EVALUATION OF CAROTID ARTERY STENOSIS IN STROKE/TRANSIENT ISCHAEMIC ATTACK Nambakam Tanuja Subramanyam 1, Naveen Kumar P 2, Girish P.
|
|
|
- Griselda Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EVALUATION OF CAROTID ARTERY STENOSIS IN STROKE/TRANSIENT ISCHAEMIC ATTACK Nambakam Tanuja Subramanyam 1, Naveen Kumar P 2, Girish P. Vakrani 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Nambakam Tanuja Subramanyam, Naveen Kumar P, Girish P. Vakrani. Evaluation of Carotid Artery Stenosis in Stroke/Transient Ischaemic Attack. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences 2015; Vol. 4, Issue 56, July 13; Page: , DOI: /jemds/2015/1406 ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: Stroke remains the second leading cause of death worldwide, after ischaemic heart disease. Patients with carotid artery stenosis are at higher risk of development of stroke. Carotid atherosclerosis occurs in patients with atherosclerotic risk factors like diabetes mellitus, hypertension, smoking and hyperlipidemia. Carotid artery stenosis can be assessed by means of noninvasive high-resolution B-mode ultrasonography of the carotid arteries. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES: 1). To estimate the prevalence of carotid artery stenosis in ischaemic stroke/transient ishaemic attack patients. 2). To estimate whether there was any association between carotid artery stenosis and important risk factors such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyper lipidemia with control group. METHODS AND MATERIALS: Acute ischaemic/tia stroke patients with CT-Brain showing infarcts were enrolled for the study. All patients were subjected to CT scan brain study and colour Doppler study of extracranial carotid arteries. The systolic and diastolic velocity of blood flow, and the ratio of peak systolic velocities of common carotid arteries were assessed. RESULTS: DM, HTN, Smoking & Hyperlipidemia acted as risk factors for carotid stenosis. The prevalence of carotid stenosis in our study was 60%. The prevalence of mild, moderate and severe stenosis were 34%, 10% and 16% respectively. The distribution of carotid stenosis was equal on both sides. The statistical significance was calculated using Chi-square test. Statistical significance was taken when P value was <0.05. Statistical analysis was carried using standard formulae. Microsoft Excel 2007 and SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Sciences) Version 17.0 software were used for data entry and analysis. CONCLUSIONS: Carotid stenosis was one of the common causes of ischaemic stroke. There was a statistically significant correlation between increasing age, male gender, smoking, diabetes mellitus, hypertension and hyperlipidemia and the prevalence of carotid stenosis. KEYWORDS: Carotid artery stenosis, Stroke, Ultrasonography. INTRODUCTION: Stroke remains the second leading cause of death worldwide 1, after ischaemic heart disease. 85% of stroke cases are due to infarction and 15% are due to haemorrhagic. Patients with carotid artery stenosis are at higher risk of development of stroke and recurrence of stroke after a stroke/tia. 2 Carotid atherosclerosis occurs in patients with atherosclerotic risk factors like diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension (HTN), smoking and hyperlipidemia. Carotid atherosclerosis leads to plaque formation and these plaques gradually increase in size and cause stenosis. Atherosclerotic plaques interrupt the endothelium and then ulcerate. As the endothelium is breached, platelets adhere to the wall and a hemostatic plug is formed. This platelet nidus initiates coagulation cascade and an occlusive thrombus is formed. 2 Thrombus formation on an atherosclerotic plaque leads to distal embolisation and causes occlusion of blood vessels (Or) a severe stenosis may cause hypoperfusion and infarct of the brain tissue. Atherosclerotic plaques and stenosis can be detected by noninvasive ultrasound imaging of the carotid arteries which has high sensitivity and specificity in detecting carotid artery stenosis. J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 56/ July 13, 2015 Page 9743
2 Carotid artery stenosis can be assessed by means of noninvasive high-resolution B-mode ultrasonography of the carotid arteries. 3 Carotid ultrasonography combines B mode ultrasound image with a doppler ultrasound assessment of blood flow velocity. These plaques alter the blood flow haemodynamics and increase the systolic flow velocity. With this increased systolic flow velocity stenosis can be detected and severity can be assessed. This can be helpful in management protocol for ischaemic stroke patients with carotid artery stenosis as a cause. 4 In this study, we attempted to find out the prevalence of carotid artery stenosis in ischaemic stroke patients and whether they are prone for recurrence or not, so that aggressive secondary preventive measures can be directed to those patients. MATERIALS AND METHODS: AIMS & OBJECTIVES: 1. To estimate the prevalence of carotid artery stenosis in ischaemic stroke/transient ischaemic attack patients. 2. To estimate whether there is any association between carotid artery stenosis and important risk factors such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperlipidemia with control group. Source of Data: Cases were selected from the patients admitted to hospital. Statistical Method: Duration based study with a minimum of 50 cases and 50 controls for a period of 18 months from January 2012 to June Study Design: Cross sectional hospital based prevalence study. Inclusion Criteria: 1. Age: 18 to 75 Yrs. 2. Sex: Both Gender. 3. Ischaemic stroke/transient ischaemia attack. 4. Patients with asymptomatic carotid bruit with hypertension/ hyperlidaemia/diabetes mellitus. Exclusion Criteria: 1. Patients with haemorrhagic stroke. 2. Patients with head injury. 3. Stroke due to infections like tuberculosis. 4. Stroke with metabolic Emergencies. METHODOLOGY: In all patients admitted with symptoms suggestive of stroke/transient ischemia attack (TIA), careful methodical examination of the central nervous system carried out recording all the physical signs in order. In all the cases, the preceding symptoms and risk factors were enquired. All patients were subjected to CT scan brain and colour doppler study of extracranial carotid arteries, the systolic and diastolic velocity of blood flow, and the ratio of peak systolic velocities of common carotid arteries, carotid intimal medial thickness, presence of atheromatous plaque and thrombus were looked for and then the percentage of stenosis of the affected patients were assessed. The doppler instrument used in the study was Philips. It has a triplex scanning system comprising of 1. High resolution B-mode imaging, 2. Pulsed wave doppler sonography, 3. Color doppler flow imaging. J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 56/ July 13, 2015 Page 9744
3 Statistical Analysis: Statistical analysis was carried out for 50 subjects (Cases) with stroke/tia symptoms and 50 patients were taken as controls without any symptoms of stroke/ TIA and risk factors. Age, presence of DM, HTN, smoking, alcoholism and hyperlipidemia were analyzed in patients with and without carotid stenosis admitted for acute ischaemic stroke/tia in cases. Carotid artery intima thickness was estimated in both cases and controls by carotid doppler. The statistical significance was calculated using Chi-square test. Statistical significance was taken when P value was <0.05. Statistical analysis was carried using standard formulae. Microsoft Excel 2007 and SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Sciences) Version 17.0 software s were used for data entry and analysis. RESULTS: We included 50 patients (Cases) with acute ischaemic/tia stroke and 50 controls in our study and all of them had a carotid doppler done. Risk Factor Analysis in Carotid Stenosis Patients: The prevalence of carotid stenosis in acute ischaemic stroke/tia patients was about 60%. Carotid artery stenosis was more common in diabetics (54%) than in non-diabetics with p value of (Table 1). the prevalence of carotid stenosis was more in hypertensives (74%) than in normotensives (18.8%) with p value of More smokers (70%) had carotid stenosis than non-smokers (18%) with p value of % of patients with stroke/tia were above 60years. It was found that percentage of patients with carotid stenosis was increasing with increase in age. 83.3% patients with carotid artery stenosis were male. The prevalence of patients with carotid stenosis with increased cholesterol (>200mg/dl), increased triglycerides (TGL >150mg/dl), decreased high density lipoproteins (HDL <40mg/dl) and increased low density lipoproteins (LDL >130 mg/dl) were 76.6%, 90%, 86% and 68.4% respectively with p valve: The prevalence of mild stenosis and moderate stenosis were more than severe stenosis. In our study, 3 cases with severe stenosis had carotid bruit. 30 patients had carotid stenosis. The prevalence of carotid stenosis in our study was 60%. The prevalence of mild, moderate and severe stenosis were 34%, 10% and 16% respectively. The distribution of carotid stenosis was equal on both sides, 12 patient had both side stenosis and out of 30 patients with carotid stenosis 16 had stenosis in CCA and 14 Patients had stenosis in ICA and 06 patients had atheromatous plaque. Out of 50 patients in our study, 30 patients had stenosis, 07 patients had atheromatous plaque and 03 patients had carotid bruit. There was no particular side preponderance of carotid stenosis and it was more or less equal on both sides and there was no statistical significance between the two sides. In our study, severe form of carotid intimal thickness was found in case group (Table 2). In our study, 03 patients had carotid stenosis and 07 patients had atheromatous plaque out of 50 patients in control group. Prevalence of stenosis was more in diabetics in cases group than control group and carotid artery media thickness was also increased in diabetics and it was statistically significant with p value of Prevalence of stenosis was more in hypertensives in cases group than control group and carotid artery media thickness was also increased in hypertensives and it was statistically significant. J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 56/ July 13, 2015 Page 9745
4 Prevalence of stenosis was more in increased cholesterol in cases group than control group and carotid artery media thickness was also increased in hyperlipidemia and it was statistically significant. DISCUSSION: In our study, we found that the prevalence of carotid stenosis in acute ischaemic stroke/tia patients was about 60%, consistent with studies done by Oliviero et al. (1) In their study, the prevalence of carotid stenosis was about 53% in ischaemic stroke patients. The percentage of patients with significant stenosis (>70%) was about 16% in our study which is associated with the recurrence of stroke. The prevalence of significant stenosis in studies conducted in Western population was about 14% (2) and 21%. (3) This variation could be due to racial differences. (4,5) Extracranial carotid artery stenosis was more commoner in whites and men. (6) The prevalence of significant stenosis in a study conducted by M. M. Singh et al was about 32%. (7) In our study, the prevalence of moderate stenosis was about 10%, mild stenosis was 34%, and 40% of stroke patients had no carotid stenosis. The prevalence of asymptomatic carotid stenosis (>50%) in a study conducted in asymptomatic carotid stenosis patients by P. P. Mineva et al was 6.4%. (8) 62 Age and Carotid Stenosis: We found in our study, the percentage of patients who had carotid stenosis, increased with increase in age. (9) The prevalence in patients <50 years, years, >60 years was about 6.7%, 26.6%, and 66.7% respectively. In a study conducted by K. Rajamani et al (9) showed increasing incidence of carotid stenosis with increase in age in African American men. Carotid stenosis in keeping with atherosclerotic diseases, increases with age. The risk of carotid atherosclerosis increases after 45 years of age. Gender and Carotid Stenosis: We found that the prevalence of carotid stenosis was more in males (83.3%) than females (16.7%), which was consistent with studies conducted by Jacob et al. (10) Risk Factors of Carotid Atherosclerosis: 1. Diabetes Mellitus and Carotid Stenosis: Carotid artery stenosis was more common in diabetics (54%) than in non-diabetics (21%) and it was statistically significant. K. Rajamani et al (9) have shown in their study that carotid stenosis was more common in diabetics (22%). In correlation with cases and controls in our study, 32 patients had DM. Out of 32 in cases group, 25 patients had stenosis and in controls, only 04 patients had stenosis and it was statistically significant (p-valve: ). 2. Hypertension and Carotid Stenosis: In our study, we found that hypertension was one of the risk factors for carotid stenosis and the prevalence of carotid stenosis was more in hypertensives (74%) than in normotensives (18.8%) consistent with studies done by Duncan et al, Sutton et al. (11) In their study, they found that asymptomatic carotid stenosis was found in 25% of adults with hypertension, than those without hypertension. Hypertension accelerates carotid atherosclerosis and stenosis. (12,13) The predictors of carotid stenosis were systolic BP >160 mmhg and in isolated systolic hypertension patients, when diastolic BP was <75 mmhg, there was a strong correlation with carotid stenosis. In correlation with cases and controls, in our study 37 patients had hypertension. Out of 37 patients, 26 had stenosis and in controls, only 04 patients had asymptomatic stenosis and it was statistically significant (p-valve: ). J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 56/ July 13, 2015 Page 9746
5 3. Smoking and Carotid Stenosis: In our study, we found that smoking acts as a risk factor for carotid stenosis. More smokers (70%) had carotid stenosis than non-smokers (18%), which was also shown by H.R. Muller et al. (14) 4. Site and Carotid Stenosis: In our study, carotid stenosis was found at the bifurcation of common carotid artery (CCA), and the origin of internal carotid artery (ICA). Carotid stenosis was equal on both sides and was more on CCA than ICA. CCA stenosis was found in 53% of patients and ICA stenosis was found in 46% of patients. Overall, we found that age, male sex, smoking, HT, DM and Hyperlipidemia were associated with increased rate of carotid stenosis. In our study, every patient with carotid artery stenosis had one or the other risk factor for carotid atherosclerosis. In other words, there was no patient with carotid artery stenosis, without any risk factor in our study. Hence, asymptomatic patients with these risk factors should be screened for carotid stenosis to prevent stroke/tia. (15) 5. Hyperlipidemia and Carotid Stenosis: In our study, the prevalence of patients with carotid stenosis with increased cholesterol (> 200mg/dl), increased TGL (>150mg/dl), decreased HDL (<40 mg/dl) and increased LDL (>130 mg/dl) were 76.6%, 90%, 86% and 68.4% respectively. The prevalence in patients with decreased cholesterol (<200mg/dl), decreased TGL (<150mg/dl), Increase HDL (>40mg/dl) and decreased LDL (<130mg/dl) were 38.8%, 10%, 20% and 8.3% respectively. In correlation with cases and controls, carotid artery intima thickness and prevalence of stenosis is increased in cases with increased cholesterol, increased LDL, decreased HDL, increased TGL with statistically significant. {p valve: (chol), (LDL), 0.002(HDL), (TGL)}. They were associated with extra cranial large vessel atherosclerosis leading to increase in IMT and plaque formation and stenosis. (16) CONCLUSIONS: Carotid stenosis is one of the common causes of ischaemic stroke. About 60% of ischaemic stroke/tia patients had carotid stenosis in our study. The prevalence of carotid stenosis increases with increase in age, male gender, smoking, DM, HT & Hyperlipidemia. DM, HTN, Smoking & Hyperlipidemia act as risk factors for carotid stenosis. Hence, patients with DM, HTN & Hyperlipidemias should have their carotid arteries screened to detect asymptomatic carotid stenosis and if present, should have their blood glucose, blood pressure and lipids under control and should be started on antiplatelet drugs and statins for plaque regression and for primary prevention of stroke. REFERENCES: 1. Oliviero U, Orefice G, Coppola G, Scherillo G, Ascione S, Casaburi C et al. Carotid atherosclerosis in ischaemic stroke patients. Int Journal of Angiology Jun; 21(2): Tsorlen et al. Cause of cerebral infarction in carotid territory. Stroke, 1985; Vol. 16: Gillian E. Mead, Helen Shingler, Anne Farrell, Paul A. O'neill, Charles N. Mccollum. Carotid disease in acute stroke. Age and ageing. 1998; 27: J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 56/ July 13, 2015 Page 9747
6 4. LR Caplan, Gorelick PB, D. B. Hier. Race, Sex and Occlusive cerebro vascular disease. Stroke. 1986; 17: L.R. Caplan, Gorelick PB. Therapeutic implications of racial differences in anterior circulation disease. Neurology. 1984; 34: Fisher et al: Occlusion of carotid arteries: Further experiences. Archieves of Neurology. 1984; 72: M.M. Singh, S. Gupta et al. Carotid stenosis in Stroke. JAPI.1996; Vol.44 No.12: P. P. Mineva, I.C. Manchev, D. I. Hadjiev. Prevalence and outcome of asymptomatic carotid stenosis: A population based ultrasonographic study. European Journal of Neurology. July 2002; Vol-9: Issue-4: Kumar Rajamani, Mohammed Sunbulli, Bradley S. Jacobs, Elizabeth Berlow, James D. Marsh, Marvin W. Kroninberg et al. Detection of carotid stenosis in African Americans with ischemic heart disease. Journal of Vascular Surgery. Vol.43: Jacob Selhub et al. Association between Homocysteine & Carotid stenosis. NEJM, 1995; Vol.333: Page Kim Sutton-Tyrrell, Hope G. Alcorn, Sidney K. Wolfson Jr., Sheryl F. Kelsey, Lewis H. Kuller. Predictors of Carotid Stenosis in Older Adults with and without Isolated Systolic Hypertension: Stroke. 1993; Vol-24: Page G.Van Melle, J. Bogousslavsky, P. A. Despland, F. Regli. Alcohol consumption and carotid atherosclerosis in the Lausanne stroke registry: Stroke. 1990; Vol-21: O'Leary DH, Anderson KM, Kase CS, Wolf PA, Kannel WB: Extracranial carotid atherosclerosis in a general population. The Framingham Study (abstract). Stroke. 1988; 19: H.R. Muller et al: Smoking and carotid stenosis: Journal of Neurology. 1990: Andrew P.Gaseki, Michael Eliasziw, Henry J.M. Barnett. Serum cholesterol is associated with severity of stenosis in symptomatic patients: Cerebro vascular disease. 1994; Vol-4: No-6: Page Glagov S, Zarins C, Giddens DP, Ku DN: Hemodynamics and atherosclerosis: Insides and perspectives gained from studies of human arteries: Arch Pathol Lab Med Oct; 112(10): TOTAL STENOSIS NO STENOSIS DM NON-DM TOTAL Table 1: Correlation between diabetes mellitus and carotid Stenosis p value: J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 56/ July 13, 2015 Page 9748
7 IMT (range) No. of patients in Cases No. of patients in Controls > TOTAL Table 2: Comparison of Intima Media thickness between Control and Case Group showing more severe intima media thickness (IMT) in case group AUTHORS: 1. Nambakam Tanuja Subramanyam 2. Naveen Kumar P. 3. Girish P. Vakrani PARTICULARS OF CONTRIBUTORS: 1. Assistant Professor, Department of General Medicine, Vydehi Institute of Medical Sciences & Research Centre. 2. Senior Resident, Department of General Medicine, Vydehi Institute of Medical Sciences & Research Centre. FINANCIAL OR OTHER COMPETING INTERESTS: None 3. Assistant Professor, Department of Nephrology, Vydehi Institute of Medical Sciences & Research Center. NAME ADDRESS ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Dr. Nambakam Tanuja Subramanyam, A-29, Vydehi Hospital Staff Quarters, #82, EPPI Area, Whitefield, Bangalore-66, India. tanuja1069@rediffmail.com Date of Submission: 21/06/2015. Date of Peer Review: 23/06/2015. Date of Acceptance: 06/07/2015. Date of Publishing: 10/07/2015. J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 56/ July 13, 2015 Page 9749
Original Research Article
 A STUDY TO ESTIMATE SUBCLINICAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS BY MEASURING THE CAROTID INTIMAL MEDIAL THICKNESS Natarajan Kandasamy 1, Rajan Ganesan 2, Thilakavathi Rajendiran
A STUDY TO ESTIMATE SUBCLINICAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS BY MEASURING THE CAROTID INTIMAL MEDIAL THICKNESS Natarajan Kandasamy 1, Rajan Ganesan 2, Thilakavathi Rajendiran
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease. Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
 Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Treatment Considerations for Carotid Artery Stenosis. Danielle Zielinski, RN, MSN, ACNP Rush University Neurosurgery
 Treatment Considerations for Carotid Artery Stenosis Danielle Zielinski, RN, MSN, ACNP Rush University Neurosurgery 4.29.2016 There is no actual or potential conflict of interest in regards to this presentation
Treatment Considerations for Carotid Artery Stenosis Danielle Zielinski, RN, MSN, ACNP Rush University Neurosurgery 4.29.2016 There is no actual or potential conflict of interest in regards to this presentation
Slide 1. Slide 2 Conflict of Interest Disclosure. Slide 3 Stroke Facts. The Treatment of Intracranial Stenosis. Disclosure
 Slide 1 The Treatment of Intracranial Stenosis Helmi Lutsep, MD Vice Chair and Dixon Term Professor, Department of Neurology, Oregon Health & Science University Chief of Neurology, VA Portland Health Care
Slide 1 The Treatment of Intracranial Stenosis Helmi Lutsep, MD Vice Chair and Dixon Term Professor, Department of Neurology, Oregon Health & Science University Chief of Neurology, VA Portland Health Care
STUDY OF C-REACTIVE PROTEIN IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Medhini V. J 1, Hally Karibasappa 2
 STUDY OF C-REACTIVE PROTEIN IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Medhini V. J 1, Hally Karibasappa 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Medhini V. J, Hally Karibasappa. Study of C-Reactive Protein in Acute Ischemic Stroke.
STUDY OF C-REACTIVE PROTEIN IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Medhini V. J 1, Hally Karibasappa 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Medhini V. J, Hally Karibasappa. Study of C-Reactive Protein in Acute Ischemic Stroke.
PAPER F National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions at the Royal College of Physicians
 6.3 Early carotid imaging in acute stroke or TIA Evidence Tables IMAG4: Which patients with suspected stroke/tia should be referred for urgent carotid imaging? Reference Ahmed AS, Foley E, Brannigan AE
6.3 Early carotid imaging in acute stroke or TIA Evidence Tables IMAG4: Which patients with suspected stroke/tia should be referred for urgent carotid imaging? Reference Ahmed AS, Foley E, Brannigan AE
Asymptomatic Carotid Stenosis To Do or Not To Do
 Asymptomatic Carotid Stenosis To Do or Not To Do October 22, 2016 Neurosciences: Updates and Controversies Andrew C. MacDougall, MD Advocate Medical Group Advocate Lutheran General Hospital Principle
Asymptomatic Carotid Stenosis To Do or Not To Do October 22, 2016 Neurosciences: Updates and Controversies Andrew C. MacDougall, MD Advocate Medical Group Advocate Lutheran General Hospital Principle
CVD Risk Assessment. Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic
 CVD Risk Assessment Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic What is Risk? A cumulative probability of an event, usually expressed as percentage e.g.: 5 CV events in 00 pts = 5% risk This
CVD Risk Assessment Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic What is Risk? A cumulative probability of an event, usually expressed as percentage e.g.: 5 CV events in 00 pts = 5% risk This
Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings?
 Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings? Dougalis A, Soulaidopoulos S, Cholongitas E, Chalevas P, Vettas Ch, Doumtsis P, Vaitsi K, Diavasti M, Mandala E, Garyfallos A 4th Department
Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings? Dougalis A, Soulaidopoulos S, Cholongitas E, Chalevas P, Vettas Ch, Doumtsis P, Vaitsi K, Diavasti M, Mandala E, Garyfallos A 4th Department
Prevalence of cerebrovascular accidents (CVA) in obese hypertensives among inpatients of Govt.General Hospital, Guntur
 Original article Prevalence of cerebrovascular accidents (CVA) in obese hypertensives among inpatients of Govt.General Hospital, Guntur 1 Dr. Dr.Uday Shankar Sanakayala, 2 Dr. T. V. Adi Seshu Babu, 3 Dr.
Original article Prevalence of cerebrovascular accidents (CVA) in obese hypertensives among inpatients of Govt.General Hospital, Guntur 1 Dr. Dr.Uday Shankar Sanakayala, 2 Dr. T. V. Adi Seshu Babu, 3 Dr.
The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke
 Smoking The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke Wei-Chieh Weng, M.D. Department of Neurology, Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital, Kee-Lung, Taiwan Smoking related mortality Atherosclerotic vascular disease
Smoking The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke Wei-Chieh Weng, M.D. Department of Neurology, Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital, Kee-Lung, Taiwan Smoking related mortality Atherosclerotic vascular disease
Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients With Coronary Atherosclerosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.8.317 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.8.317 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients
Carotid intima media thickness as an usefull tool in predicting cerebrovaskular events
 Carotid intima media thickness as an usefull tool in predicting cerebrovaskular events Poster No.: C-0005 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Rahimic - Catic; Sarajevo/BA
Carotid intima media thickness as an usefull tool in predicting cerebrovaskular events Poster No.: C-0005 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Rahimic - Catic; Sarajevo/BA
A study of brachial artery flow mediated dilatation and carotid intima media thickness in subjects having risk factors for coronary artery disease
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20171037 A study of brachial
International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20171037 A study of brachial
MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY RISK FROM CAROTID ARTERY ATHEROSCLEROSIS. 73 year old NS right-handed male applicant for $1 Million life insurance
 MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY RISK FROM CAROTID ARTERY ATHEROSCLEROSIS October 17, 2012 AAIM Triennial Conference, San Diego Robert Lund, MD What Is The Risk? 73 year old NS right-handed male applicant for $1
MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY RISK FROM CAROTID ARTERY ATHEROSCLEROSIS October 17, 2012 AAIM Triennial Conference, San Diego Robert Lund, MD What Is The Risk? 73 year old NS right-handed male applicant for $1
MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY RISK FROM CAROTID ARTERY ATHEROSCLEROSIS. 73 year old NS right-handed male applicant for $1 Million Life Insurance
 MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY RISK FROM CAROTID ARTERY ATHEROSCLEROSIS October 17, 2012 AAIM Triennial Conference, San Diego Robert Lund, MD What Is The Risk? 73 year old NS right-handed male applicant for $1
MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY RISK FROM CAROTID ARTERY ATHEROSCLEROSIS October 17, 2012 AAIM Triennial Conference, San Diego Robert Lund, MD What Is The Risk? 73 year old NS right-handed male applicant for $1
The Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program
 44 Blood Pressure Treatment Slows the Progression of Carotid Stenosis in Patients With Isolated Systolic Hypertension Kim Sutton-Tyrrell, DrPH; Sidney K. Wolfson, Jr, MD; Lewis H. Kuller, MD Background
44 Blood Pressure Treatment Slows the Progression of Carotid Stenosis in Patients With Isolated Systolic Hypertension Kim Sutton-Tyrrell, DrPH; Sidney K. Wolfson, Jr, MD; Lewis H. Kuller, MD Background
Management of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis (ICAS)/intracranial atherosclerosis
 Management of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis (ICAS)/intracranial atherosclerosis Tim Mikesell, D.O. Oct 22, 2016 Stroke facts Despite progress in decreasing stroke incidence and mortality, stroke
Management of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis (ICAS)/intracranial atherosclerosis Tim Mikesell, D.O. Oct 22, 2016 Stroke facts Despite progress in decreasing stroke incidence and mortality, stroke
Evaluation of Carotid Vessels and Vertebral Artery in Stroke Patients with Color Doppler Ultrasound and MR Angiography
 Evaluation of Carotid Vessels and Vertebral Artery in Stroke Patients with Color Doppler Ultrasound and MR Angiography Dr. Pramod Shaha 1, Dr. Vinay Raj R 2, Dr. (Brig) K. Sahoo 3 Abstract: Aim & Objectives:
Evaluation of Carotid Vessels and Vertebral Artery in Stroke Patients with Color Doppler Ultrasound and MR Angiography Dr. Pramod Shaha 1, Dr. Vinay Raj R 2, Dr. (Brig) K. Sahoo 3 Abstract: Aim & Objectives:
Stroke/TIA. Tom Bedwell
 Stroke/TIA Tom Bedwell tab1g11@soton.ac.uk The Plan Definitions Anatomy Recap Aetiology Pathology Syndromes Brocas / Wernickes Investigations Management Prevention & Prognosis TIAs Key Definitions Transient
Stroke/TIA Tom Bedwell tab1g11@soton.ac.uk The Plan Definitions Anatomy Recap Aetiology Pathology Syndromes Brocas / Wernickes Investigations Management Prevention & Prognosis TIAs Key Definitions Transient
How would you manage Ms. Gold
 How would you manage Ms. Gold 32 yo Asian woman with dyslipidemia Current medications: Simvastatin 20mg QD Most recent lipid profile: TC = 246, TG = 100, LDL = 176, HDL = 50 What about Mr. Williams? 56
How would you manage Ms. Gold 32 yo Asian woman with dyslipidemia Current medications: Simvastatin 20mg QD Most recent lipid profile: TC = 246, TG = 100, LDL = 176, HDL = 50 What about Mr. Williams? 56
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1
 ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1 HOWTOCITETHISARTICLE: Srinivasa Rao Malladi. Association between Common Carotid
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1 HOWTOCITETHISARTICLE: Srinivasa Rao Malladi. Association between Common Carotid
Protokollanhang zur SPACE-2-Studie Neurology Quality Standards
 Protokollanhang zur SPACE-2-Studie Neurology Quality Standards 1. General remarks In contrast to SPACE-1, the neurological center participating in the SPACE-2 trial will also be involved in the treatment
Protokollanhang zur SPACE-2-Studie Neurology Quality Standards 1. General remarks In contrast to SPACE-1, the neurological center participating in the SPACE-2 trial will also be involved in the treatment
Carotid Artery Stenting
 Carotid Artery Stenting JESSICA MITCHELL, ACNP CENTRAL ILLINOIS RADIOLOGICAL ASSOCIATES External Carotid Artery (ECA) can easily be identified from Internal Carotid Artery (ICA) by noticing the branches.
Carotid Artery Stenting JESSICA MITCHELL, ACNP CENTRAL ILLINOIS RADIOLOGICAL ASSOCIATES External Carotid Artery (ECA) can easily be identified from Internal Carotid Artery (ICA) by noticing the branches.
Alan Barber. Professor of Clinical Neurology University of Auckland
 Alan Barber Professor of Clinical Neurology University of Auckland Presented with Non-fluent dysphasia R facial weakness Background Ischaemic heart disease Hypertension Hyperlipidemia L MCA branch
Alan Barber Professor of Clinical Neurology University of Auckland Presented with Non-fluent dysphasia R facial weakness Background Ischaemic heart disease Hypertension Hyperlipidemia L MCA branch
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
 BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
Introduction. Risk factors of PVD 5/8/2017
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
Redgrave JN, Coutts SB, Schulz UG et al. Systematic review of associations between the presence of acute ischemic lesions on
 6. Imaging in TIA 6.1 What type of brain imaging should be used in suspected TIA? 6.2 Which patients with suspected TIA should be referred for urgent brain imaging? Evidence Tables IMAG1: After TIA/minor
6. Imaging in TIA 6.1 What type of brain imaging should be used in suspected TIA? 6.2 Which patients with suspected TIA should be referred for urgent brain imaging? Evidence Tables IMAG1: After TIA/minor
Michael Horowitz, MD Pittsburgh, PA
 Michael Horowitz, MD Pittsburgh, PA Introduction Cervical Artery Dissection occurs by a rupture within the arterial wall leading to an intra-mural Hematoma. A possible consequence is an acute occlusion
Michael Horowitz, MD Pittsburgh, PA Introduction Cervical Artery Dissection occurs by a rupture within the arterial wall leading to an intra-mural Hematoma. A possible consequence is an acute occlusion
HDL and Arterial Wall
 JIFA January 31th 2014 HDL and Arterial Wall P-J TOUBOUL INSERM698 Bichat University Conflict of Interest M Ath intellectual property owner Involvement in R & D for atherosclerosis software developments
JIFA January 31th 2014 HDL and Arterial Wall P-J TOUBOUL INSERM698 Bichat University Conflict of Interest M Ath intellectual property owner Involvement in R & D for atherosclerosis software developments
A Study to Show Postprandial Hypertriglyceridemia as a Risk Factor for Macrovascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetis Mellitus
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/21 A Study to Show Postprandial Hypertriglyceridemia as a Risk Factor for Macrovascular Complications in Bingi Srinivas
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/21 A Study to Show Postprandial Hypertriglyceridemia as a Risk Factor for Macrovascular Complications in Bingi Srinivas
Alan Barber. Professor of Clinical Neurology University of Auckland
 Alan Barber Professor of Clinical Neurology University of Auckland Presented with L numbness & slurred speech 2 episodes; 10 mins & 2 hrs Hypertension Type II DM Examination pulse 80/min reg, BP 160/95
Alan Barber Professor of Clinical Neurology University of Auckland Presented with L numbness & slurred speech 2 episodes; 10 mins & 2 hrs Hypertension Type II DM Examination pulse 80/min reg, BP 160/95
Association of Systolic Blood Pressure with Progression of Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis
 Journal of Stroke 2017;19(3):304-311 Original Article Association of Systolic Blood Pressure with Progression of Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis Jong-Ho Park, a Bruce Ovbiagele, b Keun-Sik
Journal of Stroke 2017;19(3):304-311 Original Article Association of Systolic Blood Pressure with Progression of Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis Jong-Ho Park, a Bruce Ovbiagele, b Keun-Sik
Carotid Artery Surgery for the Prevention and Treatment of Ischemic Stroke Update 2015
 Carotid Artery Surgery for the Prevention and Treatment of Ischemic Stroke Update 2015 John L. Crawford, MD, FACS Neuroscience Summit 2015 UNT Health Sciences Center September 12, 2015 www.cdc.gov/datastatistics2013
Carotid Artery Surgery for the Prevention and Treatment of Ischemic Stroke Update 2015 John L. Crawford, MD, FACS Neuroscience Summit 2015 UNT Health Sciences Center September 12, 2015 www.cdc.gov/datastatistics2013
Endothelial function is impaired in women who had pre-eclampsia
 Endothelial function is impaired in women who had pre-eclampsia Christian Delles, Catriona E Brown, Joanne Flynn, David M Carty Institute of Cardiovascular and Medical Sciences University of Glasgow United
Endothelial function is impaired in women who had pre-eclampsia Christian Delles, Catriona E Brown, Joanne Flynn, David M Carty Institute of Cardiovascular and Medical Sciences University of Glasgow United
5/2/2016. Outpatient Stroke Management Sheila Smith MD May 5, 2016
 Outpatient Stroke Management Sheila Smith MD May 5, 2016 1 Management of Outpatient Stroke Objectives Review blood pressure management post stroke Review antithrombotic therapy Review statin therapy Discuss
Outpatient Stroke Management Sheila Smith MD May 5, 2016 1 Management of Outpatient Stroke Objectives Review blood pressure management post stroke Review antithrombotic therapy Review statin therapy Discuss
Intima-Media Thickness
 European Society of Cardiology Stockholm, 30th August 2010 Intima-Media Thickness Integration of arterial assessment into clinical practice Prof Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss, MD Institute of Exercise and Health
European Society of Cardiology Stockholm, 30th August 2010 Intima-Media Thickness Integration of arterial assessment into clinical practice Prof Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss, MD Institute of Exercise and Health
Prevalence and Risk Factors of Intracranial Atherosclerosis in an Asymptomatic Korean Population
 Journal of Clinical Neurology / Volume 2 / March, 2006 Prevalence and Risk Factors of Intracranial Atherosclerosis in an Asymptomatic Korean Population Kwang-Yeol Park, M.D., Chin-Sang Chung, M.D., Ph.D.,
Journal of Clinical Neurology / Volume 2 / March, 2006 Prevalence and Risk Factors of Intracranial Atherosclerosis in an Asymptomatic Korean Population Kwang-Yeol Park, M.D., Chin-Sang Chung, M.D., Ph.D.,
ABSTRACT ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION. e-issn: p-issn: doi: /apjhs G. Vikas Naik 1 *, K. P.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE e-issn: 2349-0659 p-issn: 2350-0964 doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2018.5.1.21 Carotid intima-media thickness as a predictor of atherosclerosis in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects - A study from
ORIGINAL ARTICLE e-issn: 2349-0659 p-issn: 2350-0964 doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2018.5.1.21 Carotid intima-media thickness as a predictor of atherosclerosis in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects - A study from
Carotid Artery Disease and What s Pertinent JOSEPH A PAULISIN DO
 Carotid Artery Disease and What s Pertinent JOSEPH A PAULISIN DO Goal of treatment of carotid disease Identify those at risk of developing symptoms Prevent patients at risk from developing symptoms Prevent
Carotid Artery Disease and What s Pertinent JOSEPH A PAULISIN DO Goal of treatment of carotid disease Identify those at risk of developing symptoms Prevent patients at risk from developing symptoms Prevent
Hyperuricemia as a Prognostic Marker in Acute Ischemic Stroke
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/23 Hyperuricemia as a Prognostic Marker in Acute Ischemic Stroke B Balaji 1, Bingi Srinivas 2 1 Associate Professor,
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/23 Hyperuricemia as a Prognostic Marker in Acute Ischemic Stroke B Balaji 1, Bingi Srinivas 2 1 Associate Professor,
Recanalization of Chronic Carotid Artery Occlusion Objective Improvement Of Cerebral Perfusion
 Recanalization of Chronic Carotid Artery Occlusion Objective Improvement Of Cerebral Perfusion Paul Hsien-Li Kao, MD Assistant Professor National Taiwan University Medical School and Hospital ICA stenting
Recanalization of Chronic Carotid Artery Occlusion Objective Improvement Of Cerebral Perfusion Paul Hsien-Li Kao, MD Assistant Professor National Taiwan University Medical School and Hospital ICA stenting
Disclosures. State of the Art Management of Carotid Stenosis. NIH funding for clinical trials Consultant for Scientia Vascular and Medtronic
 State of the Art Management of Carotid Stenosis Mark R. Harrigan, MD UAB Stroke Center Professor of Neurosurgery, Neurology, and Radiology University of Alabama, Birmingham Disclosures NIH funding for
State of the Art Management of Carotid Stenosis Mark R. Harrigan, MD UAB Stroke Center Professor of Neurosurgery, Neurology, and Radiology University of Alabama, Birmingham Disclosures NIH funding for
Current role of low molecular weight heparin in the treatment of acute. ischemic stroke.
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Singh K. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Dec;4(6):1599-1604 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20175174
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Singh K. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Dec;4(6):1599-1604 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20175174
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 12 Page December 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.115 Evaluation of Carotid Intima
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.115 Evaluation of Carotid Intima
Pre-and Post Procedure Non-Invasive Evaluation of the Patient with Carotid Disease
 Pre-and Post Procedure Non-Invasive Evaluation of the Patient with Carotid Disease Michael R. Jaff, D.O., F.A.C.P., F.A.C.C. Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, Vascular Medicine
Pre-and Post Procedure Non-Invasive Evaluation of the Patient with Carotid Disease Michael R. Jaff, D.O., F.A.C.P., F.A.C.C. Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, Vascular Medicine
(Department of Radiology, Beylikdüzü State Hospital, İstanbul, Turkey) Corresponding Author: Dr. Mete Özdikici
 Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 5~ Issue 6 (2018) pp: 61-65 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Quantitative Measurements
Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 5~ Issue 6 (2018) pp: 61-65 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Quantitative Measurements
A Base of Observations and a Base of Knowledge for «Carotid constriction» Disease Formed by the Ontology for Medical Diagnostics
 A Base of Observations and a Base of Knowledge for «Carotid constriction» Disease Formed by the Ontology for Medical Diagnostics Mery Yu. Chernyakhovskaya, and Philip M. Moskalenko Abstract--The paper
A Base of Observations and a Base of Knowledge for «Carotid constriction» Disease Formed by the Ontology for Medical Diagnostics Mery Yu. Chernyakhovskaya, and Philip M. Moskalenko Abstract--The paper
Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors
 Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Update on Lipid Management in Cardiovascular Disease: How to Understand and Implement the New ACC/AHA Guidelines
 Update on Lipid Management in Cardiovascular Disease: How to Understand and Implement the New ACC/AHA Guidelines Paul Mahoney, MD Sentara Cardiology Specialists Lipid Management in Cardiovascular Disease
Update on Lipid Management in Cardiovascular Disease: How to Understand and Implement the New ACC/AHA Guidelines Paul Mahoney, MD Sentara Cardiology Specialists Lipid Management in Cardiovascular Disease
Carotid doppler ultrasonography evaluation in patients with stroke
 Original Research Article Carotid doppler ultrasonography evaluation in patients with stroke K. Karthick 1, J. A. Vasanthakumar 2 * 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor Department of General Medicine,
Original Research Article Carotid doppler ultrasonography evaluation in patients with stroke K. Karthick 1, J. A. Vasanthakumar 2 * 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor Department of General Medicine,
Statin therapy in patients with Mild to Moderate Coronary Stenosis by 64-slice Multidetector Coronary Computed Tomography
 Statin therapy in patients with Mild to Moderate Coronary Stenosis by 64-slice Multidetector Coronary Computed Tomography Hyo Eun Park 1, Eun-Ju Chun 2, Sang-Il Choi 2, Soyeon Ahn 2, Hyung-Kwan Kim 3,
Statin therapy in patients with Mild to Moderate Coronary Stenosis by 64-slice Multidetector Coronary Computed Tomography Hyo Eun Park 1, Eun-Ju Chun 2, Sang-Il Choi 2, Soyeon Ahn 2, Hyung-Kwan Kim 3,
Game Strategy: High Intensity Statin in Stroke. K.M. Osei MD, MSc Cardiovascular Conference PARMC Feb 24, 2018
 Game Strategy: High Intensity Statin in Stroke K.M. Osei MD, MSc Cardiovascular Conference PARMC Feb 24, 2018 No Disclosures Are you Mind Full or Mindful? Objectives 1. Discuss the correlation between
Game Strategy: High Intensity Statin in Stroke K.M. Osei MD, MSc Cardiovascular Conference PARMC Feb 24, 2018 No Disclosures Are you Mind Full or Mindful? Objectives 1. Discuss the correlation between
Association between arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk factors in a pediatric population
 + Association between arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk factors in a pediatric population Maria Perticone Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine University Magna Graecia of Catanzaro
+ Association between arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk factors in a pediatric population Maria Perticone Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine University Magna Graecia of Catanzaro
Case Study: Chris Arden. Peripheral Arterial Disease
 Case Study: Chris Arden Peripheral Arterial Disease Patient Presentation Diane is a 65-year-old retired school teacher She complains of left calf pain when walking 50 metres; the pain goes away after she
Case Study: Chris Arden Peripheral Arterial Disease Patient Presentation Diane is a 65-year-old retired school teacher She complains of left calf pain when walking 50 metres; the pain goes away after she
A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1
 A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ravi Keerthy M. A Study of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Hypertension. Journal of
A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ravi Keerthy M. A Study of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Hypertension. Journal of
PULSE WAVE VELOCITY AS A NEW ASSESSMENT TOOL FOR ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 PULSE WAVE VELOCITY AS A NEW ASSESSMENT TOOL FOR ATHEROSCLEROSIS Introduction Hirohide Yokokawa, M.D., Ph.D. 1 , Aya Goto, M.D., MPH, Ph.D. 2 , and Seiji Yasumura, M.D., Ph.D.
PULSE WAVE VELOCITY AS A NEW ASSESSMENT TOOL FOR ATHEROSCLEROSIS Introduction Hirohide Yokokawa, M.D., Ph.D. 1 , Aya Goto, M.D., MPH, Ph.D. 2 , and Seiji Yasumura, M.D., Ph.D.
Society for Behavioral Medicine 33 rd Annual Meeting New Orleans, LA
 Society for Behavioral Medicine 33 rd Annual Meeting New Orleans, LA John M. Violanti, PhD* a ; LuendaE. Charles, PhD, MPH b ; JaK. Gu, MSPH b ; Cecil M. Burchfiel, PhD, MPH b ; Michael E. Andrew, PhD
Society for Behavioral Medicine 33 rd Annual Meeting New Orleans, LA John M. Violanti, PhD* a ; LuendaE. Charles, PhD, MPH b ; JaK. Gu, MSPH b ; Cecil M. Burchfiel, PhD, MPH b ; Michael E. Andrew, PhD
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 42, No. 6, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /03/$30.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 42, No. 6, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(03)00922-7
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 42, No. 6, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(03)00922-7
Risk Factors of Carotid Stenosis in First-Ever Ischemic Stroke in Taiwan: A Hospital-based Study
 237 Risk Factors of Carotid Stenosis in First-Ever Ischemic Stroke in Taiwan: A Hospital-based Study Chien-Hung Chang, Yeu-Jhy Chang, Tsong-Hai Lee, Kai-Cheng Hsu, and Shan-Jin Ryu Abstract- Objective:
237 Risk Factors of Carotid Stenosis in First-Ever Ischemic Stroke in Taiwan: A Hospital-based Study Chien-Hung Chang, Yeu-Jhy Chang, Tsong-Hai Lee, Kai-Cheng Hsu, and Shan-Jin Ryu Abstract- Objective:
Reduction of flow velocities in patients with ischemic events in the middle cerebral artery long-term follow-up with ultrasound
 Acta Neurol. Belg., 20,, -5 Original articles Reduction of flow velocities in patients with ischemic events in the middle cerebral artery long-term follow-up with ultrasound Christine Kremer and Kasim
Acta Neurol. Belg., 20,, -5 Original articles Reduction of flow velocities in patients with ischemic events in the middle cerebral artery long-term follow-up with ultrasound Christine Kremer and Kasim
Carotid Ddisease, Carotid IMT and Risk of Stroke
 Carotid Ddisease, Carotid IMT and Risk of Stroke TATJANA RUNDEK, MD PhD Professor of Neurology, Epidemiology and Public Health Director, Clinical translational Division Department of Neurology, Miller
Carotid Ddisease, Carotid IMT and Risk of Stroke TATJANA RUNDEK, MD PhD Professor of Neurology, Epidemiology and Public Health Director, Clinical translational Division Department of Neurology, Miller
The presenter does not have any potential conflicts of interest to disclose
 Carotid intima-media thickness as a predictor of multi territory atherosclerotic occlusive disease in patients with symptomatic subclavian artery obstruction Leszek Wrotniak 1, Anna Kabłak Ziembicka 1,
Carotid intima-media thickness as a predictor of multi territory atherosclerotic occlusive disease in patients with symptomatic subclavian artery obstruction Leszek Wrotniak 1, Anna Kabłak Ziembicka 1,
2/7/
 Disclosure Intracranial Atherosclerosis an update None Mai N. Nguyen-Huynh, MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Neurology UCSF Neurovascular Service February 7, 2009 Case #1 60 y.o. Chinese-speaking speaking
Disclosure Intracranial Atherosclerosis an update None Mai N. Nguyen-Huynh, MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Neurology UCSF Neurovascular Service February 7, 2009 Case #1 60 y.o. Chinese-speaking speaking
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE General practice Indicators for the NICE menu
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE General practice Indicators for the NICE menu Indicator area: Pulse rhythm assessment for AF Indicator: NM146 Date: June 2017 Introduction There is evidence
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE General practice Indicators for the NICE menu Indicator area: Pulse rhythm assessment for AF Indicator: NM146 Date: June 2017 Introduction There is evidence
Carotid Endarterectomy for Symptomatic Complete Occlusion of the Internal Carotid Artery
 2011 65 4 239 245 Carotid Endarterectomy for Symptomatic Complete Occlusion of the Internal Carotid Artery a* a b a a a b 240 65 4 2011 241 9 1 60 10 2 62 17 3 67 2 4 64 7 5 69 5 6 71 1 7 55 13 8 73 1
2011 65 4 239 245 Carotid Endarterectomy for Symptomatic Complete Occlusion of the Internal Carotid Artery a* a b a a a b 240 65 4 2011 241 9 1 60 10 2 62 17 3 67 2 4 64 7 5 69 5 6 71 1 7 55 13 8 73 1
TCD in Subclavian Steal Syndrome
 ISSN 2005-7881 Journal of Neurosonology 2(Suppl. 1):25-30, 2010 TCD in Subclavian Steal Syndrome Soon-Tae Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, South Korea
ISSN 2005-7881 Journal of Neurosonology 2(Suppl. 1):25-30, 2010 TCD in Subclavian Steal Syndrome Soon-Tae Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, South Korea
Preventing Cardiovascular Disease Stroke Primary Prevention Guidelines. John Potter Professor Ageing & Stroke Medicine University of East Anglia
 Preventing Cardiovascular Disease Stroke Primary Prevention Guidelines John Potter Professor Ageing & Stroke Medicine University of East Anglia Preventing Cardiovascular Disease Stroke Primary Prevention
Preventing Cardiovascular Disease Stroke Primary Prevention Guidelines John Potter Professor Ageing & Stroke Medicine University of East Anglia Preventing Cardiovascular Disease Stroke Primary Prevention
Non-invasive Imaging of Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis
 Non-invasive Imaging of Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis 최연현 성균관의대삼성서울병원영상의학과 Noninvasive Techniques US with Doppler CT MRI Ultrasonography Techniques of Carotid US US Anatomy (ICA vs ECA) Gray scale and
Non-invasive Imaging of Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis 최연현 성균관의대삼성서울병원영상의학과 Noninvasive Techniques US with Doppler CT MRI Ultrasonography Techniques of Carotid US US Anatomy (ICA vs ECA) Gray scale and
Clinical Decision Making: Hyperacute Management of Symptomatic Carotid Artery Disease
 Clinical Decision Making: Hyperacute Management of Symptomatic Carotid Artery Disease Tarvinder Singh, MS, MD Neurohospitalist Swedish Neuroscience Institute 1 Objectives Definition Why the urgency? Evidence/Guidelines
Clinical Decision Making: Hyperacute Management of Symptomatic Carotid Artery Disease Tarvinder Singh, MS, MD Neurohospitalist Swedish Neuroscience Institute 1 Objectives Definition Why the urgency? Evidence/Guidelines
Carotid Abnormalities Coils, Kinks and Tortuosity David Lorelli M.D., RVT, FACS Michigan Vascular Association Conference Saturday, October 20, 2012
 Carotid Abnormalities Coils, Kinks and Tortuosity David Lorelli M.D., RVT, FACS Michigan Vascular Association Conference Saturday, October 20, 2012 Page 1 Table of Contents Carotid Anatomy Carotid Duplex
Carotid Abnormalities Coils, Kinks and Tortuosity David Lorelli M.D., RVT, FACS Michigan Vascular Association Conference Saturday, October 20, 2012 Page 1 Table of Contents Carotid Anatomy Carotid Duplex
Lecture Outline: 1/5/14
 John P. Karis, MD Lecture Outline: Provide a clinical overview of stroke: Risk Prevention Diagnosis Intervention Illustrate how MRI is used in the diagnosis and management of stroke. Illustrate how competing
John P. Karis, MD Lecture Outline: Provide a clinical overview of stroke: Risk Prevention Diagnosis Intervention Illustrate how MRI is used in the diagnosis and management of stroke. Illustrate how competing
Advances in the treatment of posterior cerebral circulation symptomatic disease
 Advances in the treatment of posterior cerebral circulation symptomatic disease Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, School of Health
Advances in the treatment of posterior cerebral circulation symptomatic disease Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, School of Health
03/30/2016 DISCLOSURES TO OPERATE OR NOT THAT IS THE QUESTION CAROTID INTERVENTION IS INDICATED FOR ASYMPTOMATIC CAROTID OCCLUSIVE DISEASE
 CAROTID INTERVENTION IS INDICATED FOR ASYMPTOMATIC CAROTID OCCLUSIVE DISEASE Elizabeth L. Detschelt, M.D. Allegheny Health Network Vascular and Endovascular Symposium April 2, 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no
CAROTID INTERVENTION IS INDICATED FOR ASYMPTOMATIC CAROTID OCCLUSIVE DISEASE Elizabeth L. Detschelt, M.D. Allegheny Health Network Vascular and Endovascular Symposium April 2, 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors
 Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
 CLINICAL FEATURES THAT SUPPORT ATHEROSCLEROTIC STROKE 1. cerebral cortical impairment (aphasia, neglect, restricted motor involvement, etc.) or brain stem or cerebellar dysfunction 2. lacunar clinical
CLINICAL FEATURES THAT SUPPORT ATHEROSCLEROTIC STROKE 1. cerebral cortical impairment (aphasia, neglect, restricted motor involvement, etc.) or brain stem or cerebellar dysfunction 2. lacunar clinical
CEA and cerebral protection Volodymyr labinskyy, MD
 CEA and cerebral protection Volodymyr labinskyy, MD VA Hospital 7/26/2012 63 year old male presents for the vascular evaluation s/p TIA in January 2012 PMH: HTN, long term active smoker, Hep C PSH: None
CEA and cerebral protection Volodymyr labinskyy, MD VA Hospital 7/26/2012 63 year old male presents for the vascular evaluation s/p TIA in January 2012 PMH: HTN, long term active smoker, Hep C PSH: None
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
New Guidelines in Dyslipidemia Management
 The Fourth IAS-OSLA Course on Lipid Metabolism and Cardiovascular Risk Muscat, Oman, February 2018 New Guidelines in Dyslipidemia Management Dr. Khalid Al-Waili, MD, FRCPC, DABCL Senior Consultant Medical
The Fourth IAS-OSLA Course on Lipid Metabolism and Cardiovascular Risk Muscat, Oman, February 2018 New Guidelines in Dyslipidemia Management Dr. Khalid Al-Waili, MD, FRCPC, DABCL Senior Consultant Medical
Title for Paragraph Format Slide
 Title for Paragraph Format Slide Presentation Title: Month Date, Year Atherosclerosis A Spectrum of Disease: February 12, 2015 Richard Cameron Padgett, MD Executive Medical Director, OHVI Pt RB Age 38
Title for Paragraph Format Slide Presentation Title: Month Date, Year Atherosclerosis A Spectrum of Disease: February 12, 2015 Richard Cameron Padgett, MD Executive Medical Director, OHVI Pt RB Age 38
Asian J. Exp. Sci., Vol. 27, No. 1, 2013; 67-72
 Carotid Intima-media Thickness as a Surrogate Marker of Atherosclerosis and its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors and Angiographic Severity of Coronary Artery Disease. 1 2 Rajeev Gupta and Rajendra
Carotid Intima-media Thickness as a Surrogate Marker of Atherosclerosis and its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors and Angiographic Severity of Coronary Artery Disease. 1 2 Rajeev Gupta and Rajendra
Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD INTRODUCTION
 2 Hyperlipidemia Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION RISK CATEGORIES AND TARGET LDL-CHOLESTEROL TREATMENT OF LDL-CHOLESTEROL SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS OLDER AND YOUNGER ADULTS ADDITIONAL
2 Hyperlipidemia Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION RISK CATEGORIES AND TARGET LDL-CHOLESTEROL TREATMENT OF LDL-CHOLESTEROL SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS OLDER AND YOUNGER ADULTS ADDITIONAL
NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES
 NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES Leslie M. Scoutt, MD, FACR Professor of Diagnostic Radiology & Surgery Vice Chair, Dept of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Chief, Ultrasound Section
NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES Leslie M. Scoutt, MD, FACR Professor of Diagnostic Radiology & Surgery Vice Chair, Dept of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Chief, Ultrasound Section
Epidemiologic and clinical comparison of renal artery stenosis in black patients and white patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Epidemiologic and clinical comparison of renal artery stenosis in black patients and white patients Andrew C. Novick, MD, Safwat Zald, MD, David Goldfarb, MD, and Ernest E. Hodge, MD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Epidemiologic and clinical comparison of renal artery stenosis in black patients and white patients Andrew C. Novick, MD, Safwat Zald, MD, David Goldfarb, MD, and Ernest E. Hodge, MD,
Racial Differences in Thoracic Aorta Atherosclerosis Among Ischemic Stroke Patients
 Racial Differences in Thoracic Aorta Atherosclerosis Among Ischemic Stroke Patients Vishal Gupta, MD, MPH; Navin C. Nanda, MD; Dilek Yesilbursa, MD; Wen Ying Huang, MD; Vijaya Gupta, MS; Qing Li, MD, PhD;
Racial Differences in Thoracic Aorta Atherosclerosis Among Ischemic Stroke Patients Vishal Gupta, MD, MPH; Navin C. Nanda, MD; Dilek Yesilbursa, MD; Wen Ying Huang, MD; Vijaya Gupta, MS; Qing Li, MD, PhD;
CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention
 CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention Raul D. Santos MD, PhD Heart Institute-InCor University of Sao Paulo Brazil Disclosure Honoraria for consulting and speaker activities
CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention Raul D. Santos MD, PhD Heart Institute-InCor University of Sao Paulo Brazil Disclosure Honoraria for consulting and speaker activities
Carotid Atherosclerosis in Ischemic Cerebrovascular Patients
 Original Article Carotid Atherosclerosis in Ischemic Cerebrovascular Patients Ai Juan Zhang a, c, Ai Yuan Zhang b, Chi Zhong a Abstract Background: Cerebral emboli resulting from atherosclerosis at the
Original Article Carotid Atherosclerosis in Ischemic Cerebrovascular Patients Ai Juan Zhang a, c, Ai Yuan Zhang b, Chi Zhong a Abstract Background: Cerebral emboli resulting from atherosclerosis at the
Supplemental Figures and Legends
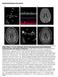 Supplemental Figures and Legends Online Figure 1. 18 year old female with SLE and acute homonymous hemianopsia, confusional state, and cognitive dysfunction. A. This TEE four chamber view demonstrates
Supplemental Figures and Legends Online Figure 1. 18 year old female with SLE and acute homonymous hemianopsia, confusional state, and cognitive dysfunction. A. This TEE four chamber view demonstrates
Study on occurrence of metabolic syndrome among patients with stroke: a descriptive study
 Original article Study on occurrence of metabolic syndrome among patients with stroke: a descriptive study Dr. Mahesh K Savadi*, Dr Manjunatha N** *Assistant Professor, **Post graduate Dept. of General
Original article Study on occurrence of metabolic syndrome among patients with stroke: a descriptive study Dr. Mahesh K Savadi*, Dr Manjunatha N** *Assistant Professor, **Post graduate Dept. of General
Stroke 101. Maine Cardiovascular Health Summit. Eileen Hawkins, RN, MSN, CNRN Pen Bay Stroke Program Coordinator November 7, 2013
 Stroke 101 Maine Cardiovascular Health Summit Eileen Hawkins, RN, MSN, CNRN Pen Bay Stroke Program Coordinator November 7, 2013 Stroke Statistics Definition of stroke Risk factors Warning signs Treatment
Stroke 101 Maine Cardiovascular Health Summit Eileen Hawkins, RN, MSN, CNRN Pen Bay Stroke Program Coordinator November 7, 2013 Stroke Statistics Definition of stroke Risk factors Warning signs Treatment
How to detect early atherosclerosis ; focusing on techniques
 How to detect early atherosclerosis ; focusing on techniques Jang-Ho Bae, MD., PhD. Heart Center Konyang University Hospital Daejeon city, S. Korea Surrogates for Atherosclerosis Measures of endothelial
How to detect early atherosclerosis ; focusing on techniques Jang-Ho Bae, MD., PhD. Heart Center Konyang University Hospital Daejeon city, S. Korea Surrogates for Atherosclerosis Measures of endothelial
The Epidemiology of Stroke and Vascular Risk Factors in Cognitive Aging
 The Epidemiology of Stroke and Vascular Risk Factors in Cognitive Aging REBECCA F. GOTTESMAN, MD PHD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY AND EPIDEMIOLOGY JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY OCTOBER 20, 2014 Outline
The Epidemiology of Stroke and Vascular Risk Factors in Cognitive Aging REBECCA F. GOTTESMAN, MD PHD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY AND EPIDEMIOLOGY JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY OCTOBER 20, 2014 Outline
Correlation of Common Carotid Artery Intima Media Thickness, Intracranial Arterial Stenosis and Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment
 207 Correlation of Common Carotid Artery Intima Media Thickness, Intracranial Arterial Stenosis and Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment Yong-Hui Lee and Shoou-Jeng Yeh Abstract- Background and Purpose: Atherosclerosis
207 Correlation of Common Carotid Artery Intima Media Thickness, Intracranial Arterial Stenosis and Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment Yong-Hui Lee and Shoou-Jeng Yeh Abstract- Background and Purpose: Atherosclerosis
Antithrombotic therapy in patients with transient ischemic attack / stroke (acute phase <48h)
 Antithrombotic therapy in patients with transient ischemic attack / stroke (acute phase
Antithrombotic therapy in patients with transient ischemic attack / stroke (acute phase
Complications of Diabetes mellitus. Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015
 Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
surtout qui n est PAS à risque?
 3*25 min et surtout qui n est PAS à risque? 2018 ESC/ESH Hypertension Guidelines 2018 ESC-ESH Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension 28 th ESH Meeting on Hypertension and Cardiovascular
3*25 min et surtout qui n est PAS à risque? 2018 ESC/ESH Hypertension Guidelines 2018 ESC-ESH Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension 28 th ESH Meeting on Hypertension and Cardiovascular
Spotty Calcification as a Marker of Accelerated Progression of Coronary Atherosclerosis : Insights from Serial Intravascular Ultrasound
 Spotty Calcification as a Marker of Accelerated Progression of Coronary Atherosclerosis : Insights from Serial Intravascular Ultrasound Department of Cardiovascular Medicine Heart and Vascular Institute
Spotty Calcification as a Marker of Accelerated Progression of Coronary Atherosclerosis : Insights from Serial Intravascular Ultrasound Department of Cardiovascular Medicine Heart and Vascular Institute
Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and carotid plaques in young Nepalese patients with angiographically documented coronary artery disease
 Original Article Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and carotid plaques in young Nepalese patients with angiographically documented coronary artery disease Yuba Raj Limbu, Rajib Rajbhandari, Ranjit
Original Article Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and carotid plaques in young Nepalese patients with angiographically documented coronary artery disease Yuba Raj Limbu, Rajib Rajbhandari, Ranjit
Shawke A. Soueidan, MD. Riverside Neurology & Sleep Specialists
 Shawke A. Soueidan, MD Riverside Neurology & Sleep Specialists 757-221-0110 Epidemiology of stroke 2018 Affects nearly 800,000 people in the US annually Approximately 600000 first-ever strokes and 185000
Shawke A. Soueidan, MD Riverside Neurology & Sleep Specialists 757-221-0110 Epidemiology of stroke 2018 Affects nearly 800,000 people in the US annually Approximately 600000 first-ever strokes and 185000
Cho et al., 2009 Journal of Cardiology (2009), 54:
 Endothelial Dysfunction, Increased Carotid Artery Intima-media Thickness and Pulse Wave Velocity, and Increased Level of Inflammatory Markers are Associated with Variant Angina Cho et al., 2009 Journal
Endothelial Dysfunction, Increased Carotid Artery Intima-media Thickness and Pulse Wave Velocity, and Increased Level of Inflammatory Markers are Associated with Variant Angina Cho et al., 2009 Journal
