Leptin-Insulin Signaling in the Brain. BY TEAM CEPHALIC Aman Hamdard, Kevin Artiga, Megan Imreh, Ronald Baldonado, and Sharri Mo
|
|
|
- Beverly Elliott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Leptin-Insulin Signaling in the Brain BY TEAM CEPHALIC Aman Hamdard, Kevin Artiga, Megan Imreh, Ronald Baldonado, and Sharri Mo
2 Agenda Leptin in the Hypothalamus: Pathways and Roles Cross-talk between Insulin and Leptin Leptin & Obesity Is Insulin really necessary for survival? An experiment Signaling in other brain areas Clinical Implications
3 Leptin s Role in the Hypothalamus Main role: Energy Homeostasis Control food intake by inhibiting feeding behavior Done through regulating orexigenic and anorectic peptide production Regulation done through two main pathways: JAK/STAT and PI3K Insulin also involved in Energy Homeostasis Leads to cross-talk between signaling pathways
4 Orexigenic and Anorexigenic Pathways Leptin is involved in both pathways Orexigenic Increase appetite Neurons involved in pathway use GABA, neuropeptide Y, and agouti-related peptide Anorexigenic Decrease Appetite POMC neurons -> -MSH released -> agonist at MC4R -> appetite decrease
5 The JAK/STAT pathway Mechanism for regulating peptide creation Ultimate goal is to regulate the genes responsible for the creation of anorexigenic/orexigenic peptides Used in the Central Melanocortin (Anorexigenic) Pathway
6 SOCS3 in JAK/STAT STAT3 translocation -> activation of SOCS3 (Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3) Provides negative feedback regulation on both leptin and insulin Leptin: JAK2 negative feedback Insulin: IRS (Insulin Receptor Substrate) negative feedback Increase of SOCS3 occurs in obesity and states of leptin resistance
7 The PI3K pathway Leptin activity -> anorexigenic effect AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinases) enhances food intake Akt activated by PI3K inhibits AMPK -> anorexic effect Akt also deactivates FOXO1 transcription factor through phosphorylation Overexpression of FOXO1 can help cause obesity and glucose intolerance Insulin also participates in this pathway
8 The Cross-Talk between Insulin and Leptin
9 Both the Insulin Receptor and the Leptin Receptor recruit IRS2 IRS2 -> Low-abundance Lack of IRS2 for IR -> may result in defective leptin signal transduction Insulin induces the phosphorylation of JAK2 -> increasing activation of STAT3 Leptin -> JACK2 -> PI3K Both suppress food intake, both involve in decrease of cortical activity (in obese rate in presence of food).
10 Binding of Leptin to its receptor SHP2 (SH2-containing phosphatase 2) -> help to dephosphorylate the STAT3 -> maintain leptin sensitivity SOCS3 inhibits the action of SHP2 -> represses STAT3 pathway PTP1B (Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B) -> reduces POMC -leptin sensitivity SOCS3 activates PTP1B -> further repress repress leptin signaling through STAT3? GRB2 -> ERK -> neural morphology, synaptic plasticity, and modulating activity of some NT
11 Activation of the Receptor Leptin depolarizes POMC neurons through PI3K (leptin activated PI3K - neuron specific) and nonspecific cation channel activation (TRP) Leptin hyperpolarize AgRP neurons by PI3K-mediated opening of KATP channels -> Potassium outflow Insulin hyperpolarize both POMC and AgRP neurons by PI3K -mediated activation of KATP channels Insulin and Leptin both stimulate the phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion of FOXO1
12 Insulin and Leptin signaling in Energy Expenditure and Glucose Homeostasis Tanycytes (Specialized glial cells) POMC (proopiomelanocortin)neuronal activation represses food intake and promotes expenditure AgRP/NPY (Agouti Related Peptide) stimulate food intake PVN (Paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus) ARC (Arcuate Nucleus) These signals -> travel to the rest of the brain and peripheral tissue (WAT, BAT, pancreas, muscle, and liver)
13 Leptin effect on β cells Leptin inhibit glucose transport through GLUT2 transporters Leptin Activates PI3K-dependent reorganization of actin cytoskeleton -> opening KATP -> hyperpolarization PI3K-dependent activation of PDE3B -> reduces camp ->inhib PKA -> inhibit exocytosis Leptin inhibit PLC/PKC pathway
14 Leptin effect on β cells Leptin activate of STAT3 and STAT5B -> SOCS3 SOCS3 inhibit the production of proinsulin
15 Participation of SOCS3 in leptin resistance Prolonged receptor stimulation by leptin -. Inhibition of JAK2 and ERK phosphorylation by SOCS3 independen of Tyr 985 of OB-Rb
16 Leptin in individual with normal body weight vs obese In normal individuals, LepRb receive inhibitory signals from multiple negative feedback loops like COCS3, PTPB1, PTPN2, PTPε and EPAC1 In obese individuals, circulating leptin level increases -> diminished leptin transport across BBB ->activation of the inhibitory feedback systems -> diminished LepRb signaling Chronic overnutrition + increase fatty acids -> lipotoxicity and ER stress -> inflammatory responses -> may contribute to reduction in response to leptin (resistance)
17 Hypothalamus-mediated glucose and insulin resistance WAT expand, leptin increase in proportion to adipose expansion -> central leptin resistance -> favoring NPY (orexigenic peptide) in hypothalamus -> result in altered sympathetic and parasympathetic outflow. As insulin level rise -> adipose, liver, pancreas and hypothalamus become insulin-resistant ->exacerbate metabolic dysfunction
18 Leptin and insulin signaling pathways in hypothalamus MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase); AKT (thymoma viral proto-oncogene 1/protein kinase B PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase); PDE3B (phosphodiesterase 3B); POMC (proopiomelanocortin) AgRP (Agouti-related protein), EPAC (Exchange protein directly activated by camp)
19 Obesity and Leptin Resistance; Martin G. Myers, Rudolph L. Leibel, Randy j. Seeley, and Michael W. Schwarts Co- existence of leptin levels and and obesity have lead many to conclude that this is the evidence for leptin resistance. There are many other important factors at play, such as genetics, the environment, diet. Structure of Leptin, generated with w:ucsf Chimera. Vossman, I
20 Leptin Action & gleptin resistance Leptin binds/ activates long form of its proper receptor: LEPR- B. Receptor exists in the brain; decrease in food intake while increasing usage of energy. It has been noted that the phenotypes of humans and rats lacking leptin or its receptor show signs of starvation, lower metabolic function, infertility, immune dysfunction, insulin resistance, etc. Leptin replacement has shown promising results with reversing the modified lowleptin states: Genetic leptin deficiency, lipodystrophy syndrome. Key regulator of metabolic neuroendocrine responses. Arriving at the key term: leptin resistance
21 LEPR- B Signaling
22 Attenuation of LEPR- B Signaling 1. Disrupting SOCS3 2. Effects of SHP2 (PTP1B) 3. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress 4. Inflammation
23 Leptin Resistance in Genetic Models Assessment of LEPR-B signaling: Detection of leptin stimulated pstat3 in hypothalamus Response to food intake and body weight/ fat content to leptin administration. To analyze these models, 4 classes of genetic obesity are considered: 1. Alterations in LEPR- B (and signaling) 2. Disruption of neural pathways participating in leptin action 3. Alteration in peripheral tissues that operate independently of food intake 4. Alterations in CNS pathway with no clear link to leptin
24 Cellular Leptin Resistance in context- dependent obesity (including DIO) Genetics vs Environment Why use DIO (diet induced obesity)? Understanding the mechanisms Is cellular leptin resistance the primary factor in weight gain? Relationship between food intake and associated adiposity
25 Returning to the notion of gselective leptin resistance DIO and leptin resistance complicates the model. DIO- leptin specific model differences. Interference with feeding but effect on energy expenditure is unclear. ARC in the major site of cellular leptin resistance in DIO, ARC leptin still modulates energy expenditure, glucose homeostasis, etc. associated with food intake. Decreases of weight loss and normal chow. Predictable novel diet effect. Increased hunger Decreased thyroid Sympathetic tone Effect of weight loss from an obese state to lack of control of eating is due to leptin resistance, then other conditions are equally true.
26 Obesity in the Overall Picture Major differences between DIO and genetic altered impairments. Mechanisms that contribute to maintenance of obesity with dietary interventions. Implications in the modern world.
27 Is Insulin really necessary for survival? An Experiment The idea that we can live without insulin has been challenged. In everyday life, those with type I diabetes inject insulin to control blood sugar.
28 The Experiment They tested rodents that did not have insulin in their bodies and then gave them leptin monotherapy. The outcome of intracerebroventricular (i.c.v) administration of leptin to rodents without insulin were the ones being tested. Mice without insulin/ mice that do not re-express leptin receptors (LEPRs) were accessed when they had I.C.V administration of leptin.
29 continued They found re expression of leptin receptors in hypothalamic GABA and POMC neurons. When the rodents have GABA and POMC neurons, its enough to mediate antidiabetes. However, if you have a lot of glucose uptake and hepatic metabolism, these effects of leptin are decreased.
30 In insulin deficient rodents, leptin administration is also very effective in improving diabetes. These latter findings may represent the groundwork for developing improved therapies for diseases of insulin deficiencies. A comprehensive understanding of molecules and cell types underlying the lifesaving and metabolic improving actions of leptin in insulin deficiency is needed.
31 Different models of insulin In this study they used two different models of insulin deficiency: (1) The streptozotocin (STZ) (1) The diphtheria toxin (DT)
32 STZ + DT -STZ treated mice retain miniscule amount of pancreatic insulin; therefore, it is unclear whether the residual insulin is required for the beneficial effect induced by leptin treatment -DT injected mice displayed overly high hyperglycemia, reduced body weight, hyperphagia, and hyperglucago
33
34
35 The results Altogether, the results demonstrated that concomitant expression of leptin receptors only in GABA and POMC neurons is sufficient to fully mediate the lifesaving and anti diabetic effects of leptin administration in context of insulin deficiency. Beta adrenergic receptors have been indicated as important components of the hypothalamic dependent pathway governing glucose metabolism. To determine the fate of glucose in insulin deficient mice undergoing leptin administration, they used glucose training analysis.
36 continued The results showed the I.C.V leptin administration does NOT affect glucose uptake in the brain or gastrocnemius and vastus skeletal muscle, but it significantly enhances glucose uptake in soleus muscle. The results were focused on glucose and glycogen metabolism because lower circulating glucagon levels brought on by I.C.V leptin administration may affect pathways(those relevant to glucose metabolism)
37 Results continued The results suggest that increased glucose uptake and utilization by soleus and improved hepatic metabolism are components of the mechanisms underlying the anti diabetic action of leptin in the context of insulin deficiency. Rodents that are able to produce insulin, hypothalamic mediated control of glucose metabolism relies on the activation of the sympathetic nervous system.
38
39 Signaling in Other Brain Areas These areas are still linked to energy homeostasis in that are involved in the regulation of eating behavior. Cerebral Cortex Cerebellum Hippocampus
40 Cerebellum - locomotor activity Leptin/Insulin are involved in the cerebellar control of motor activity through STAT3 After leptin administration: p-tyr705-stat3 levels Activation of STAT3 promotes locomotor activity Vs. leptin-deficiency contributes to reduced mobility IR levels are seen as reduced in experimental ataxia
41 Cerebral Cortex - metabolic control Cytokines in this area also exert effects for homeostatic regulation Leptin/insulin can overlook neurotransmitter activity and synaptic plasticity in this region through the ERK pathway Obese rats: are hyperleptinemic, and may have high serum insulin levels in the presence of food: activation of JAK2/STAT3 decreased activity in the cortex
42 Hippocampus - learning & memory Leptin signaling can facilitate synaptic plasticity When mice are infused with leptin, short-term potentiation shifts to long-term potentiation Caused by the enhancement of Ca2+ influx through the NMDA receptor Damage linked to an increase in appetite Can lead to weight gain/greater intake of fat-rich diets Which negatively affects processes related to energy homeostasis
43 Experimental Examples Cerebral Cortex selective lesions alter feeding behavior Cerebellum leptin-deficient rodents display reduced mobility lesions show signs of reduced food-seeking behavior Hippocampus damaged in patients inability to inhibit consumption of a second meal because they cannot remember eating beforehand
44 Hyperleptinemia Having more than normal amounts of leptin in the bloodstream Damages hippocampal synaptic transmission Causing factors not well known, but increased food intake/insulin resistance play a part Associated with the onset of depressive symptoms Suggests leptin resistance may have a deleterious effect Central infusion of leptin shown to induce antidepressive behavior But may promote an inflammatory profile - correlates with markers of the metabolic syndrome Implies an important association between obesity and depression (
45 Neurodegenerative Diseases Leptin promotes neurogenesis, axonal growth and synaptogenesis By activating JAK2/STAT3 pathways, there is neurotrophin withdrawal, leading to reduced cell death May help reverse the effects of dopaminergic neuron loss in Parkinson s Disease (PD) High leptin levels may have harmful effects on other diseases, ie. Multiple Sclerosis (MS) With MS, leptin production is only enhanced in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients
46 Neurodegenerative Diseases Alzheimer s Disease: characterized by the aggregation of β - amyloid proteins and neurofibrillary tangles of hyperphosphorylated tau Leptin modulates APOE expression and decreases activity of beta secretase APOE - role of removing β - amyloid proteins Beta secretase produces β - amyloids
47 Neurodegenerative Diseases Large connection between effects on insulin sensitivity and neuropsychiatric diseases, ie. AD Insulin receptor binding regulates cognitive functioning Promote the inhibition of apoptosis Stimulate metabolism and plasticity Mediated by Akt phosphorylation and GSK3β inhibition In an experimental model, activation of PI3K/Akt mediates neuroprotection in AD and PD Lower activation of IRS/PI3K pathways disrupts Aβ processing, Increases AD-related symptoms
Insulin-Leptin Interactions
 Insulin-Leptin Interactions Ahmed S., Al-Azzam N., Cao B. Karshaleva B., Sriram S., Vu K. If you understand a system, you can predict it. Agenda - Energy homeostasis Overview of leptin and insulin Signaling
Insulin-Leptin Interactions Ahmed S., Al-Azzam N., Cao B. Karshaleva B., Sriram S., Vu K. If you understand a system, you can predict it. Agenda - Energy homeostasis Overview of leptin and insulin Signaling
CNS Control of Food Intake. Adena Zadourian & Andrea Shelton
 CNS Control of Food Intake Adena Zadourian & Andrea Shelton Controlling Food Intake Energy Homeostasis (Change in body adiposity + compensatory changes in food intake) Background Information/Review Insulin
CNS Control of Food Intake Adena Zadourian & Andrea Shelton Controlling Food Intake Energy Homeostasis (Change in body adiposity + compensatory changes in food intake) Background Information/Review Insulin
THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN. COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar
 THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar INTRODUCTION Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas by the islets of Langerhans that regulates the
THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar INTRODUCTION Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas by the islets of Langerhans that regulates the
Neurophysiology of the Regulation of Food Intake and the Common Reward Pathways of Obesity and Addiction. Laura Gunter
 Neurophysiology of the Regulation of Food Intake and the Common Reward Pathways of Obesity and Addiction Laura Gunter The Brain as the Regulatory Center for Appetite The brain is the integration center
Neurophysiology of the Regulation of Food Intake and the Common Reward Pathways of Obesity and Addiction Laura Gunter The Brain as the Regulatory Center for Appetite The brain is the integration center
Leptin Intro/Signaling. ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph
 Leptin Intro/Signaling ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph Overview Intro to Leptin Definition & Sources Physiology Bound vs. Free Receptors Signaling JAK/STAT MAPK PI3K ACC Experimental findings
Leptin Intro/Signaling ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph Overview Intro to Leptin Definition & Sources Physiology Bound vs. Free Receptors Signaling JAK/STAT MAPK PI3K ACC Experimental findings
Internal Regulation II Energy
 Internal Regulation II Energy Reading: BCP Chapter 16 lookfordiagnosis.com Homeostasis Biologically, what is necessary for life is a coordinated set of chemical reactions. These reactions take place in
Internal Regulation II Energy Reading: BCP Chapter 16 lookfordiagnosis.com Homeostasis Biologically, what is necessary for life is a coordinated set of chemical reactions. These reactions take place in
Hormones. Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6
 Hormones Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6 Tel. 030-8385-6920 (Sekret.) 030-8385-6922 (direkt) e-mail: vhaucke@chemie.fu-berlin.de http://userpage.chemie.fu-berlin.de/biochemie/aghaucke/teaching.html
Hormones Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6 Tel. 030-8385-6920 (Sekret.) 030-8385-6922 (direkt) e-mail: vhaucke@chemie.fu-berlin.de http://userpage.chemie.fu-berlin.de/biochemie/aghaucke/teaching.html
SH2B1 Regulates Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Homeostasis by Multiple Mechanisms. David L. Morris
 SH2B1 Regulates Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Homeostasis by Multiple Mechanisms by David L. Morris A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
SH2B1 Regulates Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Homeostasis by Multiple Mechanisms by David L. Morris A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Bi156 lecture 2, 1/6/12. Eating and weight regulation
 Bi156 lecture 2, 1/6/12 Eating and weight regulation Introduction: weight regulation in an affluent society In our society much effort and money is expended on regulation of weight. Failure to maintain
Bi156 lecture 2, 1/6/12 Eating and weight regulation Introduction: weight regulation in an affluent society In our society much effort and money is expended on regulation of weight. Failure to maintain
Figure 1: The leptin/melanocortin pathway Neuronal populations propagate the signaling of various molecules (leptin, insulin, ghrelin) to control
 Leptin Deficiency Introduction The leptin/melanocortin pathway plays a key role in the hypothalamic control of food intake. It is activated following the systemic release of the adipokine leptin (LEP)
Leptin Deficiency Introduction The leptin/melanocortin pathway plays a key role in the hypothalamic control of food intake. It is activated following the systemic release of the adipokine leptin (LEP)
Leptin and the Central Nervous System Control of Glucose Metabolism
 Physiol Rev 91: 389 411, 2011; doi:10.1152/physrev.00007.2010. Leptin and the Central Nervous System Control of Glucose Metabolism GREGORY J. MORTON AND MICHAEL W. SCHWARTZ Diabetes and Obesity Center
Physiol Rev 91: 389 411, 2011; doi:10.1152/physrev.00007.2010. Leptin and the Central Nervous System Control of Glucose Metabolism GREGORY J. MORTON AND MICHAEL W. SCHWARTZ Diabetes and Obesity Center
Metabolic Syndrome. DOPE amines COGS 163
 Metabolic Syndrome DOPE amines COGS 163 Overview - M etabolic Syndrome - General definition and criteria - Importance of diagnosis - Glucose Homeostasis - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Resistance
Metabolic Syndrome DOPE amines COGS 163 Overview - M etabolic Syndrome - General definition and criteria - Importance of diagnosis - Glucose Homeostasis - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Resistance
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease. Metabolic Disorders - Obesity
 BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin by Gema FRUHBECK. Presentation by Amnesiacs Anonymous
 Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin by Gema FRUHBECK Presentation by Amnesiacs Anonymous Introduction to Leptin By Ahrial Young Why is Leptin important? Pleiotropic = it controls the
Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin by Gema FRUHBECK Presentation by Amnesiacs Anonymous Introduction to Leptin By Ahrial Young Why is Leptin important? Pleiotropic = it controls the
The role of leptin receptor signaling in feeding and neuroendocrine function
 Review TRENDS in Endocrinology and Metabolism Vol.14 No.10 December 2003 447 The role of leptin receptor signaling in feeding and neuroendocrine function Sarah H. Bates and Martin G. Myers Jr Research
Review TRENDS in Endocrinology and Metabolism Vol.14 No.10 December 2003 447 The role of leptin receptor signaling in feeding and neuroendocrine function Sarah H. Bates and Martin G. Myers Jr Research
! acts via the autonomic nervous system. ! maintaining body weight within tight limits. ! ventromedial (VMN) ! arcuate (ARC) ! neuropeptide Y (NPY)
 Brain Regulates energy homeostatis Glucose Sensing in the Brain Seminar 2012 Gareth Price! acts in response to circulating signals of nutrient states! acts via the autonomic nervous system Ensures a balance
Brain Regulates energy homeostatis Glucose Sensing in the Brain Seminar 2012 Gareth Price! acts in response to circulating signals of nutrient states! acts via the autonomic nervous system Ensures a balance
An important function of the central nervous
 Perspectives in Diabetes Insulin Signaling in the Central Nervous System A Critical Role in Metabolic Homeostasis and Disease From C. elegans to Humans Daniel Porte, Jr., 1,2,3 Denis G. Baskin, 3 and Michael
Perspectives in Diabetes Insulin Signaling in the Central Nervous System A Critical Role in Metabolic Homeostasis and Disease From C. elegans to Humans Daniel Porte, Jr., 1,2,3 Denis G. Baskin, 3 and Michael
Copyright 2017 The Guilford Press
 This is a chapter excerpt from Guilford Publications. Eating Disorders and Obesity: A Comprehensive Handbook, Third Edition. Edited by Kelly D. Brownell and B. Timothy Walsh. Copyright 2017. Purchase this
This is a chapter excerpt from Guilford Publications. Eating Disorders and Obesity: A Comprehensive Handbook, Third Edition. Edited by Kelly D. Brownell and B. Timothy Walsh. Copyright 2017. Purchase this
Neuroprotective properties of GLP-1 - a brief overview. Michael Gejl Jensen, MD Dept. Of Pharmacology, AU
 Neuroprotective properties of GLP-1 - a brief overview Michael Gejl Jensen, MD Dept. Of Pharmacology, AU mg@farm.au.dk Agenda Glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) GLP-1 and neuronal activity GLP-1 in disease-specific
Neuroprotective properties of GLP-1 - a brief overview Michael Gejl Jensen, MD Dept. Of Pharmacology, AU mg@farm.au.dk Agenda Glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) GLP-1 and neuronal activity GLP-1 in disease-specific
THE ROLE OF DIETARY FAT IN HYPOTHALAMIC INSULIN AND LEPTIN RESISTANCE AND THE PATHOGENESIS OF OBESITY. Kelly Ann Posey.
 THE ROLE OF DIETARY FAT IN HYPOTHALAMIC INSULIN AND LEPTIN RESISTANCE AND THE PATHOGENESIS OF OBESITY By Kelly Ann Posey Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University
THE ROLE OF DIETARY FAT IN HYPOTHALAMIC INSULIN AND LEPTIN RESISTANCE AND THE PATHOGENESIS OF OBESITY By Kelly Ann Posey Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University
Motivation 1 of 6. during the prandial state when the blood is filled
 Motivation 1 of 6 I. INTRODUCTION A. Motivation: a condition (usually internal) that initiates, activates, or maintains goal-directed behavior. B. Archery analogy 1. undrawn bow has no potential energy
Motivation 1 of 6 I. INTRODUCTION A. Motivation: a condition (usually internal) that initiates, activates, or maintains goal-directed behavior. B. Archery analogy 1. undrawn bow has no potential energy
Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Is obesity a brain disorder? What is the evidence to support obesity is a brain disorder? Environmental, biological, and behavioral issues Over
Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Is obesity a brain disorder? What is the evidence to support obesity is a brain disorder? Environmental, biological, and behavioral issues Over
Fatty Acid Induced Insulin Resistance in the Brain
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate Studies 5-2013 Fatty Acid Induced Insulin Resistance in the Brain Hyoung Il Oh Utah State University Follow this
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate Studies 5-2013 Fatty Acid Induced Insulin Resistance in the Brain Hyoung Il Oh Utah State University Follow this
Insulin and Neurodegenerative Diseases: Shared and Specific Mechanisms. Cogs 163 Stella Ng Wendy Vega
 Insulin and Neurodegenerative Diseases: Shared and Specific Mechanisms Cogs 163 Stella Ng Wendy Vega Overview A. Insulin and the Brain B. Alzheimer s Disease and Insulin C. Other neurodegenerative disease:
Insulin and Neurodegenerative Diseases: Shared and Specific Mechanisms Cogs 163 Stella Ng Wendy Vega Overview A. Insulin and the Brain B. Alzheimer s Disease and Insulin C. Other neurodegenerative disease:
LESSON 3.3 WORKBOOK. How do we decide when and how much to eat?
 Appetite The psychological desire to eat, driven by feelings of pleasure from the brain. Hunger The biological or physiological need to eat, caused by a release of hormones from the digestive tract. LESSON
Appetite The psychological desire to eat, driven by feelings of pleasure from the brain. Hunger The biological or physiological need to eat, caused by a release of hormones from the digestive tract. LESSON
Leptin part 2. Mary ET Boyle
 Leptin part 2 Mary ET Boyle Leptin Feedback: leptin levels drop during starvation, when fat depots are depleted to support the organism s basic energy needs, leptin levels rise during refeeding where fat
Leptin part 2 Mary ET Boyle Leptin Feedback: leptin levels drop during starvation, when fat depots are depleted to support the organism s basic energy needs, leptin levels rise during refeeding where fat
AMPK. Tomáš Kučera.
 AMPK (AMP- ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE ) Tomáš Kučera tomas.kucera@lfmotol.cuni.cz Department of Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and Motol
AMPK (AMP- ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE ) Tomáš Kučera tomas.kucera@lfmotol.cuni.cz Department of Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and Motol
The Effects of Saturated Fatty Acid Palmitate on Neuropeptide Gene. Expression, Signal Transduction, and Insulin Signaling in an Immortalized
 The Effects of Saturated Fatty Acid Palmitate on Neuropeptide Gene Expression, Signal Transduction, and Insulin Signaling in an Immortalized Hypothalamic Neuronal Cell Model, mhypoa-npy/gfp By Brian Wong
The Effects of Saturated Fatty Acid Palmitate on Neuropeptide Gene Expression, Signal Transduction, and Insulin Signaling in an Immortalized Hypothalamic Neuronal Cell Model, mhypoa-npy/gfp By Brian Wong
Ghrelin mediates stressinduced. behavior in mice. Chuang et al 2011 L3: Love, Lust, Labor
 Ghrelin mediates stressinduced food-reward behavior in mice Chuang et al 2011 L3: Love, Lust, Labor Agenda Introduction What is Ghrelin? Previous Models New model Methods Results Discussion Conclusion
Ghrelin mediates stressinduced food-reward behavior in mice Chuang et al 2011 L3: Love, Lust, Labor Agenda Introduction What is Ghrelin? Previous Models New model Methods Results Discussion Conclusion
Cronicon EC NEUROLOGY. Mini Review Dysregulation of Leptin in Clinical Depression. Michael J Chen* Abstract. Abbreviations.
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC NEUROLOGY Mini Review Dysregulation of Leptin in Clinical Depression Michael J Chen* Department of Biological Sciences, California State University, Los Angeles, CA, USA *Corresponding
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC NEUROLOGY Mini Review Dysregulation of Leptin in Clinical Depression Michael J Chen* Department of Biological Sciences, California State University, Los Angeles, CA, USA *Corresponding
Ingestive Behaviors 21. Introduction. Page 1. control and story lines. (a review of general endocrinology) Integration (or the basic reflex arc model)
 Ingestive Behaviors 21 (a review of general endocrinology) A neuroendocrine system: components, a reflex arc, the endocrine system, the AN, endocrine / nervous systems as afferents and efferents, the theoretical
Ingestive Behaviors 21 (a review of general endocrinology) A neuroendocrine system: components, a reflex arc, the endocrine system, the AN, endocrine / nervous systems as afferents and efferents, the theoretical
Ingestive Behavior: Feeding & Weight Regulation. Hypovolemic vs. Osmotic Thirst
 Ingestive Behavior: Feeding & Weight Regulation 1 Hypovolemic Thirst Receptors, CNS, Responses Salt Appetite Digestive components Glucose Homeostasis: Insulin & Glucagon Diabetes Mellitus 1 & 2 CNS Hypothalamic
Ingestive Behavior: Feeding & Weight Regulation 1 Hypovolemic Thirst Receptors, CNS, Responses Salt Appetite Digestive components Glucose Homeostasis: Insulin & Glucagon Diabetes Mellitus 1 & 2 CNS Hypothalamic
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus
 Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις
 Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 16 Κίνητρα Συμπεριφοράς ή Υποκίνηση (Motivation) Introduction Types of behavior Unconscious reflexes Voluntary
Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 16 Κίνητρα Συμπεριφοράς ή Υποκίνηση (Motivation) Introduction Types of behavior Unconscious reflexes Voluntary
Peripubertal, leptin-deficient ob/ob female mice were used in an investigation of
 ESSICK-BROOKSHIRE, ELIZABETH ANN, M.S. The Effects of Peripherally Administered 17-β Estradiol and BIBP3226, a NPY Y1 Receptor Antagonist, on Food Intake, Body Mass, Reproductive Development and Behavior
ESSICK-BROOKSHIRE, ELIZABETH ANN, M.S. The Effects of Peripherally Administered 17-β Estradiol and BIBP3226, a NPY Y1 Receptor Antagonist, on Food Intake, Body Mass, Reproductive Development and Behavior
Chapter 12. Ingestive Behavior
 Chapter 12 Ingestive Behavior Drinking a. fluid compartments b. osmometric thirst c. volumetric thirst Eating a. energy sources b. starting a meal c. stopping a meal d. eating disordersd Drinking a. fluid
Chapter 12 Ingestive Behavior Drinking a. fluid compartments b. osmometric thirst c. volumetric thirst Eating a. energy sources b. starting a meal c. stopping a meal d. eating disordersd Drinking a. fluid
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 12 Signal Transduction
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 12 Signal Transduction CHAPTER 12 Signal Transduction Key topics: General features of signal transduction Structure and function of G protein coupled receptors Structure
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 12 Signal Transduction CHAPTER 12 Signal Transduction Key topics: General features of signal transduction Structure and function of G protein coupled receptors Structure
AMPK. Tomáš Kuc era. Ústav lékar ské chemie a klinické biochemie 2. lékar ská fakulta, Univerzita Karlova v Praze
 AMPK (AMP- ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE ) Tomáš Kuc era Ústav lékar ské chemie a klinické biochemie 2. lékar ská fakulta, Univerzita Karlova v Praze 2013 AMPK AMP-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE present in all eukaryotic
AMPK (AMP- ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE ) Tomáš Kuc era Ústav lékar ské chemie a klinické biochemie 2. lékar ská fakulta, Univerzita Karlova v Praze 2013 AMPK AMP-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE present in all eukaryotic
Does chronic leptin treatment decrease glucagon responsiveness in STZ-induced type 1 diabetic rats? Kristin E. Rowland
 Does chronic leptin treatment decrease glucagon responsiveness in STZ-induced type 1 diabetic rats? by Kristin E. Rowland A thesis submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Auburn University in partial fulfillment
Does chronic leptin treatment decrease glucagon responsiveness in STZ-induced type 1 diabetic rats? by Kristin E. Rowland A thesis submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Auburn University in partial fulfillment
THE ROLE OF ENDOCANNABINOID RECEPTOR ACTIVITY IN YOUNG AND AGED RATS WITH HIGH-FAT FEEDING
 THE ROLE OF ENDOCANNABINOID RECEPTOR ACTIVITY IN YOUNG AND AGED RATS WITH HIGH-FAT FEEDING By MELANIE KAE JUDGE A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
THE ROLE OF ENDOCANNABINOID RECEPTOR ACTIVITY IN YOUNG AND AGED RATS WITH HIGH-FAT FEEDING By MELANIE KAE JUDGE A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
Stress & The Neuroprotective Factors of Exercise. Week 9: Thursday, November 29 Sonia Romo
 Stress & The Neuroprotective Factors of Exercise Week 9: Thursday, November 29 Sonia Romo Today s Agenda Old Brain in a New Society Stress and the Immune System Stress and CVD Stress and Metabolic Syndrome
Stress & The Neuroprotective Factors of Exercise Week 9: Thursday, November 29 Sonia Romo Today s Agenda Old Brain in a New Society Stress and the Immune System Stress and CVD Stress and Metabolic Syndrome
Central insulin and leptin-mediated autonomic control of glucose homeostasis
 Review Central insulin and leptin-mediated autonomic control of glucose homeostasis Joseph S. Marino 1,2, Yong Xu 4 and Jennifer W. Hill 1,2,3 1 Center for Diabetes and Endocrine Research, College of Medicine,
Review Central insulin and leptin-mediated autonomic control of glucose homeostasis Joseph S. Marino 1,2, Yong Xu 4 and Jennifer W. Hill 1,2,3 1 Center for Diabetes and Endocrine Research, College of Medicine,
FLASH CARDS. Kalat s Book Chapter 10 Alphabetical
 FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 10 Alphabetical AgRP AgRP Agouti-related peptide; synthesized in hypothalamus. Acts as an appetite stimulator. Also decreases metabolism. aldosterone
FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 10 Alphabetical AgRP AgRP Agouti-related peptide; synthesized in hypothalamus. Acts as an appetite stimulator. Also decreases metabolism. aldosterone
History of Investigation
 Acini - Pancreatic juice (1º) (2º) Secretions- neuronal and hormonal mechanisms 1) Secretin - bicarbonate rich 2) Cholecystokinin - enzyme rich Islets of Langerhans (contain 4 cell types) Alpha cells (α)-
Acini - Pancreatic juice (1º) (2º) Secretions- neuronal and hormonal mechanisms 1) Secretin - bicarbonate rich 2) Cholecystokinin - enzyme rich Islets of Langerhans (contain 4 cell types) Alpha cells (α)-
Homeostasis and Mechanisms of Weight Regulation
 Homeostasis and Mechanisms of Weight Regulation Purpose In this activity students will investigate how negative feedback mechanisms function to maintain homeostatic balance using a recently discovered
Homeostasis and Mechanisms of Weight Regulation Purpose In this activity students will investigate how negative feedback mechanisms function to maintain homeostatic balance using a recently discovered
Obesity in aging: Hormonal contribution
 Obesity in aging: Hormonal contribution Hormonal issues in obesity and aging Hormonal role in regulation of energy balance Genetic component in hormonal regulation Life style contribution to hormonal changes
Obesity in aging: Hormonal contribution Hormonal issues in obesity and aging Hormonal role in regulation of energy balance Genetic component in hormonal regulation Life style contribution to hormonal changes
Hypothalamic inflammation: a double-edged sword to nutritional diseases
 Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. ISSN 0077-8923 ANNALS OF THE NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Issue: The Year in Diabetes and Obesity Hypothalamic inflammation: a double-edged sword to nutritional diseases Dongsheng
Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. ISSN 0077-8923 ANNALS OF THE NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Issue: The Year in Diabetes and Obesity Hypothalamic inflammation: a double-edged sword to nutritional diseases Dongsheng
Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00
 Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00 CNS patterning A001-A014 Stem cells: basic biology and postnatal neurogenesis - part I Development of neural systems: Molecular and genetic characterisationa Epigenetic
Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00 CNS patterning A001-A014 Stem cells: basic biology and postnatal neurogenesis - part I Development of neural systems: Molecular and genetic characterisationa Epigenetic
Chapter 1. General introduction. Part of this chapter is adapted from Adan et.al., Br.J.Pharmacol. 2006;149:815
 Chapter 1 General introduction Part of this chapter is adapted from Adan et.al., Br.J.Pharmacol. 2006;149:815 Chapter 1 B. Tiesjema, 2007 GENERAL INTRODUCTION NEURAL CIRCUITS INVOLVED IN ENERGY BALANCE
Chapter 1 General introduction Part of this chapter is adapted from Adan et.al., Br.J.Pharmacol. 2006;149:815 Chapter 1 B. Tiesjema, 2007 GENERAL INTRODUCTION NEURAL CIRCUITS INVOLVED IN ENERGY BALANCE
Ayman Mesleh & Leen Alnemrawi. Bayan Abusheikha. Faisal
 24 Ayman Mesleh & Leen Alnemrawi Bayan Abusheikha Faisal We were talking last time about receptors for lipid soluble hormones.the general mechanism of receptors for lipid soluble hormones: 1. Receptors
24 Ayman Mesleh & Leen Alnemrawi Bayan Abusheikha Faisal We were talking last time about receptors for lipid soluble hormones.the general mechanism of receptors for lipid soluble hormones: 1. Receptors
Energy Balance. Applied Human Metabolism VII. Energy Out. Factors that effect BMR/RMR 17/03/2016
 Energy Balance Applied Human Metabolism VII Weight Regulation The balance of energy taken in or leaving the body determines body mass Energy In = Energy Out Weight Maintenance Energy In < Energy Out Weight
Energy Balance Applied Human Metabolism VII Weight Regulation The balance of energy taken in or leaving the body determines body mass Energy In = Energy Out Weight Maintenance Energy In < Energy Out Weight
Central nervous system control of food intake
 insight review article Central nervous system control of food intake Michael W. Schwartz*, Stephen C. Woods, Daniel Porte Jr*, Randy J. Seeley & Denis G. Baskin* Departments of Medicine* and Biological
insight review article Central nervous system control of food intake Michael W. Schwartz*, Stephen C. Woods, Daniel Porte Jr*, Randy J. Seeley & Denis G. Baskin* Departments of Medicine* and Biological
Hormonal Regulation of Food Intake
 Physiol Rev 85: 1131 1158, 2005; doi:10.1152/physrev.00015.2004. Hormonal Regulation of Food Intake SARAH STANLEY, KATIE WYNNE, BARBARA McGOWAN, AND STEPHEN BLOOM Endocrine Unit, Imperial College Faculty
Physiol Rev 85: 1131 1158, 2005; doi:10.1152/physrev.00015.2004. Hormonal Regulation of Food Intake SARAH STANLEY, KATIE WYNNE, BARBARA McGOWAN, AND STEPHEN BLOOM Endocrine Unit, Imperial College Faculty
KEY CONCEPT QUESTIONS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction
 Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
G-Protein Signaling. Introduction to intracellular signaling. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
Early Life Effects on Hypothalamic Circuitry. By: The Mystery Gang
 Early Life Effects on Hypothalamic Circuitry By: The Mystery Gang Hypothalamic Circuits Controlling Energy Balance ARH (Arcuate nucleus of the Hypothalamus) Subgroup of Neurons 1: coexpress Neuropeptide
Early Life Effects on Hypothalamic Circuitry By: The Mystery Gang Hypothalamic Circuits Controlling Energy Balance ARH (Arcuate nucleus of the Hypothalamus) Subgroup of Neurons 1: coexpress Neuropeptide
UNRAVELING NOVEL LEPTIN-DEPENDENT SIGNALING PATHWAYS IN THE BASOMEDIAL HYPOTHALAMUS. Eneida Cristina Villanueva
 UNRAVELING NOVEL LEPTIN-DEPENDENT SIGNALING PATHWAYS IN THE BASOMEDIAL HYPOTHALAMUS by Eneida Cristina Villanueva A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
UNRAVELING NOVEL LEPTIN-DEPENDENT SIGNALING PATHWAYS IN THE BASOMEDIAL HYPOTHALAMUS by Eneida Cristina Villanueva A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
Molecular and Physiological Adaptations to Weight Perturbation in Mice. Yann Ravussin. Submitted in partial fulfillment of the
 Molecular and Physiological Adaptations to Weight Perturbation in Mice Yann Ravussin Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy under the Executive Committee
Molecular and Physiological Adaptations to Weight Perturbation in Mice Yann Ravussin Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy under the Executive Committee
6.6 HORMONES & REPRODUCTION
 6.6 HORMONES & REPRODUCTION Endocrine system Produces and releases hormones Hormones travel in the blood to target tissues Long distance communication between cells Endocrine Glands Blood stream Hormone
6.6 HORMONES & REPRODUCTION Endocrine system Produces and releases hormones Hormones travel in the blood to target tissues Long distance communication between cells Endocrine Glands Blood stream Hormone
28/04/51. Introduction. Insulin signaling effects on memory and mood. Is accelerated brain aging a consequence of diabetes? chronic hyperglycemia
 Introduction Insulin signaling effects on memory and mood (Review) Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Long-term diabetes Lawrence
Introduction Insulin signaling effects on memory and mood (Review) Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Long-term diabetes Lawrence
5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Introduction: Variety of hormones and other molecules regulate the carbohydrates metabolism. Some of these have already been cited in previous sections.
5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Introduction: Variety of hormones and other molecules regulate the carbohydrates metabolism. Some of these have already been cited in previous sections.
The brain renin-angiotensin system in metabolic and cardiovascular regulation
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Fall 2016 The brain renin-angiotensin system in metabolic and cardiovascular regulation Kristin Elizabeth Claflin University of Iowa Copyright
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Fall 2016 The brain renin-angiotensin system in metabolic and cardiovascular regulation Kristin Elizabeth Claflin University of Iowa Copyright
Goals and Challenges of Communication. Communication and Signal Transduction. How Do Cells Communicate?
 Goals and Challenges of Communication Reaching (only) the correct recipient(s) Imparting correct information Timeliness Causing the desired effect Effective termination Communication and Signal Transduction
Goals and Challenges of Communication Reaching (only) the correct recipient(s) Imparting correct information Timeliness Causing the desired effect Effective termination Communication and Signal Transduction
Ingestive Behaviors 33. Introduction. Page 1. control and story lines. (a review of general endocrinology) Integration (or the basic reflex arc model)
 Ingestive Behaviors 33 (a review of general endocrinology) A neuroendocrine system: components, a reflex arc, the endocrine system, the AN, endocrine / nervous systems as afferents and efferents, the theoretical
Ingestive Behaviors 33 (a review of general endocrinology) A neuroendocrine system: components, a reflex arc, the endocrine system, the AN, endocrine / nervous systems as afferents and efferents, the theoretical
What systems are involved in homeostatic regulation (give an example)?
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
Neurobiology of food intake in health and disease
 Neurobiology of food intake in health and disease Gregory J. Morton, Thomas H. Meek and Michael W. Schwartz Abstract Under normal conditions, food intake and energy expenditure are balanced by a homeostatic
Neurobiology of food intake in health and disease Gregory J. Morton, Thomas H. Meek and Michael W. Schwartz Abstract Under normal conditions, food intake and energy expenditure are balanced by a homeostatic
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 FINAL EXAM REVIEW
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 FINAL EXAM REVIEW
AGE-RELATED WEIGHT LOSS IN THE 5XFAD MOUSE MODEL OF ALZHEIMER S DISEASE: A BEHAVIOURAL AND HORMONAL ANALYSIS. William Hebert Gendron
 AGE-RELATED WEIGHT LOSS IN THE 5XFAD MOUSE MODEL OF ALZHEIMER S DISEASE: A BEHAVIOURAL AND HORMONAL ANALYSIS by William Hebert Gendron Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree
AGE-RELATED WEIGHT LOSS IN THE 5XFAD MOUSE MODEL OF ALZHEIMER S DISEASE: A BEHAVIOURAL AND HORMONAL ANALYSIS by William Hebert Gendron Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree
Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 ? Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Christian S Lobsiger & Don W Cleveland (2007) Nature Neuroscience 10, 1355-1360 Astrocytes: interlinked gatekeepers of glutamate astrocytes
? Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Christian S Lobsiger & Don W Cleveland (2007) Nature Neuroscience 10, 1355-1360 Astrocytes: interlinked gatekeepers of glutamate astrocytes
Cell Communication. Chapter 11. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Molecular pathways linking metabolic inflammation and thermogenesis G. Solinas Summary
 Published in "" which should be cited to refer to this work. Molecular pathways linking metabolic inflammation and thermogenesis G. Solinas http://doc.rero.ch Laboratory of Metabolic Stress Biology, Division
Published in "" which should be cited to refer to this work. Molecular pathways linking metabolic inflammation and thermogenesis G. Solinas http://doc.rero.ch Laboratory of Metabolic Stress Biology, Division
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM
 Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? Insulin Glucagon Thyroid hormones Cortisol Epinephrine Most regulation occurs in order
Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? Insulin Glucagon Thyroid hormones Cortisol Epinephrine Most regulation occurs in order
Obesity: A Really BIG Topic
 Obesity: A Really BIG Topic Sharon Hausman Cohen, MD AAFP, AIHM and Katie Hansen, PhD University of Texas Speaker Disclosure Dr. Hausman Cohen has disclosed that she is an employee of Intellexx DNA. Obesity:
Obesity: A Really BIG Topic Sharon Hausman Cohen, MD AAFP, AIHM and Katie Hansen, PhD University of Texas Speaker Disclosure Dr. Hausman Cohen has disclosed that she is an employee of Intellexx DNA. Obesity:
AND THE REGULATION OF ENERGY AND GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS. A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM NUTRIENT-SENSING AND THE REGULATION OF ENERGY AND GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS by CAROL KA-LO LAM A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM NUTRIENT-SENSING AND THE REGULATION OF ENERGY AND GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS by CAROL KA-LO LAM A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
Amylinergic control of food intake in lean and obese rodents
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Winterthurerstr. 190 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2011 Amylinergic control of food intake in lean and obese rodents Boyle, C
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Winterthurerstr. 190 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2011 Amylinergic control of food intake in lean and obese rodents Boyle, C
Insights from Rare Obesity Disorders
 Insights from Rare Obesity Disorders Ashley Shoemaker, MD, MSCI Ian M. Burr Division of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes Disclosures Research funding: Zafgen, AstraZeneca, Rhythm Member, Zafgen Hypothalamic
Insights from Rare Obesity Disorders Ashley Shoemaker, MD, MSCI Ian M. Burr Division of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes Disclosures Research funding: Zafgen, AstraZeneca, Rhythm Member, Zafgen Hypothalamic
Lecture: CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways
 Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
Gut hormones KHATTAB
 Gut hormones PROF:ABD ALHAFIZ HASSAN KHATTAB Gut as an endocrine gland The talk will cover the following : Historical background. Why this subject is chosen. Gastro-intestinal hormones and their function.
Gut hormones PROF:ABD ALHAFIZ HASSAN KHATTAB Gut as an endocrine gland The talk will cover the following : Historical background. Why this subject is chosen. Gastro-intestinal hormones and their function.
perk/erk STAT5B
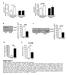 pakt/akt relative to saline (fold).5.5.5 control perk/erk relative to saline (fold).6.4..8.6.4. p=.6 control db/+ Hsp6 VDAC Hsp6/VDAC (relative to db/+) 8 6 4 db/+ C db/+ Hsp6 Hsp6/actin (relative to db/+)
pakt/akt relative to saline (fold).5.5.5 control perk/erk relative to saline (fold).6.4..8.6.4. p=.6 control db/+ Hsp6 VDAC Hsp6/VDAC (relative to db/+) 8 6 4 db/+ C db/+ Hsp6 Hsp6/actin (relative to db/+)
Myokines, Exercise, Metabolism. ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph
 Myokines, Exercise, Metabolism ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph Overview: Why? Evolutionary perspective How? Myokines: what they are and what they do Exercise and physiology Energy restriction
Myokines, Exercise, Metabolism ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph Overview: Why? Evolutionary perspective How? Myokines: what they are and what they do Exercise and physiology Energy restriction
Diabetes Mellitus and Dementia. Andrea Shelton & Adena Zadourian
 Diabetes Mellitus and Dementia Andrea Shelton & Adena Zadourian Abstract Diabetes mellitus increases the risk for developing dementia...but there is inconsistency with the subtypes of dementia Diabetes
Diabetes Mellitus and Dementia Andrea Shelton & Adena Zadourian Abstract Diabetes mellitus increases the risk for developing dementia...but there is inconsistency with the subtypes of dementia Diabetes
By the name of Allah
 By the name of Allah Receptors function and signal transduction ( Hormones and receptors Types) We were talking about receptors of the neurotransmitters; we have 2 types of receptors: 1- Ionotropic receptors
By the name of Allah Receptors function and signal transduction ( Hormones and receptors Types) We were talking about receptors of the neurotransmitters; we have 2 types of receptors: 1- Ionotropic receptors
Chapter 24 Cholesterol, Energy Balance and Body Temperature. 10/28/13 MDufilho
 Chapter 24 Cholesterol, Energy Balance and Body Temperature 10/28/13 MDufilho 1 Metabolic Role of the Liver Hepatocytes ~500 metabolic functions Process nearly every class of nutrient Play major role in
Chapter 24 Cholesterol, Energy Balance and Body Temperature 10/28/13 MDufilho 1 Metabolic Role of the Liver Hepatocytes ~500 metabolic functions Process nearly every class of nutrient Play major role in
1 Neuroregulation of Appetite
 Chapter 1 / Neuroregulation of Appetite 3 1 Neuroregulation of Appetite Ofer Reizes, PhD, Stephen C. Benoit, PhD, and Deborah J. Clegg, PhD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION THE DUAL-CENTERS HYPOTHESIS CONTROL OF
Chapter 1 / Neuroregulation of Appetite 3 1 Neuroregulation of Appetite Ofer Reizes, PhD, Stephen C. Benoit, PhD, and Deborah J. Clegg, PhD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION THE DUAL-CENTERS HYPOTHESIS CONTROL OF
ENERGY FROM INGESTED NUTREINTS MAY BE USED IMMEDIATELY OR STORED
 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
BEIGE AND BROWN FAT: BASIC BIOLOGY AND NOVEL THERAPEUTICS Dr. Carl Ascoli
 BEIGE AND BROWN FAT: BASIC BIOLOGY AND NOVEL THERAPEUTICS Dr. Carl Ascoli Symposium Co-Chairs: Bruce M. Spiegelman (Harvard/Dana Farber) and Sven Enerbäck (U.Gothenburg) April 17-23, 2015 Snowbird Resort,
BEIGE AND BROWN FAT: BASIC BIOLOGY AND NOVEL THERAPEUTICS Dr. Carl Ascoli Symposium Co-Chairs: Bruce M. Spiegelman (Harvard/Dana Farber) and Sven Enerbäck (U.Gothenburg) April 17-23, 2015 Snowbird Resort,
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane
 Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Defects in glucose utilization & GLP-1
 Defects in glucose utilization & GLP-1 Song, Dae-Kyu Department of Physiology & Chronic Disease Research Center Keimyung University School of Medicine 2800 dalgubeol-daero, Dalseo-gu, Daegu, 704-701, Korea
Defects in glucose utilization & GLP-1 Song, Dae-Kyu Department of Physiology & Chronic Disease Research Center Keimyung University School of Medicine 2800 dalgubeol-daero, Dalseo-gu, Daegu, 704-701, Korea
Molecular and anatomical determinants of central leptin resistance
 FEEDING REGULATION AND OBESITY 2005 Nature ublishing Group http://www.nature.com/natureneuroscience Molecular and anatomical determinants of central leptin resistance Heike Münzberg & Martin G Myers, Jr
FEEDING REGULATION AND OBESITY 2005 Nature ublishing Group http://www.nature.com/natureneuroscience Molecular and anatomical determinants of central leptin resistance Heike Münzberg & Martin G Myers, Jr
Digestion: Endocrinology of Appetite
 Digestion: Endocrinology of Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one on one relationship with a qualified health care professional
Digestion: Endocrinology of Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one on one relationship with a qualified health care professional
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
The Role of Leptin in Anorexia Nervosa: Clinical Implications THE INSULINATORS IRIS ULLOA, SUNDUS MOHAMED, KATIE NINH, AMANDA BUSTAMANTE
 The Role of Leptin in Anorexia Nervosa: Clinical Implications THE INSULINATORS IRIS ULLOA, SUNDUS MOHAMED, KATIE NINH, AMANDA BUSTAMANTE AN LEPTIN RELATED FINDINGS + PATHWAY Introduction What is leptin?
The Role of Leptin in Anorexia Nervosa: Clinical Implications THE INSULINATORS IRIS ULLOA, SUNDUS MOHAMED, KATIE NINH, AMANDA BUSTAMANTE AN LEPTIN RELATED FINDINGS + PATHWAY Introduction What is leptin?
The Endocannabinoid System
 The Endocannabinoid System Think of this system as the wizard behind the curtain. It underlies all the other systems, including the Autonomic Nervous System. Overall it influences well-being and the perception
The Endocannabinoid System Think of this system as the wizard behind the curtain. It underlies all the other systems, including the Autonomic Nervous System. Overall it influences well-being and the perception
Neuroendocrinology an integrative approach
 Neuroendocrinology an integrative approach JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal ciences, Cook, (848) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 06 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered:
Neuroendocrinology an integrative approach JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal ciences, Cook, (848) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 06 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered:
The role of leptin in leptin resistance and obesity
 Physiology & Behavior 88 (2006) 249 256 The role of leptin in leptin resistance and obesity Yi Zhang a,b, Philip J. Scarpace b, a Research Service, Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Gainesville,
Physiology & Behavior 88 (2006) 249 256 The role of leptin in leptin resistance and obesity Yi Zhang a,b, Philip J. Scarpace b, a Research Service, Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Gainesville,
Homeostasis. Endocrine System Nervous System
 Homeostasis Endocrine System Nervous System 2004-2005 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation
Homeostasis Endocrine System Nervous System 2004-2005 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation
