Chapter 24: The Urinary System
|
|
|
- Millicent Sutton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 24: The Urinary System
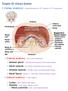
2 Overview of kidney functions n Regulation of blood ionic composition n Regulation of blood ph n Regulation of blood volume n Regulation of blood pressure n Maintenance of blood osmolarity n Production of hormones (calcitrol and erythropoitin) n Regulation of blood glucose level n Excretion of wastes from metabolic reactions and foreign substances (drugs or toxins)
3 Anatomy and histology of the kidneys n External anatomy Renal hilium indent where ureter emerges along with blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and nerves 3 layers of tissue n n n Renal capsule deep layer continuous with outer coat of ureter, barrier against trauma, maintains kidney shape Adipose capsule mass of fatty tissue that protects kidney from trauma and holds it in place Renal fascia superficial layer thin layer of connective tissue that anchors kidney to surrounding structures and abdominal wall
4 Organs of the urinary system in a female
5 Position and coverings of the kidneys
6
7 Internal anatomy Renal cortex superficial n n n Outer cortical zone Inner juxtamedullary zone Renal columns portions of cortex that extend between renal pyramids Renal medulla inner region n Several cone shaped renal pyramids base faces cortex and renal papilla points toward hilium Renal lobe renal pyramid, overlying cortex area, and ½ of each adjacent renal column
8 Anatomy of the kidneys n Parenchyma (functional portion) of kidney Renal cortex and renal pyramids of medulla n Nephron microscopic functional units of kidney n Urine formed by nephron drains into Papillary ducts Minor and major calyces Renal pelvis Ureter Urinary bladder
9 Internal anatomy of the kidneys
10 Blood and nerve supply of the kidneys n n Blood supply Although kidneys constitute less than 0.5% of total body mass, they receive 20-25% of resting cardiac output Left and right renal artery enters kidney Branches into segmental, interlobar, arcuate, interlobular arteries Each nephron receives one afferent arteriole Divides into glomerulus capillary ball Reunite to form efferent arteriole (uniue) Divide to form peritubular capillaries or some have vasa recta Peritubular venule, interlobar vein and renal vein exits kidney Renal nerves are part of the sympathetic autonomic nervous system Most are vasomotor nerves regulating blood flow
11 Blood supply of the kidneys
12 The nephron functional units of kidney 2 parts n Renal corpuscle filters blood plasma Glomerulus capillary network Glomerular (Bowman s) capsule double-walled cup surrounding glomerulus n Renal tubule filtered fluid passes into Proximal convoluted tubule Descending and ascending loop of Henle (nephron loop) Distal convoluted tubule
13 Nephrons Renal corpuscle and both convoluted tubules in cortex, loop of Henle extend into medulla Distal convoluted tubule of several nephrons empty into single collecting duct Cortical nephrons 80-85% of nephrons n Renal corpuscle in outer portion of cortex and short loops of Henle extend only into outer region of medulla Juxtamedullary nephrons other 25-20% n n n n Renal corpuscle deep in cortex and long loops of Henle extend deep into medulla Receive blood from peritubular capillaries and vasa recta Ascending limb has thick and thin regions Enable kidney to secrete very dilute or very concentrated urine
14 The structure of nephrons and associated blood vessels
15 The structure of nephrons and associated blood vessels
16 Histology of nephron and collecting duct Glomerular capsule n n n Visceral layer has podocytes that wrap projections around single layer of endothelial cells of glomerular capillaries and form inner wall of capsule Parietal layer forms outer wall of capsule Fluid filtered from glomerular capillaries enters capsular (Bowman s) space
17 Histology of a renal corpuscle
18
19 Renal tubule and collecting duct n n n Proximal convoluted tubule cells have microvilli with brush border increases surface area Juxtaglomerular appraratus helps regulate blood pressure in kidney Macula densa cells in final part of ascending loop of Henle Juxtaglomerular cells cells of afferent and efferent arterioles contain modified smooth muscle fibers Last part of distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct Principal cells receptors for antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and aldosterone Intercalated cells role in blood ph homeostasis
20 Overview of renal physiology 1. Glomerular filtration Water and most solutes in blood plasma move across the wall of the glomerular capillaries into glomerular capsule and then renal tubule 2. Tubular reabsorption As filtered fluid moves along tubule and through collecting duct, about 99% of water and many useful solutes reabsorbed returned to blood 3. Tubular secretion As filtered fluid moves along tubule and through collecting duct, other material secreted into fluid such as wastes, drugs, and excess ions removes substances from blood n Solutes in the fluid that drains into the renal pelvis remain in the fluid and are excreted n Excretion of any solute = glomerular filtration + secretion - reabsorption
21 Structures and functions of a nephron Renal corpuscle Renal tubule and collecting duct Afferent arteriole Glomerular capsule 1 Filtration from blood plasma into nephron Efferent arteriole Fluid in renal tubule 2 Tubular reabsorption 3 from fluid into blood Tubular secretion from blood into fluid Urine (contains excreted substances) Peritubular capillaries Blood (contains reabsorbed substances)
22 Glomerular filtration n Glomerular filtrate fluid that enters capsular space Daily volume liters more than 99% returned to blood plasma via tubular reabsorption n Filtration membrane endothelial cells of glomerular capillaries and podocytes encircling capillaries Permits filtration of water and small solutes Prevents filtration of most plasma proteins, blood cells and platelets 3 barriers to cross glomerular endothelial cells fenestrations, basal lamina between endothelium and podocytes and pedicels of podocytes create filtration slits Volume of fluid filtered is large because of large surface area, thin and porous membrane, and high glomerular capillary blood pressure
23 The filtration membrane
24 Podocyte of visceral layer of glomerular (Bowman s) capsule Filtration slit Pedicel Fenestration (pore) of glomerular endothelial cell: prevents filtration of blood cells but allows all components of blood plasma to pass through Basal lamina of glomerulus: prevents filtration of larger proteins Slit membrane between pedicels: prevents filtration of medium-sized proteins (a) Details of filtration membrane Pedicel of podocyte Filtration slit Basal lamina Lumen of glomerulus Fenestration (pore) of glomerular endothelial cell TEM 78,000x (b) Filtration membrane
25 Net filtration pressure n Net filtration pressure (NFP) is the total pressure that promotes filtration NFP = GBHP CHP BCOP Glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure is the blood pressure of the glomerular capillaries forcing water and solutes through filtration slits Capsular hydrostatic pressure is the hydrostatic pressure exerted against the filtration membrane by fluid already in the capsular space and represents back pressure Blood colloid osmotic pressure due to presence of proteins in blood plasma and also opposes filtration
26 The pressures that drive glomerular filtration
27 1 GLOMERULAR BLOOD HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE (GBHP) = 55 mmhg 2 CAPSULAR HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE (CHP) = 15 mmhg Afferent arteriole 3 BLOOD COLLOID OSMOTIC PRESSURE (BCOP) = 30 mmhg Proximal convoluted tubule Efferent arteriole Glomerular (Bowman's) capsule Capsular space NET FILTRATION PRESSURE (NFP) =GBHP CHP BCOP = 55 mmhg 15 mmhg 30 mmhg = 10 mmhg
28 Glomerular filtration n Glomerular filtration rate amount of filtrate formed in all the renal corpuscles of both kidneys each minute Homeostasis reuires kidneys maintain a relatively constant GFR n n Too high substances pass too uickly and are not reabsorbed Too low nearly all reabsorbed and some waste products not adeuately excreted GFR directly related to pressures that determine net filtration pressure
29 3 Mechanisms regulating GFR 1. Renal autoregulation n Kidneys themselves maintain constant renal blood flow and GFR using Myogenic mechanism occurs when stretching triggers contraction of smooth muscle cells in afferent arterioles reduces GFR Tubuloglomerular mechanism macula densa provides feedback to glomerulus, inhibits release of NO causing afferent arterioles to constrict and decreasing GFR
30 Tuboglomerular feedback
31 Mechanisms regulating GFR 2. Neural regulation Kidney blood vessels supplied by sympathetic ANS fibers that release norepinephrine causing vasoconstriction Moderate stimulation both afferent and efferent arterioles constrict to same degree and GFR decreases Greater stimulation constricts afferent arterioles more and GFR drops 3. Hormonal regulation Angiotensin II reduces GFR potent vasoconstrictor of both afferent and efferent arterioles Atrial natriuretic peptide increases GFR stretching of atria causes release, increases capillary surface area for filtration
32 Tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion n Reabsorption return of most of the filtered water and many solutes to the bloodstream About 99% of filtered water reabsorbed Proximal convoluted tubule cells make largest contribution Both active and passive processes n Secretion transfer of material from blood into tubular fluid Helps control blood ph Helps eliminate substances from the body
33 Reabsorption routes and transport mechanisms n n Reabsorption routes Paracellular reabsorption n Between adjacent tubule cells n Tight junction do not completely seal off interstitial fluid from tubule fluid n Passive Transcellular reabsorption through an individual cell Transport mechanisms Reabsorption of Na + especially important Primary active transport n Sodium-potassium pumps in basolateral membrane only Secondary active transport n Symporters, antiporters Transport maximum (T m ) n Upper limit to how fast it can work Obligatory vs. facultative water reabsorption
34 Reabsorption routes: paracellular reabsorption and transcellular reabsorption
35 Reabsorption and secretion in proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) Largest amount of solute and water reabsorption Secretes variable amounts of H +, NH 4 + and urea Most solute reabsorption involves Na + n Symporters for glucose, amino acids, lactic acid, watersoluble vitamins, phosphate and sulfate n Na + / H + antiporter causes Na + to be reabsorbed and H + to be secreted Solute reabsorption promotes osmosis creates osmotic gradient n Auaporin-1 in cells lining PCT and descending limb of loop of Henle n As water leaves tubular fluid, solute concentration increases Urea and ammonia in blood are filtered at glomerulus and secreted by proximal convoluted tubule cells
36
37
38 Reabsorption and secretion in the proximal convoluted tubule
39
40 Reabsorption in the loop of Henle Chemical composition of tubular fluid uite different from filtrate n Glucose, amino acids and other nutrients reabsorbed Osmolarity still close to that of blood n Reabsorption of water and solutes balanced For the first time reabsorption of water is NOT automatically coupled to reabsorption of solutes n Independent regulation of both volume and osmolarity of body fluids Na + -K + -2Cl - symporters function in Na + and Cl - reabsorption promotes reabsorption of cations Little or no water is reabsorbed in ascending limb osmolarity decreases
41 Na + K + -2Cl - symporter in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle
42 Reabsorption and secretion in the late distale convoluted tubule and collecting duct n Reabsorption on the early distal convoluted tubule Na + -Cl - symporters reabsorb Na + and Cl - Major site where parathyroid hormone stimulates reabsorption of Ca + depending on body s needs n Reabsorption and secretion in the late distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct 90-95% of filtered solutes and fluid have been returned by now Principal cells reabsorb Na + and secrete K + Intercalated cells reabsorb K + and HCO - 3 and secrete H + Amount of water reabsorption and solute reabsorption and secretion depends on body s needs
43 Hormonal regulation of tubular reabsorption and secretion Angiotensin II - when blood volume and blood pressure decrease n Decreases GFR, enhances reabsorption of Na +, Cl - and water in PCT Aldosterone - when blood volume and blood pressure decrease n Stimulates principal cells in collecting duct to reabsorb more Na + and Cl - and secrete more K + Parathyroid hormone n Stimulates cells in DCT to reabsorb more Ca 2+
44 Regulation of facultative water reabsorption by ADH Antidiuretic hormone (ADH or vasopressin) n Increases water permeability of cells by inserting auaporin-2 in last part of DCT and collecting duct Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) n Large increase in blood volume promotes release of ANP n Decreases blood volume and pressure by inhibiting reabsorption of Na + and water in PCT and collecting duct, suppress secretion of ADH and aldosterone
45 Production of dilute and concentrated urine n Even though your fluid intake can be highly variable, total fluid volume in your body remains stable n Depends in large part on the kidneys to regulate the rate of water loss in urine n ADH controls whether dilute or concentrated urine is formed Absent or low ADH = dilute urine Higher levels = more concentrated urine through increased water reabsorption
46 Formation of dilute urine Glomerular filtrate has same osmolarity as blood 300 mosm/liter Fluid leaving PCT is isotonic to plasma When dilute urine is being formed: the osmolarity of fluid increases as it goes down the descending loop of Henle the osmolarity of fluid decreases as it goes up the ascending limb, and decreases still more as it flows through the rest of the nephron and collecting duct
47 Formation of dilute urine n n n n Osmolarity of interstitial fluid of renal medulla becomes greater, more water is reabsorbed from tubular fluid so fluid become more concentrated Water cannot leave in thick portion of ascending limb but solutes leave making fluid more dilute than blood plasma Additional solutes but not much water leaves in DCT Low ADH makes late DCT and collecting duct have low water permeability
48 Mechanism of urine concentration in longloop juxtamedullary nephrons
49 Vasa recta Loop of Henle Juxtamedullary nephron and its blood supply together Osmotic gradient Afferent arteriole Efferent arteriole Proximal convoluted tubule Interstitial fluid in renal medulla 1 2 Symporters in thick ascending limb cause buildup of Na + and Cl Countercurrent flow through loop of Henle establishes an osmotic gradient Glomerular (Bowman s) capsule Glomerulus H 2 O H 2 O H 2 O Distal convoluted tubule Na + CI H 2 O H 2 O H 2 O Loop of Henle Urea H 2 O H 2 O H 2 O H 2 O Collecting duct 3 4 Papillary duct Interstitial fluid in renal cortex 1200 Concentrated urine 300 Principal cells in collecting duct reabsorb more water when ADH is present Urea recycling causes buildup of urea in the renal medulla H 2 O Na + CI H 2 O 1100 H 2 O Na + CI Blood flow Presense of Na + -K + -2CI symporters Flow of tubular fluid 320 H 2 O Na + CI H 2 O Na + CI (a) Reabsorption of Na + CI and water in a long-loop juxtamedullary nephron (b) Recycling of salts and urea in the vasa recta
50 Evaluation of kidney function n Urinalysis Analysis of the volume and physical, chemical and microscopic properties of urine Water accounts for 95% of total urine volume Typical solutes are filtered and secreted substances that are not reabsorbed If disease alters metabolism or kidney function, traces if substances normally not present or normal constituents in abnormal amounts may appear
51 Evaluation of kidney function n Blood tests Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) measures blood nitrogen that is part of the urea resulting from catabolism and deamination of amino acids Plasma creatinine results from catabolism of creatine phosphate in skeletal muscle measure of renal function n Renal plasma clearance More useful in diagnosis of kidney problems than above Volume of blood cleared of a substance per unit time High renal plasma clearance indicates efficient excretion of a substance into urine PAH administered to measure renal plasma flow
52 Urine transportation, storage, and elimination n Ureters Each of 2 ureters transports urine from renal pelvis of one kidney to the bladder Peristaltic waves, hydrostatic pressure and gravity move urine No anatomical valve at the opening of the ureter into bladder when bladder fills it compresses the opening and prevents backflow
53 Ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra in a female
54 Urinary bladder and urethra n Urinary bladder Hollow, distensible muscular organ Capacity averages mL Micturition discharge of urine from bladder n Combination of voluntary and involuntary muscle contractions n When volume increases stretch receptors send signals to micturition center in spinal cord triggering spinal reflex micturition reflex n In early childhood we learn to initiate and stop it voluntarily n Urethra Small tube leading from internal urethral orifice in floor of bladder to exterior of the body In males discharges semen as well as urine
55 Comparison between female and male urethras
56
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Chapter 26 The Urinary System
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System. Overview of Kidney Functions. External Anatomy of Kidney. External Anatomy of Kidney
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 25: Urinary System
 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Urinary System. BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Collin College. BIOL Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12. Urinary System INTRODUCTION. Main functions of the kidneys are
 Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 INTRODUCTION Main functions of the kidneys are regulate blood volume, water content regulate blood composition e..g. Na, Cl, K, ph
Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 INTRODUCTION Main functions of the kidneys are regulate blood volume, water content regulate blood composition e..g. Na, Cl, K, ph
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Chapter 17: Urinary System
 Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate
 Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Chapter 25 The Urinary System
 Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Kidney Structure. Renal Lobe = renal pyramid & overlying cortex. Renal Lobule = medullary ray & surrounding cortical labryinth.
 Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System Review Questions:
 Urinary System Review Questions: 1. This system would be lined with what type of membrane? 2. What type of epithelial tissue would line the opening of the urethra (the exit of the tract)? 3. What type
Urinary System Review Questions: 1. This system would be lined with what type of membrane? 2. What type of epithelial tissue would line the opening of the urethra (the exit of the tract)? 3. What type
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Other Factors Affecting GFR. Chapter 25. After Filtration. Reabsorption and Secretion. 5 Functions of the PCT
 Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Urine Formation. Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages Urine Formation. Glomerular Filtration 4/24/2016
 Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
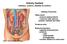 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
CHAPTER 26 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 26 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, one urinary bladder, and one urethra (Figure 26.1). B. Urine is excreted from each kidney through
CHAPTER 26 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, one urinary bladder, and one urethra (Figure 26.1). B. Urine is excreted from each kidney through
Waste Products & Kidney Function
 Waste Products & Kidney Function urinary system principal means of metabolic waste removal urinary system is closely associated with reproductive system urogenital system share embryonic development share
Waste Products & Kidney Function urinary system principal means of metabolic waste removal urinary system is closely associated with reproductive system urogenital system share embryonic development share
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 17 Urinary System 2 Glomerular Filtration Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Overview of Renal Physiology
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 17 Urinary System 2 Glomerular Filtration Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Overview of Renal Physiology
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
The functions of the kidney:
 The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology)
 Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, 2012 Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD Iranian Research Organization for Science & Technology (IROST) Tehran, Iran The Urinary System
Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, 2012 Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD Iranian Research Organization for Science & Technology (IROST) Tehran, Iran The Urinary System
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp , Chapter 19: pp ,
 P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden
 Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the
HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
1. The Fibrous Capsule covers the outside of the kidney. It is made of fat and fibers.
 Slide 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is the excretion of toxic metabolic waste through urine production. The kidneys filter blood plasma and as a result of filtering blood, the kidneys help
Slide 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is the excretion of toxic metabolic waste through urine production. The kidneys filter blood plasma and as a result of filtering blood, the kidneys help
URINARY SYSTEM. Primary functions. Major organs & structures
 URINARY SYSTEM Primary functions Excretion of metabolic wastes Regulation of water and ion balances Regulation of blood pressure Vitamin D activation Regulation of rbc s (erythropoietin) Gluconeogenesis
URINARY SYSTEM Primary functions Excretion of metabolic wastes Regulation of water and ion balances Regulation of blood pressure Vitamin D activation Regulation of rbc s (erythropoietin) Gluconeogenesis
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra. The formation of urine is the function of the kidneys, and the rest of the system is responsible
URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra. The formation of urine is the function of the kidneys, and the rest of the system is responsible
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Physiology Unit 4
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
Lesson XIV: The Urinary System
 Lesson XIV: The Urinary System The urinary system is comprised of the two kidneys, the two ureters that lead from each kidney and empty into the urinary bladder, from which extends the urethra that discharges
Lesson XIV: The Urinary System The urinary system is comprised of the two kidneys, the two ureters that lead from each kidney and empty into the urinary bladder, from which extends the urethra that discharges
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Kidney and urine formation
 Kidney and urine formation Renal structure & function Urine formation Urinary y concentration and dilution Regulation of urine formation 1 Kidney and urine formation 1.Renal structure & function 1)General
Kidney and urine formation Renal structure & function Urine formation Urinary y concentration and dilution Regulation of urine formation 1 Kidney and urine formation 1.Renal structure & function 1)General
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM
 AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
Chapter 26. The Urinary System. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Histology / First stage The Urinary System: Introduction. Kidneys
 The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
Regulate chemical composition of body fluids. Controls composition of bloods ion levels and concentration. Help maintain PCO2 & acid/base balance [ph]
![Regulate chemical composition of body fluids. Controls composition of bloods ion levels and concentration. Help maintain PCO2 & acid/base balance [ph] Regulate chemical composition of body fluids. Controls composition of bloods ion levels and concentration. Help maintain PCO2 & acid/base balance [ph]](/thumbs/76/74054884.jpg) The Urinary System Regulate chemical composition of body fluids Eliminates waste Controls composition of bloods ion levels and concentration Help maintain PCO2 & acid/base balance [ph] Help regulate blood
The Urinary System Regulate chemical composition of body fluids Eliminates waste Controls composition of bloods ion levels and concentration Help maintain PCO2 & acid/base balance [ph] Help regulate blood
active transport of! Na. C. Tubular Reabsorption of Nutrients, Water, and Ions (p. 979; Fig )
 The Urinary System Outline 25.1 The kidneys have three distinct regions and a rich blood supply (pp. 963 965; Figs. 25.1 25.5) A. Location and External Anatomy (p. 963; Figs. 25.1 25.3) 1. The kidneys
The Urinary System Outline 25.1 The kidneys have three distinct regions and a rich blood supply (pp. 963 965; Figs. 25.1 25.5) A. Location and External Anatomy (p. 963; Figs. 25.1 25.3) 1. The kidneys
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
Collin County Community College RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Functions of the kidney
 Physiology of Urinary tract Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder Urethra Kidney function Excretion Physiology of volume regulation Functions of the kidney Excretion of dangerous substances endogenous (metabolites):
Physiology of Urinary tract Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder Urethra Kidney function Excretion Physiology of volume regulation Functions of the kidney Excretion of dangerous substances endogenous (metabolites):
URINARY SYSTEM. Urinary System
 URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
Waste. Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8. Urinary System. Urinary System. Nitrogenous Wastes. Nitrogenous Wastes 4/22/2016
 Waste Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8 Metabolism produces waste products What is the primary waste product of cellular respiration? How does the body dispose of it? Urinary System Urinary
Waste Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8 Metabolism produces waste products What is the primary waste product of cellular respiration? How does the body dispose of it? Urinary System Urinary
Ch 19: The Kidneys. Functional unit of kidneys:?? Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM
 Ch 19: The Kidneys Homeostatic regulation of ECF volume and BP Osmolarity 290 mosm Ion balance Na+ and K+, etc. ph (acid-base balance Excretion of wastes & foreign substances Hormone production EPO Renin
Ch 19: The Kidneys Homeostatic regulation of ECF volume and BP Osmolarity 290 mosm Ion balance Na+ and K+, etc. ph (acid-base balance Excretion of wastes & foreign substances Hormone production EPO Renin
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19](/thumbs/77/74887026.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily.
 1 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily. Next, the kidneys filter blood. As a result of filtering blood, the kidneys
1 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily. Next, the kidneys filter blood. As a result of filtering blood, the kidneys
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX
 One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
Urinary System Functions of the Urinary system (renal) A. B. C.
 Urinary System Functions of the Urinary system (renal) A. B. C. I. Overview of fluids A. Normal volumes 1. fluid intake a. = 1500 ml b. = 750 ml c. = 250 ml (remember ETS) d. total = 2500 ml/day 2. fluid
Urinary System Functions of the Urinary system (renal) A. B. C. I. Overview of fluids A. Normal volumes 1. fluid intake a. = 1500 ml b. = 750 ml c. = 250 ml (remember ETS) d. total = 2500 ml/day 2. fluid
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 18 Urinary System 3 Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Principles of
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 18 Urinary System 3 Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Principles of
Lesson 14.1: Learning the Key Terms
 209 Lesson 14.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. collecting duct 2. distal convoluted tubule 3. glomerulus 4. nephron 5. nephron loop
209 Lesson 14.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. collecting duct 2. distal convoluted tubule 3. glomerulus 4. nephron 5. nephron loop
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Osmoregulation and Renal Function
 1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
Urinary System. Chapter 17 7/19/11. Introduction
 7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
