kabakci 1 Bengi Gürses 1 Zeynep Firat 1 Ali Bayram 1 Aziz Müfit Uluğ 2,3 Arzu Kovanlıkaya 1 İlhami Kovanlıkaya 1 Kabakci
Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience
 African Journal of Nephrology (2009) 13: 26-30 Original Article AJN Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience Mohamed Abou El-Ghar; M.D, Huda Refaie;
African Journal of Nephrology (2009) 13: 26-30 Original Article AJN Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience Mohamed Abou El-Ghar; M.D, Huda Refaie;
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Cases with Visual Field Defect after Anterior Temporal Lobectomy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:797 803, April 2005 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Cases with Visual Field Defect after Anterior Temporal Lobectomy Toshiaki Taoka, Masahiko Sakamoto, Satoru Iwasaki, Hiroyuki Nakagawa,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:797 803, April 2005 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Cases with Visual Field Defect after Anterior Temporal Lobectomy Toshiaki Taoka, Masahiko Sakamoto, Satoru Iwasaki, Hiroyuki Nakagawa,
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
Magnetic resonance (MR) diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is
 Diagn Interv Radiol DOI 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3892-10.1 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla: normative values and repeatability
Diagn Interv Radiol DOI 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3892-10.1 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla: normative values and repeatability
Injuries of neural tracts in a patient with CADASIL: a diffusion tensor imaging study
 Jang and Seo BMC Neurology (2015) 15:176 DOI 10.1186/s12883-015-0434-x CASE REPORT Open Access Injuries of neural tracts in a patient with CADASIL: a diffusion tensor imaging study Sung Ho Jang and You
Jang and Seo BMC Neurology (2015) 15:176 DOI 10.1186/s12883-015-0434-x CASE REPORT Open Access Injuries of neural tracts in a patient with CADASIL: a diffusion tensor imaging study Sung Ho Jang and You
Association of Early CT Abnormalities, Infarct Size, and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Reduction in Acute Ischemic Stroke
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:933 938, June/July 2004 Association of Early CT Abnormalities, Infarct Size, and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Reduction in Acute Ischemic Stroke Diederik M. Somford, Michael
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:933 938, June/July 2004 Association of Early CT Abnormalities, Infarct Size, and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Reduction in Acute Ischemic Stroke Diederik M. Somford, Michael
Prediction of Hemorrhage in Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Permeability MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2213 2217, October 2005 Technical Note Prediction of Hemorrhage in Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Permeability MR Imaging Andrea Kassner, Timothy Roberts, Keri Taylor, Frank Silver,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2213 2217, October 2005 Technical Note Prediction of Hemorrhage in Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Permeability MR Imaging Andrea Kassner, Timothy Roberts, Keri Taylor, Frank Silver,
Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
Diffusion Anisotropy of the Internal Capsule and the Corona Radiata in Association with Stroke and Tumors as Measured by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :56 6, March 1 Diffusion Anisotropy of the Internal Capsule and the Corona Radiata in Association with Stroke and Tumors as Measured by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Shuichi Higano,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :56 6, March 1 Diffusion Anisotropy of the Internal Capsule and the Corona Radiata in Association with Stroke and Tumors as Measured by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Shuichi Higano,
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury
 Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury Stéphane Sizonenko, MD-PhD Division of Development and Growth Department of Child and Adolescent Medicine Geneva University
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury Stéphane Sizonenko, MD-PhD Division of Development and Growth Department of Child and Adolescent Medicine Geneva University
Introduction. Abstract. Michael Yannes 1, Jennifer V. Frabizzio, MD 1, and Qaisar A. Shah, MD 1 1
 Reversal of CT hypodensity after acute ischemic stroke Michael Yannes 1, Jennifer V. Frabizzio, MD 1, and Qaisar A. Shah, MD 1 1 Abington Memorial Hospital in Abington, Pennsylvania Abstract We report
Reversal of CT hypodensity after acute ischemic stroke Michael Yannes 1, Jennifer V. Frabizzio, MD 1, and Qaisar A. Shah, MD 1 1 Abington Memorial Hospital in Abington, Pennsylvania Abstract We report
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Relationship Between Magnetic Resonance Arterial Patency and Perfusion-Diffusion in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Its Potential Clinical Use Irina A. Staroselskaya, MD; Claudia Chaves,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Relationship Between Magnetic Resonance Arterial Patency and Perfusion-Diffusion in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Its Potential Clinical Use Irina A. Staroselskaya, MD; Claudia Chaves,
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 19:6 18 (2004) Invited Review Clinical Applications of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Qian Dong, MD, Robert C. Welsh, PhD,* Thomas L. Chenevert, PhD, Ruth C. Carlos, MD,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 19:6 18 (2004) Invited Review Clinical Applications of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Qian Dong, MD, Robert C. Welsh, PhD,* Thomas L. Chenevert, PhD, Ruth C. Carlos, MD,
Dominant Limb Motor Impersistence Associated with Anterior Callosal Disconnection
 Dominant Limb Motor Impersistence Associated with Anterior Callosal Disconnection S. W. Seo, MD, 1 K. Jung, MS, 2 H. You, PhD 2, E. J. Kim, MD, PhD 1, B. H. Lee, MA, 1 D. L. Na, MD 1 1 Department of Neurology,
Dominant Limb Motor Impersistence Associated with Anterior Callosal Disconnection S. W. Seo, MD, 1 K. Jung, MS, 2 H. You, PhD 2, E. J. Kim, MD, PhD 1, B. H. Lee, MA, 1 D. L. Na, MD 1 1 Department of Neurology,
Imaging Modalities in Acute Stroke: Time is Brain
 April 2001 Imaging Modalities in Acute Stroke: Time is Brain Jeremiah Scharf, Harvard Medical School, MS IV Beth Israel-Deaconess Medical Center Department of Radiology Stroke - Definition and Statistics
April 2001 Imaging Modalities in Acute Stroke: Time is Brain Jeremiah Scharf, Harvard Medical School, MS IV Beth Israel-Deaconess Medical Center Department of Radiology Stroke - Definition and Statistics
High b value DWI in evaluation of the hyperacute cerebral ischemia at 3T: A comparative study in an embolic canine stroke model
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 12: 951-956, 2016 High b value DWI in evaluation of the hyperacute cerebral ischemia at 3T: A comparative study in an embolic canine stroke model QIGUANG CHENG 1*,
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 12: 951-956, 2016 High b value DWI in evaluation of the hyperacute cerebral ischemia at 3T: A comparative study in an embolic canine stroke model QIGUANG CHENG 1*,
Rapid Regression of White Matter Changes in Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy
 www.ksmrm.org JKSMRM 18(4) : 357-361, 2014 pissn 1226-9751 / eissn 2288-3800 Case Report Rapid Regression of White Matter Changes in Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy Sang-wook Son, Kye-ho Lee, Dong-soo Yoo
www.ksmrm.org JKSMRM 18(4) : 357-361, 2014 pissn 1226-9751 / eissn 2288-3800 Case Report Rapid Regression of White Matter Changes in Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy Sang-wook Son, Kye-ho Lee, Dong-soo Yoo
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Acute Corticospinal Tract Injury Preceding Wallerian Degeneration in the Maturing Human Brain
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1057 1066, June/July 2003 Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Acute Corticospinal Tract Injury Preceding Wallerian Degeneration in the Maturing Human Brain Avi Mazumdar, Pratik Mukherjee,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1057 1066, June/July 2003 Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Acute Corticospinal Tract Injury Preceding Wallerian Degeneration in the Maturing Human Brain Avi Mazumdar, Pratik Mukherjee,
MR Diffusion Imaging of Cerebral Infarction in Humans
 MR Diffusion Imaging of Cerebral Infarction in Humans Daisy Chien, 1 Kenneth K. Kwong, 2 Daryl R. Gress, 3 Ferdinand S. Buonanno, 3 Richard B. Buxton, 4 and Bruce R. Rosen 2 5 Purpose: MR diffusion imaging
MR Diffusion Imaging of Cerebral Infarction in Humans Daisy Chien, 1 Kenneth K. Kwong, 2 Daryl R. Gress, 3 Ferdinand S. Buonanno, 3 Richard B. Buxton, 4 and Bruce R. Rosen 2 5 Purpose: MR diffusion imaging
Cerebral Fractional Anisotropy Score in Trauma Patients: A New Indicator of White Matter Injury After Trauma
 Thomas Ptak 1 Robert L. Sheridan 2 James T. Rhea 1 Alice A. Gervasini 2 Jong H. Yun 3 Marjorie A. Curran 4 Pierre Borszuk 5 Laurie Petrovick 2 Robert A. Novelline 1 Received March 21, 2003; accepted after
Thomas Ptak 1 Robert L. Sheridan 2 James T. Rhea 1 Alice A. Gervasini 2 Jong H. Yun 3 Marjorie A. Curran 4 Pierre Borszuk 5 Laurie Petrovick 2 Robert A. Novelline 1 Received March 21, 2003; accepted after
