ATP RELEASE ENERGY THROUGH THE CONVERSION OF ATP INTO ADP AND THE RELEASE OF A PHOSPHATE.
|
|
|
- Charla Phelps
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Module 6 review 1. Describe smooth, skeletal and cardiac muscle. Also tell where you would find these in the body. Smooth around internal organs (involuntary control) (one nucleus per cell) Skeletal pulls on bones (voluntary control) (multi-nucleated) Cardiac heart (involuntary control) (are branched and have one nucleus per cell) Smooth not striated / Skeletal and cardiac are striated 2. Differentiate between actin and myosin Actin thin filament Myosin thick filament with cross - bridges 3. Describe the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. Myosin forms cross-bridges on actin and slides actin towards the center pulling the sarcomere towards the center shortening it Muscle contraction relies on the action between two types of myofilaments actin and myosin Actin is a pair of protein strands woven together that resembles a string of beads The myosin myofilament consists of protein molecules wound together The mysoin filaments have heads that stick Contraction
2 1.The myosin head is attached to the actin filament 2.The myosin head then flexes, moving the actin filament 3.The myosin head releases and unflexes, powered by ATP 4.The myosin head reattaches to the actin filament in a new location The actin slides past the myosin, and this movement is therefore known as the sliding filament model The actin is anchored to a position within the striated muscle known as a Z line When a muscle contracts, the actin moves and along with it, the Z line also moves These Z lines are attached to the membranes of other cells in the tissue, causing the contraction of the entire muscle Calcium Ions and Contraction Initially, when a muscle is relaxed, the myosin heads are ready to bind to actin but they cannot bind This is because a protein known as tropomyosin prevents their binding The tropomyosin can be moved by another protein known as troponin, which is activated when calcium is bonded to it Therefore, when muscles contract, Ca 2+ ions diffuse into the myofibrils and attaches to troponin, allowing the myosin heads to bind with actin The release of calcium is due to a a nerve impulse. Thus muscles can t contract without Calcium 4. Why are ATP and calcium required for muscle contraction? Ca required to cause the actin to change shape exposing active sites and ATP required for the sliding motion/deattachemt ATP provides energy from muscles However, the method through which this ATP is produced can vary ATP RELEASE ENERGY THROUGH THE CONVERSION OF ATP INTO ADP AND THE RELEASE OF A PHOSPHATE.
3 5. What is creatine-phosphate and how does it aid in muscle contraction/relaxation It is a pathway to reform ATP during muscle contraction
4 6. Know 3 injuries related to athletics baseball finger blocker s arm charley horse compactment syndrome pitcher s arm pulled groin pulled hamstrings rider s bones rotator cuff injury shin splints tennis elbow tennis leg What is a Muscle Strain? A muscle strain is damage caused by over-stretching of muscle tissue. In football, this is thought to occur most frequently when movements such as sprinting, stretching for the ball or kicking the ball are carried out in an unco-ordinated manner. The muscle tissue becomes overloaded and reaches a breaking point where a tear or partial tear occurs. The player will experience pain that will persist if he or she attempts to stretch or contract the muscle. How are Muscle Injuries Treated? The immediate treatment consists of the 'PRICE' protocol: Protection of the injured part from further damage, Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation. The aim of this protocol is to reduce bleeding within the muscle tissue. Ice therapy in the form of ice pack applications should be continued for the first three days after the injury (never apply ice directly to the skin). The rehabilitation after this period involves gradually stretching the muscle to elongate the scar tissue and progressively increasing the muscle strength. Once this has been achieved, the player can begin sport-specific exercises, such as running, jumping and kicking. To reduce the risk of re-injury, this should be done under the supervision of a chartered physiotherapist. 7. The strength of contraction of a muscle depends on? number of fibres stimulated. 8. What is oxygen debt? Oxygen debt is the oxygen that needs to be replaced or paid back to the various systems in the body, such as the lungs, hemoglobin and myoglobin (found in the muscles of the body) and body fluids. This repayment of oxygen would catabolize the lactic acid formed in the muscles back to carbon dioxide and water.
5 When the energy required by the body exceeds the oxygen supply available to the body, the muscles get their oxygen from the breakdown of the ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) in the body. When this is also consumed, then additional ATP is produced by glycolisis without the use of oxygen (as it normally happens when ATP is produced in the body) and this process is called anaerobic glycolisis. This in turn, converts the pyruvic acid into lactic acid, which is then transported to the liver where it is broken into its two basic components, glucose and glycogen. Hence, the muscles get their energy supply when needed. When a person goes through this process, he/she normally becomes short of breath, since all of the oxygen is consumed by the muscle cells as a result of the strenuous exercise involved, and the rest of the body feels the need to supply more oxygen faster. This is when the person starts gasping for breath, which will be fast and shallow. As soon as the demanding type of exercise has ceased, the body reverses the processes in order to refill the oxygen that it has been depleted from different parts of the body. 9. Know the following diagram 10. Understand what happens to the sacromere during muscle contraction?
6
Outline. Bio 105: Muscular System. Muscular System. Types of Muscles. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle 4/6/2016
 Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Nerve Cell (aka neuron)
 Nerve Cell (aka neuron) Neuromuscular Junction Nerve cell Muscle fiber (cell) The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential Skeletal muscles must be stimulated by a motor
Nerve Cell (aka neuron) Neuromuscular Junction Nerve cell Muscle fiber (cell) The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential Skeletal muscles must be stimulated by a motor
Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts
 Biology 067 - Muscular system A. Type of muscles: Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Function Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts tubes blood
Biology 067 - Muscular system A. Type of muscles: Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Function Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts tubes blood
Muscular System. This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions:
 Muscular System Slide 2 This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions: Movement: Muscles work as pulleys on bones to help create changes in body position. Muscles
Muscular System Slide 2 This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions: Movement: Muscles work as pulleys on bones to help create changes in body position. Muscles
CHAPTER 6 2/9/2016. Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common.
 Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
Muscles and Muscle Tissue
 1 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter 9 2 Overview of Muscle Tissues Compare and Contrast the three basic types of muscle tissue List four important functions of muscle tissue 3 Muscle Terminology Muscle
1 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter 9 2 Overview of Muscle Tissues Compare and Contrast the three basic types of muscle tissue List four important functions of muscle tissue 3 Muscle Terminology Muscle
Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet 1. What are the three categories of muscle tissue? a) b) c) 2. The smallest functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a. 3. What are the four characteristics
Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet 1. What are the three categories of muscle tissue? a) b) c) 2. The smallest functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a. 3. What are the four characteristics
Muscle Metabolism Introduction ATP is necessary for muscle contraction single muscle cell form and break the rigor bonds of cross-bridges small
 Muscle Metabolism Introduction 1. ATP is necessary for muscle contraction a. when a single muscle cell is contracting it can use up millions of ATP molecules per second to form and break the rigor bonds
Muscle Metabolism Introduction 1. ATP is necessary for muscle contraction a. when a single muscle cell is contracting it can use up millions of ATP molecules per second to form and break the rigor bonds
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 9 Muscular System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 9 Muscular System 1 Chapter 9 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle usually attached to bones under conscious control striated Three Types
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 9 Muscular System 1 Chapter 9 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle usually attached to bones under conscious control striated Three Types
Muscular System- Part 1. Unit 5 Miss Wheeler
 Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
A and P CH 8 Lecture Notes.notebook. February 10, Table of Contents # Date Title Page # /30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 2. 1 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. i 1 Turnitin.com Class #: 13551662 Password: GoViks 2 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System Objective: Students will
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 2. 1 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. i 1 Turnitin.com Class #: 13551662 Password: GoViks 2 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System Objective: Students will
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY
 MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
1. Locomotion. 2. Repositioning. 3. Internal movement
 MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. 1 Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5.
MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. 1 Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5.
1. Locomotion. 2. Repositioning. 3. Internal movement
 MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5. Striated
MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5. Striated
Chapter 8 Notes. Muscles
 Chapter 8 Notes Muscles 8.1 Intro Three muscle types Skeletal Smooth cardiac 8.2 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Composition Skeletal muscle tissue Nervous tissue Blood Connective tissue Connective tissue
Chapter 8 Notes Muscles 8.1 Intro Three muscle types Skeletal Smooth cardiac 8.2 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Composition Skeletal muscle tissue Nervous tissue Blood Connective tissue Connective tissue
Biology 20: Module 6 1 Assignment. Module 6 The Motor System and Homeostasis. Student Name:
 Biology 20: Module 6 1 Assignment Module 6 The Motor System and Homeostasis Student Name: Biology 20: Module 6 2 Assignment Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Total Marks Total Possible Marks 30 23 53 Your Mark Teacher
Biology 20: Module 6 1 Assignment Module 6 The Motor System and Homeostasis Student Name: Biology 20: Module 6 2 Assignment Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Total Marks Total Possible Marks 30 23 53 Your Mark Teacher
Muscle and Muscle Tissue
 Muscle and Muscle Tissue Make up about half of total body mass Exerts force by converting chemical energy, ATP, to mechanical energy Muscle tissue is classified based on Shape Number and position of nuclei
Muscle and Muscle Tissue Make up about half of total body mass Exerts force by converting chemical energy, ATP, to mechanical energy Muscle tissue is classified based on Shape Number and position of nuclei
Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure
 Mechanism of contraction of Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure By Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi (MBBS, M. Phil) Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Long cylindrical
Mechanism of contraction of Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure By Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi (MBBS, M. Phil) Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Long cylindrical
Class XI Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement Biology
 Question 1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions. The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows: Question 2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle
Question 1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions. The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows: Question 2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle
MUSCLE TISSUE (MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY) PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE
 PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
5. What component of the sarcomere is not attached to the Z line?
 Model 2: Anatomy of a Sarcomere 1. Label the thick filament and the thin filament in Model 2. 2. How many sarcomeres are shown in Model 2? 3. Using Model 2, based on the locations of thick and thin filaments,
Model 2: Anatomy of a Sarcomere 1. Label the thick filament and the thin filament in Model 2. 2. How many sarcomeres are shown in Model 2? 3. Using Model 2, based on the locations of thick and thin filaments,
Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal Muscle
 Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle-moves the skeleton by pulling on the tendons that are connected to the bones Cardiac muscle-pumps blood through the heart and blood vessels
Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle-moves the skeleton by pulling on the tendons that are connected to the bones Cardiac muscle-pumps blood through the heart and blood vessels
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. The Muscular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
MUSCLE METABOLISM. Honors Anatomy & Physiology
 MUSCLE METABOLISM Honors Anatomy & Physiology ROLE OF ATP ATP binds to myosin heads and upon hydrolysis into ADP and Pi, transfers its energy to the cross bridge, energizing it. ATP is responsible for
MUSCLE METABOLISM Honors Anatomy & Physiology ROLE OF ATP ATP binds to myosin heads and upon hydrolysis into ADP and Pi, transfers its energy to the cross bridge, energizing it. ATP is responsible for
Microanatomy of Muscles. Anatomy & Physiology Class
 Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions. Packet #8
 Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular System STUDY GUIDE
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List three functions of the muscular system. 1) movement 2) thermogenesis (generates heat) 3) posture & body/joint support CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List three functions of the muscular system. 1) movement 2) thermogenesis (generates heat) 3) posture & body/joint support CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular
MUSCULAR TISSUE. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 MUSCULAR TISSUE Dr. Gary Mumaugh MUSCLE OVERVIEW The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth These types differ in structure, location, function, and means of activation FUNCTIONAL
MUSCULAR TISSUE Dr. Gary Mumaugh MUSCLE OVERVIEW The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth These types differ in structure, location, function, and means of activation FUNCTIONAL
Muscle Tissue. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 10 Muscle Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: Skeletal muscle
10 Muscle Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: Skeletal muscle
Notebook Anatomy and Physiology CH 8 Muscle Structure.notebook January 08, 2015
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 08/27/14 Ch 1: Intro to Human A & P 1 2. 09/05/14 Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism 6 3. 09/09/14 Ch 5: Tissues 8 4. 09/29/14 Ch 12: Blood 25 5. 10/06/14 Ch 13: Cardiovascular
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 08/27/14 Ch 1: Intro to Human A & P 1 2. 09/05/14 Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism 6 3. 09/09/14 Ch 5: Tissues 8 4. 09/29/14 Ch 12: Blood 25 5. 10/06/14 Ch 13: Cardiovascular
Muscle Physiology. Dr. Ebneshahidi Ebneshahidi
 Muscle Physiology Dr. Ebneshahidi Skeletal Muscle Figure 9.2 (a) Functions of the muscular system 1. Locomotion body movements are due to skeletal muscle contraction. 2. Vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
Muscle Physiology Dr. Ebneshahidi Skeletal Muscle Figure 9.2 (a) Functions of the muscular system 1. Locomotion body movements are due to skeletal muscle contraction. 2. Vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
Muscular System. 3 types of muscle tissue. How skeletal muscles arrange CARDIAC SMOOTH SKELETAL
 Muscular System Functions Support the body by allowing us to stay upright Allow for movement by attaching to the skeleton Help maintain a constant body temperature Assist in movement in the cardiovascular
Muscular System Functions Support the body by allowing us to stay upright Allow for movement by attaching to the skeleton Help maintain a constant body temperature Assist in movement in the cardiovascular
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # /27/14 Ch 7: Skeletal System 01/29/14 Ch 8: Muscular System
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 01/27/14 Ch 7: Skeletal System 01/29/14 Ch 8: Muscular System 12 i 1 01/30/14 Ch 8: Muscular System 12 Objective: Students will be able to describe
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 01/27/14 Ch 7: Skeletal System 01/29/14 Ch 8: Muscular System 12 i 1 01/30/14 Ch 8: Muscular System 12 Objective: Students will be able to describe
Muscles & Muscle Tissue
 Muscles & Muscle Tissue Chapter 6 I. Overview of Muscle 1 A. MUSCLE TYPES SKELETAL: striated, voluntary CARDIAC: only in heart involuntary striated SMOOTH: walls of organs involuntary nonstriated All Muscle
Muscles & Muscle Tissue Chapter 6 I. Overview of Muscle 1 A. MUSCLE TYPES SKELETAL: striated, voluntary CARDIAC: only in heart involuntary striated SMOOTH: walls of organs involuntary nonstriated All Muscle
The Muscular System. Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle
 The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle Nervous The
The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle Nervous The
Chapter 7 The Muscular System. Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 Chapter 7 The Muscular System Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move 1. Three types of
Chapter 7 The Muscular System Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move 1. Three types of
Page 1. Chapter 9: Muscle Tissue. Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle. Gross Anatomy of Muscle:
 1 Chapter 9: Muscle Tissue Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Characteristics: Attaches to skeleton Voluntary control Striated / multi-nucleated Characteristics: Composes
1 Chapter 9: Muscle Tissue Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Characteristics: Attaches to skeleton Voluntary control Striated / multi-nucleated Characteristics: Composes
AP Biology
 Chapter 49. Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Muscles & Motor Locomotion Muscle voluntary, striated involuntary, striated auto-rhythmic involuntary, non-striated 1
Chapter 49. Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Muscles & Motor Locomotion Muscle voluntary, striated involuntary, striated auto-rhythmic involuntary, non-striated 1
Chapter 49. Muscles & Motor Locomotion. AP Biology
 Chapter 49. Muscles & Motor Locomotion Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Muscle voluntary, striated involuntary, striated auto-rhythmic involuntary, non-striated
Chapter 49. Muscles & Motor Locomotion Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Muscle voluntary, striated involuntary, striated auto-rhythmic involuntary, non-striated
About This Chapter. Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Pearson Education, Inc.
 About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
Muscles & Motor Locomotion Why Do We Need All That ATP?
 Muscles & Motor Locomotion Why Do We Need All That ATP? 2006-2007 Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Lots of ways to get around Lots of ways to get around mollusk mammal
Muscles & Motor Locomotion Why Do We Need All That ATP? 2006-2007 Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Lots of ways to get around Lots of ways to get around mollusk mammal
Protection, Support, and Movement-Skin, Skeleton, and Muscle Notes
 I. Movement in animals A. Basics: 1. different modes of transportation (running, flying, swimming) have evolved with adaptations for animals to overcome difficulties associated with each type of locomotion
I. Movement in animals A. Basics: 1. different modes of transportation (running, flying, swimming) have evolved with adaptations for animals to overcome difficulties associated with each type of locomotion
1/4/2017. Introduction. Connective Tissue Coverings. 9.1: Structure of a Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Fibers. Connective Tissue Coverings
 Introduction Chapter 09 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Introduction Chapter 09 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Muscle Tissue. Muscle Tissue Outline. General Function of Muscle Tissue
 Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue Outline General Functions of Muscle Tissue Characteristics of Muscle Tissue Classification of Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Muscle Energetics Muscle Mechanics
Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue Outline General Functions of Muscle Tissue Characteristics of Muscle Tissue Classification of Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Muscle Energetics Muscle Mechanics
Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue I. Overview of muscle tissue A. Three muscle types in the body: B. Special characteristics 1. Excitability: able to receive and respond to a stimulus 2. Contractility:
Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue I. Overview of muscle tissue A. Three muscle types in the body: B. Special characteristics 1. Excitability: able to receive and respond to a stimulus 2. Contractility:
Muscular System Module 3: Contraction and Relaxation *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m48498 1 Muscular System Module 3: Contraction and Relaxation * Donna Browne Based on Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and
OpenStax-CNX module: m48498 1 Muscular System Module 3: Contraction and Relaxation * Donna Browne Based on Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and
11.2 Muscles and Movement
 11.2 Muscles and Movement 11.2.1 - State the roles of bones, ligaments, muscles, tendons and nerves in human movement Bones Act as anchors for the muscles, and levers to control the movement of muscles,
11.2 Muscles and Movement 11.2.1 - State the roles of bones, ligaments, muscles, tendons and nerves in human movement Bones Act as anchors for the muscles, and levers to control the movement of muscles,
Page 1. Chapter 9: Muscle Tissue. Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle. Characteristics of Muscle:
 1 Chapter 9: Muscle Tissue Muscle little mouse Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Characteristics: Attaches to skeleton Voluntary control Striated / multi-nucleated Characteristics:
1 Chapter 9: Muscle Tissue Muscle little mouse Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Characteristics: Attaches to skeleton Voluntary control Striated / multi-nucleated Characteristics:
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.49 - MUSCLE SYSTEMS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
!! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
I. Overview of Muscle Tissues
 I. Overview of Muscle Tissues A. Types of Muscle Tissue 1. Terminology 1. Muscle fibers = muscle cells are greatly elongated therefore known as fibers; true for skeletal and smooth muscles only 2. Myo
I. Overview of Muscle Tissues A. Types of Muscle Tissue 1. Terminology 1. Muscle fibers = muscle cells are greatly elongated therefore known as fibers; true for skeletal and smooth muscles only 2. Myo
All three muscle types have the following CHARACTERISTICS: 1. Excitablity: responds to an electrical or chemical stimulus. 2. Conductivity: carries
 1 Muscles themselves are considered the primary organ is this system. Each muscle is considered a separate organ. The functions of muscle are movement, stability (our posture and tone to stay upright),
1 Muscles themselves are considered the primary organ is this system. Each muscle is considered a separate organ. The functions of muscle are movement, stability (our posture and tone to stay upright),
(c) sarcolemma with acethylcholine (protein) receptors
 (slide 1) Lecture Notes: Muscular System I. (slide 2) Introduction to Muscular System A) Tissues of the Muscular System: 1) Connective Tissues (a) dense fibrous (tendons and ligaments) 2) Nervous Tissue
(slide 1) Lecture Notes: Muscular System I. (slide 2) Introduction to Muscular System A) Tissues of the Muscular System: 1) Connective Tissues (a) dense fibrous (tendons and ligaments) 2) Nervous Tissue
Muscles Muscles are effectors which enable movement to be carried out
 Muscles 13.8 Muscles are effectors which enable movement to be carried out Muscle Is responsible for almost all the movements in animals 3 types Cardiac muscle Smo oth muscle Skeletal mus cle (aka striped
Muscles 13.8 Muscles are effectors which enable movement to be carried out Muscle Is responsible for almost all the movements in animals 3 types Cardiac muscle Smo oth muscle Skeletal mus cle (aka striped
AP Biology. Animal Locomotion. Muscles & Motor Locomotion. Why Do We Need All That ATP? Lots of ways to get around. Muscle
 Muscles & Motor Locomotion Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Why Do We Need All That? 2006-2007 Lots of ways to get around Lots of ways to get around mollusk mammal
Muscles & Motor Locomotion Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Why Do We Need All That? 2006-2007 Lots of ways to get around Lots of ways to get around mollusk mammal
Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue Muscles: 1. Overview of Muscle Tissue A. Review 5 functions of muscle tissue. B. Review the 5 properties of muscle tissue. WHICH do they share with nervous tissue? (2, plus the
Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue Muscles: 1. Overview of Muscle Tissue A. Review 5 functions of muscle tissue. B. Review the 5 properties of muscle tissue. WHICH do they share with nervous tissue? (2, plus the
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SPORT AND BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES SPORT AND EXERCISE SCIENCE PATHWAY SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017
 LH14 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SPORT AND BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES SPORT AND EXERCISE SCIENCE PATHWAY SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017 INTRODUCTION TO SPORT AND EXERCISE PHYSIOLOGY MODULE NO: SPS4002 Date: Thursday
LH14 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SPORT AND BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES SPORT AND EXERCISE SCIENCE PATHWAY SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017 INTRODUCTION TO SPORT AND EXERCISE PHYSIOLOGY MODULE NO: SPS4002 Date: Thursday
Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function
 Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function Muscle activity is a response to input from the nervous system The action of a muscle is always to contract Vertebrate
Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function Muscle activity is a response to input from the nervous system The action of a muscle is always to contract Vertebrate
Types of Muscle. Skeletal striated & voluntary Smooth involuntary Cardiac - heart
 Muscular System Types of Muscle Skeletal striated & voluntary Smooth involuntary Cardiac - heart The word striated means striped. Skeletal muscle appears striped under a microscope. Muscles and Muscle
Muscular System Types of Muscle Skeletal striated & voluntary Smooth involuntary Cardiac - heart The word striated means striped. Skeletal muscle appears striped under a microscope. Muscles and Muscle
Animal Locomotion. Lots of ways to get around. What are the advantages of locomotion? Why Do We Need All That ATP?
 Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? Motor Mechanisms sessile (Muscles & Motor Locomotion) motile Why Do We Need All That ATP? 2006-2007 mollusk mammal bird reptile We saw how some
Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? Motor Mechanisms sessile (Muscles & Motor Locomotion) motile Why Do We Need All That ATP? 2006-2007 mollusk mammal bird reptile We saw how some
The Muscular System and Homeostasis
 Chapter 10 Chapter 10 The Muscular System and Homeostasis The Muscular System and Homeostasis 10.1 Movement and Muscle Tissue 10.2 Muscles, Health, and Homeostasis 10.1 Movement and Muscle Tissue Muscles
Chapter 10 Chapter 10 The Muscular System and Homeostasis The Muscular System and Homeostasis 10.1 Movement and Muscle Tissue 10.2 Muscles, Health, and Homeostasis 10.1 Movement and Muscle Tissue Muscles
Exercise Science (Muscle Anatomy and Physiology) PPL10 Date: May 11 th, 2015
 Exercise Science (Muscle Anatomy and Physiology) PPL10 Date: May 11 th, 2015 Examples of Strength and Physique Athletes The Principle of Muscles The most important principle for muscles is the use it or
Exercise Science (Muscle Anatomy and Physiology) PPL10 Date: May 11 th, 2015 Examples of Strength and Physique Athletes The Principle of Muscles The most important principle for muscles is the use it or
The Muscular System 6PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6PART B Contraction of Skeletal Muscle Muscle fiber contraction is all or none
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6PART B Contraction of Skeletal Muscle Muscle fiber contraction is all or none
The Muscular System PART B
 6 The Muscular System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Sliding Filament
6 The Muscular System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Sliding Filament
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 10 Muscular Tissue Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Learn about the structure and function of the 3 types of muscular tissue
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 10 Muscular Tissue Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Learn about the structure and function of the 3 types of muscular tissue
The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law).
 The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law). This principle stipulates that, when a motor unit is stimulated to contract, it will do so to its
The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law). This principle stipulates that, when a motor unit is stimulated to contract, it will do so to its
Fig Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. Nucleus. Muscle fiber. Endomysium. Striations.
 Fig. 11.1 Nucleus Muscle fiber Endomysium Striations Ed Reschke 1 Fig. 11.2 Muscle fiber Nucleus I band A band Z disc Mitochondria Openings into transverse tubules Sarcoplasmic reticulum Triad: Terminal
Fig. 11.1 Nucleus Muscle fiber Endomysium Striations Ed Reschke 1 Fig. 11.2 Muscle fiber Nucleus I band A band Z disc Mitochondria Openings into transverse tubules Sarcoplasmic reticulum Triad: Terminal
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Chapter 9 Muscle. Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle. Striated muscle
 Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
10 - Muscular Contraction. Taft College Human Physiology
 10 - Muscular Contraction Taft College Human Physiology Muscular Contraction Sliding filament theory (Hanson and Huxley, 1954) These 2 investigators proposed that skeletal muscle shortens during contraction
10 - Muscular Contraction Taft College Human Physiology Muscular Contraction Sliding filament theory (Hanson and Huxley, 1954) These 2 investigators proposed that skeletal muscle shortens during contraction
Muscular System Anatomy
 Dr.MEGHA LAHIRI(ZOOLOGY HONOURS) MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is responsible for the movement of the human body. Attached to the bones of the skeletal system are about 700 named muscles that make
Dr.MEGHA LAHIRI(ZOOLOGY HONOURS) MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is responsible for the movement of the human body. Attached to the bones of the skeletal system are about 700 named muscles that make
Collin County Community College BIOL Muscle Physiology. Muscle Length-Tension Relationship
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Muscle Physiology 1 Muscle Length-Tension Relationship The Length-Tension Relationship Another way that muscle cells can alter their force capability, is determined
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Muscle Physiology 1 Muscle Length-Tension Relationship The Length-Tension Relationship Another way that muscle cells can alter their force capability, is determined
Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA (
 Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA ( 夏强 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C518, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: xiaqiang@zju.edu.cn Course website: http://10.71.121.151/physiology
Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA ( 夏强 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C518, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: xiaqiang@zju.edu.cn Course website: http://10.71.121.151/physiology
Nerve Muscle Relationship and Neural Muscular Junction Quiz. Remember, you need to know the structure and the function!
 Nerve Muscle Relationship and Neural Muscular Junction Quiz Remember, you need to know the structure and the function! What is this called? What is this? Schwann cell What is this called? Basal lamina
Nerve Muscle Relationship and Neural Muscular Junction Quiz Remember, you need to know the structure and the function! What is this called? What is this? Schwann cell What is this called? Basal lamina
Functions of Muscle Tissue
 The Muscular System Functions of Muscle Tissue Movement Facilitation Thermogenesis Postural Support Regulation of Organ Volume Protects Internal Organs Pumps Blood (HEART) Characteristics of Muscle Tissue
The Muscular System Functions of Muscle Tissue Movement Facilitation Thermogenesis Postural Support Regulation of Organ Volume Protects Internal Organs Pumps Blood (HEART) Characteristics of Muscle Tissue
Chapter 10! Chapter 10, Part 2 Muscle. Muscle Tissue - Part 2! Pages !
 ! Chapter 10, Part 2 Muscle Chapter 10! Muscle Tissue - Part 2! Pages 308-324! SECTION 10-5! Sarcomere shortening and muscle fiber stimulation produce tension! 2! Tension Production - Muscle FIBER! All-or-none
! Chapter 10, Part 2 Muscle Chapter 10! Muscle Tissue - Part 2! Pages 308-324! SECTION 10-5! Sarcomere shortening and muscle fiber stimulation produce tension! 2! Tension Production - Muscle FIBER! All-or-none
The Sliding Filament Theory
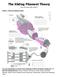 The Sliding Filament Theory Model 1: Muscle Histology Review How do muscle cells contract? Use your knowledge of muscle tissue histology to fill in the blanks numbered 1-11 with the following terms: Fasicle,
The Sliding Filament Theory Model 1: Muscle Histology Review How do muscle cells contract? Use your knowledge of muscle tissue histology to fill in the blanks numbered 1-11 with the following terms: Fasicle,
Bio Factsheet April 2000 Number 66
 April Number 66 The Physiology of Exercise This factsheet summarises the aspects of exercise physiology that relate to skeletal muscles on current syllabuses. The student should have a basic knowledge
April Number 66 The Physiology of Exercise This factsheet summarises the aspects of exercise physiology that relate to skeletal muscles on current syllabuses. The student should have a basic knowledge
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B) maintain posture C) maintain body temperature
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B) maintain posture C) maintain body temperature
Muscles and Metabolism
 Muscles and Metabolism How does the body provide the energy needed for contraction? -as muscles contract, ATP supplies the energy fro cross bridge movement and detachment and for operation of the calcium
Muscles and Metabolism How does the body provide the energy needed for contraction? -as muscles contract, ATP supplies the energy fro cross bridge movement and detachment and for operation of the calcium
Musculoskeletal Systems. Anatomy: Arrangement of Cells Physiology: Contractions
 Musculoskeletal Systems Anatomy: Arrangement of Cells Physiology: Contractions Characteristics of all muscle Contractile: it shortens Excitable: receives & responds to electrical signals Extensible: stretches
Musculoskeletal Systems Anatomy: Arrangement of Cells Physiology: Contractions Characteristics of all muscle Contractile: it shortens Excitable: receives & responds to electrical signals Extensible: stretches
The Musculoskeletal System. Chapter 46
 The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 46 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure Zoologists recognize three types: 1. Hydrostatic skeletons a fluid
The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 46 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure Zoologists recognize three types: 1. Hydrostatic skeletons a fluid
sliding filament mechanism cross-bridges myosin actin tropomyosin troponin transverse tubules (T tubules) motor unit
 CHAPTER 47: THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM THE ESSENTIALS THEME ALERT ATP-induced phosphorylation and conformational change in proteins were principles learned earlier in the course the mechanism of muscle
CHAPTER 47: THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM THE ESSENTIALS THEME ALERT ATP-induced phosphorylation and conformational change in proteins were principles learned earlier in the course the mechanism of muscle
Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton
 Lesson 15 Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Muscle Contraction Muscles: tissues that produce movement by contracting Vertebrates have three types of
Lesson 15 Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Muscle Contraction Muscles: tissues that produce movement by contracting Vertebrates have three types of
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
33.2. Muscular System. Humans have three types of muscle.
 33.2 Muscular System VOCABULARY muscular system muscle fiber skeletal muscle tendon smooth muscle cardiac muscle myofibril sarcomere 10A, 10C, 11A Key Concept Muscles are tissues that can contract, enabling
33.2 Muscular System VOCABULARY muscular system muscle fiber skeletal muscle tendon smooth muscle cardiac muscle myofibril sarcomere 10A, 10C, 11A Key Concept Muscles are tissues that can contract, enabling
Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function
 Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function Objectives Draw & label the microstructure of skeletal muscle Outline the steps leading to muscle shortening Define the concentric and isometric Discuss:
Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function Objectives Draw & label the microstructure of skeletal muscle Outline the steps leading to muscle shortening Define the concentric and isometric Discuss:
Bio 103 Muscular System 61
 61 Lecture Outline: MUSCULAR SYSTEM [Chapter 9] A. Functions of Skeletal Muscle 1. Movement 2. Maintain posture 3. Support 4. Guard openings 5. Maintain body temperature (thermogenesis) B. Muscle Tissue
61 Lecture Outline: MUSCULAR SYSTEM [Chapter 9] A. Functions of Skeletal Muscle 1. Movement 2. Maintain posture 3. Support 4. Guard openings 5. Maintain body temperature (thermogenesis) B. Muscle Tissue
Muscles and Animal Movement
 Muscles and Animal Movement Evolution of Muscle and Movement Animals are the only multicellular organisms that actively move. Movement is due to muscle cells (motor proteins) Muscle proteins have homologues
Muscles and Animal Movement Evolution of Muscle and Movement Animals are the only multicellular organisms that actively move. Movement is due to muscle cells (motor proteins) Muscle proteins have homologues
Skeletal Muscle. Cardiac Muscle. Smooth Muscle. II. Muscular System. The Muscular System
 Chapter CHAPTER 8 8 The Muscular System College Prep NOTES Smooth Muscle Found in body organs,vessels, respiratory passages Not striated, tapered, single cell nucleus involuntary, peristaltic contractions
Chapter CHAPTER 8 8 The Muscular System College Prep NOTES Smooth Muscle Found in body organs,vessels, respiratory passages Not striated, tapered, single cell nucleus involuntary, peristaltic contractions
Skeletal Muscle. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle. I. 3 Types of Muscle Tissue. 1. Smooth 2. Cardiac 3. Skeletal
 I. 3 Types of Muscle Tissue 1. Smooth 2. Cardiac 3. Skeletal Smooth Muscle Found in body organs,vessels, respiratory passages Not striated, tapered, single cell nucleus involuntary, peristaltic contractions
I. 3 Types of Muscle Tissue 1. Smooth 2. Cardiac 3. Skeletal Smooth Muscle Found in body organs,vessels, respiratory passages Not striated, tapered, single cell nucleus involuntary, peristaltic contractions
Muscular System. Honors Anatomy & Physiology. Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Muscular System Honors Anatomy & Physiology Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Skeletal, Smooth, or Cardiac SKELETAL Striated Voluntary Multinucleated Bound to bones Moves skeleton SMOOTH Not striated
Muscular System Honors Anatomy & Physiology Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Skeletal, Smooth, or Cardiac SKELETAL Striated Voluntary Multinucleated Bound to bones Moves skeleton SMOOTH Not striated
2/28/18. Muscular System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Physiology. Anatomy. Muscle Fiber
 Introduction Muscular System Chapter 20 Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
Introduction Muscular System Chapter 20 Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
2/28/18. Muscular System. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 20
 Muscular System Chapter 20 1 Introduction Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
Muscular System Chapter 20 1 Introduction Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
Muscle Cell Anatomy & Function (mainly striated muscle tissue)
 Muscle Cell Anatomy & Function (mainly striated muscle tissue) General Structure of Muscle Cells (skeletal) several nuclei (skeletal muscle) skeletal muscles are formed when embryonic cells fuse together
Muscle Cell Anatomy & Function (mainly striated muscle tissue) General Structure of Muscle Cells (skeletal) several nuclei (skeletal muscle) skeletal muscles are formed when embryonic cells fuse together
Lecture Overview. Muscular System. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Lecture 16
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Lecture 16 1 Lecture Overview Types, characteristics, functions of muscle Structure of skeletal muscle Mechanism of
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Lecture 16 1 Lecture Overview Types, characteristics, functions of muscle Structure of skeletal muscle Mechanism of
Biology 201-Worksheet on Muscle System (Answers are in your power point outlines-there is no key!)
 Bio 201 Tissues and Skin 1 February 23, 2011 Biology 201-Worksheet on Muscle System (Answers are in your power point outlines-there is no key!) 1. Name and define 5 characteristics of the muscle system.
Bio 201 Tissues and Skin 1 February 23, 2011 Biology 201-Worksheet on Muscle System (Answers are in your power point outlines-there is no key!) 1. Name and define 5 characteristics of the muscle system.
Ch 12: Muscles sarcolemma, t-tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, myofibrils, myofilaments, sarcomere...
 Ch 12: Muscles Review micro-anatomy of muscle tissue Terminology examples: sarcolemma, t-tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, myofibrils, myofilaments, sarcomere... SLOs Differentiate levels of muscle structure:
Ch 12: Muscles Review micro-anatomy of muscle tissue Terminology examples: sarcolemma, t-tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, myofibrils, myofilaments, sarcomere... SLOs Differentiate levels of muscle structure:
