Chapter 25 The Urinary System
|
|
|
- Blaze Andrews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1
2 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis during prolonged fasting Endocrine functions Renin: regulation of blood pressure and kidney function Erythropoietin: regulation of RBC production Activation of vitamin D 10/30/2013 MDufilho 2
3 10/30/2013 MDufilho 3 Figure 255
4 Figure 259 A schematic, uncoiled nephron showing the three major renal processes that adjust plasma composition Afferent arteriole Glomerular capillaries Cortical radiate artery 1 Efferent arteriole Glomerular capsule Renal tubule and collecting duct containing filtrate 2 Peritubular capillary 3 To cortical radiate vein Three major renal processes: Urine 1 Glomerular filtration 2 Tubular reabsorption 3 Tubular secretion 10/30/ MDufilho
5 Figure 255 Location and structure of nephrons (3 of 7) Basement membrane Podocyte Fenestrated endothelium of the glomerulus Glomerular capsule: visceral layer 10/30/ MDufilho
6 Figure 2510a The filtration membrane Efferent arteriole Glomerular capsular space Cytoplasmic extensions of podocytes Filtration slits Afferent arteriole Glomerular capillary covered by podocytes that form the visceral layer of glomerular capsule Parietal layer of glomerular capsule Glomerular capillaries and the visceral layer of the glomerular capsule Proximal convoluted tubule Podocyte cell body Fenestrations (pores) Glomerular capillary endothelium (podocyte covering and basement membrane removed) Foot processes of podocyte 10/30/ MDufilho
7 Figure 2510c The filtration membrane Capillary Filtration membrane Capillary endothelium Basement membrane Foot processes of podocyte of glomerular capsule Plasma Filtrate in capsular space Filtration slit Slit diaphragm Fenestration (pore) Foot processes of podocyte Three layers of the filtration membrane 10/30/ MDufilho
8 Terminology Renal Fraction = % of blood flow passing through kidneys = 20 25% Filtration Fraction = % plasma (in renal fraction) that passes through the filtration membrane to become filtrate = 20% 10/30/ MDufilho
9 Net Filtration Pressure (NFP) The pressure responsible for filtrate formation (10 mm Hg) Determined by Glomerular hydrostatic pressure (HP g ) the chief force Two opposing forces: Colloid osmotic pressure of glomerular blood (OP g ) Capsular hydrostatic pressure (HP c ) NFP = HP g (OP g + HP c ) 10/30/2013 MDufilho 9
10 Figure 2511 Forces determining net filtration pressure (NFP) Efferent arteriole Glomerular capsule HP gc = 55 mm Hg OP gc = 30 mm Hg Afferent arteriole HP cs = 15 mm Hg NFP = Net filtration pressure = outward pressures inward pressures = (HP gc ) (HP cs + OP gc ) = (55) ( ) = 10 mm Hg 10/30/ MDufilho
11 Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) Volume of filtrate formed per minute by the kidneys ( ml/min) Governed by (and directly proportional to) Total surface area available for filtration Filtration membrane permeability NFP 10/30/2013 MDufilho 11
12 Tubular Maximum Also called transport maximum When tubular load exceeds tubular maximum, the substances show up in urine e g Glucosuria 10/30/ MDufilho
13 Clinical Applications What if Hemorrhage - Blood Pressure? - NFP? - GFR? - Result Fight or flight situation - Sympathetic stimulation? - Blood Pressure? - Result? Kidney Infection - Result 10/30/ MDufilho
14 Regulation of Glomerular Filtration GFR is tightly controlled by two types of mechanisms Intrinsic controls (renal autoregulation) Act locally within the kidney Extrinsic controls Nervous and endocrine mechanisms that maintain blood pressure, but affect kidney function 10/30/2013 MDufilho 14
15 Intrinsic Controls Maintains a nearly constant GFR when MAP is in the range of mm Hg Two types of renal autoregulation Myogenic mechanism (Chapter 19) Tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism, which senses changes in the juxtaglomerular apparatus 10/30/2013 MDufilho 15
16 Figure 258 Juxtaglomerular complex (JGC) of a nephron Glomerular capsule Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole Glomerulus Efferent arteriole Parietal layer of glomerular capsule Capsular space Foot processes of podocytes Podocyte cell body (visceral layer) Red blood cell Proximal tubule cell Juxtaglomerular complex Macula densa cells of the ascending limb of nephron loop Extraglomerular mesangial cells Granular cells Afferent arteriole Juxtaglomerular complex Glomerular mesangial cells Renal corpuscle Lumens of glomerular capillaries Endothelial cell of glomerular capillary 10/30/ MDufilho
17 Intrinsic Controls: Tubuloglomerular Feedback Mechanism Macula densa cells monitor Na+ and Cl- in filtrate Macula densa cells of the JGA respond to NaCl by releasing a vasoconstricting chemical that acts on the afferent arteriole GFR The opposite occurs if GFR decreases 10/30/2013 MDufilho 17
18 Intrinsic Controls Compensate for MAP of mmhg to maintain GFR at 125 ml/min (+/- 30%) Kidney function suffers if MAP < 80 mmhg Then extrinsic controls are needed 10/30/ MDufilho
19 Extrinsic Controls: Sympathetic Nervous System Under extreme stress Norepinephrine is released by the sympathetic nervous system Epinephrine is released by the adrenal medulla Both cause constriction of afferent arterioles, inhibiting filtration and triggering the release of renin 10/30/2013 MDufilho 19
20 Extrinsic Controls: Renin-Angiotensin Mechanism Triggered when the granular cells of the JGA release renin angiotensinogen (a plasma globulin) renin angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) angiotensin I angiotensin II 10/30/2013 MDufilho 20
21 Other Factors Affecting GFR Prostaglandin E 2 Vasodilator that counteracts vasoconstriction by norepinephrine and angiotensin II Prevents renal damage when peripheral resistance is increased Intrarenal angiotensin II Reinforces the effects of hormonal angiotensin II Adenosine A vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature 10/30/2013 MDufilho 21
22 Figure 2512 Physiological mechanisms regulating glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in the kidneys SYSTEMIC BLOOD PRESSURE Blood pressure in afferent arterioles; GFR GFR Granular cells of juxtaglomerular complex of kidney Inhibits baroreceptors in blood vessels of systemic circulation Stretch of smooth muscle in walls of afferent arterioles Vasodilation of afferent arterioles Filtrate flow andnacl in ascendinglimb of nephron loop Targets Catalyzes cascade resulting in formation of Renin Angiotensin II Release Sympathetic nervous system Macula densa cells of juxtaglomerular complex of kidney Aldosterone secretion by adrenal cortex Vasoconstriction of systemic arterioles; peripheral resistance Release of vasoactive chemicals inhibited Vasodilation of afferent arterioles Na + reabsorption by kidney tubules; water follows GFR Blood volume Systemic blood pressure Myogenic mechanism of autoregulation Tubuloglomerular mechanism ofautoregulation Hormonal (renin-angiotensinaldosterone)mechanism Neural controls Intrinsic mechanisms directly regulate GFR despite moderate changes in blood pressure (between 80 and 180 mm Hg mean arterial pressure) Extrinsic mechanisms indirectly regulate GFR by maintaining systemic blood pressure, which drives filtration in the kidneys 10/30/ MDufilho
23 Regulation of Urine Concentration and Volume Really ECF Osmolality - number of solute particles in 1Kg of solvent Osmolarity number of solute particles in 1 liter of solvent Both terms reflect the solution s ability to cause osmosis Body fluids are measured in milliosmols (mosm) The kidneys keep the solute load of body fluids constant at about mosm This is accomplished by the countercurrent mechanism 10/30/ MDufilho
24 Countercurrent Mechanism Occurs when fluid flows in opposite directions in two adjacent segments of the same tube Filtrate flow in the loop of Henle (countercurrent multiplier) Blood flow in the vasa recta (countercurrent exchanger) 10/30/2013 MDufilho 24
25 Figure 257a Blood vessels of cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons Cortical nephron Short nephron loop Glomerulus further from the cortex-medulla junction Efferent arteriole supplies peritubular capillaries Renal corpuscle Glomerulus (capillaries) Glomerular capsule Proximal convoluted tubule Efferent arteriole Juxtamedullary nephron Long nephron loop Glomerulus closer to the cortex-medulla junction Efferent arteriole supplies vasa recta Cortical radiate vein Cortical radiate artery Afferent arteriole Collecting duct Distal convoluted tubule Afferent arteriole Efferent arteriole Peritubular capillaries Ascending limb of nephron loop Kidney Arcuate vein Arcuate artery Nephron loop Descending limb of nephron loop Vasa recta Cortex-medulla junction 10/30/ MDufilho
26 Cortex Medulla 10/30/2013 MDufilho 26 Figure 2515
27 Figure 2516a Juxtamedullary nephrons create an osmotic gradient within the renal medulla that allows the kidney to produce urine of varying concentration (4 of 4) Osmolality of interstitial fluid (mosm) (continued) As water and solutes are reabsorbed, the loop first concentrates the filtrate, then dilutes it Active transport Passive transport Water impermeable Cortex 1 Filtrate entering the nephron loop is isosmotic to both blood plasma and cortical interstitial fluid Filtrate is at its most dilute as it leaves the nephron loop At 100 mosm, it is hypo-osmotic to the interstitial fluid Outer medulla 2 Water moves out of the filtrate in the descending limb down its osmotic gradient This concentrates the filtrate Na + and Cl - are pumped out of the filtrate This increases the interstitial fluid osmolality 1200 Inner medulla Nephron loop Filtrate reaches its highest concentration at the bend of the loop 10/30/ MDufilho
28 Countercurrent Exchanger: Vasa Recta The vasa recta Maintain the osmotic gradient Deliver blood to the medullary tissues Protect the medullary osmotic gradient by preventing rapid removal of salt, and by removing reabsorbed H 2 O 10/30/2013 MDufilho 28
29 Figure 2516b Juxtamedullary nephrons create an osmotic gradient within the renal medulla that allows the kidney to produce urine of varying concentration Vasa recta preserve the gradient The entire length of the vasa recta is highly permeable to water and solutes Due to countercurrent exchanges between each section of the vasa recta and its surrounding interstitial fluid, the blood within the vasa recta remains nearly isosmotic to the surrounding fluid As a result, the vasa recta do not undo the osmotic gradient as they remove reabsorbed water and solutes Blood from efferent arteriole To vein The countercurrent flow of fluid moves through two adjacent parallel sections of the vasa recta /30/2013 Vasa recta 29 MDufilho
30 Formation of Dilute Urine Filtrate is diluted in the ascending loop of Henle In the absence of ADH, dilute filtrate continues into the renal pelvis as dilute urine Na + and other ions may be selectively removed in the DCT and collecting duct, decreasing osmolality to as low as 50 mosm 10/30/2013 MDufilho 30
31 Osmolality of interstitial fluid (mosm) Figure 2517a Mechanism for forming dilute or concentrated urine If we were so overhydrated we had no ADH Osmolality of extracellular fluids ADH release from posterior pituitary Number of aquaporins (H 2 O channels) in collecting duct H 2 O reabsorption from collecting duct Large volume of dilute urine Descending limb of nephron loop 100 Collecting duct 300 Cortex DCT Outer medulla Inner medulla Urea Active transport Large volume of dilute urine 10/30/2013 Passive transport 31 MDufilho
32 Formation of Concentrated Urine Depends on the medullary osmotic gradient and ADH ADH triggers reabsorption of H 2 O in the collecting ducts Facultative water reabsorption occurs in the presence of ADH so that 99% of H 2 O in filtrate is reabsorbed 10/30/2013 MDufilho 32
33 Osmolality of interstitial fluid (mosm) Figure 2517b Mechanism for forming dilute or concentrated urine If we were so dehydrated we had maximal ADH Osmolality of extracellular fluids ADH release from posterior pituitary Number of aquaporins (H 2 O channels) in collecting duct H 2 O reabsorption from collecting duct Small volume of concentrated urine Descending limb of nephron loop Collecting duct Cortex DCT Outer medulla Urea Inner medulla Urea Urea contributes to the Small volume of osmotic gradient ADH concentrated urine increases its recycling 10/30/2013 MDufilho 33
34 Diuretics Chemicals that enhance the urinary output Osmotic diuretics: substances not reabsorbed, (eg, high glucose in a diabetic patient) ADH inhibitors such as alcohol Substances that inhibit Na + reabsorption and obligatory H 2 O reabsorption such as caffeine, Lasix, Diuril, HCTZ (hydrochlorothiazide) and others 10/30/2013 MDufilho 34
35 Solvent Drag Collecting ducts water reabsorbed toward hypertonic medullary ISF What is happening to the remaining filtrate? What happens with concentration gradient? Urea, toxins and lipid soluble drugs can be dragged back into blood by water reabsorption solvent drag 10/30/ MDufilho
36 Renal Clearance Volume of plasma cleared of a particular substance in a given time Renal clearance tests are used to Determine GFR Detect glomerular damage Follow the progress of renal disease 10/30/2013 MDufilho 36
37 Renal Clearance RC = UV/P RC = renal clearance rate (ml/min) U = concentration (mg/ml) of the substance in urine V = flow rate of urine formation (ml/min) P = concentration of the same substance in plasma 10/30/2013 MDufilho 37
38 Renal Clearance For any substance freely filtered and neither reabsorbed nor secreted by the kidneys (eg, inulin), RC = GFR = 125 ml/min Kidneys have cleared all inulin present in 125ml plasma in 1 min If RC < 125 ml/min, the substance is reabsorbed If RC = 0, the substance is completely reabsorbed If RC > 125 ml/min, the substance is secreted (most drug metabolites) 10/30/2013 MDufilho 38
Urine Formation. Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages Urine Formation. Glomerular Filtration 4/24/2016
 Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
Urinary System Review Questions:
 Urinary System Review Questions: 1. This system would be lined with what type of membrane? 2. What type of epithelial tissue would line the opening of the urethra (the exit of the tract)? 3. What type
Urinary System Review Questions: 1. This system would be lined with what type of membrane? 2. What type of epithelial tissue would line the opening of the urethra (the exit of the tract)? 3. What type
Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate
 Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
URINARY SYSTEM. Primary functions. Major organs & structures
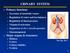 URINARY SYSTEM Primary functions Excretion of metabolic wastes Regulation of water and ion balances Regulation of blood pressure Vitamin D activation Regulation of rbc s (erythropoietin) Gluconeogenesis
URINARY SYSTEM Primary functions Excretion of metabolic wastes Regulation of water and ion balances Regulation of blood pressure Vitamin D activation Regulation of rbc s (erythropoietin) Gluconeogenesis
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Urinary System
 Urinary System What are the organs that comprise the urinary system? Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder Ureters Urethra Hepatic veins (cut) Esophagus (cut) Inferior vena cava Adrenal gland Aorta
Urinary System What are the organs that comprise the urinary system? Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder Ureters Urethra Hepatic veins (cut) Esophagus (cut) Inferior vena cava Adrenal gland Aorta
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION
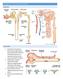 LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
Chapter 25: Urinary System
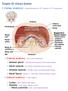 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Physiology Unit 4
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
Kidney Structure. Renal Lobe = renal pyramid & overlying cortex. Renal Lobule = medullary ray & surrounding cortical labryinth.
 Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19](/thumbs/77/74887026.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
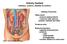 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
11/8/2017. Urinary System Functions. Organs and Vessels of the Urinary System Hepatic veins (cut)
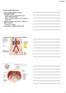 Urinary System Functions Major excretory pathway for wastes transported by blood Filtration, secretion, and reabsorption by the kidney s microscopic tubules Includes wastes from metabolism, excess water
Urinary System Functions Major excretory pathway for wastes transported by blood Filtration, secretion, and reabsorption by the kidney s microscopic tubules Includes wastes from metabolism, excess water
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Collin County Community College RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Basic Functions of the Kidneys
 Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology)
 Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, 2012 Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD Iranian Research Organization for Science & Technology (IROST) Tehran, Iran The Urinary System
Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, 2012 Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD Iranian Research Organization for Science & Technology (IROST) Tehran, Iran The Urinary System
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lecture 16: The Nephron
 Lecture 16: The Nephron Reading: OpenStax A&P Text Chapter 25 Primary functions of the kidneys 1. Regulating osmolarity (blood concentration!) A. Regulating blood pressure B. Maintaining ion balance C.
Lecture 16: The Nephron Reading: OpenStax A&P Text Chapter 25 Primary functions of the kidneys 1. Regulating osmolarity (blood concentration!) A. Regulating blood pressure B. Maintaining ion balance C.
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
Excretory System-Training Handout
 Excretory System-Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science Excretion - Excretion is the removal of the metabolic wastes of an organism. Wastes that are removed include
Excretory System-Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science Excretion - Excretion is the removal of the metabolic wastes of an organism. Wastes that are removed include
10/31/2018. Urinary System Functions. Organs and Vessels of the Urinary System Hepatic veins (cut)
 Urinary System Functions Major excretory pathway for wastes transported by blood Filtration, secretion, and reabsorption by the kidney s microscopic tubules Includes wastes from metabolism, excess water
Urinary System Functions Major excretory pathway for wastes transported by blood Filtration, secretion, and reabsorption by the kidney s microscopic tubules Includes wastes from metabolism, excess water
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY GROSS ANATOMY Location *Bean-shaped *Retroperitoneal *At level of T12 L1 vertebrae. *The right kidney lies slightly inferior to left
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY GROSS ANATOMY Location *Bean-shaped *Retroperitoneal *At level of T12 L1 vertebrae. *The right kidney lies slightly inferior to left
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Waste Products & Kidney Function
 Waste Products & Kidney Function urinary system principal means of metabolic waste removal urinary system is closely associated with reproductive system urogenital system share embryonic development share
Waste Products & Kidney Function urinary system principal means of metabolic waste removal urinary system is closely associated with reproductive system urogenital system share embryonic development share
Chapter 26 The Urinary System
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY
 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
Kidney and urine formation
 Kidney and urine formation Renal structure & function Urine formation Urinary y concentration and dilution Regulation of urine formation 1 Kidney and urine formation 1.Renal structure & function 1)General
Kidney and urine formation Renal structure & function Urine formation Urinary y concentration and dilution Regulation of urine formation 1 Kidney and urine formation 1.Renal structure & function 1)General
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Collec&ng Ducts. Types of Nephrons
 Collec&ng Ducts Receive filtrate from distal convoluted tubule Many nephrons drain to a single collec9ng duct Papillary ducts (Ducts of Bellini) Convergence of many collec9ng ducts Drain through renal
Collec&ng Ducts Receive filtrate from distal convoluted tubule Many nephrons drain to a single collec9ng duct Papillary ducts (Ducts of Bellini) Convergence of many collec9ng ducts Drain through renal
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX
 One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
Chapter 24: The Urinary System
 Chapter 24: The Urinary System Overview of kidney functions n Regulation of blood ionic composition n Regulation of blood ph n Regulation of blood volume n Regulation of blood pressure n Maintenance of
Chapter 24: The Urinary System Overview of kidney functions n Regulation of blood ionic composition n Regulation of blood ph n Regulation of blood volume n Regulation of blood pressure n Maintenance of
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - ANATOMY Glomerulus + renal tubule Each kidney has 1.3 million nephrons Cortical nephrons (85%) have shorter Loop of Henle than Juxtamedullary nephrons
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - ANATOMY Glomerulus + renal tubule Each kidney has 1.3 million nephrons Cortical nephrons (85%) have shorter Loop of Henle than Juxtamedullary nephrons
The functions of the kidney:
 The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
Kidney Physiology. Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed
 Kidney Physiology Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed The purpose of tubular secrection To dispose of certain substances that are bound to plasma proteins. To
Kidney Physiology Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed The purpose of tubular secrection To dispose of certain substances that are bound to plasma proteins. To
Chapter 17. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 17 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 17 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Overview of Kidney Function
 The Kidney Overview of Kidney Function osmolarity of the body fluids volume of ECF plasma ph waste products (urea, uric acid, creatinine, foreign compounds) synthesis of: - EPO, renin, kallikrein, prostaglandins,
The Kidney Overview of Kidney Function osmolarity of the body fluids volume of ECF plasma ph waste products (urea, uric acid, creatinine, foreign compounds) synthesis of: - EPO, renin, kallikrein, prostaglandins,
Osmoregulation and Renal Function
 1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys
 Ionic & Osmotic Homeostasis osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys extracellular intracellular 22 23 Salt Secretion: recycle Figure in Box 26.2 Hill et al. 2004 active Down electrochemical
Ionic & Osmotic Homeostasis osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys extracellular intracellular 22 23 Salt Secretion: recycle Figure in Box 26.2 Hill et al. 2004 active Down electrochemical
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Renal Functions: Renal Functions: Renal Function: Produce Urine
 Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
The Urinary System: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Mr. Barrow @ BEHS C H A P T E R 25 The Urinary System: Part A INTRODUCTION Introduction All organisms within Kingdom Animalia, including humans (homo sapiens), need
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Mr. Barrow @ BEHS C H A P T E R 25 The Urinary System: Part A INTRODUCTION Introduction All organisms within Kingdom Animalia, including humans (homo sapiens), need
Chapter 26 The Urinary System. Overview of Kidney Functions. External Anatomy of Kidney. External Anatomy of Kidney
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp , Chapter 19: pp ,
 P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Collin College. BIOL Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12. Urinary System INTRODUCTION. Main functions of the kidneys are
 Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 INTRODUCTION Main functions of the kidneys are regulate blood volume, water content regulate blood composition e..g. Na, Cl, K, ph
Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 INTRODUCTION Main functions of the kidneys are regulate blood volume, water content regulate blood composition e..g. Na, Cl, K, ph
The Urinary System. Jim Swan
 The Urinary System Jim Swan These slides are from class presentations, reformatted for static viewing. The content contained in these pages is also in the Class Notes pages in a narrative format. Best
The Urinary System Jim Swan These slides are from class presentations, reformatted for static viewing. The content contained in these pages is also in the Class Notes pages in a narrative format. Best
Functions of the kidney
 Physiology of Urinary tract Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder Urethra Kidney function Excretion Physiology of volume regulation Functions of the kidney Excretion of dangerous substances endogenous (metabolites):
Physiology of Urinary tract Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder Urethra Kidney function Excretion Physiology of volume regulation Functions of the kidney Excretion of dangerous substances endogenous (metabolites):
Body Fluid Dynamics. I. Body fluids - Must remain constant - Intake = output. Insensible H 2 0 loss Capillary Membrane
 I. Body fluids - Must remain constant - Intake = output Body Fluid Dynamics Metabolic H 2 0 Preformed Free H 2 0 in Urine Feces Sweat H 2 0 Food - Body fluid distribution: Insensible H 2 0 loss Capillary
I. Body fluids - Must remain constant - Intake = output Body Fluid Dynamics Metabolic H 2 0 Preformed Free H 2 0 in Urine Feces Sweat H 2 0 Food - Body fluid distribution: Insensible H 2 0 loss Capillary
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
November 30, 2016 & URINE FORMATION
 & URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
& URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences. Body fluids and.
 By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences Body fluids and Renal physiology 25 Volume and Osmolality of Extracellular and Intracellular Fluids
By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences Body fluids and Renal physiology 25 Volume and Osmolality of Extracellular and Intracellular Fluids
The kidneys are excretory and regulatory organs. By
 exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
Urinary System. BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Introduction to the kidney: regulation of sodium & glucose. Dr Nick Ashton Senior Lecturer in Renal Physiology Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health
 Introduction to the kidney: regulation of sodium & glucose Dr Nick Ashton Senior Lecturer in Renal Physiology Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health Objectives Overview of kidney structure & function Glomerular
Introduction to the kidney: regulation of sodium & glucose Dr Nick Ashton Senior Lecturer in Renal Physiology Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health Objectives Overview of kidney structure & function Glomerular
5.Which part of the nephron removes water, ions and nutrients from the blood?
 Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Func%ons of the Urinary System
 Func%ons of the Urinary System Excre%on Regula%on of blood volume Regula%on of blood pressure Regula%on of blood- solute concentra%on Regula%on of ph of extracellular fluid Regula%on of erythropoiesis
Func%ons of the Urinary System Excre%on Regula%on of blood volume Regula%on of blood pressure Regula%on of blood- solute concentra%on Regula%on of ph of extracellular fluid Regula%on of erythropoiesis
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Ch 19: The Kidneys. Functional unit of kidneys:?? Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM
 Ch 19: The Kidneys Homeostatic regulation of ECF volume and BP Osmolarity 290 mosm Ion balance Na+ and K+, etc. ph (acid-base balance Excretion of wastes & foreign substances Hormone production EPO Renin
Ch 19: The Kidneys Homeostatic regulation of ECF volume and BP Osmolarity 290 mosm Ion balance Na+ and K+, etc. ph (acid-base balance Excretion of wastes & foreign substances Hormone production EPO Renin
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1)
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 Functional role of the kidney 1.Homeostasis of fluid compartments (isosmia, isovolemia, isoionia, isohydria,) 2. Elimination
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 Functional role of the kidney 1.Homeostasis of fluid compartments (isosmia, isovolemia, isoionia, isohydria,) 2. Elimination
The Urinary System: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Mr. Barrow @ BEHS C H A P T E R 25 The Urinary System: Part A INTRODUCTION Introduction All organisms within Kingdom Animalia, including humans (homo sapiens), need
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Mr. Barrow @ BEHS C H A P T E R 25 The Urinary System: Part A INTRODUCTION Introduction All organisms within Kingdom Animalia, including humans (homo sapiens), need
active transport of! Na. C. Tubular Reabsorption of Nutrients, Water, and Ions (p. 979; Fig )
 The Urinary System Outline 25.1 The kidneys have three distinct regions and a rich blood supply (pp. 963 965; Figs. 25.1 25.5) A. Location and External Anatomy (p. 963; Figs. 25.1 25.3) 1. The kidneys
The Urinary System Outline 25.1 The kidneys have three distinct regions and a rich blood supply (pp. 963 965; Figs. 25.1 25.5) A. Location and External Anatomy (p. 963; Figs. 25.1 25.3) 1. The kidneys
Renal Physiology Part II. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 17 Urinary System 2 Glomerular Filtration Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Overview of Renal Physiology
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 17 Urinary System 2 Glomerular Filtration Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Overview of Renal Physiology
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Other Factors Affecting GFR. Chapter 25. After Filtration. Reabsorption and Secretion. 5 Functions of the PCT
 Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Regulate chemical composition of body fluids. Controls composition of bloods ion levels and concentration. Help maintain PCO2 & acid/base balance [ph]
![Regulate chemical composition of body fluids. Controls composition of bloods ion levels and concentration. Help maintain PCO2 & acid/base balance [ph] Regulate chemical composition of body fluids. Controls composition of bloods ion levels and concentration. Help maintain PCO2 & acid/base balance [ph]](/thumbs/76/74054884.jpg) The Urinary System Regulate chemical composition of body fluids Eliminates waste Controls composition of bloods ion levels and concentration Help maintain PCO2 & acid/base balance [ph] Help regulate blood
The Urinary System Regulate chemical composition of body fluids Eliminates waste Controls composition of bloods ion levels and concentration Help maintain PCO2 & acid/base balance [ph] Help regulate blood
Waste. Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8. Urinary System. Urinary System. Nitrogenous Wastes. Nitrogenous Wastes 4/22/2016
 Waste Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8 Metabolism produces waste products What is the primary waste product of cellular respiration? How does the body dispose of it? Urinary System Urinary
Waste Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8 Metabolism produces waste products What is the primary waste product of cellular respiration? How does the body dispose of it? Urinary System Urinary
