ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATION OR CONTUSION : A DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA. Yong Pei Yee, Ibrahim Lutfi Shuaib, Jafri Malin Abdullah*
|
|
|
- Imogene Crawford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 8, No. 2, July 2001 (47-51) CASE REPORT ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATION OR CONTUSION : A DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA Yong Pei Yee, Ibrahim Lutfi Shuaib, Jafri Malin Abdullah* Department of Radiology, *Neuroscience Unit, School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia Kubang Kerian, Kelantan, Malaysia A young man was involved in a motor vehicle accident and sustained cerebral contusion in the right frontal and occipital lobes. Computed tomography (CT) scan done 2 weeks after the injury revealed multiple serpenginous structures which enhanced following intravenous contrast media administration. The possibility of arteriovenous malformation (AVM) was raised and angiography was suggested. However, he was managed conservatively and a repeat CT scan 4 months post trauma revealed encephalomalacia in the right frontal and occipital lobes with no more surrounding enhancement. The cause for the multiple serpenginous enhancement demonstrated previously confirmed those are areas of hyperperfusion in healing surface brain contusion. The aim of this case report is to discuss on the possible causes of focal enhancement following head injury versus the features of AVM on plain and post contrast CT scan with the effort to clear the doubt and to avoid future confusion. Key words : head injury, contusion, hyperperfusion. Submitted , Revised Article , Date Accepted Introduction Head injury is one of the common causes for requesting cranial CT. In the acute stage, a plain CT scan of the brain is sufficient to achieve the diagnosis of cerebral contusion, intracranial hemorrhage or skull fracture. Only in the subacute or chronic head injury, intravenous contrast is occasionally used to facilitate detection of isodense hemorrhage or complications such as subdural empyema. In cerebral contusion, it is noted that an area of hyperemia may occur surrounding the contused brain. This has been studied and proven in both human and experimental animals. The natural history of brain contusion includes the acute damage phase, liquefaction with edema, a repair stage and a final cystic degenerative stage. During healing, there will be neovascularization but the new vessels formed have defective endothelial junctures causing disturbance in blood brain barrier. Thus, at this stage, if intravenous contrast is given for cross sectional imaging, enhancement will be demonstrated. Case Report MAO, a 17 year-old young man, was involved in a motor vehicle accident and sustained head injury with a Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) of 7/15 at presentation. CT scan brain showed a right frontal and occipital lobe contusion. A right frontal craniectomy and evacuation of clot was done immediately. He was transferred to another hospital on the request of his family members. A follow-up cranial CT scan performed two weeks later revealed focal gliosis of the right frontal and occipital lobes secondary to previous contusion (Figure 1). Post contrast scan showed serpenginous gyriform enhancement around the contusion in the right frontal and occipital lobes (Figure 2). The possibility 47
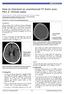
2 Yong Pei Yee, Ibrahim Lutfi Shuaib, Jafri Malin Abdullah 48 Figure 1 : Plain CT brain showing focal gliosis of the right frontal and right occipital lobes. Figure 2 : Post contrast scan showed serpenginous gyriform enhancement around the contusion in the right frontal and occipital lobes.
3 ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATION OR CONTUSION : A DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA of arteriovenous malformation was raised and cerebral angiography was suggested. However, he was managed conservatively and was discharged with GCS of 9/15. He was followed up in the clinic and noted to be improving slowly. Four months after the accident, a repeat cranial CT scan was done. His GCS was full. He was well except for poor vision (only perception of light bilaterally), probably secondary to corneal ulceration. A contrast enhanced CT scan of the brain showed areas of encephalomalacia in the right frontal and occipital lobes following previous injury. The multiple serpenginous enhancement demonstrated in the previous CT scan was not visualized any more. There was also focal dilatation of the right frontal, occipital and temporal horns due to brain volume loss (Figure 3). From this CT scan, there was no feature to suggest arteriovenous malformation. Discussion Since the introduction of CT scan as a noninvasive technique for evaluating central nervous system pathology by Hounsfield in 1972, CT has revolutionized the management of head injury patients. It has replaced cerebral angiography for identifying brain herniation and intracranial mass lesions. In the acute setting, CT is also generally preferred over Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) (1). In a case of head injury, a complete CT evaluation includes 3 main window width and levels which are (i) brain window, optimized for brain; (ii) intermediate windows, to assess subdural or epidural hematoma; and (iii) bone window, used to determined bony fracture (2). Intravenous contrast is not normally administrated in an acute case and it may mask the presence of subarachnoid hemorrhage. However, in subacute or chronic head injury, contrast enhancement may be necessary to demonstrate an isodense hematoma, post-traumatic infarction, resolving hemorrhagic contusion and other complications such as empyema or intracerebral abscess. In this patient, the initial CT scan done in this hospital was at 2 weeks post trauma. The findings of focal gliosis in the right frontal and occipital lobes reflect coup and contrecoup contusions, in which the frontal lobe lesion was most likely the coup injury. Intravenous contrast was administered then and demonstrated multiple serpenginous enhancement adjacent to and surrounding the region of contusion. It was thought that these enhancement were probably large draining veins and thus, arteriovenous malformation was suspected. Figure 3 : A repeat contrast enhanced CT scan of the brain done 4 months post trauma. There were areas of encephalomalacia in the right frontal and occipital lobes. The multiple serpenginous enhancement demonstrated in the previous CT scan was not visualized any more. 49
4 Yong Pei Yee, Ibrahim Lutfi Shuaib, Jafri Malin Abdullah However, upon reviewing the images again and after literature review, it was thought that the contrast enhancement could be just part of the course or pathophysiology of brain contusion. Clinical studies suggest that focal hyperemia can occur following traumatic brain injury. Alexander M.J. et al (3) had performed a study on regional cerebral blood flow using 133 Xenon in head injury patients with focal contusion and cerebral edema. They had demonstrated that the initial oligemia in the contused area was associated with a subsequent hyperemic rim about the contusion. In another study by Sakas D.E. et al (4), using 99m Technetium-hexamethylpropyleneamineoxime, hyperemic areas were demonstrated in 38% of patients with head injury. The hyperemia were commonest in patients with focal contusions and intracerebral hematomas. It affected both gray and white matter. From their study, most hyperemia was found to have disappeared by the second week after injury. However, in one of their patients, hyperemia was still present 3 weeks post injury. Recent tomography studies have demonstrated that hyperemia occurs most frequently between the second and fourth day after trauma. Sakas D.E. et al (4) reported that hyperemia occurs only in normal tissue directly adjacent to focal mass lesions. However, Fumeya H. et al (5) had found hyperemia within the edematous tissue revealed by MRI. They had observed that these hyperemic lesions are likely to be related to post traumatic seizures and tend to dissipate on follow up MRI. The incidence, pathophysiology significance and clinical relevance of hyperemia following head injury are not yet understood. Sakas D.E. et al (4) postulated that the swollen astrocytes found within the edematous tissue adjacent to contusions may cause a hyperemic response by compressing the microvasculature. They found that this focal and persistent hyperemia is benign and has minimal effect on intracranial pressure and level of consciousness. This benign form of hyperemia was associated with better outcome of the patient. Besides the hyperemic phenomenon, there is another possibility for the enhancement demonstrated in this patient. It could be part of the neuropathological changes that occur as a cerebral contusion undergoes resolution. Four distinct phases have been described for brain contusion (1, 2). The first phase is the acute damage. The second stage is liquefaction of the contusion with development of edema. This occurs between the third and seventh day following injury. In the third phase, repair mechanism sets in. Macrophages remove the blood elements and the damaged tissue. Neovascularisation occurs around the area of healing. The new blood vessels lack tight endothelial junctures, causing blood brain barrier disturbance. At this point, within one week of injury, if a contrast agent is administered during CT scanning or MRI, enhancement will be seen at the margin of the contusion. The final stage of evolution occurs when the necrotic tissue is sloughed and cystic cavities are formed. Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an admixture of arteries and veins. There are three morphologic components : the nidus; the feeding arteries and the draining veins. On non-contrast enhanced CT scan, intra-parenchymal AVM most commonly presents as an area of heterogeneous hyperdensity relative to brain parenchyma (2, 6, 7). The lesion is poorly defined and irregular in outline. Calcification within the vascular channels and adjacent brain parenchyma are often present. Following administration of intravenous contrast agent, there is ill-defined heterogeneous enhancement of the lesion. Feeding arteries or draining veins may be demonstrated as dilated vessels on contrast enhanced CT. Occasionally, AVMs are predominantly hyperdense and heavily calcified. The adjacent brain parenchyma shows destructive and atrophic changes. Lobato R.D. et al (9) had found that 96% of AVMs were hyperdense (either homogeneously or mottled) on pre-contrast CT study and only 19% were hypodense with the remaining being isodense to the brain. From their study, 76% of AVM showed enhancement post intravenous contrast. Correlating the CT findings with the clinical history of this patient, the serpenginous gyriform enhancement in the right frontal and occipital lobes are most appropriately explained by the focal hyperemic phenomenon following brain injury or as part of the evolution of cerebral contusion. AVM is very much unlikely and this is supported by the repeat CT scan which failed to demonstrate the similar enhancement. Conclusion Focal enhancement surrounding an area of brain injury or contusion could be the benign hyperemic phenomenon or as part of the evolution of cerebral contusion. This should not be confused with an AVM in which the patient might then be 50
5 ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATION OR CONTUSION : A DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA subjected to further invasive investigation such as cerebral angiography. Correspondence: Dr. Yong Pei Yee, MD Department of Radiology, School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Kubang Kerian, Kelantan, Malaysia. References 1. Gean A.D. Imaging Head Trauma. Raven Press, Zimmerman R.A. Cranial MRI and CT; Craniocerebral Trauma. McGraw-Hill Alexander M.J., Martin N.A., Khanna R. Caron M, Becker DP. Regional cerebral blood flow trends in head injured patient with focal contusions and cerebral edema. Acta Neurocir Suppl (Wien). 1994; 60: Sakas D.E., Bullock M.R., Patterson J. Hadley D, Wyper DJ, Teasdale GM. Focal cerebral hyperemia after focal head injury in humans : a benign phenomenon? J. Neurosurg. 1995; 83: Fumeya H., Fujisaki I. Focal cerebral hyperemia. J. Neurosurg. 1996; 84: New P.F.J., Ojemann R.G., Davis K.R. Rosen BR, Heron SR, Kjellberg RN, Adams RD, Richardson EP. MR and CT of occult vascular malformations of the brain. AJR. 1986; 147: Brunelle F.O.S., Harwood-Nash D.C.F., Fitz C.R. Chuang SH. Intracranial vascular malformations in children : computed tomographic and angiographic evaluation. Radiology. 1983; 149: Awad I.A. Neurovascular Surgery : Dural Arteriovenous Malformations. McGraw-Hill, Lobato R.D., Perez C., Rivas J.J. Cordobes F. Clinical, radiological, and pathological spectrum of angiographically occult intracranial vascular malformations : analysis of 21 cases and review of the literature. J. Neurosurg. 1988; 68:
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE
 THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage
 July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup
July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup
2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Temporal Lobe Injury in Temporal Bone Fractures. imaging (MRI) to evaluate lesions of the temporal
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Temporal Lobe Injury in Temporal Bone Fractures Richard M. Jones, MD; Michael I. Rothman, MD; William C. Gray, MD; Gregg H. Zoarski, MD; Douglas E. Mattox, MD Objective: To determine the
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Temporal Lobe Injury in Temporal Bone Fractures Richard M. Jones, MD; Michael I. Rothman, MD; William C. Gray, MD; Gregg H. Zoarski, MD; Douglas E. Mattox, MD Objective: To determine the
PRACTICE GUIDELINE. DEFINITIONS: Mild head injury: Glasgow Coma Scale* (GCS) score Moderate head injury: GCS 9-12 Severe head injury: GCS 3-8
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
Extradural hematoma (EDH) accounts for 2% of all head injuries (1). In
 CASE REPORT Conservative management of extradural hematoma: A report of sixty-two cases A. Rahim H. Zwayed 1, Brandon Lucke-Wold 2 Zwayed ARH, Lucke-wold B. Conservative management of extradural hematoma:
CASE REPORT Conservative management of extradural hematoma: A report of sixty-two cases A. Rahim H. Zwayed 1, Brandon Lucke-Wold 2 Zwayed ARH, Lucke-wold B. Conservative management of extradural hematoma:
Two-Stage Management of Mega Occipito Encephalocele
 Two-Stage Management of Mega Occipito Encephalocele CASE REPORT A I Mardzuki*, J Abdullah**, G Ghazaime*, A R Ariff!'*, M Ghazali* *Department of Neurosciences, **Department of Radiology, Hospital Universiti
Two-Stage Management of Mega Occipito Encephalocele CASE REPORT A I Mardzuki*, J Abdullah**, G Ghazaime*, A R Ariff!'*, M Ghazali* *Department of Neurosciences, **Department of Radiology, Hospital Universiti
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center. Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh
 UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh Regional cerebral blood flow is important Some essential facts Neurons are obligatory glucose users Under anerobic
UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh Regional cerebral blood flow is important Some essential facts Neurons are obligatory glucose users Under anerobic
Evaluation of Craniocerebral Trauma Using Computed Tomography
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. IV (Sep. 2014), PP 57-62 Evaluation of Craniocerebral Trauma Using Computed Tomography
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. IV (Sep. 2014), PP 57-62 Evaluation of Craniocerebral Trauma Using Computed Tomography
MR imaging as predictor of delayed posttraumatic cerebral hemorrhage
 J Neurosurg 69:203-209, 1988 MR imaging as predictor of delayed posttraumatic cerebral hemorrhage TOKUTARO TANAKA, M.D., TSUNEO SAKAI, M.D., KENICHI UEMURA, M.D., ATSUSHI TERAMURA, M.D., ICHIRO FUJISHIMA,
J Neurosurg 69:203-209, 1988 MR imaging as predictor of delayed posttraumatic cerebral hemorrhage TOKUTARO TANAKA, M.D., TSUNEO SAKAI, M.D., KENICHI UEMURA, M.D., ATSUSHI TERAMURA, M.D., ICHIRO FUJISHIMA,
A Comprehensive Study on Post Traumatic Temporal Contusion in Adults
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/318 A Comprehensive Study on Post Traumatic Temporal Contusion in Adults R Renganathan 1, P John Paul 2, Heber Anandan
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/318 A Comprehensive Study on Post Traumatic Temporal Contusion in Adults R Renganathan 1, P John Paul 2, Heber Anandan
Pediatric Subdural Hematoma and Traumatic Brain Injury J. Charles Mace MD FACS Springfield Neurological Institute CoxHealth. Objectives 11/7/2017
 Pediatric Subdural Hematoma and Traumatic Brain Injury J. Charles Mace MD FACS Springfield Neurological Institute CoxHealth Objectives 1. Be able to discuss brain anatomy and physiology as it applies to
Pediatric Subdural Hematoma and Traumatic Brain Injury J. Charles Mace MD FACS Springfield Neurological Institute CoxHealth Objectives 1. Be able to discuss brain anatomy and physiology as it applies to
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis
 Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases
 How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation
 206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
Only 30% to 40% of acute subdural hematoma (SDH)
 Contralateral Acute Epidural Hematoma After Decompressive Surgery of Acute Subdural Hematoma: Clinical Features and Outcome Thung-Ming Su, MD, Tsung-Han Lee, MD, Wu-Fu Chen, MD, Tao-Chen Lee, MD, and Ching-Hsiao
Contralateral Acute Epidural Hematoma After Decompressive Surgery of Acute Subdural Hematoma: Clinical Features and Outcome Thung-Ming Su, MD, Tsung-Han Lee, MD, Wu-Fu Chen, MD, Tao-Chen Lee, MD, and Ching-Hsiao
Brain Injuries. Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama
 Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
ORIGINAL ARTICLE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY EVALUATION OF SPONTANEOUS INTRACRANIAL HAEMORRHAGE
 Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 4, pp 647-652, April, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 4, pp 647-652, April, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
TBI are twice as common in males High potential for poor outcome Deaths occur at three points in time after injury
 Head Injury Any trauma to (closed vs. open) Skull Scalp Brain Traumatic brain injury (TBI) High incidence Most common causes Falls Motor vehicle accidents Other causes Firearm- related injuries Assaults
Head Injury Any trauma to (closed vs. open) Skull Scalp Brain Traumatic brain injury (TBI) High incidence Most common causes Falls Motor vehicle accidents Other causes Firearm- related injuries Assaults
Radiographic and statistical analysis of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations.
 Radiographic and statistical analysis of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Poster No.: C-0996 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. E. Rodriguez 1, A. Lopez Moreno 1, D. Sánchez Paré
Radiographic and statistical analysis of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Poster No.: C-0996 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. E. Rodriguez 1, A. Lopez Moreno 1, D. Sánchez Paré
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Aaron C. Sigler, DO, MS Neurosurgery Tulane Neurosciences None Disclosures Overview Anatomy Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Cerebral contusions Outline Traumatic ICH
Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Aaron C. Sigler, DO, MS Neurosurgery Tulane Neurosciences None Disclosures Overview Anatomy Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Cerebral contusions Outline Traumatic ICH
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type.
 Neurosurg Clin N Am 13 (2002) 259 264 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Abdominal injuries, in child abuse, 150, 159 Abrasions, in child abuse, 157 Abuse, child. See Child
Neurosurg Clin N Am 13 (2002) 259 264 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Abdominal injuries, in child abuse, 150, 159 Abrasions, in child abuse, 157 Abuse, child. See Child
Occlusive hyperemia: a theory for the hemodynamic complications following resection of intracerebral arteriovenous malformations
 J Neurosurg 78: 167-175, 1993 Occlusive hyperemia: a theory for the hemodynamic complications following resection of intracerebral arteriovenous malformations NAYEF R. F. AL-RODHAN, M.D., PH.D., THORALF
J Neurosurg 78: 167-175, 1993 Occlusive hyperemia: a theory for the hemodynamic complications following resection of intracerebral arteriovenous malformations NAYEF R. F. AL-RODHAN, M.D., PH.D., THORALF
WHITE PAPER: A GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE
 WHITE PAPER: A GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE Subarachnoid Hemorrhage is a serious, life-threatening type of hemorrhagic stroke caused by bleeding into the space surrounding the brain,
WHITE PAPER: A GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE Subarachnoid Hemorrhage is a serious, life-threatening type of hemorrhagic stroke caused by bleeding into the space surrounding the brain,
Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma
 July, 2005 Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma Louis Rivera, Harvard Medical School, Year III 46 y/o Female s/p Trauma - Unrestrained? MVC requiring Med Flight - Facial bruising/swelling - DEEP COMA - SEIZURES
July, 2005 Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma Louis Rivera, Harvard Medical School, Year III 46 y/o Female s/p Trauma - Unrestrained? MVC requiring Med Flight - Facial bruising/swelling - DEEP COMA - SEIZURES
Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics August 2008, Volume 10, Number 8:
 Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics August 2008, Volume 10, Number 8: 516-520. CLINICAL PEARL The Hazards of Stopping a Brain in Motion: Evaluation and Classification of Traumatic
Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics August 2008, Volume 10, Number 8: 516-520. CLINICAL PEARL The Hazards of Stopping a Brain in Motion: Evaluation and Classification of Traumatic
Where is the contre-coup? Atypical localization of occipital brain contusion
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXII Number 1 2018 January-March Article Where is the contre-coup? Atypical localization of occipital brain contusion A.I. Cucu, Claudia Florida Costea, R.A. Sascau, B. Dobrovat,
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXII Number 1 2018 January-March Article Where is the contre-coup? Atypical localization of occipital brain contusion A.I. Cucu, Claudia Florida Costea, R.A. Sascau, B. Dobrovat,
8/29/2011. Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000. Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000
 Traumatic Brain Injury Almario G. Jabson MD Section Of Neurosurgery Asian Hospital And Medical Center Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000 Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000 Hospital
Traumatic Brain Injury Almario G. Jabson MD Section Of Neurosurgery Asian Hospital And Medical Center Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000 Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000 Hospital
Acute cerebral MCA ischemia with secondary severe head injury and acute intracerebral and subdural haematoma. Case report
 214 Balasa et al - Acute cerebral MCA ischemia Acute cerebral MCA ischemia with secondary severe head injury and acute intracerebral and subdural haematoma. Case report D. Balasa 1, A. Tunas 1, I. Rusu
214 Balasa et al - Acute cerebral MCA ischemia Acute cerebral MCA ischemia with secondary severe head injury and acute intracerebral and subdural haematoma. Case report D. Balasa 1, A. Tunas 1, I. Rusu
Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography in Spontaneous Intracranial Haemorrhage: A Guide for Developing Countries
 Original Article Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography in Spontaneous Intracranial Haemorrhage: A Guide for Developing Countries Ishak Abu Bakar, Ibrahim Lutfi Shuaib, Abdul Rahman Mohd Ariff, Nyi Nyi Naing
Original Article Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography in Spontaneous Intracranial Haemorrhage: A Guide for Developing Countries Ishak Abu Bakar, Ibrahim Lutfi Shuaib, Abdul Rahman Mohd Ariff, Nyi Nyi Naing
CEREBRAL INFARCTION AS NEUROSURGICAL POST OPERATIVE COMPLICATION : SERIAL CASES
 CEREBRAL INFARCTION AS NEUROSURGICAL POST OPERATIVE COMPLICATION : SERIAL CASES Oleh Ferry Wijanarko, dr, Sp BS DR Agus Turchan, dr, Sp BS BEDAH SARAF SOLO Secretariat : Neurosurgery Subdivision Dr Moewardi
CEREBRAL INFARCTION AS NEUROSURGICAL POST OPERATIVE COMPLICATION : SERIAL CASES Oleh Ferry Wijanarko, dr, Sp BS DR Agus Turchan, dr, Sp BS BEDAH SARAF SOLO Secretariat : Neurosurgery Subdivision Dr Moewardi
Marshall Scale for Head Trauma Mark C. Oswood, MD PhD Department of Radiology Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN
 Marshall Scale for Head Trauma Mark C. Oswood, MD PhD Department of Radiology Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN History of Marshall scale Proposed by Marshall, et al in 1991 to classify head
Marshall Scale for Head Trauma Mark C. Oswood, MD PhD Department of Radiology Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN History of Marshall scale Proposed by Marshall, et al in 1991 to classify head
Chapter 57: Nursing Management: Acute Intracranial Problems
 Chapter 57: Nursing Management: Acute Intracranial Problems NORMAL INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the hydrostatic force measured in the brain CSF compartment. Normal ICP is the total
Chapter 57: Nursing Management: Acute Intracranial Problems NORMAL INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the hydrostatic force measured in the brain CSF compartment. Normal ICP is the total
Clinical Outcome of Borderline Subdural Hematoma with 5-9 mm Thickness and/or Midline Shift 2-5 mm
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/300 Clinical Outcome of Borderline Subdural Hematoma with 5-9 mm Thickness and/or Midline Shift 2-5 mm Raja S Vignesh
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/300 Clinical Outcome of Borderline Subdural Hematoma with 5-9 mm Thickness and/or Midline Shift 2-5 mm Raja S Vignesh
PA SYLLABUS. Syllabus for students of the FACULTY OF MEDICINE No.2
 Approved At the meeting of the Faculty Council Medicine No. of Approved At the meeting of the chair of Neurosurgery No. of Dean of the Faculty Medicine No.2 PhD, associate professor M. Betiu Head of the
Approved At the meeting of the Faculty Council Medicine No. of Approved At the meeting of the chair of Neurosurgery No. of Dean of the Faculty Medicine No.2 PhD, associate professor M. Betiu Head of the
Predicting the need for operation in the patient with an occult traumatic intracranial hematoma
 J Neurosurg 55:75-81, 1981 Predicting the need for operation in the patient with an occult traumatic intracranial hematoma SAM GALBRAITH, M.D., F.R.C.S., AND GRAHAM TEASDALE, M.R.C.P., F.R.C.S. Department
J Neurosurg 55:75-81, 1981 Predicting the need for operation in the patient with an occult traumatic intracranial hematoma SAM GALBRAITH, M.D., F.R.C.S., AND GRAHAM TEASDALE, M.R.C.P., F.R.C.S. Department
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
 Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Concussions This presentation is for information purposes only, not for any commercial purpose, and may not be sold or redistributed. David Wesley, M.D. Outline Epidemiology
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Concussions This presentation is for information purposes only, not for any commercial purpose, and may not be sold or redistributed. David Wesley, M.D. Outline Epidemiology
Analysis of pediatric head injury from falls
 Neurosurg Focus 8 (1):Article 3, 2000 Analysis of pediatric head injury from falls K. ANTHONY KIM, MICHAEL Y. WANG, M.D., PAMELA M. GRIFFITH, R.N.C., SUSAN SUMMERS, R.N., AND MICHAEL L. LEVY, M.D. Division
Neurosurg Focus 8 (1):Article 3, 2000 Analysis of pediatric head injury from falls K. ANTHONY KIM, MICHAEL Y. WANG, M.D., PAMELA M. GRIFFITH, R.N.C., SUSAN SUMMERS, R.N., AND MICHAEL L. LEVY, M.D. Division
Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD, Julio A. Díaz MD, Sandro Perez MD, Julio C Martin MD, Daiyan Martin MD.
 Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD, Julio A. Díaz MD, Sandro Perez MD, Julio C Martin MD, Daiyan Martin MD. Introduction: Spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage (SICH) represents one of the most severe
Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD, Julio A. Díaz MD, Sandro Perez MD, Julio C Martin MD, Daiyan Martin MD. Introduction: Spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage (SICH) represents one of the most severe
8th Annual NKY TBI Conference 3/28/2014
 Closed Head Injury: Headache to Herniation A N T H O N Y T. K R A M E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F C I N C I N N A T I B L U E A S H E M S T E C H N O L O G Y P R O G R A M Objectives Describe the pathological
Closed Head Injury: Headache to Herniation A N T H O N Y T. K R A M E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F C I N C I N N A T I B L U E A S H E M S T E C H N O L O G Y P R O G R A M Objectives Describe the pathological
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties:
 Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Trauma and Critical Care Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1, Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 and Stacey Q. Wolfe, MD 3 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University,
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Trauma and Critical Care Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1, Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 and Stacey Q. Wolfe, MD 3 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University,
The Prognostic Value of Early Follow-up Computerized Tomography of the Brain in Adult Traumatic Brain Iniury
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Prognostic Value of Early Follow-up Computerized Tomography of the Brain in Adult Traumatic Brain Iniury A Kiflie, MMed*, N A Alias, MMed*, M M Abdul Kareem, PMRD*, W Mar, MMed*, J
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Prognostic Value of Early Follow-up Computerized Tomography of the Brain in Adult Traumatic Brain Iniury A Kiflie, MMed*, N A Alias, MMed*, M M Abdul Kareem, PMRD*, W Mar, MMed*, J
Efficacy of Decompressive Craniectomy in Acute Subdural Hematoma in Head Injury Patients, Madurai Medical College, Madurai
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/107 Efficacy of Decompressive Craniectomy in Acute Subdural Hematoma in Head Injury Patients, Madurai Medical College,
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/107 Efficacy of Decompressive Craniectomy in Acute Subdural Hematoma in Head Injury Patients, Madurai Medical College,
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT. Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT
 LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT OUTLINE Causes Head Injury Clinical Features Complications Rapid Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale Classification
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT OUTLINE Causes Head Injury Clinical Features Complications Rapid Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale Classification
Management Strategies for Communited Fractures of Frontal Skull Base: An Institutional Experience
 80 Original Article THIEME Management Strategies for Communited Fractures of Frontal Skull Base: An Institutional Experience V. Velho 1 Hrushikesh U. Kharosekar 1 Jasmeet S. Thukral 1 Shonali Valsangkar
80 Original Article THIEME Management Strategies for Communited Fractures of Frontal Skull Base: An Institutional Experience V. Velho 1 Hrushikesh U. Kharosekar 1 Jasmeet S. Thukral 1 Shonali Valsangkar
Cerebrovascular Disease
 Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Traumatic brain injuries are caused by external mechanical forces such as: - Falls - Transport-related accidents - Assault
 PP2231 Brain injury Cerebrum consists of frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes Diencephalon consists of thalamus, hypothalamus Cerbellum Brain stem consists of midbrain, pons, medulla Central
PP2231 Brain injury Cerebrum consists of frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes Diencephalon consists of thalamus, hypothalamus Cerbellum Brain stem consists of midbrain, pons, medulla Central
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH
 RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
Intraventricular hemorrhage in severe head injury
 J Neurosurg58:217-222, 1983 Intraventricular hemorrhage in severe head injury FRANCISCO CORDOBI~S, M.D., MARINA DE LA FUENTE, M.D., RAMIRO D. LOBATO, M.D., RICARDO ROGER, M.D., CARLOS P~REZ, M.D., Jose
J Neurosurg58:217-222, 1983 Intraventricular hemorrhage in severe head injury FRANCISCO CORDOBI~S, M.D., MARINA DE LA FUENTE, M.D., RAMIRO D. LOBATO, M.D., RICARDO ROGER, M.D., CARLOS P~REZ, M.D., Jose
Case Conference: Neuroradiology. Case 1: Tumor Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures
 Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
Introduction. Abstract. Michael Yannes 1, Jennifer V. Frabizzio, MD 1, and Qaisar A. Shah, MD 1 1
 Reversal of CT hypodensity after acute ischemic stroke Michael Yannes 1, Jennifer V. Frabizzio, MD 1, and Qaisar A. Shah, MD 1 1 Abington Memorial Hospital in Abington, Pennsylvania Abstract We report
Reversal of CT hypodensity after acute ischemic stroke Michael Yannes 1, Jennifer V. Frabizzio, MD 1, and Qaisar A. Shah, MD 1 1 Abington Memorial Hospital in Abington, Pennsylvania Abstract We report
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5 Masses and tumors K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL part
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5 Masses and tumors K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL part
Solitary Skull Metastasis as Initial Manifestation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma A Case Report
 Solitary Skull Metastasis as Initial Manifestation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma A Case Report Ellyda MN a and Mohd Shafie A b a Department of Radiology, International Islamic University Malaysia, Kuantan,
Solitary Skull Metastasis as Initial Manifestation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma A Case Report Ellyda MN a and Mohd Shafie A b a Department of Radiology, International Islamic University Malaysia, Kuantan,
THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE
 THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE Neuroanatomy & Neuroplasticity Section 2 Contributors Erin D. Bigler, PhD Michael R. Hoane, PhD Stephanie Kolakowsky-Hayner, PhD, CBIST, FACRM Dorothy A. Kozlowski, PhD
THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE Neuroanatomy & Neuroplasticity Section 2 Contributors Erin D. Bigler, PhD Michael R. Hoane, PhD Stephanie Kolakowsky-Hayner, PhD, CBIST, FACRM Dorothy A. Kozlowski, PhD
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY. Moderate and Severe Brain Injury
 TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Moderate and Severe Brain Injury Disclosures Funded research: 1. NIH: RO1 Physiology of concussion 2016-2021, Co-PI, $2,000,000 2. American Medical Society of Sports Medicine: RCT
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Moderate and Severe Brain Injury Disclosures Funded research: 1. NIH: RO1 Physiology of concussion 2016-2021, Co-PI, $2,000,000 2. American Medical Society of Sports Medicine: RCT
Neurological examination of the neurosurgical patient. Dániel Bereczki SU Department of Neurology
 Neurological examination of the neurosurgical patient Dániel Bereczki SU Department of Neurology E-learning Indivudual study Interactive learning Self assessment at the end of chapters E-learning Indivudual
Neurological examination of the neurosurgical patient Dániel Bereczki SU Department of Neurology E-learning Indivudual study Interactive learning Self assessment at the end of chapters E-learning Indivudual
CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage
 CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, 29-30 Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular
CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, 29-30 Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular
General Data. Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30
 General Data Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30 Chief Complain Dizziness and light headache for recent 1 year. Present illness Hypertension
General Data Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30 Chief Complain Dizziness and light headache for recent 1 year. Present illness Hypertension
Characteristic features of CNS pathology. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
Moath Darweesh. Zaid Emad. Anas Abu -Humaidan
 3 Moath Darweesh Zaid Emad Anas Abu -Humaidan Introduction: First two lectures we talked about acute and chronic meningitis, which is considered an emergency situation. If you remember, CSF examination
3 Moath Darweesh Zaid Emad Anas Abu -Humaidan Introduction: First two lectures we talked about acute and chronic meningitis, which is considered an emergency situation. If you remember, CSF examination
Case Report Neuroendoscopic Removal of Acute Subdural Hematoma with Contusion: Advantages for Elderly Patients
 Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 2056190, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2056190 Case Report Neuroendoscopic Removal of Acute Subdural Hematoma with Contusion: Advantages
Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 2056190, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2056190 Case Report Neuroendoscopic Removal of Acute Subdural Hematoma with Contusion: Advantages
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury. Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center
 Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 7: Non traumatic brain haemorrhage
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 7: Non traumatic brain haemorrhage ILOS To list the causes of intracranial haemorrhage. To understand the pathogenesis of each cause.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 7: Non traumatic brain haemorrhage ILOS To list the causes of intracranial haemorrhage. To understand the pathogenesis of each cause.
Short Communications. Alcoholic Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 Short Communications 1565 Alcoholic Intracerebral Hemorrhage Leon A. Weisberg, MD Six alcoholic patients developed extensive cerebral hemispheric hemorrhages with both intraventricular and subarachnoid
Short Communications 1565 Alcoholic Intracerebral Hemorrhage Leon A. Weisberg, MD Six alcoholic patients developed extensive cerebral hemispheric hemorrhages with both intraventricular and subarachnoid
Sonography of soft-tissue vascular lesions
 Sonography of soft-tissue vascular lesions Oscar M. Navarro Associate Professor, University of Toronto Dept. of Diagnostic Imaging, The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Canada Declaration of Disclosure
Sonography of soft-tissue vascular lesions Oscar M. Navarro Associate Professor, University of Toronto Dept. of Diagnostic Imaging, The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Canada Declaration of Disclosure
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain. Dr Amy Davis
 An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
MR Characteristics of Subdural Hematomas and Hygromas at 1.5 T
 687 MR Characteristics of Subdural Hematomas and Hygromas at 1.5 T Edward S. Fobben 1 Robert I. Grossman Scott W. tlas David B. Hackney Herbert I. Goldberg Robert. Zimmerman Larissa T. Bilaniuk MR images
687 MR Characteristics of Subdural Hematomas and Hygromas at 1.5 T Edward S. Fobben 1 Robert I. Grossman Scott W. tlas David B. Hackney Herbert I. Goldberg Robert. Zimmerman Larissa T. Bilaniuk MR images
Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management
 Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management Dora Zlatareva Department of Diagnostic Imaging Medical University, Sofia, Bulgaria Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) ICH 15% of strokes
Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management Dora Zlatareva Department of Diagnostic Imaging Medical University, Sofia, Bulgaria Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) ICH 15% of strokes
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Brief Clinical Report: Recognizing Subdural Hemorrhage in Older Adults
 Research Brief Clinical Report: Recognizing Subdural Hemorrhage in Older Adults Mark T. Pfefer, RN, MS, DC *1 ; Richard Strunk MS, DC 2 Address: 1 Professor and Director of Research, Cleveland Chiropractic
Research Brief Clinical Report: Recognizing Subdural Hemorrhage in Older Adults Mark T. Pfefer, RN, MS, DC *1 ; Richard Strunk MS, DC 2 Address: 1 Professor and Director of Research, Cleveland Chiropractic
Neuropathology lecture series. III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease. Physiology of cerebral blood flow
 Neuropathology lecture series III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O
Neuropathology lecture series III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 31.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 13 15, 17, 19, 28 31.2 Describe the components and function of the nervous system and the anatomy
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 31.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 13 15, 17, 19, 28 31.2 Describe the components and function of the nervous system and the anatomy
MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition
 637 MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition William M. Needell 1 Kenneth R. Maravilla Twenty patients with known or suspected intracranial vascular lesions were evaluated
637 MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition William M. Needell 1 Kenneth R. Maravilla Twenty patients with known or suspected intracranial vascular lesions were evaluated
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
Head injuries. Severity of head injuries
 Head injuries ED Teaching day 23 rd October Severity of head injuries Minor GCS 14-15 Must not have any of the following: Amnesia 10min Neurological sign or symptom Skull fracture (clinically or radiologically)
Head injuries ED Teaching day 23 rd October Severity of head injuries Minor GCS 14-15 Must not have any of the following: Amnesia 10min Neurological sign or symptom Skull fracture (clinically or radiologically)
10/6/2017. Notice. Traumatic Brain Injury & Head Trauma
 Notice All EMS Live@Nite presentations will be recorded (both audio and video) and available for public viewing online. By participating in EMS Live@Nite, you consent to audio and video recording and its/their
Notice All EMS Live@Nite presentations will be recorded (both audio and video) and available for public viewing online. By participating in EMS Live@Nite, you consent to audio and video recording and its/their
COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY FINDINGS IN PATIENTS PRESENTING WITH HEAD INJURY IN CALABAR, NIGERIA
 Asian Journal of Medical Science, Volume-5(2014) COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY FINDINGS IN PATIENTS PRESENTING WITH HEAD INJURY IN CALABAR, NIGERIA ORIGINAL ARTICLE,Vol-5 No.2 http://nepjol.info/index.php/ajms
Asian Journal of Medical Science, Volume-5(2014) COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY FINDINGS IN PATIENTS PRESENTING WITH HEAD INJURY IN CALABAR, NIGERIA ORIGINAL ARTICLE,Vol-5 No.2 http://nepjol.info/index.php/ajms
Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation
 American Society of Neuroimaging Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation January 21, 2017 Los Angeles, California Joshua P. Klein, MD, PhD, FANA, FAAN, FASN Chief, Division of Hospital
American Society of Neuroimaging Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation January 21, 2017 Los Angeles, California Joshua P. Klein, MD, PhD, FANA, FAAN, FASN Chief, Division of Hospital
Computed Tomography Perfusion Imaging on Traumatic Cerebral Contusion: A Preliminary Report
 Brief Communication Computed Tomography Perfusion Imaging on Traumatic Cerebral Contusion: A Preliminary Report Ahmad Helmy Abdul Karim 1, Win Mar @ Salmah Jalaluddin 1, Ab Rahman Izaini Ghani 2 Submitted:
Brief Communication Computed Tomography Perfusion Imaging on Traumatic Cerebral Contusion: A Preliminary Report Ahmad Helmy Abdul Karim 1, Win Mar @ Salmah Jalaluddin 1, Ab Rahman Izaini Ghani 2 Submitted:
Neurotrauma. Béla Faludi Dept.. of Neurology University of PécsP
 Neurotrauma Béla Faludi Dept.. of Neurology University of PécsP Emergency!!! Why here? Opened cranial injury visible: neurosurgery Closed injuries sometimes diagnosed by neurologist Masking situation:
Neurotrauma Béla Faludi Dept.. of Neurology University of PécsP Emergency!!! Why here? Opened cranial injury visible: neurosurgery Closed injuries sometimes diagnosed by neurologist Masking situation:
