Standards and Guidelines
|
|
|
- Giles Lane
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Aquatic Fitness Programming Standards and Guidelines 2018 Aquatic Exercise Association
2 Aquatic Fitness Programming Standards and Guidelines OUR MISSION: The Aquatic Exercise Association (AEA) is a nonprofit organization committed to the advancement of aquatic fitness, health and wellness worldwide. Toll-free: Phone: info@aeawave.com The Aquatic Exercise Association (AEA), the world s largest certifying organization for aquatic fitness programming, has set forth the following guidelines based on the current aquatic fitness research and knowledge of exercise physiology, biomechanics, kinesiology and the physical properties of water. These guidelines may help to minimize risk of injury and provide optimal benefit and enjoyment of fitness activities conducted in the aquatic environment. AEA acknowledges that Guidelines for aquatic fitness vary with different populations and programs. The following Guidelines apply to an average healthy adult without any known limitations or restrictions for engaging in an exercise program. AEA recommends that all individuals obtain physician approval prior to initiating exercise or when significantly altering an existing exercise program. AEA recognizes and promotes the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) Guidelines for Exercise. AEA recognizes and promotes the 2008 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans published by the US Department of Health and Human Services. For additional information, AEA strongly urges you to consult the Aquatic Fitness Professional Manual. Standards and Guidelines for Aquatic Fitness Programming 1
3 Subject Guidelines Class Format An aquatic fitness program should be balanced in cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular conditioning and flexibility to promote general fitness. Exercises should be included for all major muscle groups to ensure muscle balance and reduce risk of injury. An aquatic fitness program should include the warm-up component (thermal warm up, optional pre-stretch and cardiorespiratory warm up), conditioning phase and cool-down component. Often the conditioning phase, which is the primary exercise mode, is cardiorespiratory in nature but the focus may also be strength or muscular endurance, flexibility, neuromotor exercise, skill-related training, or a combination of two or more options.. It is recommended that enough heat be generated through gross movement, during the pre- and post-stretch, to maintain warmth needed to safely and effectively stretch. Water Quality Public and private pools offering aquatic fitness programs should be maintained by a licensed pool operator or manager with the appropriate credentials as designated by state, national, or international codes. For more information on appropriate guidelines for the maintenance of pools and details on becoming a certified pool and spa operator, check with the National Swimming Pool Foundation (NSPF) at The Aquatic Fitness Professional should carefully observe pool conditions and notify management as needed. Strong chemical fumes, cloudy water and complaints from participants (rashes, eye or throat irritation, hair discoloration, excessive fading of clothing, etc.) may indicate that pool chemicals are not properly balanced. Water Temperature Water varying from degrees Fahrenheit ( degrees Celsius) is the most comfortable temperature for typical water fitness classes. This allows the body to react and respond normally to the onset of exercise and the accompanying increase in body temperature. Cooling benefits are still felt and there is little risk of overheating. POPULATION Competitive Swimming Resistance Training Therapy & Rehab Multiple Sclerosis Parkinson s Disease Pregnancy Arthritis Older Adults Children - Fitness Children Swim lessons Infant programs (4 and under) Obese * USA Swimming ** Aquatic Therapy & Rehab Institute (ATRI) *** American Parkinson Disease Association (APDA) **** Arthritis Foundation RECOMMENDED WATER TEMPERATURE F / C* F / C Minimum range F / C** Low function program cooler temperatures may be more appropriate for higher intensity programs and specific populations F / C F / C*** Ideal temperature F / C F / C*** F ( C) may be allowed with special considerations*** F / C Moderate to high intensity; F / C Low intensity F / C 84+ F / C* Varies with age, class length, and programming; ideal learn to swim programs is best suited for F / C when available F / C* F / C Standards and Guidelines for Aquatic Fitness Programming 2
4 Program modifications will be required for water temperature outside the recommended range. Aquatic Fitness Professionals should know the water temperature and modify the program accordingly based upon the population and the program format. Water temperature below the recommended range requires modifications in programming. The primary focus of the warm-up should be large, lower impact, rhythmic movements that gradually elevate core temperature of the body and may need to be extended by 5 to 10 minutes. The main segment must be of adequate intensity to maintain proper body temperature and prevent injury. Participants may find it necessary to wear specialized clothing to maintain body heat. The cool-down and post-stretch must be adjusted, in overall length as well as activity, according to the environmental conditions. Water temperature above the recommended range also requires modifications in programming. The intensity and length of the main segment should be adjusted to prevent overheating. Encourage proper hydration and apparel (e.g. avoid swimming caps that prevent heat dissipation). An extended cool down with emphasis on stretching and relaxation is appropriate. Some general guidelines for water temperatures are listed, but please note that variations to these recommendations may be necessary. Make adjustments in clothing and programming to assure participant safety. Also, specialized populations may require specific water temperatures for safe and effective programming. Multi-use pools are more cost effective to operate and thus adjustments in the suggested water temperatures are often required to accommodate a larger variety of programs. Please consult your local health department codes when adjusting pool temperatures as this may affect the ranges that are acceptable and may even alter the classification of the pool use. Limited research is available regarding prenatal women and recommended water temperatures for exercise. The upper limit for safe water temperature for prenatal water exercise has not yet been defined, however the range listed in the chart is based upon research that indicates exercise in 85 F / 29.4 C is safe for pregnant women. Water Depth Shallow-water programs are typically performed in water that ranges from mid-rib cage to mid-chest in depth. This provides the benefits of reduced impact while still maintaining proper alignment and control of movement and allows for activities that sufficiently train all the major muscle groups against the water s resistance. Specific programming options may require variations in water depth. Water that is below waistdepth will require that impact levels be modified to prevent musculoskeletal injury; this water depth will also reduce the water s cooling ability during sustained exercise so intensity should be carefully monitored. Pools with a depth range of feet ( meters) seem to be the most useful for typical shallow-water fitness classes; pools with a depth of 3-5 feet ( meters) will accommodate nearly all heights of participants. A gradual slope of the pool bottom is preferred to accommodate varying heights of participants. A steep slope may lead to musculoskeletal stress. Deep-water exercise is most successful at a depth where a body can be suspended vertically and is free to move in any direction and speed, without experiencing impact or weight bearing stress. A pool depth of 6.5 feet (1.98 meters) or more provides the ideal environment for a deep-water class. In some situations, either due to the pool slope or water depth, it is necessary to perform transitional depth training. This describes water exercise performed in pools with water depths between 4 and 6 feet ( m). Flotation equipment may be used, and shoes are recommended because there is some contact with the pool floor. Pool Entry & Exit The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) has set minimum requirements for making swimming pools accessible to people of all abilities. The ADA.gov website provides details to establish compliance. Do not jump or dive into the pool wearing flotation or resistance equipment. Do not dive into pools unless the depth is clearly marked for diving and is at least 5 feet (1.52 meters) in depth. Standards and Guidelines for Aquatic Fitness Programming 3
5 Air Temperature & Humidity Ideal air temperature and humidity levels are not easily determined as many factors must be considered. Air temperature and humidity will affect both the participants in the pool as well as the aquatic professionals working on the pool deck. Programming should be adjusted to all environmental conditions, including the air temperature and humidity, to provide safe training options for participants in the pool. Aquatic professionals working from deck must account for these conditions as well by adjusting teaching style, wearing appropriate clothing and maintaining proper hydration. The general recommendation for indoor pool air temperature is a range of F ( C). The general recommendation for indoor pool air humidity is a range of 50 60%. Temperature and humidity can also impact operation and maintenance of indoor pool facilities. The air temperature should not exceed 85 F (29.5 C) for comfort of the aquatic professionals working on the deck. A lower than 50% relative humidity will cause a chilling effect on the participants when leaving the water and will also cause more evaporation of the water. The greater the evaporation of the water the more chemicals will be used and the greater chance of the water quality becoming unbalanced. Outdoor pool air temperature cannot be controlled and will be influenced by wind, humidity and direct sunlight. Comfort and safety of the participants will also be influenced by the water temperature, class format as well as participant age, ability level and medical conditions. Appropriate attire should be considered and discussed with the participants. When teaching at outdoor pools, it is suggested to designate upper and lower limits for both air and water temperature based upon the participants and the programming. Cancel classes if these limits are exceeded to maximize safety and minimize liability. Post this information for your clientele in advance for clarification and to eliminate confusion. Air Quality Air quality for indoor pool facilities should be monitored according to the country, state and local health department guidelines. Adequate ventilation is critical to maintain proper humidity and remove chemical fumes from the pool area. Humidity level and air circulation will also influence the comfort level of the participant and thus require constant monitoring. Intensity Aquatic Fitness Professionals can alter intensity through the physical laws of motion and the properties of water.. Options would include the use of inertia, acceleration, action/ reaction, drag forces of water, buoyancy, levers and frontal resistance to increase or decrease intensity. Varying the speed of movement can alter intensity, however movement speed should not compromise range of motion or muscle balance. Many factors can affect the training heart rate, including stress, caffeine, medications, general health, and environmental factors. Additionally, research indicates that the exercise heart rate during aquatic exercise is reduced compared to the heart rate observed during exercise of the same intensity on land. This aquatic reduction is influenced by water temperature, reduced gravity, compression, partial pressure and reduced body mass. When monitoring heart rate in aquatic exercise, a 6-second count is suggested. Research also indicates that a standard percent or a standard number of beats per minute may not be as accurate as a personalized deduction in determining aquatic heart rate calculations. At this time AEA recommends the use of the Kruel Aquatic Heart Rate Deduction with the Karvonen formula for determining target heart rates in aquatic exercise. Rating of perceived exertion (RPE) is a subjective method of assessing effort, strain, discomfort, or fatigue experienced during exercise. It has been shown to be a viable method to measure exercise intensity without the influence of additional factors that can influence heart rate measurements. The AEA Aquatic Exercise Intensity Scale compares a numerical intensity rating and aquatic heart rate percentage with a standard description of perceived exertion, plus an added description to assist participants in assessing exercise level. Monitoring intensity of resistance training is also important for achieving safe and effect results. Standards and Guidelines for Aquatic Fitness Programming 4
6 Tempo Music with a tempo of beats per minute (bpm) is recommended for shallow-water aerobic programs for the general population. The slower reaction time of submerged movement benefits from the music being utilized at half tempo (i.e. every other beat of the music) in most situations. Below are general cadence guidelines for various types of aquatic programs. CLASS FORMAT Shallow-water Cardiorespiratory Deep-water Cardiorespiratory Aquatic Kick Boxing RECOMMENDED BPM Muscular Conditioning Interval Shallow-water Interval Deep-water Circuit Training Basic Techniques/ Skills & Drills CR Combinations/ Advanced Level Interspersed with higher or lower tempos Interspersed with higher or lower tempos Aerobic Segments Resistance Training Segments Arm Positioning AEA recommends that the majority of arm movements be performed submerged in the water, but recognizes that some choreography, conditioning exercises and/ or stretching techniques will take the arms above the water s surface. Utilizing the arms under the water s surface during aquatic exercise will maximize use of the water s resistance for improving upper body musculature, developing balance and coordination and altering intensity. Range of motion above shoulder height should be included but in a careful and controlled manner; creativity should not compromise safety. Extended use of the arms in an overhead position is not recommended due to the potential stress to the cervical spine, shoulders and shoulder girdle. This may also create an inaccurate perception of aerobic intensity. The hands are primarily utilized under the water in deep programming. They play a vital role in maintaining stability and balance, form and technique, as well as providing muscle conditioning for the upper body musculature. In general, arms should stay either in the water or out of the water throughout the combination or pattern. If you need to make the transition from out of the water to in the water, consider using short levers to avoid stress on the shoulder and elbow joints. You can add variety to the upper-body base moves in five basic ways in both deep and shallow water. See Upper Body Techniques in the Terminology section. Equipment Considerations Equipment should always be appropriate for the participant and the program. Aquatic Fitness Professionals should have a complete understanding of how the equipment can be safely and effectively incorporated. AEA recommends that deep-water exercise be performed with flotation equipment attached to the trunk of the body (flotation belt or vest) or attached to the upper arms (flotation upper arm cuffs specifically designed for water exercise). With proper progression and training, ankle cuffs may be an appropriate flotation option for some participants. In deep water, flotation equipment that is attached to the body eliminates the potential for letting go of the buoyancy assistance device, even if the individual becomes panicked. Flotation equipment that requires an individual to hold on to the device, such as a noodle, kickboard, or hand bars, can create a false sense of well-being and could lead to a water rescue. The participant s swimming skills, core strength, and personal comfort in deep water should all be considered when choosing floatation equipment. Hand-held buoyancy equipment may be utilized for additional upper body resistance in both shallow-water and deep-water programs. If hand-held buoyancy equipment is used, AEA recommends providing options for participants who lack the ability or fitness level to use the equipment appropriately. Periods of Standards and Guidelines for Aquatic Fitness Programming 5
7 training with the equipment submerged should be limited and frequent breaks should be incorporated into the workout. Cue participants to maintain neutral alignment of the wrists and avoid tight gripping of the equipment. Carefully observe and cue to make sure that proper alignment of the shoulder girdle is maintained, including scapular depression and retraction. Proper Footwear AEA recommends the use of aquatic shoes for most shallow aquatic fitness, especially programs involving impact or traveling movements. Shoes reduce impact stress to the weight-bearing joints, allow for better footing during grounded techniques, increase traction during traveling patterns, protect the feet from injury and improve the quality of the workout. Shoes are especially important for individuals with the following special considerations: pregnancy, obesity, diabetes and musculoskeletal disorders. For a traditional non-impact deep-water format, shoes would not be required and may not be preferred if they hamper full range of motion at the ankle, especially during plantar flexion. However, shoes (depending upon the type selected) may provide additional weight to the legs that can assist in maintaining correct vertical alignment. Additionally, specific resistance shoes are manufactured to enhance training benefits of water exercise and these may be incorporated for added intensity. Shoes should be considered when walking on deck and in dressing rooms to reduce the chance for slips and falls. Shoes may also be needed for safe entry and exiting of the pool. Street shoes should not be worn in the pool area to reduce contamination and the potential spread of disease as well as general safety considerations from possible slips and falls. Shoes worn in the pool should be used exclusively for this purpose. Aquatic Fitness Professionals on deck should wear appropriate footwear to absorb shock, provide stability and prevent slipping. Proper Clothing Most aquatic fitness programs involve some degree of rebounding and thus it is important for Aquatic Fitness Professionals as well as participants to wear supportive clothing. Exercise clothing may provide more support, coverage and comfort than swim suits. Aquatic Fitness Professionals and participants exercising in outdoor pools need also to consider protection from the sun, which might include hats/ visors, sunglasses, waterproof sunscreen and sunprotective clothing. Other outdoor considerations include cool air and/ or water temperatures. Wearing vests or long-sleeve jackets designed for water exercise can help to maintain core body temperature, thus increasing comfort and safety. Professionalism should be considered when selecting exercise attire. Hydration Aquatic fitness participants and professionals must maintain proper hydration even though the loss of fluids through sweating is not as obvious when training in the water. Drink water before, during and after all training sessions. Increase fluid intake when the water and air temperatures are above recommendations, when the workout is extremely intense, if you consume caffeine or other diuretics and if you are pregnant. Professional Education AEA recommends that Aquatic Fitness Professionals receive and maintain certification through an internationally recognized organization that specializes in aquatic fitness leadership. When working with special populations or specialized class formats, AEA recommends additional education and/or certification specific to that population or method of instruction. AEA recommends that all Aquatic Fitness Professionals maintain cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) training. AEA mandates that all AEA Certified Aquatic Fitness Professionals maintain current and valid CPR. Standards and Guidelines for Aquatic Fitness Programming 6
8 AEA recommends that all Aquatic Fitness Professionals are trained in proper use of an automated external defibrillator (AED). AEA mandates that all AEA Certified Aquatic Fitness Professionals maintain current and valid AED training. AEA recommends that all Aquatic Fitness Professionals be trained in water safety techniques. AEA recommends that all Aquatic Fitness Professionals be trained in standard first aid techniques. AEA recommends that all Aquatic Fitness Professionals be aware of the pool facility s emergency action plan (EAP) and know his/her role in the plan. AEA recommends that all Aquatic Fitness Professionals teaching/training in private pools develop an EAP. This should be clearly posted for participants reference. Deck Instruction AEA recommends deck instruction as the preferred method of leading aquatic fitness in most situations. Deck instruction provides the highest level of safety for the participants by allowing better observation and quicker response to emergency situations. Deck instruction also provides greater visibility of the Aquatic Fitness Professional to the participant and the participant to the Aquatic Fitness Professional. AEA recommends that the Aquatic Fitness Professional remain on deck when there is no additional lifeguard on duty, there are new participants in the program, or when new movements are being demonstrated. The safety of the Aquatic Fitness Professional does not have to be compromised if proper precautions are taken. Suggestions for safe deck instruction include: Avoid high impact movement demonstration Utilize a chair for low impact demonstrations and balance needs Consider non-impact teaching techniques Wear proper footwear for deck instruction When available, use a teaching mat to reduce impact stress Wear appropriate clothing for the environment in which you work Drink sufficient water to stay hydrated and protect your voice Use a microphone when available or incorporate nonverbal cues Position the music source where it provides the least interference with vocal cueing Use caution when utilizing any electrical source including sound systems near a pool due to potential hazard of electrical shock Lead the workout rather than participate in the workout Train for endurance, strength, flexibility and balance within your personal workout program to assure the ability to perform safely on deck Classes Per Week The number of classes an Aquatic Fitness Professional can safely lead per week will be determined by many factors, including the individual s personal health and fitness levels, environmental considerations, types of programs offered, length of classes, and of course the degree of leadership versus participation. General recommendations would be for the Aquatic Fitness Professional to lead no more than 15 classes per week and to monitor for signs/symptoms of overtraining and chronic dehydration. This recommendation is made assuming that the Aquatic Fitness Professional is utilizing safe deck instruction techniques and is leading the class rather than participating in the workout. Classes Per Day The number of classes an Aquatic Fitness Professional can safely lead per day will be determined by many factors, including the individual s personal health and fitness levels, environmental considerations, types of programs offered and length of classes. General recommendations would be for the Aquatic Fitness Professional to lead no more than 2 classes per day at a high intensity or up to 4 classes if the class format and the teaching style allows lower intensity performance. Monitor for signs/symptoms of overtraining and chronic dehydration. Rest periods between classes will also influence the number of classes that can be safely taught per day. This recommendation is made assuming that the Aquatic Fitness Professional is utilizing safe deck instruction techniques. Standards and Guidelines for Aquatic Fitness Programming 7
9 Class Size AEA recommends a space of 4 x 8 (32 square feet) per person for a typical shallow-water cardiorespiratory format without equipment. This space requirement may increase if equipment is added. To determine the number of students for your pool, measure the square footage of the useable area (based upon depth and bottom slope for shallow water) then divide by 32. The working space for deep-water exercise is a little larger than shallow-water, because deep-water participants tend to drift. Ideally, each deep-water exercise participant should have square feet of working space depending upon the level of the class, the type of programming and equipment choices. To determine the number of students for your pool, measure the square footage of the useable area (based upon appropriate water depth) then divide by A maximum of 25 students per Aquatic Fitness Professional is recommended when an additional lifeguard is not present. It is recommended to have a maximum of 50 students per Aquatic Fitness Professional when one additional lifeguard is on duty. Lifeguard Country, state, county and local codes relating to lifeguard regulations should always be followed. For maximal safety of participants and limited liability for the Aquatic Fitness Professional and facility, AEA recommends that a certified lifeguard, in addition to the Aquatic Fitness Professional leading the class/session, should be on duty at the pool facility when aquatic fitness classes are being held. If an additional certified lifeguard is not present during the aquatic fitness class/session, AEA recommends: 1 The Aquatic Fitness Professional to be certified in water safety and basic water rescue techniques. 2 The Aquatic Fitness Professional to remain on deck while leading the class/session unless it is a one-onone session or small group training (2-5 participants) that requires in-water assistance or guidance. 3 The Aquatic Fitness Professional to be fully aware of the facility s Emergency Action Plan (EAP) and his/ her role in this plan. Thunder/Lightning Swimming pools are connected to a much larger surface area through underground water pipes, gas lines, and electric and telephone wiring. According to the National Lightning Safety Institute (NLSI), lightning that strikes anywhere on this metallic network could result in electrical shocks elsewhere. You must comply with state, county, and local safety codes. In an electrical storm, adhere to safety policies and know your role in the emergency action plans for all pools where you work or train. The National Swimming Pool Foundation Pool and Spa Operator Handbook (NSPF 2014) follows the American Red Cross guidelines pertaining to outdoor swimming pools. Clear everyone from the outdoor pool and the surrounding deck area at the first sound of thunder or first sighting of lightning. When possible, move everyone inside and away from the water. Most organizations also recommend clearing indoor swimming pools during a thunderstorm. It is generally recommended to wait 30 minutes after the last observed lightning or thunder before resuming activities in or around the pool. Standards and Guidelines for Aquatic Fitness Programming 8
10 Terminology Shallow-water Aquatic Training Exercise typically performed in water that ranges from mid-rib cage to mid-chest. This provides the benefits of both reduced impact and grounding forces, allows for proper alignment and movement control. Deep-water Aquatic Training Exercise program performed suspended in water at a depth that allows participants to remain vertical while not touching the bottom of the pool. Flotation equipment is typically utilized to maintain correct alignment. Transitional Depth Aquatic Training Exercise performed in water depths between 4 and 6 feet ( m). Flotation equipment may be used, and shoes are recommended because there is some contact with the pool bottom. Body Positions for Aquatic Fitness Supine Lying in a face up position. Water exercise programs may utilize a modified supine position where the hips are slightly lower than the shoulders and the knees or feet. Prone Lying in a face down position. Water exercise programs may utilize a modified prone position or plank position where body is on an angle with the feet lower in the water (either touching the pool bottom or suspended) to allow the head to remain above the water s surface. Vertical Most shallow- and deep-water fitness programs are conducted primarily in a vertical (standing) position, or modified vertical position (seated, Level II, or Level III), allowing participants with limited swim skills to safely and comfortably enjoy the water. Focus on maintaining, or returning to, proper neutral alignment when training in the water, both shallow and deep programming. The following will influence body alignment: exercise/movement selection, speed of movement, transitions, and equipment. Upper Body Techniques Arms can be used to assist or impede movement and thus alter intensity, aid with balance, or create a challenge to the core muscles. Arms can be used both in and out of the water, depending upon the goals of the exercise and the abilities of the population. There are five basic ways to add variety using arm movements. Change typical arm and leg patterns. Create specific combinations with the arms. Use the arms above the water s surface. Hold the arms in a neutral position. Float the arms on the surface of the water. Surface area created by the hand position while moving through the water can alter exercise intensity. Impact Options for Shallow Water Grounded Movements performed in an upright position, but one foot remains in contact with the pool bottom at all times. Level I Movements performed in an upright position that involve impacting. Both feet are off the pool bottom for a brief period of time and then land or rebound. Level II Movements performed by flexing the hips and knees to submerge the body to shoulder depth. Both feet are off the pool bottom for a brief period of time, but impact is reduced due to body position. Level III Movements performed with the hips and knees flexed to submerge the body and the feet do not touch the pool bottom (body is suspended). Simulates deepwater training in shallow water. Standards and Guidelines for Aquatic Fitness Programming 9
11 Power Tucks Variations of movements performed in levels I, II, and III where the knees pull forcefully toward the chest and then the legs push forcefully away toward the pool bottom. Power tucks increase impact with level I moves. Propelled Plyometric movements performed in the water; jump training. Movement Tempos Water Tempo Movement occurs on every other beat of the music. 1/2 Water Tempo Water tempo movements with an added bounce or pause on every other beat of the music. A movement, including the bounce or pause, requires four beats of the music Land Tempo or Double Time The same speed of movement used on land; movement occurs at each beat of the music. Transitions Shallow-water Basic A transition where the next move begins where the previous move ended or it passes through neutral alignment. A basic transition passes from: a one-footed move to a one-footed move in the same plane a one-footed move to a two-footed (or vice versa) move with a center bounce a two-footed move to a two-footed move with a center bounce Intermediate A transition that requires more coordination and core strength to maintain safe alignment; the arms assist with balance as needed. An intermediate transition passes from: a one-footed move to a one-footed move in a different plane a one-footed move to a two-footed move (or vice versa) without a center bounce a two-footed move to a two-footed move without a center bounce Advanced A transition designed for experienced aquatic participants, fit participants, or athletes. An advanced transition passes from: a one-footed move to a two-footed move (or vice versa) with a change in impact level any transition that involves a change in plane and a change in impact level Deep-water Basic Transition A transition where the next move begins where the previous move ended, or it passes through neutral alignment. Transitional Move The addition of a simple move, often a jog or vertical flutter kick, to allow more time to prepare for the next movement in a pattern; may be needed to change planes or direction of travel, or simply to stabilize the body. Tempo Transition A transition that uses 1/2 water tempo movements to aid in smooth transitions. A one-count return to the center position (pause center) or a center tuck replaces the bounce center found in shallow-water programming. One can also incorporate doubles in Tempo Transitions for deep-water formats. Standards and Guidelines for Aquatic Fitness Programming 10
AEA Aquatic Fitness Professional Learning Objectives
 AEA Aquatic Fitness Professional Learning Objectives GENERAL CATEGORIES Categories correspond to chapters of the Aquatic Fitness Professional Manual, Seventh Edition PART I: Foundations of Fitness and
AEA Aquatic Fitness Professional Learning Objectives GENERAL CATEGORIES Categories correspond to chapters of the Aquatic Fitness Professional Manual, Seventh Edition PART I: Foundations of Fitness and
AQUA 101: Principles of Water
 AQUA 101: Principles of Water Here is a summary of what you are about to learn: Laws of Motion: Sir Isaac Newton An object in motion will stay in motion (same with rest) Action/ Reaction: for every action
AQUA 101: Principles of Water Here is a summary of what you are about to learn: Laws of Motion: Sir Isaac Newton An object in motion will stay in motion (same with rest) Action/ Reaction: for every action
PAULINE S WORKSHOPS. If you don t see what you want here, I have another list of workshops that I can send you.
 PAULINE S WORKSHOPS The following is a list of current workshops I am offering to host facilities. All my workshops are approved by AEA for Continuing Education Credits. You are welcome to ask me for special
PAULINE S WORKSHOPS The following is a list of current workshops I am offering to host facilities. All my workshops are approved by AEA for Continuing Education Credits. You are welcome to ask me for special
Aquatic Fitness Professional Practical & Skill Applications Course Outline Please bring this handout to the course for reference.
 Aquatic Fitness Professional Practical & Skill Applications Course Outline Please bring this handout to the course for reference. The Aquatic Fitness Professional (AFP) Practical & Skill Applications Course
Aquatic Fitness Professional Practical & Skill Applications Course Outline Please bring this handout to the course for reference. The Aquatic Fitness Professional (AFP) Practical & Skill Applications Course
Aquatic Fitness Professional Certification Examination Study Objectives
 Aquatic Fitness Professional Certification Examination Study Objectives AEA s Mission The Aquatic Exercise Association (AEA) is a nonprofit organization committed to the advancement of aquatic fitness,
Aquatic Fitness Professional Certification Examination Study Objectives AEA s Mission The Aquatic Exercise Association (AEA) is a nonprofit organization committed to the advancement of aquatic fitness,
Hockey Canada. 8.0 Injury Prevention Techniques. 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning
 8.0 Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they are physically fit. In addition, well conditioned athletes
8.0 Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they are physically fit. In addition, well conditioned athletes
return to sports after injury IMPROVING STRENGTH, POWER, AND AGILITY
 return to sports after injury IMPROVING STRENGTH, POWER, AND AGILITY This booklet is designed for people recovering from a knee or leg injury who participate in recreational or competitive sports such
return to sports after injury IMPROVING STRENGTH, POWER, AND AGILITY This booklet is designed for people recovering from a knee or leg injury who participate in recreational or competitive sports such
INJURY PREVENTION TECHNIQUES
 Hockey Canada Safety Program Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning INJURY PREVENTION TECHNIQUES It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they
Hockey Canada Safety Program Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning INJURY PREVENTION TECHNIQUES It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they
Ashley Bishop Session #325 Cardio Combos: Dual Depth
 Take the mystery out of aquatic choreography and gain a better understanding of Add-On, Pyramid & Pure Repetition choreography styles. In this session, we will use the basic principles of the choreography
Take the mystery out of aquatic choreography and gain a better understanding of Add-On, Pyramid & Pure Repetition choreography styles. In this session, we will use the basic principles of the choreography
CEC ARTICLE: Basics of Deep Water By Cynthia Holcomb
 CEC ARTICLE: Basics of Deep Water By Cynthia Holcomb INTRODUCTION Deep versus shallow: They both have benefits and precautions and use the muscles very differently. In a good cross training program both
CEC ARTICLE: Basics of Deep Water By Cynthia Holcomb INTRODUCTION Deep versus shallow: They both have benefits and precautions and use the muscles very differently. In a good cross training program both
Lower Body Plyometric Exercises
 Lower Body Plyometric Exercises These animated lower body plyometric exercises can be used to develop power in any sport that involves sprinting, jumping, quick changes of direction and kicking etc. They
Lower Body Plyometric Exercises These animated lower body plyometric exercises can be used to develop power in any sport that involves sprinting, jumping, quick changes of direction and kicking etc. They
EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD
 EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD My exercise goals Name What is my target heart rate? What is the maximum heart rate I should not exceed? What is my target rating of perceived exertion?
EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD My exercise goals Name What is my target heart rate? What is the maximum heart rate I should not exceed? What is my target rating of perceived exertion?
GUIDE TO RIDE SPIN (7746) 1
 GUIDE TO RIDE www.spinning.com 800.847.SPIN (7746) 1 WELCOME TO THE SPINNING PROGRAM As the creators and global leaders of indoor cycling equipment and education, we know what it takes to help you get
GUIDE TO RIDE www.spinning.com 800.847.SPIN (7746) 1 WELCOME TO THE SPINNING PROGRAM As the creators and global leaders of indoor cycling equipment and education, we know what it takes to help you get
MVP Most Versatile Power Tool!
 MVP Most Versatile Power Tool! IDEA World session 736 Aileen Sheron This workshop showcases the tremendous versatility of resistance tubing by integrating strength, cardio and flexibility exercises. Combinations
MVP Most Versatile Power Tool! IDEA World session 736 Aileen Sheron This workshop showcases the tremendous versatility of resistance tubing by integrating strength, cardio and flexibility exercises. Combinations
EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD
 EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD My exercise goals Name What is my target heart rate? What is the maximum heart rate I should not exceed? What is my target rating of perceived exertion?
EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD My exercise goals Name What is my target heart rate? What is the maximum heart rate I should not exceed? What is my target rating of perceived exertion?
Preparing for ORPAT. Major areas of fitness: 1. Flexibility 2. Cardiopulmonary Endurance 3. Muscular Strength 4. Muscular Endurance
 Preparing for ORPAT This guide is a resource for those individuals preparing for the Oregon Physical Ability Test (ORPAT). Individuals should consult with a medical or health professional before beginning
Preparing for ORPAT This guide is a resource for those individuals preparing for the Oregon Physical Ability Test (ORPAT). Individuals should consult with a medical or health professional before beginning
WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT AND HOW CAN IT BE TRAINED SUCCESSFULLY IN THE WATER?
 WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT AND HOW CAN IT BE TRAINED SUCCESSFULLY IN THE WATER? The #1 Reason for introducing Functional Movement into an aquatic program is to help people complete a specific task or
WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT AND HOW CAN IT BE TRAINED SUCCESSFULLY IN THE WATER? The #1 Reason for introducing Functional Movement into an aquatic program is to help people complete a specific task or
Gulf Indian High School, Dubai
 Gulf Indian High School, Dubai Department of Physical Education Workout Routine for Overweight /Obese children s GRADES 4 12 Best Workouts for Overweight Beginners Beginner Exercises foroverweight /Obesechildren
Gulf Indian High School, Dubai Department of Physical Education Workout Routine for Overweight /Obese children s GRADES 4 12 Best Workouts for Overweight Beginners Beginner Exercises foroverweight /Obesechildren
Sports Conditioning for the Knee A guide to conditioning and knee injury prevention
 Alex Petruska, PT, SCS, LAT Sports Conditioning for the Knee A guide to conditioning and knee injury prevention This program has been developed to provide a comprehensive guide to the conditioning of the
Alex Petruska, PT, SCS, LAT Sports Conditioning for the Knee A guide to conditioning and knee injury prevention This program has been developed to provide a comprehensive guide to the conditioning of the
Exercise Library. Exercise Image Description. Air Squats. Assisted Dips. Assisted Pull- Ups
 Exercise Library Exercise Image Description Air Squats Start in standing position with arms by side or in front of you. Squat down until your thighs are parallel to the ground, then return to standing.
Exercise Library Exercise Image Description Air Squats Start in standing position with arms by side or in front of you. Squat down until your thighs are parallel to the ground, then return to standing.
PLYOMETRIC TRAINING. for performance
 Written & modelled by Nicole Seymour PLYOMETRIC TRINING for performance For many years finess coaches and professional athletes have been on a quest to try and improve their power, in order to enhance
Written & modelled by Nicole Seymour PLYOMETRIC TRINING for performance For many years finess coaches and professional athletes have been on a quest to try and improve their power, in order to enhance
JENKS FIRE RESCUE PAT TEST PREPARATION GUIDE. Guide for the Physical Ability Test. Section 1 General Information and Stretching
 JENKS FIRE RESCUE PAT TEST PREPARATION GUIDE Preparation Guide for the Physical Ability Test Section 1 General Information and Stretching The job of a firefighter is one of the most physically demanding
JENKS FIRE RESCUE PAT TEST PREPARATION GUIDE Preparation Guide for the Physical Ability Test Section 1 General Information and Stretching The job of a firefighter is one of the most physically demanding
Circuits Held in our Wellness Center, this class will provide you with an introduction to our state-of-the-art fitness equipment.
 Aqua Our water-based classes are designed to maintain or improve strength and cardiovascular fitness in a low impact environment that is easier on the joints. Water and aqua equipment provide gentle resistance
Aqua Our water-based classes are designed to maintain or improve strength and cardiovascular fitness in a low impact environment that is easier on the joints. Water and aqua equipment provide gentle resistance
Physical Education Standards GRADE: K
 Physical Education Standards GRADE: K Strand: MOVEMENT COMPETENCY Standard 1: Demonstrate competency in many, and proficiency in a few, movement forms from a variety of categories. CODE PE.K.M.1.1 PE.K.M.1.10
Physical Education Standards GRADE: K Strand: MOVEMENT COMPETENCY Standard 1: Demonstrate competency in many, and proficiency in a few, movement forms from a variety of categories. CODE PE.K.M.1.1 PE.K.M.1.10
Plyometrics. Ankle Bounces. Bounding. Butt Kuck
 Plyometrics Plyometric exercises are good for power, speed and strength. These exercises are not easy so you need to be in good shape before doing them. Check with your coach and/or trainer before adding
Plyometrics Plyometric exercises are good for power, speed and strength. These exercises are not easy so you need to be in good shape before doing them. Check with your coach and/or trainer before adding
Body Bar FLEX. Exercises for the Core and Abdominals. by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc.
 Body Bar FLEX Exercises for the Core and Abdominals by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc. 1 Exercises for the Core and Abdominals This presentation features stretching and strengthening exercises
Body Bar FLEX Exercises for the Core and Abdominals by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc. 1 Exercises for the Core and Abdominals This presentation features stretching and strengthening exercises
21-Day Belly Blast Challenge!
 21-Day Belly Blast Challenge! "BONUS" Workouts! Copyright 2013 by LifeFuel Fitness and BrightLion Fitness LLC DISCLAIMER: This e-book is for information purposes only. The information presented is in no
21-Day Belly Blast Challenge! "BONUS" Workouts! Copyright 2013 by LifeFuel Fitness and BrightLion Fitness LLC DISCLAIMER: This e-book is for information purposes only. The information presented is in no
OFF-ICE. Plyometrics and Agilities. The USA Hockey Coaching Education Program is presented by REVISED 6/15
 OFF-ICE Plyometrics and Agilities The USA Hockey Coaching Education Program is presented by REVISED 6/5 OBJECTIVES To understand the importance of athleticism To determine what activities can enhance performance
OFF-ICE Plyometrics and Agilities The USA Hockey Coaching Education Program is presented by REVISED 6/5 OBJECTIVES To understand the importance of athleticism To determine what activities can enhance performance
Aquatic Exercise: Creating Opportunities for Wellness for Adults with Neurological Conditions Sarah Fishel, PT, DPT, NCS & Christine McNamara, PT, DPT
 Denver, CO October 18-20, 2017 Aquatic Exercise: Creating Opportunities for Wellness for Adults with Neurological Conditions Sarah Fishel, PT, DPT, NCS & Christine McNamara, PT, DPT Dr. Christine McNamara
Denver, CO October 18-20, 2017 Aquatic Exercise: Creating Opportunities for Wellness for Adults with Neurological Conditions Sarah Fishel, PT, DPT, NCS & Christine McNamara, PT, DPT Dr. Christine McNamara
Volunteer Instructions
 Body Mass Index (1 Volunteer / 2 Minutes) The athlete s weight and height will be measured to determine their Body Mass Index (BMI). Portable Weighing System or Scales, Measuring Tape Set-Up: Remove Portable
Body Mass Index (1 Volunteer / 2 Minutes) The athlete s weight and height will be measured to determine their Body Mass Index (BMI). Portable Weighing System or Scales, Measuring Tape Set-Up: Remove Portable
PGYVC Volleyball Circuit Athletic Plan
 PGYVC Volleyball Circuit Athletic Plan Workout Plan: This workout plan is to introduce and promote off court training for PGYVC athletes as well as to build confidence for athletes who have not done physical
PGYVC Volleyball Circuit Athletic Plan Workout Plan: This workout plan is to introduce and promote off court training for PGYVC athletes as well as to build confidence for athletes who have not done physical
Increase Strength, Flexibility, Range of Motion and Endurance. NeckXsystems Guidelines & Exercise. NeckX is Patent Pending
 Increase Strength, Flexibility, Range of Motion and Endurance NeckXsystems Guidelines & Exercise Instructions www.neckxsystems.com NeckX is Patent Pending Guidelines NeckX is an innovative neck exercise
Increase Strength, Flexibility, Range of Motion and Endurance NeckXsystems Guidelines & Exercise Instructions www.neckxsystems.com NeckX is Patent Pending Guidelines NeckX is an innovative neck exercise
ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL
 ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL page 1 INTRODUCTION The STOTT PILATES Athletic Conditioning stream serves as a bridge between STOTT PILATES standard repertoire and the CORE Athletic Conditioning
ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL page 1 INTRODUCTION The STOTT PILATES Athletic Conditioning stream serves as a bridge between STOTT PILATES standard repertoire and the CORE Athletic Conditioning
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
Snow Angels on Foam Roll
 Thoracic Mobilization on Foam Roll Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally across your mid back, and arms crossed in front of your body. Bend your knees so your feet are resting flat
Thoracic Mobilization on Foam Roll Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally across your mid back, and arms crossed in front of your body. Bend your knees so your feet are resting flat
CONTENT WHY SHOULD I USE RESISTANCE LOOP BANDS? Resistance Exercise... 1 Flexibility Exercise... 1 THE RESISTANCE LEVEL... 2
 CONTENT WHY SHOULD I USE RESISTANCE LOOP BANDS?... 1 Resistance Exercise... 1 Flexibility Exercise... 1 THE RESISTANCE LEVEL... 2 5 Band Set... 2 FLOOR EXERCISES... 4 Hip Abduction in sidelying (good for
CONTENT WHY SHOULD I USE RESISTANCE LOOP BANDS?... 1 Resistance Exercise... 1 Flexibility Exercise... 1 THE RESISTANCE LEVEL... 2 5 Band Set... 2 FLOOR EXERCISES... 4 Hip Abduction in sidelying (good for
SKAD456 (SQA Unit Code - FT7R 04) Instruct water-based exercise
 Overview This standard is about instructing water-based (aqua) exercise to apparently healthy adults. This may include young people in the 14-16 age range, provided they are part of a larger adult group.
Overview This standard is about instructing water-based (aqua) exercise to apparently healthy adults. This may include young people in the 14-16 age range, provided they are part of a larger adult group.
Older Adult Advanced
 Older Adult Advanced Older Adult - Advanced Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women above the age of 55, who have experience in exercise and are relatively fit. The workout includes
Older Adult Advanced Older Adult - Advanced Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women above the age of 55, who have experience in exercise and are relatively fit. The workout includes
Lower Body. Exercise intensity moderate to high.
 Lower Body Lower Body Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women with the goals of strengthening the lower body. Along with increasing strength of the leg muscles this workout will
Lower Body Lower Body Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women with the goals of strengthening the lower body. Along with increasing strength of the leg muscles this workout will
 1 of 8 9/21/2006 1:02 PM Smith College Dept. of Athletics Program for The Average Division III Female Athlete Trainer : Timothy Bacon Introduction Core, functional and complementary exercises. Warm Up
1 of 8 9/21/2006 1:02 PM Smith College Dept. of Athletics Program for The Average Division III Female Athlete Trainer : Timothy Bacon Introduction Core, functional and complementary exercises. Warm Up
CERTIFIED WEIGHTLIFTING PERFORMANCE COACH. Notebook THE SQUAT
 CERTIFIED WEIGHTLIFTING PERFORMANCE COACH Notebook THE SQUAT THE SQUAT Squatting as a part of Olympic weightlifting cannot be overlooked. It will be a large part of any good training program, but also
CERTIFIED WEIGHTLIFTING PERFORMANCE COACH Notebook THE SQUAT THE SQUAT Squatting as a part of Olympic weightlifting cannot be overlooked. It will be a large part of any good training program, but also
Source: Exercise in Arthritis
 Exercise in Arthritis Regular exercise boosts fitness and helps reverse joint stiffness with RA. Decrease Pain, Increase Energy Exercise more to decrease pain and feel more energetic? Hardly seems possible
Exercise in Arthritis Regular exercise boosts fitness and helps reverse joint stiffness with RA. Decrease Pain, Increase Energy Exercise more to decrease pain and feel more energetic? Hardly seems possible
The Human Trainer Full Body Express Workout
 The Human Trainer Full Body Express Workout The Human Trainer Full Body Express workout is designed to be performed nearly anywhere. This is a full body workout designed with functional exercises to increase
The Human Trainer Full Body Express Workout The Human Trainer Full Body Express workout is designed to be performed nearly anywhere. This is a full body workout designed with functional exercises to increase
319 Creating Cardio Combinations (AWS) Lindsay Mondick IAFC 2019
 319 Creating Cardio Combinations (AWS) Lindsay Mondick IAFC 2019 OBJECTIVES: Develop class planning skills and make the most out of each class you lead o Review the fundamentals of the components of fitness
319 Creating Cardio Combinations (AWS) Lindsay Mondick IAFC 2019 OBJECTIVES: Develop class planning skills and make the most out of each class you lead o Review the fundamentals of the components of fitness
AQUATIC ARSENAL. Shoulders & More By Melanie Sparks
 AQUATIC ARSENAL Shoulders & More By Melanie Sparks According to Livestron.com website, The shoulder is the most mobile and flexible joint in the human body. The truth is, we all use our shoulders a lot
AQUATIC ARSENAL Shoulders & More By Melanie Sparks According to Livestron.com website, The shoulder is the most mobile and flexible joint in the human body. The truth is, we all use our shoulders a lot
Strength Training for the Knee
 Strength Training for the Knee 40 Allied Drive This handout is to help you rebuild the strength of the muscles surrounding the knee after injury. It is intended as a guideline to help you organize a structured
Strength Training for the Knee 40 Allied Drive This handout is to help you rebuild the strength of the muscles surrounding the knee after injury. It is intended as a guideline to help you organize a structured
2002 Physioball Supplement
 2002 Physioball Supplement These exercises are not detailed on the 2002 Off-Ice Training video but will be taught in detail during the 2002 Reach for the Stars Seminar. CORE STRENGTH Physioball/ Sport
2002 Physioball Supplement These exercises are not detailed on the 2002 Off-Ice Training video but will be taught in detail during the 2002 Reach for the Stars Seminar. CORE STRENGTH Physioball/ Sport
Do the same as above, but turn your head TOWARDS the side that you re holding on to the chair.
 Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
EATA Workshop 2010 Boston
 EATA Workshop 2010 Boston Master s Degree in Strength & Conditioning Certified Athletic Trainer Certified Strength & Conditioning Coach Certified Personal Trainer USA Weightlifting Club Coach Next Level
EATA Workshop 2010 Boston Master s Degree in Strength & Conditioning Certified Athletic Trainer Certified Strength & Conditioning Coach Certified Personal Trainer USA Weightlifting Club Coach Next Level
BOGSTACLE training guide
 BOGSTACLE training guide BOGSTACLE is not just a run with a few extra obstacles thrown in the way. Being running fit will help but to avoid getting bogged down on the day you also need to practise being
BOGSTACLE training guide BOGSTACLE is not just a run with a few extra obstacles thrown in the way. Being running fit will help but to avoid getting bogged down on the day you also need to practise being
Inspiring Athleticism in Children and Youth. By Peter Twist. IDEA World 2011
 Inspiring Athleticism in Children and Youth By Peter Twist IDEA World 2011 Critical Factors to Consider When Training Young Athletes o Children are not little adults they have very specialized needs o
Inspiring Athleticism in Children and Youth By Peter Twist IDEA World 2011 Critical Factors to Consider When Training Young Athletes o Children are not little adults they have very specialized needs o
Pole Vaulting for the Athlete and Coach. Sam Houston State University Clint Blinka
 Pole Vaulting for the Athlete and Coach Sam Houston State University Clint Blinka Overview Technique physics and biomechanics: how to pole vault Pole grip and carry Approach / Pole Drop Plant / Take-Off
Pole Vaulting for the Athlete and Coach Sam Houston State University Clint Blinka Overview Technique physics and biomechanics: how to pole vault Pole grip and carry Approach / Pole Drop Plant / Take-Off
CHOOSE YOUR MOVEMENTS
 CHOOSE YOUR MOVEMENTS In each phase of the OPT model stability, strength, and power you can build a workout easily by mixing and matching movements from each of the following categories: upper- and lowerbody
CHOOSE YOUR MOVEMENTS In each phase of the OPT model stability, strength, and power you can build a workout easily by mixing and matching movements from each of the following categories: upper- and lowerbody
Standing Shoulder Internal Rotation with Anchored Resistance. Shoulder External Rotation Reactive Isometrics
 Standing Shoulder Row with Anchored Resistance Begin standing upright, holding both ends of a resistance band that is anchored in front of you at chest height, with your palms facing inward. Pull your
Standing Shoulder Row with Anchored Resistance Begin standing upright, holding both ends of a resistance band that is anchored in front of you at chest height, with your palms facing inward. Pull your
Warm Up. Shoulder Circles. Starting Position. Execution. Benefits. Fitness Test. Push Ups in 60 seconds. Burpees in 60 seconds.
 Use this tool to record your results for each test, which you take three times throughout the challenge. At the end of the challenge you can see how you have improved. Fitness Test Push Ups in 60 seconds
Use this tool to record your results for each test, which you take three times throughout the challenge. At the end of the challenge you can see how you have improved. Fitness Test Push Ups in 60 seconds
3 Moves To Improve Your Lifts
 1 Each lift has three exercises outlined to help you perform at your best. Muscle strength, endurance and stability are taken into account and serves as a guide to help coordinate all of your systems.
1 Each lift has three exercises outlined to help you perform at your best. Muscle strength, endurance and stability are taken into account and serves as a guide to help coordinate all of your systems.
Mathias Method Strength to Change the World By Ryan Mathias
 Mathias Method Strength to Change the World By Ryan Mathias Level 2- Expanding the Base This is a beginning weights program for anyone with a strong physical activity background. Level 2 teaches more basic
Mathias Method Strength to Change the World By Ryan Mathias Level 2- Expanding the Base This is a beginning weights program for anyone with a strong physical activity background. Level 2 teaches more basic
a. appropriate techniques for health history assessment. b. developing and implementing pre-participation screening procedures.
 ACSM CERTIFIED GROUP EXERCISE INSTRUCTOR SM JOB TASK ANALYSIS The job task analysis is intended to serve as a blueprint of the job of an ACSM Certified Group Exercise Instructor SM. As you prepare for
ACSM CERTIFIED GROUP EXERCISE INSTRUCTOR SM JOB TASK ANALYSIS The job task analysis is intended to serve as a blueprint of the job of an ACSM Certified Group Exercise Instructor SM. As you prepare for
Low Back Pain Home Exercises
 Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Core Strength and Stability Exercises for Swimmers
 Core Strength and Stability Exercises for Swimmers by Sharon Johnson and Bill Steele 2007 Breakwater Sports. All rights reserved. Introduction This sequence of exercises was developed by Sharon Johnson.
Core Strength and Stability Exercises for Swimmers by Sharon Johnson and Bill Steele 2007 Breakwater Sports. All rights reserved. Introduction This sequence of exercises was developed by Sharon Johnson.
Starting a Strength Training Program
 MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Starting a Strength Training Program About This Kit The key to improving strength is applying resistance to the muscle
MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Starting a Strength Training Program About This Kit The key to improving strength is applying resistance to the muscle
April 2-7 Wednesday 4
 5:30 2 8:30 20/20/20 /Cardio/Core Alexandra 9:45 11:00 4:15 5:45 6:00 7:00 (45min) Amy 3 (45min) Method April 2-7 4 Cycle/ (sign in at front desk) Anna Kendall 5 (45min) Method Cardio Step & Core 6 7 9:00
5:30 2 8:30 20/20/20 /Cardio/Core Alexandra 9:45 11:00 4:15 5:45 6:00 7:00 (45min) Amy 3 (45min) Method April 2-7 4 Cycle/ (sign in at front desk) Anna Kendall 5 (45min) Method Cardio Step & Core 6 7 9:00
Fitness Friends: Aqua Favorites
 Fitness Friends: Aqua Favorites Stephanie Thielen: Tri-Core Segment Course Description: To build a strong core you need to train a variety of muscles from your hips to your shoulders. Through a series
Fitness Friends: Aqua Favorites Stephanie Thielen: Tri-Core Segment Course Description: To build a strong core you need to train a variety of muscles from your hips to your shoulders. Through a series
Lower Extremity Physical Performance Testing. Return to Function (Level I): Core Stability
 Physical performance testing is completed with patients in order to collect data and make observations regarding the overall function of the limb integrated into the entire functional unit of the body,
Physical performance testing is completed with patients in order to collect data and make observations regarding the overall function of the limb integrated into the entire functional unit of the body,
TRAINING HIPS & THIGHS WORKOUT 50 MINUTES
 HIPS & THIGHS WORKOUT 50 MINUTES INCREASE MUSCLE STRENGTH, TONE AND ENDURANCE IN THE HIPS, THIGHS AND BUTTOCKS LEADING TO LONGER MORE POWERFUL SKATING. ROLLERBLADE HIPS & THIGHS WORKOUT 50 MINUTES SKILLS
HIPS & THIGHS WORKOUT 50 MINUTES INCREASE MUSCLE STRENGTH, TONE AND ENDURANCE IN THE HIPS, THIGHS AND BUTTOCKS LEADING TO LONGER MORE POWERFUL SKATING. ROLLERBLADE HIPS & THIGHS WORKOUT 50 MINUTES SKILLS
November 3-8 Wednesday 5 Xpress Sport Conditioning
 5:30 8:30 9:45 3 ½ & ½ Step & Strength 4 Core Initiatives November 3-8 5 Xpress Sport Conditioning Wendy HIIT w/strap Work 6 Tabatha Flow 7 Body Bar+ 8 9:00 Body Bar Kerri 10:15 Cardio Dance 11:00 Bryson
5:30 8:30 9:45 3 ½ & ½ Step & Strength 4 Core Initiatives November 3-8 5 Xpress Sport Conditioning Wendy HIIT w/strap Work 6 Tabatha Flow 7 Body Bar+ 8 9:00 Body Bar Kerri 10:15 Cardio Dance 11:00 Bryson
DEVELOPING SHOT PUT GLIDE TECHNIQUE
 DEVELOPING SHOT PUT GLIDE TECHNIQUE Attitude: This is the most powerful and explosive event in sports and you need to attack the shot. Teaching technique: Whole or partial. Great research on both but one
DEVELOPING SHOT PUT GLIDE TECHNIQUE Attitude: This is the most powerful and explosive event in sports and you need to attack the shot. Teaching technique: Whole or partial. Great research on both but one
Muscular Training This is a sample session for strength, endurance & power training exercises
 Muscular Training This is a sample session for strength, endurance & power training exercises Presenter: Leslie McAdam CCAA Trainer Education Coordinator lbrown59@uwo.ca 519-661-1607 1-866-661-1603 X81607
Muscular Training This is a sample session for strength, endurance & power training exercises Presenter: Leslie McAdam CCAA Trainer Education Coordinator lbrown59@uwo.ca 519-661-1607 1-866-661-1603 X81607
Home Workout with Household Items
 Home Workout Home Workout with Household Items Introduction This home routine is created for women and men to workout while they are at home. It incorporates the use of household items to imitate weights
Home Workout Home Workout with Household Items Introduction This home routine is created for women and men to workout while they are at home. It incorporates the use of household items to imitate weights
chapter Plyometric Training
 chapter 18 Plyometric Training Chapter Objectives Explain the physiology of plyometric exercise. Identify the phases of the stretch-shortening cycle. Identify components of a plyometric training program.
chapter 18 Plyometric Training Chapter Objectives Explain the physiology of plyometric exercise. Identify the phases of the stretch-shortening cycle. Identify components of a plyometric training program.
Dauphin County Chiefs of Police Testing Consortium Physical Fitness Test Standards
 Dauphin County Chiefs of Police Testing Consortium Physical Fitness Test Standards The standard used in the physical fitness test were derived from law enforcement physical fitness norms that are based
Dauphin County Chiefs of Police Testing Consortium Physical Fitness Test Standards The standard used in the physical fitness test were derived from law enforcement physical fitness norms that are based
Chapter 6 Group Exercise Program Design
 ACE Group Fitness Instructor Manual Chapter 6 Group Exercise Program Design 1 Participant-centered teaching approach This approach involves designing a class based on the specific needs of the participants.
ACE Group Fitness Instructor Manual Chapter 6 Group Exercise Program Design 1 Participant-centered teaching approach This approach involves designing a class based on the specific needs of the participants.
WHOLE BODY VIBRATION THERAPY
 Body Vibe WHOLE BODY VIBRATION THERAPY Instruction manual INCREASES CIRCULATION STIMULATES LYMPHATICS REDUCES CELLULITE LIQUIFIES FAT IMPROVES BALANCE DECREASES CORTISOL INCREASES ENDURANCE NON-IMPACT
Body Vibe WHOLE BODY VIBRATION THERAPY Instruction manual INCREASES CIRCULATION STIMULATES LYMPHATICS REDUCES CELLULITE LIQUIFIES FAT IMPROVES BALANCE DECREASES CORTISOL INCREASES ENDURANCE NON-IMPACT
Weight Loss Interval (Beginner)
 Program for BP Fitness Center Introduction Weight Loss Interval (Beginner) This is a full body interval workout. Keep your heart rate up to safe levels by not resting between exercises. Please workout
Program for BP Fitness Center Introduction Weight Loss Interval (Beginner) This is a full body interval workout. Keep your heart rate up to safe levels by not resting between exercises. Please workout
Prevent Falls. with the Moore Balance Brace. Many falls can be prevented. By making minor changes, you can lower your chances of falling
 Prevent Falls with the Moore Balance Brace Many falls can be prevented. By making minor changes, you can lower your chances of falling Moore Balance Brace (MBB) Instructions for use Putting the MBB into
Prevent Falls with the Moore Balance Brace Many falls can be prevented. By making minor changes, you can lower your chances of falling Moore Balance Brace (MBB) Instructions for use Putting the MBB into
 Instructions Functional Strength Workouts Do workouts 2 3 times per week alternating between Workout A and Workout B. For example, if you are working out 3 times per week, in week 1 you will do A,B,A,
Instructions Functional Strength Workouts Do workouts 2 3 times per week alternating between Workout A and Workout B. For example, if you are working out 3 times per week, in week 1 you will do A,B,A,
LETS MAKE A START. Warm up - we strongly advise that you warm up before every session. Exercise A Lung with forward reach
 LETS MAKE A START We understand that not everyone has the time to be going to the gym four times a week, which is why we have created a fitness plan that can be done in the comfort of your own home at
LETS MAKE A START We understand that not everyone has the time to be going to the gym four times a week, which is why we have created a fitness plan that can be done in the comfort of your own home at
anchor point. Essentially, the more the body is parallel to the floor, the more difficult the exercise. The third set of pictures shows two common
 ST BOWLER SQUAT The bowler squat performed with a suspension trainer is a great little single leg squat/hinge combo! The suspension trainer assists with balance and I believe makes the exercise more effective.
ST BOWLER SQUAT The bowler squat performed with a suspension trainer is a great little single leg squat/hinge combo! The suspension trainer assists with balance and I believe makes the exercise more effective.
Exercise for Health Aging
 Exercise for Health Aging General Training Guidelines Perform workouts two or three days per week Allow for at least one day of rest in between workouts Include exercises in each workout that use different
Exercise for Health Aging General Training Guidelines Perform workouts two or three days per week Allow for at least one day of rest in between workouts Include exercises in each workout that use different
Monster Walk Stand with your feet slightly closer than shoulder-width apart in an athletic stance. Loop an elastic band around your ankles.
 Off-season Lower-Body Tennis Exercises Research conducted on elite tennis players shows that lower-body strength is the same on both the left and right sides. Therefore, lower-body training for tennis
Off-season Lower-Body Tennis Exercises Research conducted on elite tennis players shows that lower-body strength is the same on both the left and right sides. Therefore, lower-body training for tennis
BODY WEIGHT EDITION. Who needs the gym when you can exercise in the convenience of your living room floor?
 Legal Disclaimer The information presented in this work is by no way intended as medical advice or as a substitute for medical counseling. The information should be used in conjunction with the guidance
Legal Disclaimer The information presented in this work is by no way intended as medical advice or as a substitute for medical counseling. The information should be used in conjunction with the guidance
Bench Press (free weights) Pullover (dumbbell) Prone-grip pull-up (tower/assisted platform
 When exercising always incorporate a warm-up for at least 5 minutes. Typically a warm-up should be a whole body exercise i.e. jumping jacks, jogging, calisthenics, etc The repetitions represent how much
When exercising always incorporate a warm-up for at least 5 minutes. Typically a warm-up should be a whole body exercise i.e. jumping jacks, jogging, calisthenics, etc The repetitions represent how much
POST-THROWING RECOVERY WORK
 POST-THROWING RECOVERY WORK 8 A comprehensive post-throwing recovery program is just as important as a pre-throwing warm-up phase. Whether the athlete has just finished pitching in a game, completed a
POST-THROWING RECOVERY WORK 8 A comprehensive post-throwing recovery program is just as important as a pre-throwing warm-up phase. Whether the athlete has just finished pitching in a game, completed a
Cumberland County Police Testing Consortium Applicant Fitness Test
 Cumberland County Police Testing Consortium Applicant Fitness Test This is a pass or fail test. The individual tests will be conducted in the order displayed below. 1. Vertical Jump Requirement Jump at
Cumberland County Police Testing Consortium Applicant Fitness Test This is a pass or fail test. The individual tests will be conducted in the order displayed below. 1. Vertical Jump Requirement Jump at
Strength Training Sessions for Runners: Plyometrics
 Strength Training Sessions for Runners: Plyometrics Plyometrics, or Jump Training focuses on increasing power and explosive movement. Plyometric exercises involve jumping movements and expending large
Strength Training Sessions for Runners: Plyometrics Plyometrics, or Jump Training focuses on increasing power and explosive movement. Plyometric exercises involve jumping movements and expending large
suspense Aquatic center
 suspense Aquatic center Suspense, a creation for aquatic convenience HydroCo, a world leader in hydrotherapy equipment introduces a revolutionary approach to aquatic convenience Suspense. The use of water
suspense Aquatic center Suspense, a creation for aquatic convenience HydroCo, a world leader in hydrotherapy equipment introduces a revolutionary approach to aquatic convenience Suspense. The use of water
Fitness is a big part of this new program, and will be an important part of your training season.
 Fitness, Strength and Sport Training Staying physically fit is very important to being a good athlete. To excel at your sport you have to make healthy choices in your lifestyle. Fitness is a big part of
Fitness, Strength and Sport Training Staying physically fit is very important to being a good athlete. To excel at your sport you have to make healthy choices in your lifestyle. Fitness is a big part of
Unit 1: Fitness for Sport and Exercise. Fitness Testing
 Unit 1: Fitness for Sport and Exercise Fitness Testing Importance of fitness testing Gives baseline data for monitoring/improving performance Can design training programmes based on test results and determine
Unit 1: Fitness for Sport and Exercise Fitness Testing Importance of fitness testing Gives baseline data for monitoring/improving performance Can design training programmes based on test results and determine
IFA Aqua Fitness Certification Test Answer Form
 IFA Aqua Fitness Certification Test Answer Form In order to receive your certification card, take the following test and mail this single page answer sheet in with your check or money order in US funds.
IFA Aqua Fitness Certification Test Answer Form In order to receive your certification card, take the following test and mail this single page answer sheet in with your check or money order in US funds.
Presented by Maureen Hagan BScPT (Physiotherapist), BA PE ACE, Can-Fit-Pro Certified 2006 IDEA Fitness Instructor & 1998 Program Director of the Year
 Presented by Maureen Hagan BScPT (Physiotherapist), BA PE ACE, Can-Fit-Pro Certified 2006 IDEA Fitness Instructor & 1998 Program Director of the Year 1. Overview the most common age-related risk factors
Presented by Maureen Hagan BScPT (Physiotherapist), BA PE ACE, Can-Fit-Pro Certified 2006 IDEA Fitness Instructor & 1998 Program Director of the Year 1. Overview the most common age-related risk factors
RIB FRACTURE. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms. Diagnosis
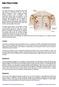 RIB FRACTURE Explanation The heart and lungs are encased by the chest wall, which is composed of the ribs. The ribs must be flexible in order to allow movement during expansion and contraction. This movement
RIB FRACTURE Explanation The heart and lungs are encased by the chest wall, which is composed of the ribs. The ribs must be flexible in order to allow movement during expansion and contraction. This movement
Posture Pump PENTAVEC Model 2500 Instructions
 Posture Pump PENTAVEC Model 2500 Instructions page 1 of 6 TRAINING INSTRUCTIONS CAUTION: CAREFULLY READ AND ADJUST THE PELVIC AND FOOT-UNIT BELTS PER "ADJUSTING THE PELVIC PULL" INSTRUCTIONS ON THE FOLLOWING
Posture Pump PENTAVEC Model 2500 Instructions page 1 of 6 TRAINING INSTRUCTIONS CAUTION: CAREFULLY READ AND ADJUST THE PELVIC AND FOOT-UNIT BELTS PER "ADJUSTING THE PELVIC PULL" INSTRUCTIONS ON THE FOLLOWING
THERMAL - ASSISTED CAPSULORRAPHY With or without SLAP Repair
 THERMAL - ASSISTED CAPSULORRAPHY With or without SLAP Repair **It is important for the clinician to determine the capsular response to the heat probe. Patients that have excessive ROM early in the rehab
THERMAL - ASSISTED CAPSULORRAPHY With or without SLAP Repair **It is important for the clinician to determine the capsular response to the heat probe. Patients that have excessive ROM early in the rehab
REMEMBER GOOD POSTURE DURING ALL YOUR EXERCISES, AVOID SLOUCHING AS YOUR CURRENT PROGRAM BECOMES EASY SLOWLY INCREASE:
 REMEMBER GOOD POSTURE DURING ALL YOUR EXERCISES, AVOID SLOUCHING Apr 06, 2017 AS YOUR CURRENT PROGRAM BECOMES EASY SLOWLY INCREASE: # OF LAPS YOU ARE WALKING # OF REPITITIONS # OF SECONDS YOU HOLD A STRETCH
REMEMBER GOOD POSTURE DURING ALL YOUR EXERCISES, AVOID SLOUCHING Apr 06, 2017 AS YOUR CURRENT PROGRAM BECOMES EASY SLOWLY INCREASE: # OF LAPS YOU ARE WALKING # OF REPITITIONS # OF SECONDS YOU HOLD A STRETCH
Jennifer L. Cook, MD
 Jennifer L. Cook, MD Florida Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Center 5243 Hanff Lane New Port Richey, FL 34652 Phone: (727)848-4249 Fax: (727) 841-8934 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE
Jennifer L. Cook, MD Florida Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Center 5243 Hanff Lane New Port Richey, FL 34652 Phone: (727)848-4249 Fax: (727) 841-8934 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE
Active-Assisted Stretches
 1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
CORE EXERCISES INTRODUCTION NOTES FREQUENCY PAGE 1 OF 9. Trainer: Chad Benson
 JORDAN TRAINING. WORKOUT SUMMARY CORE Trainer: Chad Benson EXERCISES INTRODUCTION 1. Dead Bug 2. Side Bend Crunch 3. Assisted Cobra 4. Prison Side Bend 5. Roll-Up Ball Crunch 6. Lying Bridge 7. V-Sit Rotations
JORDAN TRAINING. WORKOUT SUMMARY CORE Trainer: Chad Benson EXERCISES INTRODUCTION 1. Dead Bug 2. Side Bend Crunch 3. Assisted Cobra 4. Prison Side Bend 5. Roll-Up Ball Crunch 6. Lying Bridge 7. V-Sit Rotations
February 5-10 Wednesday 7
 5:30 5 8:30 20/20/20 Strength/Cardio/Core 9:45 11:00 4:15 5:45 6:00 7:00 6 Barre Cardio & Strength Insanity Anna HIIT Agility February 5-10 7 Cycle/Strength (sign in at front desk) Pilates Matwork Kendall
5:30 5 8:30 20/20/20 Strength/Cardio/Core 9:45 11:00 4:15 5:45 6:00 7:00 6 Barre Cardio & Strength Insanity Anna HIIT Agility February 5-10 7 Cycle/Strength (sign in at front desk) Pilates Matwork Kendall
ACTIVITY TYPE. Stretching COACHING RESOURCE
 ACTIVITY TYPE Stretching 161 Stretching, Warm-up and Cool-down A regular stretching, warm-up and cool-down routine is an essential component of any athlete s program no matter what their age or competition
ACTIVITY TYPE Stretching 161 Stretching, Warm-up and Cool-down A regular stretching, warm-up and cool-down routine is an essential component of any athlete s program no matter what their age or competition
VERTICAL LEAP TRAINER INSTRUCTION MANUAL AND EXERCISE GUIDE
 VERTICAL LEAP TRAINER INSTRUCTION MANUAL AND EXERCISE GUIDE WARNING: PLEASE READ!» Do not use without shoes.» Recommended for athletes over 14 years old. Athletes under 18 years of age should use under
VERTICAL LEAP TRAINER INSTRUCTION MANUAL AND EXERCISE GUIDE WARNING: PLEASE READ!» Do not use without shoes.» Recommended for athletes over 14 years old. Athletes under 18 years of age should use under
