MRI of newly developing MS lesions provides a window
|
|
|
- Curtis Wilson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Eisele K. Szabo M. Griebe C. Roßmanith A. Förster M. Hennerici A. Gass Reduced Diffusion in a Subset of Acute MS Lesions: A Serial Multiparametric MRI Study BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: MRI studies have focused on newly developing MS lesions to characterize the early pathology of the disease. DWI is highly sensitive to acute and chronic tissue changes in MS. We characterized the development of acute MS lesions by using DWI in a multiparametric MRI protocol. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Seventy-two consecutive patients presenting with a new symptom with definite MS or a CIS suggestive of central nervous system demyelination were screened with MRI. Patients who showed an acute MRI lesion with a reduction of ADC were studied with serial MRI for up to 4 months after presentation. RESULTS: Ten of 72 screened patients who showed a lesion with a reduced ADC were each examined 4 7 times, resulting in 52 examinations in total. We identified a characteristic sequence of signalintensity changes: 1) days 0 7: slight T2 hyperintensity and prominent ADC reduction (maximum, 66%), faint or no enhancement on postcontrast T1-weighted images; 2) days 7 10: prominent T2 hyperintensity and contrast enhancement, ADC normalization/pseudonormalization; 3) up to 4 weeks: elevated ADC values, prominent enhancement on postcontrast images; 4) after 4 weeks: partial reversibility of T2 hyperintensity, ADC elevation, and resolution of contrast enhancement. CONCLUSIONS: In a subgroup of patients with MS presenting soon after new symptom onset, a transient reduction of the ADC delineated a short and very early phase of MS lesion evolution. Subsequent pseudonormalization of the ADC occurred along with signs of the development of vasogenic edema. ABBREVIATIONS: CIS clinically isolated syndrome; EP echo-planar; NAWM normal-appearing white matter; RRMS relapsing-remitting MS Received August 23, 2011; accepted after revision October 28. From the Department of Neurology, UniversitätsMedizin Mannheim, University of Heidelberg, Mannheim, Germany. Please address correspondence to Achim Gass, MD, Department of Neurology, UniversitätsMedizin Mannheim, University of Heidelberg, Theodor-Kutzer-Ufer 1 3, Mannheim, Germany; achim.gass@medma.uni-heidelberg.de Indicates open access to non-subscribers at MRI of newly developing MS lesions provides a window to the early pathology of MS. The development of new lesions has, therefore, been the focus of numerous MRI studies. Increased permeability of the BBB on postcontrast T1- weighted MRI and new hyperintensities on T2-weighted images are usually the earliest clearly visible conventional MRI signs of new lesions. 1,2 DWI investigates water mobility, which is increased in chronic lesions and in acute vasogenic edema in MS. 3-5 This increase is thought to reflect expanded extracellular space, even though the individual contributions from edema, demyelination, and axonal loss are yet unknown. 6-8 DWI also may detect reductions of normal water mobility, which is typically but not exclusively demonstrated in acute ischemic stroke. 9,10 Reductions in water mobility are identified as hyperintense DWI signal intensity and corresponding low signal intensity on maps of the ADC. Most MRI studies report an increased ADC in acute MS lesions. However in a relatively small number of patients with MS and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, a reduction of the ADC in the very early phase in acute MS lesions has also been documented. 7,11 Several recent case studies have reported a reduced ADC in acute demyelinating lesions and have emphasized their strokelike ADC appearance The temporal evolution of the ADC signal intensity has been well characterized in acute ischemic stroke showing typical phases of an initial reduction, followed by a pseudonormalization and an ADC elevation in the subacute-to-chronic phases. 9,16 In this study, we report the development of multiparametric MRI signal-intensity characteristics in hyperacute lesions of patients with MS with the main focus on the time course of the ADC signal intensity. Materials and Methods Patient Selection A total of 72 patients who presented with an acute new symptom were investigated with MRI before steroid treatment. The patients had either definite MS or a CIS suggestive of central nervous system demyelination. Patients who showed a lesion with a reduced ADC that appeared suitable ( 1 cm) for a quantitative analysis were followed with serial MRI after the initial examination. The study was designed for frequent follow-up MRI examinations during 4 months after the initial presentation. The study was approved by the local ethics committee, and informed consent was obtained in written form from all patients. MRI Initial and follow-up MRI studies were performed on a 1.5T MRI system (Magnetom Sonata; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). A standardized protocol was used in all patients: 1) transverse, coronal, and sagittal localizing sequences followed by transverse oblique contiguous 5-mm sections aligned with the inferior borders of the corpus callosum; 2) T2-weighted images; 3) T1-weighted images; 4) FLAIR BRAIN ORIGINAL RESEARCH AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33: August
2 Table 1: Summary of clinical data No. Age (yr)/ Sex Disease Duration/ Diagnosis New Clinical Symptoms Symptom Onset to MRI (days) Max. ADC 2 Treatment Acute/Prophylaxis 1 19/F 2 yr/rrms Right internuclear ophthalmoplegia 1 41% IV cortisone/interferon 2 21/F 1 yr/rrms Dysarthria 0 66% IV cortisone/ 3 20/F 1 yr/rrms Vertigo, left-sided numbness % IV cortisone/ 4 45/F 1.5 yr/rrms Right-sided weakness 2 20% IV cortisone/ 5 25/F 1 yr/rrms Dysarthria, right-sided weakness 4 17% IV cortisone/ 6 25/F Initial presentation/cis Dysarthria, left-sided weakness 2 51% IV cortisone/ and numbness 7 30/F 1.5 yr/rrms Left-sided arm weakness 2 16% IV cortisone/ 8 33/F 0.5 yr/rrms Hemianopia 3 22% IV cortisone/ 9 31/M 1 yr/rrms N.V. numbness 1 24% IV cortisone/ 10 44/M 2 yr/rrms Right-sided weakness 3 41% IV cortisone/interferon Note: OCB indicates oligoclonal bands;, positive OCB;, negative OCB. OCB images; 5) DWI EP spin-echo images (TR/TE, 4000/110 ms; b 0/500/1000 s/mm 2 ; FOV, 240 mm 2 ; matrix size, ; sequential application of 3 separate diffusion-sensitizing gradients in perpendicular directions); and 6) T1-weighted images 10 minutes after manual injection of single-dose contrast agent (gadoterate dimeglumine [Dotarem; Guerbet, Aulnay-sous-Bois, France]). Data Processing and Analysis ADC maps were calculated on a pixel-by-pixel basis by a linear leastsquares fit after averaging of the direction-dependent DWI. The ADC value was determined by manual ROI analysis. ADC values were compared with those in the corresponding NAWM of the contralateral hemisphere. Signal-intensity ratios in the respective ROIs were also recorded on conventional MRI. Results Of the 72 patients with new acute symptoms, 10 showed a lesion with a reduced ADC that appeared suitable ( 1 cm) for a quantitative analysis. The lesion size ranged from 1.2 to 2.1 cm in the largest diameter in the transverse plane. Most patients were in the early phase of RRMS and were not on immunomodulatory treatment at the time of their relapse. The presenting new symptoms and further clinical information are given in Table 1. The mean delay between symptom onset and the first MRI examination was 47 hours. The patients were subsequently examined serially 4 7 times (mean, 5) with an interval of 2 days to 5 months, resulting in 52 examinations in total. Most patients had recovered fully from their relapse symptoms at 4 months. Time Course of the ADC in Acute MS Lesions The acute lesions were hyperintense on DWI at the initial measurement with a corresponding reduction of the ADC value relative to the contralateral normal-appearing brain tissue in every case. The mean ADC of control regions in healthy-appearing white matter correlated with previously obtained ADC values in healthy controls (for stroke studies). 17 The ADC was lowest on the initial MRI in all 10 patients and ranged between 66% and 17% (mean, 33.9%). Subsequently, the ADC value was increased at the second time point, to reach a pseudonormalization between days 7 and 10. The longest duration of an ADC reduction was observed in patient 2 (10 days), who also showed the most pronounced ADC reduction initially. At time points later than 4 weeks, in 6/10 Fig 1. Time course of intralesional ADC values during the first 90 days in all 10 patients. Note that measurements outside the 90-day range are not shown for better visualization of early time points. cases there was only a slight further increase of the ADC observed (Fig 1). MRI Signal-Intensity Changes on Conventional MRI On initial MRI, all lesions subject to analysis showed slight hyperintense signal intensity on T2-weighted images, which became more pronounced and increased in size (examples are shown in Figs 2 and 3) (Table 2). There was no enhancement on postcontrast T1-weighted images in 8/10 patients, while there was very slight contrast enhancement in 2/10 cases (patients 3 and 4), and it became more prominent, parallel to the ADC increase, sometimes parallel to the T2 signal-intensity hyperintensity. Reduced diffusion delineated a short very early phase of the evolution of symptomatic lesions. While lesions progressed to the typical acute edematous appearance (increase of T2 hyperintensity and contrast enhancement), the ADC increased parallel to pseudonormal and elevated values. Intrinsic Acute MS Lesion Patterns In 3 patients (patients 1, 2, and 4), a concentric arrangement of signal-intensity alterations and course was detected with a low ADC in the rim and an already increased ADC in the center of the lesion. This corresponded to a central enhancement, 1370 Eisele AJNR 33 August
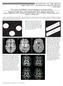
3 Fig 2. Exemplary ADC, contrast-enhanced T1-weighted, DWI, and FLAIR images of the first 4 MRI time points of patient 4 during the first 14 days after new symptom onset. The initially low ADC is associated with only slight T2 hyperintensity. The increasing ADC signal intensity on follow-ups is paralleled by the development of prominent T2 hyperintensity. Contrast enhancement is minimal in the zone of reduced ADC initially and becomes very prominent at time points 3 and 4. Fig 3. Exemplary ADC, DWI, contrast-enhanced T1-weighted, and T2-weighted images of the first 3 examinations of patient 9 in the first 15 days after new onset trigeminal sensory loss. The fascicular trigeminal fibers are affected by an acute lesion (circled in green). The lesion shows hyperintensity on DWI and a reduced ADC, while minimal T2 hyperintensity is noted without contrast enhancement on T1-weighted MRI initially. With time, the ADC pseudonormalizes and increases, while T2 hyperintensity and contrast enhancement become more prominent. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33: 兩 August 2012 兩
4 Table 2: Intralesional signal change on ADC and T2-weighted images a Patient Day Patient 1 Day 1 Day 8 Day 17 Day 55 ADC T Patient 2 Day 0 Day 7 Day 14 Day 21 Day 49 Day 83 Day 207 ADC T Patient 3 Day 1 Day 8 Day 35 Day 42 ADC T Patient 4 Day 2 Day 6 Day 10 Day 14 Day 85 Day 175 ADC T Patient 5 Day 4 Day 12 Day 20 Day 29 Day 65 ADC T Patient 6 Day 2 Day 6 Day 14 Day 28 ADC T Patient 7 Day 2 Day 10 Day 21 Day 30 Day 66 Day 106 ADC T Patient 8 Day 3 Day 6 Day 9 Day 21 Day 64 ADC T Patient 9 Day 1 Day 8 Day 15 Day 21 Day 34 ADC T Patient 10 Day 3 Day 15 Day 30 Day 37 Day 51 Day 66 ADC T a Values are given relative to the NAWM in the contralateral hemisphere. which regressed and was followed by an enhancement of the rim of the lesion at the time of ADC pseudonormalization. The intensity of the T2 signal intensity varied accordingly with high central signal intensity and an intermediate T2 hyperintensity in the periphery of the lesion. Discussion We searched for acute MS lesions with a reduced ADC and followed their evolution and signal-intensity changes serially. Our screening approach resulted in a highly selected lesion population that was identified in approximately 10/72 of the screened patients with acute MS. The subsequently detected time course of ADC change is interesting in several respects. Several reports have demonstrated increased ADC values both in acute contrast-enhancing and chronic MS lesions as well as in the NAWM, confirming that diffusion measurements are sensitive for detecting pathologic changes associated with states of increased water mobility. 3-5,8,18 In chronic MS lesions, the ADC increase is highly variable (most pronounced ADC increase in T1 hypointense lesions) and higher than that in NAWM; this finding confirms the concept that the severity of tissue matrix damage of MS lesions is heterogeneous. 8 It has been suggested that inflammatory vasogenic edema, axonal loss, and demyelination are the most likely pathologic substrates of increased ADC. 8 Our results are in line with these reports because we also observed an increase of the ADC in the subacute stages of lesion development. However, the main finding of this study is that a significant ADC reduction of up to 66% can be present as a transient (2 7 days) finding in the earliest/hyperacute phase of MRI lesion development in MS. The results of the time course of lesions with a reduced ADC demonstrate clearly that there is a very narrow time window to detect such lesions. We recruited patients in this study with a particular focus on a very early MRI after the onset of a new symptom, and MRI was therefore performed as soon as possible after patients came to our attention. Only patients presenting early after symptom onset showed lesions with a reduced ADC. Along with the gradual development of signs of prominent inflammatory edematous changes, the phase of ADC reduction is followed by transient brief pseudonormalization and a subsequent increase of the ADC (3 7 days after symptom onset). The rather faint contrast enhancement and only mild T2 hyperintensity in the hyperacute phase in our series indicate that the increased permeability of the BBB and edematous tissue change were not fully developed at this point. Contrast enhancement showed both a change with time in that it became more prominent and/or a change in the spatial distribution of enhancement starting in the center of the lesion and progressing sometimes in a centrifugal direction to the rim of the lesion. This is in accordance with serial studies of plaque evolution on MRI in patients with MS showing a centrifugal evolution of pathologic processes. 1 Two longitudinal studies that also used longer intervals between MRI examinations (minimum of 4 weeks) have observed increased ADC signal intensity in the lesions already at the first MRI. 5,6 We think that both patient selection and the time from symptom onset to the first MRI are important in this regard and that it might well be that the hyperacute phase was missed in these studies. Another cross-sectional study extrapolated different phases of lesion acuity by using DWI findings; however, this was done without the opportunity to ascertain DWI findings on serial analysis. 11 ADC reduction in the acute phase of MS lesions has been reported in several recent case studies, some stressing the strokelike appearance of their findings and resulting problems of differential diagnosis ,19 In contrast to MS, the evolution of the ADC has been analyzed in numerous studies in hyperacute ischemic stroke. 9,16 It may be for this reason that an ischemic mechanism has been suggested as involved in the ADC reduction. We would not share this view but favor another potential mechanism for the reduction of the ADC in MS. Lesion locations and clinical presentations of acute relapses in MS were very different from those in acute stroke. The location and extent of MS lesions did not match those in arterial vascular territories or lacunar stroke. Comparing the ADC time course of MS lesions with that of acute ischemic lesions is also made difficult by the fact that the onset of symptoms in MS is not as acute as in stroke and can therefore not be identified with the same precision. This is reflected by our symptom-to-mri times of days as opposed to a few hours in MRI studies of acute stroke. However, in contrast to a previous study of 2 patients with MS with a mild ADC reduction of 22% 33% in the acute lesions, we also found a pronounced ADC reduction in early lesions. 10 It is known that ischemia is not a prerequisite for the development of lesions with a reduced ADC as studies in patients after prolonged epileptic seizures have clearly shown. In these patients, ADC reductions of 11% 37% have been demon Eisele AJNR 33 August
5 strated, while signs of increased brain perfusion (due to the high energy demand) were noted in affected tissue. 20 A reduction of the ADC has been detected in different acute neurologic diseases (eg, stroke, 21,22 focal epilepsy, 23 toxic demyelination 24 ). We would favor an inflammatory mechanism that could lead to disturbances of energy metabolism, namely mitochondrial dysfunction, and, in turn, lead to reduced diffusion. This would be in line with recent evidence that an aggressive inflammatory milieu including tumor necrosis factor- and nitric oxide may lead to mitochondrial dysfunction and compromise of energy metabolism. 25 Furthermore, there is experimental evidence that lesions may exhibit a reduced ADC and contrast enhancement in central nervous system inflammation induced by intraparenchymal injection of interleukin It is also interesting in this respect that lesions with a low ADC in our study correlated with clinical symptoms, which would be in line with mitochondrial dysfunction and subsequent electrical compromise. Theoretically, these events might even take place in the absence of demyelination, which may be more prominent in slightly later stages of the lesion development. ADC reduction is present before MRI signs of tissue destruction become prominent and might be predominantly related to parenchymal inflammation. Most interesting, a new CSF marker of hypoxialike tissue damage in active MS lesions has recently been described, which may also point to a mechanism related to energy-metabolism compromise in MS lesions. 27 Further proposed hypotheses have been contributions from the presence of cytotoxic edema of oligodendroglia or hypercellularity in acute MS lesions. 11 These proposed mechanisms, disturbances of energy metabolism, and cytotoxic cell swelling and hypercellularity might well contribute to reduced diffusion. Conclusions In a subgroup of patients with MS presenting early after new symptom onset, a transient reduction of the ADC delineated a short and very early phase of MS lesion evolution. Subsequent pseudonormalization of the ADC occurred along with signs of the development of vasogenic edema. Further studies in larger patient samples are necessary to confirm and elucidate whether the observed MRI findings indeed indicate a small subgroup of active lesions. Such studies may also clarify whether early MRI immediately after new symptoms will increase the detection rate of reduced diffusion in acute MS lesions. Disclosures: Achim Gass UNRELATED: Travel/Accommodations/Meeting Expenses Unrelated to Activities Listed: honoraria for lecturing, travel expenses for attending meetings, and financial support for research from Bayer Schering, Biogen Idec, Merck Serono, Novartis, and Teva Neurosciences. References 1. Guttmann CR, Ahn SS, Hsu L, et al. The evolution of multiple sclerosis lesions on serial MR. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1995;16: Kermode AG, Thompson AJ, Tofts P, et al. Breakdown of the bloodbrain barrier precedes symptoms and other MRI signs of new lesions in multiple sclerosis. Pathogenetic and clinical implications. Brain 1990;113(pt 5): Schaefer PW, Grant PE, Gonzalez RG. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 2000;217: Horsfield MA, Larsson HB, Jones DK, et al. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1998;64(suppl 1):S Castriota-Scanderbeg A, Sabatini U, Fasano F, et al. Diffusion of water in large demyelinating lesions: a follow-up study. Neuroradiology 2002;44: Werring DJ, Brassat D, Droogan AG, et al. The pathogenesis of lesions and normal-appearing white matter changes in multiple sclerosis: a serial diffusion MRI study. Brain 2000;123(pt 8): Roychowdhury S, Maldjian JA, Grossman RI. Multiple sclerosis: comparison of trace apparent diffusion coefficients with MR enhancement pattern of lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2000;21: Cercignani M, Iannucci G, Rocca MA, et al. Pathologic damage in MS assessed by diffusion-weighted and magnetization transfer MRI. Neurology 2000;54: Fiebach JB, Jansen O, Schellinger PD, et al. Serial analysis of the apparent diffusion coefficient time course in human stroke. Neuroradiology 2002; 44: Schlaug G, Siewert B, Benfield A, et al. Time course of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) abnormality in human stroke. Neurology 1997;49: Tievsky AL, Ptak T, Farkas J. Investigation of apparent diffusion coefficient and diffusion tensor anisotropy in acute and chronic multiple sclerosis lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1999;20: Rosso C, Remy P, Creange A, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging characteristics of an acute strokelike form of multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006;27: Przeklasa-Auth M, Ovbiagele B, Yim C, et al. Multiple sclerosis with initial stroke-like clinicoradiologic features: case report and literature review. J Child Neurol 2010;25: Balashov KE, Aung LL, Dhib-Jalbut S, et al. Acute multiple sclerosis lesion: conversion of restricted diffusion due to vasogenic edema. J Neuroimaging 2011;21: Bugnicourt JM, Garcia PY, Monet P, et al. Teaching neuroimages: marked reduced apparent diffusion coefficient in acute multiple sclerosis lesion. Neurology 2010;74:e Munoz Maniega S, Bastin ME, Armitage PA, et al. Temporal evolution of water diffusion parameters is different in grey and white matter in human ischaemic stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2004;75: Gass A, Gaa J, Sommer A, et al. Echo-planar diffusion-weighted MRI in the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke: characterisation of tissue abnormalities and limitations in the interpretation of imaging findings [in German]. Radiologe 1999;39: Rocca MA, Cercignani M, Iannucci G, et al. Weekly diffusion-weighted imaging of normal-appearing white matter in MS. Neurology 2000;55: Rovira A, Pericot I, Alonso J, et al. Serial diffusion-weighted MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopy of acute large demyelinating brain lesions: case report. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002;23: Szabo K, Poepel A, Pohlmann-Eden B, et al. Diffusion-weighted and perfusion MRI demonstrates parenchymal changes in complex partial status epilepticus. Brain 2005;128: Lovblad KO, Baird AE, Schlaug G, et al. Ischemic lesion volumes in acute stroke by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging correlate with clinical outcome. Ann Neurol 1997;42: Warach S, Dashe JF, Edelman RR. Clinical outcome in ischemic stroke predicted by early diffusion-weighted and perfusion magnetic resonance imaging: a preliminary analysis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1996;16: Wieshmann UC, Symms MR, Shorvon SD. Diffusion changes in status epilepticus. Lancet 1997;350: McKinney AM, Kieffer SA, Paylor RT, et al. Acute toxic leukoencephalopathy: potential for reversibility clinically and on MRI with diffusion-weighted and FLAIR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009;193: Su KG, Banker G, Bourdette D, et al. Axonal degeneration in multiple sclerosis: the mitochondrial hypothesis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2009;9: Blamire AM, Anthony DC, Rajagopalan B, et al. Interleukin-1beta -induced changes in blood-brain barrier permeability, apparent diffusion coefficient, and cerebral blood volume in the rat brain: a magnetic resonance study. J Neurosci 2000;20: Lassmann H, Reindl M, Rauschka H, et al. A new paraclinical CSF marker for hypoxia-like tissue damage in multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain 2003;126: AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33: August
MRI of newly developing MS lesions provides a window
 Published May 10, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2975 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Eisele K. Szabo M. Griebe C. Roßmanith A. Förster M. Hennerici A. Gass Reduced Diffusion in a Subset of Acute MS Lesions: A Serial Multiparametric
Published May 10, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2975 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Eisele K. Szabo M. Griebe C. Roßmanith A. Förster M. Hennerici A. Gass Reduced Diffusion in a Subset of Acute MS Lesions: A Serial Multiparametric
Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department
 298 / = Abstract = Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department Sung Pil Chung, M.D, Suk Woo Lee, M.D., Young Mo Yang, M.D., Young Rock Ha, M.D., Seung Whan Kim, M.D., and
298 / = Abstract = Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Emergency Department Sung Pil Chung, M.D, Suk Woo Lee, M.D., Young Mo Yang, M.D., Young Rock Ha, M.D., Seung Whan Kim, M.D., and
Naoaki Yamada, Satoshi Imakita, and Toshiharu Sakuma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging
 Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Noncontrast CT scan is currently the imaging modality
 Original Contributions MRI Features of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Within 2 Hours From Symptom Onset Italo Linfante, MD; Rafael H. Llinas, MD; Louis R. Caplan, MD; Steven Warach, MD, PhD Background and Purpose
Original Contributions MRI Features of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Within 2 Hours From Symptom Onset Italo Linfante, MD; Rafael H. Llinas, MD; Louis R. Caplan, MD; Steven Warach, MD, PhD Background and Purpose
The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke. Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV
 The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV Patient CR 62 yo F w/ 2 wk h/o altered mental status Presents to ED w/ confusion following a fall 1 day prior New onset left facial droop
The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV Patient CR 62 yo F w/ 2 wk h/o altered mental status Presents to ED w/ confusion following a fall 1 day prior New onset left facial droop
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Dong Gyu Na, Vincent N. Thijs, Gregory W. Albers, Michael E. Moseley, and Michael P. Marks. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25: , September 2004
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1331 1336, September 2004 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Acute Ischemia: Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Signal Intensity Thresholds in Predicting Tissue at Risk
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1331 1336, September 2004 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Acute Ischemia: Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Signal Intensity Thresholds in Predicting Tissue at Risk
Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1491 1499, September 1999 Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Andrew L. Tievsky, Thomas
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1491 1499, September 1999 Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Andrew L. Tievsky, Thomas
Kurtosis is a descriptor of the peakedness of a variable relative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Identifies the Clinically Relevant Small-Penetrator Infarcts
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Identifies the Clinically Relevant Small-Penetrator Infarcts Jamary Oliveira-Filho, MD; Hakan Ay, MD; Pamela W. Schaefer, MD; Ferdinando
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Identifies the Clinically Relevant Small-Penetrator Infarcts Jamary Oliveira-Filho, MD; Hakan Ay, MD; Pamela W. Schaefer, MD; Ferdinando
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Patients with Subacute Cerebral Ischemia: Comparison with Conventional and Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1596 1602, October 2000 Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Patients with Subacute Cerebral Ischemia: Comparison with Conventional and Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging Michael Augustin,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1596 1602, October 2000 Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Patients with Subacute Cerebral Ischemia: Comparison with Conventional and Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging Michael Augustin,
Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
CSM is the most common cause of spinal cord dysfunction
 Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Quantitative divusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging, cerebral atrophy, and disability in multiple sclerosis
 318 Division of Clinical Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, University Hospital, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham NG7 2UH, UK M Wilson X Lin B P Turner L D Blumhardt Division of Academic Radiology P S Morgan
318 Division of Clinical Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, University Hospital, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham NG7 2UH, UK M Wilson X Lin B P Turner L D Blumhardt Division of Academic Radiology P S Morgan
Tumefactive multiple sclerosis lesions: Diagnostic challenge for the radiologist
 Tumefactive multiple sclerosis lesions: Diagnostic challenge for the radiologist Poster No.: C-0679 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Gargallo Vaamonde, M. Iridoy Zulet, I. Rubio
Tumefactive multiple sclerosis lesions: Diagnostic challenge for the radiologist Poster No.: C-0679 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Gargallo Vaamonde, M. Iridoy Zulet, I. Rubio
Diffusion Tensor Imaging for the Differentiation of Microangiopathy, Infarction and Perfusion-Diffusion Mismatch Lesions 1
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging for the Differentiation of Microangiopathy, Infarction and Perfusion-Diffusion Mismatch Lesions 1 Dong-Ho Ha, M.D., Sunseob Choi, M.D., Myong-Jin Kang, M.D., Jin Hwa Lee, M.D.,
Diffusion Tensor Imaging for the Differentiation of Microangiopathy, Infarction and Perfusion-Diffusion Mismatch Lesions 1 Dong-Ho Ha, M.D., Sunseob Choi, M.D., Myong-Jin Kang, M.D., Jin Hwa Lee, M.D.,
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
Predicting Final Infarct Size Using Acute and Subacute Multiparametric MRI Measurements in Patients With Ischemic Stroke
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 21:495 502 (2005) Original Research Predicting Final Infarct Size Using Acute and Subacute Multiparametric MRI Measurements in Patients With Ischemic Stroke Mei Lu,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 21:495 502 (2005) Original Research Predicting Final Infarct Size Using Acute and Subacute Multiparametric MRI Measurements in Patients With Ischemic Stroke Mei Lu,
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences
 Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences Nils Daniel Forkert 1, Dennis Säring 1, Andrea Eisenbeis 2, Frank Leypoldt 3, Jens Fiehler 2, Heinz Handels
Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences Nils Daniel Forkert 1, Dennis Säring 1, Andrea Eisenbeis 2, Frank Leypoldt 3, Jens Fiehler 2, Heinz Handels
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disabling chronic demyelinating disease
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:106 111 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging of active multiple sclerosis plaques: efficiency of contrast-enhanced magnetization transfer
Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:106 111 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging of active multiple sclerosis plaques: efficiency of contrast-enhanced magnetization transfer
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Cases with Visual Field Defect after Anterior Temporal Lobectomy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:797 803, April 2005 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Cases with Visual Field Defect after Anterior Temporal Lobectomy Toshiaki Taoka, Masahiko Sakamoto, Satoru Iwasaki, Hiroyuki Nakagawa,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:797 803, April 2005 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Cases with Visual Field Defect after Anterior Temporal Lobectomy Toshiaki Taoka, Masahiko Sakamoto, Satoru Iwasaki, Hiroyuki Nakagawa,
Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:692 698, May 2004 Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain Pierre Brugières, Philippe Thomas, Anne Maraval, Hassan Hosseini, Catherine Combes,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:692 698, May 2004 Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain Pierre Brugières, Philippe Thomas, Anne Maraval, Hassan Hosseini, Catherine Combes,
Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging F. A. Fellner 1, M. R. Vosko 2, C. M. Fellner 1, D. Flöry 1 1. AKH Linz, Institute of Radiology, Austria. 2.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging F. A. Fellner 1, M. R. Vosko 2, C. M. Fellner 1, D. Flöry 1 1. AKH Linz, Institute of Radiology, Austria. 2.
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Prediction of Hemorrhage in Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Permeability MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2213 2217, October 2005 Technical Note Prediction of Hemorrhage in Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Permeability MR Imaging Andrea Kassner, Timothy Roberts, Keri Taylor, Frank Silver,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2213 2217, October 2005 Technical Note Prediction of Hemorrhage in Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Permeability MR Imaging Andrea Kassner, Timothy Roberts, Keri Taylor, Frank Silver,
Masayuki Maeda, Tatsuya Yamamoto, Shouichiro Daimon, Hajime Sakuma, and Kan Takeda
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :6 66, April 001 Arterial Hyperintensity on Fast Fluid-attenuated Inversion Recovery Images: A Subtle Finding for Hyperacute Stroke Undetected by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Masayuki
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :6 66, April 001 Arterial Hyperintensity on Fast Fluid-attenuated Inversion Recovery Images: A Subtle Finding for Hyperacute Stroke Undetected by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Masayuki
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
The Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Maps in Early Cerebral Ischemia
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1260 1267, August 2001 The Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Maps in Early Cerebral Ischemia Patricia M. Desmond, Amanda C. Lovell, Andrew A. Rawlinson, Mark W. Parsons,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1260 1267, August 2001 The Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Maps in Early Cerebral Ischemia Patricia M. Desmond, Amanda C. Lovell, Andrew A. Rawlinson, Mark W. Parsons,
Characterization and Evolution of Diffusion MR Imaging Abnormalities in Stroke Patients Undergoing Intra-Arterial Thrombolysis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:951 957, June/July 2004 Characterization and Evolution of Diffusion MR Imaging Abnormalities in Stroke Patients Undergoing Intra-Arterial Thrombolysis Pamela W. Schaefer, Alvand
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:951 957, June/July 2004 Characterization and Evolution of Diffusion MR Imaging Abnormalities in Stroke Patients Undergoing Intra-Arterial Thrombolysis Pamela W. Schaefer, Alvand
MRI in MS: the radiologist perspective
 MS Preceptorship - Updating Knowledge in Multiple Sclerosis - June, 1-3 2010 Barcelona MRI in MS: the radiologist perspective Àlex Rovira Unidad de Resonancia Magnética Servicio de Radiología Hospital
MS Preceptorship - Updating Knowledge in Multiple Sclerosis - June, 1-3 2010 Barcelona MRI in MS: the radiologist perspective Àlex Rovira Unidad de Resonancia Magnética Servicio de Radiología Hospital
The Role of MRI in Multiple Sclerosis
 September 2006 The Role of MRI in Multiple Sclerosis David Cochran, Harvard Medical School Year IV Meet our patient WM 49yoF presents to Multiple Sclerosis Clinic for follow-up regarding worsening symptoms
September 2006 The Role of MRI in Multiple Sclerosis David Cochran, Harvard Medical School Year IV Meet our patient WM 49yoF presents to Multiple Sclerosis Clinic for follow-up regarding worsening symptoms
Spontaneous Intracerebral Hematoma on Diffusion-weighted Images: Influence of T2- shine-through and T2-blackout Effects
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:236 241, February 2005 Spontaneous Intracerebral Hematoma on Diffusion-weighted Images: Influence of T2- shine-through and T2-blackout Effects Stéphane Silvera, Catherine Oppenheim,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:236 241, February 2005 Spontaneous Intracerebral Hematoma on Diffusion-weighted Images: Influence of T2- shine-through and T2-blackout Effects Stéphane Silvera, Catherine Oppenheim,
ADC evaluations of the hippocampus and amygdala in multiple sclerosis
 Neurology Asia 2014; 19(4) : 387 391 ADC evaluations of the hippocampus and amygdala in multiple sclerosis 1 Mikail Inal, 1 Birsen Unal Daphan, 1 Yasemin Karadeniz Bilgili, 2 Yakup Turkel, 3 Ibrahim Kala
Neurology Asia 2014; 19(4) : 387 391 ADC evaluations of the hippocampus and amygdala in multiple sclerosis 1 Mikail Inal, 1 Birsen Unal Daphan, 1 Yasemin Karadeniz Bilgili, 2 Yakup Turkel, 3 Ibrahim Kala
DWI that measures overall diffusivity in terms of directionally
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.H. Toh K.-C. Wei C.-N. Chang P.-W. Hsu H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng M. Castillo C.-P. Lin Differentiation of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses from Necrotic Glioblastomas with Use of Susceptibility-Weighted
ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.H. Toh K.-C. Wei C.-N. Chang P.-W. Hsu H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng M. Castillo C.-P. Lin Differentiation of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses from Necrotic Glioblastomas with Use of Susceptibility-Weighted
Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy: Insights into the Pathology and Pathophysiology of Multiple Sclerosis.
 Chapter 10 (pp 139-167) of Multiple Sclerosis 2 - Blue Books of Practical Neurology, vol. 27. J.H Noseworthy, W.I. McDonald (eds.). Elsevier Science (USA), 2003. Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy:
Chapter 10 (pp 139-167) of Multiple Sclerosis 2 - Blue Books of Practical Neurology, vol. 27. J.H Noseworthy, W.I. McDonald (eds.). Elsevier Science (USA), 2003. Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy:
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
Relevance of Hypointense Lesions on Fast Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Images as a Marker of Disease Severity in Cases of Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:813 820, May 1999 Relevance of Hypointense Lesions on Fast Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Images as a Marker of Disease Severity in Cases of Multiple Sclerosis Marco Rovaris,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:813 820, May 1999 Relevance of Hypointense Lesions on Fast Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Images as a Marker of Disease Severity in Cases of Multiple Sclerosis Marco Rovaris,
False-negative and False-positive Diffusion-weighted MR Findings in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Stroke-like Episodes
 JRural Med 2005 ; 1 : 27 32 Original Article False-negative and False-positive Diffusion-weighted MR Findings in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Stroke-like Episodes Shuzo Shintani 1,HiroakiYokote 1,KaoruHanabusa
JRural Med 2005 ; 1 : 27 32 Original Article False-negative and False-positive Diffusion-weighted MR Findings in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Stroke-like Episodes Shuzo Shintani 1,HiroakiYokote 1,KaoruHanabusa
Imaging ischemic strokes: Correlating radiological findings with the pathophysiological evolution of an infarct
 Imaging ischemic strokes: Correlating radiological findings with the pathophysiological evolution of an infarct Jay Chyung,, PhD, HMS III Patient A: history 91 y.o. woman Acute onset R sided weakness and
Imaging ischemic strokes: Correlating radiological findings with the pathophysiological evolution of an infarct Jay Chyung,, PhD, HMS III Patient A: history 91 y.o. woman Acute onset R sided weakness and
Traumatic axonal injury is a frequent cause of impaired clinical
 Published July 10, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1213 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.R. Rutgers P. Fillard G. Paradot M. Tadié P. Lasjaunias D. Ducreux Diffusion Tensor Imaging Characteristics of the Corpus Callosum in Mild,
Published July 10, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1213 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.R. Rutgers P. Fillard G. Paradot M. Tadié P. Lasjaunias D. Ducreux Diffusion Tensor Imaging Characteristics of the Corpus Callosum in Mild,
The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry
 WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
et al.. Extensive white matter lesions after 2 years of fingolimod: progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy or MS relapse?
 Extensive white matter lesions after 2 years of fingolimod: progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy or MS relapse? Marine Boudot de La Motte, Céline Louapre, Anne Bertrand, Pauline Reach, Catherine
Extensive white matter lesions after 2 years of fingolimod: progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy or MS relapse? Marine Boudot de La Motte, Céline Louapre, Anne Bertrand, Pauline Reach, Catherine
Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging features of intracranial lesions
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
Clinical Experience with Diffusion-Weighted MR in Patients with Acute Stroke
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1061 1066, June 1998 Clinical Experience with Diffusion-Weighted MR in Patients with Acute Stroke Karl-Olof Lövblad, Hans-Joachim Laubach, Alison E. Baird, François Curtin, Gottfried
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1061 1066, June 1998 Clinical Experience with Diffusion-Weighted MR in Patients with Acute Stroke Karl-Olof Lövblad, Hans-Joachim Laubach, Alison E. Baird, François Curtin, Gottfried
Evidence for Cytotoxic Edema in the Pathogenesis of Cerebral Venous Infarction
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:450 455, March 200 Evidence for Cytotoxic Edema in the Pathogenesis of Cerebral Venous Infarction Kirsten P.N. Forbes, James G. Pipe, and Joseph E. Heiserman BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:450 455, March 200 Evidence for Cytotoxic Edema in the Pathogenesis of Cerebral Venous Infarction Kirsten P.N. Forbes, James G. Pipe, and Joseph E. Heiserman BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Neonatal Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy: Detection with Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :9 96, September Neonatal Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy: Detection with Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Kirsten P. N. Forbes, James G. Pipe, and Roger Bird BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :9 96, September Neonatal Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy: Detection with Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Kirsten P. N. Forbes, James G. Pipe, and Roger Bird BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
SHORTLY AFTER ITS FIRST DEpiction
 OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
CT Perfusion Parameter Values in Regions of Diffusion Abnormalities
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1205 1210, August 2004 CT Perfusion Parameter Values in Regions of Diffusion Abnormalities Marcello Galvez, Gerald E. York, II, and James D. Eastwood BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Dynamic
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1205 1210, August 2004 CT Perfusion Parameter Values in Regions of Diffusion Abnormalities Marcello Galvez, Gerald E. York, II, and James D. Eastwood BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Dynamic
Lo et al. BMC Neurology 2014, 14:100
 Lo et al. BMC Neurology 2014, 14:100 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of diffusion-weighted imaging and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging on a single baseline MRI for demonstrating dissemination
Lo et al. BMC Neurology 2014, 14:100 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of diffusion-weighted imaging and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging on a single baseline MRI for demonstrating dissemination
Imaging Modalities in Acute Stroke: Time is Brain
 April 2001 Imaging Modalities in Acute Stroke: Time is Brain Jeremiah Scharf, Harvard Medical School, MS IV Beth Israel-Deaconess Medical Center Department of Radiology Stroke - Definition and Statistics
April 2001 Imaging Modalities in Acute Stroke: Time is Brain Jeremiah Scharf, Harvard Medical School, MS IV Beth Israel-Deaconess Medical Center Department of Radiology Stroke - Definition and Statistics
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction
 Original Article ISSN (o):2321 7251 Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction Kalidindi Ravi Kumar Varma 1, Chaparla Lakshmana Rao 2 1 - Associate Professor,Maharajah
Original Article ISSN (o):2321 7251 Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction Kalidindi Ravi Kumar Varma 1, Chaparla Lakshmana Rao 2 1 - Associate Professor,Maharajah
Evolution of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions on Serial Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted and Magnetization-Transfer MR Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1939 1945, November/December 1999 Evolution of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions on Serial Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted and Magnetization-Transfer MR Images Alex Rovira, Juli Alonso,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1939 1945, November/December 1999 Evolution of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions on Serial Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted and Magnetization-Transfer MR Images Alex Rovira, Juli Alonso,
Accuracy of Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Detection of Acute Cerebral Infarcts
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Accuracy of Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Detection of Acute Cerebral Infarcts SARAH NISAR 1, AWAIS AHMAD NIZAMI 2, SHAZIA F. KHAN 3 ABSTRACT Aim: To determine the
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Accuracy of Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Detection of Acute Cerebral Infarcts SARAH NISAR 1, AWAIS AHMAD NIZAMI 2, SHAZIA F. KHAN 3 ABSTRACT Aim: To determine the
MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS
 Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Marchiafava-Bignami Disease
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Marchiafava-Bignami Disease Fahd Al-Khamis, MBBS, UODFN* Fozaih Al-Shamrani, MBBS, UODFN** Ibrahim Al- Ghanimi, MBBS, UODFN*** Sarah Abdulhafiz,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Marchiafava-Bignami Disease Fahd Al-Khamis, MBBS, UODFN* Fozaih Al-Shamrani, MBBS, UODFN** Ibrahim Al- Ghanimi, MBBS, UODFN*** Sarah Abdulhafiz,
MRI in MS. MRI in multiple sclerosis. MS T2 Lesions: Pathology. Brain lesions Morphology Matters. Sagittal FLAIR Morphology Matters
 MRI in multiple sclerosis MRI in MS Rohit Bakshi, MD, MA Breakstone Professor of Neurology & Radiology Director, Laboratory for Neuroimaging Research Senior Neurologist, MS Center Brigham & Women s Hospital
MRI in multiple sclerosis MRI in MS Rohit Bakshi, MD, MA Breakstone Professor of Neurology & Radiology Director, Laboratory for Neuroimaging Research Senior Neurologist, MS Center Brigham & Women s Hospital
Amide Proton Transfer Imaging: A Novel MR Method for High-grade Brain Tumors.
 Amide Proton Transfer Imaging: A Novel MR Method for High-grade Brain Tumors. Poster No.: C-1732 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Ida, M. Ishizuka, T. Suzuki, Y. Kubo, K. Hino, S.
Amide Proton Transfer Imaging: A Novel MR Method for High-grade Brain Tumors. Poster No.: C-1732 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Ida, M. Ishizuka, T. Suzuki, Y. Kubo, K. Hino, S.
A Comparison of MR Imaging with Fast-FLAIR, HASTE-FLAIR, and EPI-FLAIR Sequences in the Assessment of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1931 1938, November/December 1999 A Comparison of MR Imaging with Fast-FLAIR, HASTE-FLAIR, and EPI-FLAIR Sequences in the Assessment of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Massimo
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1931 1938, November/December 1999 A Comparison of MR Imaging with Fast-FLAIR, HASTE-FLAIR, and EPI-FLAIR Sequences in the Assessment of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Massimo
The MRI Appearance of Tumefactive Demyelinating Lesions
 ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.148 on 12/05/17 from IP address 37.44.198.148. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved The MRI ppearance of Tumefactive emyelinating Lesions
ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.148 on 12/05/17 from IP address 37.44.198.148. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved The MRI ppearance of Tumefactive emyelinating Lesions
STROKE - IMAGING. Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli.
 STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
Case Report. Case Report
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
1 Maiser. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Induced Acute Toxic Leukoencephalopathy. Samuel Maiser, MD. Department of Neurology, University of Minnesota
 1 Maiser 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Induced Acute Toxic Leukoencephalopathy Samuel Maiser, MD Department of Neurology, University of Minnesota Case This is a 57-year-old right-handed male with a history of
1 Maiser 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Induced Acute Toxic Leukoencephalopathy Samuel Maiser, MD Department of Neurology, University of Minnesota Case This is a 57-year-old right-handed male with a history of
Formation of lesions in multiple sclerosis (MS) comprises a
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.S. Meier H.L. Weiner C.R.G. Guttmann MR Imaging Intensity Modeling of Damage and Repair In Multiple Sclerosis: Relationship of Short-Term Lesion Recovery to Progression and Disability
ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.S. Meier H.L. Weiner C.R.G. Guttmann MR Imaging Intensity Modeling of Damage and Repair In Multiple Sclerosis: Relationship of Short-Term Lesion Recovery to Progression and Disability
Marchiafava-Bignami Disease: Longitudinal MR Imaging and MR Spectroscopy Study
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:249 253, February 2003 Case Report Marchiafava-Bignami Disease: Longitudinal MR Imaging and MR Spectroscopy Study Anna Gambini, Andrea Falini, Lucia Moiola, Giancarlo Comi, and
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:249 253, February 2003 Case Report Marchiafava-Bignami Disease: Longitudinal MR Imaging and MR Spectroscopy Study Anna Gambini, Andrea Falini, Lucia Moiola, Giancarlo Comi, and
POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES
 Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Basilar Artery Occlusion Richard du Mesnil de Rochemont, MD; Tobias Neumann-Haefelin, MD; Joachim Berkefeld, MD; Matthias Sitzer, MD; Heinrich Lanfermann,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Basilar Artery Occlusion Richard du Mesnil de Rochemont, MD; Tobias Neumann-Haefelin, MD; Joachim Berkefeld, MD; Matthias Sitzer, MD; Heinrich Lanfermann,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Arch Neurol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2008 November 5.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Arch Neurol. 2008 June ; 65(6): 812 816. doi:10.1001/archneur.65.6.812. 7T MRI: New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Arch Neurol. 2008 June ; 65(6): 812 816. doi:10.1001/archneur.65.6.812. 7T MRI: New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple
A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence
 A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence Poster No.: C-1347 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Hodel, A. GUILLONNET, M. Rodallec, S. GERBER, R. 1
A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence Poster No.: C-1347 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Hodel, A. GUILLONNET, M. Rodallec, S. GERBER, R. 1
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
mr brain volume analysis using brain assist
 mr brain volume analysis using brain assist This Paper describes the tool named BrainAssist, which can be used for the study and analysis of brain abnormalities like Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD), Heterotopia
mr brain volume analysis using brain assist This Paper describes the tool named BrainAssist, which can be used for the study and analysis of brain abnormalities like Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD), Heterotopia
3D high-resolution MR imaging can provide reliable information
 Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
Association of Early CT Abnormalities, Infarct Size, and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Reduction in Acute Ischemic Stroke
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:933 938, June/July 2004 Association of Early CT Abnormalities, Infarct Size, and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Reduction in Acute Ischemic Stroke Diederik M. Somford, Michael
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:933 938, June/July 2004 Association of Early CT Abnormalities, Infarct Size, and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Reduction in Acute Ischemic Stroke Diederik M. Somford, Michael
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI)
 Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
Spinal cord MR imaging in Multiple Sclerosis
 43ème CONGRÈS ANNUEL de la Société Française de NeuroRadiologie 30 mars au 1 er avril 2016 Novotel Paris Tour Eiffel Spinal cord MR imaging in Multiple Sclerosis Àlex Rovira Unitat de Neurorradiología.
43ème CONGRÈS ANNUEL de la Société Française de NeuroRadiologie 30 mars au 1 er avril 2016 Novotel Paris Tour Eiffel Spinal cord MR imaging in Multiple Sclerosis Àlex Rovira Unitat de Neurorradiología.
Traumatic injuries of the cervical spine are potentially catastrophic.
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Shanmuganathan R.P. Gullapalli J. Zhuo S.E. Mirvis Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging in Cervical Spine Trauma BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our aim was to investigate the extent and severity of
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Shanmuganathan R.P. Gullapalli J. Zhuo S.E. Mirvis Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging in Cervical Spine Trauma BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our aim was to investigate the extent and severity of
Long-Term Changes of Magnetization Transfer Derived Measures from Patients with Relapsing-Remitting and Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:821 827, May 1999 Long-Term Changes of Magnetization Transfer Derived Measures from Patients with Relapsing-Remitting and Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Maria A. Rocca,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:821 827, May 1999 Long-Term Changes of Magnetization Transfer Derived Measures from Patients with Relapsing-Remitting and Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Maria A. Rocca,
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection. Page inserted by evaluation version
 PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype S E V E N
 CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype S E V E N CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype R. van den Boom S.A.J. Lesnik Oberstein A.A. van den
CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype S E V E N CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype R. van den Boom S.A.J. Lesnik Oberstein A.A. van den
Magnetization Transfer and Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging of Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:267 272, February 2002 Magnetization Transfer and Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging of Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Matilde Inglese, Fabrizio Salvi, Giuseppe Iannucci, Gian Luigi
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:267 272, February 2002 Magnetization Transfer and Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging of Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Matilde Inglese, Fabrizio Salvi, Giuseppe Iannucci, Gian Luigi
Hypoglycemic encephalopathy mimicking acute ischemic stroke in clinical presentation and magnetic resonance imaging: a case report
 Chuang et al. BMC Medical Imaging (2019) 19:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-019-0310-z CASE REPORT Hypoglycemic encephalopathy mimicking acute ischemic stroke in clinical presentation and magnetic resonance
Chuang et al. BMC Medical Imaging (2019) 19:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-019-0310-z CASE REPORT Hypoglycemic encephalopathy mimicking acute ischemic stroke in clinical presentation and magnetic resonance
High b value DWI in evaluation of the hyperacute cerebral ischemia at 3T: A comparative study in an embolic canine stroke model
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 12: 951-956, 2016 High b value DWI in evaluation of the hyperacute cerebral ischemia at 3T: A comparative study in an embolic canine stroke model QIGUANG CHENG 1*,
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 12: 951-956, 2016 High b value DWI in evaluation of the hyperacute cerebral ischemia at 3T: A comparative study in an embolic canine stroke model QIGUANG CHENG 1*,
MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis
 J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
Detection of Diffusion-Weighted MRI Abnormalities in Patients With Transient Ischemic Attack. Correlation With Clinical Characteristics
 Detection of Diffusion-Weighted MRI Abnormalities in Patients With Transient Ischemic Attack Correlation With Clinical Characteristics Ralph A. Crisostomo, BS; Madelleine M. Garcia, BS; David C. Tong,
Detection of Diffusion-Weighted MRI Abnormalities in Patients With Transient Ischemic Attack Correlation With Clinical Characteristics Ralph A. Crisostomo, BS; Madelleine M. Garcia, BS; David C. Tong,
24-25 February Siena, Italy
 WORKSHOP FINAL PROGRAMME AND ABSTRACT BOOK Clinical and research application of MRI in diagnosis and monitoring of multiple sclerosis 24-25 February 2016 - Siena, Italy Clinical and research application
WORKSHOP FINAL PROGRAMME AND ABSTRACT BOOK Clinical and research application of MRI in diagnosis and monitoring of multiple sclerosis 24-25 February 2016 - Siena, Italy Clinical and research application
Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients
 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med Med J 2006; J 2006; 47(3) 47(3) : 198 : 1 Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients Parmar H, Golay
O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med Med J 2006; J 2006; 47(3) 47(3) : 198 : 1 Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients Parmar H, Golay
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
The estimated annual incidence of central nervous system
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!!
 Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!! Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Agawane, M. R. Verma, D. P.
Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!! Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Agawane, M. R. Verma, D. P.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging
 Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
