The spectrum of neurological manifestations of Fabry disease in alarge Turkish family with c.[680g>a] p.[r227q]mutation
|
|
|
- Louise Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neurology Asia 2017; 22(3) : The spectrum of neurological manifestations of Fabry disease in alarge Turkish family with c.[680g>a] p.[r227q]mutation 1 Aslı Aksoy Gündoğdu, 1 Zeynep Özözen Ayas, 1 Murat Alemdar, 2 DilcanKotan 1 Department of Neurology, Sakarya University Research and Training Hospital, Sakarya; 2 Department of Neurology, Sakarya University Faculty of Medicine, Sakarya, Turkey Abstract Background& Objectives: Fabry disease (FD) is a rare lysosomal storage disease with X-linked recessive inheritance caused by a mutation in the α-galactosidase A gene (GLA) (X ) on chromosome X, leading to α-galactosidase (α-gal A) (EC: ) enzyme deficiency. In this report, we present the genetic mutations, clinical features and the neurological involvement of a large Turkish family with FD diagnosed in our clinic during the etiological investigation of a young index patient with recurrent ischemic stroke episodes. Methods: We evaluated 20 members (9 male, 11 female) of a large Turkish family including the index patient. All of them were investigated with a detailed medical history, systemic and neurological examination. Enzyme activity of α-gal A and GLA gene mutation were tested using dried blood spot (DBS) method. The normative value of α-gal A enzyme activity was above the cut-off value of 1.2 μmol/l/h. Results: The α-gal A activity was low in 13 cases (5 male, 27.7%). A total of 13 patients (4 male patients out of 5 males with low enzyme activity and 9 female patients) were found to have a c.[680g>a] p.[r227q] missense mutation in the GLA gene. Ischemic stroke, renal disorder, cardiomyopathy, neuropathic pain, acroparesthesia, hearing loss, ocular involvement, angiokeratoma, hypohydrosis and hyperhydrosis were the clinical manifestations of FD in the affected family members. Conclusion: The clinical and genetic features of this large Turkish family with FD support an association between the neurological phenotype and the c.[680g>a] p.[r227q] mutation. Since FD is treatable, it is recommended to perform enzymatic and genetic studies among family members. Key words: Fabry Disease, GLA mutation, family screening, pedigree INTRODUCTION Fabry s disease (FD) is a rare hereditary lysosomal storage disease with X-linked recessive inheritance. Mutation of the α-galactosidase A gene (GLA) (X ) causes altered α-galactosidase (α-gal A) (EC: ) activity leading the lysosomal accumulation of neutral glycosphingolipids inside the various cell types. 1 Localization of glycosphingolipid depositions determines the clinical features of the FD. Deposits could be accumulated in in endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells of the blood vessels, renal epithelial cells, pericytes, myocardial cells, neurons of the spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia. 1,2 Therefore, multiple organs get damaged concurrently in FD patients. Renal, cardiac and cerebrovascular disorders generally occur with the progression of the disease. 1 In accordance to the inheritance pattern of the disease, the males with the hemizygous GLA mutations developed the FD. The heterozygous females can also show the clinical symptoms of the disease from mild to severe. 3 Up to date, approximately 2000 GLA gene mutations have been reported. 4 In general, the same genetic mutation is shared among the members of the families. 5 In this report, we present the genetic mutations, clinical features and the neurological involvement of a large Turkish family with FD diagnosed in our clinic during the investigation of a young patient with recurrent ischemic stroke. METHODS Patients and clinical investigation Twenty participants including the index patient and 19 members of his large family were enrolled Address correspondence to: Dr. Aslı Aksoy Gündogdu, Department of Neurology, Sakarya University Training and Research Hospital, Sakarya, Turkey, Postal Address: Adnan Menderes Avenue, Saglık Street, No:195, Adapazarı, Sakarya, Turkey. Tel: , asliaksoy_84@hotmail.com 253
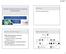
2 Neurology Asia September 2017 in this study. In each individual, medical history, physical examination, α-gal A enzyme activity, and GLA mutation analysis were performed. Those with a mutation and having relevant symptoms, were further investigated by a detailed systemic and neurological examination, ophthalmological and audiological evaluations, electrocardiography (EKG), echocardiogram (ECHO), electroneuromyography (ENMG), Electroencephalogram (EEG), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), carotid ultrasonography, urinalysis, renal ultrasonography and blood analysis. Gal A activity analysis Measurement of enzyme activity in dried blood spot samples was performed via DBS method using filter paper containing DBS as a source of DNA. 6 Four drops of the blood were transferred to a filter paper, allowed to dry at room temperature, and kept at 2 4 C until analysis. Patients with values <1.2 µmol/l/h were considered to have low α-gal A activity. GLA mutation on genetic analysis The genetic screening of the GLA mutation was performed in patients with low α-gal A activity by using the DBS cards. However, the genetic study was performed in women even if the enzyme activity was normal. DNA analysis of the GLA gene was used to confirm the diagnosis of FD. The gene encoding GLA is found on Xq22.1 (chrx:101,397, ,407,925 10,123 bp) and spans 13kb of genomic DNA (7 exons, cdna of 1290 bases). The GLA gene encodes a 429 amino acid protein, of which the first 31 residues form a lysosomal signal peptide. The coding sequences and flanking intronic sequences (minimum of 20 base pairs) of exons 1-7 of the GLA gene are amplified from purified genomic DNA and sequenced in the forward and reverse directions. Sequencing of a single exon is available for targeted mutation analysis. Patient sequences are compared to the reference DNA sequence. 7 A written informed consent was obtained from the patients for publication of this report and any accompanying images. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis of our study was performed by using statistical package for social sciences (SPSS) program (18.0 windows; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Descriptive statistics were calculated for all continuous and categorical variables. Continuous data were described by mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median and interquartile range (IQR), categorical data are presented as numbers or percentages. RESULTS A 23-year-old male patient (index patient, IV.1) presented to the emergency department with left-sided hemiparesthesia. His past medical history was notable for cerebrovascular disease (left-sided hemiparesis and paresthesia, improved without sequel) 4 years earlier, followed by herpes simplex virus (HSV) I encephalitis 1 months later. There consanguineous marriage between his parents (first cousins). The brain diffusionweighted and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) MRI of this patient revealed an acute infarction in the right globus pallidus (Figure 1). There were no abnormalities in routine laboratory tests including hemogram, serum glucose and electrolyte levels, lipid profile, hepatic and renal function tests. Further studies were performed to determine the underlying cause of stroke. Electrocardiography (ECG) showed normal sinus rhythm. Carotid ultrasonography (USG) and ECHO were also normal. Carotid MRA did not reveal any pathological findings. The markers for vasculitis were negative. Prothrombin mutation G20210A and factor V Leiden mutation were not present. The levels of antithrombin III, protein C, and protein S were within normal limits. However, he had a homozygous mutation in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677 gene. The serum homocysteine was normal (9 umol/l; nv: 5-15). He was referred to the hematology service, whose opinion was that the patient had low risk for thrombosis, and did not recommend anticoagulant treatment. Assessment of the enzyme α-gal A and gene analysis with DBS method showing a very low enzymatic activity (0.1 nmols/h/ml; nv>1.2) and a hemizygous missense mutation of the c.[680g>a] p.[r227q]gene. The patient was diagnosed as having FD. A subsequent screening for FD was performed on 20 members of the family (9 males, 45%). The mean age of the study patients was 36.7±16.67 (range 8-73 years). The pedigree is shown in Figure 2 and relevant clinical, enzymatic and genetic data are given in the Table 1. The mean α-gal A enzyme activity of the 20 cases was 1.21±1.12nmols/h/mL. The molecular analysis of the GLA gene revealed the known c.[680g>a] p.[r227q] mutation in 13 patients aged from 8 254
3 Figure 1. Brain MRI of the index patient. Axial diffusion-weighted image (a) shows diffusion restriction (arrow) in the right globus pallidus. The corresponding ADC image (b) shows decreased ADC, as evident by the dark signal (arrow) in the region of reduced diffusion. to 44 years (mean 30.46±11.6). Beside the index patient, 3 hemizygous males and 9 symptomatic heterozygous females were identified. The mean α-gal A enzyme activity of the cases with GLA mutation was measured as 0.66±0.64 nmols/h/ ml. Figure 2. Pedigree of the Fabry disease 255
4 Neurology Asia September 2017 Table 1: Demographic, clinical features, α-gal A enzyme activities and GLA gene mutation results of the cases Case Age Sex GLA Mutation α-gal A Enzyme activity Stroke Cardiac Renal Ocular Dermatological Other neurological AK Hyperh Hypoh NP AP ES HL II.1 73 M II M II F III.1 47 F III.2 34 M III.3 45 M III.4 44 F Heterozygous III.5 43 M Hemizygous III.6 42 M Hemizygous III.7 41 F Heterozygous III.8 40 F Heterozygous III F Heterozygous III M Hemizygous III F Heterozygous III F Heterozygous IV.1 24 M Hemizygous IV.2 16 M IV.3 20 F Heterozygous IV.4 17 F Heterozygous IV.5 8 F Heterozygous AK: Angiokeratoma, Hyperh: Hyperhidrosis, Hypoh: Hypohidrosis, NP: Neuroapathic Pain, AP: Acroparesthesia, ES: Epileptic Seizure, HL: Hearing loss 256
5 The enzyme level was low in 13 members (8 females, 5 males) of the family. Four of 5 males with low enzyme activity and 9 females were found to have a known missense mutation of the c.[680g>a] p.[r227q]gene. Although a female case (IV.3) had the GLA mutation, her enzyme activity was within normal limits. She had hyperhydrosis and acroparesthesia. On the other hand, the enzyme activity of a male (III.2) with no GLA mutation was low. He had a history of epileptic seizure, cognitive impairment and neuropathic pain. Whole gene sequence analysis did not reveal any mutation in this male case with a different clinical picture from other siblings. DISCUSSION Anderson-Fabry disease was first described by two separate scientists in ,9 In general population, the incidence of the disease was reported to range from 1:476,000 to 1:117, A prevalence study revealed the frequency of FD as per 100,000 live births in Turkey. 11 In a study among Turkish patients undergoing hemodialysis, the prevalence of FD was determined to be % Because of the atypical or oligosymptomatic forms of the disease, precise incidence and prevalence of FD are still not known. 15 Although the average delay from onset of symptom to the time of diagnosis is years, it may take up to 20 years in some cases. In a recent paper, more than 25% of FD patients are reported to be misdiagnosed. 16 Measurement of α-gal A enzyme activity in males and molecular genetic testing of GLA in females are the reliable methods for diagnosing FD. 17,18 Mutations detected in the classical type of FD are large splicing defects, missense or nonsense mutations, while the variant (mild) type is characterized by splicing defects or missense mutations. 2 Missense mutation or substitution refers to a change in one amino acid in a protein, arising from a point mutation in a single nucleotide. In case of FD, missense mutations in GLA gene render the gene nonfunctional. As a result of the X-linked recessive inheritance pattern, FD typically affects males, whereas, heterozygous females may show high variability in clinical manifestations which is attributed to random X-chromosome inactivation. The levels of activity of α-gal A enzyme were helpful for the diagnosis but did not have prognostic value. In male patients, the diagnosis of FD could be made by detecting low levels of α-gal A activity in plasma or white blood cells. As the carrier females may have low or normal enzyme activity, molecular genetic testing is a more preferred method in the diagnosis of FD in females. 1,19 In our study, the enzyme level was low in 13 members (8 females, 5 males) of the family. Four of 5 males with low enzyme activity and 9 females were found to have a known missense mutation of the c.[680g>a] p.[r227q] gene. 19 Although a female case (IV.3) had the GLA mutation, her enzyme activity was within normal limits. She had hyperhydrosis and acroparesthesia. These findings showed the importance of searching for GLA gene mutation in female members of the family even if they had normal enzyme levels. FD may cause various clinical manifestations. In classical form with deficient activity of α-gla, the symptoms of the disease typically begin to occur in childhood. Acroparesthesias, angiokeratomas, hypohidrosis, hearing loss and corneal dystrophy are common initial symptoms. In general, prominent skin symptoms occur in adolescence. Renal failure, cardiac or neurological diseases mostly occur in adulthood. In later-onset variant form with residual enzyme activity, cardiac disease and/or renal failure develop after the fourth decade. It is recognized that central and peripheral neurological complications are frequently seen in the course of FD, and cerebrovascular diseases are often the first cause of hospitalization. 1,2,16 Our index case had none of the classical initial symptoms of the disease and was diagnosed to have FD upon investigation for recurrent stroke episodes at a young age. As an another risk factor for stroke, homozygous MTHFR gene mutation was not considered as major etiology in this case, because of his normal serum homocysteine level. The major cause of early morbidity and mortality in FD is the young onset cerebrovascular disease. Neuronal accumulation of globotriaosylceramide (Gb-3) in the cerebral cortex and brain stem, vascular occlusion, endothelial dysfunction and a prothrombotic state have been proposed for the development of stroke. 20,21 Our index patient had two stroke episodes when he was 19 and 23 years old. Family screening identified the FD diagnosis in his 43-year-old maternal uncle (III.5), who also had a minor stroke episode previously. A history of ischemic stroke was also present in two more cases (II.1, III.1) that were not diagnosed with FD. Notwithstanding that the affected females manifesting neurological symptoms, none of them had cerebrovascular disease. A homozygous MTHFR C677 gene mutation has been identified in our index patient. To the best of our knowledge, a link between factor V Leiden mutation, stroke 257
6 Neurology Asia September 2017 and the FD has been reported; but a connection between GLA and MTHFR mutations has not been established. 22 Our index patient also had a history of HSV I encephalitis. In Fabry patients with cerebrovascular complications, the occurrence of concomitant aseptic meningitis has been reported previously. 23 The close occurrence of HSV I encephalitis and stroke in FD has not been reported previously. The symptoms of early neurological involvement may include acroparesthesia, neuropathic pain, hearing loss, and tinnitus. Seven of our patients (III.2, III.4-8, III.11) had neuropathic pain, 7 had (III.5-8, IV.3, IV.4, IV.5) acroparesthesia and 2 had hearing loss (III.4, III.5). Cardiac involvement in FD consists of left ventricular hypertrophy, mitral valve regurgitation, coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy, and arrhythmia. 24,25 Two FD cases (III.5, III.8) in our study had cardiomyopathy. One case of age of 73 years (II.1) had coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction. It has been said that renal manifestations are usually nonspecific. Asymptomatic proteinuria and hematuria episodes, which are often the first signs of renal involvement, may be missed. Renal symptoms mostly appear in the third decade in half of the FD patients, but the severity of renal disease worsen with advancing age. In all of the FD patients, an end-stage renal failure will be expected by the age of Five of our patients (III.4-8) had renal involvement. However, only one patient (III.5) progressed to end-stage requiring hemodialysis. Corneal verticillate (the most common and earliest sign), whirlpool-shaped corneal opacities, cataract, conjunctival and retinal dilatation and tortuosity may occur as the ocular involvement of the FD. 27 In our study, 3 patients (III.6-8) had ocular involvement of FD. One case (II.1) had age-related cataract. Diffuse angiokeratoma is a characteristic, but a nonspecific sign of the FD and is generally the earliest sign in affected males. It is observed in 66 % of males and 33 % of females. Other common skin lesions are telangiectasia, lymphedema, hyperhydrosis and hypohydrosis. 28,29 One patient (III.7) in our study had angiokeratomas, 3 had (III.5-7) hypohydrosis and 6 had (III.1, III.3, III.8, IV.3-5) hyperhydrosis. Medical or surgical treatment of the symptoms provides benefit for the patients. Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) developed for FD is a promising treatment option. ERT may prevent the Gb-3 accumulation and progression of the disease before irreversible organ damage occurs In our study, 5 patients have been treated with ERT. Although various clinical manifestations in the families with different GLA gene mutations are reported, the genotype phenotype correlations of FD are not confirmed. In 2009, Mehta et al. reported the clinical outcomes of 1,453 FD patients from 19 countries participating in the Fabry Outcome Survey (FOS). The most frequently reported signs and symptoms were neurologic, affecting 68% of the patients. 33 Stroke was reported in 23% of FD patients and the mean age of onset was 33.7 years. However, researchers did not report a correlation between the neurologic manifestation of FD and the type of genetic mutation. In 2010, Brouns et al. reported that Ser126Gly and Ala143Thr mutations were associated with strokeas atypical variants of FD with late-onset cerebrovascular disease. 34 In 2014, Schelleckes et al. reported that 13 of 15 FD patients carrying the GLA haplotype -10C>T [rs ], IVS2-81_-77delCAGCC [rs ], IVS4-16A>G [rs ], and IVS6-22C>T [rs ] had neurological manifestations such as neuropathic pain, allodynia and stroke. 35 In our study, all of the newly diagnosed relatives have been carrying the same mutation c.[680g>a] p.[r227q] and frequently (76.9%) had neurological symptoms. Beside, other organ system involvements were not prominent in our patients. Therefore, we hypothesize that this mutation may be related to the neurological phenotype of FD. However, further studies with larger populations are needed to confirm this association. In this study, we presented the spectrum of neurological manifestations in a large Turkish family of FD with c.[680g>a] p.[r227q] mutation detected during the investigation of a young stroke patient. FD should be screened among young stroke patients particularly in those with multiorgan involvement. Our study demonstrate the importance of early diagnosis, constructing a detailed pedigree and providing a genetic counseling for the FD patients. Since FD is a treatable disorder, performing the enzymatic and genetic tests is valuable in the family members. We proposed that the hemizygous missense mutation of the c.[680g>a] p.[r227q]gene as a predictor of the neurological phenotype of FD. DISCLOSURE Financial support: None Conflict of interest: None 258
7 REFERENCES 1. Desnick RJ, Ioannou YA, Eng CM. Alphagalactosidase A deficiency: Fabry disease. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, Kinzler KE, Vogelstein B, eds. The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited diseases. 8 ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2001: Mehta A, Hughes DA. Fabry Disease Aug 5 [Updated 2017 Jan 5]. In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, et al., editors. GeneReviews [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; Available from: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk1292/ 3. Wang RY, Lelis A, Mirocha J, Wilcox WR. Heterozygous Fabry women are not just carriers, but have a significant burden of disease and impaired quality of life. Genet Med 2007;9(1): Schäfer E, Baron K, Widmer U, et al. Thirty-four novel mutations of the GLA gene in 121 patients with Fabry disease. Hum Mutat 2005;25(4): Chamoles NA, Blanco M, Gaggioli D. Fabry disease: enzymatic diagnosis in dried blood spots on filter paper. Clin Chim Acta2001; 308: aspx?id=10028&menuitem=3 8. Anderson W. A case of Angio-Keratoma. Br J Dermatol 1898;10: Fabry J. Purpura papulosa haemorrhagica Hebrae. Arch Dermatol Syph 1898;43: Germain DP. Fabry disease. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2010;5: Ozkara HA, Topcu M. Sphingolipidoses in Turkey. Brain Dev 2004;26: Okur I, Ezgu F, Biberoglu G,et al. Screening for Fabry disease in patients undergoing dialysis for chronic renal failure in Turkey: identification of new case with novel mutation. Gene 2013;527: Okur I, Biberoglu G, Ezgu FS, et al. Identification of novel mutations and prevalence for Fabry disease (FD) via screening studies using dried blood samples (DBS) among hemodialysis patients in Turkey. Mol Genet Metab 2015;114: Sayilar EI, Ayar Y, Yavuz M. Prevalence of Fabry disease among Turkish dialysis patients: Data from hemodialysis centers in Bursa province. Clin Nephrol 2016;85(3): Barba-Romero MÁ, Rivera-Gallego A, Pintos-Morell G; Spanish FOS-Study Group. Fabry disease in Spain: description of Spanish patients and a comparison with other European countries using data from the Fabry Outcome Survey (FOS). Int J Clin Pract 2011;65(8): Mehta A, Ricci R, Widmer U, et al. Fabry disease defined: baseline clinical manifestations of 366 patients in the Fabry Outcome Survey. Eur J Clin Invest 2004;34(3): Linthorst GE, Poorthuis BJ, Hollak CE. Enzyme activity for determination of presence of Fabry disease in women results in 40% false-negative results. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008; 51:2082; author reply Linthorst GE, Vedder AC, Aerts JM, Hollak CE. Screening for Fabry disease using whole blood spots fails to identify one-third of female carriers. Clin Chim Acta 2005;353: Eng CM, Resnick-Silverman LA, Niehaus DJ, Astrin KH, Desnick RJ. Nature and frequency of mutations in the alpha-galactosidase A gene that cause Fabry disease. Am J Hum Genet 1993;53(6): DeGraba T, Azhar S, Dignat-George F, et al. Profile of endothelial and leukocyte activation in Fabry patients. Ann Neurol2000;47(2): Fellgiebel A, Müller MJ, Ginsberg L. CNS manifestations of Fabry s disease. Lancet Neurol 2006;5(9): Lenders M, Karabul N, Duning T, et al. Thromboembolic events in Fabry disease and the impact of factor V Leiden. Neurology 2015;84(10): Lidove O, Chauveheid MP, Caillaud C, et al. Aseptic meningitis and ischaemic stroke in Fabry disease. Int J Clin Pract 2009;63(11): Kampmann C, Baehner F, Ries M, Beck M. Cardiac involvement in Anderson-Fabry disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2002;13(Suppl 2):S Duro G, Musumeci MB, Colomba P, et al. Novel α-galactosidase A mutation in patients with severe cardiac manifestations of Fabry disease. Gene 2014;535(2): Branton M, Schiffmann R, Kopp JB. Natural history and treatment of renal involvement in Fabry disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2002;13(Suppl 2):S Davey PG. Fabry disease: A survey of visual and ocular symptoms. Clin Ophthalmol 2014;8: Orteu CH, Jansen T, Lidove O, et al. FOS Investigators. Fabry disease and the skin: data from FOS, the Fabry outcome survey. Br J Dermatol2007;157(2): Zampetti A, Orteu CH, Antuzzi D, et al. Angiokeratoma: decision-making aid for the diagnosis of Fabry disease. Br J Dermatol 2012;166: Ortiz A, Abiose A, Bichet DG, et al. Time to treatment benefit for adult patients with Fabry disease receiving agalsidase β: data from the Fabry Registry. J Med Genet 2016;53(7): Germain DP, Charrow J, Desnick RJ, et al. Tenyear outcome of enzyme replacement therapy with agalsidase beta in patients with Fabry disease. J Med Genet 2015;52(5): Rombach SM, Smid BE, Bouwman MG, Linthorst GE, Dijkgraaf MG, Hollak CE. Long term enzyme replacement therapy for Fabry disease: effectiveness on kidney, heart and brain. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2013;8: Mehta A, Clarke JT, Giugliani R, et al. FOS Investigators. Natural course of Fabry disease: changing pattern of causes of death in FOS - Fabry Outcome Survey. J Med Genet 2009;46(8): Brouns R, Thijs V, Eyskens F, et al. Belgian Fabry study: prevalence of Fabry disease in a cohort of 1000 young patients with cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 2010;41(5): Schelleckes M, Lenders M, Guske K, et al. Cryptogenic stroke and small fiber neuropathy of unknown etiology in patients with alpha-galactosidase A -10T genotype. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2014;9:
Heart disease. Other symptoms too? FABRY DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH UNEXPLAINED HEART CONDITIONS
 Heart disease Other symptoms too? FABRY DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH UNEXPLAINED HEART CONDITIONS You have been given this brochure because your heart condition may be linked to Fabry disease, which is a rare,
Heart disease Other symptoms too? FABRY DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH UNEXPLAINED HEART CONDITIONS You have been given this brochure because your heart condition may be linked to Fabry disease, which is a rare,
Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard
 Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: GLA DISORDER: Fabry disease HGNC ID: 4296 OMIM ID: 301500 ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as a practice guideline or systematic
Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: GLA DISORDER: Fabry disease HGNC ID: 4296 OMIM ID: 301500 ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as a practice guideline or systematic
FABRY DISEASE: Phenotypic Spectrum Genotype/Phenotype Correlations Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) R. J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D.
 FABRY DISEASE: Phenotypic Spectrum Genotype/Phenotype Correlations Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) R. J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D. Director, International Center for Fabry Disease Dean for Genetic & Genomic
FABRY DISEASE: Phenotypic Spectrum Genotype/Phenotype Correlations Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) R. J. Desnick, Ph.D., M.D. Director, International Center for Fabry Disease Dean for Genetic & Genomic
A Unique Disease Uniquely Experienced
 A Unique Disease Uniquely Experienced Understanding Fabry disease a serious, progressive disorder with complex pathology 1 Fabry disease is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder. 1 Caused by a deficiency
A Unique Disease Uniquely Experienced Understanding Fabry disease a serious, progressive disorder with complex pathology 1 Fabry disease is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder. 1 Caused by a deficiency
Yin-Hsiu Chien, 1 Ni-Chung Lee, 1 Shu-Chuan Chiang, 1 Robert J Desnick, 2 and Wuh-Liang Hwu 1
 Fabry Disease: Incidence of the Common Later-Onset α-galactosidase A IVS4+919G A Mutation in Taiwanese Newborns Superiority of DNA-Based to Enzyme-Based Newborn Screening for Common Mutations Yin-Hsiu
Fabry Disease: Incidence of the Common Later-Onset α-galactosidase A IVS4+919G A Mutation in Taiwanese Newborns Superiority of DNA-Based to Enzyme-Based Newborn Screening for Common Mutations Yin-Hsiu
Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness
 Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Running Title: Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Professor Perry Elliott MBBS; MD; FRCP; FESC; FACC Chair of Cardiovascular
Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Running Title: Fabry Disease: A rare condition emerging from the darkness Professor Perry Elliott MBBS; MD; FRCP; FESC; FACC Chair of Cardiovascular
Pedigree analysis of Mexican families with Fabry disease as a powerful tool for identification of heterozygous females
 Pedigree analysis of Mexican families with Fabry disease as a powerful tool for identification of heterozygous females B.E. Gutiérrez-Amavizca 1,2, R. Orozco-Castellanos 3,4, J. R. Padilla-Gutiérrez 5,
Pedigree analysis of Mexican families with Fabry disease as a powerful tool for identification of heterozygous females B.E. Gutiérrez-Amavizca 1,2, R. Orozco-Castellanos 3,4, J. R. Padilla-Gutiérrez 5,
Fabry Outcome Survey
 Fabry Outcome Survey Annual Report 2016 Reporting Period: 17-04-2001 to 05-01-2017 This report has been prepared by Shire Outcome Surveys, on behalf of the FOS Steering Committee Date of preparation: August
Fabry Outcome Survey Annual Report 2016 Reporting Period: 17-04-2001 to 05-01-2017 This report has been prepared by Shire Outcome Surveys, on behalf of the FOS Steering Committee Date of preparation: August
Cardiomyopathy in Fabry s disease
 Cardiomyopathy in Fabry s disease Herzinsuffizienzlunch Basel, 11.09.2018 Christiane Gruner Kardiologie, UniversitätsSpital Zürich Content Background / epidemiology Differential diagnosis Clinical presentations
Cardiomyopathy in Fabry s disease Herzinsuffizienzlunch Basel, 11.09.2018 Christiane Gruner Kardiologie, UniversitätsSpital Zürich Content Background / epidemiology Differential diagnosis Clinical presentations
Fabry Disease in Latin America: Data from the Fabry Registry
 JIMD Reports DOI 10.1007/8904_2012_165 RESEARCH REPORT Fabry Disease in Latin America: Data from the Fabry Registry J. Villalobos J.M. Politei A.M. Martins G. Cabrera H. Amartino R. Lemay S. Ospina S.
JIMD Reports DOI 10.1007/8904_2012_165 RESEARCH REPORT Fabry Disease in Latin America: Data from the Fabry Registry J. Villalobos J.M. Politei A.M. Martins G. Cabrera H. Amartino R. Lemay S. Ospina S.
Misdiagnosis of familial Mediterranean fever in patients with Anderson Fabry disease
 Clin Genet 2013: 83: 576 581 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2012.01940.x
Clin Genet 2013: 83: 576 581 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2012.01940.x
Medication Policy Manual. Topic: Fabrazyme, agalsidase beta Date of Origin: February 17, 2015
 Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru391 Topic: Fabrazyme, agalsidase beta Date of Origin: February 17, 2015 Committee Approval Date: March 13, 2015 Next Review Date: March 2016 Effective Date: July
Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru391 Topic: Fabrazyme, agalsidase beta Date of Origin: February 17, 2015 Committee Approval Date: March 13, 2015 Next Review Date: March 2016 Effective Date: July
Fabry RADAR 2007 The Fabry Registry Aggregate Data Annual Report
 Fabry RADAR 2007 The Fabry Registry Aggregate Data Annual Report A program supported by Genzyme Fabr/GL/P341/05/07 2007 Genzyme Corporation. All rights reserved. Table of Contents I. II. III. IV. V. VI.
Fabry RADAR 2007 The Fabry Registry Aggregate Data Annual Report A program supported by Genzyme Fabr/GL/P341/05/07 2007 Genzyme Corporation. All rights reserved. Table of Contents I. II. III. IV. V. VI.
Screening for Fabry Disease in Left Ventricular Hypertrophy: Documentation of a Novel Mutation
 Screening for Fabry Disease in Left Ventricular Hypertrophy: Documentation of a Novel Mutation Ana Baptista, Pedro Magalhães, Sílvia Leão, Sofia Carvalho, Pedro Mateus, Ilídio Moreira Centro Hospitalar
Screening for Fabry Disease in Left Ventricular Hypertrophy: Documentation of a Novel Mutation Ana Baptista, Pedro Magalhães, Sílvia Leão, Sofia Carvalho, Pedro Mateus, Ilídio Moreira Centro Hospitalar
Inborn Errors of Metabolism. Landi Lombard Endocrinologist Kuilsrivier
 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Landi Lombard Endocrinologist Kuilsrivier Classification of Inborn Errors of Metabolism Amino acid disorders eg Phenylketonuria Organic acidemias eg Maple syrup urine disease
Inborn Errors of Metabolism Landi Lombard Endocrinologist Kuilsrivier Classification of Inborn Errors of Metabolism Amino acid disorders eg Phenylketonuria Organic acidemias eg Maple syrup urine disease
Genomic analysis of Brazilian patients with Fabry disease
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2007) 40: 1599-1604 Genomic analysis of patients with Fabry disease ISSN 0100-879X 1599 Genomic analysis of Brazilian patients with Fabry disease F.S.
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2007) 40: 1599-1604 Genomic analysis of patients with Fabry disease ISSN 0100-879X 1599 Genomic analysis of Brazilian patients with Fabry disease F.S.
Clinical Appearance and Management of Fabry Nephropathy in Greece
 BANTAO Journal 2010; 8 (2): 75-80 BJ BANTAO Journal Original article Clinical Appearance and Management of Fabry Nephropathy in Greece Andrikos K. Emilios 1, Iatrou E. Christos 2, Boletis N. John 3, Diamandopoulos
BANTAO Journal 2010; 8 (2): 75-80 BJ BANTAO Journal Original article Clinical Appearance and Management of Fabry Nephropathy in Greece Andrikos K. Emilios 1, Iatrou E. Christos 2, Boletis N. John 3, Diamandopoulos
What is a rare disease?
 What is a rare disease? A disease or disorder is defined as rare in Europe when it affects less than 1 in 2000 citizens (Orphan Drug Regulation 141/2000) Rare diseases may affect 30 million European Union
What is a rare disease? A disease or disorder is defined as rare in Europe when it affects less than 1 in 2000 citizens (Orphan Drug Regulation 141/2000) Rare diseases may affect 30 million European Union
Fabry Disease and the Kidneys
 Department of Human Genetics Division of Medical Genetics Lysosomal Storage Disease Center www.genetics.emory.edu Fabry Disease and the Kidneys What is Fabry Disease? Fabry disease (FD) is an X-linked
Department of Human Genetics Division of Medical Genetics Lysosomal Storage Disease Center www.genetics.emory.edu Fabry Disease and the Kidneys What is Fabry Disease? Fabry disease (FD) is an X-linked
FEP Medical Policy Manual
 FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: July 15, 2018 Related Policies: None Genetic Testing for PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome Description The PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome (PHTS) includes several syndromes
FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: July 15, 2018 Related Policies: None Genetic Testing for PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome Description The PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome (PHTS) includes several syndromes
Figure S1. LVMi Change over 18 months on Migalastat and ERT
 Figure S1. LVMi Change over 18 months on Migalastat and ERT Mean change to month 18 in mitt patients (all randomized, treated patients with amenable mutations); LVMi decreased significantly (95% CI does
Figure S1. LVMi Change over 18 months on Migalastat and ERT Mean change to month 18 in mitt patients (all randomized, treated patients with amenable mutations); LVMi decreased significantly (95% CI does
Galafold (migalastat) or Fabrazyme (agalsidase beta) Prior Authorization Criteria:
 Request for Prior Authorization for Fabry Disease Medications Website Form www.highmarkhealthoptions.com Submit request via: Fax - 1-855-476-4158 All requests for Galafold (migalastat) or Fabrazyme (agalsidase
Request for Prior Authorization for Fabry Disease Medications Website Form www.highmarkhealthoptions.com Submit request via: Fax - 1-855-476-4158 All requests for Galafold (migalastat) or Fabrazyme (agalsidase
Heterozygous Fabry Disease Females Are Not Just Carriers, But Suffer From
 Heterozygous Fabry Disease Females Are Not Just Carriers, But Suffer From Significant Burden of Disease And Impaired Quality of Life Raymond Wang, M.D. Children s Hospital of Orange County Division of
Heterozygous Fabry Disease Females Are Not Just Carriers, But Suffer From Significant Burden of Disease And Impaired Quality of Life Raymond Wang, M.D. Children s Hospital of Orange County Division of
The use of pathology surrogate markers in Fabry Disease. Beth L. Thurberg MD PhD Vice President of Pathology Genzyme
 Disclaimer: Presentation slides from the Rare Disease Workshop Series are posted by the EveryLife Foundation for Rare Diseases for educational purposes only. They are for use by drug development professionals
Disclaimer: Presentation slides from the Rare Disease Workshop Series are posted by the EveryLife Foundation for Rare Diseases for educational purposes only. They are for use by drug development professionals
Fabry disease: when to suspect it and how to treat it
 Fabry disease: when to suspect it and how to treat it Catalina Martín Cleary Alberto Ortiz Arduán, MD, PhD IIS-Fundacion Jimenez Diaz, UAM IRSIN, REDINREN Madrid, Spain Conflict of interest Consultant:
Fabry disease: when to suspect it and how to treat it Catalina Martín Cleary Alberto Ortiz Arduán, MD, PhD IIS-Fundacion Jimenez Diaz, UAM IRSIN, REDINREN Madrid, Spain Conflict of interest Consultant:
Enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease, towards individualized treatment Arends, M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease, towards individualized treatment Arends, M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Arends, M. (2017).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease, towards individualized treatment Arends, M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Arends, M. (2017).
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Neonatal cerebral infarction
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal cerebral infarction May 2002 2 Mann C, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Landeskrankenhaus und Akademisches Lehrkrankenhaus Feldkirch, Austria Swiss Society
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal cerebral infarction May 2002 2 Mann C, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Landeskrankenhaus und Akademisches Lehrkrankenhaus Feldkirch, Austria Swiss Society
Fabry disease is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder,
 Stroke in Fabry Disease Frequently Occurs Before Diagnosis and in the Absence of Other Clinical Events Natural History Data From the Fabry Registry Katherine Sims, MD; Juan Politei, MD; Maryam Banikazemi,
Stroke in Fabry Disease Frequently Occurs Before Diagnosis and in the Absence of Other Clinical Events Natural History Data From the Fabry Registry Katherine Sims, MD; Juan Politei, MD; Maryam Banikazemi,
Mutation identification of Fabry disease in families with other lysosomal storage disorders
 Clin Genet 2013: 84: 281 285 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/cge.12071 Mutation identification
Clin Genet 2013: 84: 281 285 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/cge.12071 Mutation identification
Clinical Diversity in Patients with Anderson-Fabry Disease with the R301Q Mutation
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0959-18 Intern Med Advance Publication http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Clinical Diversity in Patients with Anderson-Fabry Disease with the R301Q Mutation Saori Yamamoto 1,
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0959-18 Intern Med Advance Publication http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Clinical Diversity in Patients with Anderson-Fabry Disease with the R301Q Mutation Saori Yamamoto 1,
FABRY DISEASE 12/30/2012. Ataxia-Telangiectasia. Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease
 Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease ES ROACH,MD. Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease Conjunctival lesions Corneal lesions Lesions of iris & lens Retinal vascular lesions
Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease ES ROACH,MD. Ophthalmologic Signs of Genetic Neurological Disease Conjunctival lesions Corneal lesions Lesions of iris & lens Retinal vascular lesions
Clinical Study Vascular Tortuosities of the Upper Eyelid: A New Clinical Finding in Fabry Patient Screening
 Ophthalmology Volume 2013, Article ID 207573, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/207573 Clinical Study Vascular Tortuosities of the Upper Eyelid: A New Clinical Finding in Fabry Patient Screening Langis
Ophthalmology Volume 2013, Article ID 207573, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/207573 Clinical Study Vascular Tortuosities of the Upper Eyelid: A New Clinical Finding in Fabry Patient Screening Langis
Clinical features and diagnosis of Fabry disease
 Clinical features and diagnosis of Fabry disease Monique E Cho, MD Jeffrey B Kopp, MD UpToDate performs a continuous review of over 375 journals and other resources. Updates are added as important new
Clinical features and diagnosis of Fabry disease Monique E Cho, MD Jeffrey B Kopp, MD UpToDate performs a continuous review of over 375 journals and other resources. Updates are added as important new
GALAFOLD (migalastat) oral capsule
 GALAFOLD (migalastat) oral capsule Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy Coverage
GALAFOLD (migalastat) oral capsule Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy Coverage
S2 Protein augmentation therapies for inherited disorders 1
 Disease category Disorder S2 Protein augmentation therapies for inherited 1 Augmented protein 2 Source of therapeutic protein / peptide Outcome References 3 Membrane transport Coagulation Cystic fibrosis
Disease category Disorder S2 Protein augmentation therapies for inherited 1 Augmented protein 2 Source of therapeutic protein / peptide Outcome References 3 Membrane transport Coagulation Cystic fibrosis
Fabry disease in children:correlation between ocular manifestations, genotype and systemic clinical severity.
 Fabry disease in children:correlation between ocular manifestations, genotype and systemic clinical severity. Louise E Allen, Edel M Cosgrave, James P Kersey, Uma Ramaswami To cite this version: Louise
Fabry disease in children:correlation between ocular manifestations, genotype and systemic clinical severity. Louise E Allen, Edel M Cosgrave, James P Kersey, Uma Ramaswami To cite this version: Louise
Review Article Fabry Disease and Early Stroke
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Stroke Research and Treatment Volume 2011, Article ID 615218, 7 pages doi:10.4061/2011/615218 Review Article Fabry Disease and Early Stroke U. Feldt-Rasmussen 1, 2 1 Department
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Stroke Research and Treatment Volume 2011, Article ID 615218, 7 pages doi:10.4061/2011/615218 Review Article Fabry Disease and Early Stroke U. Feldt-Rasmussen 1, 2 1 Department
Case Report Early Renal Involvement in a Girl with Classic Fabry Disease
 Hindawi Case Reports in Nephrology Volume 2017, Article ID 9543079, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9543079 Case Report Early Renal Involvement in a Girl with Classic Fabry Disease Fernando Perretta,
Hindawi Case Reports in Nephrology Volume 2017, Article ID 9543079, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9543079 Case Report Early Renal Involvement in a Girl with Classic Fabry Disease Fernando Perretta,
Fabry Disease Glossary
 Fabry Disease Glossary A Acroparesthesia: A tingling sensation in the hands and feet. Angiokeratoma: Localized collection of thin-walled blood vessels covered by a cap of warty material. Also described
Fabry Disease Glossary A Acroparesthesia: A tingling sensation in the hands and feet. Angiokeratoma: Localized collection of thin-walled blood vessels covered by a cap of warty material. Also described
Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke: Electrocardiographic Findings
 Original Articles 232 Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke: Electrocardiographic Findings Elley H.H. Chiu 1,2, Teng-Yeow Tan 1,3, Ku-Chou Chang 1,3, and Chia-Wei Liou 1,3 Abstract- Background: Standard 12-lead
Original Articles 232 Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke: Electrocardiographic Findings Elley H.H. Chiu 1,2, Teng-Yeow Tan 1,3, Ku-Chou Chang 1,3, and Chia-Wei Liou 1,3 Abstract- Background: Standard 12-lead
Fabry disease is a rare X-linked metabolic disorder caused by
 ARTICLE Agalsidase beta treatment is associated with improved quality of life in patients with Fabry disease: Findings from the Fabry Registry Torquil Watt, MD 1, Alessandro P. Burlina, MD 2, Chiara Cazzorla,
ARTICLE Agalsidase beta treatment is associated with improved quality of life in patients with Fabry disease: Findings from the Fabry Registry Torquil Watt, MD 1, Alessandro P. Burlina, MD 2, Chiara Cazzorla,
Redgrave JN, Coutts SB, Schulz UG et al. Systematic review of associations between the presence of acute ischemic lesions on
 6. Imaging in TIA 6.1 What type of brain imaging should be used in suspected TIA? 6.2 Which patients with suspected TIA should be referred for urgent brain imaging? Evidence Tables IMAG1: After TIA/minor
6. Imaging in TIA 6.1 What type of brain imaging should be used in suspected TIA? 6.2 Which patients with suspected TIA should be referred for urgent brain imaging? Evidence Tables IMAG1: After TIA/minor
Result Navigator. Positive Test Result: PTEN. After a positive test result, there can be many questions about what to do next. Navigate Your Results
 Result Navigator Positive Test Result: PTEN Positive test results identify a change, or misspelling, of DNA that is known or predicted to cause an increased risk for cancer. DNA is the blueprint of life
Result Navigator Positive Test Result: PTEN Positive test results identify a change, or misspelling, of DNA that is known or predicted to cause an increased risk for cancer. DNA is the blueprint of life
Anderson Fabry disease: Ten year outcome of enzyme replacement therapy in a renal transplant patient
 CASE REPORT Port J Nephrol Hypert 2016; 30(2): 000-000 Advance Access publication 24 April 2016 Anderson Fabry disease: Ten year outcome of enzyme replacement therapy in a renal transplant patient Department
CASE REPORT Port J Nephrol Hypert 2016; 30(2): 000-000 Advance Access publication 24 April 2016 Anderson Fabry disease: Ten year outcome of enzyme replacement therapy in a renal transplant patient Department
Assessment report. for
 Assessment report for FABRAZYME agalsidase beta Assessment report on the shortage of Fabrazyme Overview of Shortage Period: Spontaneous Reports from June 2009 through 15 September and Registry Data from
Assessment report for FABRAZYME agalsidase beta Assessment report on the shortage of Fabrazyme Overview of Shortage Period: Spontaneous Reports from June 2009 through 15 September and Registry Data from
Questioning the Pathogenic Role of the GLA p.ala143thr Mutation in Fabry Disease: Implications for Screening Studies and ERT
 JIMD Reports DOI 10.1007/8904_2012_167 RESEARCH REPORT Questioning the Pathogenic Role of the GLA p.ala143thr Mutation in Fabry Disease: Implications for Screening Studies and ERT W. Terryn R. Vanholder
JIMD Reports DOI 10.1007/8904_2012_167 RESEARCH REPORT Questioning the Pathogenic Role of the GLA p.ala143thr Mutation in Fabry Disease: Implications for Screening Studies and ERT W. Terryn R. Vanholder
Prevalence of symptoms in female Fabry disease patients: a case-control survey
 J Inherit Metab Dis (2012) 35:891 898 DOI 10.1007/s10545-011-9447-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of symptoms in female Fabry disease patients: a case-control survey Machtelt G. Bouwman & Saskia M. Rombach
J Inherit Metab Dis (2012) 35:891 898 DOI 10.1007/s10545-011-9447-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of symptoms in female Fabry disease patients: a case-control survey Machtelt G. Bouwman & Saskia M. Rombach
Result Navigator. Positive Test Result: CDH1. After a positive test result, there can be many questions about what to do next. Navigate Your Results
 Result Navigator Positive Test Result: CDH1 Positive test results identify a change, or misspelling, of DNA that is known or predicted to cause an increased risk for cancer. DNA is the blueprint of life
Result Navigator Positive Test Result: CDH1 Positive test results identify a change, or misspelling, of DNA that is known or predicted to cause an increased risk for cancer. DNA is the blueprint of life
This presentation contains forward looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 relating to business,
 American Society of Nephrology (ASN) Migalastat Monotherapy Phase 3 Data N November b 15 15, 2014 Safe Harbor This presentation contains forward looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities
American Society of Nephrology (ASN) Migalastat Monotherapy Phase 3 Data N November b 15 15, 2014 Safe Harbor This presentation contains forward looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities
Fabry Disease X-linked genetic, multi-organ disorder. Fabry disease screening program in Hypertrophic p Cardiomyopathy: preliminary results.
 Fabry Disease X-linked genetic, multi-organ disorder Fabry disease screening program in Hypertrophic p Cardiomyopathy: y preliminary results. Globotriaosylceramide, GL3 Brain -galactosidase A Eyes Lactosylceramide
Fabry Disease X-linked genetic, multi-organ disorder Fabry disease screening program in Hypertrophic p Cardiomyopathy: y preliminary results. Globotriaosylceramide, GL3 Brain -galactosidase A Eyes Lactosylceramide
INVESTIGATION THE PREVALENCE OF MUTATIONS IVS 10 AND R158Q IN A NUMBER OF IRANIAN PATIENTS WITH PKU
 : 293-297 ISSN: 2277 4998 INVESTIGATION THE PREVALENCE OF MUTATIONS IVS 10 AND R158Q IN A NUMBER OF IRANIAN PATIENTS WITH PKU SHIRIN JAHANBAZI, FATEMEHKESHAVARZI* Department of Biology, Sanandaj Branch,
: 293-297 ISSN: 2277 4998 INVESTIGATION THE PREVALENCE OF MUTATIONS IVS 10 AND R158Q IN A NUMBER OF IRANIAN PATIENTS WITH PKU SHIRIN JAHANBAZI, FATEMEHKESHAVARZI* Department of Biology, Sanandaj Branch,
Hemizygous Fabry disease associated with IgA nephropathy: A case report
 1 Hemizygous Fabry disease associated with IgA nephropathy: A case report Fabry disease and IgA nephropathy Homare Shimohata 1, 3, Keigyou Yoh 1, Kenji Takada 2, Hiroaki Tanaka 2, Joichi Usui 1, Kouichi
1 Hemizygous Fabry disease associated with IgA nephropathy: A case report Fabry disease and IgA nephropathy Homare Shimohata 1, 3, Keigyou Yoh 1, Kenji Takada 2, Hiroaki Tanaka 2, Joichi Usui 1, Kouichi
Plasma lyso-gb3: a biomarker for monitoring fabry patients during enzyme replacement therapy
 Clinical and Experimental Nephrology (218) 22:843 849 https://doi.org/1.17/s1157-17-1525-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Plasma lyso-gb3: a biomarker for monitoring fabry patients during enzyme replacement therapy
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology (218) 22:843 849 https://doi.org/1.17/s1157-17-1525-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Plasma lyso-gb3: a biomarker for monitoring fabry patients during enzyme replacement therapy
Long Term Follow-Up Clinical Guidelines for X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy
 Long Term Follow-Up Clinical Guidelines for X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy Gerald Raymond, M.D. Department of Pediatrics and Neurology Penn State Medical Center Hershey, PA June 20, 2018 Disclosure Information
Long Term Follow-Up Clinical Guidelines for X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy Gerald Raymond, M.D. Department of Pediatrics and Neurology Penn State Medical Center Hershey, PA June 20, 2018 Disclosure Information
Morbus Fabry. Bruno Conti Rossini. Sostituto primario Ospedale Regionale di Locarno
 Morbus Fabry Bruno Conti Rossini Sostituto primario Ospedale Regionale di Locarno Problem: Anesthesiologic ambulatory preanesthetic consultation for peripartal epidural anesthesia the call: we have a pregnant
Morbus Fabry Bruno Conti Rossini Sostituto primario Ospedale Regionale di Locarno Problem: Anesthesiologic ambulatory preanesthetic consultation for peripartal epidural anesthesia the call: we have a pregnant
A Case Refort of Sandhoff Disease
 Korean J Ophthalmol Vol. 19:68-72, 2005 A Case Refort of Sandhoff Disease Yie-Min Yun, MD, Su-Na Lee, MD Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea Sandhoff
Korean J Ophthalmol Vol. 19:68-72, 2005 A Case Refort of Sandhoff Disease Yie-Min Yun, MD, Su-Na Lee, MD Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea Sandhoff
Wiskott-Aldrich Registry Data Collection Form Patient Identification: Patient Name (first, middle, last)
 Patient Identification: Patient Name (first, middle, last) Patient s USIDNET Registry Number assigned after online enrollment Date of Birth / / (mm/dd/yyyy) or Year of Birth Gender: male [ ], female [
Patient Identification: Patient Name (first, middle, last) Patient s USIDNET Registry Number assigned after online enrollment Date of Birth / / (mm/dd/yyyy) or Year of Birth Gender: male [ ], female [
Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT?
 Carotid artery stenosis and risk of stroke Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT? Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS Faculty of Medicine of University of Porto Munich, 2016
Carotid artery stenosis and risk of stroke Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT? Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS Faculty of Medicine of University of Porto Munich, 2016
Date of commencement: February Principal Investigator Dr. Jayesh J. Sheth CASE RECORD FORM
 ICMR-FRIGE-MULTICENTRIC LSDs Project Foundation for Research in Genetics & Endocrinology [FRIGE], FRIGE House, Jodhpur Gam road, Satellite, Ahmedabad-380015 Tel no: 079-26921414, Fax no: 079-26921415 E-mail:
ICMR-FRIGE-MULTICENTRIC LSDs Project Foundation for Research in Genetics & Endocrinology [FRIGE], FRIGE House, Jodhpur Gam road, Satellite, Ahmedabad-380015 Tel no: 079-26921414, Fax no: 079-26921415 E-mail:
Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome
 Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome L.H. Cao 1, B.H. Kuang 2, C. Chen 1, C. Hu 2, Z. Sun 1, H. Chen 2, S.S. Wang
Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome L.H. Cao 1, B.H. Kuang 2, C. Chen 1, C. Hu 2, Z. Sun 1, H. Chen 2, S.S. Wang
Result Navigator. Positive Test Result: STK11. After a positive test result, there can be many questions about what to do next. Navigate Your Results
 Result Navigator Positive Test Result: STK11 Positive test results identify a change, or misspelling, of DNA that is known or predicted to cause an increased risk for cancer. DNA is the blueprint of life
Result Navigator Positive Test Result: STK11 Positive test results identify a change, or misspelling, of DNA that is known or predicted to cause an increased risk for cancer. DNA is the blueprint of life
A Sporadic Case of Fabry Disease Involving Repeated Fever, Psychiatric Symptoms, Headache, and Ischemic Stroke in an Adult Japanese Woman
 CASE REPORT A Sporadic Case of Fabry Disease Involving Repeated Fever, Psychiatric Symptoms, Headache, and Ischemic Stroke in an Adult Japanese Woman Jun Sawada 1, Takayuki Katayama 1, Kohei Kano 1, Asuka
CASE REPORT A Sporadic Case of Fabry Disease Involving Repeated Fever, Psychiatric Symptoms, Headache, and Ischemic Stroke in an Adult Japanese Woman Jun Sawada 1, Takayuki Katayama 1, Kohei Kano 1, Asuka
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_ testing_ for_heterozygous_ familial_
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_ testing_ for_heterozygous_ familial_
Vertebrobasilar Insufficiency
 Equilibrium Res Vol. (3) Vertebrobasilar Insufficiency Toshiaki Yamanaka Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Nara Medical University School of Medicine Vertebrobasilar insufficiency (VBI)
Equilibrium Res Vol. (3) Vertebrobasilar Insufficiency Toshiaki Yamanaka Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Nara Medical University School of Medicine Vertebrobasilar insufficiency (VBI)
Result Navigator. Positive Test Result: BMPR1A. After a positive test result, there can be many questions about what to do next. Navigate Your Results
 Result Navigator Positive Test Result: BMPR1A Positive test results identify a change, or misspelling, of DNA that is known or predicted to cause an increased risk for cancer. DNA is the blueprint of life
Result Navigator Positive Test Result: BMPR1A Positive test results identify a change, or misspelling, of DNA that is known or predicted to cause an increased risk for cancer. DNA is the blueprint of life
DR as a Biomarker for Systemic Vascular Complications
 DR as a Biomarker for Systemic Vascular Complications Lihteh Wu MD Asociados de Mácula, Vítreo y Retina de Costa Rica San José, Costa Rica LW65@cornell.edu Disclosures Dr Wu has received lecture fees from
DR as a Biomarker for Systemic Vascular Complications Lihteh Wu MD Asociados de Mácula, Vítreo y Retina de Costa Rica San José, Costa Rica LW65@cornell.edu Disclosures Dr Wu has received lecture fees from
What Clinicians Need to Know About Genetic Testing for Patients and Families with HCM
 What Clinicians Need to Know About Genetic Testing for Patients and Families with HCM Sharon Cresci, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Assistant Professor of Genetics Cardiovascular Division Washington
What Clinicians Need to Know About Genetic Testing for Patients and Families with HCM Sharon Cresci, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Assistant Professor of Genetics Cardiovascular Division Washington
Hearing loss in children with Fabry disease
 J Inherit Metab Dis (2017) 40:725 731 DOI 10.1007/s10545-017-0051-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hearing loss in children with Fabry disease E. Suntjens 1 & W. A. Dreschler 2 & J. Hess-Erga 3 & R. Skrunes 4,5 & F.
J Inherit Metab Dis (2017) 40:725 731 DOI 10.1007/s10545-017-0051-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hearing loss in children with Fabry disease E. Suntjens 1 & W. A. Dreschler 2 & J. Hess-Erga 3 & R. Skrunes 4,5 & F.
Guidelines for management of stroke in childhood
 Guidelines for management of stroke in childhood A clinical syndrome typified by rapidly developing signs of focal or global disturbance of cerebral functions, lasting more than 24 hrs or leading to death,
Guidelines for management of stroke in childhood A clinical syndrome typified by rapidly developing signs of focal or global disturbance of cerebral functions, lasting more than 24 hrs or leading to death,
Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy
 Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy Jeong-Am Ryu 1, Oh Young Bang 2, Daesang Lee 1, Jinkyeong Park 1, Jeong Hoon Yang 1, Gee Young Suh 1, Joongbum Cho 1, Chi Ryang Chung 1, Chi-Min
Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy Jeong-Am Ryu 1, Oh Young Bang 2, Daesang Lee 1, Jinkyeong Park 1, Jeong Hoon Yang 1, Gee Young Suh 1, Joongbum Cho 1, Chi Ryang Chung 1, Chi-Min
Thromboembolic events in Fabry disease and the impact of factor V Leiden
 Thromboembolic events in Fabry disease and the impact of factor V Leiden Malte Lenders, PhD* Nesrin Karabul, MD* Thomas Duning, MD Boris Schmitz, PhD Michael Schelleckes, PhD Rolf Mesters, MD Hans-Werner
Thromboembolic events in Fabry disease and the impact of factor V Leiden Malte Lenders, PhD* Nesrin Karabul, MD* Thomas Duning, MD Boris Schmitz, PhD Michael Schelleckes, PhD Rolf Mesters, MD Hans-Werner
Neuropathy. Nerves before and after TTR. Márcia Waddington Cruz. CEPARM HUCFF-UFRJ.
 Neuropathy. Nerves before and after TTR. Márcia Waddington Cruz. CEPARM HUCFF-UFRJ. Amyloidosis Amyloid deposit. Precursor proteins. Fibrilar ptn. Lesion to tissues. Mechanism? 2 A TTR. SSA or Wild Type
Neuropathy. Nerves before and after TTR. Márcia Waddington Cruz. CEPARM HUCFF-UFRJ. Amyloidosis Amyloid deposit. Precursor proteins. Fibrilar ptn. Lesion to tissues. Mechanism? 2 A TTR. SSA or Wild Type
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Kidney Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 September 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
Annalisa Sechi 1*, Gaetano Nucifora 2, Gianluca Piccoli 3, Andrea Dardis 1 and Bruno Bembi 1
 Sechi et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders 2014, 14:86 CASE REPORT Open Access Myocardial fibrosis as the first sign of cardiac involvement in a male patient with Fabry disease: report of a clinical case
Sechi et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders 2014, 14:86 CASE REPORT Open Access Myocardial fibrosis as the first sign of cardiac involvement in a male patient with Fabry disease: report of a clinical case
Cryptogenic Strokes: Evaluation and Management
 Cryptogenic Strokes: Evaluation and Management 77 yo man with hypertension and hyperlipidemia developed onset of left hemiparesis and right gaze preference, last seen normal at 10:00 AM Brought to ZSFG
Cryptogenic Strokes: Evaluation and Management 77 yo man with hypertension and hyperlipidemia developed onset of left hemiparesis and right gaze preference, last seen normal at 10:00 AM Brought to ZSFG
What s New in Newborn Screening?
 What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is administered by the Illinois Department of Public Health.
What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is administered by the Illinois Department of Public Health.
HCM GUIDELINES ESC 2014 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY ASYMPTOMATIC PATIENT
 HCM GUIDELINES ESC 2014 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY ASYMPTOMATIC PATIENT Division of Inherited Cardiac Diseases Heart Center for the Young and Athletes A Dpt of Cardiology University of Athens ASYMPTOMATIC
HCM GUIDELINES ESC 2014 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY ASYMPTOMATIC PATIENT Division of Inherited Cardiac Diseases Heart Center for the Young and Athletes A Dpt of Cardiology University of Athens ASYMPTOMATIC
Cardiovascular Disease in CKD. Parham Eftekhari, D.O., M.Sc. Assistant Clinical Professor Medicine NSUCOM / Broward General Medical Center
 Cardiovascular Disease in CKD Parham Eftekhari, D.O., M.Sc. Assistant Clinical Professor Medicine NSUCOM / Broward General Medical Center Objectives Describe prevalence for cardiovascular disease in CKD
Cardiovascular Disease in CKD Parham Eftekhari, D.O., M.Sc. Assistant Clinical Professor Medicine NSUCOM / Broward General Medical Center Objectives Describe prevalence for cardiovascular disease in CKD
DNA Day Illinois 2013 Webinar: Newborn Screening and Family Health History. Tuesday, April 16, 2013
 DNA Day Illinois 2013 Webinar: Newborn Screening and Family Health History Tuesday, April 16, 2013 Objectives Recognize the importance & impact of newborn screening Describe the process of newborn screening
DNA Day Illinois 2013 Webinar: Newborn Screening and Family Health History Tuesday, April 16, 2013 Objectives Recognize the importance & impact of newborn screening Describe the process of newborn screening
Fabry disease: a review of current management strategies
 Fabry disease: a review of current management strategies A. MEHTA 1, M. BECK 2, F. EYSKENS 3, C. FELICIANI 4, I. KANTOLA 5, U. RAMASWAMI 6, A. ROLFS 7, A. RIVERA 8, S. WALDEK 9, D.P. GERMAIN 10 1 Lysosomal
Fabry disease: a review of current management strategies A. MEHTA 1, M. BECK 2, F. EYSKENS 3, C. FELICIANI 4, I. KANTOLA 5, U. RAMASWAMI 6, A. ROLFS 7, A. RIVERA 8, S. WALDEK 9, D.P. GERMAIN 10 1 Lysosomal
ST - segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction complicating an atypical Kawasaki disease
 ST - segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction complicating an atypical Kawasaki disease Raluca PRISECARU, Marc VINCENT, Steven VERCAUTEREN Brussels Heart Center, Brussels, Belgium Disclosure None Clinical
ST - segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction complicating an atypical Kawasaki disease Raluca PRISECARU, Marc VINCENT, Steven VERCAUTEREN Brussels Heart Center, Brussels, Belgium Disclosure None Clinical
Fabry disease. A case report
 Fabry disease. A case report J. Kotnik, F. Kotnik and R. J. Desnick S U M M A R Y K E Y WORDS Fabry disease, angiokeratoma corporis diffusum, X-linked recessive inheritance, α-galactosidase A activity,
Fabry disease. A case report J. Kotnik, F. Kotnik and R. J. Desnick S U M M A R Y K E Y WORDS Fabry disease, angiokeratoma corporis diffusum, X-linked recessive inheritance, α-galactosidase A activity,
Fabry Disease: A complex multisystem disorder
 Fabry Disease: A complex multisystem disorder Dr. Bertram Henderson Division of Clinical Genetics, UFS/FPA 1 2 Speaker Disclosure The speaker has received sponsorship from Sanofi Genzyme to attend workshops,
Fabry Disease: A complex multisystem disorder Dr. Bertram Henderson Division of Clinical Genetics, UFS/FPA 1 2 Speaker Disclosure The speaker has received sponsorship from Sanofi Genzyme to attend workshops,
Result Navigator. Positive Test Result: MEN1. After a positive test result, there can be many questions about what to do next. Navigate Your Results
 Result Navigator Positive Test Result: MEN1 Positive test results identify a change, or misspelling, of DNA that is known or predicted to cause an increased risk for cancer. DNA is the blueprint of life
Result Navigator Positive Test Result: MEN1 Positive test results identify a change, or misspelling, of DNA that is known or predicted to cause an increased risk for cancer. DNA is the blueprint of life
Antithrombotic therapy in patients with transient ischemic attack / stroke (acute phase <48h)
 Antithrombotic therapy in patients with transient ischemic attack / stroke (acute phase
Antithrombotic therapy in patients with transient ischemic attack / stroke (acute phase
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies
 Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Result Navigator. Positive Test Result: RAD51C. After a positive test result, there can be many questions about what to do next. Navigate Your Results
 Result Navigator Positive Test Result: RAD51C Positive test results identify a change, or misspelling, of DNA that is known or predicted to cause an increased risk for cancer. DNA is the blueprint of life
Result Navigator Positive Test Result: RAD51C Positive test results identify a change, or misspelling, of DNA that is known or predicted to cause an increased risk for cancer. DNA is the blueprint of life
Phase 3 investigation of lucerastat for patients with Fabry disease. Investor Webcast May 2018
 Phase 3 investigation of lucerastat for patients with Fabry disease Investor Webcast May 2018 The following information contains certain forward-looking statements, relating to the company s business,
Phase 3 investigation of lucerastat for patients with Fabry disease Investor Webcast May 2018 The following information contains certain forward-looking statements, relating to the company s business,
What s New in Newborn Screening?
 What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is mandated and administered by the Illinois Department of
What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is mandated and administered by the Illinois Department of
Effectiveness of agalsidase alfa enzyme replacement in Fabry disease: cardiac outcomes after 10 years treatment
 Kampmann et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (205) 0:25 DOI 0.86/s02-05-08-2 RESEARCH Open Access Effectiveness of agalsidase alfa enzyme replacement in Fabry disease: cardiac outcomes after 0 years
Kampmann et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (205) 0:25 DOI 0.86/s02-05-08-2 RESEARCH Open Access Effectiveness of agalsidase alfa enzyme replacement in Fabry disease: cardiac outcomes after 0 years
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35456 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Hassan, Suha Mustafa Title: Toward prevention of Hemoglobinopathies in Oman Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35456 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Hassan, Suha Mustafa Title: Toward prevention of Hemoglobinopathies in Oman Issue
Enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease, towards individualized treatment Arends, M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease, towards individualized treatment Arends, M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Arends, M. (2017).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease, towards individualized treatment Arends, M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Arends, M. (2017).
Should Universal Carrier Screening be Universal?
 Should Universal Carrier Screening be Universal? Disclosures Research funding from Natera Mary E Norton MD University of California, San Francisco Antepartum and Intrapartum Management June 15, 2017 Burden
Should Universal Carrier Screening be Universal? Disclosures Research funding from Natera Mary E Norton MD University of California, San Francisco Antepartum and Intrapartum Management June 15, 2017 Burden
Asaad Khoury 2,3 MD, Monther Boulos 1,3 MD, Mahmoud Suleiman 1,3 MD, Miry Blich 1,3 MD, Michael Eldar 4 MD, Ibrahim Marai 1,3 MD,
 Flecainide therapy suppresses exercise induced ventricular arrhythmias in patients with CASQ2 associated catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia Asaad Khoury 2,3 MD, Monther Boulos 1,3 MD,
Flecainide therapy suppresses exercise induced ventricular arrhythmias in patients with CASQ2 associated catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia Asaad Khoury 2,3 MD, Monther Boulos 1,3 MD,
Clinical benefit of enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease
 original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 2006 International Society of Nephrology Clinical benefit of enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease F Breunig 1, F Weidemann 2, J Strotmann 2,
original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 2006 International Society of Nephrology Clinical benefit of enzyme replacement therapy in Fabry disease F Breunig 1, F Weidemann 2, J Strotmann 2,
Left ventricular non-compaction: the New Cardiomyopathy on the Block
 Left ventricular non-compaction: the New Cardiomyopathy on the Block Aamir Jeewa MB BCh, FAAP, FRCPC Section Head, Cardiomyopathy & Heart Function Program The Hospital for Sick Children Assistant Professor
Left ventricular non-compaction: the New Cardiomyopathy on the Block Aamir Jeewa MB BCh, FAAP, FRCPC Section Head, Cardiomyopathy & Heart Function Program The Hospital for Sick Children Assistant Professor
Serum Globotriaosylceramide Assay as a Screening Test for Fabry Disease in Patients with ESRD on Maintenance Dialysis in Korea
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2010.25.4.415 Serum Globotriaosylceramide Assay as a Screening Test for Fabry Disease in Patients with ESRD on Maintenance Dialysis in Korea Jeong-Yup Kim 1, Young-Youl
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2010.25.4.415 Serum Globotriaosylceramide Assay as a Screening Test for Fabry Disease in Patients with ESRD on Maintenance Dialysis in Korea Jeong-Yup Kim 1, Young-Youl
American Journal of Human Genetics. American Journal of Hypertension. American Journal of Neuroradiology
 A) Acta Neurochir AJNR Am J Neuroradiol Am Coll Rheumatol Am J Cardiol Am J Hum Genet Am J Hypertens Am J Neuroradiol AJNR Am J Physiol Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol Am J Physiol Heart Circ physiol
A) Acta Neurochir AJNR Am J Neuroradiol Am Coll Rheumatol Am J Cardiol Am J Hum Genet Am J Hypertens Am J Neuroradiol AJNR Am J Physiol Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol Am J Physiol Heart Circ physiol
Fabry disease: An underrecognized cause of proteinuria
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2008 International Society of Nephrology the renal consult Fabry disease: An underrecognized cause of proteinuria FC Fervenza 1, R Torra 2 and DJ Lager 3 1 Department
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2008 International Society of Nephrology the renal consult Fabry disease: An underrecognized cause of proteinuria FC Fervenza 1, R Torra 2 and DJ Lager 3 1 Department
