ABSTRACT ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION. e-issn: p-issn: doi: /apjhs G. Vikas Naik 1 *, K. P.
|
|
|
- Emily Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE e-issn: p-issn: doi: /apjhs Carotid intima-media thickness as a predictor of atherosclerosis in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects - A study from tertiary care hospital in coastal city of South India G. Vikas Naik 1 *, K. P. Shivaranjan 2 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Kanachur Institute of Medical Sciences, Mangalore, Karnataka, India, 2 Department of Gastroenterology, Gleneagles Global Health Centre, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India ABSTRACT Background and Objectives: Atherosclerosis typically occurs over a period of many years, usually many decades. After a generally prolonged silent period, atherosclerosis may become clinically manifest. Evaluation of intimal medial thickness is considered as surrogate marker of atherosclerosis. B-mode ultrasound was a suitable non-invasive method to visualize the arterial walls and to monitor the early stages of the atherosclerotic process. Materials and Methods: This is a cross-sectional hospital-based study. A total of 100 patients were selected with 50 patients each in diabetic and non-diabetic groups. After taking consent, patients were subjected for carotid Doppler examination. Results: The mean intimal medial thickness values of the diabetic subjects (0.12) were significantly higher than those of the non-diabetic (0.07 mm) subjects (P < 0.001). Both in the normal and diabetic subjects, these values increased with age. At any given age, the diabetic subjects had higher values than the non-diabetic subjects. Intimal medial thickness showed a positive correlation with age, gender, hypertension (HTN), hemoglobin A1C, and duration of diabetes with statistically significant P value. Conclusion: Diabetic subjects have higher intimal medial thickness values than non-diabetic subjects. Diabetes, duration of diabetes, age, gender, and HTN are the most important risk factors associated with increased intimal medial thickness. Key words: Atherosclerosis, carotid intima-media thickness, ultrasound INTRODUCTION Sonographic evaluation of the carotid artery intima-media thickness is a simple, non-invasive, and reproducible imaging parameter to evaluate atherosclerosis and atherosclerotic vascular diseases. Recently, considerable attention has been directed at the wall thickness of the carotid arteries as an early marker of atherosclerotic disease and as a means of showing the effectiveness of medical therapies in treating atherosclerosis. Noninvasive techniques such as B-mode ultrasound (USG) can directly assess the intima-media thickness (IMT), which corresponds to the thickness of the histologic intima and media. [1-3] USG imaging of carotid vessels can provide information on carotid intima-media thickness (), plaque presence and type, calcification, and wall diameter, offers the ability to examine pre-symptomatic lesions, and assess atherosclerotic burden, and hence, the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events. Such non-invasive screening procedures are valuable in identifying diabetic patients at risk for coronary artery disease (CAD) and cerebrovascular disease. In clinical settings, this can potentially lead to early interventions. The carotid arteries are among the vessels that are prone to developing overt atherosclerotic lesions in the presence of risk factors such as cigarette smoking, hypertension (HTN), diabetes, and dyslipidemia. [4,5] Patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) suffer unduly from premature and severe atherosclerosis. The Framingham study pointed out that diabetic individuals have higher serum concentrations of lipids and more HTN, obesity, and thus are more prone to metabolic syndrome and its sequelae, namely, CAD, cerebrovascular disease, and vascular atherosclerosis. [6] In type 2 DM, carotid intimal thickness is significantly higher than in corresponding healthy age- and sex-matched non-diabetic subjects. There is also evidence for an excess prevalence of intimal thickening and atherosclerotic lesions in patients suffering from definite HTN compared with normotensive controls. [7-9] Hence, measurement of carotid intimal thickness using highresolution B-mode ultrasonography which is non-invasive Address of Correspondence: Dr. G. Vikas Naik, Department of Internal Medicine, Kanachur Institute of Medical Sciences, University Road, Natekal, Mangalore , Karnataka, India. Phone: drvikasnaikmdgm@gmail.com Received: ; Revised: ; Accepted: Page 128
2 Naik and Shivaranjan: Carotid intima-media thickness and atherosclerosis in diabetics well-validated method is used to assess early manifestations of atherosclerosis such as early cardiovascular disease, T1A, stroke in symptomatic, as well as high-risk patients such as dyslipidemia, DM, HTN, and cigarette smoking. Aims and Objectives To measure in subjects with and without DM. Correlation of with risk factors such as age, HTN, smoking, and dyslipidemia. MATERIALS AND METHODS This study is a comparative study of 50 cases and 50 controls in which we have studied the values in diabetic and non-diabetics. Method of Collection of Data Inclusion criteria Patients aged more than 30 years with type2 DM. Patients with HTN. Exclusion criteria Patients with ischemic heart disease (acute coronary syndrome, stable angina, prior history of coronary artery bypass graft, and percutaneous coronary angioplasty). Patients with congestive heart failure. Patients with renal disease both acute and chronic. Patients with stroke. Patients with type 1 DM. Statistics The data obtained from the above was filled in the master chart and analyzed further for their statistical significance. Data were presented as mean ± SD values were called statistically significant (if P < 0.05). The correlation coefficient test and Student s t-test was used in most cases to compare frequency distribution. RESULTS In age group years, there are 10 cases and 11 controls. In age group years, there are 13 cases and 12 controls. In age group years, there are 27 cases and 27 controls which correspond to 54% [Table 1]. In age group years, in cases is 0.08 ± 0.03, in controls, it is 0.07 ± In age group years, in cases is 0.11 ± 0.04, in controls, it is ± In age group years, in cases is 0.13 ± 0.021, in controls, it is 0.07 ± 0.02 (0.13 ± 0.021) is more in the age group of years, as age increases, also increased in cases [Table 2]. In cases, 74% (n = 37) are males and 26% (n = 13) are females. In controls, 74% (n = 37) are males and 26% (n = 13) are females [Table 3]. In cases, mean in males is ± 0.04 and in females 0.17 ± In controls, mean in males is 0.07 ± 0.02 and in females 0.07 ± [Table 4]. between 0.01 and 0.05 cm group, there are 4 cases and 5 controls. between 0.06 and 0.10 cm group, there are 28 cases and 42 controls. between 0.11 and 0.15 cm group, there are 14 cases and 3 controls. between 0.16 and 0.20 cm group, there are 4 cases. Of 50 cases, 46 patients had between 0.06 and 0.20 cm (92%), and of 50 controls, 45 had between 0.06 and 0.20 cm (90%). in cases is ± cm, and in controls, it is 0.07 ± 0.02 cm [Table 5]. Patients with above the normal values in the profile were defined as risk group and patients with normal and below normal values were defined as non-risk group normal total cholesterol (TC) Table 1: Age distribution of patients studied Age in years Cases n (%) Controls n (%) (20.0) 11 (22.0) (26.0) 12 (24.0) (54.0) 27 (54.0) Total 50 (100.0) 50 (100.0) ±SD 60.62± ±8.35 SD: Standard deviation Table 2: Comparison of in two groups studied according to age in years Age in years Cases Controls P ± ± ± ± * ± ± Table 3: Gender distribution of patients studied Age in years Cases Controls Male 37 (74.0) 37 (74.0) Female 13 (26.0) 13 (26.0) Total 50 (100.0) 50 (100.0) Table 4: Comparison of in two groups studied according to gender Gender Cases Controls P Male 0.097± ±0.02 <0.001** Female 0.17± ± Page 129
3 Naik and Shivaranjan: Carotid intima-media thickness and atherosclerosis in diabetics value 200, triglyceride (TG) value 150, high-density lipoprotein value 40, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) value 100, very LDL value 30 [Tables 6-9]. Table 5: Comparison of average in two groups studied Cases Controls (8.0) 5 (10.0) (56.0) 42 (84.0) (28.0) 3 (6.0) (8.0) 0 (0.0) Total 50 (100.0) 50 (100.0) ±SD 0.121± ±0.002 Inference is significantly more in cases when compared to controls with P=0.035*, SD: Standard deviation Table 6: Distribution of blood sugar parameters in two groups of patients studied Cases Controls P FBS mg/dl <110 0 (0.0) 39 (78.0) <0.001** (18.0) 11 (22.0) > (82.0) 0 (0.0) PPBS mg/dl <140 0 (0.0) 24 (48.0) <0.001** (0.0) 26 (52.0) > (100.0) 0 (0.0) value 1.30 ± 0.23 is highest between 7 and 10 years duration. There is incremental increase in value as the duration of DM progress. Statistical significance was achieved when the duration of DM was compared with value. Risk group and non-risk group has been categorized depending on hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) level >7 and <7, respectively. in risk group of DM subjects is higher than the non-risk group, but P = highly statistically significant [Graph 1 and Table 10]. There were 15 and 14 patients in risk and non-risk group with <0.08 and 5 and 16 patients among risk and non-risk group with >0.08. P = 0.04 which is statistically significant [Table 11]. The mean in BMI <23 is and BMI >23 mean is 0.072, P = [Graph 2 and Table 12]. The mean in the study group is more in patients with DM+HTN+SMOKING (0.16 ± 0.25) compared to other patients [Table 13]. The mean in control group is relatively more in patients with HTN+SMOKING (0.08 ± 0.001) group compared to other group [Table 14]. The mean is increased in DM+HTN+SMOKING group (0.16 ± 0.25) which indicates risk factors contributes to the development of atherosclerosis [Table 15]. Table 7: Effect of FBS/PPBS on Parameter Risk Non risk FBS n= ±0.03 n= ±0.04 PPBS n= ±0.03 n= ±0.04 P= Table 8: Distribution of serum lipid profile parameters in two groups of patients studied Lipid parameters Cases Controls P TC mg/dl < (36.0) 39 (78.0) <0.001** > (64.0) 11 (22.0) LDL mg/dl < (54.0) 40 (80.0) <0.001** > (46.0) 10 (20.0) TG mg/dl <150 1 (2.0) 27 (54.0) <0.001** > (98.0) 23 (46.0) HDL mg/dl <40 34 (64.0) 13 (26.0) <0.001** >40 16 (32.0) 37 (74.0) TG: Triglyceride, HDL: High density lipoprotein, TC: Total cholesterol Graph 1: Effect of hemoglobin A1C on among diabetes mellitus Graph 2: Effect of body mass index on carotid intima-media thickness Page 130
4 Naik and Shivaranjan: Carotid intima-media thickness and atherosclerosis in diabetics Table 9: Effect of lipid profile on Parameter Risk group Non risk group SD SD difference TC (NS) TG (NS) HDL (NS) LDL (NS), TC: Total cholesterol, TG: Triglyceride, HDL: High density lipoprotein, LDL: Low density lipoprotein, NS: Not significant P Table 10: Effect of duration of diabetes on DM Duration (years) No ± ± ±0.23 ANOVA, F=18.82, P<0.001 HS., HS: Highly significant, DM: Diabetes mellitus Table 11: Effect of HTN on Parameter <0.08 >0.08 Total Risk Non risk Total P=0.04., HTN: Hypertension Table 12: Effect of smoking on Parameter <0.08 >0.08 Total Risk Non risk Total P=0.39. DISCUSSION Effect of Age on In the present study, cases and controls in the age groups of 40 50, 51 60, and years, mean age being 60 years and more number of patients are in the age group of years (27 cases). As the age increases, mean in cases has increased compared to controls that is mean in cases in the age group of years is 0.08 cm, years is 0.11 cm, and years is 0.13 cm. In cases, mean is cm (range cm), and in controls, mean is 0.07 cm (range cm). Sahoo et al., [4] Salonen et al., [10] Howard et al., [12] and Allan et al. [11] showed a positive correlation between age and [Table 16] Effect of Gender on In this study, there are 37 males and 13 females in both cases and control groups, in cases, mean in males is ± 0.04 cm and in females is 0.17 ± 0.03 cm. In controls, mean is 0.07 ± 0.02 cm in both males and females. is more in female cases than males, but female cases are less in number in our study. is significantly more in male cases when compared to male controls with P < The present study correlates with the study conducted by Sahoo et al. showed differences in mean between males and females in cases were not significant; however, the difference was statistically significant in both the genders when compared to controls with P < [Table 17]. Comparison of among Diabetic and Nondiabetics In this study, in cases, mean is cm (range cm), and in controls, mean is 0.07 cm (range cm). is significantly more in cases when compared to controls with P = This study is correlating with the study conducted by Sahoo et al., mean in cases was cm (range cm), and in controls, it was cm (range cm) with P<0.0001, and also with the study conducted by Mohan et al. (P = ) [Table 18]. Effect of HTN on In this study, mean of hypertensive and non-hypertensive patients in study group was 0.12 ± 0.25 and 0.09 ± of hypertensive and non-hypertensive patients in control group was 0.08 ± 0.02 and 0.06 ± 0.01 (P = 0.04). This study is correlating with the study by O Leary et al. (P = 0.01) and Agarwal et al. (P = 0.05) [Table 19]. Effect of Smoking on In this study, 10% of study group are smokers with mean of 0.09 ± 0.04 and non-smokers with mean of 0.08 ± 0.04 (P = 0.63). In control group, mean of smokers 0.06 ± 0.01 and non-smokers 0.06 ± 0.01 (P = 1.0). In this study, there was no significant difference in between smokers and non-smokers. Due to less number of patients and duration of smoking was not considered in this study, hence, this study failed to achieve statistical significance on the effect of smoking on. Effect of Lipid Profile on In this study, various parameters of lipid profile have shown a positive correlation with in study group though a statistical difference could not be assumed between risk and non-risk group due to the less sample size. Effect of FBS and PPBS on Role of FBS-PPBS as an influencing factor on is doubtful, due to the selection of random samples. In this study failed to assume the significant difference between risk and non-risk group due to the selection of random value. Page 131
5 Naik and Shivaranjan: Carotid intima-media thickness and atherosclerosis in diabetics Table 13: Comparison of in DM with or without HTN and smoking DM±HTN (N) DM without HTN DM±HTN±smoking ± ± ±0.25, HTN: Hypertension, DM: Diabetes mellitus Table 14: Comparison of in non diabetic with or without HTN and smoking Non DM with HTN Non DM without HTN Non DM±smoking Non DM±HTN±smoking ± ± ± ±0.01, HTN: Hypertension Table 15: Comparison of in both diabetic and non diabetic with risk factors No DM±HTNDM±smoking DM±HTN±smoking Non DM±HTN Non DM±smokingNon DM±HTN±smoking 0.12± ± ± ± ± ±0.01, HTN: Hypertension, DM: Diabetes mellitus Table 16: Showing effect of age on I various studies Study Sahoo et al. [4] Salonen et al. [12] Allan et al. [16] Howard et al. [11] Present study P < Table 17: Showing effect of gender on in various studies Study Mohan et al. [13] Sahoo et al. [4] Present study P <0.001 < Table 18: Comparative P values of in diabetics and non diabetics in different studies Study Sahoo et al. [4] Mohan et al. [13] Kawamori et al. [19] Frauchiger B, Pujia et al. [14] Present Geroulakos et al. [15] study P < Effect of duration of DM on In this study, there is positive correlation between duration of DM with value (P = 0.001). This study is correlating with the study by Mohan et al. (P = 0.001) [Table 20]. Effect of HbA1C on In this study, there is positive correlation between HbA1C levels with (P = ) on comparing risk and non-risk group in DM subjects. This study is correlating with the study; Udaybaskaran et al. showed HbA1C had statistically significant positive correlation with [Table 21]. Effect of BMI on In this study, there is positive correlation between BMI and (P = ). This study is correlating with study Sutton-Tyrrell et al. (P = 0.001) showed strong positive correlation of BMI with [Table 22]. CONCLUSION The present study showed increased values of in DM patients. Along with this risk factors such as age, HTN, BMI, and duration of DM, may actually have a correlation with either directly or indirectly influencing the disease process itself and contributing to atherosclerosis. USG-guided measurement is non-invasive, reproducible method for detecting of early arterial structural changes associated with various risk factors for atherosclerosis. The present study shows that increases with age, which is a non-modifiable risk factor for atherosclerosis and the correlation is statistically significant. is significantly more in male cases (0.097 ± 0.04 cm) when compared to male controls (0.07 ± 0.02 cm) with P < The present study emphasized that as the duration of diabetes increases there is a progression of which is statistically significant. HTN an established risk factor for atherosclerosis is found to have a positive correlation with progression of which is statistically significant in the present study. BMI is shown to have statistical significance when compared between both study and control groups. The present study has demonstrated the role of traditional risk factors such as TC, HDL cholesterol, and TG in the progression of atherosclerosis but not found to have statistical significance with. Page 132
6 Naik and Shivaranjan: Carotid intima-media thickness and atherosclerosis in diabetics Table 19: Showing effect of HTN on in various studies Study Leary et al. [17] Agarwal et al. [18] Present study P , HTN: Hypertension Table 20: Showing effect of duration of DM on in various studies Study Rathnakar shoo et al. [4] Mohan et al. [13] Pujia et al. [16] Kawamori et al. [14] Present study P , DM: Diabetes mellitus Table 21: Showing effect of HbA1c on in various studies Study Udaybaskaran et al. Yokoyama et al. [19] Yamasaki et al. [20] Present study P , HbA1C: Hemoglobin A1C Table 22: Showing effect of BMI on in various studies Study Sutton Tyrrell K et al. [21] Stevens et al. [22] Stevens et al. [23] Present study P , BMI: Body mass index The role of FBS and PPBS on is doubtful. This could be explained by due to the selection of the random values. There was a positive correlation of HbA1C with value among risk and non-risk group. Hence, measurement of by USG Doppler is reliable and helps in early medical intervention to take care of risk factors and lifestyle modification. REFERENCES 1. Jadhav UM, Kadam NN. Carotid intima-media thickness as an independent predictor of coronary artery disease. Indian Heart J 2001;53: O Leary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Savage PJ, Borhani NO, Kittner SJ, et al. Thickening of the carotid wall. A marker for atherosclerosis in the elderly? Cardiovascular health study collaborative research group. Stroke 1996;27: Baldassarre D, Amato M, Bondioli A, Sirtori CR, Tremoli E. Carotid artery intima-media thickness measured by ultrasonography in normal clinical practice correlates well with atherosclerosis risk factors. Stroke 2000;31: Sahoo R, Krishna MV, Subrahmaniyan DK, Dutta TK, Elangovan S. Common carotid intima-media thickness in acute ischemic stroke: A case control study. Neurol India 2009;57: Park K. Parks Textbook of Preventive and Social Medicine. 19 th ed. Jabalpur India: Banarsidas Bhanot Publishers; p Garcia MJ, McNamara PM, Gordon T, Kannel WB. Morbidity and mortality in diabetics in the framingham population. Sixteen year follow-up study. Diabetes 1974;23: Shaper AG, Phillips AN, Pocock SJ, Walker M, Macfarlane PW. Risk factors for stroke in middle aged british men. BMJ 1991;302: Touboul PJ, Elbaz A, Koller C, Lucas C, Adraï V, Chédru F, et al. Common carotid artery intima-media thickness and brain infarction: The etude du profil génétique de l infarctus cérébral (GENIC) case-control study. The GENIC investigators. Circulation 2000;102: Hatano S. Experience from a multicentre stroke register: A preliminary report. Bull World Health Organ 1976;54: Chobanian AV. Vascular effects of systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol 1992;69:3E-7E. 11. Howard G, Sharrett AR, Heiss G, Evans GW, Chambless LE, Riley WA, et al. Carotid artery intimal-medial thickness distribution in general populations as evaluated by B-mode ultrasound. ARIC investigators. Stroke 1993;24: Salonen R, Salonen JT. Determinants of carotid intima-media thickness: A population-based ultrasonography study in eastern Finnish men. J Intern Med 1991;229: Mohan V, Ravikumar R, Shanthi Rani S, Deepa R. Intimal medial thickness of the carotid artery in south indian diabetic and non-diabetic subjects: The chennai urban population study (CUPS). Diabetologia 2000;43: Pujia A, Gnasso A, Irace C, Colonna A, Mattioli PL. Common carotid arterial wall thickness in NIDDM subjects. Diabetes Care 1994;17: Frauchiger B, Schmid HP, Roedel C, Moosmann P, Staub D. Comparison of carotid arterial resistive indices with intimamedia thickness as sonographic markers of atherosclerosis. Stroke 2001;32: Allan PL, Mowbray PI, Lee AJ, Fowkes FG. Relationship between carotid intima-media thickness and symptomatic and asymptomatic peripheral arterial disease. The Edinburgh artery study. Stroke 1997;28: Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med 1998;15: O Leary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Manolio TA, Burke GL, Wolfson SK Jr, et al. Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults. Cardiovascular health study collaborative research group. N Engl J Med 1999;340: Kawamori R, Yamasaki Y, Matsushima H, Nishizawa H, Nao K, Hougaku H, et al. Prevalence of carotid atherosclerosis in diabetic patients. Ultrasound high-resolution B-mode imaging on carotid arteries. Diabetes Care 1992;15: Yokoyama H, Katakami N, Yamasaki Y. Recent advances of intervention to inhibit progression of carotid intima-media Page 133
7 Naik and Shivaranjan: Carotid intima-media thickness and atherosclerosis in diabetics thickness in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Stroke 2006;37: Yamasaki Y, Kodama M, Nishizawa H, Sakamoto K, Matsuhisa M, Kajimoto Y, et al. Carotid intima-media thickness in Japanese Type 2 diabetic subjects: Predictors of progression and relationship with incident coronary heart disease. Diabetes Care 2000;23: Sutton-Tyrrell K, Lassila HC, Meilahn E, Bunker C, Matthews KA, Kuller LH, et al. Carotid atherosclerosis in premenopausal and postmenopausal women and its association with risk factors measured after menopause. Stroke 1998;29: Stevens J, Tyroler HA, Cai J, Paton CC, Folsom AR, Tell GS, et al. Body weight change and carotid artery wall thickness. The atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Am J Epidemiol 1998;147: How to cite this Article: Naik G, Shivaranjan KP. Carotid intima-media thickness as a predictor of atherosclerosis in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects - A study from tertiary care hospital in coastal city of South India. Asian Pac. J. Health Sci., 2018; 5(1): Source of Support: Nil, Conflict of Interest: None declared. Page 134
Asian J. Exp. Sci., Vol. 27, No. 1, 2013; 67-72
 Carotid Intima-media Thickness as a Surrogate Marker of Atherosclerosis and its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors and Angiographic Severity of Coronary Artery Disease. 1 2 Rajeev Gupta and Rajendra
Carotid Intima-media Thickness as a Surrogate Marker of Atherosclerosis and its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors and Angiographic Severity of Coronary Artery Disease. 1 2 Rajeev Gupta and Rajendra
ARIC Manuscript Proposal #1233. PC Reviewed: 4_/_10/07 Status: _A Priority: 2_ SC Reviewed: Status: Priority:
 ARIC Manuscript Proposal #1233 PC Reviewed: 4_/_10/07 Status: _A Priority: 2_ SC Reviewed: Status: Priority: 1.a. Full Title: Subclinical atherosclerosis precedes type 2 diabetes in the ARIC study cohort
ARIC Manuscript Proposal #1233 PC Reviewed: 4_/_10/07 Status: _A Priority: 2_ SC Reviewed: Status: Priority: 1.a. Full Title: Subclinical atherosclerosis precedes type 2 diabetes in the ARIC study cohort
Correlation between triglyceride level and carotid intima media thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
 International Journal of Clinical Trials Bendwal K et al. Int J Clin Trials. 2018 May;5(2):97-101 http://www.ijclinicaltrials.com pissn 2349-3240 eissn 2349-3259 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3259.ijct20181051
International Journal of Clinical Trials Bendwal K et al. Int J Clin Trials. 2018 May;5(2):97-101 http://www.ijclinicaltrials.com pissn 2349-3240 eissn 2349-3259 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3259.ijct20181051
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 12 Page December 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.115 Evaluation of Carotid Intima
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.115 Evaluation of Carotid Intima
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1
 ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1 HOWTOCITETHISARTICLE: Srinivasa Rao Malladi. Association between Common Carotid
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1 HOWTOCITETHISARTICLE: Srinivasa Rao Malladi. Association between Common Carotid
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 10 Page October 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i10.82 Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Can
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i10.82 Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Can
Carotid Intimomedial Thickness in Type 2 Diabetic Patients and Its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors
 Original Article# Carotid Intimomedial Thickness in Type 2 Diabetic Patients and Its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors AK Agarwal*, PK Gupta**, S Singla***, U Garg+, A Prasad++, R Yadav+++ Abstract
Original Article# Carotid Intimomedial Thickness in Type 2 Diabetic Patients and Its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors AK Agarwal*, PK Gupta**, S Singla***, U Garg+, A Prasad++, R Yadav+++ Abstract
A study of brachial artery flow mediated dilatation and carotid intima media thickness in subjects having risk factors for coronary artery disease
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20171037 A study of brachial
International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20171037 A study of brachial
JCD. Correlation of In flammatory Markers and Dyslipidemia with Carotid Intima- Media Thickness in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 JCD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation of In flammatory Markers and Dyslipidemia with Carotid Intima- Media Thickness in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects Mukhopadhyay Saptarshi*, Banerjee Samar**, Bhattacharya Kingshuk***
JCD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation of In flammatory Markers and Dyslipidemia with Carotid Intima- Media Thickness in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects Mukhopadhyay Saptarshi*, Banerjee Samar**, Bhattacharya Kingshuk***
Original Research Article
 A STUDY TO ESTIMATE SUBCLINICAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS BY MEASURING THE CAROTID INTIMAL MEDIAL THICKNESS Natarajan Kandasamy 1, Rajan Ganesan 2, Thilakavathi Rajendiran
A STUDY TO ESTIMATE SUBCLINICAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS BY MEASURING THE CAROTID INTIMAL MEDIAL THICKNESS Natarajan Kandasamy 1, Rajan Ganesan 2, Thilakavathi Rajendiran
A Study to Show Postprandial Hypertriglyceridemia as a Risk Factor for Macrovascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetis Mellitus
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/21 A Study to Show Postprandial Hypertriglyceridemia as a Risk Factor for Macrovascular Complications in Bingi Srinivas
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/21 A Study to Show Postprandial Hypertriglyceridemia as a Risk Factor for Macrovascular Complications in Bingi Srinivas
JMEDS ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Study of Atherosclerotic Risk Factors in Patients 10.5005/jp-journals-10045-0048 with Prediabetes and Type II DM Study of Atherosclerotic Risk Factors in Patients with Prediabetes and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Study of Atherosclerotic Risk Factors in Patients 10.5005/jp-journals-10045-0048 with Prediabetes and Type II DM Study of Atherosclerotic Risk Factors in Patients with Prediabetes and
Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients With Coronary Atherosclerosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.8.317 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.8.317 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients
How would you manage Ms. Gold
 How would you manage Ms. Gold 32 yo Asian woman with dyslipidemia Current medications: Simvastatin 20mg QD Most recent lipid profile: TC = 246, TG = 100, LDL = 176, HDL = 50 What about Mr. Williams? 56
How would you manage Ms. Gold 32 yo Asian woman with dyslipidemia Current medications: Simvastatin 20mg QD Most recent lipid profile: TC = 246, TG = 100, LDL = 176, HDL = 50 What about Mr. Williams? 56
JMSCR Vol 4 Issue 06 Page June 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i6.69 Role of Aging, Hypertension and Dyslipidaemia
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i6.69 Role of Aging, Hypertension and Dyslipidaemia
Is Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Useful in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment? The Rotterdam Study
 Is Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Useful in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment? The Rotterdam Study Antonio Iglesias del Sol, MD; Karel G.M. Moons, MD, PhD; Monika Hollander, MD; Albert Hofman, MD,
Is Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Useful in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment? The Rotterdam Study Antonio Iglesias del Sol, MD; Karel G.M. Moons, MD, PhD; Monika Hollander, MD; Albert Hofman, MD,
The New England Journal of Medicine CAROTID-ARTERY INTIMA AND MEDIA THICKNESS AS A RISK FACTOR FOR MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AND STROKE IN OLDER ADULTS
 CAROTID-ARTERY INTIMA AND MEDIA THICKNESS AS A RISK FACTOR FOR MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AND STROKE IN OLDER ADULTS DANIEL H. O LEARY, M.D., JOSEPH F. POLAK, M.D., M.P.H., RICHARD A. KRONMAL, PH.D., TERI A.
CAROTID-ARTERY INTIMA AND MEDIA THICKNESS AS A RISK FACTOR FOR MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AND STROKE IN OLDER ADULTS DANIEL H. O LEARY, M.D., JOSEPH F. POLAK, M.D., M.P.H., RICHARD A. KRONMAL, PH.D., TERI A.
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: carotid_intimal_medial_thickness 12/2006 10/2016 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Ultrasonographic
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: carotid_intimal_medial_thickness 12/2006 10/2016 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Ultrasonographic
Objective Calcium score carotid IMT hs-crp
 P3952 Role of coronary calcium score, carotid intima-media thickness and C-reactive protein in predicting extent of coronary artery disease in young patients. Bedside Poster P3952 Role of coronary calcium
P3952 Role of coronary calcium score, carotid intima-media thickness and C-reactive protein in predicting extent of coronary artery disease in young patients. Bedside Poster P3952 Role of coronary calcium
Rates and Determinants of Site-Specific Progression of Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness. The Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study
 Rates and Determinants of Site-Specific Progression of Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness The Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study Andrew D. Mackinnon, MRCP; Paula Jerrard-Dunne, MRCPI; Matthias
Rates and Determinants of Site-Specific Progression of Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness The Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study Andrew D. Mackinnon, MRCP; Paula Jerrard-Dunne, MRCPI; Matthias
Diagnostic Accuracy of Carotid Ultrasonography in Screening for Coronary Artery Disease
 J Cardiol 2000 ; 36: 295 302 Diagnostic Accuracy of Carotid Ultrasonography in Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Tomohiro Nobuhiko Yutaka Yoshihiko Katsuhiro Takayoshi Tsuyoshi Toshinori Shigeyasu
J Cardiol 2000 ; 36: 295 302 Diagnostic Accuracy of Carotid Ultrasonography in Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Tomohiro Nobuhiko Yutaka Yoshihiko Katsuhiro Takayoshi Tsuyoshi Toshinori Shigeyasu
A comparative study on the fasting and post prandial lipid levels as a cardiovascular risk factor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
 Original Research Article A comparative study on the fasting and post prandial lipid levels as a cardiovascular risk factor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus Deepa Kalikavil Puthenveedu 1, Sundaraj
Original Research Article A comparative study on the fasting and post prandial lipid levels as a cardiovascular risk factor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus Deepa Kalikavil Puthenveedu 1, Sundaraj
CVD Risk Assessment. Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic
 CVD Risk Assessment Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic What is Risk? A cumulative probability of an event, usually expressed as percentage e.g.: 5 CV events in 00 pts = 5% risk This
CVD Risk Assessment Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic What is Risk? A cumulative probability of an event, usually expressed as percentage e.g.: 5 CV events in 00 pts = 5% risk This
Is the Ankle-Brachial Index a Useful Screening Test for Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic, Middle-Aged Adults?
 Is the Ankle-Brachial Index a Useful Screening Test for Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic, Middle-Aged Adults? Rachael A. Wyman, MD; Jon G. Keevil, MD; Kjersten L. Busse, RN, MSN; Susan E. Aeschlimann,
Is the Ankle-Brachial Index a Useful Screening Test for Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic, Middle-Aged Adults? Rachael A. Wyman, MD; Jon G. Keevil, MD; Kjersten L. Busse, RN, MSN; Susan E. Aeschlimann,
Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients
 2012 international Conference on Diabetes and metabolism (ICDM) Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients Nan Hee Kim, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University
2012 international Conference on Diabetes and metabolism (ICDM) Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients Nan Hee Kim, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University
Clinical Investigation and Reports. Predictive Value of Noninvasive Measures of Atherosclerosis for Incident Myocardial Infarction
 Clinical Investigation and Reports Predictive Value of Noninvasive Measures of Atherosclerosis for Incident Myocardial Infarction The Rotterdam Study Irene M. van der Meer, MD, PhD; Michiel L. Bots, MD,
Clinical Investigation and Reports Predictive Value of Noninvasive Measures of Atherosclerosis for Incident Myocardial Infarction The Rotterdam Study Irene M. van der Meer, MD, PhD; Michiel L. Bots, MD,
1. Which one of the following patients does not need to be screened for hyperlipidemia:
 Questions: 1. Which one of the following patients does not need to be screened for hyperlipidemia: a) Diabetes mellitus b) Hypertension c) Family history of premature coronary disease (first degree relatives:
Questions: 1. Which one of the following patients does not need to be screened for hyperlipidemia: a) Diabetes mellitus b) Hypertension c) Family history of premature coronary disease (first degree relatives:
Evaluation of hs-crp levels in acute coronary syndromes
 Original Research Article Evaluation of hs-crp levels in acute coronary syndromes R. S. Pushpa Kumari 1*, Priya John 2, V. A. Vipula 3 1 Professor, Department of General Medicine, MNR Medical College and
Original Research Article Evaluation of hs-crp levels in acute coronary syndromes R. S. Pushpa Kumari 1*, Priya John 2, V. A. Vipula 3 1 Professor, Department of General Medicine, MNR Medical College and
EVALUATION OF CAROTID ARTERY STENOSIS IN STROKE/TRANSIENT ISCHAEMIC ATTACK Nambakam Tanuja Subramanyam 1, Naveen Kumar P 2, Girish P.
 EVALUATION OF CAROTID ARTERY STENOSIS IN STROKE/TRANSIENT ISCHAEMIC ATTACK Nambakam Tanuja Subramanyam 1, Naveen Kumar P 2, Girish P. Vakrani 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Nambakam Tanuja Subramanyam, Naveen
EVALUATION OF CAROTID ARTERY STENOSIS IN STROKE/TRANSIENT ISCHAEMIC ATTACK Nambakam Tanuja Subramanyam 1, Naveen Kumar P 2, Girish P. Vakrani 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Nambakam Tanuja Subramanyam, Naveen
Individuals of African and African Caribbean descent living
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.D. Mackinnon P. Jerrard-Dunne L. Porteous H.S. Markus Carotid Intima-Media Thickness is Greater but Carotid Plaque Prevalence is Lower in Black Compared with White Subjects BACKGROUND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.D. Mackinnon P. Jerrard-Dunne L. Porteous H.S. Markus Carotid Intima-Media Thickness is Greater but Carotid Plaque Prevalence is Lower in Black Compared with White Subjects BACKGROUND
HDL-C. J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2008, 48: NIPPON DATA80, MEGA study, JELIS, dyslipidemia, risk assessment chart
 Online publication March 25, 2009 48 6 2007 2007 HDL-C LDL-C HDL-C J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2008, 48: 463 470 NIPPON DATA80, MEGA study, JELIS, dyslipidemia, risk assessment chart 1987 NIPPON DATA80 Iso 10 MRFIT
Online publication March 25, 2009 48 6 2007 2007 HDL-C LDL-C HDL-C J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2008, 48: 463 470 NIPPON DATA80, MEGA study, JELIS, dyslipidemia, risk assessment chart 1987 NIPPON DATA80 Iso 10 MRFIT
Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and carotid plaques in young Nepalese patients with angiographically documented coronary artery disease
 Original Article Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and carotid plaques in young Nepalese patients with angiographically documented coronary artery disease Yuba Raj Limbu, Rajib Rajbhandari, Ranjit
Original Article Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and carotid plaques in young Nepalese patients with angiographically documented coronary artery disease Yuba Raj Limbu, Rajib Rajbhandari, Ranjit
ANKLE BRACHIAL PRESSURE INDEX: AS A PREDICTOR OF PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE IN DIABETIC & NON DIABETIC SUBJECTS
 RESEARCH ARTICLE ANKLE BRACHIAL PRESSURE INDEX: AS A PREDICTOR OF PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE IN DIABETIC & NON DIABETIC SUBJECTS Dharmesh Patel 1, MB Jani 2 1 Department of Physiology, GMERS Medical College,
RESEARCH ARTICLE ANKLE BRACHIAL PRESSURE INDEX: AS A PREDICTOR OF PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE IN DIABETIC & NON DIABETIC SUBJECTS Dharmesh Patel 1, MB Jani 2 1 Department of Physiology, GMERS Medical College,
Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings?
 Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings? Dougalis A, Soulaidopoulos S, Cholongitas E, Chalevas P, Vettas Ch, Doumtsis P, Vaitsi K, Diavasti M, Mandala E, Garyfallos A 4th Department
Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings? Dougalis A, Soulaidopoulos S, Cholongitas E, Chalevas P, Vettas Ch, Doumtsis P, Vaitsi K, Diavasti M, Mandala E, Garyfallos A 4th Department
Introduction. Risk factors of PVD 5/8/2017
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
Study on occurrence of metabolic syndrome among patients with stroke: a descriptive study
 Original article Study on occurrence of metabolic syndrome among patients with stroke: a descriptive study Dr. Mahesh K Savadi*, Dr Manjunatha N** *Assistant Professor, **Post graduate Dept. of General
Original article Study on occurrence of metabolic syndrome among patients with stroke: a descriptive study Dr. Mahesh K Savadi*, Dr Manjunatha N** *Assistant Professor, **Post graduate Dept. of General
Carotid artery intima-media thickness is a marker for coronary artery disease
 Scientific Journal of Medical Science (2013) 2(8) 145-150 ISSN 2322-5025 doi: 10.14196/sjms.v2.i8.894 Contents lists available at Sjournals Journal homepage: www.sjournals.com Original article Carotid
Scientific Journal of Medical Science (2013) 2(8) 145-150 ISSN 2322-5025 doi: 10.14196/sjms.v2.i8.894 Contents lists available at Sjournals Journal homepage: www.sjournals.com Original article Carotid
Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD INTRODUCTION
 2 Hyperlipidemia Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION RISK CATEGORIES AND TARGET LDL-CHOLESTEROL TREATMENT OF LDL-CHOLESTEROL SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS OLDER AND YOUNGER ADULTS ADDITIONAL
2 Hyperlipidemia Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION RISK CATEGORIES AND TARGET LDL-CHOLESTEROL TREATMENT OF LDL-CHOLESTEROL SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS OLDER AND YOUNGER ADULTS ADDITIONAL
Journal of American Science 2014;10(8)
 Role of Doppler Ultrasound and Peripheral Angiography (as a Diagnostic Modality of Atherosclerosis) in Combination with Conventional Atherosclerosis Risk Factors in Coronary Artery Disease Prediction Hussein
Role of Doppler Ultrasound and Peripheral Angiography (as a Diagnostic Modality of Atherosclerosis) in Combination with Conventional Atherosclerosis Risk Factors in Coronary Artery Disease Prediction Hussein
The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke
 Smoking The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke Wei-Chieh Weng, M.D. Department of Neurology, Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital, Kee-Lung, Taiwan Smoking related mortality Atherosclerotic vascular disease
Smoking The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke Wei-Chieh Weng, M.D. Department of Neurology, Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital, Kee-Lung, Taiwan Smoking related mortality Atherosclerotic vascular disease
Plasma fibrinogen level, BMI and lipid profile in type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypertension
 World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
Predictors of progression and relationship with incident coronary heart disease. Diabetes Care 23: , 2000
 Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Japanese Type 2 Diabetic Subjects Predictors of progression and relationship with incident
Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Japanese Type 2 Diabetic Subjects Predictors of progression and relationship with incident
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Am J Cardiol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2008 January 24.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Am J Cardiol. 2008 January 15; 101(2): 186 192. Coronary Artery Calcium, Carotid Artery Wall Thickness and Cardiovascular Disease
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Am J Cardiol. 2008 January 15; 101(2): 186 192. Coronary Artery Calcium, Carotid Artery Wall Thickness and Cardiovascular Disease
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only.
 The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
Preclinical Detection of CAD: Is it worth the effort? Michael H. Crawford, MD
 Preclinical Detection of CAD: Is it worth the effort? Michael H. Crawford, MD 1 Preclinical? No symptoms No physical findings No diagnostic ECG findings No chest X-ray X findings No diagnostic events 2
Preclinical Detection of CAD: Is it worth the effort? Michael H. Crawford, MD 1 Preclinical? No symptoms No physical findings No diagnostic ECG findings No chest X-ray X findings No diagnostic events 2
4/7/ The stats on heart disease. + Deaths & Age-Adjusted Death Rates for
 + Update on Lipid Management Stacey Gardiner, MD Assistant Professor Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Medical College of Wisconsin + The stats on heart disease Over the past 10 years for which statistics
+ Update on Lipid Management Stacey Gardiner, MD Assistant Professor Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Medical College of Wisconsin + The stats on heart disease Over the past 10 years for which statistics
Unraveling the concealed and calculated cardiovascular risks in diabetes
 15 P B Fernando Memorial Oration 2015 Unraveling the concealed and calculated cardiovascular risks in diabetes Weerarathna T P 1 Journal of the Ceylon College of Physicians, 2016, 47, 15-19 Abstract Cardiovascular
15 P B Fernando Memorial Oration 2015 Unraveling the concealed and calculated cardiovascular risks in diabetes Weerarathna T P 1 Journal of the Ceylon College of Physicians, 2016, 47, 15-19 Abstract Cardiovascular
The investigation of serum lipids and prevalence of dyslipidemia in urban adult population of Warangal district, Andhra Pradesh, India
 eissn: 09748369, www.biolmedonline.com The investigation of serum lipids and prevalence of dyslipidemia in urban adult population of Warangal district, Andhra Pradesh, India M Estari, AS Reddy, T Bikshapathi,
eissn: 09748369, www.biolmedonline.com The investigation of serum lipids and prevalence of dyslipidemia in urban adult population of Warangal district, Andhra Pradesh, India M Estari, AS Reddy, T Bikshapathi,
Received: March 2008; in final form May 2008.
 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BRACHIAL ARTERY FLOW- MEDIATED DILATION AND CAROTID ARTERY INTIMA MEDIA THICKNESS IN THE MIDDLE-AGED SUBJECTS WITH LOW CARDIOVASCULAR RISK GERMAINE SĂVOIU*, LAVINIA NOVEANU**, O. FIRA-MLADINESCU*,
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BRACHIAL ARTERY FLOW- MEDIATED DILATION AND CAROTID ARTERY INTIMA MEDIA THICKNESS IN THE MIDDLE-AGED SUBJECTS WITH LOW CARDIOVASCULAR RISK GERMAINE SĂVOIU*, LAVINIA NOVEANU**, O. FIRA-MLADINESCU*,
Association between Plasma Homocysteine Concentrations and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
 Association between Plasma Homocysteine Concentrations and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease ROXANA BUZAŞ, CORINA ŞERBAN, IOANA SUCEAVA, DANIEL LIGHEZAN University
Association between Plasma Homocysteine Concentrations and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease ROXANA BUZAŞ, CORINA ŞERBAN, IOANA SUCEAVA, DANIEL LIGHEZAN University
Clinical Study of Lipid Profile Pattern in Acute Coronary Syndromes
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/359 Clinical Study of Lipid Profile Pattern in Acute Coronary Syndromes V Suresh Kumar, Madavaram Sreelatha Assistant
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/359 Clinical Study of Lipid Profile Pattern in Acute Coronary Syndromes V Suresh Kumar, Madavaram Sreelatha Assistant
A novel method for evaluating human carotid artery elasticity: Possible detection of early stage atherosclerosis in subjects with type 2 diabetes
 Atherosclerosis 196 (2008) 391 397 A novel method for evaluating human carotid artery elasticity: Possible detection of early stage atherosclerosis in subjects with type 2 diabetes Hisashi Okimoto a,1,
Atherosclerosis 196 (2008) 391 397 A novel method for evaluating human carotid artery elasticity: Possible detection of early stage atherosclerosis in subjects with type 2 diabetes Hisashi Okimoto a,1,
atherosclerosis; carotid arteries; cohort studies; risk factors MATERIALS AND METHODS Cohort examination
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2002 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 155, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Risk Factors for Progression of Atherosclerosis
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2002 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 155, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Risk Factors for Progression of Atherosclerosis
Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden
 Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Cardiovascular Disease Prevention (CVD) Three Strategies for CVD
Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Cardiovascular Disease Prevention (CVD) Three Strategies for CVD
Citation for published version (APA): Terpstra, W. F. (2003). Beyond blood pressure monitoring Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Beyond blood pressure monitoring Terpstra, Willem Fopke IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Beyond blood pressure monitoring Terpstra, Willem Fopke IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
Imaging Biomarkers: utilisation for the purposes of registration. EMEA-EFPIA Workshop on Biomarkers 15 December 2006
 Imaging Biomarkers: utilisation for the purposes of registration EMEA-EFPIA Workshop on Biomarkers 15 December 2006 Vascular Imaging Technologies Carotid Ultrasound-IMT IVUS-PAV QCA-% stenosis 2 ICH E
Imaging Biomarkers: utilisation for the purposes of registration EMEA-EFPIA Workshop on Biomarkers 15 December 2006 Vascular Imaging Technologies Carotid Ultrasound-IMT IVUS-PAV QCA-% stenosis 2 ICH E
A study on clinical profile of acute coronary syndrome in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with relevance to HbA1c
 Original Research Article A study on clinical profile of acute coronary syndrome in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with relevance to HbA1c K. Babu Raj 1, G. Sivachandran 2* 1 Reader, 2 Final Year Post
Original Research Article A study on clinical profile of acute coronary syndrome in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with relevance to HbA1c K. Babu Raj 1, G. Sivachandran 2* 1 Reader, 2 Final Year Post
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST. None
 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST None BURDEN OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE IN DIABETES IN INDIA Amal Kumar Banerjee MD, DM,FACC,FESC,FACP,FAPSC,FICC President Association of Physicians of India SAARC Cardiac
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST None BURDEN OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE IN DIABETES IN INDIA Amal Kumar Banerjee MD, DM,FACC,FESC,FACP,FAPSC,FICC President Association of Physicians of India SAARC Cardiac
Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis
 Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology 2008 Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis The purpose of this exercise is to allow students to recapitulate issues discussed throughout the course which
Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology 2008 Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis The purpose of this exercise is to allow students to recapitulate issues discussed throughout the course which
Study of relationship of serum Lipid Profile and etiological factors of Ischaemic Heart Diseases
 Original article: Study of relationship of serum Lipid Profile and etiological factors of Ischaemic Heart Diseases Dr Abhijit Nikam, Dr Sonu Yadav, Dr Vivek Chiddarwar, Dr A L Kakrani Dept of Medicine,
Original article: Study of relationship of serum Lipid Profile and etiological factors of Ischaemic Heart Diseases Dr Abhijit Nikam, Dr Sonu Yadav, Dr Vivek Chiddarwar, Dr A L Kakrani Dept of Medicine,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein
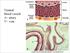 Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Original Article. Study of Lipid Profile in Postmenopausal Rural Women and Its Correlation with Carotid Intima Media Thickness Chaoji S A, Humne N
 Original Article Vidarbha Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 19 July 2015 Study of Lipid Profile in Postmenopausal Rural Women and Its Correlation with Carotid Intima Media Thickness 1 2 Chaoji S A, Humne
Original Article Vidarbha Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 19 July 2015 Study of Lipid Profile in Postmenopausal Rural Women and Its Correlation with Carotid Intima Media Thickness 1 2 Chaoji S A, Humne
Association of Major Modifiable Risk Factors Among Patients with Coronary Artery Disease - A Retrospective Analysis
 Original Article Association of Major Modifiable Risk Factors Among Patients with Coronary Artery Disease - A Retrospective Analysis V Achari, AK Thakur Abstract Background : The relative importance of
Original Article Association of Major Modifiable Risk Factors Among Patients with Coronary Artery Disease - A Retrospective Analysis V Achari, AK Thakur Abstract Background : The relative importance of
year resident, Department of Medicine, B. J. Medical college, Ahmedabad.
 Clinical Study of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with or without Cerebrovascular Feature and Its Correlation with Other Comorbidity / Diabetic Complication Vivek Sidhapura 1*, Bipin Amin 2, Amit Potulwar
Clinical Study of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with or without Cerebrovascular Feature and Its Correlation with Other Comorbidity / Diabetic Complication Vivek Sidhapura 1*, Bipin Amin 2, Amit Potulwar
Rehabilitation and Research Training Center on Secondary Conditions in Individuals with SCI. James S. Krause, PhD
 Disclosure The contents of this presentation were developed with support from educational grants from the Department of Education, NIDRR grant numbers H133B090005, H133B970011 and H133G010160. However,
Disclosure The contents of this presentation were developed with support from educational grants from the Department of Education, NIDRR grant numbers H133B090005, H133B970011 and H133G010160. However,
Isolated Post-challenge Hyperglycemia: Concept and Clinical Significance
 CLINICAL PRACTICE Isolated Post-challenge Hyperglycemia: Concept and Clinical Significance John MF. Adam*, Daniel Josten** ABSTRACT The American Diabetes Association has strongly recommended that fasting
CLINICAL PRACTICE Isolated Post-challenge Hyperglycemia: Concept and Clinical Significance John MF. Adam*, Daniel Josten** ABSTRACT The American Diabetes Association has strongly recommended that fasting
Frequency of Dyslipidemia and IHD in IGT Patients
 Frequency of Dyslipidemia and IHD in IGT Patients *Islam MS, 1 Hossain MZ, 2 Talukder SK, 3 Elahi MM, 4 Mondal RN 5 Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) is often associated with macrovascular complications.
Frequency of Dyslipidemia and IHD in IGT Patients *Islam MS, 1 Hossain MZ, 2 Talukder SK, 3 Elahi MM, 4 Mondal RN 5 Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) is often associated with macrovascular complications.
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors
 Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Study of serum Lipid Profile patterns of Indian population in young Ischaemic Heart Disease
 Original article: Study of serum Lipid Profile patterns of Indian population in young Ischaemic Heart Disease Dr Sonu Yadav, Dr Abhijit Nikam, Dr Vivek Chiddarwar, Dr A L Kakrani Department of Medicine,
Original article: Study of serum Lipid Profile patterns of Indian population in young Ischaemic Heart Disease Dr Sonu Yadav, Dr Abhijit Nikam, Dr Vivek Chiddarwar, Dr A L Kakrani Department of Medicine,
ARIC Manuscript Proposal # 1036r. PC Reviewed: _07/26/05 Status: D Priority: SC Reviewed: Status: Priority:
 ARIC Manuscript Proposal # 1036r PC Reviewed: _07/26/05 Status: D Priority: SC Reviewed: Status: Priority: 1.a. Full Title: The Association between Isolated vs Combined Large and Small Artery Disease with
ARIC Manuscript Proposal # 1036r PC Reviewed: _07/26/05 Status: D Priority: SC Reviewed: Status: Priority: 1.a. Full Title: The Association between Isolated vs Combined Large and Small Artery Disease with
Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in South Indian Essential Hypertensive Patient
 Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in South Indian Essential Hypertensive Patient Dr. Peersab.M. Pinjar 1, Dr Praveenkumar Devarbahvi 1 and Dr Vasudeva Murthy.C.R 2, Dr.S.S.Bhat 1, Dr.Jayaraj S G 1
Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in South Indian Essential Hypertensive Patient Dr. Peersab.M. Pinjar 1, Dr Praveenkumar Devarbahvi 1 and Dr Vasudeva Murthy.C.R 2, Dr.S.S.Bhat 1, Dr.Jayaraj S G 1
Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes
 VBWG Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes Nicola Abate, M.D., F.N.L.A. Professor and Chief Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston, Texas Coronary
VBWG Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes Nicola Abate, M.D., F.N.L.A. Professor and Chief Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston, Texas Coronary
Study of fixed dose combination for the management of cardiovascular diseases
 World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-331; ISSN (Online): 2321-386 Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original Article Study of fixed dose combination for the management
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-331; ISSN (Online): 2321-386 Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original Article Study of fixed dose combination for the management
Established Risk Factors for Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
 Getting Patients to Make Small Lifestyle Changes That Result in SIGNIFICANT Improvements in Health - Prevention of Diabetes and Obesity for Better Health Maureen E. Mays, MD, MS, FACC Director ~ Portland
Getting Patients to Make Small Lifestyle Changes That Result in SIGNIFICANT Improvements in Health - Prevention of Diabetes and Obesity for Better Health Maureen E. Mays, MD, MS, FACC Director ~ Portland
The New England Journal of Medicine CUMULATIVE EFFECTS OF HIGH CHOLESTEROL LEVELS, HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE, AND CIGARETTE SMOKING ON CAROTID STENOSIS
 CUMULATIVE EFFECTS OF HIGH CHOLESTEROL LEVELS, HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE, AND CIGARETTE SMOKING ON CAROTID STENOSIS PETER W.F. WILSON, M.D., JEFFREY M. HOEG, M.D., RALPH B. D AGOSTINO, PH.D., HALIT SILBERSHATZ,
CUMULATIVE EFFECTS OF HIGH CHOLESTEROL LEVELS, HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE, AND CIGARETTE SMOKING ON CAROTID STENOSIS PETER W.F. WILSON, M.D., JEFFREY M. HOEG, M.D., RALPH B. D AGOSTINO, PH.D., HALIT SILBERSHATZ,
Associations between cardiovascular risk factors and
 Predictors of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Progression in Young Adults The Bogalusa Heart Study Heather M. Johnson, MD; Pamela S. Douglas, MD; Sathanur R. Srinivasan, PhD; M. Gene Bond, PhD; Rong Tang,
Predictors of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Progression in Young Adults The Bogalusa Heart Study Heather M. Johnson, MD; Pamela S. Douglas, MD; Sathanur R. Srinivasan, PhD; M. Gene Bond, PhD; Rong Tang,
Assessing Cardiovascular Risk to Optimally Stratify Low- and Moderate- Risk Patients. Copyright. Not for Sale or Commercial Distribution
 CLINICAL Viewpoint Assessing Cardiovascular Risk to Optimally Stratify Low- and Moderate- Risk Patients Copyright Not for Sale or Commercial Distribution By Ruth McPherson, MD, PhD, FRCPC Unauthorised
CLINICAL Viewpoint Assessing Cardiovascular Risk to Optimally Stratify Low- and Moderate- Risk Patients Copyright Not for Sale or Commercial Distribution By Ruth McPherson, MD, PhD, FRCPC Unauthorised
Risk Factors of Carotid Stenosis in First-Ever Ischemic Stroke in Taiwan: A Hospital-based Study
 237 Risk Factors of Carotid Stenosis in First-Ever Ischemic Stroke in Taiwan: A Hospital-based Study Chien-Hung Chang, Yeu-Jhy Chang, Tsong-Hai Lee, Kai-Cheng Hsu, and Shan-Jin Ryu Abstract- Objective:
237 Risk Factors of Carotid Stenosis in First-Ever Ischemic Stroke in Taiwan: A Hospital-based Study Chien-Hung Chang, Yeu-Jhy Chang, Tsong-Hai Lee, Kai-Cheng Hsu, and Shan-Jin Ryu Abstract- Objective:
CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention
 CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention Raul D. Santos MD, PhD Heart Institute-InCor University of Sao Paulo Brazil Disclosure Honoraria for consulting and speaker activities
CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention Raul D. Santos MD, PhD Heart Institute-InCor University of Sao Paulo Brazil Disclosure Honoraria for consulting and speaker activities
Title for Paragraph Format Slide
 Title for Paragraph Format Slide Presentation Title: Month Date, Year Atherosclerosis A Spectrum of Disease: February 12, 2015 Richard Cameron Padgett, MD Executive Medical Director, OHVI Pt RB Age 38
Title for Paragraph Format Slide Presentation Title: Month Date, Year Atherosclerosis A Spectrum of Disease: February 12, 2015 Richard Cameron Padgett, MD Executive Medical Director, OHVI Pt RB Age 38
Evaluation of Carotid Arterial Intima-Media Thickness (IMT) and Its Relation to Clinical Parameters in Japanese Children
 Evaluation of Carotid Arterial Intima-Media Thickness (IMT) and Its Relation to Clinical Parameters in Japanese Children a a* b a a b ʼ ʼ ʼ ʼ Clinical profiles of enrolled subjects All (n 52) Boys (n 39)
Evaluation of Carotid Arterial Intima-Media Thickness (IMT) and Its Relation to Clinical Parameters in Japanese Children a a* b a a b ʼ ʼ ʼ ʼ Clinical profiles of enrolled subjects All (n 52) Boys (n 39)
Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD: Risk stratification & management Raul Santos, MD
 Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD: Risk stratification & management Raul Santos, MD Sao Paulo Medical School Sao Paolo, Brazil Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD risk: Stratification & management Prof.
Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD: Risk stratification & management Raul Santos, MD Sao Paulo Medical School Sao Paolo, Brazil Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD risk: Stratification & management Prof.
Data Alert. Vascular Biology Working Group. Blunting the atherosclerotic process in patients with coronary artery disease.
 1994--4 Vascular Biology Working Group www.vbwg.org c/o Medical Education Consultants, LLC 25 Sylvan Road South, Westport, CT 688 Chairman: Carl J. Pepine, MD Eminent Scholar American Heart Association
1994--4 Vascular Biology Working Group www.vbwg.org c/o Medical Education Consultants, LLC 25 Sylvan Road South, Westport, CT 688 Chairman: Carl J. Pepine, MD Eminent Scholar American Heart Association
Carotid-Wall Intima Media Thickness and Cardiovascular Events
 original article Carotid-Wall Intima Media Thickness and Cardiovascular Events Joseph F. Polak, M.D., M.P.H., Michael J. Pencina, Ph.D., Karol M. Pencina, Ph.D., Christopher J. O Donnell, M.D., M.P.H.,
original article Carotid-Wall Intima Media Thickness and Cardiovascular Events Joseph F. Polak, M.D., M.P.H., Michael J. Pencina, Ph.D., Karol M. Pencina, Ph.D., Christopher J. O Donnell, M.D., M.P.H.,
3/25/2010. Age-adjusted incidence rates for coronary heart disease according to body mass index and waist circumference tertiles
 Outline Relationships among Regional Adiposity, Physical Activity, and CVD Risk Factors: Preliminary Results from Two Epidemiologic Studies Molly Conroy, MD, MPH Obesity Journal Club February 18, 2010
Outline Relationships among Regional Adiposity, Physical Activity, and CVD Risk Factors: Preliminary Results from Two Epidemiologic Studies Molly Conroy, MD, MPH Obesity Journal Club February 18, 2010
It is currently estimated that diabetes prevalence by
 clinical Study The Prevalence and Pattern of Dyslipidemia among Type 2 Diabetic Patients at Rural Based Hospital in Gujarat, India Hetal Pandya*, JD Lakhani**, J Dadhania, A Trivedi Abstract Only proper
clinical Study The Prevalence and Pattern of Dyslipidemia among Type 2 Diabetic Patients at Rural Based Hospital in Gujarat, India Hetal Pandya*, JD Lakhani**, J Dadhania, A Trivedi Abstract Only proper
The Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program
 44 Blood Pressure Treatment Slows the Progression of Carotid Stenosis in Patients With Isolated Systolic Hypertension Kim Sutton-Tyrrell, DrPH; Sidney K. Wolfson, Jr, MD; Lewis H. Kuller, MD Background
44 Blood Pressure Treatment Slows the Progression of Carotid Stenosis in Patients With Isolated Systolic Hypertension Kim Sutton-Tyrrell, DrPH; Sidney K. Wolfson, Jr, MD; Lewis H. Kuller, MD Background
Hyperuricemia as a Prognostic Marker in Acute Ischemic Stroke
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/23 Hyperuricemia as a Prognostic Marker in Acute Ischemic Stroke B Balaji 1, Bingi Srinivas 2 1 Associate Professor,
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/23 Hyperuricemia as a Prognostic Marker in Acute Ischemic Stroke B Balaji 1, Bingi Srinivas 2 1 Associate Professor,
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease. Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
 Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
C oronary artery disease (CAD) remains the main cause
 1286 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Association of increased carotid intima-media thickness with the extent of coronary artery disease A Kablak-Ziembicka, W Tracz, T Przewlocki, P Pieniazek, A Sokolowski, M Konieczynska...
1286 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Association of increased carotid intima-media thickness with the extent of coronary artery disease A Kablak-Ziembicka, W Tracz, T Przewlocki, P Pieniazek, A Sokolowski, M Konieczynska...
A: Epidemiology update. Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups
 A: Epidemiology update Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups Women (n = 27,939; mean age 54.7 years) who were free of symptomatic cardiovascular (CV) disease at baseline were
A: Epidemiology update Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups Women (n = 27,939; mean age 54.7 years) who were free of symptomatic cardiovascular (CV) disease at baseline were
CLINICAL STUDY. Yasser Khalil, MD; Bertrand Mukete, MD; Michael J. Durkin, MD; June Coccia, MS, RVT; Martin E. Matsumura, MD
 117 CLINICAL STUDY A Comparison of Assessment of Coronary Calcium vs Carotid Intima Media Thickness for Determination of Vascular Age and Adjustment of the Framingham Risk Score Yasser Khalil, MD; Bertrand
117 CLINICAL STUDY A Comparison of Assessment of Coronary Calcium vs Carotid Intima Media Thickness for Determination of Vascular Age and Adjustment of the Framingham Risk Score Yasser Khalil, MD; Bertrand
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Leibowitz M, Karpati T, Cohen-Stavi CJ, et al. Association between achieved low-density lipoprotein levels and major adverse cardiac events in patients with stable ischemic
Supplementary Online Content Leibowitz M, Karpati T, Cohen-Stavi CJ, et al. Association between achieved low-density lipoprotein levels and major adverse cardiac events in patients with stable ischemic
THE EFFECT OF VITAMIN-C THERAPY ON HYPERGLYCEMIA, HYPERLIPIDEMIA AND NON HIGH DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN LEVEL IN TYPE 2 DIABETES
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2013 Varikasuvu Seshadri Reddy et al., 2013 Review Article ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 2, No. 1, January 2013 2013 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved THE EFFECT OF VITAMIN-C
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2013 Varikasuvu Seshadri Reddy et al., 2013 Review Article ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 2, No. 1, January 2013 2013 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved THE EFFECT OF VITAMIN-C
Short stature is an inflammatory disadvantage among middle-aged Japanese men
 Environ Health Prev Med (2016) 21:361 367 DOI 10.1007/s12199-016-0538-y REGULAR ARTICLE Short stature is an inflammatory disadvantage among middle-aged Japanese men Yuji Shimizu 1,2 Hiroyuki Yoshimine
Environ Health Prev Med (2016) 21:361 367 DOI 10.1007/s12199-016-0538-y REGULAR ARTICLE Short stature is an inflammatory disadvantage among middle-aged Japanese men Yuji Shimizu 1,2 Hiroyuki Yoshimine
The metabolic syndrome is increasingly
 Metabolic Syndrome/Insulin Resistance Syndrome/Pre-Diabetes O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E The Metabolic Syndrome in Older Individuals: Prevalence and Prediction of Cardiovascular Events The Cardiovascular
Metabolic Syndrome/Insulin Resistance Syndrome/Pre-Diabetes O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E The Metabolic Syndrome in Older Individuals: Prevalence and Prediction of Cardiovascular Events The Cardiovascular
Correlation of Common Carotid Artery Intima Media Thickness, Intracranial Arterial Stenosis and Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment
 207 Correlation of Common Carotid Artery Intima Media Thickness, Intracranial Arterial Stenosis and Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment Yong-Hui Lee and Shoou-Jeng Yeh Abstract- Background and Purpose: Atherosclerosis
207 Correlation of Common Carotid Artery Intima Media Thickness, Intracranial Arterial Stenosis and Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment Yong-Hui Lee and Shoou-Jeng Yeh Abstract- Background and Purpose: Atherosclerosis
the U.S. population, have some form of cardiovascular disease. Each year, approximately 6 million hospitalizations
 Cardioprotection: What is it? Who needs it? William B. Kannel, MD, MPH From the Department of Preventive Medicine and Epidemiology, Evans Department of Clinical Research, Boston University School of Medicine,
Cardioprotection: What is it? Who needs it? William B. Kannel, MD, MPH From the Department of Preventive Medicine and Epidemiology, Evans Department of Clinical Research, Boston University School of Medicine,
Atherosclerosis is a complex cardiovascular disorder that
 Genetic Basis of Variation in Carotid Artery Plaque in the San Antonio Family Heart Study Kelly J. Hunt, PhD; Ravindranath Duggirala, PhD; Harald H.H. Göring, PhD; Jeff T. Williams, PhD; Laura Almasy,
Genetic Basis of Variation in Carotid Artery Plaque in the San Antonio Family Heart Study Kelly J. Hunt, PhD; Ravindranath Duggirala, PhD; Harald H.H. Göring, PhD; Jeff T. Williams, PhD; Laura Almasy,
