Paediatric Hypoglycaemia and the Laboratory. AACB Webinar, 8 th April 2015 Tina Yen
|
|
|
- Patrick McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Paediatric Hypoglycaemia and the Laboratory AACB Webinar, 8 th April 2015 Tina Yen
2 Synopsis Definition and classification Newborn and Neonatal Hypoglycaemia Transient Persistant Hypoglycaemia in infants Hypoglycaemia in childhood Essential sample
3 Definition of hypoglycaemia plasma glucose < 2.6 mmol/l a practical working definition SYMPTOMS Note: some infants are asymptomatic with very low blood glucose levels. Others have symptoms of hypoglycaemia at glucose > 2.6 mmol/l and require treatment (but unusual).
4 NEWBORN HYPOGLYCAEMIA
5 40 mg/dl = 2.2 mmol/l PEDIATRICS 2011;127: Clinical Report; Postnatal Glucose Homeostasis in Late-Preterm and Term Infants.
6 AAP 2011 Guidelines on neonatal hypoglycaemia Routine screening and monitoring of blood glucose not needed in healthy term newborn infants after normal pregnancy and delivery. 2. Blood glucose concentration only be measured in term infants who have clinical manifestations or who are known to be at risk: A). Plasma glucose should be measured ASAP (minutes) in symptomatic infant. B). Glucose monitoring advised if at risk infants who are small for gestational age, infants who are large for gestational age (>34/40), infants who were born to mothers who have diabetes late-preterm infants (LPT 34 36(+6)/ 40)
7 AAP 2011 Guidelines on neonatal hypoglycaemia Breastfed term infants have lower plasma glucose but higher levels of ketone bodies than formula-fed infants. Breastfed infants may tolerate lower plasma glucose without any clinical manifestations of hypoglycaemia because of high ketones. PEDIATRICS 2011;127: Clinical Report; Postnatal Glucose Homeostasis in Late-Preterm and Term Infants.
8 Case-1 Your lab is called about a baby born at term. Infant is 8h of age and reported to have poor feeding and hypothermia. Lab plasma glucose was 1.4 mmol/l. What are the most likely causes?
9 Neonatal hypoglycaemia is common Hypoglycaemia occurs more commonly during the first days after birth than at any other time of life. ~ 10% of normal term newborns unable to maintain plasma glucose > 1.7 mmol/l if first feeding is delayed for 3 6h after birth. A transient phenomenon in majority of cases The significant complexity of the metabolic and endocrine adaptations that occur at birth
10 Paediatric hypoglycaemia by age NEWBORN NEONATAL INFANT birth 7 days 2 weeks 1 month 6 months 12 months 5 years Transient hypoglycaemia 1. Persistent Hyperinsulinism 2. Endocrine disorders 3. Inborn error of metabolism Idiopathic ketotic hypoglycaemia
11 A. Transient (or physiological) hypoglycaemia Occurs in first 3 days (<72h) after birth prior to establishing feeds full biochemical screen is not required unless hypoglycaemia fails to respond to a feed blood glucose remains persistently or recurrently low. Neonatal hypoglycaemia may be secondary to septicaemia, severe systemic illness, intrauterine growth retardation or maternal diabetes (ie. NON- PHYSIOLOGICAL)* * Can have non-physiological causes of transient hypoglycaemia
12 Hypoglycaemia in newborns A Transient B Persistent SGA/ LBW Preterm Stress at delivery Maternal diabetes Neonatal illness (infection, hypothermia) C Inborn error of metabolism Hypoglycaemia in neonates and infants
13 Transient or persistent? Peds in Review 1999; 20; e6 e15.
14 Case-1 Your lab is called about a baby born at term. Infant is 8h of age and reported to have poor feeding and hypothermia. Lab plasma glucose was 1.4 mmol/l. What are the most likely causes? IDM - infant of diabetic mother
15 IDM - infant of diabetic mother Normal pregnancy preservation of glucose for the foetus. If prolonged maternal hyperglycaemia: foetal hyperglycaemia foetus produces high levels of insulin and GH (maternal GH and insulin do not cross placenta). Reactive hyperinsulinaemia in foetus macrosomia chronic foetal hyperinsulinaemia increases the risk of hypoglycaemia after birth. Newborn may require high concentrations of glucose to maintain euglycaemia. Neonatal hypoglycaemia due to maternal diabetes should resolve within 7 days. If it does not, the infant should be evaluated for other causes of hypoglycaemia.
16 B. Persistent hypoglycaemia of newborn May also have hepatomegaly Neonatal presentation of Inborn Error (IEM) I. Hepatic enzyme deficiencies Galactosaemia Fructosaemia, HFI Hereditary Tyrosinaemia Glycogen Storage Disease 1 II. Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and ketogenesis defects > 2 days
17 C. Hypoglycaemia in neonates and infants same as those causing newborn hypoglycaemia Additional include: Hyperinsulinism Endocrine disorders B. Hypopituitarism C. Adrenal disorders Inborn error of metabolism
18 HYPOGLYCAEMIA OF INFANCY
19 Case-2 Female aged 7 months presenting with a bit of gastro plasma glucose 0.3 mmol/l Insulin elevated 61 pmol/l Cortisol (> 1000 nmol/l) and GH (20.9 nmol/l) (appropriately elevated). blood glucose and insulin study over 10h - insulin levels were not suppressed by hypoglycaemia. Dx: PHHI Persistent hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia of infancy
20 PHHI or persistent hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia of infancy 1950s described as idiopathic hypoglycemia of infancy. 1960s first insulin RIAs showed that idiopathic hypoglycemia was associated with dysregulation of insulin secretion. 1970s - problem thought to be islet cell maturation because persistence of ß-cells budding off ductal epithelium. Termed nesidioblastosis. Subsequent investigations showed that nesidioblastosis is a normal feature of the pancreas during the first several months after birth so this term should no longer be used. 1990s renamed Congenital Hyperinsulinism and thought to be inherited as recessive or dominant traits. Genetic loci associated with HI begin to be defined.
21 Congenital Hyperinsulinism (CH) Children with this condition present during the neonatal period with severe, intractable hypoglycaemia, later (aged 0 3 months) usually at the time of an intercurrent illness. Plasma insulin concentrations are inappropriately elevated at time of hypoglycaemia. However insulin levels may not be clearly elevated in CH. Dx requires evidence of excess insulin activity
22 Criteria for evidence of excess insulin activity Suppression of plasma bohb (hypoketotic) Suppression of free FA. Inappropriate glycaemic response (glucose > 1.7 mmol/l) to glucagon
23 Causes of Congenital Hyperinsulinism (CH) Frequency: rare ~ 1/30,000-50,000 live births. Five different mutations have been found to cause CH: sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR-1), Kir6.2, glucokinase, Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) mitochondrial enzyme shortchain-3-hydroxyacyl-coa dehydrogenase (SCHAD) The most severe forms of CH may require pancreatectomy is the only effective therapeutic option to prevent severe, recurrent hypoglycaemia.
24 Full list of causes of Congenital Hyperinsulinism Update on investigating hypoglycaemia in childhood. Tim Lang. Ann Clin Biochem 2011: 1 12.
25 Case-2 Female aged 7 months presenting with a bit of gastro plasma glucose 0.3 mmol/l Insulin elevated 61 pmol/l Cortisol (> 1000 nmol/l) and GH (20.9 nmol/l) (appropriately elevated). blood glucose and insulin study over 10h - insulin levels were not suppressed by hypoglycaemia. Dx: PHHI Persistent hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia of infancy
26 Further Ix Transferrin isoform studies - consistent with CDG (Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation type 1) CDG type 1 defect in synthesis of mannose persistently elevated insulin that is disproportionate to glucose prone to hypoglycaemia.
27 Hypoglycaemia due to endocrine disorders Addison s or other adrenal insufficiency Congenital or acquired bilateral adrenal haemorrhage Hypopituitarism GH deficiency +/- ACTH deficiency Midline facial defect (cleft lip, and palate) Males may have hypoplastic external genitalia and micropenis.
28 Most important laboratory findings Low plasma GH in presence of hypoglycaemia short synacthen test showed low basal cortisol and no rise after synacthen In panhypopituitarism, isolated ACTH deficiency, isolated GH deficiency, or combined ACTH and GH deficiencies, the rate of hypoglycaemia is 20% In children with CAH, hypoglycaemia is common (prevalence of ~ 8-9%).
29 Hypoglycaemia due to inborn errors GSD 1 Fructose 1,6 bisphophatase def galactosaemia MCAD final enzyme step for glycogen breakdown and for gluconegenesis block of gluconeogenesis from precursors below pathway level of fructose 1,6 diphosphate. Hypoglycaemia if glycogen reserves depleted accumulation of gal-1-phosphate inhibits phosphoglucomutase (hence cannot convert glycogen to glucose) toxic metabolite accumulation inhibits pyruvate carboxylase (gluconeogenesis). Also faster depletion of glucose due to inability to use ketones as glucose substitute
30 Full list of IEM which present with hypoglycaemia Update on investigating hypoglycaemia in childhood. Tim Lang. Ann Clin Biochem 2011: 1 12.
31 Fasting study for evaluation of paediatric patient with hypoglycaemia
32 Evaluation of metabolic pathways resulting in hypoglycaemia 1. Glycogenolysis 2. Gluconeogenesis (reverse glycolysis) 3. Substrates for carbohydrate metabolism 4. Ketogenesis and Fatty acid oxidation
33 Glycogen storage disease 1a GSD 1a von Gierke s disease commonest GSD causing hypoglycaemia Deficiency of glucose-6-phosphatase The most serious GSD because of complete block in glucose generation from hepatic glycogen stores PRIMARY Fasting hypoglycaemia SECONDARY Hyperlactataemia, metabolic acidosis, hyperuricaemia and hyperlipidaemia Glycogen stores accumulating in the liver leading to marked hepatomegaly.
34 Glucose 6 phosphatase deficiency Absence of hepatic G6Pase means glucose unable to leave the hepatocyte phosphorylated Accumulation of G6P G6P is metabolized by glycolysis (G6P pyruvate lactate). or G6P is incorporated into glycogen. Lactate provides the brain with alternative energy source. Lactate competes with uric acid reducing renal urate clearance hyperuricemia.
35 Importance of glycogen Hepatic glycogen breakdown fundamental role in maintaining blood glucose Deficiency in G6Pase (GSD 1a and 1b) can present with no measurable blood glucose level. Tendency to hypoglycaemia - improvement with age due to more efficient utilitisation of gluconeogenic pathways Note: in GSD 1 (a and b) there is no muscle involvement (muscle does not have G6Pase enzyme).
36 Case 3 (from CHW records) 17 year old male Glycogen storage disease 1a. Dx at 3.5 months of age Now has multiple hepatic ademonas, gout, hyperlipidemia, cholelithiasis. AST 206; ALT 206, GGT 390; Chol 4.9; TG 4.2. Younger brother Justin also affected (Trig 10.0; Chol 9.2 mmol/l).
37 Case from literature 3-month-old boy presented to ED 3-day Hx of poor feeding, reduced urinary output, fever, cough and rhinorrhoea. Critical hypoglycaemia 0.3 mmol/l In GSD Ib even profound hypoglycaemia might be clinically unapparent because of the brain s capability to metabolise ketones and lactate to create energy. GSD type Ia are genetically deficient in glucose-6- phosphate activity, while those affected with GSD type Ib lack translocase. Bock DE et al (2010) Acta Pædiatrica , pp. e130 e132 Asymptomatic critical hypoglycaemia: a dangerous presentation of glycogen storage disease type Ib in infancy.
38 Abnormality with substrates for carbohydrate metabolism All exogenous carbohydrates like fructose, galactose, lactose, sucrose and starch are converted to glucose for generation of energy. inability to utilise dietary carbohydrate predispose to hypoglycaemia. Note: Galactosaemia can cause hypoglycaemia
39 Case 4 (from RCPA) 9 day old baby boy Emergency Department Term baby, 600 g marked weight loss and jaundice Total BR 442 umol/l Conjugated BR 74 umol/l (0 10) Additional Information Random glucose 1.9 mmol/l (Urine reducing substances +++)
40 Galactosaemia Most common form of galactosaemia is deficiency of the enzyme galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GALT) GK 1. Galactose Gal-1-Phosphate GALT 2. Gal-1-P UDP Galactose + Glu-1-P epimerase 3. UDP Galactose UDP Glucose GK = Galactokinase
41 Galactosaemia Occurs ~ in 60,000 births in Australia (autosomal recessive) vomiting, hypoglycaemia and liver failure with introduction of lactose-containing milk feeds Gram negative sepsis Hepatomegaly. Later cataract occurs. Can be diagnosed by newborn screening
42 Galactosaemia Normal Lactose metabolism produces: glucose as immediate supply of energy galactose which requires conversion into glucose (provides ongoing carbohydrate availability). Deficiency of galactose-1- phosphate uridyltransferase (GALT) 1:47,000 = Classical Galactosaemia toxic accumulation of galactose-1-phosphate leads to hepatomegaly, hepatic failure, hypoglycaemia with ketones and predisposition to sepsis particularly Escherichia coli. Hypoglycaemia is usually only seen once liver impairment has developed.
43 (1) Intestinal lactase (2) Galactokinase (3) Galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GALT) (4) UDP-galactose-1,4-epimerase (GALE)
44
45 HYPOGLYCAEMIA IN CHILDREN
46 Hypoglycaemia in children > 1 year Ketotic hypoglycaemia Most common cause of hypoglycaemia in > 12 month old Occurs between 12 months and 5 years Develop hypoglycaemia and ketosis when there is carbohydrate restriction Medications/ Drugs Intoxication - ETOH Beta-blockers Oral hypoglycaemics or insulin
47 Causes continued: Secondary hypoglycaemia (acquired causes) systemic illness, sepsis, poor nutritional status (poor diet, malabsorption, coeliac disease). Malignancy Insulinoma Hypoglycemia complicating dehydration due to acute gastroenteritis; Clin Ped 2003; 42:
48 Essential Diagnostic Sample to be collected on child during hypoglycaemic episode plasma glucose < 2.6 mmol/l serum for GH, cortisol, insulin, bhb, free FA, lactate, plasma NH3 and acylcarnitines. Urine ketones and reducing substances (galactose), organic acids (urine metabolic screen), and urine drug screen.
49 Summary Definition: plasma glucose < 2.6 mmol/l hypoglycaemia is more common in paediatrics compared to adult medicine. Acquired causes - systemic illness, sepsis, medications, and poor nutritional status. Hypopituitarism and adrenal insufficiency should be excluded. First presentation of an inborn errors of amino acid and organic acid metabolism urine metabolic screen (organic and amino acids). Thank you
National Metabolic Biochemistry Network Guidelines for the investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and children
 National Metabolic Biochemistry Network Guidelines for the investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and children Aim To provide guidance on the biochemical investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and
National Metabolic Biochemistry Network Guidelines for the investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and children Aim To provide guidance on the biochemical investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and
Neonatal Hypoglycaemia
 Neonatal Hypoglycaemia Dr Shubha Srinivasan Paediatric Endocrinologist The Children s Hospital at Westmead Hypoglycaemia and the Brain CSF glucose is 2/3 that of plasma Intracerebral glucose 1/3 that of
Neonatal Hypoglycaemia Dr Shubha Srinivasan Paediatric Endocrinologist The Children s Hospital at Westmead Hypoglycaemia and the Brain CSF glucose is 2/3 that of plasma Intracerebral glucose 1/3 that of
Hyperglycaemia. Clinical presentation. Definition of hyperglycaemia. Approach to the problem
 Hyperglycaemia 1 Clinical presentation Hyperglycaemia is usually picked up incidentally on routine blood glucose assessment or in response to finding glycosuria. It may be noted as part of the workup of
Hyperglycaemia 1 Clinical presentation Hyperglycaemia is usually picked up incidentally on routine blood glucose assessment or in response to finding glycosuria. It may be noted as part of the workup of
Neonatal Hypoglycemia
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Neonatal Hypoglycemia. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics.
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Neonatal Hypoglycemia. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics.
NEONATAL HYPOGLYCEMIA HEATHER MCKNIGHT-MENCI, MSN, CRNP CHILDREN S HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
 NEONATAL HYPOGLYCEMIA HEATHER MCKNIGHT-MENCI, MSN, CRNP CHILDREN S HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA WHAT IS NEONATAL HYPOGLYCEMIA? Glucose concentration low enough to cause signs and symptoms of impaired brain
NEONATAL HYPOGLYCEMIA HEATHER MCKNIGHT-MENCI, MSN, CRNP CHILDREN S HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA WHAT IS NEONATAL HYPOGLYCEMIA? Glucose concentration low enough to cause signs and symptoms of impaired brain
Controversies in Neonatal Hypoglycemia PAC / LAC CONFERENCE, JUNE 1 ST 2017
 Controversies in Neonatal Hypoglycemia PRIYA JEGATHEESAN, MD PAC / LAC CONFERENCE, JUNE 1 ST 2017 Disclosure I have no conflicts of interest to disclose Objectives Review Recommendations from different
Controversies in Neonatal Hypoglycemia PRIYA JEGATHEESAN, MD PAC / LAC CONFERENCE, JUNE 1 ST 2017 Disclosure I have no conflicts of interest to disclose Objectives Review Recommendations from different
Overview. o Limitations o Normal regulation of blood glucose o Definition o Symptoms o Clinical forms o Pathophysiology o Treatment.
 Pål R. Njølstad MD PhD KG Jebsen Center for Diabetes Research University of Bergen, Norway Depertment of Pediatrics Haukeland University Hospital Broad Institute of Harvard & MIT Cambridge, MA, USA Hypoglycemia
Pål R. Njølstad MD PhD KG Jebsen Center for Diabetes Research University of Bergen, Norway Depertment of Pediatrics Haukeland University Hospital Broad Institute of Harvard & MIT Cambridge, MA, USA Hypoglycemia
Glycogen Storage Disease
 Glycogen Storage Disease 1 Introduction The food we eat is usually used for growth, tissue repair and energy. The body stores what it does not use. Excess sugar, or glucose, is stored as glycogen in the
Glycogen Storage Disease 1 Introduction The food we eat is usually used for growth, tissue repair and energy. The body stores what it does not use. Excess sugar, or glucose, is stored as glycogen in the
Hypoglycaemia of the neonate. Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics
 Hypoglycaemia of the neonate Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics Why is glucose important? It provides 60-70% of energy needs Utilization obligatory by red blood cells, brain and kidney as major source of
Hypoglycaemia of the neonate Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics Why is glucose important? It provides 60-70% of energy needs Utilization obligatory by red blood cells, brain and kidney as major source of
Beyond the Naked Eye: A Case Presentation on a Rare Form of Congenital Hyperinsulinism (HI) Patient Demographics 5/12/2016
 Beyond the Naked Eye: A Case Presentation on a Rare Form of Congenital Hyperinsulinism (HI) Pediatric Endocrine Nursing Society May 14, 2016 Enyo Dzata, MSN, CRNP Congenital Hyperinsulinism Center Division
Beyond the Naked Eye: A Case Presentation on a Rare Form of Congenital Hyperinsulinism (HI) Pediatric Endocrine Nursing Society May 14, 2016 Enyo Dzata, MSN, CRNP Congenital Hyperinsulinism Center Division
ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018
 ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018 Inborn Errors Of Metabolism Inborn errors of carbohydrate metabolism G. Pintos (ES) INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM INBORN ERRORS OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Guillem Pintos-Morell,
ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018 Inborn Errors Of Metabolism Inborn errors of carbohydrate metabolism G. Pintos (ES) INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM INBORN ERRORS OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Guillem Pintos-Morell,
Genética e Hígado: Cómo contribuye la genética en el algoritmo diagnóstico de la enfermedad hepática pediátrica? Nicholas Ah Mew, MD
 Genética e Hígado: Cómo contribuye la genética en el algoritmo diagnóstico de la enfermedad hepática pediátrica? Nicholas Ah Mew, MD April 24, 2017 SAP 2017 Buenos Aires Genetic disorders are rare why
Genética e Hígado: Cómo contribuye la genética en el algoritmo diagnóstico de la enfermedad hepática pediátrica? Nicholas Ah Mew, MD April 24, 2017 SAP 2017 Buenos Aires Genetic disorders are rare why
Module : Clinical correlates of disorders of metabolism Block 3, Week 2
 Module : Clinical correlates of disorders of metabolism Block 3, Week 2 Department of Paediatrics and Child Health University of Pretoria Tutor : Prof DF Wittenberg : dwittenb@medic.up.ac.za Aim of this
Module : Clinical correlates of disorders of metabolism Block 3, Week 2 Department of Paediatrics and Child Health University of Pretoria Tutor : Prof DF Wittenberg : dwittenb@medic.up.ac.za Aim of this
Not Your Typical Case of Ketotic Hypoglycemia
 Not Your Typical Case of Ketotic Hypoglycemia Linda Steinkrauss, RN, MSN, CPNP Objectives By the end of this session, attendees should be able to: 1. Discuss the difference between idiopathic ketotic hypoglycemia
Not Your Typical Case of Ketotic Hypoglycemia Linda Steinkrauss, RN, MSN, CPNP Objectives By the end of this session, attendees should be able to: 1. Discuss the difference between idiopathic ketotic hypoglycemia
Staff at the Nottingham Children s Hospital. Guidelines process; paediatric endocrinology team
 Hypoglycaemia Title of Guideline Contact Name and Job Title (author) Hypoglycaemia in infants and children: aetiology, investigation and treatment Dr. Hoong-Wei Gan ST6 Paediatric Endocrinology & Diabetes
Hypoglycaemia Title of Guideline Contact Name and Job Title (author) Hypoglycaemia in infants and children: aetiology, investigation and treatment Dr. Hoong-Wei Gan ST6 Paediatric Endocrinology & Diabetes
بنام خدا هیپوگلیسمی درنوزادان و گاالکتوزمی دکتر انتظاری
 بنام خدا هیپوگلیسمی درنوزادان و گاالکتوزمی دکتر انتظاری Serum glucose< 35 mg/dl 1-3 hr of life < 40 mg/dl 3-24 hr < 45 mg/dl after 24 hr 10% NL newborns can t maintain BS>30 if delayed feeding >3-6 hrs
بنام خدا هیپوگلیسمی درنوزادان و گاالکتوزمی دکتر انتظاری Serum glucose< 35 mg/dl 1-3 hr of life < 40 mg/dl 3-24 hr < 45 mg/dl after 24 hr 10% NL newborns can t maintain BS>30 if delayed feeding >3-6 hrs
W1A- Cases I Learned From
 W1A- Cases I Learned From David H Adamkin, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Division of Neonatology Director of Nutritional Research Rounsavall Chair of Neonatal Medicine Co-Director of Neonatal Fellowship
W1A- Cases I Learned From David H Adamkin, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Division of Neonatology Director of Nutritional Research Rounsavall Chair of Neonatal Medicine Co-Director of Neonatal Fellowship
Disorders of Carbohydrates. Disorders of Galactose Metabolism Glycogen Storage Diseases Diabetes Mellitus
 Disorders of Carbohydrates Metabolism Disorders of Galactose Metabolism Glycogen Storage Diseases Diabetes Mellitus Disorders of Galactose Metabolism GALACTOSE Galactose is a sugar that is found mainly
Disorders of Carbohydrates Metabolism Disorders of Galactose Metabolism Glycogen Storage Diseases Diabetes Mellitus Disorders of Galactose Metabolism GALACTOSE Galactose is a sugar that is found mainly
Metabolic Disorders. Chapter Thomson - Wadsworth
 Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nayef Karadsheh
 number 16 Done Huda shaheen by Corrected by حسام أبو عوض Doctor Nayef Karadsheh 1 In the previous lecture, we talked about glycogen metabolism and regulation. In this sheet we will talk about the metabolism
number 16 Done Huda shaheen by Corrected by حسام أبو عوض Doctor Nayef Karadsheh 1 In the previous lecture, we talked about glycogen metabolism and regulation. In this sheet we will talk about the metabolism
What systems are involved in homeostatic regulation (give an example)?
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
Week 3 The Pancreas: Pancreatic ph buffering:
 Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
Paediatric Clinical Chemistry
 Paediatric Clinical Chemistry Dr N Oosthuizen Dept Chemical Pathology UP 2011 Paediatric biochemistry The child is not a miniature adult Physiological development Immature organ systems Growing individual
Paediatric Clinical Chemistry Dr N Oosthuizen Dept Chemical Pathology UP 2011 Paediatric biochemistry The child is not a miniature adult Physiological development Immature organ systems Growing individual
Learning Objectives. At the conclusion of this module, participants should be better able to:
 Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this module, participants should be better able to: Treat asymptomatic neonatal hypoglycemia with buccal dextrose gel Develop patient-specific approaches to intravenous
Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this module, participants should be better able to: Treat asymptomatic neonatal hypoglycemia with buccal dextrose gel Develop patient-specific approaches to intravenous
Metabolic diseases of the liver
 Metabolic diseases of the liver Central role in metabolism Causes and mechanisms of dysfunction Clinical patterns of metabolic disease Clinical approach to problem-solving Specific disorders Liver s central
Metabolic diseases of the liver Central role in metabolism Causes and mechanisms of dysfunction Clinical patterns of metabolic disease Clinical approach to problem-solving Specific disorders Liver s central
Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM
 Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? Insulin Glucagon Thyroid hormones Cortisol Epinephrine Most regulation occurs in order
Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? Insulin Glucagon Thyroid hormones Cortisol Epinephrine Most regulation occurs in order
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease. Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes
 BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes Diabetes mellitus is, after heart disease and cancer, the third leading cause of death in the west. Insulin is either not secreted in sufficient
BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes Diabetes mellitus is, after heart disease and cancer, the third leading cause of death in the west. Insulin is either not secreted in sufficient
PES Recommendations for Evaluation and Management of Hypoglycemia in Neonates, Infants, and Children Paul S. Thornton On behalf of the Team
 Cook Children s 1 PES Recommendations for Evaluation and Management of Hypoglycemia in Neonates, Infants, and Children Paul S. Thornton On behalf of the Team Cook Children s 2 Co-Chair: Charles Stanley
Cook Children s 1 PES Recommendations for Evaluation and Management of Hypoglycemia in Neonates, Infants, and Children Paul S. Thornton On behalf of the Team Cook Children s 2 Co-Chair: Charles Stanley
CARE OF THE NEWBORN HYPOGLYCAEMIA
 CARE OF THE NEWBORN HYPOGLYCAEMIA Background Definition A true blood glucose of less than 2.6 mmol/l venous sample. Neonatal hypoglycaemia is commonly defined as a true blood glucose of less than 2.6 mmol/l
CARE OF THE NEWBORN HYPOGLYCAEMIA Background Definition A true blood glucose of less than 2.6 mmol/l venous sample. Neonatal hypoglycaemia is commonly defined as a true blood glucose of less than 2.6 mmol/l
INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) IAP UG Teaching slides
 INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) 1 OBJECTIVES What are IEMs? Categories When to suspect? History and clinical pointers Metabolic presentation Differential diagnosis Emergency and long term management
INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) 1 OBJECTIVES What are IEMs? Categories When to suspect? History and clinical pointers Metabolic presentation Differential diagnosis Emergency and long term management
Newborn Hypoglycemia
 Newborn Hypoglycemia Self Learning Module Developed by the Interprofessional Education and Research Committee of the Champlain Maternal Newborn Regional Program (CMNRP) 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS Definition....3
Newborn Hypoglycemia Self Learning Module Developed by the Interprofessional Education and Research Committee of the Champlain Maternal Newborn Regional Program (CMNRP) 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS Definition....3
1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DIABETES MELLITUS
 1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DIABETES MELLITUS Prof. Vladimir Palicka, M.D., Ph.D. Institute for Clinical Biochemistry and Diagnostics, University Hospital Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic Diabetes mellitus is
1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DIABETES MELLITUS Prof. Vladimir Palicka, M.D., Ph.D. Institute for Clinical Biochemistry and Diagnostics, University Hospital Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic Diabetes mellitus is
THE GLUCOSE-FATTY ACID-KETONE BODY CYCLE Role of ketone bodies as respiratory substrates and metabolic signals
 Br. J. Anaesth. (1981), 53, 131 THE GLUCOSE-FATTY ACID-KETONE BODY CYCLE Role of ketone bodies as respiratory substrates and metabolic signals J. C. STANLEY In this paper, the glucose-fatty acid cycle
Br. J. Anaesth. (1981), 53, 131 THE GLUCOSE-FATTY ACID-KETONE BODY CYCLE Role of ketone bodies as respiratory substrates and metabolic signals J. C. STANLEY In this paper, the glucose-fatty acid cycle
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders- an update. Fiona Carragher Biochemical Sciences, GSTS Pathology St Thomas Hospital, London
 Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders- an update Fiona Carragher Biochemical Sciences, GSTS Pathology St Thomas Hospital, London An update. Overview of metabolism Clinical presentation and outcome Diagnostic
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders- an update Fiona Carragher Biochemical Sciences, GSTS Pathology St Thomas Hospital, London An update. Overview of metabolism Clinical presentation and outcome Diagnostic
Hypoglycemia in congenital hyperinsulinism
 How a normal body works: Our body is constantly at work. Our cells need a source of energy, and this source of energy is called glucose. The process is quite simple; think of it like an assembly line.
How a normal body works: Our body is constantly at work. Our cells need a source of energy, and this source of energy is called glucose. The process is quite simple; think of it like an assembly line.
By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1
 By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Gluconeogenesis is the process of converting noncarbohydrate precursors to glucose or glycogen. The major substrates are the glucogenic amino acids, and lactate, glycerol, and propionate.
By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Gluconeogenesis is the process of converting noncarbohydrate precursors to glucose or glycogen. The major substrates are the glucogenic amino acids, and lactate, glycerol, and propionate.
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM)
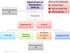 Clinical Presentation Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) Click on the following: - Clinical Pearl - link to movie clip - link to picture Investigations Blood Work Urine No Acidosis NH 4 + Metabolic Acidosis
Clinical Presentation Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) Click on the following: - Clinical Pearl - link to movie clip - link to picture Investigations Blood Work Urine No Acidosis NH 4 + Metabolic Acidosis
Evidence-Based Update: Using Glucose Gel to Treat Neonatal Hypoglycemia
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Evidence-Based Update: Using Glucose Gel to Treat Neonatal Hypoglycemia http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcare-professionals/education/continuing-medicalnursing-education/neonatal-nursing-education-briefs/
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Evidence-Based Update: Using Glucose Gel to Treat Neonatal Hypoglycemia http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcare-professionals/education/continuing-medicalnursing-education/neonatal-nursing-education-briefs/
Neonatal Hypoglycemia. Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010
 Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
Glycogen function. Cellular glucose store. Local emergency store Local short term use
 Glycogen function Cellular glucose store Liver Brain Muscle Body sump Local emergency store Local short term use Glycogen storage diseases Accumulation abnormal amount/type glycogen Hypoglycaemia, lactic
Glycogen function Cellular glucose store Liver Brain Muscle Body sump Local emergency store Local short term use Glycogen storage diseases Accumulation abnormal amount/type glycogen Hypoglycaemia, lactic
Management of Glucose in the Preterm Infant. Charles A. Stanley, MD Division of Endocrinology Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
 Management of Glucose in the Preterm Infant Charles A. Stanley, MD Division of Endocrinology Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Disclosures Charles Stanley, MD I have no relevant financial relationships
Management of Glucose in the Preterm Infant Charles A. Stanley, MD Division of Endocrinology Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Disclosures Charles Stanley, MD I have no relevant financial relationships
Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department. Will Davies June 2014
 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Will Davies June 2014 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Overview Although individually rare, altogether they are 1:1000-2500
Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Will Davies June 2014 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Overview Although individually rare, altogether they are 1:1000-2500
Metabolism of pentoses, glycogen, fructose and galactose. Jana Novotna
 Metabolism of pentoses, glycogen, fructose and galactose Jana Novotna 1. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP): (hexose monophosphate or 6-phosphogluconate patway) Process that
Metabolism of pentoses, glycogen, fructose and galactose Jana Novotna 1. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP): (hexose monophosphate or 6-phosphogluconate patway) Process that
Neurodevelopmental Risk?
 Normal Newborn During transitional hypoglycemia normal newborns have an enhanced ketogenic response to fasting. Newborn brains have enhanced capability to use ketone bodies for fuel Allows newborns to
Normal Newborn During transitional hypoglycemia normal newborns have an enhanced ketogenic response to fasting. Newborn brains have enhanced capability to use ketone bodies for fuel Allows newborns to
Biochemistry of carbohydrates
 Biochemistry of carbohydrates الفريق الطبي األكاديمي Done By: - Hanan Jamal لكية الطب البرشي البلقاء التطبيقية / املركز 6166 6102/ In the last lecture we talked about Pyruvate, pyruvate is a central intermediate;
Biochemistry of carbohydrates الفريق الطبي األكاديمي Done By: - Hanan Jamal لكية الطب البرشي البلقاء التطبيقية / املركز 6166 6102/ In the last lecture we talked about Pyruvate, pyruvate is a central intermediate;
Inborn errors of metabolism
 ESPEN Congress Nice 2010 From child to adult nutrition Inborn errors of metabolism Pascal Crenn Inborn errors of metabolism: from child to adult Pascal Crenn Hôpital Raymond Poincaré 92380 Garches. France
ESPEN Congress Nice 2010 From child to adult nutrition Inborn errors of metabolism Pascal Crenn Inborn errors of metabolism: from child to adult Pascal Crenn Hôpital Raymond Poincaré 92380 Garches. France
Glycogen Storage Disease Type I
 Abstract Glycogen Storage Disease Type I 1 2 3 Kavitha MM, Kashinakunti Sangappa, Pattar Ramesh, Yalameli Bhuvaneshwari, Basavaraj Sajjan, Domble VM 1 2 3 4 5 6 Glycogen storage diseases (GSD) are inherited
Abstract Glycogen Storage Disease Type I 1 2 3 Kavitha MM, Kashinakunti Sangappa, Pattar Ramesh, Yalameli Bhuvaneshwari, Basavaraj Sajjan, Domble VM 1 2 3 4 5 6 Glycogen storage diseases (GSD) are inherited
7 Medical Genetics. Hemoglobinopathies. Hemoglobinopathies. Protein and Gene Structure. and Biochemical Genetics
 SESSION 7 Medical Genetics Hemoglobinopathies and Biochemical Genetics J a v a d F a s a J a m s h i d i U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 Hemoglobinopathies
SESSION 7 Medical Genetics Hemoglobinopathies and Biochemical Genetics J a v a d F a s a J a m s h i d i U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 Hemoglobinopathies
e-learning Fatty Acid Oxidation Defects Camilla Reed and Dr Simon Olpin Sheffield Children s Hospital
 e-learning Fatty Acid Oxidation Defects Camilla Reed and Dr Simon Olpin Sheffield Children s Hospital Fatty Acids Fatty acids are a major source of energy and body fat is an energy dense material. They
e-learning Fatty Acid Oxidation Defects Camilla Reed and Dr Simon Olpin Sheffield Children s Hospital Fatty Acids Fatty acids are a major source of energy and body fat is an energy dense material. They
7/11/2018. Oral Dextrose Gel Treatment for Newborns with Hypoglycemia Reduces NICU Admissions DISCLOSURE. Objectives
 Gaps in Knowledge, Competence, Performance, or Patient Outcomes DISCLOSURE The content of this presentation does not relate to any product of a commercial entity; therefore, I have no relationships to
Gaps in Knowledge, Competence, Performance, or Patient Outcomes DISCLOSURE The content of this presentation does not relate to any product of a commercial entity; therefore, I have no relationships to
METABOLISM CATABOLIC Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins
 Index: - Overview: Catabolism and Anabolism. Few concepts:, NADPH. - Overview: Metabolism glucose, fatty acids and amino acids. - Table summary: Principal anabolic and catabolic pathways, and their main
Index: - Overview: Catabolism and Anabolism. Few concepts:, NADPH. - Overview: Metabolism glucose, fatty acids and amino acids. - Table summary: Principal anabolic and catabolic pathways, and their main
Clinical Director for Women s and Children s Directorate
 TREATMENT OF NEONATAL HYPOGLYCAEMIA IN THE HIGH RISK INFANT CLINICAL GUIDELINES Register No: 12025 Status: Public Developed in response to: Intrapartum NICE Guidelines RCOG guideline Contributes to CQC
TREATMENT OF NEONATAL HYPOGLYCAEMIA IN THE HIGH RISK INFANT CLINICAL GUIDELINES Register No: 12025 Status: Public Developed in response to: Intrapartum NICE Guidelines RCOG guideline Contributes to CQC
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Chronic metabolic disorder with a predisposition of hyperglycaemia (increased blood glucose).
 DIABETES WHAT IS DIABETES? Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Chronic metabolic disorder with a predisposition of hyperglycaemia (increased blood glucose). Diabetes Insipidus (DI) Condition in which the body has lack
DIABETES WHAT IS DIABETES? Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Chronic metabolic disorder with a predisposition of hyperglycaemia (increased blood glucose). Diabetes Insipidus (DI) Condition in which the body has lack
Intrapartum and Postpartum Management of the Diabetic Mother and Infant
 Intrapartum and Postpartum Management of the Diabetic Mother and Infant Intrapartum Management Women with gestational diabetes who maintain normal glucose levels during pregnancy on diet and exercise therapy
Intrapartum and Postpartum Management of the Diabetic Mother and Infant Intrapartum Management Women with gestational diabetes who maintain normal glucose levels during pregnancy on diet and exercise therapy
Guideline for the Prevention and Management of Neonatal Hypoglycaemia GL359
 Guideline for the Prevention and Management of Neonatal Hypoglycaemia GL359 Approval and Authorisation Approved by Job Title Date Paediatric Clinical Chair of Paediatric Clinical Governance Governance
Guideline for the Prevention and Management of Neonatal Hypoglycaemia GL359 Approval and Authorisation Approved by Job Title Date Paediatric Clinical Chair of Paediatric Clinical Governance Governance
The spectrum and outcome of the. neonates with inborn errors of. metabolism at a tertiary care hospital
 The spectrum and outcome of the neonates with inborn errors of metabolism at a tertiary care hospital Dr. Sevim Ünal Neonatology Division, Ankara Children s Hematology Oncology Research Hospital, Ankara,
The spectrum and outcome of the neonates with inborn errors of metabolism at a tertiary care hospital Dr. Sevim Ünal Neonatology Division, Ankara Children s Hematology Oncology Research Hospital, Ankara,
PRACTICE GUIDELINES WOMEN S HEALTH PROGRAM
 C Title: NEWBORN: HYPOGLYCEMIA IN NEONATES BORN AT 35+0 WEEKS GESTATION AND GREATER: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT IN THE FIRST 72 HOURS Authorization Section Head, Neonatology, Program Director, Women s Health
C Title: NEWBORN: HYPOGLYCEMIA IN NEONATES BORN AT 35+0 WEEKS GESTATION AND GREATER: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT IN THE FIRST 72 HOURS Authorization Section Head, Neonatology, Program Director, Women s Health
Deb Cobie Judy Evans Professionally Approved By Dr Saravanan Consultant Lead for Risk Management June 2009
 TREATMENT OF NEONATAL HYPOGLYCAEMIA Developed in response to: Contributes to CQC Standards No CLINICAL GUIDELINES Register No: 04219 Status: Public Intrapartum NICE Guidelines RCOG guideline C5a Consulted
TREATMENT OF NEONATAL HYPOGLYCAEMIA Developed in response to: Contributes to CQC Standards No CLINICAL GUIDELINES Register No: 04219 Status: Public Intrapartum NICE Guidelines RCOG guideline C5a Consulted
Hypoglycemia. Objectives. Glucose Metabolism
 Hypoglycemia Instructor: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Outline: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Summer Morgan, MSN, RNC-NIC, CPNP UC San Diego Health System Objectives State the blood glucose level at
Hypoglycemia Instructor: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Outline: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Summer Morgan, MSN, RNC-NIC, CPNP UC San Diego Health System Objectives State the blood glucose level at
Hormonal regulation of. Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
DIABETES 20/02/2014 WHAT IS DIABETES? GLUCOSE WHAT IS DIABETES? GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS GLUCOSE METABOLISM
 WHAT IS DIABETES? DIABETES Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Chronic metabolic disorder with a predisposition of hyperglycaemia (increased blood glucose). Diabetes Insipidus (DI) Condition in which the body has lack
WHAT IS DIABETES? DIABETES Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Chronic metabolic disorder with a predisposition of hyperglycaemia (increased blood glucose). Diabetes Insipidus (DI) Condition in which the body has lack
The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments
 CPT1a deficiency The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments of the cell known as mitochondria. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase Ia (CPT1a) is a protein that
CPT1a deficiency The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments of the cell known as mitochondria. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase Ia (CPT1a) is a protein that
By: Dr. Doaa Khater Yassin, MM and M.D Paed Sr. specialist of Pediatrics SQUH
 By: Dr. Doaa Khater Yassin, MM and M.D Paed Sr. specialist of Pediatrics SQUH Born SGA with birth weight of 2.4 kg, had IUGR Hospitalized at the age of 2 month with severe dehydration Diagnosed as DKA
By: Dr. Doaa Khater Yassin, MM and M.D Paed Sr. specialist of Pediatrics SQUH Born SGA with birth weight of 2.4 kg, had IUGR Hospitalized at the age of 2 month with severe dehydration Diagnosed as DKA
Glycogen Metabolism. BCH 340 lecture 9
 Glycogen Metabolism BC 340 lecture 9 Structure of glycogen Glycogen is homopolysaccharide formed of branched D-glucose units The primary glycosidic bond is 1-4-linkage Each branch is made of 6-12 glucose
Glycogen Metabolism BC 340 lecture 9 Structure of glycogen Glycogen is homopolysaccharide formed of branched D-glucose units The primary glycosidic bond is 1-4-linkage Each branch is made of 6-12 glucose
Pancreatic Lesions. Valerie Jefford Pediatric Surgery Rounds June 6, 2003
 Pancreatic Lesions Valerie Jefford Pediatric Surgery Rounds June 6, 2003 Embryology 4 th week 2 buds of endodermal origin from caudal foregut Dorsal and ventral bud Ventral migrates dorsally with CBD (below/behind
Pancreatic Lesions Valerie Jefford Pediatric Surgery Rounds June 6, 2003 Embryology 4 th week 2 buds of endodermal origin from caudal foregut Dorsal and ventral bud Ventral migrates dorsally with CBD (below/behind
Intermediary metabolism. Eva Samcová
 Intermediary metabolism Eva Samcová Metabolic roles of tissues Four major tissues play a dominant role in fuel metabolism : liver, adipose, muscle, and brain. These tissues do not function in isolation.
Intermediary metabolism Eva Samcová Metabolic roles of tissues Four major tissues play a dominant role in fuel metabolism : liver, adipose, muscle, and brain. These tissues do not function in isolation.
Protein & Amino Acid Metabolism
 Pathophysiology 101-823 Unit 4 Metabolism & Metabolic Disease Protein & Amino Acid Metabolism Paul Anderson FALL 2008 Learning Objectives 1. List the metabolic functions of proteins & amino acids. 2. Explain
Pathophysiology 101-823 Unit 4 Metabolism & Metabolic Disease Protein & Amino Acid Metabolism Paul Anderson FALL 2008 Learning Objectives 1. List the metabolic functions of proteins & amino acids. 2. Explain
ENERGY FROM INGESTED NUTREINTS MAY BE USED IMMEDIATELY OR STORED
 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
Hypoglycemia. When recognized early, hypoglycemia can be treated successfully.
 Hypoglycemia Introduction Hypoglycemia is a condition that causes blood sugar level to drop dangerously low. It mostly shows up in diabetic patients who take insulin. When recognized early, hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia Introduction Hypoglycemia is a condition that causes blood sugar level to drop dangerously low. It mostly shows up in diabetic patients who take insulin. When recognized early, hypoglycemia
Hormones and Target Tissues
 Hormones and Target Tissues The hypothalamus is the coordination center of the endocrine system Hypothalamus is a small region of the forebrain in animals with skulls It receives and integrates nerve signals
Hormones and Target Tissues The hypothalamus is the coordination center of the endocrine system Hypothalamus is a small region of the forebrain in animals with skulls It receives and integrates nerve signals
Biol 219 Lec 7 Fall 2016
 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
Moh Tarek. Razi Kittaneh. Jaqen H ghar
 14 Moh Tarek Razi Kittaneh Jaqen H ghar Naif Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis is making glucose from non-carbohydrates precursors. Although Gluconeogenesis looks like Glycolysis in many steps, it is not the simple
14 Moh Tarek Razi Kittaneh Jaqen H ghar Naif Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis is making glucose from non-carbohydrates precursors. Although Gluconeogenesis looks like Glycolysis in many steps, it is not the simple
Guideline for the diagnosis and management of isovaleryl-coa-dehydrogenase deficiency (isovaleric acidemia) - a systematic review -
 Guideline for the diagnosis and management of isovaleryl-coa-dehydrogenase deficiency (isovaleric acidemia) - a systematic review - Guideline development group International interdisciplinary guideline
Guideline for the diagnosis and management of isovaleryl-coa-dehydrogenase deficiency (isovaleric acidemia) - a systematic review - Guideline development group International interdisciplinary guideline
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion , version 1.1
 EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
GALACTOSEMIA. Incidence
 GALACTOSEMIA Lactose, or milk sugar, is broken down into its constituent simple sugars, glucose and galactose, before absorption in the intestine. Galactosemia, which is an increased concentration of galactose
GALACTOSEMIA Lactose, or milk sugar, is broken down into its constituent simple sugars, glucose and galactose, before absorption in the intestine. Galactosemia, which is an increased concentration of galactose
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Hypoglycaemic disorders
 Hypoglycaemic disorders 1. Hypoglycaemia in patients with diabetes mellitus 2. Hypoglycaemia in non-diabetic patients 3. Clinical, laboratory and imaging diagnosis 4. Case report 5. GLP-1 receptor scintigraphy
Hypoglycaemic disorders 1. Hypoglycaemia in patients with diabetes mellitus 2. Hypoglycaemia in non-diabetic patients 3. Clinical, laboratory and imaging diagnosis 4. Case report 5. GLP-1 receptor scintigraphy
Permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus. Case Report
 Rawal Medical Journal An official publication of Pakistan Medical Association Rawalpindi Islamabad branch Established 1975 Volume 36 Number 4 October - December 2011 Case Report Permanent neonatal diabetes
Rawal Medical Journal An official publication of Pakistan Medical Association Rawalpindi Islamabad branch Established 1975 Volume 36 Number 4 October - December 2011 Case Report Permanent neonatal diabetes
Inborn Error Of Metabolism :
 Inborn Error Of Metabolism : Inborn Error Of Metabolism inborn error of metabolism are a large group of hereditary biochemical diseases in which specific gene mutation cause abnormal or missing proteins
Inborn Error Of Metabolism : Inborn Error Of Metabolism inborn error of metabolism are a large group of hereditary biochemical diseases in which specific gene mutation cause abnormal or missing proteins
Glycolysis. Intracellular location Rate limiting steps
 Glycolysis Definition Fx Fate Site Intracellular location Rate limiting steps Regulation Consume ATP Subs level phosphoryla tion Key reactions control points Nb Oxidation of glucose to give pyruvate (
Glycolysis Definition Fx Fate Site Intracellular location Rate limiting steps Regulation Consume ATP Subs level phosphoryla tion Key reactions control points Nb Oxidation of glucose to give pyruvate (
Introduction to Organic Acidemias. Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.
 Introduction to Organic Acidemias Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.2014 A Brief Historical Overview Garrod, Archibald E. 1902. The Incidence of
Introduction to Organic Acidemias Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.2014 A Brief Historical Overview Garrod, Archibald E. 1902. The Incidence of
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1
 CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1 web 2017 József Mandl Strategy of metabolism 1 Strategy of metabolism to extract energy ( hydrogen ) from the environment to store the energy excess to store hydrogen CH 3 O 2
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1 web 2017 József Mandl Strategy of metabolism 1 Strategy of metabolism to extract energy ( hydrogen ) from the environment to store the energy excess to store hydrogen CH 3 O 2
ACUTE & CHRONIC ETHANOL EFFECTS An Overview
 ACUTE & CHRONIC ETHANOL EFFECTS An Overview University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences Clinical Biochemistry: PBL Seminar MBBS Yr 4 VJ Temple
ACUTE & CHRONIC ETHANOL EFFECTS An Overview University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences Clinical Biochemistry: PBL Seminar MBBS Yr 4 VJ Temple
Glycogen Storage Diseases (A group of genetic diseases)
 Glycogen Storage Diseases (A group of genetic diseases) Glycogen Storage Diseases (GSD) Inherited genetic defects related to glycogen metabolism. Glycogenosis. Characterized by deposition of glycogen in
Glycogen Storage Diseases (A group of genetic diseases) Glycogen Storage Diseases (GSD) Inherited genetic defects related to glycogen metabolism. Glycogenosis. Characterized by deposition of glycogen in
Infant Of Diabetic Mother(IDM)
 Infant Of Diabetic Mother(IDM) Sangram Satish Magar 1, Sanskriti Mirashi 2 1. M.D. Sch.(Kaumarbhrutya-Balrog) 2.Guide (Kaumarbhrutya-Balrog), L.R.P.Medical college,islampur,tal- Walwa, dist- Sangli, Maharashtra,
Infant Of Diabetic Mother(IDM) Sangram Satish Magar 1, Sanskriti Mirashi 2 1. M.D. Sch.(Kaumarbhrutya-Balrog) 2.Guide (Kaumarbhrutya-Balrog), L.R.P.Medical college,islampur,tal- Walwa, dist- Sangli, Maharashtra,
Glycogen Storage Disease Type III, VI and IX - basics -
 Glycogen Storage Disease Type III, VI and IX - basics - Wyboston Lakes 10.10.2015 Urike Steuerwald Tórshavn / Hannover usteuerwald@web.de GSD III, VI and IX - Questions What goes wrong in glycogen storage
Glycogen Storage Disease Type III, VI and IX - basics - Wyboston Lakes 10.10.2015 Urike Steuerwald Tórshavn / Hannover usteuerwald@web.de GSD III, VI and IX - Questions What goes wrong in glycogen storage
Diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus - 1. Diabetes mellitus Lecture from pathological physiology
 Diabetes mellitus Lecture from pathological physiology Oliver Rácz, 2007-2018 Šafárik University, Košice, Slovakia In cooperation with F. Ništiar, (immunology) A. Chmelárová, (biochemistry) D. Kuzmová,
Diabetes mellitus Lecture from pathological physiology Oliver Rácz, 2007-2018 Šafárik University, Košice, Slovakia In cooperation with F. Ništiar, (immunology) A. Chmelárová, (biochemistry) D. Kuzmová,
HEREDITARY METABOLIC DISEASES
 HEREDITARY METABOLIC DISEASES Particular risk factors are: Advanced maternal age (e.g. Down's syndrome) Family history of inherited diseases (e.g. fragile X syndrome, Huntington's chorea) Previous child
HEREDITARY METABOLIC DISEASES Particular risk factors are: Advanced maternal age (e.g. Down's syndrome) Family history of inherited diseases (e.g. fragile X syndrome, Huntington's chorea) Previous child
2. What is molecular oxygen directly converted into? a. Carbon Dioxide b. Water c. Glucose d. None of the Above
 Biochem 1 Mock Exam 3 Chapter 11: 1. What is glucose completely oxidized into? a. Carbon Dioxide and Water b. Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen c. Oxygen and Water d. Water and Glycogen 2. What is molecular oxygen
Biochem 1 Mock Exam 3 Chapter 11: 1. What is glucose completely oxidized into? a. Carbon Dioxide and Water b. Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen c. Oxygen and Water d. Water and Glycogen 2. What is molecular oxygen
Work-Up and Initial Management of Common Metabolic Emergencies in the Inpatient Setting
 Work-Up and Initial Management of Common Metabolic Emergencies in the Inpatient Setting Kristin Lindstrom, MD Division of Genetics and Metabolism Phoenix Children s Hospital AzAAP Pediatrics in the Red
Work-Up and Initial Management of Common Metabolic Emergencies in the Inpatient Setting Kristin Lindstrom, MD Division of Genetics and Metabolism Phoenix Children s Hospital AzAAP Pediatrics in the Red
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 16 Glycolysis 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 16 Outline Why is glucose such a prominent fuel in all life forms? 1. Glucose
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 16 Glycolysis 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 16 Outline Why is glucose such a prominent fuel in all life forms? 1. Glucose
CEDIAMATE Metformin Tablets USP 500 mg
 CEDIAMATE Metformin Tablets USP 500 mg COMPOSITION: Cediamate Each un-coated tablet contains: Metformin Hydrochloride USP Excipients 500 mg Q.S PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacotherapeutic group: Blood Glucose lowering
CEDIAMATE Metformin Tablets USP 500 mg COMPOSITION: Cediamate Each un-coated tablet contains: Metformin Hydrochloride USP Excipients 500 mg Q.S PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacotherapeutic group: Blood Glucose lowering
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus
 Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Clinical Guideline. SPEG MCN Protocols Sub Group SPEG Steering Group
 Clinical Guideline SECONDARY CARE MANAGEMENT OF SUSPECTED ADRENAL CRISIS IN CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE Date of First Issue 24/01/2015 Approved 28/09/2017 Current Issue Date 16/06/2017 Review Date 01/09/2019
Clinical Guideline SECONDARY CARE MANAGEMENT OF SUSPECTED ADRENAL CRISIS IN CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE Date of First Issue 24/01/2015 Approved 28/09/2017 Current Issue Date 16/06/2017 Review Date 01/09/2019
5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Introduction: Variety of hormones and other molecules regulate the carbohydrates metabolism. Some of these have already been cited in previous sections.
5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Introduction: Variety of hormones and other molecules regulate the carbohydrates metabolism. Some of these have already been cited in previous sections.
Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis)
 Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis) 1) Argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) a) Incidence: ~1 in 70,000 b) Deficiency in an enzyme of
Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis) 1) Argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) a) Incidence: ~1 in 70,000 b) Deficiency in an enzyme of
Diseases Associated with Glycogen Synthesis
 Paper : 04 Metabolism of carbohydrates Module: 29 Principal Investigator, Dr. S.K.Khare, Professor IIT Delhi. Paper Coordinator Content Writer Dr. Ramesh Kothari, Professor Dr. Vijaya Khader UGC-CAS Dr.
Paper : 04 Metabolism of carbohydrates Module: 29 Principal Investigator, Dr. S.K.Khare, Professor IIT Delhi. Paper Coordinator Content Writer Dr. Ramesh Kothari, Professor Dr. Vijaya Khader UGC-CAS Dr.
Contraindications to breast feeding. Dr. Ahmed Isam
 Contraindications to breast feeding Dr. Ahmed Isam When should a mother avoid breastfeeding? Health professionals agree that human milk provides the most complete form of nutrition for infants, including
Contraindications to breast feeding Dr. Ahmed Isam When should a mother avoid breastfeeding? Health professionals agree that human milk provides the most complete form of nutrition for infants, including
