Sedated gastroscopy improves detection of gastric polyps
|
|
|
- Suzanna Gardner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3116 Sedated gastroscopy improves detection of gastric polyps MENG JUN CHEN, WEI WU, SHUANG PAN, CHUN JING LIN, LE MEI DONG, ZHOU FENG CHEN, JIAN SHENG WU and ZHI MING HUANG Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang , P.R. China Received December 3, 2017; Accepted April 16, 2018 DOI: /etm Abstract. The detection rate of gastric polyps (GPs) is low, improving the detection rate would be good. The present study aimed to evaluate the role of sedated gastroscopy in GP detection. The data of patients who underwent gastroscopic examination from January 2014 to December 2016 at the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University (Wenzhou, China) were retrospectively reviewed. Endoscopic records of 6,195 patients diagnosed with GPs were analyzed. The GP detection rate was 3.12 and 5.11% in the unsedated and sedated gastroscopy group, respectively (P<0.05). Also after stratification by sex, the GP detection rate was significantly higher in the sedated gastroscopy group (P<0.05). In addition, patients aged 20 years in the sedated gastroscopy group had a higher GP detection rate than those in the unsedated gastroscopy group (P<0.05). The incidence of cardiac, gastric fundus, gastric body and multiple site GPs was significantly different between the two groups (P<0.05). GPs 0.5 and >0.5 cm were more common in the sedated gastroscopy group than in the unsedated gastroscopy group (P<0.05). The common pathologic types of GPs were gastric fundus gland (52.27%) and hyperplastic polyps (34.74%). In conclusion, the GP detection rate may be improved by inhibition of gastric muscle cramping with sedation. Introduction Gastric polyps (GPs) are defined as protuberant mucosal lesions that are usually detected endoscopically. Most patients are asymptomatic; however, depending on their size and location, some large GPs may cause symptoms, including bleeding, chest pain, abdominal pain, anemia and even gastric tract obstruction (1 4). Correspondence to: Professor Jian Sheng Wu, Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, 12 Nanbaixiang Road, Ouhai, Wenzhou, Zhejiang , P.R. China E mail: wzwujs@163.com Key words: gastroscopy, sedated, gastric polyps, detection rate The widespread use of gastroscopy in China contributes to the improvement of the detection rate of GPs. Previous studies have reported that the rate of GPs was between % and the prevalence of GPs has been gradually increasing over the past decade (4 6). In addition, GPs were less common in males than in females, with a ratio of 1:1.8 to 1:2.5 (4 6). Other studies also indicated that the detection rate of GPs increases with increasing age (7,8). The most common pathologic type of GPs are gastric fundus gland polyp and hyperplastic polyp, which are associated with an increased risk of gastric cancer (7,8). Thus, it is important to further improve the detection rate of GPs. Sedated gastroscopy, i.e., gastroscopy under conscious sedation, improves the patients' tolerance of procedures and in recent years, it has become increasingly popular in China. The present study hypothesized that the GP detection rate on gastroscopy may be improved with sedation. Thus, the aim of this retrospective observational study was to assess the superiority of sedated gastroscopy over unsedated gastroscopy in detecting GPs. Patients and methods Patients. In the present retrospective study, patients who underwent gastroscopy with gastrointestinal symptoms, including abdominal distention, abdominal pain, belching and sour regurgitation or without symptoms at the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University (Wenzhou, China) between January 1, 2014 and December 31, 2016 were included. Patients decided to undergo gastroscopic examination with or without sedation by themselves, after having been informed about the benefits, risks and limitations of sedation, as well as those of unsedated gastroscopy, according to the recommendations of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (9). No additional procedures were performed during the gastroscopic examination. Those patients with GPs diagnosed under gastroscopy were recorded, and the pathologies were confirmed as inflammatory polyp, hyperplastic polyp, gastric fundus gland polyp adenomas, juvenile polyp, squamous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma, while pathologies confirmed as pathology negative polyp, xanthelasma, mesenchymoma, lymphoma, leiomyoma, ectopic pancreas, carcinoid and hamartoma were excluded within 7 working days by experienced pathologists. In addition, patients who had a history of gastric cancer, colon cancer, stomach surgery
2 CHEN et al: IMPROVED GASTRIC POLYPS DETECTION UNDER SEDATION 3117 or colon surgery were excluded. Patients who met the exclusion criteria were deleted when detection rate was calculated. A total of 165,142 patients were included in the current study. A total of 112,512 patients underwent unsedated gastroscopy, whereas 52,630 patients underwent sedated gastroscopy (propofol, 2 mg/kg, intravenous) with monitoring via electrocardiograms. Data. The present study retrospectively analyzed the data of 165,142 patients who underwent gastroscopy, and 6,195 patients with GPs were diagnosed on gastroscopy. The patient data were obtained from endoscopy and pathologic reports, with parameters extracted including sex, age, inspection time and GP characteristics (location, histological diagnosis, number and size). Statistical analysis. Data were analyzed using SPSS (version 17.0; SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Patient age was expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. The detection rate in the two groups was standardized prior to the c 2 test due to a disproportionate age distribution. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. Results Patient characteristics and procedure time are not different. A total of 165,142 gastroscopies were performed within 3 years at the Digestive Endoscopy unit of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University (Wenzhou, China). No statistically significant difference in the sex distribution and procedure time were identified between the two groups (Table I). Comparison of GP detection rate between sedated and unsedated gastroscopy group. A total of 6,195 GPs were diagnosed by gastroscopy and pathologic examination. Patients were stratified into 5 different groups based on age. The detection rate significantly differed between the unsedated and sedated gastroscopy groups of patients aged 20 39, 40 59, and 80 years, but not of those aged <20 years (Table II). Considering the age distribution, the GP detection rate of these two groups was standardized prior to the statistical analysis, and the result indicated a significantly higher detection rate in the sedated gastroscopy group compared with that in the unsedated gastroscopy group (Table III). The present analysis indicated that the rate of GP detection in female patients was significantly higher than that in male patients regardless of sedation (P=0.001). In addition, the GP detection rates for male and female patients receiving sedated gastroscopy were significantly higher than for those receiving unsedated gastroscopy (Table II). The location of GPs between the unsedated and sedated gastroscopy groups included cardiac, gastric fundus, gastric body and multiple sites, which means that GPs were detected in 2 anatomy sections of the stomach. The incidence of cardiac, gastric fundus, gastric body and multiple site GPs was significantly different between the unsedated and sedated gastroscopy groups, due to the different diagnostic performance of sedated and unsedated gastroscopy (Figs. 1 and 2). Whereas the incidence of gastric angular and gastric antrum Table I. Sex distribution and procedure time in the two groups. Unsedated gastroscopy Sedated gastroscopy Parameter group (112,512) group (52,630) Sex Male 60,880 (54.11%) 28,108 (53.41%) Female 51,632 (45.89%) 24,522 (46.59%) Age (years) 51.90± ±12.23 Procedure 321.2± ±90.4 time (sec) Values are expressed as n or the mean ± standard deviation or number (%). There were no significant differences between the groups. polyps was not significantly different between these two groups (Table IV). Pathological characteristics of GPs. As presented in Table IV, the standardized GP detection rates in the sedated gastroscopy group with lesion diameters of 0.5 and >0.5 cm were significantly higher than those in the unsedated gastroscopy group. Pathologic examination of tissue samples of the 6,195 GPs identified them as gastric fundus gland polyp (n=3,238), hyperplastic polyp (n=2,152), inflammatory polyp (n=531), squamous hyperplasia (n=103), adenomatous polyp (n=116), adenocarcinoma (n=35) and juvenile polyp (n=20) (Table V). Discussion GPs are usually detected endoscopically. It has been reported that ~11% of gastric adenomatous polyps developed into carcinoma in situ within 4 years of follow up (10). After excision, the recurrence rate is 16% (6). At present, no precise and relevant epidemiological data on GPs are available. In the present study, the overall detection rate of GPs was 3.75%, which is in accordance with the results of previous studies (4 6). The patients were stratified into an unsedated gastroscopy group and a sedated gastroscopy group. No statistically significant difference in the procedure time was present between these two groups, but a disproportion regarding patient age was encountered. A lower proportion of patients aged 60 years underwent sedated gastroscopy, which may be attributed to cautious anesthesia evaluation. Thus, the GP detection rate of these two groups was standardized prior to statistical analysis. The GP detection rate was higher in the sedated gastroscopy group than that in the unsedated gastroscopy group, and the difference was statistically significant, which implies that GPs may be more easily detected under sedated gastroscopy. Furthermore, the present study suggested that patients aged 20 years have a significantly higher GP detection rate under sedated gastroscopy. In patients aged <20 years, GPs were more often detected in the unsedated gastroscopy group than in the sedated gastroscopy group, but the difference was not statistically significant. This may be due to the limited sample size. The present study assessed and quantified the location of the GPs, and the results indicated that the detection rates of
3 3118 Table II. Clinicopathological characteristics of GP patients. GP detection rate, % (n/m) Feature Unsedated gastroscopy group Sedated gastroscopy group χ 2 P value Age (years) <20 a 0.97 (5/515) 1.32 (2/151) (410/20,482) 3.54 (387/10,945) (1,754/57,301) 5.19 (1,538/29,606) (1,247/31,536) 6.41 (740/11,538) (89/2,678) 5.90 (23/390) Sex Male 2.11 (1,284/60,880) 3.86 (1,086/28,108) Female 4.30 (2,221/51,632) 6.54 (1,604/24,522) GP location Cardiac 0.35 (398/112,512) 0.46 (242/52,630) Gastric fundus 0.49 (552/112,512) 0.93 (487/52,630) Gastric body 1.15 (1,297/11,2512) 2.28 (1,201/52,630) Gastric angular 0.81 (910/112,512) 0.85 (445/52,630) Gastric antrum 0.07 (79/112,512) 0.08 (43/52,630) Multiple sites 0.24 (268/112,512) 0.52 (272/52,630) Diameter of GPs (cm) (3,089/112,512) 4.57 (2,405/52,630) > (416/112,512) 0.54 (285/52,630) a P value was calculated by Fisher's Exact Test as the minimum expected count was >5. GP, gastric polyp; n, number of patients with positive detection; m, number of patients examined. Table III. Standardized calculation of GP detection rate. Unsedated gastroscopy group Sedated gastroscopy group Age group (years) Standard population a Detection rate (%) Expected GPs (n) Detection rate (%) Expected GPs (n) < , , , , , , , , , Total b 165,142 5,097 (3.09%) 8,574 (5.19%) a Sum of patients with two groups based on age level. b χ 2 =922.5, P=0.001 (expected GPs between the sedated and unsedated groups). GP, gastric polyp. cardiac, gastric fundus, gastric body and multiple site GPs in the sedated gastroscopy group were statistically higher than those in the unsedated gastroscopy group. The poorer diagnostic performance of unsedated gastroscopy may be attributed to the following: i) Patients always vomit when undergoing unsedated gastroscopy, which causes shaking of the video screen; ii) vomiting causes the gastric muscle to shrink, making it inconvenient for the clinicians to observe each part of the gastral cavity, particularly the side of the gastric body with the greater curvature, which has numerous mucosal folds (Fig. 1); iii) drastic gastric muscle shrinking may cause mucosal hyperemia and edema during unsedated gastroscopy within a short time, which changes the base color of the gastric mucosa (Fig. 2). These factors may affect the diagnosis of GPs. In the present study, a slight difference in the incidence of gastric angular polyps and gastric antrum polyps was identified between the two groups, but with no statistically significant difference. This is in accord with the actual situation, as the gastric smooth muscles of the antrum do not shrink as severely
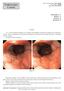
4 CHEN et al: IMPROVED GASTRIC POLYPS DETECTION UNDER SEDATION 3119 Table IV. Standardized calculation of GP location and size. Unsedated gastroscopy group Sedated gastroscopy group GP location Detection rate (%) Expected GPs (n) Detection rate (%) Expected GPs (n) χ 2 P value Cardiac Gastric fundus , Gastric body , , Gastric antrum , , Gastric angular Multiple site Size of GP (cm) , , > GP, gastric polyp. Table V. Pathology type of GPs. Pathological type of GP Unsedated gastroscopy group, n (%) Sedated gastroscopy group, n (%) Total, n (%) Gastric fundus gland polyp 1,282 (20.69) 1,956 (31.57) 3,238 (52.27) Hyperplastic polyp 1,020 (16.46) 1,132 (18.27) 2,152 (34.74) Inflammatory polyp 253 (4.08) 278 (4.49) 531 (8.57) Adenomatous polyp 52 (0.84) 64 (1.03) 116 (1.87) Adenocarcinoma 25 (0.40) 10 (0.16) 35 (0.56) Juvenile polyp 8 (0.13) 12 (0.19) 20 (0.32) Squamous hyperplasia 50 (0.81) 53 (0.86) 103 (1.66) GP, gastric polyp. Figure 1. (A) Vomiting causes the gastric muscle to shrink during unsedated gastroscopy. (B) Relaxation of the gastric muscle during sedated gastroscopy. Figure 2. (A) Drastic gastric muscle shrinking causes mucosal hyperemia and edema during unsedated gastroscopy. (B) Normal appearing gastric mucosa of gastric fundus during sedated gastroscopy.
5 3120 as those of the gastric body and are easier to expand by gas injection. Furthermore, the limited sample size of gastric angular polyps in the two groups may have affected the statistical analysis. As the current study was a single center study, it was limited. Studies with larger samples sizes, may be able to demonstrate that the GP detection rate can be improved by sedated gastroscopy. More studies should be performed to further confirm the diagnostic advantage of sedated gastroscopy. A study has reported that the predilection site of GPs was the gastric antrum (5). In another study, the gastric body has been reported to be the most common location (4). In the present study, the most common predilection site of polyps in the two groups was the gastric body. However, the second most common predilection sites were the gastric antrum in the unsedated gastroscopy group and the gastric fundus in the sedated gastroscopy group. The third most common predilection sites were the gastric fundus in the unsedated gastroscopy group and the gastric antrum in the sedated gastroscopy group. Therefore, it is implied that sedation not only makes patients comfortable during gastroscopy, but it will also make it easier for doctors to observe the gastric body and gastric fundus. Various studies have reported on the common pathologic types of GP. Evans et al (10) reported that the most common pathologic type of GPs was the gastric fundus gland polyp, whereas other studies reported inflammatory polyp or hyperplastic polyp to be the most common pathologic types (5,11). The present study indicated that the most common pathologic type of GPs was gastric fundus gland polyp (52.27%), followed by hyperplastic (34.74%) and inflammatory polyps (8.57%). Sections from biopsies of the cardiac polyps were diagnosed as squamous epithelial hyperplasia, which may be due to the proliferation and migration of squamous epithelia to the cardiac site. Inaccurate positioning of biopsy to contain parts of the esophageal mucosal epithelium maybe another reason. Certain lesions were confirmed as adenomatous polyp (1.87%), adenocarcinoma (0.56%), and juvenile polyp (0.32%), which require polypectomy or surgical treatment as soon as possible. In conclusion, the results of the present study indicated that sedation enhances the diagnostic yield of GPs on gastroscopy. Considering its low cost and convenient application in South China, sedated gastroscopy is a better diagnostic option than unsedated gastroscopy. Acknowledgements Not applicable. Funding No funding received. Availability of data and materials and interpretation of data and drafting of the manuscript. Z FC, J SW and Z MH performed a critical revision of the manuscript and were responsible for the intellectual content, statistical analysis, supporting material and study supervision. The final version of the manuscript has been read and approved by all authors, and each author believes that the manuscript represents honest work. Ethics approval and consent to participate Not required due to the retrospective nature of the study. Patient consent for publication Not applicable. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. References 1. Nayudu SK, Niazi M, Balar B and Kumbum K: A rare complication of hyperplastic gastric polyp. Case Rep Gastrointest Med 2013: , He HY, Shen ZB, Fang Y, Sun YH and Qin XY: Bleeding and hyperpyrexia in an adult with gastric inflammatory fibroid polyp. Chin Med J (Engl) 126: 2594, Vlacancich R, Sultan M and Al Kawas F: Gastric outlet obstruction caused by prolapsed gastric polyp into the pyloric channel. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 12: A27 A28, Fan NN, Yang J, Sun G, Lu ZS, Ling Hu EQ, Wang XD and Yang YS: Changes in the spectrum of gastric polyps in the Chinese population. World J Gastroenterol 21: , Cao H, Wang B, Zhang Z, Zhang H and Qu R: Distribution trends of gastric polyps: An endoscopy database analysis of northern Chinese patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27: , Carmack SW, Genta RM, Schuler CM and Saboorian MH: The current spectrum of gastric polyps: A 1 year national study of over 120,000 patients. Am J Gastroenterol 104: , Zheng E, Ni S, Yu Y, Wang Y, Weng X and Zheng L: Impact of gender and age on the occurrence of gastric polyps: Data analysis of southeastern Chinese patients. Turk J Gastroenterol 26: , Buyukasik K, Sevinc MM, Gunduz UR, Ari A, Gurbulak B, Toros AB and Bektas H: Upper gastrointestinal tract polyps: What do we know about them? Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16: , Standards of Practice Committee; Lichtenstein DR, Jagannath S, Baron TH, Anderson MA, Banerjee S, Dominitz JA, Fanelli RD, Gan SI, Harrison ME, et al: Sedation and anesthesia in GI endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 68: , ASGE Standards of Practice Committee; Evans JA, Chandrasekhara V, Chathadi KV, Decker GA, Early DS, Fisher DA, Foley K, Hwang JH, Jue TL, et al: The role of endoscopy in the management of premalignant and malignant conditions of the stomach. Gastrointest Endosc 82: 1 8, Lin Y, Nie Y, Wang H, Li QQ and Li Y: Analysis of clinical pathological characteristics and pattern changes of 2643 gastric polyps in the past 15 years. Chin J Digest 4: , The analyzed data sets generated during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Authors' contributions MJC and J SW conceived and designed the study. WW, SP, C JL and L MD were involved in the acquisition, analysis
Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Sequential screening in the early diagnosis of colorectal cancer in the community
 Journal of Public Health: From Theory to Practice https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-019-01024-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sequential screening in the early diagnosis of colorectal cancer in the community Ming-sheng
Journal of Public Health: From Theory to Practice https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-019-01024-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sequential screening in the early diagnosis of colorectal cancer in the community Ming-sheng
Gastric Polyps. Bible class
 Gastric Polyps Bible class 29.08.2018 Starting my training in gastroenterology, some decades ago, my first chief always told me that colonoscopy may seem technically more challenging but gastroscopy has
Gastric Polyps Bible class 29.08.2018 Starting my training in gastroenterology, some decades ago, my first chief always told me that colonoscopy may seem technically more challenging but gastroscopy has
Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects identifies susceptibility loci at PLCE1 and C20orf54
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 42, 759 763 (2010); published online 22 August 2010; corrected online 27 August 2014 Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 42, 759 763 (2010); published online 22 August 2010; corrected online 27 August 2014 Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects
Barrett s Esophagus. Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI
 Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with Atrophic gastritis in patients with Dyspepsia
 ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on the regression of gastric polyps in National Cancer Screening Program
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2018;33:506-511 Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on the regression of gastric polyps in National Cancer Screening Program Su Youn Nam 1,2, Bum Joon Park 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2018;33:506-511 Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on the regression of gastric polyps in National Cancer Screening Program Su Youn Nam 1,2, Bum Joon Park 2,
Helicobacter pylori Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
Fluoroscopy-Guided Endoscopic Removal of Foreign Bodies
 CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2017;50:197-201 https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.085 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Fluoroscopy-Guided Endoscopic Removal of Foreign odies Junhwan Kim
CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2017;50:197-201 https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.085 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Fluoroscopy-Guided Endoscopic Removal of Foreign odies Junhwan Kim
Fundic Gland Polyposis in Patients Without Familial Adenomatosis Coli: Its Incidence and Clinical Features
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1984;86;1437-42 ALIMENTARY TRACT Fundic Gland Polyposis in Patients Without Familial Adenomatosis Coli: Its Incidence and Clinical Features MITSUO IIDA, TSUNEYOSHI YAO, HIDENOBU WATANABE,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1984;86;1437-42 ALIMENTARY TRACT Fundic Gland Polyposis in Patients Without Familial Adenomatosis Coli: Its Incidence and Clinical Features MITSUO IIDA, TSUNEYOSHI YAO, HIDENOBU WATANABE,
Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule
 Original Article Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule Xuan Zhang*, Hong-Hong Yan, Jun-Tao Lin, Ze-Hua Wu, Jia Liu, Xu-Wei Cao, Xue-Ning Yang From
Original Article Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule Xuan Zhang*, Hong-Hong Yan, Jun-Tao Lin, Ze-Hua Wu, Jia Liu, Xu-Wei Cao, Xue-Ning Yang From
Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci. Colon polyps. Colorectal cancer
 Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Colon polyps Colorectal cancer Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine 18 Ed. 2012 Colorectal cancer 70% Colorectal cancer CRC and colon
Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Colon polyps Colorectal cancer Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine 18 Ed. 2012 Colorectal cancer 70% Colorectal cancer CRC and colon
Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts
 Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts Liu Jing Bian Zheng system had developed about 1800 years
Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts Liu Jing Bian Zheng system had developed about 1800 years
Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer
 He et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:87 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer Chao-Zhu He 1,2, Kun-He Zhang
He et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:87 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer Chao-Zhu He 1,2, Kun-He Zhang
Clinical studies of indicative biopsies in opportunistic screening in high risk population of oesophageal cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (9): 4121-4125 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Clinical studies of indicative biopsies in opportunistic screening in high risk population of o. Jie Gao #, Ailan Xian #, Tingfeng
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (9): 4121-4125 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Clinical studies of indicative biopsies in opportunistic screening in high risk population of o. Jie Gao #, Ailan Xian #, Tingfeng
Alberta Colorectal Cancer Screening Program (ACRCSP) Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines
 Alberta Colorectal Cancer Screening Program (ACRCSP) Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines June 2013 ACRCSP Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines - 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Background... 3 Terms, Definitions
Alberta Colorectal Cancer Screening Program (ACRCSP) Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines June 2013 ACRCSP Post Polypectomy Surveillance Guidelines - 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Background... 3 Terms, Definitions
Colonic Polyp. Najmeh Aletaha. MD
 Colonic Polyp Najmeh Aletaha. MD 1 Polyps & classification 2 Colorectal cancer risk factors 3 Pathogenesis 4 Surveillance polyp of the colon refers to a protuberance into the lumen above the surrounding
Colonic Polyp Najmeh Aletaha. MD 1 Polyps & classification 2 Colorectal cancer risk factors 3 Pathogenesis 4 Surveillance polyp of the colon refers to a protuberance into the lumen above the surrounding
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks
 Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection: A single-center retrospective study
 JBUON 2019; 24(2): 679-685 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection:
JBUON 2019; 24(2): 679-685 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection:
Gastrointestinal Malignancies. Dr Rodney ITAKI Pathology Division, SMHS, UPNG Anatomical Pathology Discipline
 Gastrointestinal Malignancies Dr Rodney ITAKI Pathology Division, SMHS, UPNG Anatomical Pathology Discipline Esophagus normal anatomy Hollow tube 23-25cm long in adults Extends from pharynx to level of
Gastrointestinal Malignancies Dr Rodney ITAKI Pathology Division, SMHS, UPNG Anatomical Pathology Discipline Esophagus normal anatomy Hollow tube 23-25cm long in adults Extends from pharynx to level of
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD
 Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (2): 365-370 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (2): 365-370 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric
Diagnostic and prognostic value of CEA, CA19 9, AFP and CA125 for early gastric cancer
 Feng et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:737 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3738-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Diagnostic and prognostic value of CEA, CA19 9, AFP and CA125 for early gastric cancer Fan Feng 1, Yangzi
Feng et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:737 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3738-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Diagnostic and prognostic value of CEA, CA19 9, AFP and CA125 for early gastric cancer Fan Feng 1, Yangzi
GIQIC18 Appropriate follow-up interval of not less than 5 years for colonoscopies with findings of 1-2 tubular adenomas < 10 mm
 GI Quality Improvement Consortium, Ltd. (GIQuIC) 1 Following is an overview of the clinical quality measures in GIQuIC that can be reported to CMS for the Quality performance category of the Merit-Based
GI Quality Improvement Consortium, Ltd. (GIQuIC) 1 Following is an overview of the clinical quality measures in GIQuIC that can be reported to CMS for the Quality performance category of the Merit-Based
Hyperplastische Polyps Innocent bystanders?
 Hyperplastische Polyps Innocent bystanders?? K. Geboes P th l i h O tl dk d Pathologische Ontleedkunde, KULeuven Content Historical Classification Relation Hyperplastic polyps carcinoma The concept cept
Hyperplastische Polyps Innocent bystanders?? K. Geboes P th l i h O tl dk d Pathologische Ontleedkunde, KULeuven Content Historical Classification Relation Hyperplastic polyps carcinoma The concept cept
Diagnostic test pepsinogen I and combination with tumor marker CEA in gastric cancer
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Diagnostic test pepsinogen I and combination with tumor marker CEA in gastric cancer To cite this article: J Sembiring et al 2018
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Diagnostic test pepsinogen I and combination with tumor marker CEA in gastric cancer To cite this article: J Sembiring et al 2018
Anesthesia for Routine Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Procedures (Additional description)
 Anesthesia for Routine Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Procedures (Additional description) Date of Origin: 05/2012 Last Review Date: 12/06/2017 Effective Date: 01/01/2018 Dates Reviewed: 12/2013, 11/2014,
Anesthesia for Routine Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Procedures (Additional description) Date of Origin: 05/2012 Last Review Date: 12/06/2017 Effective Date: 01/01/2018 Dates Reviewed: 12/2013, 11/2014,
Oesophageal Disorders
 Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Clinical Management of Obscure- Overt Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Presented by Dr. 張瀚文
 Clinical Management of Obscure- Overt Gastrointestinal Bleeding Presented by Dr. 張瀚文 Definition Obscure: : hard to understand; not clear. Overt: : public; not secret. Occult: : hidden from the knowledge
Clinical Management of Obscure- Overt Gastrointestinal Bleeding Presented by Dr. 張瀚文 Definition Obscure: : hard to understand; not clear. Overt: : public; not secret. Occult: : hidden from the knowledge
Clinical value of endoscopic ultrasonography for esophageal leiomyoma in elder patients
 Original Article on Endoscopic Ultrasonography Clinical value of endoscopic ultrasonography for esophageal leiomyoma in elder patients Ting Jiang, Jinghua Yu, Lihua Chen, Hongtan Chen, Guodong Shan, Ming
Original Article on Endoscopic Ultrasonography Clinical value of endoscopic ultrasonography for esophageal leiomyoma in elder patients Ting Jiang, Jinghua Yu, Lihua Chen, Hongtan Chen, Guodong Shan, Ming
Colon Cancer Detection by Rendezvous Colonoscopy : Successful Removal of Stuck Colon Capsule by Conventional Colonoscopy
 19 Colon Cancer Detection by Rendezvous Colonoscopy : Successful Removal of Stuck Colon Capsule by Conventional Colonoscopy István Rácz Márta Jánoki Hussam Saleh Department of Gastroenterology, Petz Aladár
19 Colon Cancer Detection by Rendezvous Colonoscopy : Successful Removal of Stuck Colon Capsule by Conventional Colonoscopy István Rácz Márta Jánoki Hussam Saleh Department of Gastroenterology, Petz Aladár
Stage 4 gastric adenocarcinoma icd 10
 > Stage 4 gastric adenocarcinoma icd 10 stage iii; Carcinoma of colon, stage iv; Colon cancer metastatic to unspecified site; Hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer; Malignant tumor of colon; Metastasis.
> Stage 4 gastric adenocarcinoma icd 10 stage iii; Carcinoma of colon, stage iv; Colon cancer metastatic to unspecified site; Hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer; Malignant tumor of colon; Metastasis.
Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy
 Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy Educational Objectives Identify classifications of polyps Describe several types of polyps Verbalize rationale for polypectomy Identify risk factors
Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy Educational Objectives Identify classifications of polyps Describe several types of polyps Verbalize rationale for polypectomy Identify risk factors
Comparison of lymph node number and prognosis in gastric cancer patients with perigastric lymph nodes retrieved by surgeons and pathologists
 Original Article Comparison of lymph node number and prognosis in gastric cancer patients with perigastric lymph nodes retrieved by surgeons and pathologists Lixin Jiang, Zengwu Yao, Yifei Zhang, Jinchen
Original Article Comparison of lymph node number and prognosis in gastric cancer patients with perigastric lymph nodes retrieved by surgeons and pathologists Lixin Jiang, Zengwu Yao, Yifei Zhang, Jinchen
The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011
 DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
DIAGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF CHANGES IN SERUM HUMAN EPIDIDYMIS EPITHELIAL SECRETORY PROTEIN 4 AND CARBOHYDRATE ANTIGEN 125 IN ENDOMETRIAL CARCINOMA
 Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2018, 34: 785 DIAGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF CHANGES IN SERUM HUMAN EPIDIDYMIS EPITHELIAL SECRETORY PROTEIN 4 AND CARBOHYDRATE ANTIGEN 125 IN ENDOMETRIAL CARCINOMA PATIENTS JING-LI
Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2018, 34: 785 DIAGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF CHANGES IN SERUM HUMAN EPIDIDYMIS EPITHELIAL SECRETORY PROTEIN 4 AND CARBOHYDRATE ANTIGEN 125 IN ENDOMETRIAL CARCINOMA PATIENTS JING-LI
Type 2 gastric neuroendocrine tumor: report of one case
 Case Report Type 2 gastric neuroendocrine tumor: report of one case Yuanliang Li, Xin Su, Huangying Tan Department of Integrative Oncology, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China Correspondence
Case Report Type 2 gastric neuroendocrine tumor: report of one case Yuanliang Li, Xin Su, Huangying Tan Department of Integrative Oncology, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China Correspondence
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
 Gastroenter oenterology 2005 Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh Screening and surveillance for upper and lower gastrointestinal cancer JN Plevris Consultant Gastroenterologist and Honorary Senior
Gastroenter oenterology 2005 Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh Screening and surveillance for upper and lower gastrointestinal cancer JN Plevris Consultant Gastroenterologist and Honorary Senior
Changing Trends in Gastric Polyps
 Revista de InvestigaciÓn ClÍnica Contents available at PubMed www.clinicalandtranslationalinvestigation.com PERMANYER Rev Inves Clin. 2018;70:40-45 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Changing Trends in Gastric Polyps Magali
Revista de InvestigaciÓn ClÍnica Contents available at PubMed www.clinicalandtranslationalinvestigation.com PERMANYER Rev Inves Clin. 2018;70:40-45 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Changing Trends in Gastric Polyps Magali
instrument. When 13C-UBT positive value is greater than or equal to / - 0.4, the the subject can be 1. Data and methods details are as follows:
 Application of 13 C-urea breath test in screening helicobacter pylori infection during health examination in Chengdu, Sichuan YANG Yan-hua. LIU Yu-ping. CHENG You-fu, SHUAI Ping. LU Qiao. ZHENG Xiao-xia,
Application of 13 C-urea breath test in screening helicobacter pylori infection during health examination in Chengdu, Sichuan YANG Yan-hua. LIU Yu-ping. CHENG You-fu, SHUAI Ping. LU Qiao. ZHENG Xiao-xia,
Pathology perspective of colonic polyposis syndromes
 Pathology perspective of colonic polyposis syndromes When are too many polyps too many? David Schaeffer Head and Consultant Pathologist, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Vancouver General
Pathology perspective of colonic polyposis syndromes When are too many polyps too many? David Schaeffer Head and Consultant Pathologist, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Vancouver General
malignant polyp Daily Challenges in Digestive Endoscopy for Endoscopists and Endoscopy Nurses BSGIE Annual Meeting 18/09/2014 Mechelen
 Plan Incidental finding of a malignant polyp 1. What is a polyp malignant? 2. Role of the pathologist and the endoscopist 3. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment 4. How to decide what to do? Hubert
Plan Incidental finding of a malignant polyp 1. What is a polyp malignant? 2. Role of the pathologist and the endoscopist 3. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment 4. How to decide what to do? Hubert
The Use of Pancreatoscopy in the Diagnosis of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor Lesions of the Pancreas
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S53 S57 The Use of Pancreatoscopy in the Diagnosis of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor Lesions of the Pancreas KENJIRO YASUDA, MUNEHIRO SAKATA, MOOSE
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S53 S57 The Use of Pancreatoscopy in the Diagnosis of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor Lesions of the Pancreas KENJIRO YASUDA, MUNEHIRO SAKATA, MOOSE
Barrett s Esophagus: What to Do for No Dysplasia, LGD, and HGD?
 Barrett s Esophagus: What to Do for No Dysplasia, LGD, and HGD? Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina 1 Outline What are the risks of progression
Barrett s Esophagus: What to Do for No Dysplasia, LGD, and HGD? Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina 1 Outline What are the risks of progression
Early detection and treatment for Esophageal Cancer in Africa
 Early detection and treatment for Esophageal Cancer in Africa Dr Michael Mwachiro Tenwek Hospital NCI-IARC ESCC Tumor Workshop Where is Tenwek Hospital? Tenwek Nairobi Tenwek Hospital Identification of
Early detection and treatment for Esophageal Cancer in Africa Dr Michael Mwachiro Tenwek Hospital NCI-IARC ESCC Tumor Workshop Where is Tenwek Hospital? Tenwek Nairobi Tenwek Hospital Identification of
Large Colorectal Adenomas An Approach to Pathologic Evaluation
 Anatomic Pathology / LARGE COLORECTAL ADENOMAS AND PATHOLOGIC EVALUATION Large Colorectal Adenomas An Approach to Pathologic Evaluation Elizabeth D. Euscher, MD, 1 Theodore H. Niemann, MD, 1 Joel G. Lucas,
Anatomic Pathology / LARGE COLORECTAL ADENOMAS AND PATHOLOGIC EVALUATION Large Colorectal Adenomas An Approach to Pathologic Evaluation Elizabeth D. Euscher, MD, 1 Theodore H. Niemann, MD, 1 Joel G. Lucas,
A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES. Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus
 A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus CASE DESCRIPTION 63yo, F, single, attending nurse. PMH includes T2DM (Sitagliptin/Metformin), Hyperlipidemia
A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus CASE DESCRIPTION 63yo, F, single, attending nurse. PMH includes T2DM (Sitagliptin/Metformin), Hyperlipidemia
Clinical analysis of 29 cases of nasal mucosal malignant melanoma
 1166 Clinical analysis of 29 cases of nasal mucosal malignant melanoma HUANXIN YU and GANG LIU Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Tianjin Huanhu Hospital, Tianjin 300060, P.R. China
1166 Clinical analysis of 29 cases of nasal mucosal malignant melanoma HUANXIN YU and GANG LIU Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Tianjin Huanhu Hospital, Tianjin 300060, P.R. China
C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang. Shi Jue Ming ** Properties: Salty, mild cold LV. Actions: Suppress LV yang, clear eye heat
 C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang Shi Jue Ming ** Zhen Zhu Mu * (Long Gu -)*** Mu Li *** Dai Zhe Shi ** Bai Ji Li/Ci Ji Li Wind/spasm Gou Teng ** Tian Ma *** Di Long ** Quan Xie
C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang Shi Jue Ming ** Zhen Zhu Mu * (Long Gu -)*** Mu Li *** Dai Zhe Shi ** Bai Ji Li/Ci Ji Li Wind/spasm Gou Teng ** Tian Ma *** Di Long ** Quan Xie
Analysis of the prognosis of patients with testicular seminoma
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 11: 1361-1366, 2016 Analysis of the prognosis of patients with testicular seminoma WEI DONG 1, WANG GANG 1, MIAOMIAO LIU 2 and HONGZHEN ZHANG 2 1 Department of Urology; 2 Department of
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 11: 1361-1366, 2016 Analysis of the prognosis of patients with testicular seminoma WEI DONG 1, WANG GANG 1, MIAOMIAO LIU 2 and HONGZHEN ZHANG 2 1 Department of Urology; 2 Department of
Original Article Hand-assisted laparoscopic versus open surgery radical gastrectomy for advanced distal gastric cancer: a prospective randomized study
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(3):5001-5010 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0042542 Original Article Hand-assisted laparoscopic versus open surgery radical gastrectomy for advanced distal gastric cancer:
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(3):5001-5010 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0042542 Original Article Hand-assisted laparoscopic versus open surgery radical gastrectomy for advanced distal gastric cancer:
Helicobacter Pylori Testing HELICOBACTER PYLORI TESTING HS-131. Policy Number: HS-131. Original Effective Date: 9/17/2009
 Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Endoscopic Corner CASE 1. Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R
 170 Endoscopic Corner Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 54-year-old woman underwent a colorectal cancer screening. Her fecal immunochemical test was positive.
170 Endoscopic Corner Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 54-year-old woman underwent a colorectal cancer screening. Her fecal immunochemical test was positive.
Title: unusual case report of inflammatory. fibrous polyps in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Authors: Baifang Wang, Guoqing Xiang, Jia Zhu
 Title: An unusual case report of inflammatory fibrous polyps in the upper gastrointestinal tract Authors: Baifang Wang, Guoqing Xiang, Jia Zhu DOI: 10.17235/reed.2018.5734/2018 Link: PubMed (Epub ahead
Title: An unusual case report of inflammatory fibrous polyps in the upper gastrointestinal tract Authors: Baifang Wang, Guoqing Xiang, Jia Zhu DOI: 10.17235/reed.2018.5734/2018 Link: PubMed (Epub ahead
Original Article Application of AFP whole blood one-step rapid detection kit in screening for HCC in Qidong
 Am J Cancer Res 2017;7(6):1384-1388 www.ajcr.us /ISSN:2156-6976/ajcr0048028 Original Article Application of AFP whole blood one-step rapid detection kit in screening for HCC in Qidong Jie Jin 1*, Xiao-yan
Am J Cancer Res 2017;7(6):1384-1388 www.ajcr.us /ISSN:2156-6976/ajcr0048028 Original Article Application of AFP whole blood one-step rapid detection kit in screening for HCC in Qidong Jie Jin 1*, Xiao-yan
Summary. Cezary ŁozińskiABDF, Witold KyclerABCDEF. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother, 2007; 12(4):
 Rep Pract Oncol Radiother, 2007; 12(4): 201-206 Original Paper Received: 2006.12.19 Accepted: 2007.04.02 Published: 2007.08.31 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection C Statistical Analysis
Rep Pract Oncol Radiother, 2007; 12(4): 201-206 Original Paper Received: 2006.12.19 Accepted: 2007.04.02 Published: 2007.08.31 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection C Statistical Analysis
Principles of diagnosis, work-up and therapy The Gastroenterologist s role
 Principles of diagnosis, work-up and therapy The Gastroenterologist s role Dr. Christos G. Toumpanakis MD PhD FRCP Consultant in Gastroenterology/Neuroendocrine Tumours Hon. Senior Lecturer University
Principles of diagnosis, work-up and therapy The Gastroenterologist s role Dr. Christos G. Toumpanakis MD PhD FRCP Consultant in Gastroenterology/Neuroendocrine Tumours Hon. Senior Lecturer University
Chien-Hua Chen MD, MPH. Show-Chwan Memorial Hospital, Taiwan Taiwan. Position: Dean of Community Health Promotion Center
 Chien-Hua Chen MD, MPH Show-Chwan Memorial Hospital, Taiwan Taiwan Position: Dean of Community Health Promotion Center Major Field:Digestive US, EUS, Digestive endoscopy Education: MD, China Medical University
Chien-Hua Chen MD, MPH Show-Chwan Memorial Hospital, Taiwan Taiwan Position: Dean of Community Health Promotion Center Major Field:Digestive US, EUS, Digestive endoscopy Education: MD, China Medical University
Accepted Manuscript. Unexpected high incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C in the era of DAAs: too alarming?
 Accepted Manuscript Unexpected high incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C in the era of DAAs: too alarming? Qing-Lei Zeng, Zhi-Qin Li, Hong-Xia Liang, Guang-Hua Xu, Chun-Xia
Accepted Manuscript Unexpected high incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C in the era of DAAs: too alarming? Qing-Lei Zeng, Zhi-Qin Li, Hong-Xia Liang, Guang-Hua Xu, Chun-Xia
The Clinicopathological Features of Gastric Hyperplastic Polyps with Neoplastic Transformations: A Suggestion of Indication for
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 3, No. 4, December 2009, pp. 271-275 original article The Clinicopathological Features of Gastric Hyperplastic Polyps with Neoplastic Transformations: A Suggestion of Indication for
Gut and Liver, Vol. 3, No. 4, December 2009, pp. 271-275 original article The Clinicopathological Features of Gastric Hyperplastic Polyps with Neoplastic Transformations: A Suggestion of Indication for
Retroflexion and prevention of right-sided colon cancer following colonoscopy: How I approach it
 Retroflexion and prevention of right-sided colon cancer following colonoscopy: How I approach it Douglas K Rex 1 MD, MACG 1. Indiana University School of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology
Retroflexion and prevention of right-sided colon cancer following colonoscopy: How I approach it Douglas K Rex 1 MD, MACG 1. Indiana University School of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology
Title Description Type / Priority
 Merit-based Incentive Payment system (MIPS) 2019 Qualified Clinical Data Registry (QCDR) Measure Specifications Summary Listing of QCDR measures supported by the NHCR Measure # NHCR4 NHCR5 GIQIC12 GIQIC15
Merit-based Incentive Payment system (MIPS) 2019 Qualified Clinical Data Registry (QCDR) Measure Specifications Summary Listing of QCDR measures supported by the NHCR Measure # NHCR4 NHCR5 GIQIC12 GIQIC15
Disclosures. Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Early Gastric Cancer: Screening, Surveillance, and Endoscopic Therapy. ASGE Guidelines.
 Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Early Gastric Cancer: Screening, Surveillance, and Endoscopic Therapy Consultant for: Olympus Medtronic US Endoscopy Disclosures Joo Ha Hwang, MD, PhD Associate Professor
Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Early Gastric Cancer: Screening, Surveillance, and Endoscopic Therapy Consultant for: Olympus Medtronic US Endoscopy Disclosures Joo Ha Hwang, MD, PhD Associate Professor
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus. Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery
 Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery Objectives Identify the use of different diagnostic modalities for hiatal hernias List the different types of hiatal hernias
Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery Objectives Identify the use of different diagnostic modalities for hiatal hernias List the different types of hiatal hernias
Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia
 Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia Ralf Kiesslich I. Medical Department Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany Cumulative cancer risk in ulcerative colitis 0.5-1.0%
Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia Ralf Kiesslich I. Medical Department Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany Cumulative cancer risk in ulcerative colitis 0.5-1.0%
Signet-ring cell carcinoma arising from a fundic gland polyp in the stomach
 Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.18044 World J Gastroenterol 2014 December 21; 20(47): 18044-18047 ISSN 1007-9327
Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.18044 World J Gastroenterol 2014 December 21; 20(47): 18044-18047 ISSN 1007-9327
Xiaohuan Pan 1,2 *, Xinguan Yang 1,2 *, Jingxu Li 1,2, Xiao Dong 1,2, Jianxing He 2,3, Yubao Guan 1,2. Original Article
 Original Article Is a 5-mm diameter an appropriate cut-off value for the diagnosis of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ on chest computed tomography and pathological examination?
Original Article Is a 5-mm diameter an appropriate cut-off value for the diagnosis of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ on chest computed tomography and pathological examination?
ratio in patients treated by sorafenib alone decreased after treatment (P<0.05), while CD 8
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4625-4629 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015836 Original Article Effect of sorafenib combined with CIK cell treatment on immunity and adverse events in patients with late-stage
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4625-4629 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015836 Original Article Effect of sorafenib combined with CIK cell treatment on immunity and adverse events in patients with late-stage
EMR, ESD and Beyond. Peter Draganov MD. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida
 EMR, ESD and Beyond Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated by Endoscopy
EMR, ESD and Beyond Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated by Endoscopy
Gastroenterology Fellowship Program
 Gastroenterology Fellowship Program Outpatient Clinical Rotations I. Overview A. Three Year Continuity Clinic Experience All gastroenterology fellows will be required to have a ½ day continuity clinic
Gastroenterology Fellowship Program Outpatient Clinical Rotations I. Overview A. Three Year Continuity Clinic Experience All gastroenterology fellows will be required to have a ½ day continuity clinic
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4. Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath
 Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Topics to be covered Peptic ulcer disease Hiatal hernia Gastric neoplasms Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)= chronic gastric ulcer Causes H pylori
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Topics to be covered Peptic ulcer disease Hiatal hernia Gastric neoplasms Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)= chronic gastric ulcer Causes H pylori
Endoscopic Resection of Subepithelial Tumors
 REVIEW Clin Endosc ;45:240-244 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce..45.3.240 Open Access Endoscopic Resection of Subepithelial Tumors Gwang Ha Kim Department of Internal
REVIEW Clin Endosc ;45:240-244 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce..45.3.240 Open Access Endoscopic Resection of Subepithelial Tumors Gwang Ha Kim Department of Internal
Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah
 Original Article Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah ABSTRACT Objective: To determine the diagnostic
Original Article Capsule Endoscopy: Is it Really Helpful in the Diagnosis of Small Bowel Diseases? Kashif Malik, Muhammad Joher Amin, Syed Waqar Hassan Shah ABSTRACT Objective: To determine the diagnostic
Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer
 Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer Tumors of the Stomach Gastric adenocarcinoma Incidence and Epidemiology Incidence mortality rates USA High incidence: Japan, China, Chile, Ireland risk lower socioeconomic
Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer Tumors of the Stomach Gastric adenocarcinoma Incidence and Epidemiology Incidence mortality rates USA High incidence: Japan, China, Chile, Ireland risk lower socioeconomic
Comparative study of ultrasonic contrast and endoscopic ultrasonography in preoperative staging of gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7862-7866 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Comparative study of ultrasonic contrast and endoscopic ultrasonography in preoperative staging of gastric cancer. Yan Cai
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7862-7866 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Comparative study of ultrasonic contrast and endoscopic ultrasonography in preoperative staging of gastric cancer. Yan Cai
Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행
 Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행 JGCA classification - Japanese Gastric Cancer Association - Type 0 superficial polypoid, flat/depressed, or excavated tumors Type 1 polypoid carcinomas, usually attached
Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행 JGCA classification - Japanese Gastric Cancer Association - Type 0 superficial polypoid, flat/depressed, or excavated tumors Type 1 polypoid carcinomas, usually attached
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy reconstructed by Rouxen-Y with D2 lymphadenectomy and needle catheter jejunostomy for gastric cancer
 Masters of Gastrointestinal Surgery Totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy reconstructed by Rouxen-Y with D2 lymphadenectomy and needle catheter jejunostomy for gastric cancer Xin Ye, Jian-Chun Yu, Wei-Ming
Masters of Gastrointestinal Surgery Totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy reconstructed by Rouxen-Y with D2 lymphadenectomy and needle catheter jejunostomy for gastric cancer Xin Ye, Jian-Chun Yu, Wei-Ming
Metachronous Esophageal Cancer and Colon Cancer Treated by Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
 CASE REPORT Metachronous Esophageal Cancer and Colon Cancer Treated by Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Chun-Chao Chang, Chia-Lang Fang, Horng-Yuan Lou, Ching-Ruey Hsieh, Sheng-Hsuan Chen* Most cases of esophageal
CASE REPORT Metachronous Esophageal Cancer and Colon Cancer Treated by Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Chun-Chao Chang, Chia-Lang Fang, Horng-Yuan Lou, Ching-Ruey Hsieh, Sheng-Hsuan Chen* Most cases of esophageal
What is a Gastroscopy?
 GASTROSCOPY INFORMATION SHEET PLEASE READ THIS, SIGN THE 2 CONSENT FORMS ATTACHED AND BRING THESE WITH YOU ON THE DAY OF YOUR PROCEDURE Why do I need to have a Gastroscopy? You have been advised to undergo
GASTROSCOPY INFORMATION SHEET PLEASE READ THIS, SIGN THE 2 CONSENT FORMS ATTACHED AND BRING THESE WITH YOU ON THE DAY OF YOUR PROCEDURE Why do I need to have a Gastroscopy? You have been advised to undergo
References. GI Biopsies. What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD
 What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
Endoscopic Corner CASE 1. Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R
 Endoscopic Corner Sirimontaporn N, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Vol. 11 No. 3 Sept. - Dec. 2010 171 Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 47- year-old female presented to the
Endoscopic Corner Sirimontaporn N, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Vol. 11 No. 3 Sept. - Dec. 2010 171 Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 47- year-old female presented to the
Latest Endoscopic Guidelines for FAP, HNPCC, IBD, and the General Population
 Latest Endoscopic Guidelines for FAP, HNPCC, IBD, and the General Population David T. Rubin, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center MacLean Center for Clinical Medical Ethics
Latest Endoscopic Guidelines for FAP, HNPCC, IBD, and the General Population David T. Rubin, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center MacLean Center for Clinical Medical Ethics
Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection of upper gastrointestinal tract tumors arising from muscularis propria
 REVIEW ARTICLE Annals Gastroenterology (2017) 30, 1-11 Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection upper gastrointestinal tract tumors arising from muscularis propria Deepanshu Jain a, Aakash Desai b, Ejaz
REVIEW ARTICLE Annals Gastroenterology (2017) 30, 1-11 Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection upper gastrointestinal tract tumors arising from muscularis propria Deepanshu Jain a, Aakash Desai b, Ejaz
Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics
 Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics Stephen Kim, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Interventional Endoscopy Services UCLA Division of Digestive Diseases September 29, 2018 1 Disclosures
Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics Stephen Kim, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Interventional Endoscopy Services UCLA Division of Digestive Diseases September 29, 2018 1 Disclosures
ENDOLUMINAL APPROACH FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF GASTROINTESTINAL CARCINOID
 ENDOLUMINAL APPROACH FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF GASTROINTESTINAL CARCINOID Manoop S. Bhutani, MD, FASGE, FACG, FACP, AGAF, Doctor Honoris Causa Professor of Medicine Eminent Scientist of the Year 2008, World
ENDOLUMINAL APPROACH FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF GASTROINTESTINAL CARCINOID Manoop S. Bhutani, MD, FASGE, FACG, FACP, AGAF, Doctor Honoris Causa Professor of Medicine Eminent Scientist of the Year 2008, World
YES NO UNKNOWN. Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE SIGNIFICANCE/BURDEN OF DISEASE NEXT STEPS. YES ( 1 of above)
 Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: SMAD4, BMPR1A DISORDER: Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome HGNC ID: 6670, 1076 OMIM ID: 174900, 175050 ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE 1. Is there a qualifying resource,
Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: SMAD4, BMPR1A DISORDER: Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome HGNC ID: 6670, 1076 OMIM ID: 174900, 175050 ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE 1. Is there a qualifying resource,
Hereditary Gastric Cancer
 Hereditary Gastric Cancer Dr Bastiaan de Boer Consultant Pathologist Department of Anatomical Pathology PathWest Laboratory Medicine, QE II Medical Centre Clinical Associate Professor School of Pathology
Hereditary Gastric Cancer Dr Bastiaan de Boer Consultant Pathologist Department of Anatomical Pathology PathWest Laboratory Medicine, QE II Medical Centre Clinical Associate Professor School of Pathology
GI Coding Updates. Rhonda Buckholtz, CPC, CPCI, CPMS, CRC, CDEO, CHPSE, CGSC, COBGC, CENTC, CPEDC
 GI Coding Updates Rhonda Buckholtz, CPC, CPCI, CPMS, CRC, CDEO, CHPSE, CGSC, COBGC, CENTC, CPEDC Copyright/Disclaimer 2014 AAPC text CPT copyright 2016 American Medical Association. All rights reserved.
GI Coding Updates Rhonda Buckholtz, CPC, CPCI, CPMS, CRC, CDEO, CHPSE, CGSC, COBGC, CENTC, CPEDC Copyright/Disclaimer 2014 AAPC text CPT copyright 2016 American Medical Association. All rights reserved.
Colo-Colonic Intussusception Caused by a Submucosal Lipoma
 168 Colo-Colonic Intussusception Caused by a Submucosal Lipoma Case Report and Review of the Literature B.A. Twigt S.K. Nagesser D.J.A. Sonneveld Department of Surgery, Diakonessenhuis, Utrecht, The Netherlands
168 Colo-Colonic Intussusception Caused by a Submucosal Lipoma Case Report and Review of the Literature B.A. Twigt S.K. Nagesser D.J.A. Sonneveld Department of Surgery, Diakonessenhuis, Utrecht, The Netherlands
The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
Expression of lncrna TCONS_ in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
Combination of Paris and Vienna Classifications may Optimize Follow-Up of Gastric Epithelial Neoplasia Patients
 CLINICAL RESEARCH e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.892697 Received: 2014.10.09 Accepted: 2014.12.03 Published: 2015.04.05 Combination of Paris and Vienna Classifications may Optimize Follow-Up of Gastric
CLINICAL RESEARCH e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.892697 Received: 2014.10.09 Accepted: 2014.12.03 Published: 2015.04.05 Combination of Paris and Vienna Classifications may Optimize Follow-Up of Gastric
Endometrial line thickness in different conditions.
 Endometrial line thickness in different conditions 1 Endometrial thickens in response to Rising estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle and then shedding endometrial at the times of menses 2 The thickens
Endometrial line thickness in different conditions 1 Endometrial thickens in response to Rising estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle and then shedding endometrial at the times of menses 2 The thickens
Study on prevalence of neoplastic lesions of the esophagus in patients referred to health centers of Ahvaz in the years
 Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 29-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 26, 5, :5-54 Study on prevalence of neoplastic lesions of the esophagus in patients referred
Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 29-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 26, 5, :5-54 Study on prevalence of neoplastic lesions of the esophagus in patients referred
Clinical presentations of small bowel tumor
 Original Research Article Clinical presentations of small bowel tumor Arige Subodh Kumar 1*, N L Eshwar Prasad 2, Avula Krishnaveni 3, Anuradha 4 1 In-charge Professor, Department of Plastic Surgery, Gandhi
Original Research Article Clinical presentations of small bowel tumor Arige Subodh Kumar 1*, N L Eshwar Prasad 2, Avula Krishnaveni 3, Anuradha 4 1 In-charge Professor, Department of Plastic Surgery, Gandhi
Quality ID #343: Screening Colonoscopy Adenoma Detection Rate National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Quality ID #343: Screening Colonoscopy Adenoma Detection Rate National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Outcome DESCRIPTION:
Quality ID #343: Screening Colonoscopy Adenoma Detection Rate National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Outcome DESCRIPTION:
Clinical profiles and trend analysis of newly diagnosed lung cancer in a tertiary care hospital of East China during
 Original Article Clinical profiles and trend analysis of newly diagnosed lung cancer in a tertiary care hospital of East China during 2011 2015 Pingli Wang 1 *, Jixia Zou 1 *, Jingni Wu 1 *, Chengyan Zhang
Original Article Clinical profiles and trend analysis of newly diagnosed lung cancer in a tertiary care hospital of East China during 2011 2015 Pingli Wang 1 *, Jixia Zou 1 *, Jingni Wu 1 *, Chengyan Zhang
