Practical Application for Long-Term Athletic Development
|
|
|
- Michael Palmer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 nsca.com NSCA by DR. LARRY MEADORS Practical Application for Long-Term Athletic Development by Dr. Larry Meadors Learn about the framework for practical, functional, and sequential skill development for a best practices model. This model is designed to develop a movement vocabulary, physical literacy, and movement skills for improved athleticism. INTRODUCTION Developing a comprehensive long-term athletic development program in the United States is critical. The program must start at the youth level. This article will focus on ages 3 14 years. The following information is for coaches, parents, and sport organization directors. To date, little has been done to provide youth coaches with knowledge of how to teach and develop proper movement techniques. Coaches are left often with an excessive number of competitions, incomplete athlete development, and an emphasis on sports-specific skills only. Many athletes suffer systemic overuse injuries caused by improper training and repeated sub-maximal repetition stress, followed by inadequate recovery (26). This article will offer a framework for practical, functional, and sequential skill development to assist coaches with a best practices model to develop a movement vocabulary, physical literacy, and movement skills that improve athleticism. UNCOVERING THE DISCONNECT BETWEEN ATHLETICISM AND ATHLETIC DEVELOPMENT For several decades, sport coaches have expressed the need for a 1 of 13 11/14/12 5:08 AM
2 long-term strategy to develop athletes (19). A massive amount of information (available to coaches, teachers, parents, and youth sport organizations) has been written about the development, growth, and maturation of developing athletes (13). Somehow, the importance of the message has gotten lost (12). It is clear that a better job of education and dissemination of information from scientific-based research to the parent and practitioner/coach of the athletes are needed (17). An Albert Einstein quote perhaps summarizes the situation best, the definition of insanity is doing the same thing over and over, and expecting different results. In today s society, many issues face young athletes. Sport participation can be a countermeasure to a sedentary lifestyle which is clearly prevalent and dangerous (18). Often, individuals experience failed attempts to participate in organized sports because too much emphasis is placed on competition, with little attention on developing proper athleticism (appropriate movement skills) (20,21). Individuals with limited sports and movement skills often stop participating (3,4). In turn, this neglect often leads to a decreased interest in any type of physical activity (5). The result is a failure to learn or develop physical literacy, or proper athletic movement in a sequential and progressive manner (31). A sedentary lifestyle then follows. Sedentary living causes such health problems as obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, and other chronic diseases that evolve from a lifelong problem starting in childhood. Applied to athletics, these factors result in increased injury incidences and rates, and limited skill development (26,27). These musculoskeletal injury factors are the result of overall low strength levels, incorrect landing mechanics, incorrect deceleration techniques, ligament laxity, muscle tightness, overly developed quadriceps, and over-reliance on a particular limb. These factors often lead to low back and limb misalignment and mechanics due to poor recruitment and control of the gluteals (19,23,28). PARADIGM SHIFT TO LONG-TERM ATHLETIC DEVELOPMENT School health and physical education programs, for kindergarten through 2 of 13 11/14/12 5:08 AM
3 high school, and local youth sports programs, need to implement a long-term athletic development (LTAD) model (24). LTAD is a unique concept in the United States. Similar models are being implemented in Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, and Asia. Compared with programs in other countries, the U.S. is several decades behind in its development and implementation of a comprehensive LTAD program. According to Balyi, his theoretical model can, when properly implemented, provide a change in sports programs and athletic development by identifying gaps, and providing guidelines for movement problem solving, improving performance at various stages of athletic development, and outlining a framework to develop physical literacy, physical fitness for life, and competitive athletics (2). A long-term commitment to physical literacy, proper training to improve athleticism, and sport skill development is vital to produce optimal athletic potential. Proper training and athletic development require time. Moreover, a paradigm shift needs to occur regarding the pace and process of athletic development. This paradigm shift has its own language: Physical Literacy is a fundamental and valued human capability that can be described as a disposition acquired by human individuals encompassing the motivation, confidence, and physical competence that establishes purposeful physical activity as an integral part of their lifestyle, (34). Athleticism is the result of athletic movement skills development that involves learning proper techniques for agility, balance, coordination, flexibility, metabolic training, power, reaction time, speed, strength, and strength endurance (18). TALENT DEVELOPMENT Scientific research concludes that it takes 8 12 years of training for a talented athlete to reach elite levels (6,14). It also can be argued that it takes that long, if not longer, to produce quality youth coaches who understand how to develop proper skills in children. There are no shortcuts to athletic success (13,33). Unfortunately, some coaches and parents overemphasize competition, while at the same time, approach 3 of 13 11/14/12 5:08 AM
4 proper movement skills and development to improve athleticism with little or no interest. A well-planned and balanced schedule of training, practice, competition, and recovery will enhance optimum development throughout the individual s athletic career (32). Often, change for implementation of LTAD models is difficult, because program administrators and coaches are uninformed and at times reticent to such change. Moreover, parental perspective and involvement is unresponsive (games versus appropriate training and practice time), the modern sports culture is misleading ( everyone is an expert, immediate gratification, and entitlement ), and the early specialization training model for team sports is inadequate, making LTAD implementation difficult (9). IMPORTANCE OF COACH EDUCATION Balyi reports that the early specialization training model leads to increased dropout rates, overuse injuries, early burnout, overemphasis on sport-specific preparation and a lack of basic movement skill development (2). Coach education is the foundation of long-term athletic development. Many individuals only observe the tip of the iceberg, and overlook that athletic performance occurs far beyond the sports season (7). A comprehensive LTAD program, along with skills and knowledge of both the sports coach and the strength and conditioning coach is invaluable to enhance performance (8). Proper technique and skill development must be taught and supervised by informed and experienced coaches. Also, youth coaches should be educated and qualified to the highest standard and work in an environment that is appropriately managed. FOCUS ON FUNDAMENTAL MOVEMENT SKILLS Regardless of the sports organization, the most important elements are teaching proper physical literacy and improvement of athleticism through proper skill movements learned in a sequential and progressive program design (19). These components will help an athlete become less susceptible to injuries, improve an athlete s ability to perform technical and tactical skills more effectively, and assist the athlete to cope with the demands of the sport (29). Without these components of training, individuals might never reach optimal athletic development (19). Here is 4 of 13 11/14/12 5:08 AM
5 an overview of a Sequential Sports Program Movement Development Model: Areas of focus for the entire scope of a sports program development are physical literacy and athletic movement skills development built upon a sequential program design model. Athletic development should not focus on a high performance model, but on skill improvement and on athlete retention. Each individual is an athlete at his/her own level. Emphasis should be on increasing each individual s athleticism, which will keep individuals playing longer and create a larger pool of potential talent (24). Often, coaches will implement a cookbook of thoughtless drills, which is an ineffective way of teaching proper athletic skill techniques. Anyone can purchase equipment or create a drill, which are only a means to an end. Instead, focus on essentials what needs to be encouraged, and what is best for the athlete at that particular time with knowledge of what is to come in the future. Coaches/teachers must know what correct techniques look like and how to teach and make corrections. The instructors must know the proper position of the trunk, arms, legs, and head as the individual performs various movements. The majority of athletic movements are one-dimensional (i.e., vertical, lateral, linear, diagonal, and rotational. All directly affect proper acceleration and deceleration skills. Jeffries lists five important terms to assist a coach in identifying proper body position in relationship to these movements (25): Base of support (BOS): trunk, arms Center of mass (COM): proper foot position in relation to head, proper position of head, trunk, arms, legs Line of force (LOF): proper alignment of head, trunk arms, legs Body control (BC): proper control of head, trunk, arms, legs 5 of 13 11/14/12 5:08 AM
6 Posture alignment (PA): proper position of head, trunk, arms, legs PRACTICAL APPLICATION OF LONG-TERM ATHLETIC DEVELOPMENT After listening to various LTAD presentations and having conversations with sport and strength coaches and youth sports program directors, I have yet to observe an in-depth comprehensive LTAD program in the U.S. other than a regurgitation of Balyi s language and vocabulary in explaining his program. To Balyi s credit, he has provided a model to follow. However, little has been done to provide coaches with scientific data to support his theory or the knowledge of how to teach and develop proper movement technique. Sport programs and coaches resort to overemphasizing competition and related sport skills. From a coach s standpoint, there is need for practical, functional, and sequential athlete document that will provide coaches with best practices for the development of strength, flexibility, and stability in their athletes. This document must include movement vocabulary, physical literacy, and athletic movement skills, if athleticism is to be achieved. In the fall of 2009, I was asked to develop a sequential LTAD model focused on physical literacy and athleticism for a youth baseball program utilizing physical literacy and athletic movement components. The target program encompasses a large number of volunteer coaches with athletes (ages 3 14) on an annual basis. Coach education is vital to teach proper and appropriate physical literacy and athletic movement skills in a sequential manner. The following overview is designed to identify general areas needed for physical literacy and fundamental and movement skill foundations. The objective of this overview is to teach proper movement as opposed to just running drills (15,16,22,30). Within the above categories, there is a need for developmental progression of movements and skills. For example, balance, stability, and fundamental movements should be mastered before progressing. The individual should demonstrate age appropriate competency of these 6 of 13 11/14/12 5:08 AM
7 components before attempting to demonstrate more complex object control skills because gross motor skills should be developed before fine motor skills (19). The following list of program components contains a series of movement component categories that correspond and expand the physical literacy and movement foundation: Balance and stability Fundamental/dynamic movement Object control Plyometrics Speed and agility (multidirectional) Fun drills Strength/endurance/power This list is not intended to be all-inclusive, but to provide a series of categories in which fundamental movements and other areas of athleticism must be taught in a sequential manner. The selection of movement skills is based on a modified program design model, which includes a needs analysis and exercise selection, order, volume, intensity, and frequency (1). A baseline assessment will identify the individual s athletic training background and movement competencies. Regardless of the assessment process, too much emphasis is placed on the outcome and not enough on the importance of proper technique. Misguided emphasis will result in delayed proper athletic development. The intent of this endeavor is to teach foundational movement skills and improve athleticism. Coaches often become possessive of their sport s skill practice time and are not willing to relinquish time to teach fundamental movement. Regardless of an athlete s talent level, the desire to achieve agility, power, speed, and strength dominates a sport coach s plan to win, and results in missed opportunities to develop, based on the individual s maturation. Coach education is the foundation of the program s success and must involve understanding the importance of exercise selection and sequence, and how these influence physical literacy and athleticism. 7 of 13 11/14/12 5:08 AM
8 Exercise selection should be based on an individual s background and experience paired with coaching points and progression standards. An example of sequence includes simple to complex, slow to fast, static to dynamic, and unloaded to loaded. The athlete must be able to control his/her bodyweight, develop physical resilience, and master proper movement of all joints, in all directions and through all planes. Coaches must understand the theory of LTAD and deliver best practices at each level. Emphasis must be placed on development, which starts with an assessment or screening to determine the individual s strengths and weaknesses (11,19). A basic principle of maturation indicates that all children are at different stages within certain age levels. There can be a four-year difference in cognitive, emotional, and physical development in individuals of the same chronological age group (2). Often, volunteer coaches (parents), with limited knowledge of teaching and identifying proper movements, are in charge of providing the only fundamental movement skills for youth. Limited knowledge is due to lack of priority to provide health and physical education programs at all levels within a school. Therefore, youth sports programs may be the only entity to provide the basis for fundamental movements and physical literacy. A successful LTAD program must provide coach education to implement a sequential pathway and should be able to answer these questions: Is the process evidence-based? Are best practices implemented to provide proper training, competition, and recovery? Is exercise selection sequential and progressive? Has coach education been provided in all aspects of athletic development? Does the program provide for individual maturation variables (physical, mental, emotional)? Is education and communication provided for coaches, parents, and athletes? The following tables provide a series of sequential movements and serve as yearly benchmarks for the individual to accomplish in a reasonable 8 of 13 11/14/12 5:08 AM
9 amount of time (i.e., when there is an age change or at the end of the year). The structure of the youth baseball program is divided into age groups for training and competition. To correspond with the sports program s age-related organization the following movements are introduced: Ages 3 and 4: Teach balance/stability, fundamental/dynamic movement, object control Ages 5 and 6: Teach and review the above skills, add plyometrics, speed and agility Ages 7 and 8: Teach and review the above skills, add strength, endurance, power Ages 9 through 14: Teach and review the above skills Only a list of movements is provided. Due to limited space, an explanation of the complete description of each movement and/or exercise is restricted. SUMMARY The future of LTAD in the U.S. depends on the education and involvement of parents, coaches, and sport program organizations with an educational system. Regardless of who is involved, priority must be on what is best for 9 of 13 11/14/12 5:08 AM
10 the athlete. At present, the best coaches work with the most advanced athletes while volunteers coach the most critical areas during critical periods of development. Often, the focus of programs and coaches is to promote winning rather than developing proper technical and tactical skills. Coaches at all levels must be trained and supported so proper skills can be taught, and corrections, if necessary, can be made. Frequently, adult programs are imposed on young athletes, thus the basic components of physical literacy or athleticism are not implemented in a sequential manner. As a result, many athletes never reach optimal performance levels. The results of these inadequacies create poor skill movements due to a lack of proper development, poor skill development because of poor teaching skills, and poor sport skill development because of excessive competition. The dilemma associated with injury rates in turn reduces the individual s general fitness level, which leads to the possibility of increased obesity and other health-related problems. A successful LTAD program must implement, and become committed to, coach education at all levels. It should be coach-driven and athletefocused in an attempt to create a family concept, and include proper training, competition, and a recovery plan. Also, it must allow for individual physical, mental, and emotional development. Typically, we fear what we do not understand; we distrust what is different. Change is inevitable, progress is optional. References Baechle, TR, and Earle, RW. Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; , Balyi, I. Sport System Building and Long Term Athlete Development in Canada, The Situations and Solutions, Coaches Report. The Official Publication of the Professional Coaches Association 8(1): 25-28, Barnett, LM, Van Beurden, E, Morgan, PJ, Brooks, LO, and Beard, JR. Does Childhood Motor Skill Proficiency Predict Adolescent Fitness? Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 40(12): , 10 of 13 11/14/12 5:08 AM
11 Barnett, LM, Van Beurden, E, Morgan, PJ, Brooks, LO, and Beard, JR. Childhood Motor Skill Proficiency as a Predictor of Adolescent Activity. Journal of Adolescent Health 44(3): , Barnett, LM, Morgan, P.J, Van Beurden, E, Ball, K, and Lubans, DR. A Reverse Pathway? Actual and Perceived Skill Proficiency and Physical Activity. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 43(5): , Bloom, B. Developing Talent in Young People. New York: Ballantine Books; Bompa, T. Total Training for Young Champions. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; Brewer, C. Strength and Conditioning for Sport: A Practical Guideline for Coaches. Leeds, UK: Coachwise Business Solutions; Council on Sports Medicine and Fitness. Intensive and Sports Specialization in Young Athletes. Pediatrics (Electronic version) 106: , Chu, D, Faigenbaum, A, and Falkel, J. Progression Plyometrics for Kids. Monterey, CA: Healthy Learning; Cook, G. Athletic Body in Balance. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; 11-16, 25-86, Drabik, J. Children & Sports Training How Your Future Champions Should Exercise to Be Healthy, Fit and Happy. Island Pond, VR: Stadion Publishing Company Inc.; Earle, C. Coaching Young Performers. Sport Coach UK. (2 nd Ed.). Chelsea, England: Coachwise Business Solutions, Ericcson, KA, Krampe, RT, and Clemens, TR. The Role of Deliberate Practice in the Acquisition of Expert Performance. Psychological Review 100(3): , Gabbard, CP. Lifelong Motor Development. Toronto: Allyn & Bacon; Gallahue, DL. Fundamental Movement Abilities. Indianapolis, IN: Brown & Benchmark; Gamble, P. Approaching Physical Preparation for Youth Team-Sports 11 of 13 11/14/12 5:08 AM
12 Players. Strength and Conditioning Journal 30(1): 29-42, Gambetta, V, and Winkler, G. Sports Specific Speed the 3 S System. Sarasota, FL: Gambetta Sports Training System, Inc.; Giles, K. Assessment Manual Langford, Bedfordshire: Movement Dynamics, UK, Ltd. 20. Gorman, C. Why More Kids Are Getting Hurt. Time Magazine May 31, Gorman, C. How We re Harming Young Athletes. Time Magazine September 10, Haywood, K, and Gretchen, N. Lifespan Motor Development. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; Hawkins, D. and Metheny, J. Overuse Injuries in Youth Sports: Biomechanical Considerations. Medicine & Science in Sport & Exercise (Electronic version) 33(10): , Howard, R, and Faigenbaum, A. Issues in Training Youth That Impact High School Athletic Preparation. Strength and Conditioning Journal 31(3): 55-57, Jefferies, I. Gamespeed: Movement Training for Superior Sport Performance. Monterey, CA: Coaches Choice; Johnson, J. Overuse Injuries in Young Athletes: Causes and Prevention. Strength and ConditioningJournal 30(2): 27-31, Little Athletes, Big Injuries. Time Magazine February 14, Lysens, R, Ostyn, M, Vanden Auweela, Y, Lefevre, J, Vuysteke, M, and Renson, L. The Accident-Prone and Over-Prone Profiles of Young Athletes. American Journal of SportsMedicine (Electronic versions) 17(1): , Myer, G, Faigenbaum, A, Ford, K, Best, T, Bergeron, M, and Hewett, T. When to Initiate Integrative Neuromuscular Training to Reduce Sport-Related Injures and Enhance Health inyouth? Current Sports medical Reports 10(3): , Payne, GV, and Isaacs, LD. Human Motor Development. Toronto: McGraw-Hill; Shanmugan, C, and Maffulli, N. Sport Injuries in Children. British Medical Bulletin (Electronic version) 86(1): 33-57, Stone, MH, Stone, M, and Sands, W. Principles of Resistance 12 of 13 11/14/12 5:08 AM
13 Training and Practices. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; , Wickel, E, and Elsenmann, J. Contributions of Youth Sports to Daily Physical Activity Among 6-12 year old Boys. Medicine & Science in Sport & Exercise 39(9): , Whitehead, M. The Concept of Physical Literacy. European Journal of Physical Education (6): , About the Author Larry Meadors PhD, CSCS,*D, NSCA-CPT,*D, RSCC*E, USAW-level 2. Currently in his 50th year of teaching and coaching, Dr. Larry Meadors was the NSCA s National High School Strength & Conditioning Coach of the Year in2003, and was the recipient of the prestigious President s Award in He currently works with Burnsville Youth Development as the Program Director. He can be reached through: lgmeadors@comcast.net Original URL: /PublicationArticleDetail.aspx?id= of 13 11/14/12 5:08 AM
NATIONAL STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING ASSOCIATION (Position Statement on Long-Term Athletic Development)
 NATIONAL STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING ASSOCIATION (Position Statement on Long-Term Athletic Development) Introduction Developing a comprehensive long-term athletic development program in the United States
NATIONAL STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING ASSOCIATION (Position Statement on Long-Term Athletic Development) Introduction Developing a comprehensive long-term athletic development program in the United States
SOUTH AFRICAN HOCKEY ASSOCIATION LONG TERM PARTICIPANTS DEVELOPMENT (LTPD) SUMMARY GUIDE
 South African Hockey SOUTH AFRICAN HOCKEY ASSOCIATION LONG TERM PARTICIPANTS DEVELOPMENT (LTPD) SUMMARY GUIDE INTRODUCTION Parents want to provide their children with the opportunities to excel to the
South African Hockey SOUTH AFRICAN HOCKEY ASSOCIATION LONG TERM PARTICIPANTS DEVELOPMENT (LTPD) SUMMARY GUIDE INTRODUCTION Parents want to provide their children with the opportunities to excel to the
REBUILDING ATHLETES IN AMERICA
 REBUILDING ATHLETES IN AMERICA AMERICAN DEVELOPMENT MODEL TABLE OF CONTENTS State of the Games: Why Create ADM?.... 2 How This Impacts Sport in America... 4 Overview... 5 ADM Statement.... 6 Key Principles...
REBUILDING ATHLETES IN AMERICA AMERICAN DEVELOPMENT MODEL TABLE OF CONTENTS State of the Games: Why Create ADM?.... 2 How This Impacts Sport in America... 4 Overview... 5 ADM Statement.... 6 Key Principles...
Why Movement Experiences at U6 Impact a Soccer Career
 Why Movement Experiences at U6 Impact a Soccer Career Readiness for Soccer Readiness for sports is the match between a child s level of growth, maturity and development, and the task demands presented
Why Movement Experiences at U6 Impact a Soccer Career Readiness for Soccer Readiness for sports is the match between a child s level of growth, maturity and development, and the task demands presented
THE YOUTH PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT MODEL: A New Approach to Long Term Athletic Development
 THE YOUTH PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT MODEL: A New Approach to Long Term Athletic Development Lindsay Dunn ASA England Programmes Officer and AASE Technical Lead Youth Physical Development Model Alternative to
THE YOUTH PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT MODEL: A New Approach to Long Term Athletic Development Lindsay Dunn ASA England Programmes Officer and AASE Technical Lead Youth Physical Development Model Alternative to
ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4 th edition. Chapter 10: Resistance Training: Programming and Progressions
 ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4 th edition Chapter 10: Resistance Training: Programming and Progressions 1 Learning Objectives This session, which is based on Chapter 10 of the ACE Personal Trainer Manual,
ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4 th edition Chapter 10: Resistance Training: Programming and Progressions 1 Learning Objectives This session, which is based on Chapter 10 of the ACE Personal Trainer Manual,
Wellness to World Cup
 Wellness to World Cup Presented by BMO Canadian Soccer LTPD Supporting wellness through to World Cup excellence The diagram shows how the LTPD model accommodates athletes at all levels of interest, ability
Wellness to World Cup Presented by BMO Canadian Soccer LTPD Supporting wellness through to World Cup excellence The diagram shows how the LTPD model accommodates athletes at all levels of interest, ability
The Phenomena of Movement pg 3. Physical Fitness and Adolescence pg 4. Fitness as a Lifestyle pg 5. Physical Education and the Student pg 6
 Introduction pg 2 The Phenomena of Movement pg 3 Physical Fitness and Adolescence pg 4 Fitness as a Lifestyle pg 5 Physical Education and the Student pg 6 The Program pg 7 Program Outline pg 8 Proposal
Introduction pg 2 The Phenomena of Movement pg 3 Physical Fitness and Adolescence pg 4 Fitness as a Lifestyle pg 5 Physical Education and the Student pg 6 The Program pg 7 Program Outline pg 8 Proposal
506 Kids Energy Boost By: Tinoca (Cristina Senra) Facebook: YoguitosTinoca
 1 506 Kids Energy Boost By: Tinoca (Cristina Senra) mundohidro_tinoca@yahoo.com; Facebook: YoguitosTinoca Kids and teens are busy, have strict timetables and goals to achieve. The new concept of time brings
1 506 Kids Energy Boost By: Tinoca (Cristina Senra) mundohidro_tinoca@yahoo.com; Facebook: YoguitosTinoca Kids and teens are busy, have strict timetables and goals to achieve. The new concept of time brings
Readiness for Soccer
 Youth Fitness? Readiness for Soccer Readiness for sports is the match between a child s level of growth, maturity and development, and the task demands presented in competitive sports. Robert M. Malina,
Youth Fitness? Readiness for Soccer Readiness for sports is the match between a child s level of growth, maturity and development, and the task demands presented in competitive sports. Robert M. Malina,
FRESNO PACIFIC UNIVERSITY CENTER FOR PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT HPT 904 PLYOMETRIC TRAINING FOR SPORTS
 FRESNO PACIFIC UNIVERSITY CENTER FOR PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT HPT 904 PLYOMETRIC TRAINING FOR SPORTS Instructor s Name: Andrew Herrick, Ph.D. & Dennis Janzen, Ph.D. Contact Phone: 559.325.0282 or 602-751-2528
FRESNO PACIFIC UNIVERSITY CENTER FOR PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT HPT 904 PLYOMETRIC TRAINING FOR SPORTS Instructor s Name: Andrew Herrick, Ph.D. & Dennis Janzen, Ph.D. Contact Phone: 559.325.0282 or 602-751-2528
Overtraining in Young Athletes
 Overtraining in Young Athletes Avery D. Faigenbaum, Ed.D. The College of New Jersey Millions of school-age youth in the United States participate in some type of organized or recreational sport program.
Overtraining in Young Athletes Avery D. Faigenbaum, Ed.D. The College of New Jersey Millions of school-age youth in the United States participate in some type of organized or recreational sport program.
Coaches Guide: Physical Preparation for Ice Hockey. Michael Donoghue, CSCS
 Coaches Guide: Physical Preparation for Ice Hockey Michael Donoghue, CSCS What does Good Training look like? Training Philosophy 1. Do no harm Make sure that everything we do is done correctly. Quality
Coaches Guide: Physical Preparation for Ice Hockey Michael Donoghue, CSCS What does Good Training look like? Training Philosophy 1. Do no harm Make sure that everything we do is done correctly. Quality
Developing Talent and Potential
 Developing Talent and Potential Stuart Armstrong Development Manager Talent and Potential England Golf England Golf is looking to adopt the Long Term Athlete Development (LTAD) model of talent development
Developing Talent and Potential Stuart Armstrong Development Manager Talent and Potential England Golf England Golf is looking to adopt the Long Term Athlete Development (LTAD) model of talent development
ACL Injury Prevention: Considerations for Children and Adolescents
 ACL Injury Prevention: Considerations for Children and Adolescents Susan Sigward PhD, PT, ATC Human Performance Laboratory University of Southern California 1 ACL Injury Season ending/ Career ending 82%
ACL Injury Prevention: Considerations for Children and Adolescents Susan Sigward PhD, PT, ATC Human Performance Laboratory University of Southern California 1 ACL Injury Season ending/ Career ending 82%
Strength Training for the Average Collegiate or H.S. Athlete: A Return to Push-Ups & Sit-Ups
 Strength Training for the Average Collegiate or H.S. Athlete: A Return to Push-Ups & Sit-Ups Tim Bacon October 2006 10 Problems with Traditional College Weight Training Programs 1. Too short, intensive
Strength Training for the Average Collegiate or H.S. Athlete: A Return to Push-Ups & Sit-Ups Tim Bacon October 2006 10 Problems with Traditional College Weight Training Programs 1. Too short, intensive
Coaching without these age-appropriate needs in mind may lead to short-term success, but will undermine the athlete's long-term potential.
 The USSA Freestyle Training System (FTS) is the long-term athlete development framework for a freestyle coach, athlete, or parent to design age-appropriate training and competition plans that allow them
The USSA Freestyle Training System (FTS) is the long-term athlete development framework for a freestyle coach, athlete, or parent to design age-appropriate training and competition plans that allow them
Strength and Core Stability - Handout
 Strength and Core Stability - Handout The National Physical Activity Guidelines for Australians are simple to achieve by focusing on: Thinking of movement as an opportunity, not an inconvenience. Being
Strength and Core Stability - Handout The National Physical Activity Guidelines for Australians are simple to achieve by focusing on: Thinking of movement as an opportunity, not an inconvenience. Being
Better Movers Make Better Athletes
 Better Movers Make Better Athletes 1 We gratefully acknowledge the Traditional Territory of the Anishinaabeg, Haudenosaunee, Lunaapeewak and Attawandaron peoples and the First Nations of this region
Better Movers Make Better Athletes 1 We gratefully acknowledge the Traditional Territory of the Anishinaabeg, Haudenosaunee, Lunaapeewak and Attawandaron peoples and the First Nations of this region
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Physical Education Grade 10
 West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Physical Education Grade 10 Page 1 of 6 GRADE 10 PHYSICAL EDUCATION Content Area: Physical Education Course & Grade Level: Physical Education, Grade 10
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Physical Education Grade 10 Page 1 of 6 GRADE 10 PHYSICAL EDUCATION Content Area: Physical Education Course & Grade Level: Physical Education, Grade 10
International School of Turin
 International School of Turin Adapted from the IB PSE scope and sequence Personal, Social and Physical Education Scope and Sequence Identity An understanding of our own beliefs, values, attitudes, experiences
International School of Turin Adapted from the IB PSE scope and sequence Personal, Social and Physical Education Scope and Sequence Identity An understanding of our own beliefs, values, attitudes, experiences
LONG TERM PLAYER DEVELOPMENT Gary White, Technical Director
 LONG TERM PLAYER DEVELOPMENT Gary White, Technical Director Parent Education Parents play a vital role in supporting their children's long term soccer development Gary White, Technical Director Washington
LONG TERM PLAYER DEVELOPMENT Gary White, Technical Director Parent Education Parents play a vital role in supporting their children's long term soccer development Gary White, Technical Director Washington
Wellness to World Cup
 Wellness to World Cup Presented by BMO Supporting wellness through to World Cup excellence The diagram shows how the LTPD model accommodates athletes at all levels of interest, ability and achievement.
Wellness to World Cup Presented by BMO Supporting wellness through to World Cup excellence The diagram shows how the LTPD model accommodates athletes at all levels of interest, ability and achievement.
AGES 14 AND UNDER American Development Model LESSON WORKBOOK ROGER GRILLO
 AGES 14 AND UNDER American Development Model LESSON WORKBOOK ROGER GRILLO 2 The (ADM) is a nationwide initiative that provides local associations across the country with a blueprint for optimal athlete
AGES 14 AND UNDER American Development Model LESSON WORKBOOK ROGER GRILLO 2 The (ADM) is a nationwide initiative that provides local associations across the country with a blueprint for optimal athlete
Inspiring Athleticism in Children and Youth. By Peter Twist. IDEA World 2011
 Inspiring Athleticism in Children and Youth By Peter Twist IDEA World 2011 Critical Factors to Consider When Training Young Athletes o Children are not little adults they have very specialized needs o
Inspiring Athleticism in Children and Youth By Peter Twist IDEA World 2011 Critical Factors to Consider When Training Young Athletes o Children are not little adults they have very specialized needs o
HADDONFIELD PUBLIC SCHOOLS Curriculum Map for (Physical Education 6 th 8 th Grades) PHYSICAL FITNESS
 Curriculum Map for (Physical Education 6 th 8 th Grades) PHYSICAL FITNESS Targeted Standard(s): NJCCCS 2.2.6.A.1 thru 2.2.6.A.2 2.2.6.C.1 thru 2.2.6.C.3 2.5.6.A.1 thru 2.5.6.A.4 2.5.6.B.1 thru 2.5.6.B.2
Curriculum Map for (Physical Education 6 th 8 th Grades) PHYSICAL FITNESS Targeted Standard(s): NJCCCS 2.2.6.A.1 thru 2.2.6.A.2 2.2.6.C.1 thru 2.2.6.C.3 2.5.6.A.1 thru 2.5.6.A.4 2.5.6.B.1 thru 2.5.6.B.2
STAR Research Journal
 STAR Research Journal Available online at www.starresearchjournal.com (Star International Journal) PHYSICAL EDUCATION Star. Phy. Edn. 04 (2013) EFFECT OF PLYOMETRIC AND CIRCUIT TRAINING ON LEG STRENGTH,
STAR Research Journal Available online at www.starresearchjournal.com (Star International Journal) PHYSICAL EDUCATION Star. Phy. Edn. 04 (2013) EFFECT OF PLYOMETRIC AND CIRCUIT TRAINING ON LEG STRENGTH,
Introduction to Training Beginning Athletes. Beginning Athletes 19/04/2018. Fundamental Movement Skills for Beginning Athletes. Training Progressions
 Introduction to Training Beginning Athletes Version 17 March 2018 Athletics Australia 2018 Training Principles for Beginning Athletes Remember: That as a Coach you are responsible for creating a welcoming,
Introduction to Training Beginning Athletes Version 17 March 2018 Athletics Australia 2018 Training Principles for Beginning Athletes Remember: That as a Coach you are responsible for creating a welcoming,
GROWING RUGBY PLAYERS
 GROWING RUGBY PLAYERS Are they really that different? Simon Harries Simon.Harries@rugby.com.au Table of Contents page page page 3 11 15 19 Kids are different Thinking long term Getting what they need page
GROWING RUGBY PLAYERS Are they really that different? Simon Harries Simon.Harries@rugby.com.au Table of Contents page page page 3 11 15 19 Kids are different Thinking long term Getting what they need page
The Youth Tennis Player
 The Youth Tennis Player ALEXIS COLVIN, MD Chief Medical Officer USTA US Fed Cup team physician US Open physician JANUARY 31, 2015 Introduction For the 1st time in American history, younger generations
The Youth Tennis Player ALEXIS COLVIN, MD Chief Medical Officer USTA US Fed Cup team physician US Open physician JANUARY 31, 2015 Introduction For the 1st time in American history, younger generations
Sports Performance and Resistance Training for Young Clients 1. Sport Performance and Resistance Training for Young Clients
 Sports Performance and Resistance Training for Young Clients 1 Sport Performance and Resistance Training for Young Clients Participation in organized youth sports and training for performance is occurring
Sports Performance and Resistance Training for Young Clients 1 Sport Performance and Resistance Training for Young Clients Participation in organized youth sports and training for performance is occurring
LATE ADOLESCENCE. "Optimising the engine" & speedskating specific skills and fitness Male 16-18; Female Male 16-18; Female 15-17
 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Stage 5 FUNdamentals Train Training to train Training to Win Training to Win CHILDHOOD LATE CHILDHOOD ADOLESCENCE LATE ADOLESCENCE EARLY ADULTHOOD ADULTHOOD ADULTHOOD PHASES
Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Stage 5 FUNdamentals Train Training to train Training to Win Training to Win CHILDHOOD LATE CHILDHOOD ADOLESCENCE LATE ADOLESCENCE EARLY ADULTHOOD ADULTHOOD ADULTHOOD PHASES
Fitness Planning Consultants, Inc.
 Fitness Planning Consultants, Inc. Presents RUN FASTER METHOD S Quick Speed Improvement Workout By Adam E. Kessler, CSCS, USAW Sport Performance Coach Fitness Planning Consultants, Inc. P.O. Box 20323
Fitness Planning Consultants, Inc. Presents RUN FASTER METHOD S Quick Speed Improvement Workout By Adam E. Kessler, CSCS, USAW Sport Performance Coach Fitness Planning Consultants, Inc. P.O. Box 20323
Quick Feet Donuts Games, Drills, and Exercises For Fun and Fitness
 Quick Feet Donuts Games, Drills, and Exercises For Fun and Fitness by Joe Dinoffer President, OnCourt OffCourt, Ltd. About the Author Joe Dinoffer has had an extensive "world class" career in the tennis
Quick Feet Donuts Games, Drills, and Exercises For Fun and Fitness by Joe Dinoffer President, OnCourt OffCourt, Ltd. About the Author Joe Dinoffer has had an extensive "world class" career in the tennis
MULTI-SPORTS academy ACADEMY GUIDE
 MULTI-SPORTS academy ACADEMY GUIDE Introduction At Legacy Sports we believe that children should play as many sports as possible before choosing which one/s they enjoy the most. We also believe that a
MULTI-SPORTS academy ACADEMY GUIDE Introduction At Legacy Sports we believe that children should play as many sports as possible before choosing which one/s they enjoy the most. We also believe that a
HOCKEY. Long-Term Athlete Development Philosophy YOUTH HOCKEY DEVELOPMENT MODEL YOUTH HOCKEY DEVELOPMENT MODEL
 HOCKEY DRYLAND TRAINING Long-Term Athlete Development Philosophy We must first develop athletes who are capable of moving confidently in a variety of athletic environments. We can then develop these athletes
HOCKEY DRYLAND TRAINING Long-Term Athlete Development Philosophy We must first develop athletes who are capable of moving confidently in a variety of athletic environments. We can then develop these athletes
SOUTH AFRICAN HOCKEY ASSOCIATION LONG TERM PARTICIPANTS DEVELOPMENT (LTPD) PARENTAL GUIDE
 South African Hockey SOUTH AFRICAN HOCKEY ASSOCIATION LONG TERM PARTICIPANTS DEVELOPMENT (LTPD) PARENTAL GUIDE PARENTAL GUIDE CONTENT 1. INTRODUCTION 2. WHY IS CHANGE NEEDED 3. PARENT INFORMATION 4. ADVICE
South African Hockey SOUTH AFRICAN HOCKEY ASSOCIATION LONG TERM PARTICIPANTS DEVELOPMENT (LTPD) PARENTAL GUIDE PARENTAL GUIDE CONTENT 1. INTRODUCTION 2. WHY IS CHANGE NEEDED 3. PARENT INFORMATION 4. ADVICE
2016 St. Amant Gator Football Camps
 2016 St. Amant Gator Football Camps 2016 RISING STARS ST. AMANT FOOTBALL CAMPS are led by Head Coach David Oliver and Head Strength & Conditioning Coach Dwayne Thomassee and the rest of the SAHS Gator
2016 St. Amant Gator Football Camps 2016 RISING STARS ST. AMANT FOOTBALL CAMPS are led by Head Coach David Oliver and Head Strength & Conditioning Coach Dwayne Thomassee and the rest of the SAHS Gator
Content Area: Physical Education Grade Level Expectations: High School Standard: 1. Movement Competence & Understanding in Physical Education
 Colorado Academic Standards Physical Education - High School Content Area: Physical Education Grade Level Expectations: High School Standard: 1. Movement Competence & Understanding in Physical Education
Colorado Academic Standards Physical Education - High School Content Area: Physical Education Grade Level Expectations: High School Standard: 1. Movement Competence & Understanding in Physical Education
We see sport and physical activity as something all Canadians can do to promote wellness and the health of our communities.
 Introduction Sport Canada's Long Term Athlete Development (LTAD) is a key part of the Canadian Sport for Life (CS4L) movement to improve the quality of sport and physical activity in Canada. Through improved
Introduction Sport Canada's Long Term Athlete Development (LTAD) is a key part of the Canadian Sport for Life (CS4L) movement to improve the quality of sport and physical activity in Canada. Through improved
Health and Exercise Science Courses-1
 Health and Exercise Science Courses-1 HES 099/Emergency Care 0 course unit Basic safety and emergency first-aid knowledge and skills with opportunity to attain American Red Cross CPR and first-aid certification.
Health and Exercise Science Courses-1 HES 099/Emergency Care 0 course unit Basic safety and emergency first-aid knowledge and skills with opportunity to attain American Red Cross CPR and first-aid certification.
ACL and Knee Injury Prevention. Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS
 ACL and Knee Injury Prevention Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS ACL Anatomy ACL Mechanism of Injury Contact ACL Tear Noncontact ACL Tear ACL MOI and Pathology Common in young individual who
ACL and Knee Injury Prevention Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS ACL Anatomy ACL Mechanism of Injury Contact ACL Tear Noncontact ACL Tear ACL MOI and Pathology Common in young individual who
Why Do Kids Play Soccer? Why Do You Coach Soccer?
 COMMUNICATION MOTIVATION Why Do Kids Play Soccer? Why Do You Coach Soccer? Why Do Kids Play Soccer? Because they want to have fun Because they want to learn, develop, and get better Because they want to
COMMUNICATION MOTIVATION Why Do Kids Play Soccer? Why Do You Coach Soccer? Why Do Kids Play Soccer? Because they want to have fun Because they want to learn, develop, and get better Because they want to
LTAD in Athletics in Canada Prepared by Gerald Dragomir
 Prepared by Gerald Dragomir August 2014 Long Term Athlete Development (LTAD) in Athletics... 2 The Athletics LTAD Model... 2 Learning to Train... 3 Training to Train... 3 Training to Train... 4 Learning
Prepared by Gerald Dragomir August 2014 Long Term Athlete Development (LTAD) in Athletics... 2 The Athletics LTAD Model... 2 Learning to Train... 3 Training to Train... 3 Training to Train... 4 Learning
Lesson 1.1 PREVIEWING THE COURSE AND THE OVERALL SOCIETAL CONTEXT
 Lesson 1.1 PREVIEWING THE COURSE AND THE OVERALL SOCIETAL CONTEXT ~ ~ ~ TOPICS COVERED IN THIS LESSON (a) Is This the Right Course for You? (b) Inactivity & Obesity: Causes, Risks, and Costs 2015 Thompson
Lesson 1.1 PREVIEWING THE COURSE AND THE OVERALL SOCIETAL CONTEXT ~ ~ ~ TOPICS COVERED IN THIS LESSON (a) Is This the Right Course for You? (b) Inactivity & Obesity: Causes, Risks, and Costs 2015 Thompson
ULTIMATE CANADA Long-term Athlete Development Model
 ULTIMATE CANADA Long-term Athlete Development Model Active Start (AS) FUNdamentals (FUN) Learn to Play (L2P) Train to Play (T2P) Train to Compete (T2C) Learn to Win (L2W) Train to Win (T2W) Ultimate for
ULTIMATE CANADA Long-term Athlete Development Model Active Start (AS) FUNdamentals (FUN) Learn to Play (L2P) Train to Play (T2P) Train to Compete (T2C) Learn to Win (L2W) Train to Win (T2W) Ultimate for
Physical Education 10 Outcomes
 Physical Education 10 Outcomes Outdoor Pursuits 1.1 demonstrate effective interpersonal and communication skills through cooperative activities in group settings 1.2 understand how poor group cohesion
Physical Education 10 Outcomes Outdoor Pursuits 1.1 demonstrate effective interpersonal and communication skills through cooperative activities in group settings 1.2 understand how poor group cohesion
AGES 16 / 18 AND UNDER Age Appropriate Strength and Conditioning LESSON WORKBOOK DARRYL NELSON
 AGES 16 / 18 AND UNDER Age Appropriate Strength and Conditioning LESSON WORKBOOK DARRYL NELSON 2 Coaches need to create an environment in which athletes can participate in functional strength training
AGES 16 / 18 AND UNDER Age Appropriate Strength and Conditioning LESSON WORKBOOK DARRYL NELSON 2 Coaches need to create an environment in which athletes can participate in functional strength training
Individualized Lifetime Activities
 Individualized Lifetime Activities Individualized Lifetime Activities is a number of one-semester classes. They are designed to offer a higher level of proficiency and more in-depth instruction in up to
Individualized Lifetime Activities Individualized Lifetime Activities is a number of one-semester classes. They are designed to offer a higher level of proficiency and more in-depth instruction in up to
HEALTH AND HUMAN PERFORMANCE (HHP)
 Health and Human Performance (HHP) 1 HEALTH AND HUMAN PERFORMANCE (HHP) HHP 1713 Introduction to Athletic Training Prerequisites: Admission to the athletic training program. Description: An introduction
Health and Human Performance (HHP) 1 HEALTH AND HUMAN PERFORMANCE (HHP) HHP 1713 Introduction to Athletic Training Prerequisites: Admission to the athletic training program. Description: An introduction
Coac. Coaching Manitoba Presents: Professional Development Workshops
 Coac Coaching Manitoba Presents: Professional Development Workshops Coaching Professional Development Opportunities Coaching Manitoba has a menu of sessions and topics that we can deliver across the province,
Coac Coaching Manitoba Presents: Professional Development Workshops Coaching Professional Development Opportunities Coaching Manitoba has a menu of sessions and topics that we can deliver across the province,
St Benedict s School Skills Coach Job Description and Responsibilities
 St Benedict s School Skills Coach Job Description and Responsibilities To maintain high standards of quality coaching. Be an outstanding role model to the pupils and demonstrate a professional approach
St Benedict s School Skills Coach Job Description and Responsibilities To maintain high standards of quality coaching. Be an outstanding role model to the pupils and demonstrate a professional approach
EFFECTIVENESS OF NEUROMUSCULAR TRAINING IN YOUNG ATHLETES AT RISK OF LOWER EXTREMITY MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES
 EFFECTIVENESS OF NEUROMUSCULAR TRAINING IN YOUNG ATHLETES AT RISK OF LOWER EXTREMITY MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES Original Research Article ABSTRACT ISSN CODE: 2456-1045 (Online) (ICV-MDS/Impact Value): 3.08
EFFECTIVENESS OF NEUROMUSCULAR TRAINING IN YOUNG ATHLETES AT RISK OF LOWER EXTREMITY MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES Original Research Article ABSTRACT ISSN CODE: 2456-1045 (Online) (ICV-MDS/Impact Value): 3.08
INJURY PREVENTION TECHNIQUES
 Hockey Canada Safety Program Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning INJURY PREVENTION TECHNIQUES It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they
Hockey Canada Safety Program Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning INJURY PREVENTION TECHNIQUES It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they
ProView. BC Region Winter Season 2014/2015 FEATURED ARTICLE. the INSIDE SCOOP What to know about stretching EFFECTIVELY by Majorie Lauzon
 ProView BC Region Winter Season 2014/2015 FEATURED ARTICLE the INSIDE SCOOP What to know about stretching EFFECTIVELY by Majorie Lauzon photo: Tom Fuller SKIING Biomechanics What to KNOW the inside scoop
ProView BC Region Winter Season 2014/2015 FEATURED ARTICLE the INSIDE SCOOP What to know about stretching EFFECTIVELY by Majorie Lauzon photo: Tom Fuller SKIING Biomechanics What to KNOW the inside scoop
2006 HEALTH-RELATED FITNESS TESTING GUIDELINES
 2006 HEALTH-RELATED FITNESS TESTING GUIDELINES Health-related fitness education is an important component of a physical education program. A well-designed fitness assessment process provides students,
2006 HEALTH-RELATED FITNESS TESTING GUIDELINES Health-related fitness education is an important component of a physical education program. A well-designed fitness assessment process provides students,
EXCERPT ADAPTED FROM CARL PETERSEN S NEW BOOK FIT 2 SKI
 ACL THE ABC S OF PROTECTION EXCERPT ADAPTED FROM CARL PETERSEN S NEW BOOK FIT 2 SKI by CARL PETERSEN BPE, BSc (PT) Injuries to the knee are a regular occurrence for skiing professionals and anterior cruciate
ACL THE ABC S OF PROTECTION EXCERPT ADAPTED FROM CARL PETERSEN S NEW BOOK FIT 2 SKI by CARL PETERSEN BPE, BSc (PT) Injuries to the knee are a regular occurrence for skiing professionals and anterior cruciate
Manitoba Action Plan for Sport (MAPS)
 2016-2020 Manitoba Action Plan for Sport (MAPS) About Sport Manitoba Sport Manitoba is the lead planning, programming and funding agency for the development of amateur sport in the province. The primary
2016-2020 Manitoba Action Plan for Sport (MAPS) About Sport Manitoba Sport Manitoba is the lead planning, programming and funding agency for the development of amateur sport in the province. The primary
Coach Development Seminar. Valencia July 2015
 Coach Development Seminar Valencia July 2015 Session Objective Measuring / Monitoring the young athlete Why do we use Postural analysis What is Coaching Essential Components of a Development Pathway What
Coach Development Seminar Valencia July 2015 Session Objective Measuring / Monitoring the young athlete Why do we use Postural analysis What is Coaching Essential Components of a Development Pathway What
Club Excellence Workshop USSA Club Programming Aligning with LTAD. November 14, 2013
 Club Excellence Workshop USSA Club Programming Aligning with LTAD November 14, 2013 Club Excellence Workshops Month Topic May Leadership and Governance June Finance and Fundraising July Fostering Club
Club Excellence Workshop USSA Club Programming Aligning with LTAD November 14, 2013 Club Excellence Workshops Month Topic May Leadership and Governance June Finance and Fundraising July Fostering Club
The BADMINTON England Brand Vision is :
 The BADMINTON England Brand Vision is : Badminton is well known and widely recognised by the public as an ideal, healthy activity, part of a lifelong healthy lifestyle; and as a well-organised and serious
The BADMINTON England Brand Vision is : Badminton is well known and widely recognised by the public as an ideal, healthy activity, part of a lifelong healthy lifestyle; and as a well-organised and serious
Written by Keith Wassung Thursday, 01 September :00 - Last Updated Thursday, 27 March :43
 Athletes have been benefiting from Chiropractic care for many years; however, it has only recently been receiving attention from the media. Athletes of all types, from the weekend warrior to the world-class
Athletes have been benefiting from Chiropractic care for many years; however, it has only recently been receiving attention from the media. Athletes of all types, from the weekend warrior to the world-class
US Youth Soccer in conjunction with American Sport Education Plan USYOUTHSOCCER.ORG
 US Youth Soccer in conjunction with American Sport Education Plan What youth coaches need to know for a successful season» Four elements of Coach Preparation Training activities» Five Characteristics of
US Youth Soccer in conjunction with American Sport Education Plan What youth coaches need to know for a successful season» Four elements of Coach Preparation Training activities» Five Characteristics of
Black Horse Pike Regional School District. Physical Education. Long Term Medical Assignments
 Black Horse Pike Regional School District Physical Education Long Term Medical Assignments The physical education assignments below are for students who are unable to participate in their physical education
Black Horse Pike Regional School District Physical Education Long Term Medical Assignments The physical education assignments below are for students who are unable to participate in their physical education
Development of young beginner and intermediate players
 ITF Coaches Education Programme Coaching Beginner and Intermediate Players Course Development of young beginner and intermediate players Growth and development in tennis Playing tennis for life Providing
ITF Coaches Education Programme Coaching Beginner and Intermediate Players Course Development of young beginner and intermediate players Growth and development in tennis Playing tennis for life Providing
Strength Training in Children and Teens: Implementing Safe, Effective & Fun Programs Part Two by Pat R. Vehrs, Ph.D., FACSM
 Strength Training in Children and Teens: Implementing Safe, Effective & Fun Programs Part Two by Pat R. Vehrs, Ph.D., FACSM Learning Objective To learn how to develop and implement a safe, effective, and
Strength Training in Children and Teens: Implementing Safe, Effective & Fun Programs Part Two by Pat R. Vehrs, Ph.D., FACSM Learning Objective To learn how to develop and implement a safe, effective, and
British Columbia & Yukon - Curriculum Links
 Training to Train Stage Males 12-16, Females 11-15 Grades Corresponding to Training to Train Stage of LTAD: Males Grades 6-11, Females Grades 5-10 Provincial Curriculum Document Organization: The curricula
Training to Train Stage Males 12-16, Females 11-15 Grades Corresponding to Training to Train Stage of LTAD: Males Grades 6-11, Females Grades 5-10 Provincial Curriculum Document Organization: The curricula
NATIONAL PROGRAM POLICY
 NATIONAL PROGRAM POLICY LEVELS & STAGES VERSION: 16 th January 2013 DATE PUBLISHED: 1 st December 2011 DATE REVIEWED: 1 st January 2013 DATE TO BE REVIEWED: December 2013 File path: C:\Users\Ellie\Dropbox\SG
NATIONAL PROGRAM POLICY LEVELS & STAGES VERSION: 16 th January 2013 DATE PUBLISHED: 1 st December 2011 DATE REVIEWED: 1 st January 2013 DATE TO BE REVIEWED: December 2013 File path: C:\Users\Ellie\Dropbox\SG
Download Test Bank for Dynamic Physical Education for Secondary School Students 7th Edition
 Download Test Bank for Dynamic Physical Education for Secondary School Students 7th Edition Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/download-test-bankfor-dynamic-physical-education-for-secondary-school-students-7th-edition
Download Test Bank for Dynamic Physical Education for Secondary School Students 7th Edition Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/download-test-bankfor-dynamic-physical-education-for-secondary-school-students-7th-edition
NATURAL DEVELOPMENT AND TRAINABILITY OF PLYOMETRIC ABILITY DURING CHILDHOOD BY KIRSTY QUERL SPORT SCIENTIST STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING COACH
 NATURAL DEVELOPMENT AND TRAINABILITY OF PLYOMETRIC ABILITY DURING CHILDHOOD BY KIRSTY QUERL SPORT SCIENTIST STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING COACH The truth... Youth are not as active as they used to be, Decline
NATURAL DEVELOPMENT AND TRAINABILITY OF PLYOMETRIC ABILITY DURING CHILDHOOD BY KIRSTY QUERL SPORT SCIENTIST STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING COACH The truth... Youth are not as active as they used to be, Decline
Speed-endurance allows for the. Speed is the result of applying explosive. What is our recipe? Speed, Agility, and Speed- 11/5/2007
 C H A P T E R Speed, Agility, and Speed- Endurance Development 20 What is our recipe? Increase Fast twitch fibers Train Fast Run Properly (Force Applications) + Stride Frequency/length Speed is the result
C H A P T E R Speed, Agility, and Speed- Endurance Development 20 What is our recipe? Increase Fast twitch fibers Train Fast Run Properly (Force Applications) + Stride Frequency/length Speed is the result
YOUTH ATHLETIC DEVELOPMENT WHY IS IT SO IMPORTANT? Dylan Vizzarri
 YOUTH ATHLETIC DEVELOPMENT WHY IS IT SO IMPORTANT? A proactive approach to enhance athletic potential, prevent injury and educate junior players (U/12+) on the importance of physical preparation for sport
YOUTH ATHLETIC DEVELOPMENT WHY IS IT SO IMPORTANT? A proactive approach to enhance athletic potential, prevent injury and educate junior players (U/12+) on the importance of physical preparation for sport
Cumann Lúthchleas Gael Builds Character
 Cumann Lúthchleas Gael Builds Character New cover slide Free Intro Ulster GAA Coaching Resources Introduction: Ulster GAA has, for many years been working at the forefront in the production of resources
Cumann Lúthchleas Gael Builds Character New cover slide Free Intro Ulster GAA Coaching Resources Introduction: Ulster GAA has, for many years been working at the forefront in the production of resources
National Junior and Youth Participation Overview
 National Junior and Youth Participation Overview 2014 Mission To facilitate and support the participation of deaf and hard of hearing Australian children into sport Vision Building and Strengthening Opportunities
National Junior and Youth Participation Overview 2014 Mission To facilitate and support the participation of deaf and hard of hearing Australian children into sport Vision Building and Strengthening Opportunities
Develop great racers first, then develop great skiers
 Strategies and Tools for Getting Club and Parent Buy-In for LTAD USSA Club Excellence Conference May 13, 2014 Develop great racers first, then develop great skiers #& ()*+&,-./0&.123&14)&#!5&!"#$%&'()%
Strategies and Tools for Getting Club and Parent Buy-In for LTAD USSA Club Excellence Conference May 13, 2014 Develop great racers first, then develop great skiers #& ()*+&,-./0&.123&14)&#!5&!"#$%&'()%
Physical Development. Academic Support. Opportunities ALKIRA SPORTS ACADEMY THE TOTAL ATHLETE
 THE TOTAL ATHLETE At the Alkira Sports Academy we focus on developing the student as a TOTAL ATHLETE. This gives the student the ability to develop physically in their current sport. Students will be supported
THE TOTAL ATHLETE At the Alkira Sports Academy we focus on developing the student as a TOTAL ATHLETE. This gives the student the ability to develop physically in their current sport. Students will be supported
Hockey Canada. 8.0 Injury Prevention Techniques. 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning
 8.0 Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they are physically fit. In addition, well conditioned athletes
8.0 Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they are physically fit. In addition, well conditioned athletes
RHP Training Centre. PREMIUM OFF-SEASON VOLLEYBALL TRAINING (Players Manual)
 RHP Training Centre PREMIUM OFF-SEASON VOLLEYBALL TRAINING (Players Manual) Table of Contents Program Overview 2 Description 3 Summary Breakdown 3 Our Goals For The Program 3 Dryland Training 4 1st Period-
RHP Training Centre PREMIUM OFF-SEASON VOLLEYBALL TRAINING (Players Manual) Table of Contents Program Overview 2 Description 3 Summary Breakdown 3 Our Goals For The Program 3 Dryland Training 4 1st Period-
Coaching the Injury Prone Athlete
 Coaching the Injury Prone Athlete Rob Thickpenny National Coach Mentor - Physical Preparation High Knee Drill Foot cocked, heel to butt, knee high, step over opposite knee, tall hips, extend hips in drive,
Coaching the Injury Prone Athlete Rob Thickpenny National Coach Mentor - Physical Preparation High Knee Drill Foot cocked, heel to butt, knee high, step over opposite knee, tall hips, extend hips in drive,
chapter Age- and Sex- Related Differences and Their Implications for Resistance Exercise
 chapter 7 Age- and Sex- Related Differences and Their Implications for Resistance Exercise Chapter Objectives Evaluate evidence regarding the safety and effectiveness of resistance exercise for children.
chapter 7 Age- and Sex- Related Differences and Their Implications for Resistance Exercise Chapter Objectives Evaluate evidence regarding the safety and effectiveness of resistance exercise for children.
Foundations of Youth Athletic Development
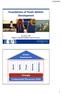 Speed Agility Power Stamina Robustness 27/11/2015 Foundations of Youth Athletic Development Jon Oliver, PhD Reader in Applied Paediatric Exercise Science Athletic Development Strength Fundamental Movement
Speed Agility Power Stamina Robustness 27/11/2015 Foundations of Youth Athletic Development Jon Oliver, PhD Reader in Applied Paediatric Exercise Science Athletic Development Strength Fundamental Movement
Youth Strength Training
 Youth Strength Training Michael J. Sampson, DO FAOASM Associate Dean/Chief Academic Officer Associate Professor Family/Sports Medicine Medical Director Simulation Center PCOM South Georgia Secretary/Treasurer
Youth Strength Training Michael J. Sampson, DO FAOASM Associate Dean/Chief Academic Officer Associate Professor Family/Sports Medicine Medical Director Simulation Center PCOM South Georgia Secretary/Treasurer
PHASE 2: MOVEMENT TRAINING PHASE 2: MOVEMENT TRAINING
 PHASE 2: MOVEMENT TRAINING 1 The ability to perform movements with skill and efficiency is essential for health, fitness, and performance. Movement efficiency not only helps reduce the physiological burden
PHASE 2: MOVEMENT TRAINING 1 The ability to perform movements with skill and efficiency is essential for health, fitness, and performance. Movement efficiency not only helps reduce the physiological burden
Cambridge TECHNICALS. OCR Level 2 CAMBRIDGE TECHNICAL SPORT R/502/5410 GUIDED LEARNING HOURS: 30
 Cambridge TECHNICALS OCR Level 2 CAMBRIDGE TECHNICAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA in SPORT Fitness Testing and Training R/502/5410 LEVEL 2 UNIT 3 GUIDED LEARNING HOURS: 30 UNIT CREDIT VALUE: 5 Fitness Testing and
Cambridge TECHNICALS OCR Level 2 CAMBRIDGE TECHNICAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA in SPORT Fitness Testing and Training R/502/5410 LEVEL 2 UNIT 3 GUIDED LEARNING HOURS: 30 UNIT CREDIT VALUE: 5 Fitness Testing and
Fastpitch Softball: Physiological Demands and Performance Factors
 Fastpitch Softball: Physiological Demands and Performance Factors By Marc Dagenais Published by: M.O. Dagenais & Associates, Inc. Author : Marc O. Dagenais, Softball Peak Performance Coach 154 Charlotte
Fastpitch Softball: Physiological Demands and Performance Factors By Marc Dagenais Published by: M.O. Dagenais & Associates, Inc. Author : Marc O. Dagenais, Softball Peak Performance Coach 154 Charlotte
Jay Dawes, MS Velocity
 February 20, 2011 Thank You Power Development- Not Just for Athletes Anymore! P R E S E N T E D B Y Jay Dawes, MS INSPIRE THE WORLD TO FITNESS Objectives What is Power? Basic Terminology Benefits of Power
February 20, 2011 Thank You Power Development- Not Just for Athletes Anymore! P R E S E N T E D B Y Jay Dawes, MS INSPIRE THE WORLD TO FITNESS Objectives What is Power? Basic Terminology Benefits of Power
Training Age. Patrick McHenry Rick Howard, M.Ed., CSCS, *D. Rihoward41
 Training Age Patrick McHenry Rick Howard, M.Ed., CSCS, *D rihoward41@gmail.com Rihoward41 Training Age Purpose Biological approach may lead to further development Continuous development of motor potential
Training Age Patrick McHenry Rick Howard, M.Ed., CSCS, *D rihoward41@gmail.com Rihoward41 Training Age Purpose Biological approach may lead to further development Continuous development of motor potential
Train to Train, Phase 2:
 Train to Train, Phase 2: (13-15 females, 14-16 males) Fundamental Movement Skills Refine same skills as FUNdamentals stage Fundamental Basketball Skills Basic Motor Movement Skills - Without Ball Stances
Train to Train, Phase 2: (13-15 females, 14-16 males) Fundamental Movement Skills Refine same skills as FUNdamentals stage Fundamental Basketball Skills Basic Motor Movement Skills - Without Ball Stances
Alpine Training Systems
 Alpine Training Systems Development Phases Domain Phase Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4 Phase 5 Phase 6 Biological Age Early Childhood Late Childhood Pre-puberty before growth spurt Puberty and growth
Alpine Training Systems Development Phases Domain Phase Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4 Phase 5 Phase 6 Biological Age Early Childhood Late Childhood Pre-puberty before growth spurt Puberty and growth
PERFORMANCE COACH CONTEXT
 PERFORMANCE COACH CONTEXT EVALUATION TOOLS AND FORMS (Version 0.2 JAN 19, 2017) 1 2 3 4 Evaluation Tools & Forms This document outlines a series of forms that Evaluators will use when evaluating Performance
PERFORMANCE COACH CONTEXT EVALUATION TOOLS AND FORMS (Version 0.2 JAN 19, 2017) 1 2 3 4 Evaluation Tools & Forms This document outlines a series of forms that Evaluators will use when evaluating Performance
The Effectiveness of Injury-Prevention Programs in Reducing the Incidence of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Sprains in Adolescent Athletes
 Critically Appraised Topics Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2012, 21, 371-377 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. The Effectiveness of Injury-Prevention Programs in Reducing the Incidence of Anterior Cruciate Ligament
Critically Appraised Topics Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2012, 21, 371-377 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. The Effectiveness of Injury-Prevention Programs in Reducing the Incidence of Anterior Cruciate Ligament
SKAES13 SQA Unit Code H9AG 04 Develop your physical capability to achieve excellence in your sport
 Develop your physical to achieve excellence in your sport Overview Physical fitness is vital to achieving excellence in your sport. To be successful, elite athletes need to develop and maintain high levels
Develop your physical to achieve excellence in your sport Overview Physical fitness is vital to achieving excellence in your sport. To be successful, elite athletes need to develop and maintain high levels
Understanding Functional Training Part one of a two-part series
 Understanding Functional Training Part one of a two-part series By Douglas Brooks, MS Generally, functional training is tied to balance training and sport-, activity-, or occupation-specific practice.
Understanding Functional Training Part one of a two-part series By Douglas Brooks, MS Generally, functional training is tied to balance training and sport-, activity-, or occupation-specific practice.
Introduction. Coaches should leave the training with a clear understanding of the following: How to use the Special Olympics Athletics Coaching Guide
 Introduction On behalf of Special Olympics International, THANK YOU for contributing your time and expertise. The knowledge you share with the course participants will make a significant impact on the
Introduction On behalf of Special Olympics International, THANK YOU for contributing your time and expertise. The knowledge you share with the course participants will make a significant impact on the
ACALANES UNION HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT Adopted: 12/15/04 PHYSICAL EDUCATION Subject Area
 ACALANES UNION HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT Adopted: 12/15/04 PHYSICAL EDUCATION Subject Area COURSE TITLE: COURSE CODE: Weight Training P0615N GRADE LEVEL: Grades 11 12 COURSE LENGTH: One Semester PREREQUISITE:
ACALANES UNION HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT Adopted: 12/15/04 PHYSICAL EDUCATION Subject Area COURSE TITLE: COURSE CODE: Weight Training P0615N GRADE LEVEL: Grades 11 12 COURSE LENGTH: One Semester PREREQUISITE:
K-5 PHYSICAL EDUCATION Standards/Benchmarks/Grade Level Expectations (GLE)
 Standard 1: Uses a variety of basic and advanced movement forms Interval Benchmark 1: Uses a variety of basic locomotor movements (e.g., running, skipping, hopping, sliding) Interval Benchmark 2: Uses
Standard 1: Uses a variety of basic and advanced movement forms Interval Benchmark 1: Uses a variety of basic locomotor movements (e.g., running, skipping, hopping, sliding) Interval Benchmark 2: Uses
Dance Department Philosophy
 Dance Department Philosophy The purpose of the dance department at the Grand Center Arts Academy (GCAA) is to expose students to the historical, technical, and artistic elements of dance. Students are
Dance Department Philosophy The purpose of the dance department at the Grand Center Arts Academy (GCAA) is to expose students to the historical, technical, and artistic elements of dance. Students are
Content Topics CCRS TEKS TEKS Elaboration Resources Notes. Time Period. sspeir Page 1 3/23/
 sspeir Page 1 3/23/2012 Time Content Topics CCRS TEKS TEKS Elaboration Resources Notes Safety, Rules & Skills 1g 2c 5a 5b 5c 5d 5e 6a 7c (G) combine skills competently to participate in modified versions
sspeir Page 1 3/23/2012 Time Content Topics CCRS TEKS TEKS Elaboration Resources Notes Safety, Rules & Skills 1g 2c 5a 5b 5c 5d 5e 6a 7c (G) combine skills competently to participate in modified versions
CSCS EXAMINATION Detailed Content Outline PRACTICAL / APPLIED
 1. EXERCISE TECHNIQUE 7 21 10 38 A. Teach and Evaluate Resistance Training Exercise Technique 1. Free weight training equipment: 2. Resistance machines (e.g., pulley, cam, hydraulic, friction, air, tubing)
1. EXERCISE TECHNIQUE 7 21 10 38 A. Teach and Evaluate Resistance Training Exercise Technique 1. Free weight training equipment: 2. Resistance machines (e.g., pulley, cam, hydraulic, friction, air, tubing)
